Submitted:
13 September 2024
Posted:
13 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pelliccia A, Sharma S, Gati S, Bäck M, Börjesson M, Caselli S, Collet JP, Corrado D, Drezner JA, Halle M, Hansen D, Heidbuchel H, Myers J, Niebauer J, Papadakis M, Piepoli MF, Prescott E, Roos-Hesselink JW, Graham Stuart A, Taylor RS, Thompson PD, Tiberi M, Vanhees L, Wilhelm M; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2020 ESC Guidelines on sports cardiology and exercise in patients with cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. 2021 Jan 1;42(1):17-96. Erratum in: Eur Heart J. 2021 Feb 1;42(5):548-549. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa835. [CrossRef]
- Mancia G, Kreutz R, Brunström M, Burnier M, Grassi G, Januszewicz A, Muiesan ML, Tsioufis K, Agabiti-Rosei E, Algharably EAE, Azizi M, Benetos A, Borghi C, Hitij JB, Cifkova R, Coca A, Cornelissen V, Cruickshank JK, Cunha PG, Danser AHJ, Pinho RM, Delles C, Dominiczak AF, Dorobantu M, Doumas M, Fernández-Alfonso MS, Halimi JM, Járai Z, Jelaković B, Jordan J, Kuznetsova T, Laurent S, Lovic D, Lurbe E, Mahfoud F, Manolis A, Miglinas M, Narkiewicz K, Niiranen T, Palatini P, Parati G, Pathak A, Persu A, Polonia J, Redon J, Sarafidis P, Schmieder R, Spronck B, Stabouli S, Stergiou G, Taddei S, Thomopoulos C, Tomaszewski M, Van de Borne P, Wanner C, Weber T, Williams B, Zhang ZY, Kjeldsen SE. 2023 ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension: Endorsed by the International Society of Hypertension (ISH) and the European Renal Association (ERA). J Hypertens. 2023 Dec 1;41(12):1874-2071. [CrossRef]
- Whelton SP, Chin A, Xin X, He J. Effect of aerobic exercise on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Ann Intern Med. 2002 Apr 2;136(7):493-503. [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen VA, Fagard RH, Coeckelberghs E, Vanhees L. Impact of resistance training on blood pressure and other cardiovascular risk factors: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Hypertension. 2011 Nov;58(5):950-8. [CrossRef]
- López-Valenciano A, Ruiz-Pérez I, Ayala F, Sánchez-Meca J, Vera-Garcia FJ. Updated systematic review and meta-analysis on the role of isometric resistance training for resting blood pressure management in adults. J Hypertens. 2019 Jul;37(7):1320-1333. [CrossRef]
- Mcleod JC, Stokes T, Phillips SM. Resistance Exercise Training as a Primary Countermeasure to Age-Related Chronic Disease. Front Physiol. 2019 Jun 6;10:645. [CrossRef]
- Paluch AE, Boyer WR, Franklin BA, Laddu D, Lobelo F, Lee DC, McDermott MM, Swift DL, Webel AR, Lane A; on behalf the American Heart Association Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health; Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology; Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; and Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. Resistance Exercise Training in Individuals With and Without Cardiovascular Disease: 2023 Update: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2024 Jan 16;149(3):e217-e231. [CrossRef]
- Fan Y, Yu M, Li J, Zhang H, Liu Q, Zhao L, Wang T, Xu H. Efficacy and Safety of Resistance Training for Coronary Heart Disease Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Nov 5;8:754794. [CrossRef]
- Marzolini S, Oh PI, Brooks D. Effect of combined aerobic and resistance training versus aerobic training alone in individuals with coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2012 Feb;19(1):81-94. [CrossRef]
- Carlson, D. J., Dieberg, G., Hess, N. C., Millar, P. J., & Smart, N. A. (2014). Isometric exercise training for blood pressure management: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 2014;89; 327–334. [CrossRef]
- López-Valenciano, A., Ruiz-Pérez, I., Ayala, F., Sánchez-Meca, J., & Vera-Garcia, F. J. Updated systematic review and meta-analysis on the role of isometric resistance training for resting blood pressure management in adults. Journal of Hypertension. 2019;37:1320–1333. [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen VA, Smart NA. Exercise training for blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013 Feb 1;2(1):e004473. [CrossRef]
- Kounoupis A, Papadopoulos S, Galanis N, Dipla K, Zafeiridis A. Are Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Stress Greater in Isometric or in Dynamic Resistance Exercise? Sports (Basel). 2020 Mar 28;8(4):41. [CrossRef]
- Goessler K, Buys R, Cornelissen VA. Low-intensity isometric handgrip exercise has no transient effect on blood pressure in patients with coronary artery disease. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2016 Aug;10(8):633-9. [CrossRef]
- Gois MO, Simões RP, Porta A, Kunz VC, Pastre CM, Catai AM. Cardiovascular responses to low-intensity isometric handgrip exercise in coronary artery disease: effects of posture. Braz J Phys Ther. 2020 Sep-Oct;24(5):449-457. [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos K, Özden Tok Ö, Mitrousi K, Ikonomidis I. Myocardial Work: Methodology and Clinical Applications. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Mar 22;11(3):573.
