Submitted:
13 September 2024
Posted:
15 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Experimental Birds and Sample Collection
2.3. RNA Isolation and Quality Check
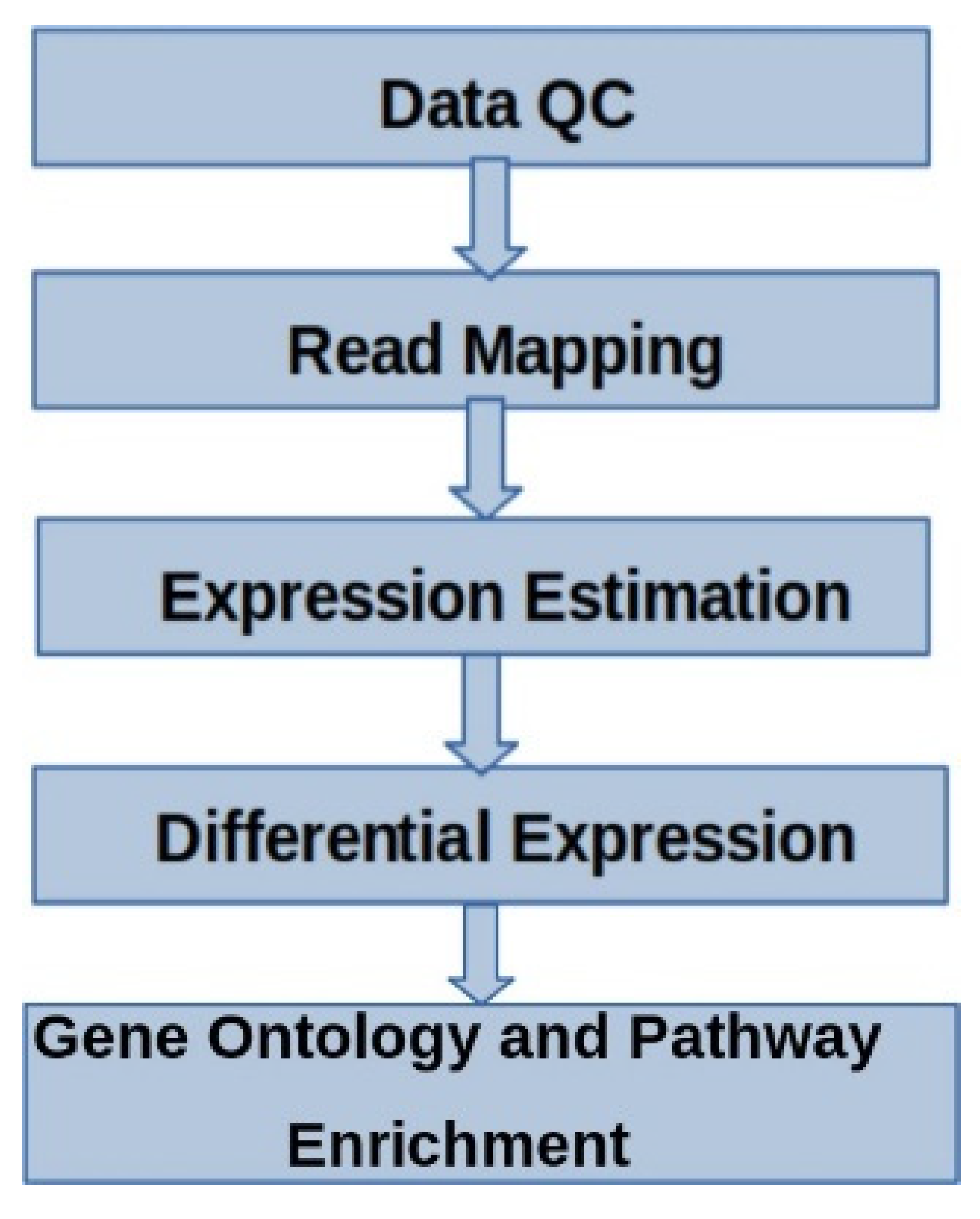
2.4. Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.5. Functional Analysis
2.6. Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI)
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR) Validation
3. Results
3.1. RNA-Seq Data Analysis
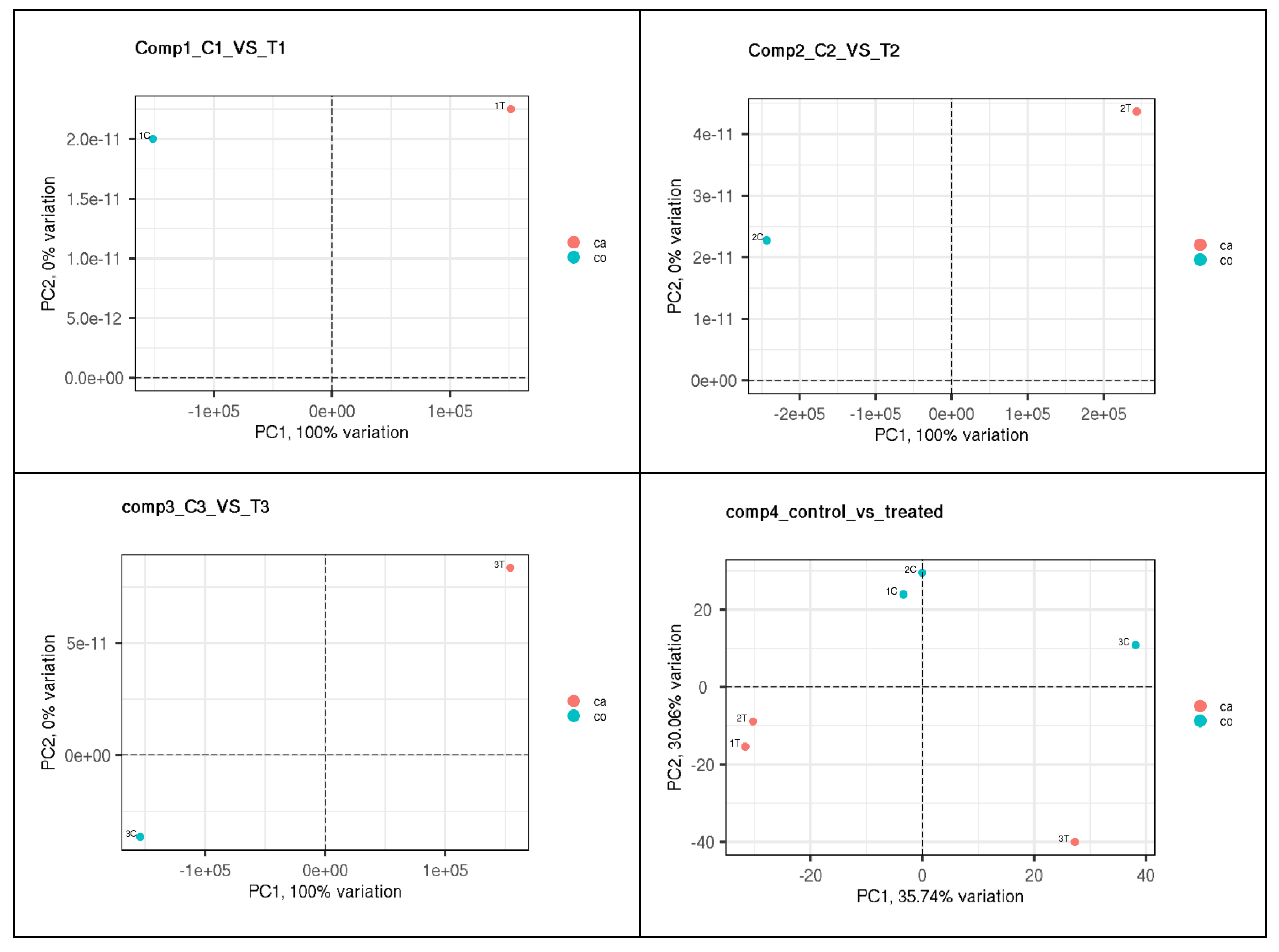
3.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
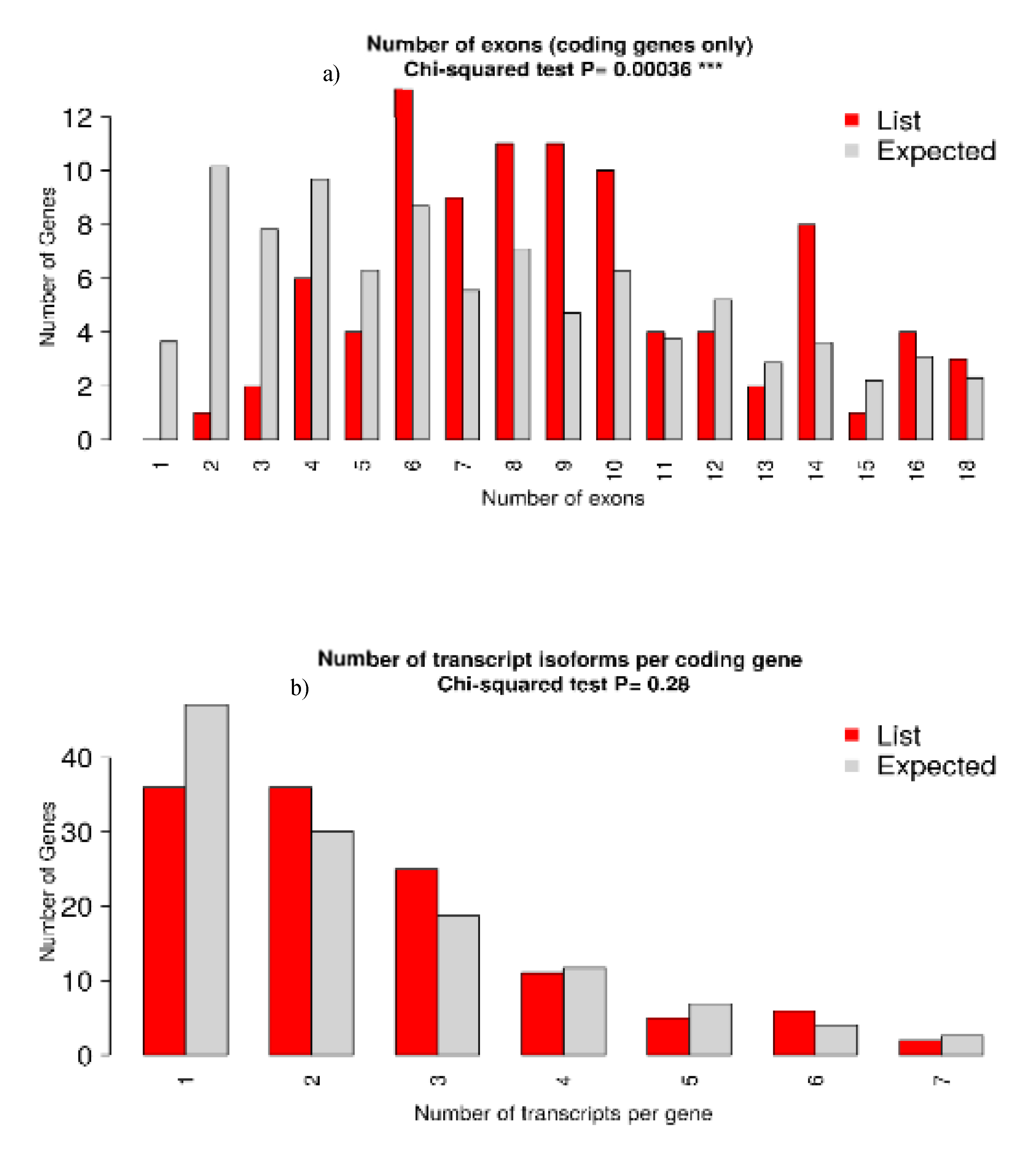
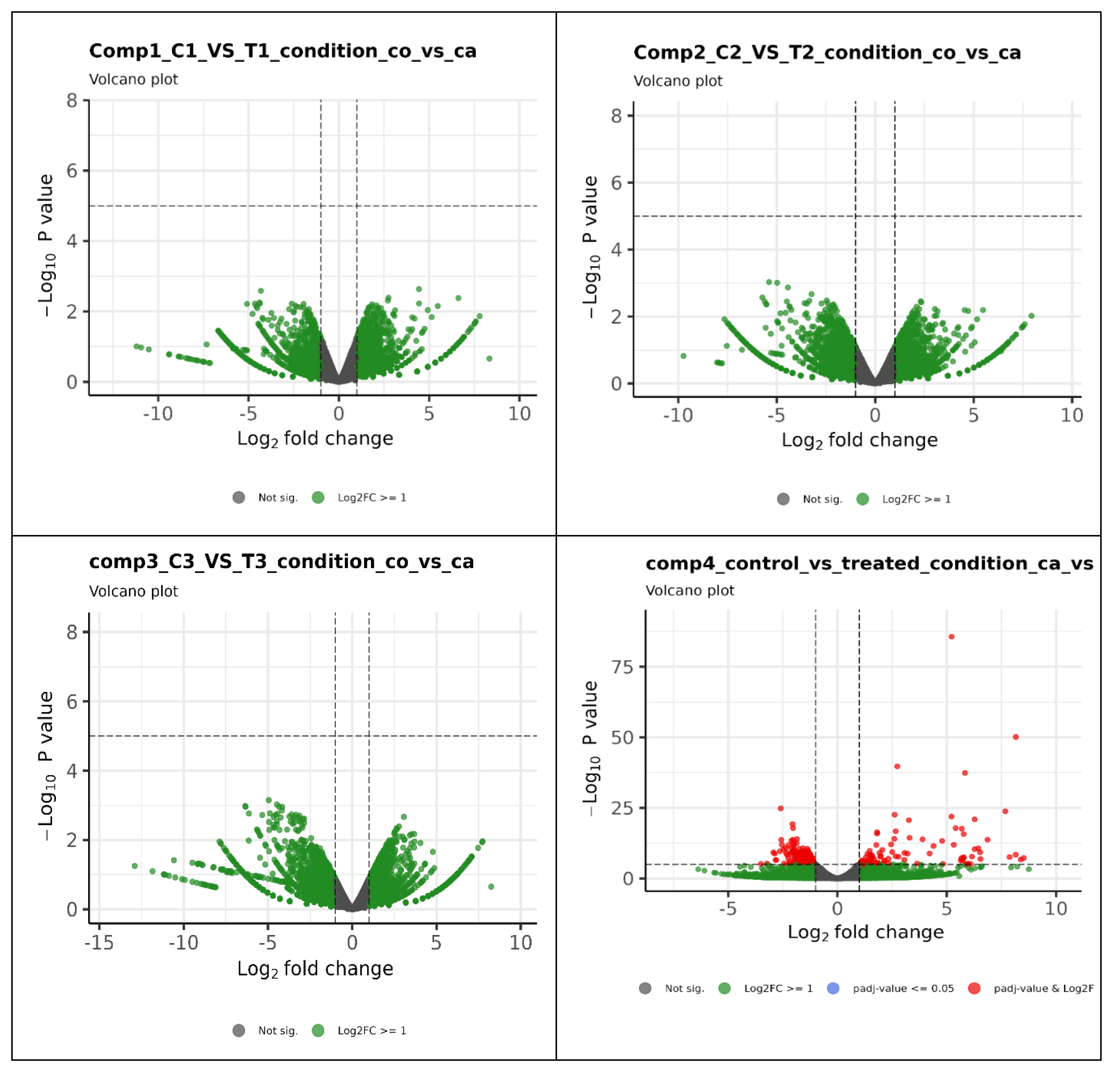
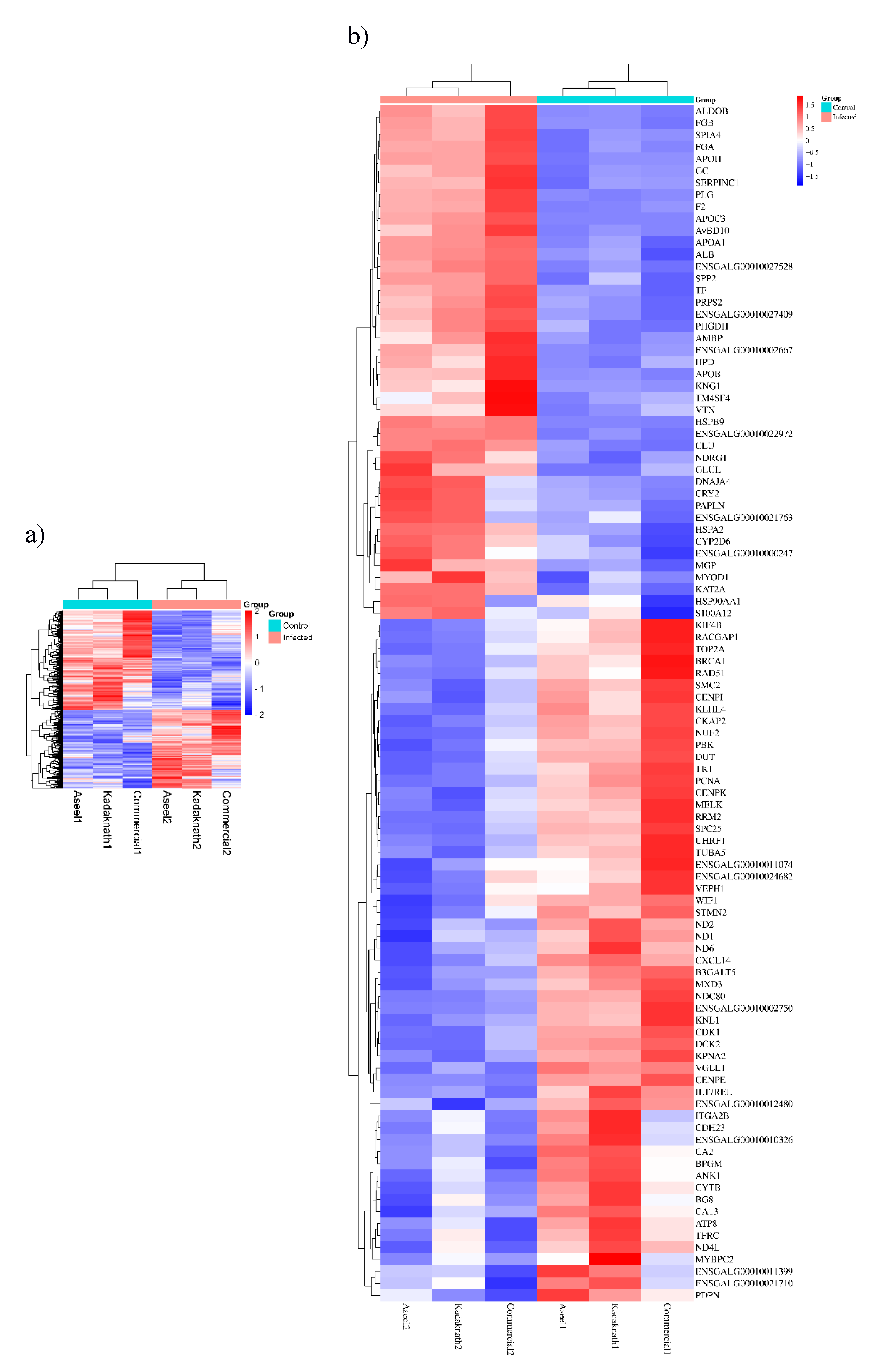
3.3. Identification, Characterization of Transcripts and Differential Expression Analysis
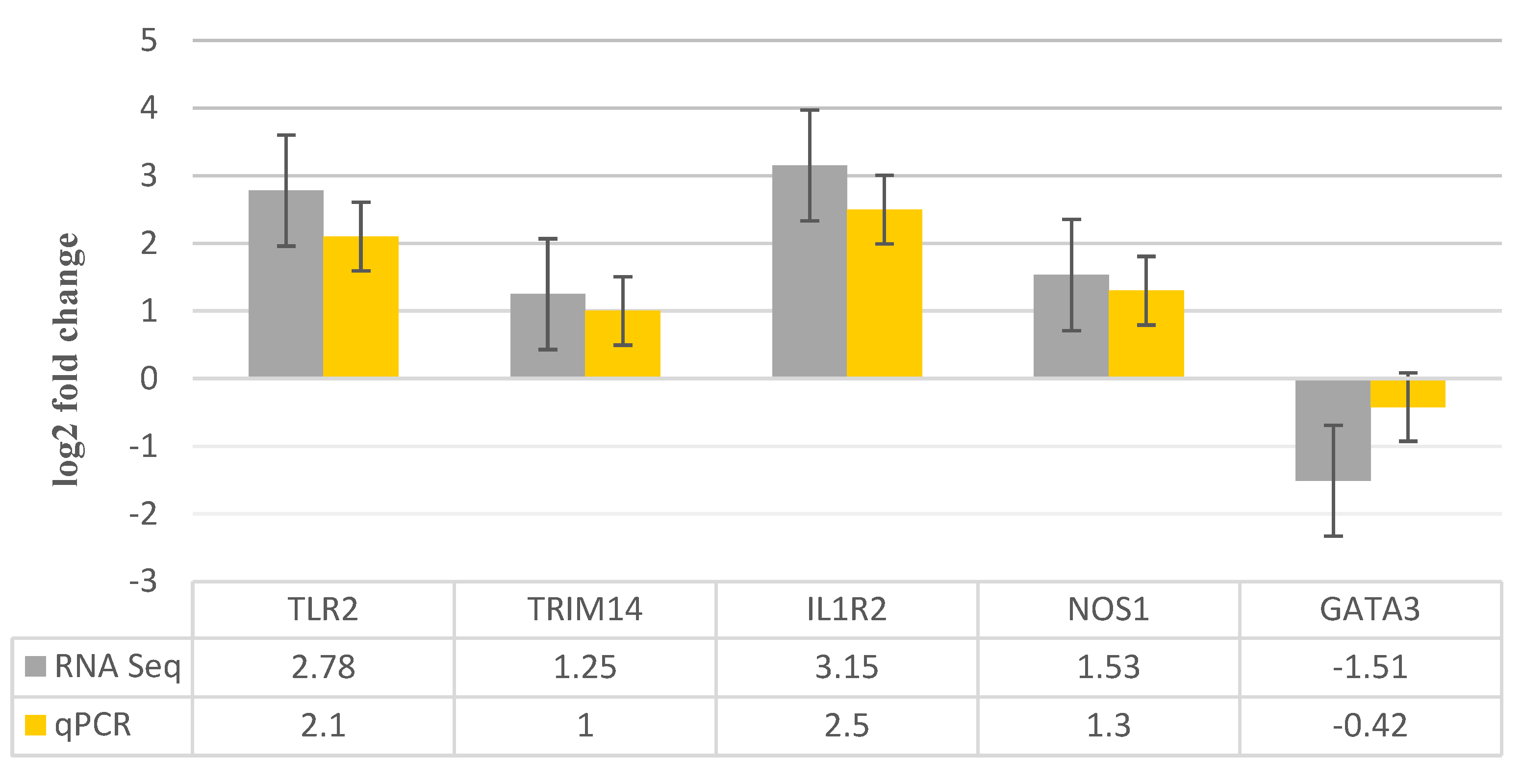
3.4. RNA-Seq Data Validation by RT-qPCR
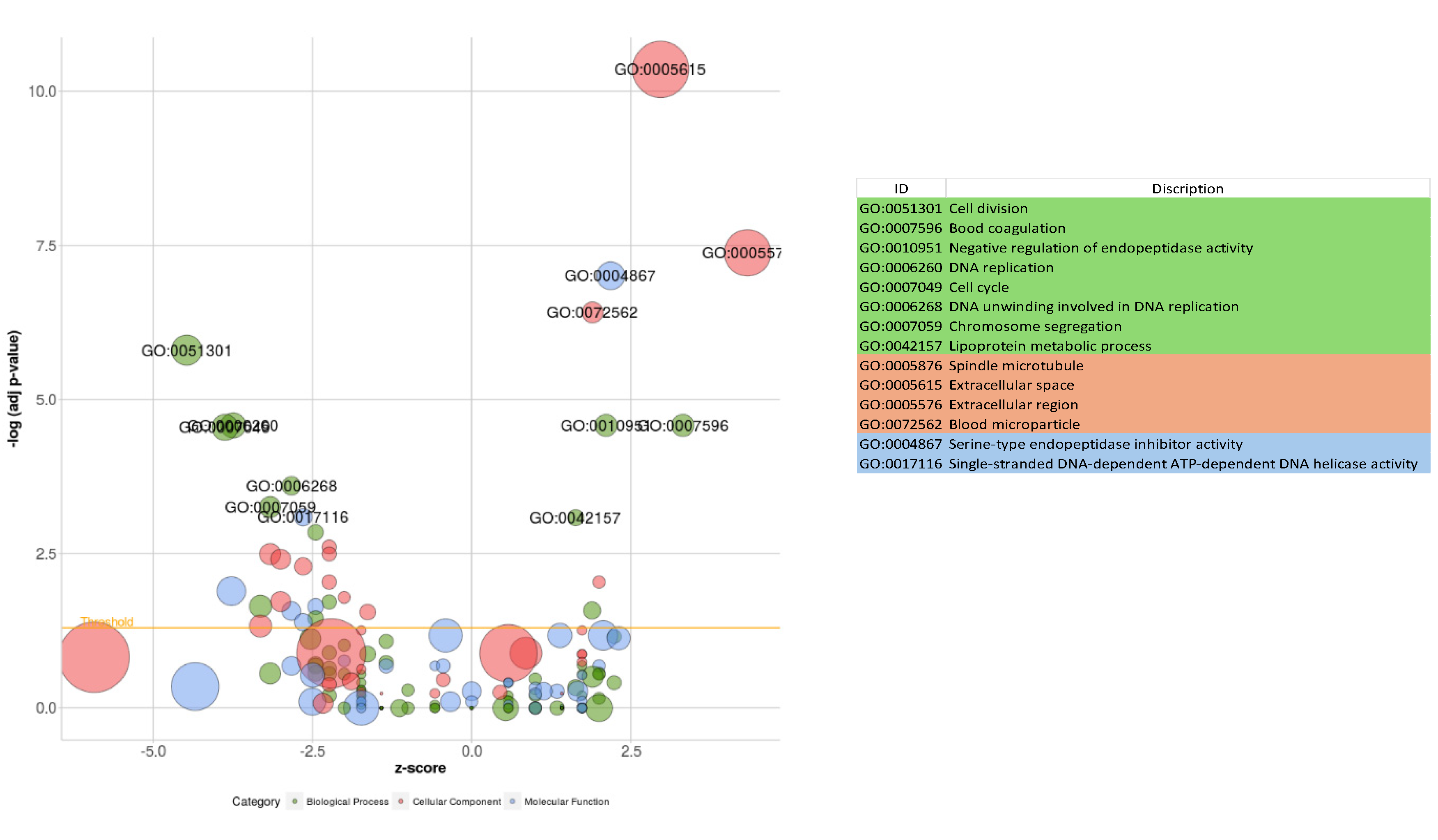
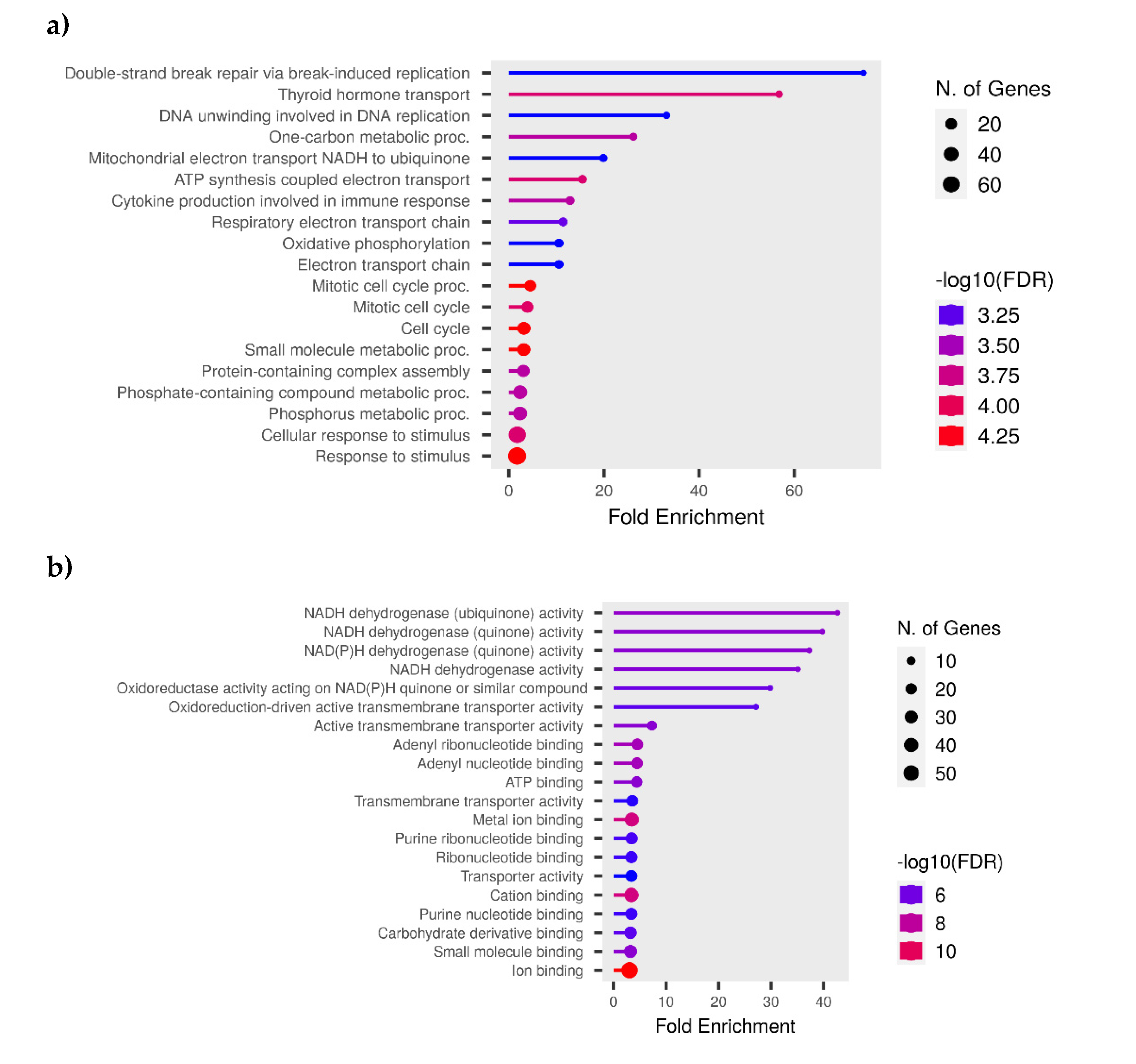
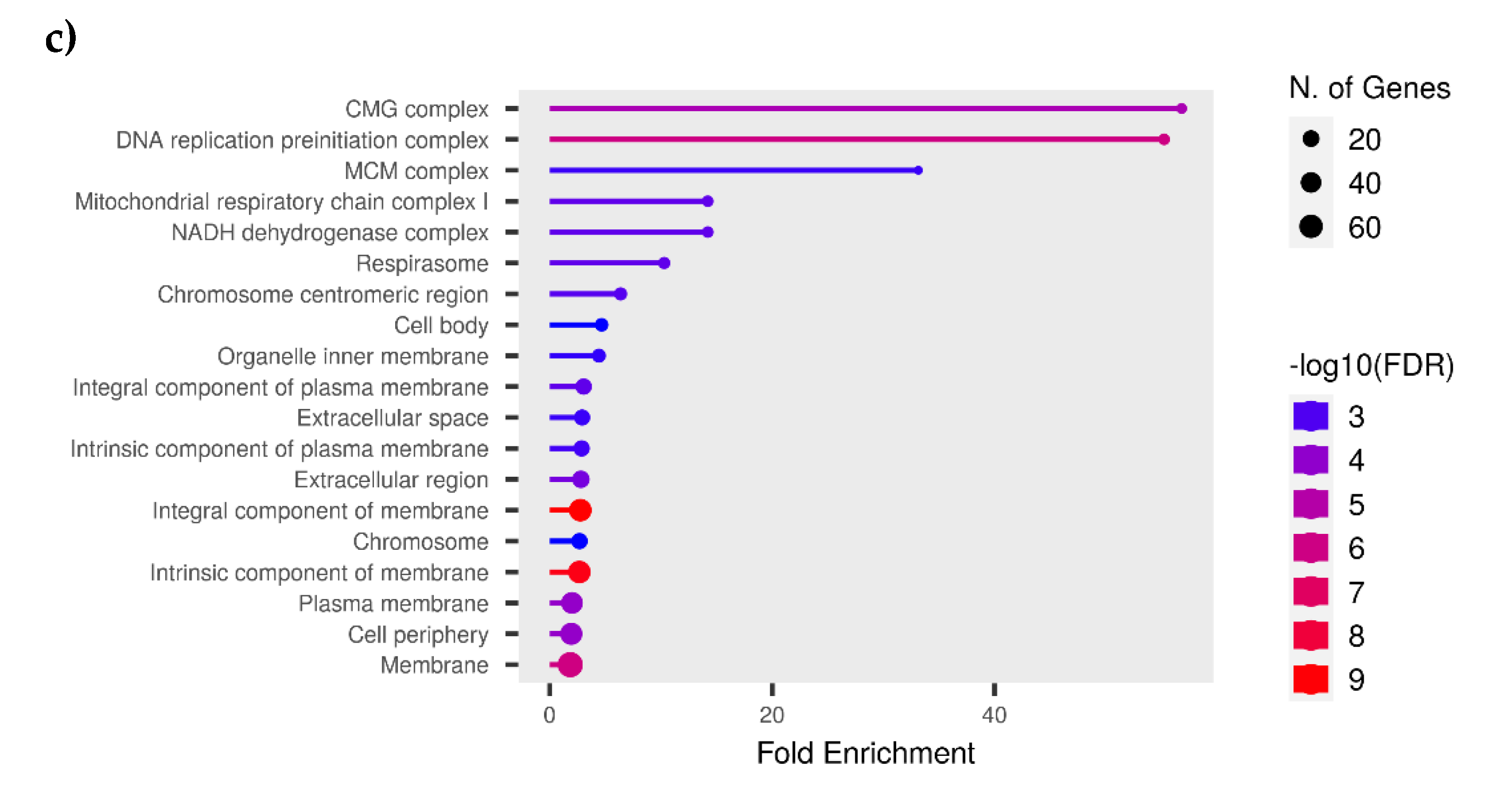
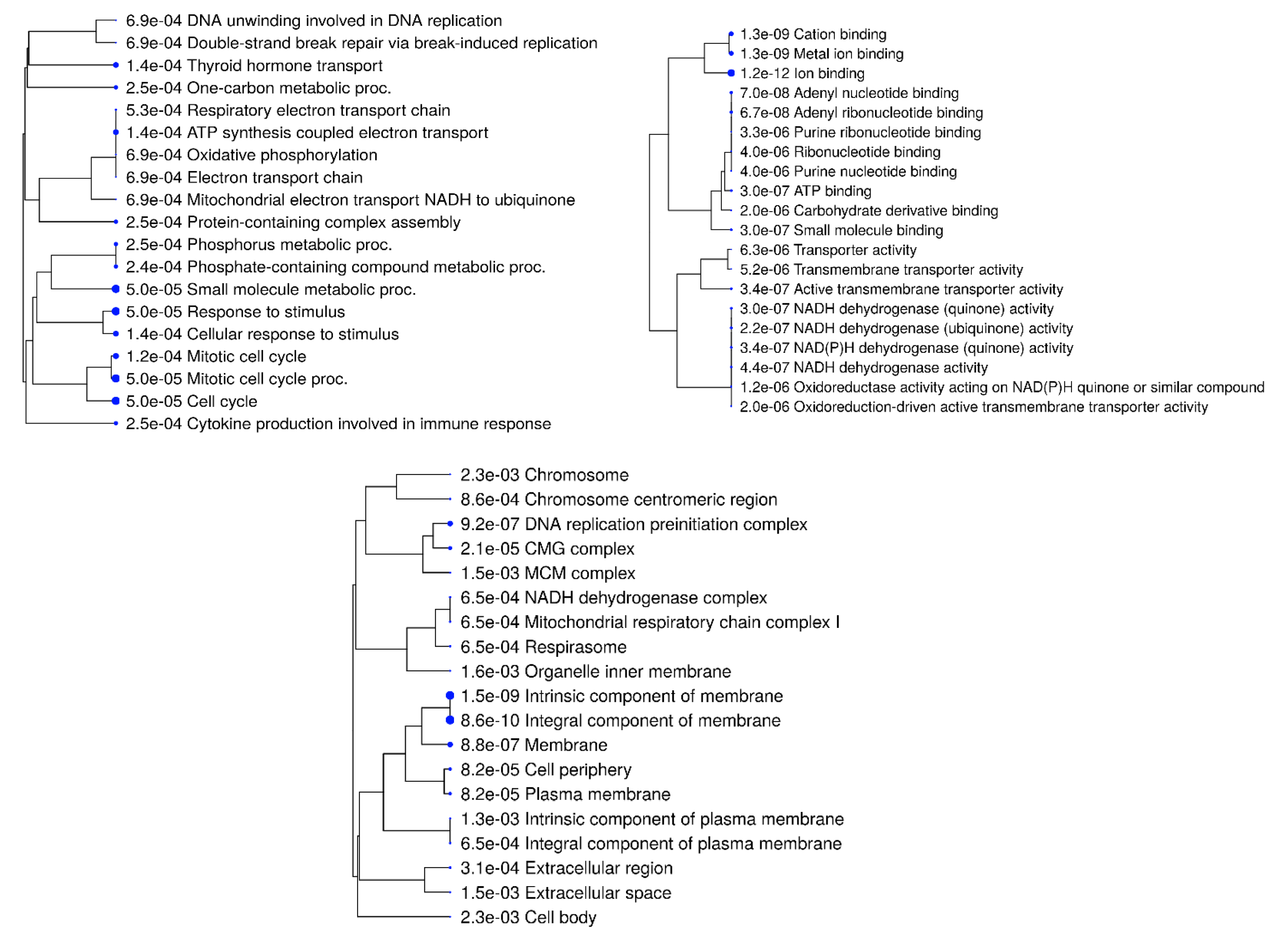
3.5. Functional Analysis
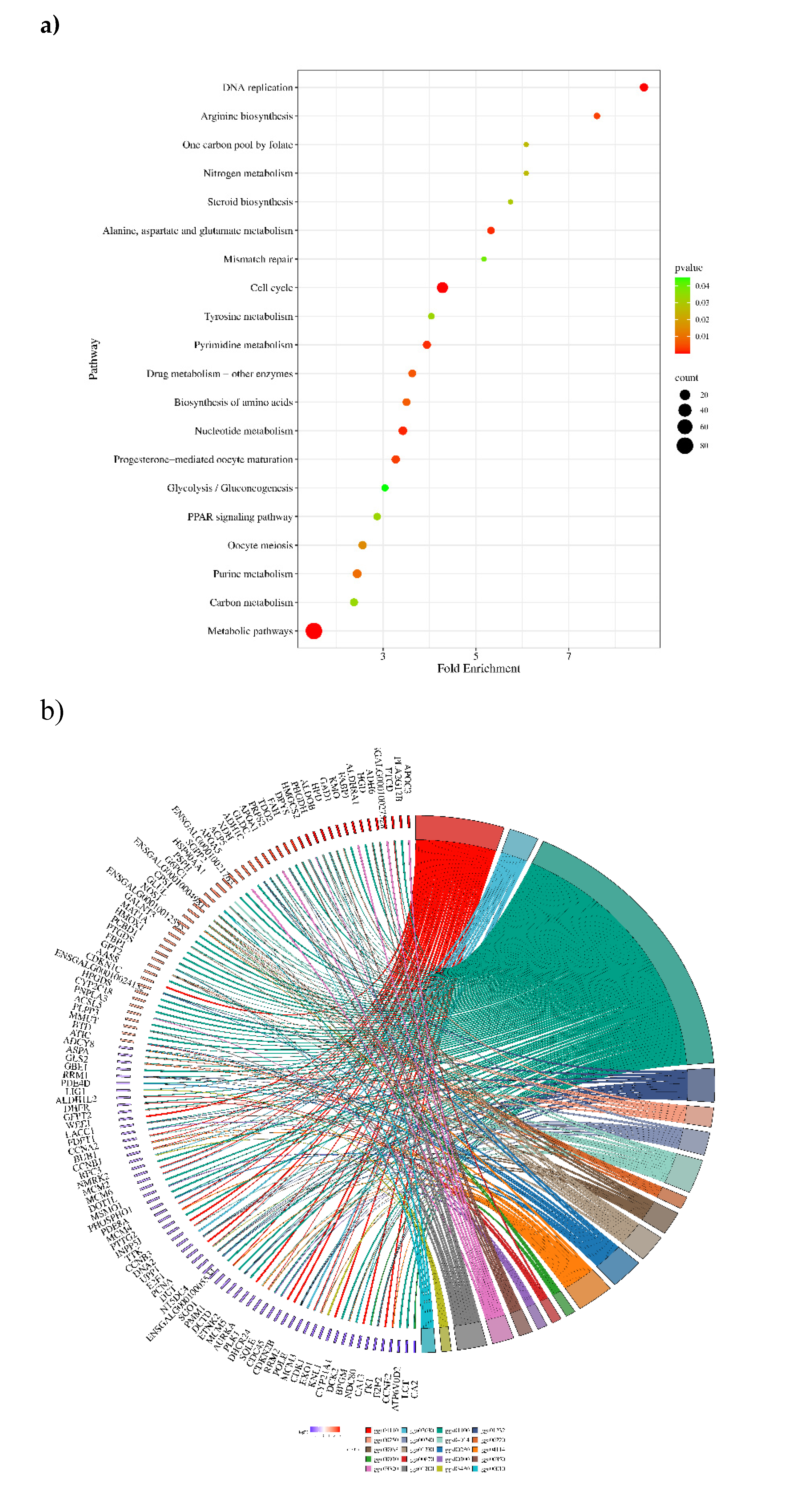
3.6. KEGG Pathway Analysis
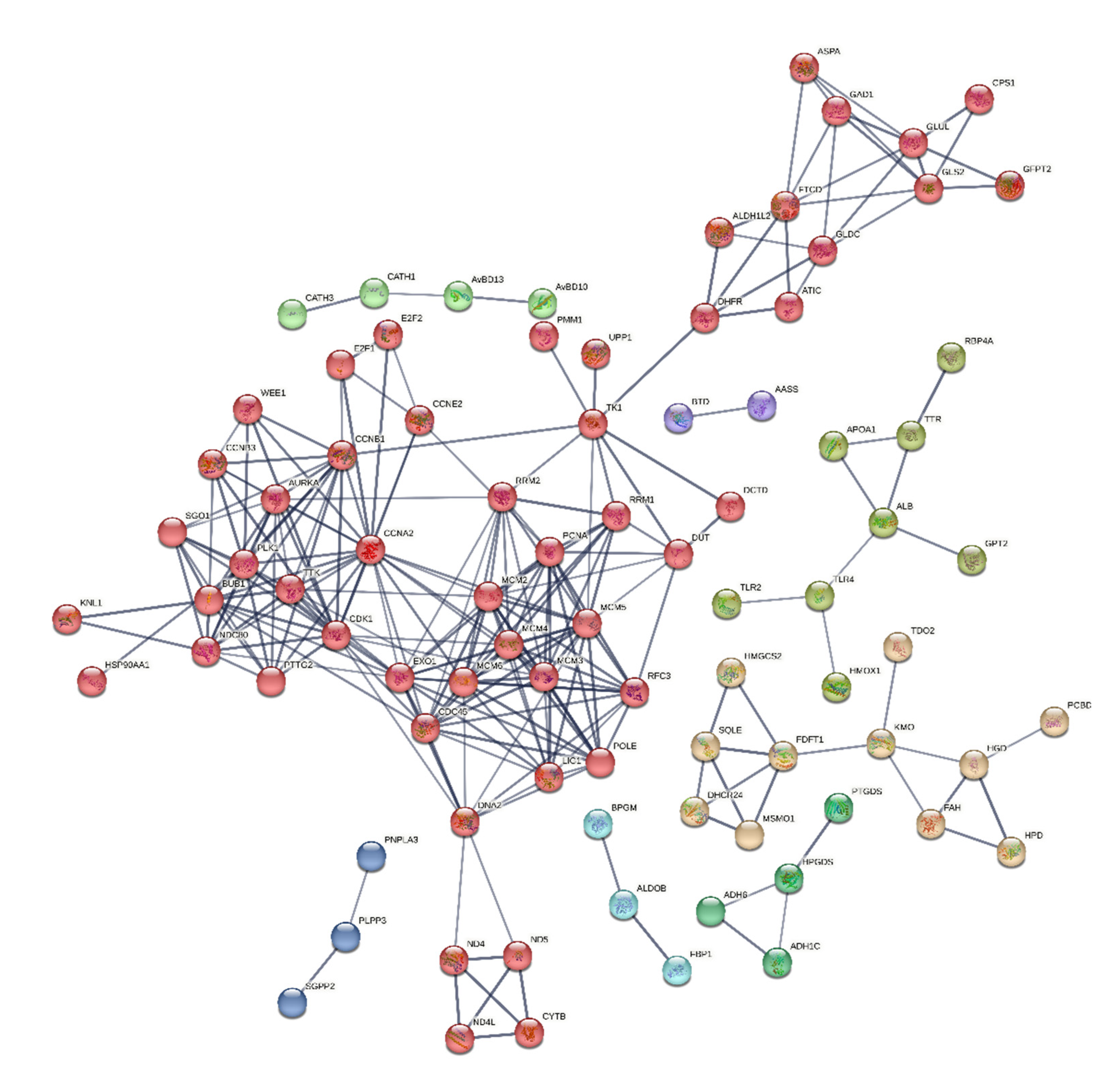
3.7. Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI)
4. Discussion
4.1. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
4.2. GO and KEGG Pathwy Analysis
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Saelao, P.; Chanthavixay, G.; Gallardo, R.A.; Wolc, A.; Fulton, J.E.; Dekkers, J.M.; Lamont, S.J.; Kelly, T.R.; Zhou, H. Genomic Regions and Candidate Genes Affecting Response to Heat Stress with Newcastle Virus Infection in Commercial Layer Chicks Using Chicken 600K Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Array. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2024, 25, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaynudin, K.; Joshi, B.; Mathakiya, R.; Prajapati, K.; Sipai, S. Economic Impact of Genotype- Xiii Newcastle Disease Virus Infection on Commercial Vaccinated Layer Farms in India. International Journal of Livestock Research 2018, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Saran, S.; Yadav, A.S.; Kumar, S.; Verma, M.R.; Kumar, D.; Tyagi, J.S. Economic Losses Due to Newcastle Disease in Layers in Subtropical India. The Indian Journal of Animal Sciences 2023, 93, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadouriya, S.; Kapoor, S.; Krishan, B.; Chhabra, R. Isolation and Characterization of the Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) of Haryana Region Based on F-Gene Sequence. 2018, 999–1003.
- Narayanan, M.S.; Parthiban, M.; Sathiya, P.; Kumanan, K. Molecular Detection of Newcastle Disease Virus Using Flinders Tehnology Associates-PCR. Vet. arhiv 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Saelao, P.; Wang, Y.; Chanthavixay, G.; Yu, V.; Gallardo, R.A.; Dekkers, J.C.M.; Lamont, S.J.; Kelly, T.; Zhou, H. Integrated Proteomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of Differential Expression of Chicken Lung Tissue in Response to NDV Infection during Heat Stress. Genes (Basel) 2018, 9, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, R; Thiagarajan, D; Veeramani, P.; Karthickeyan, S.M.K. Aseel, Kadaknath and White Leghorn Chicken Immune Response to Variation in Sheep Red Blood Cell. Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 2017, 5, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.K.; Pani, P.K.; Naithani, S. Genetic Susceptibility of Indigenous Chicks to Subgroup A Rous Sarcoma Virus Inoculated via the Chorioallantoic Membrane. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology 1992, 33, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.P.; Kannaki, T.R.; Mahapatra, R.K.; Reddy, M.R.; Paul, S.S.; Bhattacharya, T.K.; Laxmi, N.A.; Jayakumar, S.; Chatterjee, R.N. Immunocompetence Profile of Indian Native vs Exotic Chicken Breeds. Indian Journal of Animal Research 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerjal, T.; Härtle, S.; Gourichon, D.; Guillory, V.; Bruneau, N.; Laloë, D.; Pinard-van der Laan, M.-H.; Trapp, S.; Bed’hom, B.; Quéré, P. Assessment of Trade-Offs between Feed Efficiency, Growth-Related Traits, and Immune Activity in Experimental Lines of Layer Chickens. Genetics Selection Evolution 2021, 53, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarmathi, M.; Murali, N.; Selvaraju, M.; Sivakumar, K.; Gowthaman, V.; Raghavendran, V.B.; Raja, A.; Peters, S.O.; Thiruvenkadan, A.K. In Vitro Characterization of chIFITMs of Aseel and Kadaknath Chicken Breeds against Newcastle Disease Virus Infection. Biology 2023, 12, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, S.F. Developmental Biology, the Stem Cell of Biological Disciplines. PLoS Biol 2017, 15, e2003691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. Babraham Bioinformatics - FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 2018, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Ca, D.; F, S.; J, D.; C, Z.; S, J.; P, B.; M, C.; Tr, G. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 2013, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Gordon, K.S. Wei Shi RNA-Seq Profiling between Commercial and Indigenous Iranian Chickens Highlights Differences in Innate Immune Gene Expression. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4425/14/4/793 (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biology 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes Among Gene Clusters. OMICS : a Journal of Integrative Biology 2012, 16, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Brouwer, C. Pathview: An R/Bioconductor Package for Pathway-Based Data Integration and Visualization. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 2013, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter W; F, S.-C.; M, R. GOplot: An R Package for Visually Combining Expression Data with Functional Analysis. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 2015, 31. [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A Graphical Gene-Set Enrichment Tool for Animals and Plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y. SRplot: A Free Online Platform for Data Visualization and Graphing. PLOS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING Database in 2023: Protein-Protein Association Networks and Functional Enrichment Analyses for Any Sequenced Genome of Interest. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaf, M.W. A New Mathematical Model for Relative Quantification in Real-Time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2001, 29, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Song, J.J.; Wooming, A.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Bottje, W.G.; Kong, B.-W. Transcriptional Profiling of Host Gene Expression in Chicken Embryo Lung Cells Infected with Laryngotracheitis Virus. BMC Genomics 2010, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, M.; Ou, X.; Ma, Y.; Cheng, A.; Zhao, X.-X.; Liu, M.; Zhu, D.; Chen, S.; et al. Transcriptomic Characterization of a Chicken Embryo Model Infected With Duck Hepatitis A Virus Type 1. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, R.; Qu, G.; Peng, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, C.; Huang, C.; Wang, Q. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals New Insight of Fowl Adenovirus Serotype 4 Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; He, F.; Wu, C.; Zhao, G.; Hardwidge, P.R.; Li, N.; Peng, Y. Transcriptomic Analysis of Chicken Lungs Infected With Avian and Bovine Pasteurella Multocida Serotype A. Front Vet Sci 2020, 7, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.P.; Wen, B.; Zhang, X.J.; Ma, L.; Liang, X.L.; Zhang, M.L. Transcriptome Analysis of Genes Responding to Infection of Leghorn Male Hepatocellular Cells With Fowl Adenovirus Serotype 4. Front Vet Sci 2022, 9, 871038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Luo, R.; Sun, Y.; Peng, X. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Innate Immune Response to Mycoplasma Gallisepticum Infection in Chicken Embryos and Newly Hatched Chicks. Animals (Basel) 2023, 13, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, M.; Mehrabani-Yeganeh, H.; Barjesteh, N.; Nikbakht, G.; Thompson-Crispi, K.; Charkhkar, S.; Mallard, B. The Influence of Genetic Background versus Commercial Breeding Programs on Chicken Immunocompetence. Poult Sci 2014, 93, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Hua, G.; Li, J.; Deng, X.; Deng, X. Transcriptome Analyses of Differential Gene Expression in the Bursa of Fabricius between Silky Fowl and White Leghorn. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 45959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadr, A.S.; Nassiri, M.; Ghaderi-Zefrehei, M.; Heidari, M.; Smith, J.; Muhaghegh Dolatabady, M. RNA-Seq Profiling between Commercial and Indigenous Iranian Chickens Highlights Differences in Innate Immune Gene Expression. Genes 2023, 14, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Qiu, X.; Tan, L.; Song, C.; Sun, Y.; Liao, Y.; Liu, X.; Ding, C. Single-Cell Transcriptome Atlas of Newcastle Disease Virus in Chickens Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Microbiology Spectrum 2023, 11, e05121–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Bai, H.; Huang, Y.; Kang, N.; Ding, X.; Liu, J.; Luo, H.; Yang, C.; Chen, W.; et al. Evolutionary Analysis of a Complete Chicken Genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 120, e2216641120. [CrossRef]
