1. Introduction
In the world, there is significant rise has been seen in energy consumption. According to the International Energy Outlook, by 2040 there will be a 48% increase in the total energy consumption globally. Countries which are not part of Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) are major contributors in this rise of energy consumption[
1]. In these regions, population growth and economic expansion are key factors for the consumption of energy. In growing economies, rising living standards results in an increase in demand for energy. This together with population growth leads to the rise in energy consumption [
2].
1.1. Biodiesel
Biodiesel is the type of fuel derived from plants seeds or oil, animal fats, minerals, and algae materials. Biodiesel is used as the energy for renewable sources. These are also used as alternative fuel for fossil fuel because these are non-toxic, environmentally friendly because they don’t contain aromatic and Sulphur compounds. Also, biodiesel has low emission hydrocarbons and other particles which can pollute the environment. Triglycerides are lipids which are found in fats of animal and oils for feedstock resources. These are converted into fuel for diesel engine [
3]. There are four possible methods to convert these lipids into oil: pyrolysis, direct blending of oils, micro-emulsion, and transesterification reaction [
3,
4,
5,
6]. Transesterification reaction is the most used because during the process alkyl esters are produced from triglycerides with same viscosity as diesel fuel using primary and secondary monohydric aliphatic alcohol and with or without the help of catalysts. The catalysts used in transesterification may be alkaline, acidic which can be homogeneous or heterogeneous. Homogeneous catalysts are widely used in industries because of their low economy and fast kinetic rate. The use of less expensive non-edible feedstock usually produces soap by free fatty acid (FFA) as their side products which cannot be suitable for homogeneous catalyzed transesterification [
7]. To overcome the problem, the process is divided into two steps in, the first step involves the pre-treatment of free fatty acid by acidic catalyst and second step involves the alkaline catalyst in which transesterification of remaining triglycerides occurred. The disadvantages of using a two-step process are high energy intensive and time consuming. The reaction in which acidic catalyst is used can convert both free fatty acid and triglycerides of oil into diesel but this is not used because of longer reaction time and lower yield. Also in some studies, enzymatic catalysts are used [
7].
1.2. Biodiesel Production
Biodiesel is produced through a reaction called transesterification in which oils and fats are reacted with alcohol. Transesterification occurs in two ways, one in which catalysts is used and other in which catalysts are not used. The non-catalyst methods are usually supercritical process and co-solvent process. The alkaline catalysts or base catalysts which are used in this process are Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH), Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) and Sodium Methoxide (NaMeO) etc. Acid catalysts which are used in transesterification are Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4), Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4) and Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) and enzyme which are used as catalyst is lipase enzyme. The main alcohols which are used for biodiesel production process are methanol and ethanol [
8].
Catalysts initiate the esterification process to produce biodiesel. Catalysts increase the rate of reaction by improving the solubility of oil/fat in alcohol. The conventional biodiesel production through transesterification reaction is achieved by base or homogeneous catalysts. Alkali catalysts are used in feedstock with less than 1% Free Fatty Acid (FFA) content and Acidic catalysts are used in feedstock with more than 1% free fatty acid content. Now a day, heterogeneous catalysts are used more because they do not produce soap through triglyceride saponification and free fatty acid neutralization. The key factor affecting the reaction rate is Temperature, higher the temperature means shorten the time and faster rate of reaction. The reaction is done under the boiling point of methanol which is 60°C and for ethanol which is 78°C [
8].
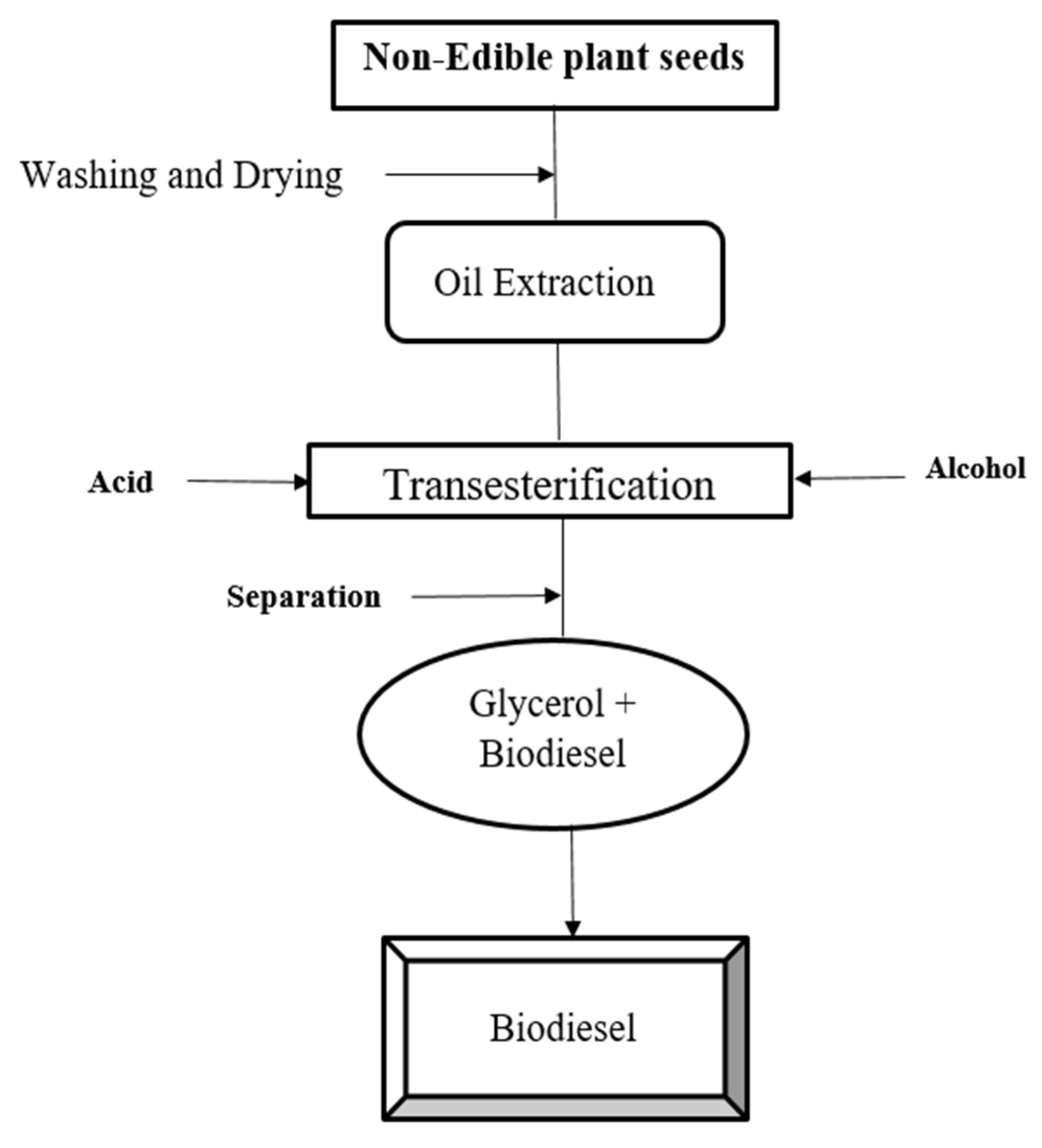
Figure 1.
Process and step for the biodiesel production.