- Boe E, Skulstad H, Smiseth OA. Myocardial work by echocardiography: a novel method ready for clinical testing. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Jan 1;20(1):18-20. [CrossRef]
- D'Andrea A, Carbone A, Radmilovic J, Russo V, Fabiani D, Maio MD, Ilardi F, Giallauria F, Caputo A, Cirillo T, Bossone E, Picano E. Myocardial Work Efficiency in Physiologic Left Ventricular Hypertrophy of Power Athletes. J Cardiovasc Echogr. 2022 Jul-Sep;32(3):154-159. [CrossRef]
- Meldrum D, Cahalane E, Conroy R, Fitzgerald D, Hardiman O. Maximum voluntary isometric contraction: reference values and clinical application. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2007 Feb;8(1):47-55. [CrossRef]
- Nagueh SF, Smiseth OA, Appleton CP, Byrd BF 3rd, Dokainish H, Edvardsen T, Flachskampf FA, Gillebert TC, Klein AL, Lancellotti P, Marino P, Oh JK, Alexandru Popescu B, Waggoner AD; Houston, Texas; Oslo, Norway; Phoenix, Arizona; Nashville, Tennessee; Hamilton, Ontario, Canada; Uppsala, Sweden; Ghent and Liège, Belgium; Cleveland, Ohio; Novara, Italy; Rochester, Minnesota; Bucharest, Romania; and St. Louis, Missouri. Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016 Dec;17(12):1321-1360. [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos K, Özden Tok Ö, Mitrousi K, Ikonomidis I. Myocardial Work: Methodology and Clinical Applications. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Mar 22;11(3):573.
- Edwards JJ, Coleman DA, Ritti-Dias RM, Farah BQ, Stensel DJ, Lucas SJE, Millar PJ, Gordon BDH, Cornelissen V, Smart NA, Carlson DJ, McGowan C, Swaine I, Pescatello LS, Howden R, Bruce-Low S, Farmer CKT, Leeson P, Sharma R, O'Driscoll JM. Isometric Exercise Training and Arterial Hypertension: An Updated Review. Sports Med. 2024 Jun;54(6):1459-1497. [CrossRef]
- Taylor KA, Wiles JD, Coleman DD, Sharma R, Oʼdriscoll JM. Continuous Cardiac Autonomic and Hemodynamic Responses to Isometric Exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017 Aug;49(8):1511-1519. [CrossRef]
- Hanson P, Nagle F. Isometric exercise: cardiovascular responses in normal and cardiac populations. Cardiol Clin. 1987 May;5(2):157-70.