- Ayers, K.L.; Davidson, N.M.; Demiyah, D.; Roeszler, K.N.; Grützner, F.; Sinclair, A.H.; Oshlack, A.; Smith, C.A. RNA Sequencing Reveals Sexually Dimorphic Gene Expression before Gonadal Differentiation in Chicken and Allows Comprehensive Annotation of the W-Chromosome. Genome Biology 2013, 14, R26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Che, T.; Li, F.; Tian, K.; Zhu, Q.; Mishra, S.K.; Dai, Y.; Li, M.; Li, D. The Temporal Expression Patterns of Brain Transcriptome during Chicken Development and Ageing. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, H.; Crooijmans, R.; Bastiaansen, J.; Megens, H.-J.; Groenen, M. Regional Regulation of Transcription in the Chicken Genome. BMC genomics 2010, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadders, M.A.; Beringer, D.X.; Gros, P. Structure of C8α-MACPF Reveals Mechanism of Membrane Attack in Complement Immune Defense. Science 2007, 317, 1552–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monson, M.S.; Van Goor, A.G.; Persia, M.E.; Rothschild, M.F.; Schmidt, C.J.; Lamont, S.J. Genetic Lines Respond Uniquely within the Chicken Thymic Transcriptome to Acute Heat Stress and Low Dose Lipopolysaccharide. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 13649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Mi, C.; Wang, Q.; Dai, G.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, G.; Xie, K.; Zhao, Z. Long Noncoding RNA Profiling Reveals That LncRNA BTN3A2 Inhibits the Host Inflammatory Response to Eimeria Tenella Infection in Chickens. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 891001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, C.; Wang, Y.; Chitwood, J.; Korf, I.; Delany, M.; Cheng, H.; Medrano, J.F.; Van Eenennaam, A.L.; Ernst, C.; Ross, P.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of Tissue-Specific Long Non-Coding RNA in Three Farm Animal Species. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, P.; Bakhtiarizadeh, M.R.; Salehi, A.; Izadnia, H.R. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Potential Roles of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Feed Efficiency of Chicken. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinska-Selbi, B.; Mielczarek, M.; Szyda, J. Review: Long Non-Coding RNA in Livestock. Animal 2020, 14, 2003–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagarrigue, S.; Lorthiois, M.; Degalez, F.; Gilot, D.; Derrien, T. LncRNAs in Domesticated Animals: From Dog to Livestock Species. Mamm Genome 2022, 33, 248–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jehl, F.; Muret, K.; Bernard, M.; Boutin, M.; Lagoutte, L.; Désert, C.; Dehais, P.; Esquerré, D.; Acloque, H.; Giuffra, E.; et al. An Integrative Atlas of Chicken Long Non-Coding Genes and Their Annotations across 25 Tissues. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 20457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.; Ebert, D.; Muruganujan, A.; Mills, C.; Albou, L.