Figure 1.
Process and step for the biodiesel production.
Transesterification using base-catalyst is the most common way for biodiesel synthesis as it proceeds at low temperature and has high rate. Transesterification reaction is preferred over direct fatty acid esterification because direct esterification needed excess alcohol for the production of biodiesel[
9]. Generally, a high amount of methanol is combined with triacylglycerol (TAGs) in the presence of sodium methoxide and sodium hydroxide to manufacture biodiesel.
Transesterification is a two-step process. First TAGs are converted into monoacylglycerols (MAGs) and then to diacylglycerols (DAGs). If TAGs are converted into DAGs that means they are mixed with methanol and now have higher chances of reacting than moving back to phase of oil.
| TAG + CH3OH ⇒ DAG + R1COOCH3 [10] |
| DAG + CH3OH ⇒ MAG + R2COOCH3 [11] |
| MAG + CH3OH ⇒ Glycerol + R3COOCH3 [12] |
Using butanol instead of methanol, the rate of reaction is higher because oil and butanol mixture forms single layer more easily [
10]. Using tetrahydrofuran as co-solvent yield 99.7% conversion to methyl esters in 7 minutes [
13].
Other than transesterification, Fatty acids and TAG can undergo two side reactions:
- (1)
Hydrolysis TAG + H2O → FFA + Glycerol [
14]
- (2)
Saponification FFA + NaOH → Soap(sodium salt of fatty acid) + Glycerol [
15]
1.3. Biological Sources
Biological sources (i-e plants, animal, and algae) are used to produce biodiesel through the process called transesterification. Transesterification is the process in which biodiesel ester and glycerol is produced by the reaction of fats and oils with the alcohol [
8]. Transesterification is used to overcome the problem of high viscosity of straight vegetable oils and low volatility of using consumable oil for fuel of engine. Also in the process of transesterification, alkaline and acid catalysts are used to increase the rate of reaction and biodiesel yield [
8].
1.4. Biodiesel Separation
Different methods are used to improve separation and enhancement of reaction i-e sonication method, microwaving method, co-solvent method, reactive distillation, and in-situ biodiesel production.
1.5. Edible Feedstock
Biodiesel feedstock contains free fatty acids, water, sterols, phospholipids, and other impurities. According to a few years studies the production of biodiesel is from edible oils or seeds (i-e palm, sunflower, rapeseed, soybean, coconut seed or oil etc.). Due to vast availability of edible seeds and oils in the world they produced more than 95% of biodiesel, but these also faces many criticisms from food security[
16,
17]. Therefore, the disadvantages of using edible seeds or oil involve lower heating value, higher nitrogen oxides, oxidative instability, and high cost of feedstock. Therefore, the general cost for biodiesel synthesis from edible oils and seeds is 60-75% [
16,
18,
19].
1.6. Non-Edible Feedstock
Therefore, to overcome the disadvantages related to edible feedstocks, non-edible feedstocks are used to produce biodiesel. By using the non-edible feedstock, it helps to solve the problems like food versus fuel concern, irrigation canals, can be cultivated on fallow land etc. Non-edible feedstock also helps in upgrading the non-agricultural sector and produces renewable energy. Also not consumable feedstock is great source for production of biodiesel because they are renewable, low sulfur content, easily transferred in liquid form, and has low fragrance content and also biodegradable[
16,
19].
The mostly used feedstocks from non-edible sources for biodiesel production are Jatropha, Polanga, Mahua, Karanja, Tobacco, Linseed, Rubber seed etc. However, the usage of non-edible feedstock also faces challenges like variations in oil contents and seed yields and the annual cultivation. To check the standard production of biodiesel quality of fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) is predicted. The quality of fatty acid methyl ester is predicted by lipid profile and other biodiesel properties like iodine number, saponification number and cetane number.
2. Catalysts For Biodiesel Production
The catalysts which are used to produce biodiesel are as follow:
2.1. Acidic Catalyst
Acidic catalysts are used to form ester as pre-treatment step by the conversion of FFA or soap. These have slow reaction rate; therefore, high ratio of triglycerides and alcohol is required. Due to excess need of alcohol, larger alkali distillation column and biodiesel reactor are needed to produce biodiesel in same capacity. By increasing the alcohol to oil molar ratio, acid catalyst concentration, reaction temperature and reaction rate, higher conversion efficiency will be achieved by acid-catalyst transesterification[
20].
2.2. Alkali Catalyst
It is usually a fast process. In this soap and water are formed by the reaction on free fatty acid and alkali catalysts. Due to the presence of soap and water the fast rate is affected. Soap also increases the difficulty of separating glycerol and biodiesel and also decreases the yield of alkyl esters. According to some studies and observations, methoxide catalysts can be used to increase biodiesel yield and potassium-based catalysts can be used to get better yield[
21].
2.3. Heterogeneous Catalyst
Calcium methoxide and calcium oxide are heterogeneous catalysts. These are insoluble in organic solvents. During the reaction for biodiesel production, three mixture phases of oil-alcohol- catalyst are formed by heterogeneous catalyst. Because of insolubility and three mixtures phase, reaction rate gets slow and mass transfer efficiency become poor. Tetrahydrofuran is used as co-solvent between the reactants to enhance the mass transfer efficiency. By using this co-solvent, the reaction becomes fast (i-e., 5-10 min at temperature 30°C). Furthermore, the resultant product is free of catalyst residue like phase of glycerol and ester[
8].
2.4. Bio Catalytic
Biocatalyst is also called enzyme catalysis because in this immobilized lipase is used as transesterification reaction agent. The given time is from 4-40 hours or more at temperature 35 to 45°C in these reactions. Therefore, these are very slow occurring reactions. This process is very high cost therefore they are not used commercially. This process is very promising for the feedstock which has very high FFA content [
20].
2.5. Supercritical Methanol Transesterification
In triglyceride phase the low solubility of alcohol causes a slow rate of reaction. So, to overcome this slow rate reaction or time lag of reaction supercritical transesterification is designed, in which the pressure and temperature given to its solvent is above its critical point. Therefore, in this, the resultant phase will be liquid phase with no separate phases. This reaction is completed in 2-4 mins because of the supercritical conditions like temperature range 350-400°C, pressure above 80 atm and high molar ratio of methanol and oil (42:1). Advantages of this method include; trouble free, environment-friendly, glycerol recovery and easy purification of biodiesel in the absence of catalyst [
22].
3. Non-Edible Feedstock Necessity
Non-edible and edible oils have almost the same compositions. The main difference is that non-edible oils contain toxics substances (i-e cyanogenic glucoside, and purgative etc.) which are suitable for human usage[
23,
24,
25,
26]. Non-edible feedstocks are considered as the promising source of biodiesel production because they can be agricultural harvest and derived from the farmed land. Non-edible feedstocks can be grown anywhere on land with least cultivation efforts therefore the biodiesel production cost is minimized. The planation cost of non-edible feedstock is less because they can grow where food crop production is not suitable. Another factor which makes non-edible feedstock more suitable for the production of biodiesel is oil content or oil percentage [
27].
Table 1.
List of non-edible plants, their oil content (wt %) and annual yield.
Table 1.