- Russell K, Eriksen M, Aaberge L, Wilhelmsen N, Skulstad H, Gjesdal O, Edvardsen T, Smiseth OA. Assessment of wasted myocardial work: a novel method to quantify energy loss due to uncoordinated left ventricular contractions. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013 Oct 1;305(7):H996-1003. [CrossRef]
- Lustosa R.P., van der Bijl P., El Mahdiui M., Montero-Cabezas J.M., Kostyukevich M.V., Marsan N.A., Bax J.J., Delgado V. Noninvasive Myocardial Work Indices 3 Months after ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Prevalence and Characteristics of Patients with Postinfarction Cardiac Remodeling. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2020;33:1172–1179. [CrossRef]
- El Mahdiui M, van der Bijl P, Abou R, Ajmone Marsan N, Delgado V, Bax JJ. Global Left Ventricular Myocardial Work Efficiency in Healthy Individuals and Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2019 Sep;32(9):1120-1127. [CrossRef]
- Azevedo P.S., Minicucci M.F., Santos P.P., Paiva S., Zornoff L. Energy Metabolism in Cardiac Remodeling and Heart Failure. Cardiol. Rev. 2013;21:135–140. [CrossRef]
- Erevik CB, Kleiven Ø, Frøysa V, Bjørkavoll-Bergseth M, Chivulescu M, Klæboe LG, Dejgaard L, Auestad B, Skadberg Ø, Melberg T, Urheim S, Haugaa K, Edvardsen T, Ørn S. Myocardial inefficiency is an early indicator of exercise-induced myocardial fatigue. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jan 11;9:1081664. [CrossRef]