-P.; Mushayamaha, T.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER Version 16: A Revised Family Classification, Tree-Based Classification Tool, Enhancer Regions and Extensive API. Nucleic Acids Research 2021, 49, D394–D403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, G.; Kumar, S.; Prasad, Y. Immunocompetence Traits and Their Inheritance Pattern in Kadaknath Native Chicken. Indian Journal of Animal Research 2014, 48, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Phelan, J.D.; Wright, G.W.; Häupl, B.; Huang, D.W.; Shaffer, A.L.; Young, R.M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Yu, X.; et al. Regulation of B Cell Receptor-Dependent NF-κB Signaling by the Tumor Suppressor KLHL14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020, 117, 6092–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Takemoto, N.; Kurata, H.; Kamogawa, Y.; Miyatake, S.; O’Garra, A.; Arai, N. Gata-3 Induces T Helper Cell Type 2 (Th2) Cytokine Expression and Chromatin Remodeling in Committed Th1 Cells. J Exp Med 2000, 192, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Flavell, R.A. The Transcription Factor GATA-3 Is Necessary and Sufficient for Th2 Cytokine Gene Expression in CD4 T Cells. Cell 1997, 89, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, M.H.; Nassiri, M. Genetic Analysis of ND4 and ND4L Regions of Mitochondrial Genome in Khorasan Native Chickens. 2014.
- Bao, H.G.; Zhao, C.J.; Li, J.Y.; Wu, C. Association of MT-ND5 Gene Variation with Mitochondrial Respiratory Control Ratio and NADH Dehydrogenase Activity in Tibet Chicken Embryos. Anim Genet 2007, 38, 514–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacoub, H.A.; Fathi, M.M.; Sadek, M.A. Using Cytochrome b Gene of mtDNA as a DNA Barcoding Marker in Chicken Strains. Mitochondrial DNA 2015, 26, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Ding, Y.; Cai, W.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Song, J. Marek’s Disease Virus Infection Induced Mitochondria Changes in Chickens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Mu, Z.; Nie, F.; Chang, X.; Duan, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Ji, Y.; Li, M. Thymic Transcriptome Analysis after Newcastle Disease Virus Inoculation in Chickens and the Influence of Host Small RNAs on NDV Replication. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 10270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, A.H.; Lin, S.; Wang, F.; Zheng, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.; Jiao, Z.; Zhu, Z.; An, L.; Zhang, L. Investigating the Heat Tolerance and Production Performance in Local Chicken Breed Having Normal and Dwarf Size. Animal 2023, 17, 100707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachman, M.P.; Bamidele, O.; Dessie, T.; Smith, J.; Hanotte, O.; Gheyas, A.A. Genomic Analysis of Nigerian Indigenous Chickens Reveals Their Genetic Diversity and Adaptation to Heat-Stress. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beere, H.M. ‘The Stress of Dying’: The Role of Heat Shock Proteins in the Regulation of Apoptosis. Journal of Cell Science 2004, 117, 2641–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, S.; Zhao, K.; Han, L. Expression Profiles of the Heat Shock Protein 70 Gene in Response to Heat Stress in Agrotis C-Nigrum (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Insect Sci 2015, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-L. Ranking Gene Ontology Terms for Predicting Non-Classical Secretory Proteins in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes. Journal of Theoretical Biology 2012, 312, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, C.B.; dos Santos, É.C.; Ispada, J.; Fontes, P.K.; Nogueira, M.F.G.; dos Santos, C.M.D.; Milazzotto, M.P. The Dynamics between in Vitro Culture and Metabolism: Embryonic Adaptation to Environmental Changes. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 15672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Every, H.A.; Schmidt, C.J. Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Characterization of Post-Hatch Metabolic Reprogramming during Hepatic Development in the Chicken. BMC Genomics 2021, 22, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, H.; Choo, H.; Iskender, A.U.; Srikanth, K.; Kim, H.; Zhunushov, A.T.; Jang, G.W.; Lim, Y.; Song, K.-D.; Park, J.-E. RNA Seq Analyses of Chicken Reveals Biological Pathways Involved in Acclimation into Different Geographical Locations. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 19288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WU, H.; LI, X.; SHEN, C. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ in White and Brown Adipocyte Regulation and Differentiation. Physiol Res 2020, 69, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlie, R.; Zhu, J.; Allan, B.; Mutwiri, G.K.; Babiuk, L.A.; Potter, A.; Griebel, P. Chicken TLR21 Acts as a Functional Homologue to Mammalian TLR9 in the Recognition of CpG Oligodeoxynucleotides. Molecular Immunology 2009, 46, 3163–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, Y.-C.; Tseng, J.-C.; Yang, J.-X.; Liu, Y.-L.; Yeh, D.-W.; Lai, C.-Y.; Yu, G.-Y.; Hsu, L.-C.; Huang, C.-M.; Chuang, T.-H. Toll-Like Receptor 21 of Chicken and Duck Recognize a Broad Array of Immunostimulatory CpG-Oligodeoxynucleotide Sequences. Vaccines 2020, 8, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawab, A.; An, L.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xiao, M. Chicken Toll-like Receptors and Their Significance in Immune Response and Disease Resistance. International Reviews of Immunology 2019, 38, 284–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, B.J.; Somerville, C.C. Modulating Cytokine Production via Select Packaging and Secretion From Extracellular Vesicles. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, G.; Garner, W.L. Inflammatory Mediators in Wound Healing. Surgical Clinics of North America 2003, 83, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, W.; Freeman, M.L.; Lederman, M.M.; Vasilieva, E.; Romero, R.; Margolis, L. A System of Cytokines Encapsulated in ExtraCellular Vesicles. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Balasubramaniam, S.D.; Lee, Y.J.; Balakrishnan, V.; Oon, C.E. Minichromosome Maintenance Complex (MCM) Genes Profiling and MCM2 Protein Expression in Cervical Cancer Development. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2019, 20, 3043–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.-S.; Kang, Y.-H. The Human Replicative Helicase, the CMG Complex, as a Target for Anti-Cancer Therapy. Front Mol Biosci 2018, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czernik, M.; Winiarczyk, D.; Sampino, S.; Gręda, P.; Parillo, S.; Modliński, J.A.; Loi, P. Mitochondrial Function and Intracellular Distribution Is Severely Affected in in Vitro Cultured Mouse Embryos. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 16152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, A.; Peng, J.; Ramatchandirin, B.; Pearah, A.; He, L. Development and Functions of Mitochondria in Early Life. Newborn 2022, 1, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukonen, J.; Juselius, J.K.; Tiranti, V.; Kyttälä, A.; Zeviani, M.; Comi, G.P.; Keränen, S.; Peltonen, L.; Suomalainen, A. Role of Adenine Nucleotide Translocator 1 in mtDNA Maintenance. Science 2000, 289, 782–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornblum, C.; Nicholls, T.J.; Haack, T.B.; Schöler, S.; Peeva, V.; Danhauser, K.; Hallmann, K.; Zsurka, G.; Rorbach, J.; Iuso, A.; et al. Loss-of-Function Mutations in MGME1 Impair mtDNA Replication and Cause Multi-Systemic Mitochondrial Disease. Nat Genet 2013, 45, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Ronchi, D.; Comi, G.P. Genes and Pathways Involved in Adult Onset Disorders Featuring Muscle Mitochondrial DNA Instability. Int J Mol Sci 2015, 16, 18054–18076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, K.; Majd, H.; Dallabona, C.; Reinson, K.; King, M.S.; Alston, C.L.; He, L.; Lodi, T.; Jones, S.A.; Fattal-Valevski, A.; et al. Recurrent De Novo Dominant Mutations in SLC25A4 Cause Severe Early-Onset Mitochondrial Disease and Loss of Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number. Am J Hum Genet 2016, 99, 860–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.-J.; Monson, M.; Kaiser, M.; Lamont, S.J. Induction of Chicken Host Defense Peptides within Disease-Resistant and -Susceptible Lines. Genes (Basel) 2020, 11, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuperus, T.; Coorens, M.; van Dijk, A.; Haagsman, H.P. Avian Host Defense Peptides. Developmental & Comparative Immunology 2013, 41, 352–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, S.G. The Pathophysiology of the Cell Cycle in Cancer and Treatment Strategies Using Various Cell Cycle Checkpoint Inhibitors. Pathology - Research and Practice 2023, 251, 154854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Feng, K.; Wang, X. Expression and Prognostic Value of CDK1, CCNA2, and CCNB1 Gene Clusters in Human Breast Cancer. J Int Med Res 2021, 49, 0300060520980647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelman, L.M.; Kelman, Z. Replication | DNA Replication Fork, Eukaryotic. In Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry III (Third Edition); Jez, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, 2013; pp. 63–66. ISBN 978-0-12-822040-5. [Google Scholar]