List of non-edible plants, their oil content (wt %) and annual yield.
| Non-edible Plant |
Annual yield (kg per ha per year) |
Oil content (wt %) |
Ref |
| Jatropha |
2500 |
40-60 % |
[27] |
| Mahua |
20-200 |
35-50 % |
[28] |
| Rubber |
100-150 |
40-50 % |
[29] |
| Jojoba |
500-5000 |
40-50 % |
[30] |
| Tobacco |
1170 |
35-49 % |
[31] |
| Neem |
2670 |
25-45 % |
[32] |
| Karanja |
900-9000 |
30-50 % |
[33] |
| Polanga |
3700 |
65-75 % |
[34] |
| Castor |
450 |
45-50 % |
[35] |
| Sea mango |
1900-2500 |
40-50 % |
[36] |
| Bottle tree |
250-300 |
50-60 % |
[37] |
| Tung |
450-600 |
30-40 % |
[33] |
| Cotton |
649 |
17-23 % |
[38] |
4. Sources of Non-Edible Oil
Several sources of refined oil in the world such as oils from Honge tree and Jatropha curcas are not based on annual food crops and oils. Due to its limited supply and availability, edible oils are such expensive that developing countries must import to fulfill their need. This makes edible oils out of reach, compelling buyers to shift their focus to non-edible feedstocks.
4.1. Jatropha (Jatropha curcas)
Jatropha oil and seeds are mostly used for biodiesel production in Africa, Europe and Asia due to its diverse ability to grow under various climatic conditions. Oil content of jatropha based on geographical location, species type and climatic conditions as it mostly grows on waste lands and uncultivated area with specific altitude. It has many prominent advantages such as some parts of it are effective for medical treatments and reduces CO2 concentration from the environment. In Asia,
J.curcas is identified as a major source for biodiesel production. It has 30-40% oil content, Myristic acid 0.5-1.4, Palmitic acid 12.0-17.0, Stearic acid 5.0-9.5, Oleic acid 37-63, Linoleic acid 19-41, and Arachidic acid 0.3 [
39].
4.2. Pongamia (Pongamia pinnata)
This hard-texture tree in Asian sub-continent of 12-15 m height is capable of surviving under harsh and adverse climatic conditions. Except for high Conradson carbon, residue in extracted oil, its physical and chemical properties are like diesel. However, some toxic substances can restrict their use as cooking oil. So, its seedcake can serve as nematicide in many places [
40].
4.3. Neem (Azadirachta indica)
Asian countries are prominent places for presence of this light to dark brown oil producing tree, which prominently grows on marginal soils with rocky and shallow texture. It has shown promising results for being used as pesticides, medicines, and organic fertilizers. Being able to tolerate extreme temperatures of 45°C, neem oils contain sulfurous compounds that give it pungent odor and less- clean burn. ‘Azadirachtin’ is the main component of neem seed oil. The concentration (i-e., 300-2500ppm) of its depends on seeds crushed quality and technology used for extraction [
41]. It contains 40-50% oil content, Myristic acid 0.2-2.6, Palmitic acid 13.6-16.2, Stearic acid 14.4-24.0, Oleic acid 49-62, Linoleic acid 2.3-15.8, and Arachidic acid 0.8-3.4.
4.4. Mahua (Madhuca indica)
Mahua oil is obtained from kernel of Mahua tree commonly found in India and is greenish yellow in color. With an estimate production capacity of 181,000 metric tons, the properties of biodiesel produce from mahua is comparable to both Europe and US standards[
42,
43]. This deciduous tree, based on its tropical region, requires 8-15 years to fully mature and then for almost 60 years can bear the fruits. Mahua oil contains 35-42% oil content, Palmitic acid 20.0-25.0, Stearic acid 20.0-25.0, Oleic acid 41.0-51.0, Linoleic acid 10.0-14.0, and Arachidic acid 0-3.3.
4.5. Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis)
Jojoba plant originating from desert regions of South-western and North American continent have relatively recent history in production of biodiesel. It is a mixture of 97-98 wt. % long ester chain of fatty acids and alcohols that can grow best in warm desert temperatures. Jojoba oil is specifically referred to as wax based on its composition and is easy to work with due various advantages such as: [
44,
45]
- ➢
Do not become rancid
- ➢
Needs little refining comparatively
- ➢
Can endure repeated cycles of heating and cooling at 250°C.
It contains 45-50% oil content, Oleic acid 0.55-0.77, Arachidic acid 28.0-31.0, Palmitoleic acid 0.25, and Behenic acid 14.2.
4.6. Algae (Cyanobacteria)
Both micro and macro algae are stated as best biodiesel source, microalgae surpass in the procedure due to its high yielding feedstock and easier faster growth process[
46]. They have potential to yield up to 250 times the oil per acre as soybeans and its oil content exceeds 80% of dry biomass. Being rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids with four or more double bonds, they differ quite uniquely from other vegetable oils [
47]. Some studies also documented the use of macro algae for biodiesel production but due to their low content of lipid (i-e., 1.3-7.8% dw) microalgae are preferable for the production of renewable biodiesel and meet the global requirements with its specific productivity [
47,
48].
4.7. Tall (Carnegiea gigantean)
Tall oil is the byproduct of kraft pulp mill which is the mixture of fatty acids, triglyceride oils, terpenoids, resin acids and other materials. These components can be used as an enhancing agents for petrol-diesel or raw material for biodiesel fuel [
49]. The presence of oleic acid and less linolenic acid or no linoleic acid in fatty acids derived from tall oil produces less gum during oil combustion and ultimately enhances the quality in comparison to other vegetable oils [
50].
4.8. Castor (Ricinus communis)
Castor oil is found to have greater potential for oil production due to its mixed complex composition. It contains 90% of triglycerides of ricinoleic acid with the presence of hydroxyl group at C-12 which renders it more useful due to unique physical and chemical properties. Being categorized ad potential source of biodiesel production in Brazil, its use in research field is still limited. Because it is considered a weed in agricultural processes, the final castor oil viscosity range in biodiesel production is still debatable[
51]. It has 45-50 % oil content, Palmitic acid 2.0, Stearic acid 1.0, Oleic acid 7.0, Linoleic acid 5.0, Ricinoleic acid 86-90, and dihydroxy Stearic acid 0.7
4.9. Coffee Ground (Coffea arabica)
A study conducted in Latin America showed that 20% of coffee beans produced were defective and the best methods to utilize those defective beans were their use in the biodiesel production by extracting oil from their seeds[
52]. 11 to 20% oil by weight can be found in spent coffee grounds which can be utilized as environment friendly source for production of biodiesel[
53]. The high antioxidant content of coffee-based oil gives it the upper hand among traditional production methods for biodiesel. Coffee oil contains Palmitic acid 34, Stearic acid 7, Oleic acid 9, and Linoleic acid 44.
5. Oil Extraction Process from Non-Edible Seeds
Many processes have been developed to extract oil from the non-edible plants. These processes are as follows:
5.1. Mechanical Extraction
Mechanical extraction involves three steps: pressing, filtration and separation. Oil extraction process is done after pressing step. Pressing can be done in two ways one engine screw and manual ram. Oil content efficiency of engine-driven screw is 68-80% and manual pressing is 60-65%. Oil recovery is done through filtration and separation after pressing step [
54]. Oil content efficiency can be increased by pre-treatment procedure. The only problem with this extraction process is this is only applicable on specific seeds [
55].