- Taylor KA, Wiles JD, Coleman DD, Sharma R, Oʼdriscoll JM. Continuous Cardiac Autonomic and Hemodynamic Responses to Isometric Exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017 Aug;49(8):1511-1519. [CrossRef]
- MacDougall JD, McKelvie RS, Moroz DE, Sale DG,McCartney N, Buick F. Factors affecting blood pressure during heavy weight lifting and static contractions. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1992;73(4):1590---1597. [CrossRef]
- Haskell WL, Savin WM, Schroeder JS, Alderman EA, Ingles NB Jr, Daughters GT 2nd, Stinson EB. Cardiovascular responses to handgrip isometric exercise in patients following cardiac transplantation. Circ Res. 1981 Jun;48(6 Pt 2):I156-61.
- Nóbrega AC, Williamson JW, Garcia JA, Mitchell JH. Mechanisms for increasing stroke volume during static exercise with fixed heart rate in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1997 Sep;83(3):712-7. [CrossRef]
- Nagueh SF. Non-invasive assessment of left ventricular filling pressure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2018 Jan;20(1):38-48. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee JH, Park JH, Hwang IC, Park JJ, Park JB. Decreased Peak Left Atrial Longitudinal Strain Is Associated with Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Left Heart Disease. J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 18;11(12):3510. [CrossRef]
