Submitted:
11 September 2024
Posted:
14 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
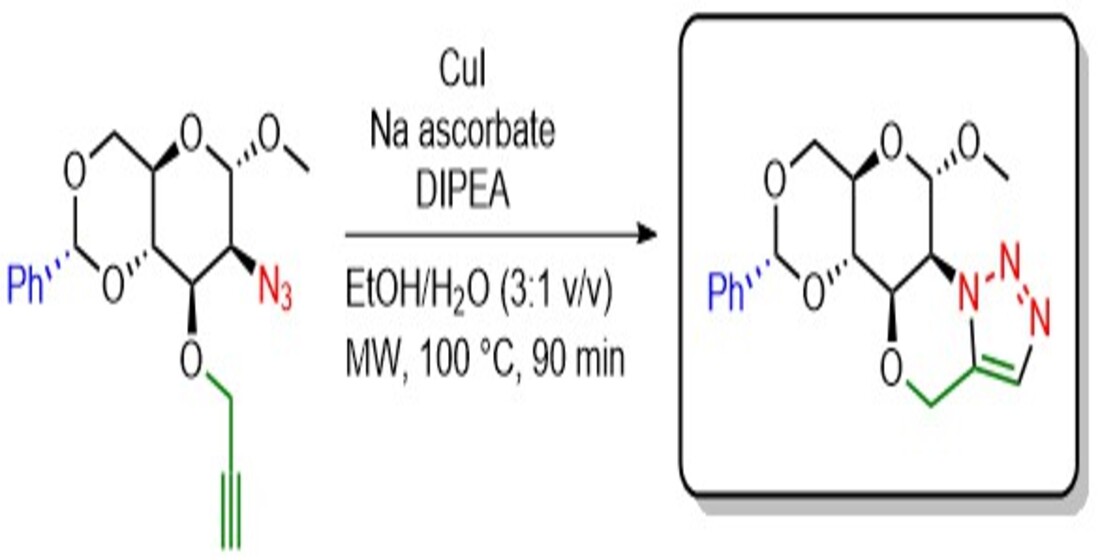
Keywords:
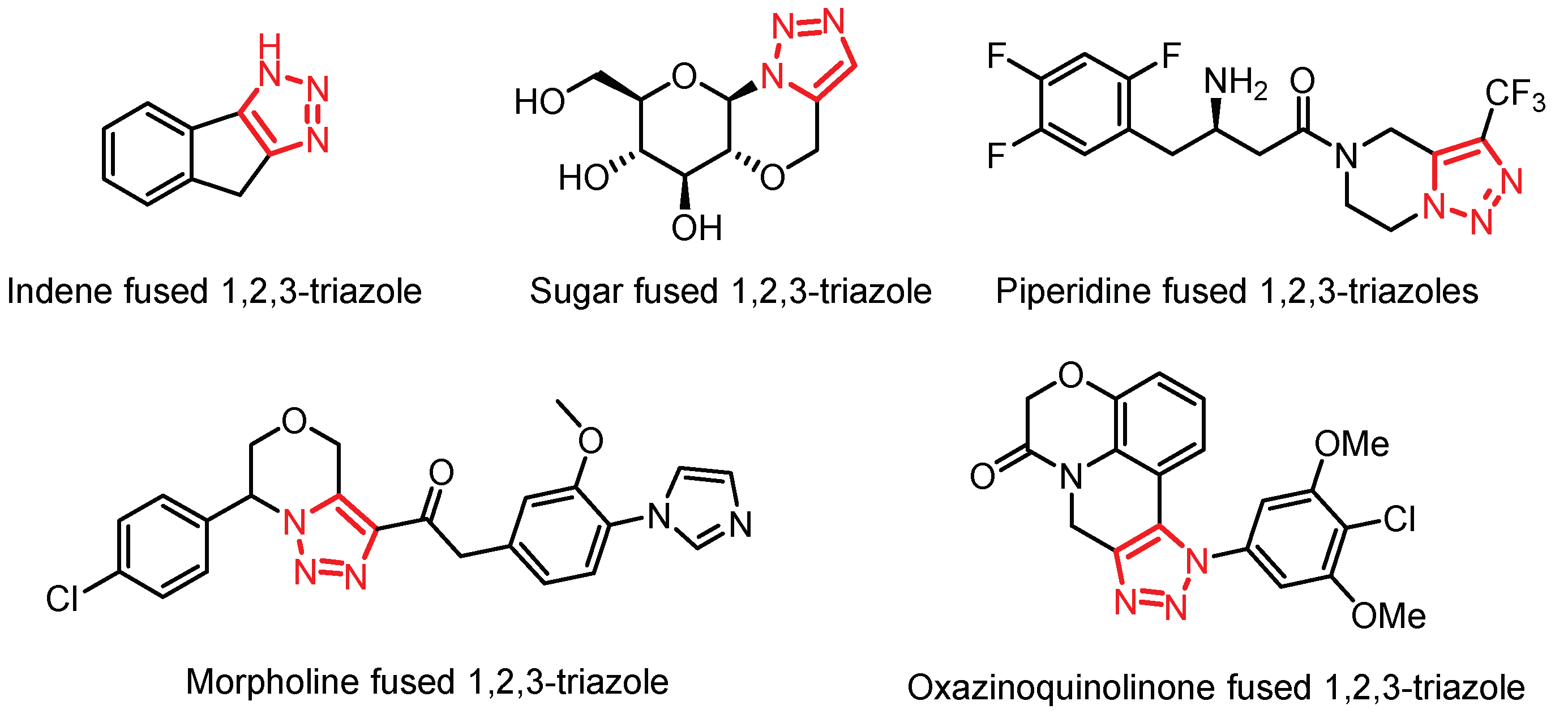
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
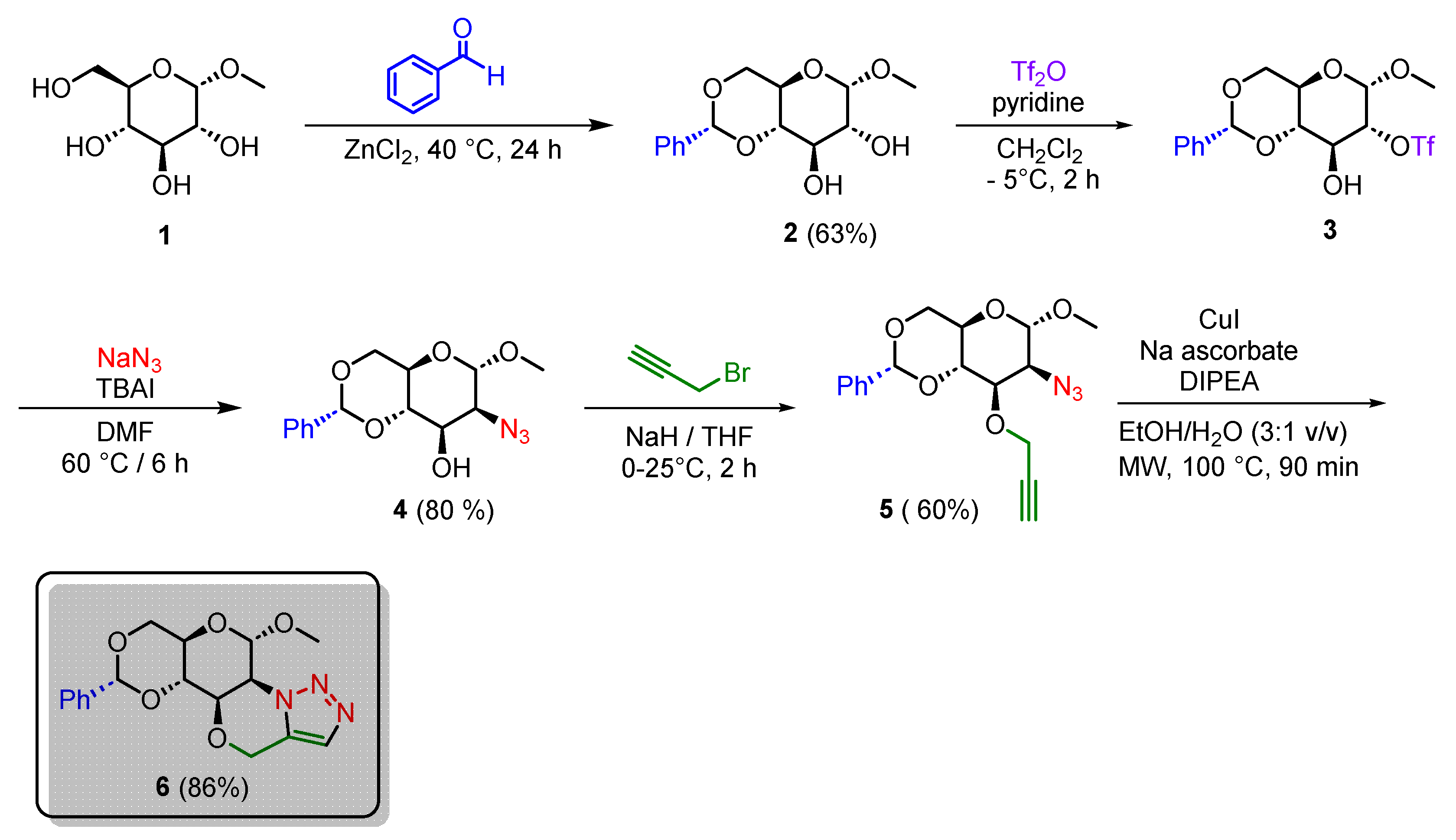
3. Materials and Methods
Synthesis de Methyl 2-azido-4,6-O-benzyliden-2-deoxy-3-O-propargyl- a-D-glycopyranoside 5
Synthesis Morpholine-fused [5,1-c]triazole 6
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shiro, T.; Fukaya, T.; Tobe, M. The chemistry and biological activity of heterocycle-fused quinolinone derivatives: A review, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Shreeve, J.M. Fused heterocycle-based energetic materials (2012–2019). J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020; 8, 4193–4216. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Z.; Peng, M.; Fan, H.; Lu, Q.; Lu, P.; Zhao, C.; Chen, Y. Discovery of potent dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors derived from β-aminoamides bearing substituted [1,2,3]-triazolopiperidines for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 1731–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, B.; Steele, C.; Hardick, D.; Dale, M.; Pomel, V.; Quattropani, A.; Beher, D. Fused Triazole Derivatives as Gamma Secretase Modulators. Eur. Pat. Appl 2014, EP 2687528 A1. [Google Scholar]
- Narsimha, S.; Battula, K.S.; Nukala, S.K.; Gondru, R.; Reddy, Y.N. Nagavelli, V.R. One-pot synthesis of fused benzoxazino[1,2,3]triazolyl[4,5-c]quinolinone derivatives and their anticancer activity. RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 74332–74339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, I.; Santoni, G.; Lucciarini, R.; Amantini, C.; Sparapani, S.; Magnano, A. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of New Asymmetrical Bisintercalators as Potential Antitumor Drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 7198–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, K.C.; Ray, K. Synthesis of 1,2,3-Triazole-Fused Heterocycles via Intramolecular Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition Reactions. Synthesis 2011, 23, 3767–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vala, D.P.; Vala, R.M.; Patel, H.M. Versatile Synthetic Platform for 1,2,3-Triazole Chemistry. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 36945–36987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, M.M. , Matin P.; Rahman, Md.R., Ben, H.T.; Almalki, F.A.; Mahmud, S., Ghoneim, M.M.; Alruwaily, M.; Alshehri, S. Triazoles and Their Derivatives: Chemistry, Synthesis, and Therapeutic Applications. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Hu, H.; Zhang, M.; Hu, X.; Chen, M.; Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Xiao, G.; Wanga, Y.; Wen, Z. A mini review of the synthesis of poly-1,2,3-triazole-based functional materials. RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, M.C.; Swarts, A.J.; Mapolie, S.F. Transition metal complexes of click-derived 1,2,3-triazoles as catalysts in various transformations: An overview and recent developments. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 493, 215317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, J.R.; Beke-Somfai, T.; Stålsmeden, A.S.; Kann, N. Ruthenium-Catalyzed Azide Alkyne Cycloaddition Reaction: Scope, Mechanism, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14726–14768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- P, R.; Thomas, J.; Dehaen, W.; John, J. Advances in the Synthesis of Fused 1,2,3-Triazoles via a MCR-Intramolecular Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition Approach. Molecules 2023, 28, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, T.; Bose, A. 1,5-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazolylated carbohydrates and nucleosides. Carbohydr. Res. 2024, 541, 109126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotha, S.; Anegundi, R.I.; Natu, A.A. Expedient synthesis of 1,2,3-triazole-fused tetracyclic compounds by intramolecular Huisgen (click) reactions on carbohydrate-derived azido-alkynes, Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 4585–4588.