5.2. Soxhlet Extraction
Soxhlet extraction is a method used to extract the oil from some solid compounds like seeds. In this the seeds are treated with the solvent for some time or for the day to get the oil from the desirable seed. It was designed by Fran von Soxhlet in 1879 [
56]. It consists of stirrer pot, stirrer bar, thimble, distillation bath, condenser, expansion adopter, siphon top/exit and cooling water in/out. In Soxhlet extraction process, Soxhlet extractor is the main chamber which has thimble inside it. Thimble contains the seed through which oil is extracted. After the placement of thimble into Soxhlet extractor, extractor is placed in the flash containing solvent. After this, the heat is given to solvent because of which vapors of solvent start to move in condenser from distillation arm. After that condensation of vapors occurs and form hot liquid which then falls into the thimble containing seeds because of which the level of siphon tube rises and Soxhlet extractor gets filled with solvent. After the extractor filled with solvent the oil starts to run down to flask from thimble. And certain amount of oil is collected in the flask through extraction [
57].
According to some studies, mostly used solvent for the extraction process is n-hexane. N-hexane in 30 min gives 15% of oil yield. The advantage of Soxhlet extraction is quit process with efficient yield and remove sulfur elements. The disadvantage of this process is lengthy process and requires same concentration amount of vapors and fluid [
58].
5.3. Enzymatic Oil Extraction
It is the process of extracting oil from seeds in the presence of suitable enzymes.it is the conventional process of oil recovery [
54]. In this process, the seeds are grinded then water and enzymes are added to cause enzymatic hydrolysis. After which solvent is added to increase the yield, then after the final process of distillation the solvent and oil are separated, and we get the yield of oil. The problem with this process is the high time of incubation, ultra-sonication pre-treatment required and high cost of enzymes. The only solution to overcome the problems is enzyme immobilization which minimizes the cost and loss of enzyme [
59].
5.4. Microwave Extraction
It is the process through which bioactive compounds of plants are extracted using microwave heating. It is the direct process which means the materials of plant are in direct contact of microwave heating. It occurs in two processes; one ionic conduction in which energy is transferred through ion movement and second dipole rotation it leads to the disruption of hydrogen bonds which are weak. This process depends on the electric field because microwave heat is produced through it. The only limitation regarding this process is the variation in the temperature because it depends on the solvent boiling capacity [
60].
5.5. Pyrolysis
This method is used for biodiesel production from non-edible oils, animal fats etc. Pyrolysis is used for biodiesel production from biomass. This process can occur at both temperatures [i-e., medium (300-800 C) and high (850-1300 C)] in an inert like atmosphere[
3,
61]. This process is known as thermochemical degradation of feedstocks for biodiesel production. Pyrolysis is the process in which material is given heat in a minimal amount of oxygen at evaluated temperature. In this process, catalysts are also required which enhance the decomposition of feedstock to produce biodiesel. The process in which catalyst is required is called catalytic pyrolysis. Pyrolysis process is used to break the long fatty acid chains into the small chains and those short chains are known as bio-oils. Through pyrolysis maximum percent of oil produce from non-edible feedstock is 67% [
62].
There are different reactors i-e., bubbling fluidized bed, focused solar, circulating fluidized bed, ablative and rotating cone etc. can be used to produce the biodiesel using pyrolysis process[
63]. The oil produced from pyrolysis has properties like low quantities of Sulphur, low viscosity and high cetane number. Pyrolytic oil advantages are easy to handle, store and transport. The main disadvantages of oil produce from pyrolysis process is that they have high moisture and are acidic [
62].
5.6. Micro-Emulsification
Micro-emulsification is the process in which oil is surrounded by water droplets in continuous phase. Alcohol is used as the emulsion agents to minimize the oils viscosity. This process is thermodynamically stable. In this process, low energy is needed to produce biodiesel with suitable properties [
27]. Blending, hydrodeoxygenation and cracking processes are pre-treated processes used to reduce the content of free fatty acids and oil viscosity during the biodiesel production. But during the production of biodiesel by micro-emulsification these processes are not required. In micro-emulsification, surfactants (hydrophobic span) are used to enhance the stability and yield from non-edible oils [
64]. The advantages of using micro-emulsification process are increase in combustion performance, minimize time of ignition, and exhaust less smoke which reduces the pollution. The disadvantages of using micro-emulsification involve deposition of carbon and incomplete combustion [
62,
65].
5.7. Transesterification
Biodiesel production is done through transesterification in which oil and alcohol react with each other. Transesterification is mostly utilized process for the biodiesel production through non-edible oils because it reduces the viscosity, moisture and FFAs of non-edible oils during the production of biodiesel [
66]. Two alcohols (methanol and ethanol) are used in the process of transesterification. Methanol is used because of low cost, short carbon chains and low physical properties than aliphatic alcohols [
67]. Ethanol is used because it’s renewable, non-toxic, and eco-friendly. Transesterification is of two types; one in which catalyst is used called catalytic transesterification and second in which catalyst is not used called non-catalytic transesterification. The advantages of transesterification process are suitable for biodiesel, non-toxic chemical reactions and eco-friendly [
68,
69].
5.7.1. Catalytic Transesterification
It is the process of biodiesel production through transesterification in the catalyst presence. There are two types of catalyst used during this process i-e homogeneous catalysts and heterogeneous catalysts [
66,
70]. The mostly used catalysts are homogeneous because less time is required for high yield and simple purification[
71]. NaOH, KOH, methanolic hydrogen chloride, methanolic boron trifluoride, NaOCH3, ferric sulphate, NaOCH3 and methanolic sulfuric acid [
68,
72]. The homogeneous catalyst cannot be used for non-edible oils with high free fatty acid content. Therefore, oils which have high free fatty acid content heterogeneous catalysts are used. Mostly catalytic transesterification processes are carried out by alkaline catalysts [
73,
74]. The reactions with alkaline catalyst have short reaction time and low operating temperature. The mostly utilized alkaline catalysts are methoxide, potassium and sodium hydroxide[
67,
75]. Alkaline catalysts cannot be used for industrial processes because they require low FFA content in oil and absence of water. According to few studies, sodium methoxide is used produce biodiesel with high yield in fast time [
76].
5.7.2. Non-Catalytic Transesterification
It is the production of biodiesel in catalyst absence during transesterification process. This reaction is conducted using co-solvent called BIOX and supercritical fluids. In non-catalytic transesterification process, the two mostly used BIOX co-solvents are tetrahydrofuran and methyl
tert-butyl[
64]. Supercritical methanol (scMeOH) is also used as the solvent in non-catalytic transesterification process because in supercritical state there is no distinction between the liquid and gas phase. The supercritical state of methanol is the state above the critical temperature and pressure of methanol which 512.6K and 8.09 MPa respectively[
77]. The advantages of using Supercritical methanol as a solvent includes glycerol easy separation from biodiesel, doesn’t affect the water and FFA content presence in the oil. The disadvantages using Supercritical Methanol are high cost and also require high pressure and temperature for biodiesel production[
76].
5.8. Non-Edible Oils Blending
The blending process does not require any chemical reaction. In this, the non-edible oil directly blends with diesel fuel and is used as fuel. This process enhances the oil volatility and reduce the oil viscosity[
78]. By blending process, the engine performance increases also enhances the fuels storability and physical properties [
79].