- Seals, DR. Influence of muscle mass on sympathetic neural activation during isometric exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1989 Nov;67(5):1801-6. [CrossRef]
- Coneglian JC, Barcelos GT, Bandeira ACN, Carvalho ACA, Correia MA, Farah BQ, Ritti-Dias RM, Gerage AM. Acute Blood Pressure Response to Different Types of Isometric Exercise: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Feb 10;24(2):60. [CrossRef]
- Ewing DJ, Irving JB, Kerr F, Kirby BJ. Static exercise in untreated systemic hypertension. Br Heart J. 1973 Apr;35(4):413-21. [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.I. Strength and aerobic exercise training in coronary artery disease; it’s not “either-or.” Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2017;24(16):1686–1691. [CrossRef]
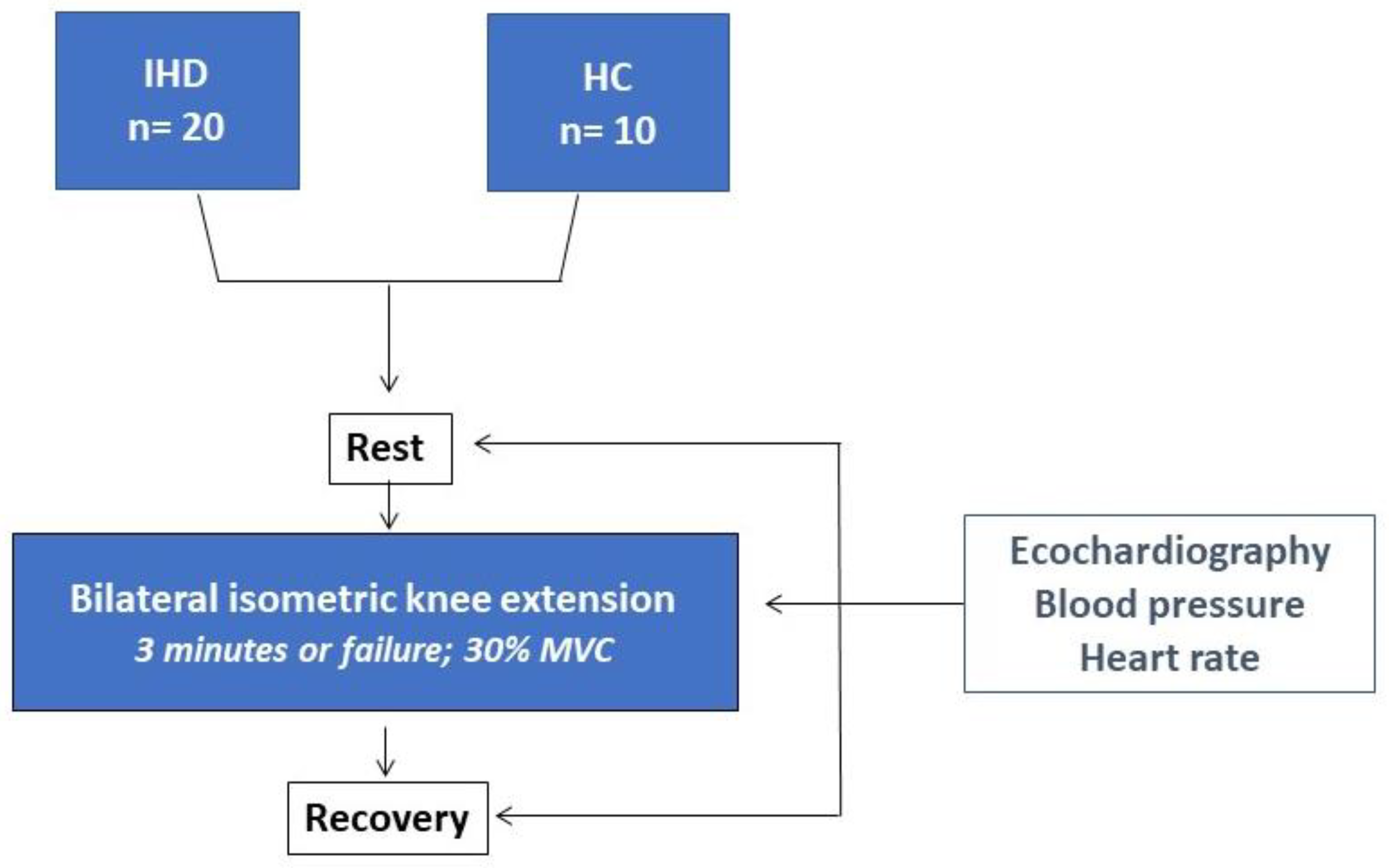
| IHD (n= 20) | HC (n=10) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 63.4±7.5 | 61.8±4.8 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 27.5±6.3 | 26.7±7.1 |
| Male/female | 16/4 | 7/3 |
| Previous PCI/CABG | 17/8 | - |
| EF, (%) | 50.2± 6.1† | 61.5± 7.3 |
| NT-pro BNP | 95.0±59.3 | 22 |
| Comorbidities | ||
| Carotid artery disease, n (%) | 8 (40) | - |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 20/(100) | - |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 5 (25) | - |
| Hypercholesterolemia, n (%) | 18 (90) | 4 (40) |
| Previous Smoke habit, n (%) | 13 (65) | 3 (30) |
| Treatment | ||