- Adhikary, N. D.; Chattopadhyay, P. Design and synthesis of 1,2,3-triazole-fused chiral medium-ring benzo-heterocycles, scaffolds mimicking benzolactams. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 5399–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panday, N.; Meyyappan, M.; Vasella, A. A comparison of glucose- and glucosamine-related inhibitors: probing the interaction of the 2-hydroxy group with retaining β-glucosidases. Helv. Chim. Acta 2000, 83, 513–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayl, A.A.; Aly, A.A.; Arafa, W.A.A.; Ahmed, I.M.; Abd-Elhamid, A.I.; El-Fakharany, E.M.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Tawfeek, H.N.; Bräse, S. Azides in the Synthesis of Various Heterocycles. Molecules 2022, 27, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K. B.; Tiwari, V. K. Click Chemistry Inspired Synthesis of Morpholine-Fused Triazoles. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 5752–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, Y. S.; John Pal, A. P.; Gupta, P.; Ansari, A. A.; Vankar, Y. D. Ceric Ammonium Nitrate-Catalyzed Azidation of 1,2-Anhydro Sugars: Application in the Synthesis of Structurally Diverse Sugar-Derived Morpholine 1,2,3-Triazoles and 1,4-Oxazin-2-ones. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K. B.; Shasi, S.; Tiwari, V. K. Metal free synthesis of morpholine fused [5,1-c] triazolyl glycoconjugates via glycosyl azido alcohols. RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 86840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Vázquez, A.; Cervantes, R. M. A.; Negrón-Silva, G. E.; Rodríguez Gómez F., J. , Palomar, P. M.; Lomas, R. L., Ángeles Beltrán D., Pérez Martínez, D. Carbohydrates as Corrosion Inhibitors of API 5L X70 Steel Immersed in Acid Medium. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci 2019, 14, 9206–9220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, S.; Kukkola, P. J.; Sharma, S.; Dhar, T. G. M.; Naughton, A. B. J. , Amino Alcohol and Amino Sugar Synthesis by Benzoylcarbamate Cyclization. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 5700–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popelová, A.; Kefurt, K.; Hlaváckova, M.; Moravcová, J. A concise synthesis of 4-nitrophenyl-2-azido-2-deoxy and 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-d-mannopyranosides. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