5.9. Different Processes for Biodiesel Production Using Non-Edible Feedstocks
Biodiesel is comprised of fatty acids of long chains that are mono-alkyl esters. The main problem of biodiesel synthesis from non-edible feedstock is the presence of free fatty acids (FFAs). Therefore, many processes have been developed for biodiesel production through non-edible feedstock which can lower the FFA occurrence. These processes are transesterification, micro-emulsion, dilution, and pyrolysis.
Table 2.
Processes for the biodiesel production from non-edible feedstocks.
Table 2.
Processes for the biodiesel production from non-edible feedstocks.
| Non-edible oil |
Processes |
Pressure (MPa) |
Temp (C) |
Time (min) |
Catalyst (%) |
Alcohol: oil |
Yield (%) |
Ref |
| Jatropha |
scMeOH transesterification |
11 |
250-290 |
15 |
NA |
3:1 |
99 |
[76] |
| Castor |
Catalytic transesterification |
|
60 |
45 |
KOH |
6:1 |
97 |
[80] |
| Castor |
Catalytic transesterification |
|
55 |
60 |
Ni-ZnO |
8:1 |
95 |
[74] |
| Cotton seed |
Catalytic transesterification |
|
50 |
60 |
Eggshell |
12:1 |
92 |
[56] |
| Cotton seed |
Catalytic transesterification |
|
65 |
90 |
CH3ONa |
6:1 |
97 |
[66] |
| Jojoba |
Catalytic transesterification |
|
25 |
60 |
KOH |
6:1 |
83.5 |
[81] |
| Karanja |
ScMeOH transesterification |
43 |
300 |
90 |
NA |
43:1 |
81 |
[75] |
| Karanja |
Transesterification |
|
66.8 |
120 |
KOH |
10.44:1 |
91.01 |
[82] |
| Kusum |
Catalytic transesterification |
|
65 |
90 |
K2Al2O4 |
15:1 |
97 |
[72] |
| Neem |
Catalytic transesterification |
|
60 |
23 |
Cu-ZnO |
0.23 |
91 |
[61] |
| Mahua |
Catalytic transesterification |
|
65 |
60 |
KOH |
5:1 |
91 |
[83] |
| Polanga |
Pyrolysis |
|
550 |
|
NA |
NA |
46 |
[62] |
6. Physiochemical Properties of Biodiesel
Biodiesel’s main properties are acid number, viscosity, flash point, cloud point, calorific number, pour point, carbon content and ash content. If these properties are according to standard values the biodiesel can be used as the emission of engine [
84]. Also, these properties indicate the performance of biodiesel. Also to study these properties of biodiesel there are standard tests which are given in
Table 3 [
84,
85]:
6.1. Acid Number
The total number of fatty acids present in the substance (oil) is known as acid number of fatty acid number. To estimate the acid number of biodiesel titration method is used. In this method KOH or any other base which is used to neutralize the acid of one gram of oil. The formula used to determine the acid number is as follows [
84]:
56.1 = Molar Mass of KOH
M = Molarity of bass
W = Weight of sample .
a = volume of titer for blank
b = volume of titer for oil
6.2. Calorific Number
The number of calories generated when unit amount of oil is oxidized. The bomb calorimeter apparatus is used to determine the number of calories. The apparatus contains the bomb in which oil is filled, the nichrome wire of 8cm long and insulated container filled with distilled water. The formula used to determine the number or value of calories is as follow [
84]
The unit of calorific value is Kilo joule per kilo gram (KJ/kg) [
84].
6.3. Kinematic Viscosity:
The quotient of density and dynamic viscosity is called kinematic viscosity. The measure of resistance of fluid to deform at given rate is called viscosity. The more viscous diesel means less performance and damaging of fuel pump. The kinematic viscosity of biodiesel is determined by the Redwood viscometer. Redwood viscometer component includes heat chamber to provide heat, stopper to drain the heat and measuring cylinder to measure the amount of biodiesel. The formula to determine the value of kinematic viscosity is.
A and B are two constants of specific redwood viscometer. For time less than 100 sec the A = 0.26 and B = 179, for time more than 100 sec the A = 0.24 and B = 50 [
84].
6.4. Relative Density
Density is the mass per volume of the substance. Relative density is defined as the ration between the density of substance and standard of substance. The relative density is determined by the Pycnometer. The formula is as follows.
6.5. Ash Content
The powdery substance which is left after burning it is called Ash. Or the powdery residue left after the burning of substance. The apparatus for determine ash content of biodiesel is Muffle furnace. In this sample is taken in crucible quartz and placed in muffle furnace. The biodiesel is turned into ashes after providing heating of 450°C. The formula to calculate is as content is as follow [
84];
6.6. Carbon Residue Content
The left-over carbon compounds after providing the high temperature. It is determined by the carbon residue content apparatus. It contains a glass bulb in which a sample is placed and given a heat of 450°C. To measure the carbon residue the formula is as follows [
84]
6.7. Flash and Fire Point
Flash point of biodiesel is temperature at which spark came out of first thread and Fire point is temperature at which threat starts burning. These points are noticed in the flash and fire point apparatus. In this, two cotton threats are present, first thread is placed inside it and second is placed on surface of first thread. By noticing both spark and burning point we can determine the flash and fire point of biodiesel [
84] .
6.8. Non-Edible Feedstock Physiochemical Properties
Below table shows the physiochemical properties of different non-edible oils [
86,
87]:
Table 4.
Phytochemicals properties of non-edible feedstock.
Table 4.
Phytochemicals properties of non-edible feedstock.
| Oil |
Titer
(C) |
MIU
(%) |
Density
(kg/m3) |
Kinematic viscosity at 40 C |
Cetane No. |
High Heating value (MJ/kg) |
Flash point (C) |
Saponification value |
Iodine value |
| Sesame |
21–24 |
|
913.3 |
36.00 |
41.8 |
39.4 |
260 |
196.50 |
103–116 |
| Jatropha |
31 |
0.16 |
940 |
33.90 |
46-55 |
38.65 |
225 |
200.80 |
82-98 |
| Neem |
35-36 |
2.16 |
918.5 |
50.30 |
51 |
39.5 |
110 |
207 |
65-80 |
| Karanja |
30-31 |
0.72 |
936.5 |
43.61 |
52-58 |
38 |
187 |
188.50 |
81-90 |
| Mahua |
23-31 |
|
960 |
24.50 |
51-52 |
36.0 |
232 |
190.5 |
58-70 |
| Linseed |
19-21 |
0.64 |
923.6 |
25.75 |
34.6 |
39.3 |
241 |
187.63 |
177 |
| Castor |
3 |
0.41 |
955 |
251.20 |
42.3 |
37.4 |
294 |
191.08 |
83-86 |
| Tobacco |
16-18 |
|
917.5 |
27.70 |
49-51.9 |
39.81 |
165.4 |
191.50 |
125-154 |
7. Factors Affecting Production of Biodiesel
There are some chemical and physical factors that can affect the production and quality of biodiesel. These are as follows [
88];
7.1. Fatty Acid Composition
Different plant oils of non-edible feedstocks contain different number of fatty acids in them. The production of biodiesel from them varies with different amount of fats, oils and ester produced from them which affect the biodiesel production [
8]. In below,
Table 5 fatty acid profile of different non-edible feedstocks is shown [
20,
89].