| Anti-platelets agents, n (%) | 20 (100) | |
| ACE-Is/ARBs, n (%) | 18 (90) | - |
| Betablockers, n (%) | 20 (100) | - |
| Diuretics, n (%) | 8 (40) | - |
| Ranolazine, n (%) | 4 (20) | |
| Ivabradine, n (%) | 1 (5) | |
| Statins, n (%) | 20 (100) | 3 (30) |
| Ezetimibe, n (%) | 12 (60) | 1 (10) |
| IHD (n=20) | HC (n=10) | |||||
| Rest | Peak | Recovery | Rest | Peak | Recovery | |
| HR, b/mim | 68.7 ± 10.2 | 77.1 ± 14.6 | 63.1 ± 7.7 | 71.4 ± 12.0 | 91.1 ± 9.3*† | 75.1 ± 11.0 |
| SBP, mmHg | 124.6 ± 15.8 | 162.2 ± 34.6*† | 121.5 ± 14.6 | 124.1 ± 13 | 132.5 ± 11.2 | 120.7 ± 16.5 |
| DBP, mmHg | 77.8 ± 9.3 | 97.2 ± 20.2*† | 76.5 ± 6.0 | 75.0 ± 11.3 | 82.4 ± 7.6 | 76.3 ± 12.9 |
| DP | 8560.0±952.7 | 12505.6±883.1 | 7666.6±874.5 | 8860.7±652.8 | 12070,7±1023.2 | 9064.5±789.5 |
| Echocardiography | ||||||
| LVEDV, ml | 140.4 ± 33,4 | 122.3 ± 35.6*† | 137.1 ± 35.2 | 118.9 ± 18.2 | 119.4 ± 15.3 | 119.6 ± 16.1 |
| LVESV, ml | 70.5 ± 11.7 | 67.2 ± 16,1 | 72.2 ± 14.5 | 50.2 ± 7.9 | 49.3 ± 7.4 | 47.4 ± 6.5 |
| LVEF, % | 50.3 ± 7.4 | 49.7 ± 7.2 | 48.3 ± 5.6 | 58.4 ± 3.6 | 59.3 ± 3.2 | 59.5 ± 2.2 |
| LVGLS, % | -11.4 ± 3.8 | - 7.9 ± 2.7*† | -12.2 ± 3.8 | -18.4 ± 2.4 | -18.6 ± 2.5 | - 20.1 ± 2.6 |
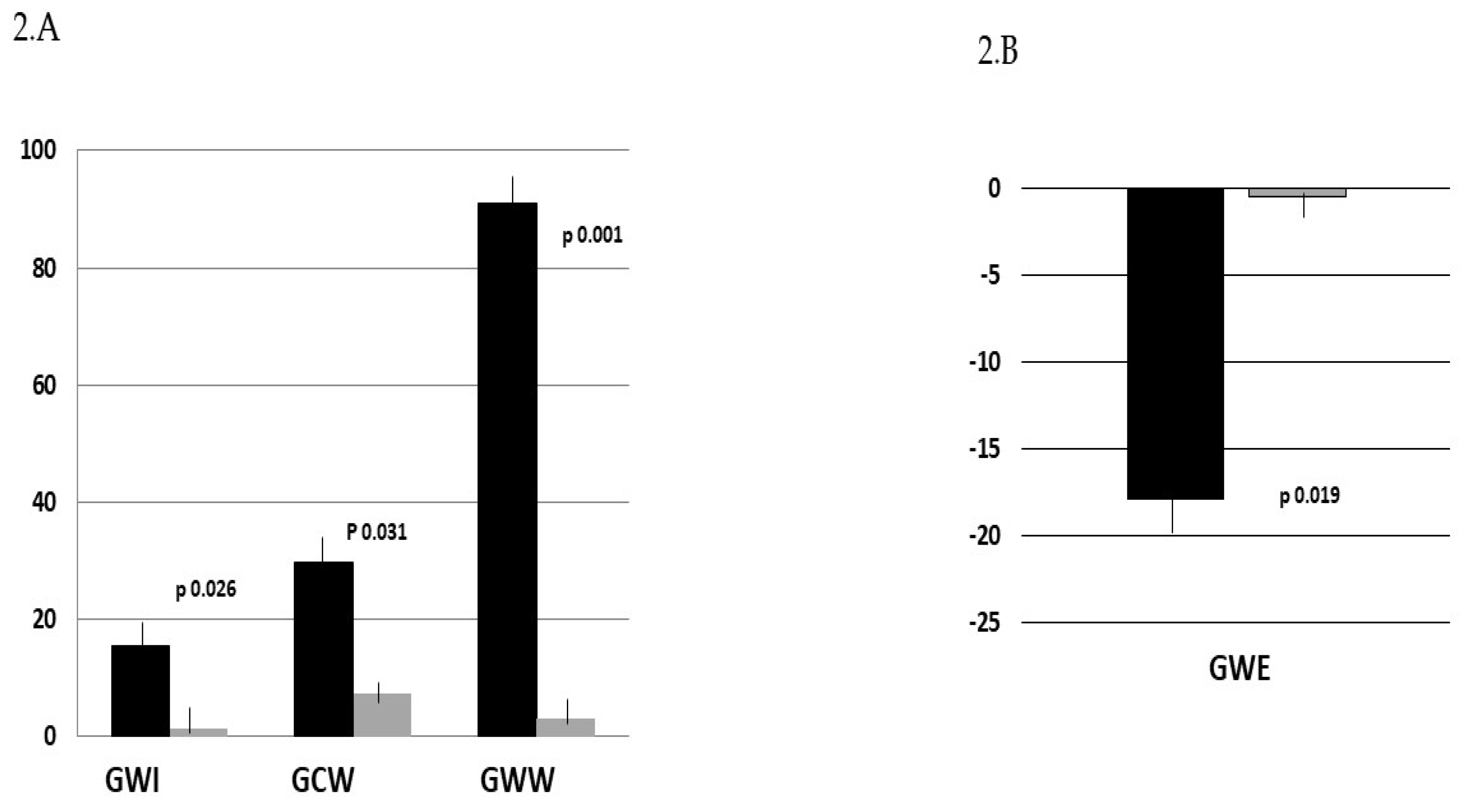
| GWI, % | 1050.5 ± 412.6 | 1212.7 ± 356.4*† | 1145.6 ± 521.8 | 2033.0 ± 108.5 | 2025.7 ± 130.2 | 1573.1 ± 413.3 |
| GCW, % | 1501.3 ± 491.8 | 1958.1 ± 328.3*† | 1391.9 ± 469.0 | 2231.3 ± 85.8 | 2114.3 ± 126.7 | 2085.0 ± 348.6 |