| Gene Name | Primer sequence | Product size | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | ||
| TLR2 | CAAGACCTACCTGGAGTGGC | GGATGGCTACAGTCTCCATTTT | 116 |
| TRIM14 | GATTGGTGCAGCCTACCCTT | TCTCCCCCTTGTGAAATGCC | 128 |
| IL1R2 | TTCCCTCGCTCTTCTTCCCATTT | ATGGTGTGATCTGGGCAGTTT | 137 |
| NOS1 | ATGCACAAACAGCAGGGAGT | CCAGGACAGGGATTGGGTTG | 196 |
| GATA3 | CCTTTGGACCTCACCATCCC | AAGCATTCAGCAGGGGAGTC | 72 |
| β-Actin | TATGTGCAAGGCCGGTTTC | TGTCTTTCTGGCCCATACCAA | 110 |
| Sample ID | Total reads | q20 rate | q30 rate | GC content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aseel control | 11712582 | 0.956 | 0.906 | 0.518 |
| Aseel infected | 19473512 | 0.959 | 0.911 | 0.520 |
| Kadaknath control | 27264370 | 0.958 | 0.907 | 0.549 |
| Kadaknath infected | 22294792 | 0.962 | 0.917 | 0.526 |
| White Leghorn control | 45866934 | 0.953 | 0.892 | 0.588 |
| White Leghorn infected | 27691980 | 0.957 | 0.910 | 0.532 |
|
Sample ID |
QC Passed
Reads |
Unique
Mapped % |
Multi
Mapped % |
Unmapped % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aseel control | 9665406 | 88.71 | 1.77 | 9.53 |
| Aseel infected | 16400020 | 88.81 | 1.71 | 9.48 |
| Kadaknath control | 20680458 | 86.49 | 1.98 | 11.53 |
| Kadaknath infected | 19415268 | 89.71 | 1.69 | 8.6 |
| White Leghorn control | 31375608 | 88.89 | 1.43 | 9.68 |
| White Leghorn infected | 23667448 | 88.2 | 1.69 | 10.11 |
| Sample ID | Total Number of Genes | Expressed Genes |
|---|---|---|
| Aseel control | 30108 | 17410 |
| Aseel infected | 30108 | 18733 |
| Kadaknath control | 30108 | 18502 |
| Kadaknath infected | 30108 | 18998 |
| White Leghorn control | 30108 | 20332 |
| White Leghorn infected | 30108 | 19915 |
| Chromosome No | lncRNA | Protein coding | Total number of transcripts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ch 1 | 8 | 72 | 80 |
| Ch 2 | 7 | 52 | 59 |
| Ch 3 | 2 | 42 | 44 |
| Ch 4 | 3 | 49 | 52 |
| Ch 5 | 2 | 34 | 36 |
| Ch 6 | 3 | 30 | 33 |
| Ch 7 | 1 | 19 | 20 |
| Ch 8 | 1 | 18 | 19 |
| Ch 9 | 3 | 15 | 18 |
| Ch 10 | 0 | 15 | 15 |
| Ch 11 | 3 | 12 | 15 |
| Ch 12 | 1 | 10 | 11 |
| Ch 13 | 2 | 13 | 15 |
| Ch 14 | 0 | 7 | 7 |
| Ch 15 | 0 | 12 | 12 |
| Ch 16 | 0 | 8 | 8 |
| Ch 17 | 1 | 7 | 8 |
| Ch 18 | 2 | 8 | 10 |
| Ch 19 | 2 | 9 | 11 |
| Ch 20 | 0 | 8 | 8 |
| Ch 21 | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| Ch 22 | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| Ch 23 | 1 | 6 | 7 |
| Ch 24 | 2 | 8 | 10 |
| Ch 25 | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| Ch 26 | 0 | 8 | 8 |
| Ch 27 | 0 | 12 | 12 |
| Ch 28 | 0 | 7 | 7 |
| Ch 30 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Ch 31 | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| Ch 34 | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| Ch Z | 6 | 26 | 32 |
| Mitochondrial | 0 | 8 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