7.2. Free Fatty Acid Content
Fatty acid which does not contain triglyceride molecule is known as free fatty acid and the amount at which they are present is called free fatty acid content. These are formed when heat is given to oil to break long chains of carbon. The formation of soap and glycerol can be seen by free fatty acids during transesterification process. Because of these formations of soap and water the production of biodiesel is affected. Therefore, to remove both the soap and glycerol filtration process in done so that we can get pure biodiesel [
8].
Table 6.
Free Fatty Acid content of non-edible feedstock.
Table 6.
Free Fatty Acid content of non-edible feedstock.
| Non-edible feedstock (oil) |
FFA Content (%) |
Ref |
| Castor |
2.41% |
[90] |
| Karanja |
5% |
[91] |
| Mahua |
18% |
[28] |
| Jatropha |
1.50% |
[70] |
| Neem |
17% |
[54] |
| Cotton |
1.07% |
[92] |
| Rubber |
17% |
[93] |
| Jojoba |
0.96% |
[94] |
| Polanga |
22% |
[95] |
7.3. Heat Content
It is also known as energy content which depends on the energy content of oil used. It is determined based on weight and saturation. If saturation is more the energy content increases, if saturation is less the energy content decreases. Also, if the fuel has high density, it means that it has higher potential energy.
Table 4 shows the heating value of non-edible feedstock [
8].
7.4. Moisture, Impurities and Unsaponifiable (MIU)
During the process of transesterification and esterification, the amount of water, impurities (filterable solids) and other non-triglycerides molecules are produced. These are known as MIU. These molecules are not converted into mono alkyl esters. These should be removed before production of biodiesel to get the pure biodiesel. Above
Table 4 describes the MIU present in different non-edible feedstocks [
11]. There are different methods to removes the MIU from the biodiesel, these are as follows.
7.4.1. Removal of Water
Water is present in very low amount. But even the low amount of water and produce the free fatty acid from which the formation of soap can be seen during the production of biodiesel. At high temperature water produces diglycerides by the hydrolyzing of triglycerides by which free fatty acid is produced. After that during transesterification, free fatty acid produces soap which affects the production of biodiesel. There are three methods to remove water. First, heating method in which heat is given to the solution water settle at bottom and then can be removed easily. Second, centrifugation method in which solution is centrifuge to separate both water and oil. Third is also heating but with pressure, in this after heating the vacuum chamber is sprayed by which the water content gets to very low level. These three methods are used to remove the water, so the clean biodiesel production is seen [
11].
7.4.2. Removal of Insoluble Impurities
Seed fragments, sand and dirt and solid particles are considered insoluble impurities. Because these are not dissolved in liquid solution of biodiesel, so these affects its production. So therefore, to remove these impurities a filtration process is used. In which Whatman or filter paper is used, and solution is pass through this. When the solution is passed through this paper the insoluble impurities do not go pass through this paper and the solution which is passed through this gets clean from impurities [
11].
7.4.3. Removal of Unsaponifiable
Unsaponifiable are organic matters which do not react with base. During crude oil refining these matters are removed. Water washing is also used to remove these matters when crude oil is directly used for production of biodiesel. High molecular weight alcohols, sterols, waxes and hydrocarbons are considered as unsaponifiable matters [
8].
7.4.4. Titer
Titer is the process to determine the quantity concentration of oils or seeds of plant. For solid structures like seeds of plant, the temperature at which oil is produced from seeds is called titer. The plants seed like palm, neem, Karanja and cotton seeds require high temperature range of 30-45°C, more heating (which increases production cost and energy) to form oil through which biodiesel production occurs [
8].
8 Non-Edible Oils as Potential Source of Biodiesel Production
With the development of the biofuel industry, non-edible feedstocks are getting more attention for the production because these are clean source and can be used as the renewable resource of energy [
96]. According to studies, potential advantages of utilizing non-edible feedstocks for production of biodiesel are: It is non-toxic, Eco-friendly, Reduce global warming, Increase engine life, Low Sulphur content, High heating content, Biodegradable.
Due to above distinct properties of biodiesel from the non-edible feedstock makes non-edible feedstock more potential and utilizing source to produce biodiesel [
96,
97].
9. Conclusion
Through this study we can determine that non-edible oils can be used as the potential source of production of biodiesel. In recent times, the demand of non-edible oil to produce biodiesel is increasing because these are not consumed by humans; therefore, there is no debating concern between the food and fuel. Also, there is no concern of specific land for the growth because non-edible plants can grow anywhere even at non-fertile land. The only main concern about the utilization of non-edible feedstock as biodiesel production is high water and free fatty acid contents. However, by using the supercritical methanol process the biodiesel rate can be enhanced with minimum production of free fatty acid and water content. The properties of biodiesel from non-edible oils are like the edible oils therefore, non-edible feedstock can be considered as the potential source for production of biodiesel without any concern like affecting global food economy and global warming.
Authorship Contribution
Muhammad Ammad Jamil contributes in writing, drafting, and reviewing the article. Shamsa Aziz contributes in Characterization and Discussion. Muhammad Salman Khalid contributes in Literature review.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable
Acknowledgements
Nil
Source of Support: Nil
Conflicts of Interest
Nil
References
- Conti, J., et al., International energy outlook 2016 with projections to 2040. 2016, USDOE Energy Information Administration (EIA), Washington, DC (United States ….
- Gebremariam, S.N., J.M.J.E.C. Marchetti, and Management, Economics of biodiesel production. 2018. 168: p. 74-84. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.C. and B.P.J.F. Singh, An ideal feedstock, kusum (Schleichera triguga) for preparation of biodiesel: Optimization of parameters. 2010. 89: p. 1470-1474. [CrossRef]
- Ma, F. and M.A.J.B.t. Hanna, Biodiesel production: a review. 1999. 70(1): p. 1-15.
- Sharma, Y., B. Singh, and S.J.F. Upadhyay, Advancements in development and characterization of biodiesel: A review. 2008. 87(12): p. 2355-2373. [CrossRef]
- Karmee, S.K. and A.J.B.t. Chadha, Preparation of biodiesel from crude oil of Pongamia pinnata. 2005. 96(13): p. 1425-1429. [CrossRef]
- Farnetti, E., et al., Homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. 2009. 2(6): p. 50-86.
- Karmakar, A., S. Karmakar, and S. Mukherjee, Properties of various plants and animals feedstocks for biodiesel production. Bioresour Technol, 2010. 101(19): p. 7201-10. [CrossRef]
- Saraf, S., B.J.P.s. Thomas, and e. protection, Influence of feedstock and process chemistry on biodiesel quality. 2007. 85(5): p. 360-364. [CrossRef]
- Freedman, B., R.O. Butterfield, and E.H.J.J.o.t.A.o.c.s. Pryde, Transesterification kinetics of soybean oil 1. 1986. 63: p. 1375-1380. [CrossRef]
- Knothe, G., A.C. Matheaus, and T.W.J.F. Ryan III, Cetane numbers of branched and straight-chain fatty esters determined in an ignition quality tester☆. 2003. 82(8): p. 971-975. [CrossRef]
- Lee, R., J. Pedley, and C.J.S.t. Hobbs, Fuel quality impact on heavy duty diesel emissions:-a literature review. 1998: p. 1952-1970.