| GWW, % | 289.7 ± 127.7 | 554.9 ± 304.7*† | 218.8 ± 128.7 | 52.7 ± 5.2 | 54.4 ± 3.1 | 58.5 ± 156.5 |
| GWE, % | 80.7 ± 11.7 | 66.4 ± 8.1*† | 82.3 ± 11.2 | 96.0 ± 2.9 | 95.3 ± 3.6 | 95.2 ± 9.6 |
| DT, ms | 248.7 ± 60.4 | 220.3 ± 57.6*† | 254.6 ± 56.3 | 194.8 ± 38.4 | 192.1 ± 53.6 | 192.4 ± 53.2 |
| E, cm/s | 48.1 ± 9.0 | 60.4 ± 15.2 | 48.5 ± 13.1 | 55.7 ± 13.4 | 55.4 ± 17.0 | 64.3 ± 12.9 |
| A, cm/s | 66.4 ± 16.1 | 77.5 ± 23.2 | 63.0 ± 15.2 | 48.6 ± 9.3 | 54.8 ± 9.8 | 51.2 ± 11.3 |
| E/A ratio | 0.75 ± 0.16 | 0.84 ± 15.2 | 0.78 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.4 |
| E’, cm/s | 7.4 ± 1.5 | 5.4 ± 4.4*† | 6.2± 3.1 | 11.7 ± 1.6 | 11.5 ± 2.8 | 11.9 ± 2.3 |
| E/E’ ratio | 6.7 ± 1.9 | 10.4 ± 7.4*† | 7.4 ± 2.4 | 5.2 ± 0.8 | 5.0 ± 1.1 | 6.4 ± 2.4 |
| TRV, m/s | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 0.4 |
| PALS, % | 19.7 ± 8.5 | 16.8 ± 6.7 | 22.2 ± 8.4 | 22.6 ± 4.7 | 22.4 ± 8.1 | 23.7 ± 9.4 |
| PACS, % | -8.9 ± 3.5 | -11.7 ± 6.7 | -12.3 ± 8.0 | -12.6 ± 4.5 | -12.5 ± 7.5 | -13.4 ± 6.1 |
| LAVI, ml/m2 | 25.6 ± 7.2 | 21.3 ± 7.8 | 22.9 ± 7.2 | 19.4 ± 3.2 | 20.25 ± 6.2 | 18.8 ± 3.5 |
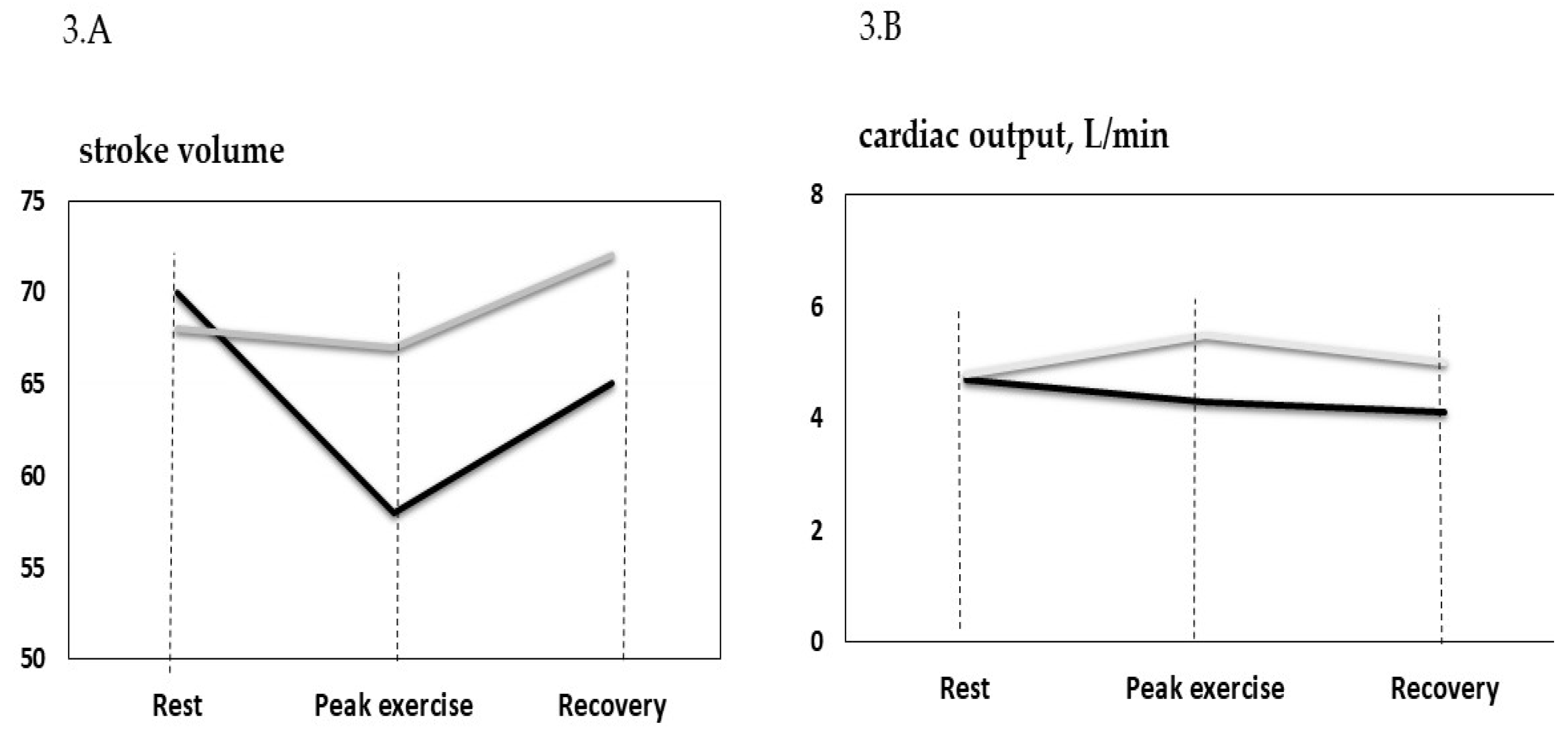
| SV, ml | 70.3 ± 14.3 | 58.5 ± 12.1*† | 64.7 ± 14.1 | 68.6 ± 11.8 | 67.1 ± 15.2 | 72.2 ± 6.1 |
| CO, l/min | 4.7 ± 1.1 | 4.3 ± 1.3† | 4.1 ± 1.1 | 4.9 ± 0.8 | 5.5 ± 0.7 | 5.2 ± 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