- Boocock, D.G., et al., Fast formation of high-purity methyl esters from vegetable oils. 1998. 75: p. 1167-1172. [CrossRef]
- Lepper, H. and L. Friesenhagen, Process for the production of fatty acid esters of short-chain aliphatic alcohols from fats and/or oils containing free fatty acids. 1986, Google Patents.
- Noureddini, H. and D.J.J.o.t.A.O.C.S. Zhu, Kinetics of transesterification of soybean oil. 1997. 74: p. 1457-1463. [CrossRef]
- Takase, M., et al., An expatiate review of neem, jatropha, rubber and karanja as multipurpose non-edible biodiesel resources and comparison of their fuel, engine and emission properties. 2015. 43: p. 495-520. [CrossRef]
- Moser, B.R.J.B., Biodiesel production, properties, and feedstocks. 2011: p. 285-347.
- Gui, M.M., K. Lee, and S.J.E. Bhatia, Feasibility of edible oil vs. non-edible oil vs. waste edible oil as biodiesel feedstock. 2008. 33(11): p. 1646-1653. [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y., X. Wu, and M.J.A.e. Leung, A review on biodiesel production using catalyzed transesterification. 2010. 87(4): p. 1083-1095. [CrossRef]
- Van Gerpen, J., et al., Biodiesel production technology. 2004. 1617: p. 80401-3393.
- Singh, A., et al., Process optimization of biodiesel production using alkaline catalysts. 2006. 22(4): p. 597-600. [CrossRef]
- Encinar, J.M., et al., Preparation and properties of biodiesel from Cynara C ardunculus L. oil. 1999. 38(8): p. 2927-2931.
- Shaah, M.A.H., et al., A review on non-edible oil as a potential feedstock for biodiesel: physicochemical properties and production technologies. 2021. 11(40): p. 25018-25037. [CrossRef]
- Atabani, A., et al., Non-edible vegetable oils: a critical evaluation of oil extraction, fatty acid compositions, biodiesel production, characteristics, engine performance and emissions production. 2013. 18: p. 211-245. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A., S.J.I.c. Sharma, and products, An evaluation of multipurpose oil seed crop for industrial uses (Jatropha curcas L.): a review. 2008. 28(1): p. 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, B.M., et al., Occurrence of cyanogenic glycoside and cyanide in the Malaysian rubber seed oil. 2013. 14(1): p. 83-86. [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A., et al., Biodiesel production from non-edible plant oils. 2016. 34(2): p. 290-318. [CrossRef]
- Acharya, N., et al., Analysis of properties and estimation of optimum blending ratio of blended mahua biodiesel. 2017. 20(2): p. 511-517. [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.K.G., et al., Refining of crude rubber seed oil as a feedstock for biofuel production. 2017. 203: p. 1011-1016. [CrossRef]
- Sandouqa, A. and Z.J.R.e. Al-Hamamre, Energy analysis of biodiesel production from jojoba seed oil. 2019. 130: p. 831-842.
- Gravalos, I., et al., A mechatronic system for automated topping and suckering of tobacco plants. 2019. 166: p. 104986. [CrossRef]
- Aransiola, E., et al., Prospects of biodiesel feedstock as an effective ecofuel source and their challenges. 2019: p. 53-87.
- Patel, R.L., C.J.R. Sankhavara, and S.E. Reviews, Biodiesel production from Karanja oil and its use in diesel engine: A review. 2017. 71: p. 464-474. [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P., et al., Biodiesel development from high acid value polanga seed oil and performance evaluation in a CI engine. 2007. 86(3): p. 448-454. [CrossRef]
- Mubofu, E.B.J.S.C.P., Castor oil as a potential renewable resource for the production of functional materials. 2016. 4(1): p. 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S. and S.P. Khurana, Importance of actinobacteria for bioremediation, in Plant Biotechnology: Progress in Genomic Era. 2019, Springer. p. 277-307.
- Akhtar, M.T., et al., Comparative study of liquid biodiesel from Sterculia foetida (bottle tree) using CuO-CeO2 and Fe2O3 nano catalysts. 2019. 7: p. 4.
- Durairaj, R., et al., Performance and Emission characteristics of cotton seed and neem oil biodiesel with CeO2 additives in a single-cylinder diesel engine. 2019. 40(4): p. 396-400. [CrossRef]
- Koh, M.Y., T.I.M.J.R. Ghazi, and s.e. reviews, A review of biodiesel production from Jatropha curcas L. oil. 2011. 15(5): p. 2240-2251. [CrossRef]
- Arjuna, R., et al., A REVIEW ON SUSTAINABLE BIODIESEL PRODUCTION USING DIFFERENT MATERIALS.
- Karmakar, A., et al., Biodiesel production from neem towards feedstock diversification: Indian perspective. 2012. 16(1): p. 1050-1060. [CrossRef]
- Kaul, S., et al. Biodiesel: a clean and sustainable fuel for future. in Scientific strategies for production of non-edible vegetable oils for use as biofuels. All India seminar on national policy on non-edible oils as biofuels. SUTRA, IISc Bangalore. 2003.
- Ghadge, S.V., H.J.B. Raheman, and bioenergy, Biodiesel production from mahua (Madhuca indica) oil having high free fatty acids. 2005. 28(6): p. 601-605. [CrossRef]
- Canoira, L., et al., Biodiesel from Jojoba oil-wax: Transesterification with methanol and properties as a fuel. 2006. 30(1): p. 76-81. [CrossRef]
- Duke, J.A.J.H.o.E.C., Handbook of energy crops. 1983.
- Shay, E.G.J.B. and bioenergy, Diesel fuel from vegetable oils: status and opportunities. 1993. 4(4): p. 227-242. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.S., et al., Biodiesel fuel production from algae as renewable energy. 2008. 4(3): p. 250-254. [CrossRef]
- Chisti, Y.J.B.a., Biodiesel from microalgae. 2007. 25(3): p. 294-306.
- Lee, S.Y., M.A. Hubbe, and S.J.B. Saka, Prospects for biodiesel as a byproduct of wood pulping–a review. 2006. 1(1): p. 150-171. [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.J.B., By-product recovery and valorisation in the kraft industry: A review of current trends in the recovery and use of turpentine and tall oil derivatives. 1982. 2: p. 103-113. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, M.G., S.B.J.E.j.o.l.s. Sawant, and technology, Some physical properties of castor oil esters and hydrogenated castor oil esters. 2003. 105(5): p. 214-218. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.S., et al., Coffee oil as a potential feedstock for biodiesel production. 2008. 99(8): p. 3244-3250. [CrossRef]
- King, A., Research advances: fill ‘er up on chicken, shrimp, and coffee? 2010, ACS Publications.
- Rattanaphra, D. and P.J.J.o.c.e.o.J. Srinophakun, Biodiesel production from crude sunflower oil and crude jatropha oil using immobilized lipase. 2010. 43(1): p. 104-108.
- Tang, D.Y.Y., et al., Green technology for the industrial production of biofuels and bioproducts from microalgae: a review. 2020: p. 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Singh, D., et al., Chemical compositions, properties, and standards for different generation biodiesels: A review. 2019. 253: p. 60-71. [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, W.N.M.W., et al., Effects of biodiesel from different feedstocks on engine performance and emissions: A review. 2015. 51: p. 585-602. [CrossRef]
- Istadi, I., S.A. Prasetyo, and T.S.J.P.E.S. Nugroho, Characterization of K2O/CaO-ZnO catalyst for transesterification of soybean oil to biodiesel. 2015. 23: p. 394-399.
- Oltean-Dumbrava, C., G. Watts, and A.J.J.o.c.p. Miah, Transport infrastructure: making more sustainable decisions for noise reduction. 2013. 42: p. 58-68. [CrossRef]
- Brachet, A., et al., Focused microwave-assisted extraction of cocaine and benzoylecgonine from coca leaves. 2002. 13(3): p. 162-169. [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, B. and A.J.B.t. Ravi, Process optimization and kinetics of biodiesel production from neem oil using copper doped zinc oxide heterogeneous nanocatalyst. 2015. 190: p. 424-428.
- Shadangi, K.P. and R.K.J.F. Singh, Thermolysis of polanga seed cake to bio-oil using semi batch reactor. 2012. 97: p. 450-456. [CrossRef]
- Yan, B., et al., Pyrolysis of tobacco wastes for bio-oil with aroma compounds. 2018. 136: p. 248-254. [CrossRef]
- Liang, J., et al., Span80/Tween80 stabilized bio-oil-in-diesel microemulsion: Formation and combustion. 2018. 126: p. 774-782. [CrossRef]
- de Jesus, A., M.M. Silva, and M.G.R.J.T. Vale, The use of microemulsion for determination of sodium and potassium in biodiesel by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. 2008. 74(5): p. 1378-1384. [CrossRef]
- Naik, M., et al., Production of biodiesel from high free fatty acid Karanja (Pongamia pinnata) oil. 2008. 32(4): p. 354-357. [CrossRef]
- Rashid, U., F. Anwar, and G.J.F.P.T. Knothe, Evaluation of biodiesel obtained from cottonseed oil. 2009. 90(9): p. 1157-1163. [CrossRef]
- Adewale, P., et al., Recent trends of biodiesel production from animal fat wastes and associated production techniques. 2015. 45: p. 574-588. [CrossRef]
- Sinha, D. and S.J.P.i.s. Murugavelh, Biodiesel production from waste cotton seed oil using low cost catalyst: Engine performance and emission characteristics. 2016. 8: p. 237-240. [CrossRef]
- Salimon, J. and R.J.S.M. Abdullah, Physicochemical properties of Malaysian Jatropha curcas seed oil. 2008. 37(4): p. 379-382.
- Onukwuli, D.O., et al., Optimization of biodiesel production from refined cotton seed oil and its characterization. 2017. 26(1): p. 103-110. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y. and B.J.F. Singh, An ideal feedstock, kusum (Schleichera triguga) for preparation of biodiesel: Optimization of parameters. 2010. 89(7): p. 1470-1474. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K., et al., Comparative study of biodiesel production methods from Yellow Oleander oil and its performance analysis on an agricultural diesel engine. 2019. 40(2): p. 152-157. [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, K.J.E.S. and P. Research, Experimental investigation on emission reduction in neem oil biodiesel using selective catalytic reduction and catalytic converter techniques. 2018. 25(14): p. 13548-13559.
- Ortiz-Martínez, V., et al., In-depth study of the transesterification reaction of Pongamia pinnata oil for biodiesel production using catalyst-free supercritical methanol process. 2016. 113: p. 23-30. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H., et al., Biodiesel production from supercritical carbon dioxide extracted Jatropha oil using subcritical hydrolysis and supercritical methylation. 2010. 52(2): p. 228-234. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S., et al., Modeling the inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus and Serratia marcescens in clinical solid waste using supercritical fluid carbon dioxide. 2013. 83: p. 47-56.
- Agarwal, A.K. and K.J.A.e. Rajamanoharan, Experimental investigations of performance and emissions of Karanja oil and its blends in a single cylinder agricultural diesel engine. 2009. 86(1): p. 106-112. [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.N.A., et al., A review on primary and Sustainable Energy Scenario in Bangladesh. 2018. 6(1): p. 1-10.
- Makam, B., O. Wilson, and J.H.J.A.J.O.E.P. Claver, Synthesis and Physicochemical Study of Methyl Ester from Black and Caster Seed Oil Admixture. 2018. 6(2): p. 35-38.
- Abdelmoez, W., et al., Green Approach for Biodiesel Production from Jojoba Oil Supported by Process Modeling and Simulation %J International Journal of Chemical Reactor Engineering. 2016. 14(1): p. 185-193.
- Verma, P. and M.J.F. Sharma, Comparative analysis of effect of methanol and ethanol on Karanja biodiesel production and its optimisation. 2016. 180: p. 164-174. [CrossRef]
- Devarajan, Y., et al., Performance, combustion and emission analysis on the effect of ferrofluid on neat biodiesel. 2017. 111: p. 283-291. [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, R., et al., Production of biodiesel from unused algal biomass in Punjab, India. 2018. 15(1): p. 164-175. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R., et al., Effect of process parameters for standardization of esterification of cotton seed oil for the production of biodiesel. 2013(8): p. 74-78.
- Barnwal, B., M.J.R. Sharma, and s.e. reviews, Prospects of biodiesel production from vegetable oils in India. 2005. 9(4): p. 363-378. [CrossRef]
- Sanford, S., et al., Feedstock and biodiesel characteristics report. Ames, IA: Renewable Energy Group. 2009, Inc.
- Gunstone, F., The chemistry of oils and fats: sources, composition, properties and uses. 2009: John Wiley & Sons.
- Ngugi Kariuki, P., et al., Passiflora edulis seed oil methyl ester as a potential source of biodiesel. 2012. 2: p. 2224-3186.
- Yusuf, A., et al., Extraction and characterization of castor seed oil from wild Ricinus communis Linn. 2015. 4(5): p. 1392-1404.
- Eipeson, W.S., et al., Extraction and recovery of karanjin: A value addition to karanja (Pongamia pinnata) seed oil. 2010. 32(2): p. 118-122. [CrossRef]
- Onukwuli, D.O., et al., Optimization of biodiesel production from refined cotton seed oil and its characterization. Egyptian Journal of Petroleum, 2017. 26(1): p. 103-110. [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, B.M., et al., Occurrence of cyanogenic glycoside and cyanide in the Malaysian rubber seed oil. Journal of the Association of Arab Universities for Basic and Applied Sciences, 2013. 14(1): p. 83-86. [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamamre, Z. and A. Al-Salaymeh, Physical properties of (jojoba oil + biodiesel), (jojoba oil + diesel) and (biodiesel + diesel) blends. Fuel, 2014. 123: p. 175-188.
- Sahoo, P., et al., Biodiesel development from high acid value polanga seed oil and performance evaluation in a CI engine. Fuel, 2007. 86: p. 448-454. [CrossRef]
- Atabani, A.E., et al., Non-edible vegetable oils: A critical evaluation of oil extraction, fatty acid compositions, biodiesel production, characteristics, engine performance and emissions production. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2013. 18: p. 211-245. [CrossRef]
- Rani, S., M.L. Joy, and K.P. Nair, Evaluation of physiochemical and tribological properties of rice bran oil – biodegradable and potential base stoke for industrial lubricants. Industrial Crops and Products, 2015. 65: p. 328-333. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).