1. Introduction
The growing demand for renewable energy technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) for electronic devices and electric vehicles, has driven significant advancements in sustainability. However, as LIBs replace conventional fossil-fuel-based energy sources, the sustainability of the critical materials used in these technologies has become an urgent issue. Much research has focused on recycling valuable metals like lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese from spent batteries through environmentally friendly recovery processes [
1,
2]. However, the reuse of other high-performance materials remains considerably underexplored [
3,
4].
Among these materials, fluorinated carbon materials [
5], especially fluorinated carbon nanotubes (FCNTs) are particularly notable due to their unique physicochemical properties, which make them valuable in various energy storage, electronics, and environmental applications. For example, in supercapacitor applications, FCNTs demonstrate enhanced performance compared to non-fluorinated counterparts, with improvements in specific capacitance, rate capability, and cycling stability [
6]. Additionally, FCNTs are used in silicon heterojunction solar cells [
7]
, perovskite solar cells [
8], various batteries [
9], catalysts [
10,
11], and reinforced composites [
12], where partial fluorination balances conductivity and functionality, leading to superior electrochemical properties. Research has shown that FCNTs with an optimal fluorine-to-carbon ratio, when used as cathode materials in lithium and sodium primary batteries, achieve both high energy density (1147 Wh kg⁻¹) and power density (8998 W kg⁻¹), outperforming conventional carbon-fluoride materials [
13]. Further studies have highlighted the potential of FCNTs as cathode materials in primary lithium batteries, where the selective fluorination of the outer nanotube layers preserves electronic conductivity while enhancing performance [
14]. This synergy enables FCNTs to deliver high energy and power densities, making them promising candidates for advanced battery applications.
Beyond energy storage, FCNTs play a critical role as efficient electrocatalysts, with applications including urea synthesis from CO
2 and nitrate under ambient conditions, offering higher urea yields and enhanced electro-catalytic efficiency [
15], or modulating the electron configuration of other metalloporphyrin-like active sites to reduce the energy barrier for CO
2 reduction [
16]. They also enhance the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in fuel cells by providing a higher density of active sites [
17]. Moreover, FCNTs serve as valuable reinforcing fillers in polymer composites [
18].
Despite their diverse applications, the production of FCNTs is both energy- and resource-intensive, raising concerns about their sustainability. Additionally, our previous research has shown that the stability of fluorine content on nanotube surfaces decreases as the curvature strain of the carbon lattice increases [
19,
20]. High-curvature fluorinated nanostructures, such as fluorinated single-walled carbon nanotubes, are prone to defluorination under mild chemical conditions or even after prolonged storage. This degradation leads to a quality downgrade of these high-value, resource-intensive materials, further driving up the cost of utilizing FCNTs.
To address these challenges, repurposing quality-downgraded fluorinated carbon nanotubes (QD-FCNTs) for other high-value applications presents a viable solution for reducing production costs, conserving energy, and minimizing environmental impacts. This approach aligns with the principles of the circular economy, where waste is minimized through innovative resource repurposing. Additionally, re-functionalization is often necessary to restore the properties of carbon nanotubes for reuse. Conventional methods for re-functionalization typically involve energy-intensive processes that rely on large quantities of environmentally harmful chemicals, such as heated concentrated nitric acid or piranha solutions [
21]. However, a unique aspect of QD-FCNTs is that during the quality downgrade process, the removal of fluorine tends to leave surface defects on the nanotubes under certain conditions [
22]. These defects could potentially be leveraged for QD-FCNT re-functionalization under milder conditions, opening up the possibility of developing eco-friendly processes for reusing QD-FCNTs. This approach is essential for maintaining the value of QD-FCNTs while ensuring their cost-effectiveness and environmental responsibility for future applications.
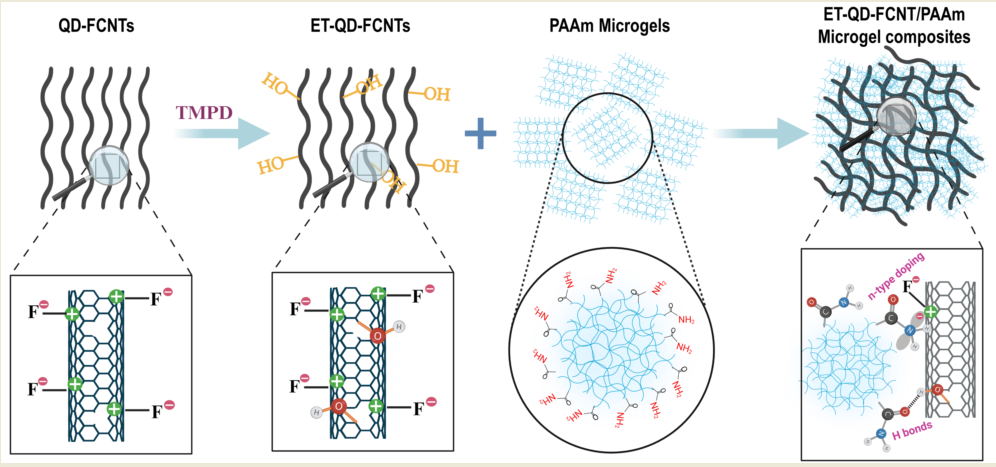
In this study, we explore the potential of using QD-FCNTs as eco-friendly nano-additives in microgel composites designed for water retention applications. Microgels are micro-sized, hydrophilic 3D polymer networks capable of retaining significant amounts of water, making them ideal for agricultural and environmental applications aimed at mitigating water scarcity. However, while their small size provides a larger surface area and rapid moisture absorption, this same large surface area also accelerates water evaporation, limiting their effectiveness in sustained water release over extended periods.
By incorporating QD-FCNTs into polyacrylamide (PAAm) microgels, we aim to create QD-FCNT/PAAm microgel composites that enhance water retention properties, thus extending the duration of water release. To improve the interaction between QD-FCNTs and PAAm microgels within the composites, we developed a mild surface treatment process for QD-FCNTs that avoids high energy consumption and the use of environmentally harmful chemicals. As illustrated in
Scheme 1, a small amount of the strong organic electron donor
N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-
p-phenylenediamine (TMPD) was used to treat the defects on the QD-FCNT surface, introducing increased hydrophilicity at room temperature with virtually no energy input. This method enhances the compatibility and interaction between QD-FCNTs and PAAm microgels, resulting in a more stable composite material with improved water retention capabilities. These findings support the sustainable use of downgraded materials and provide new insights into the design of eco-friendly, green materials.
3. Results and Discussions
Fluorinated carbon nanotubes can experience significant defluorination under mild conditions, depending on their fluorination method [
22] and the curvature strain on the C-F bonds [
19]. In our research, we found that certain highly fluorinated single-walled carbon nanotubes (FSWNTs) lose nearly all their fluorine content after long-term storage at room temperature. We used a type of FSWNT with an initial fluorine content of above 50% by mass, as provided by the manufacturer. As shown in
Table 1, after 1.5 years of storage at room temperature, the fluorine content had dramatically decreased to approximately 1.5%. According to Mickelson
et al., the maximum C ratio for FSWNTs that can be achieved through non-invasive fluorination is 2:1, which corresponds to a fluorine fraction of 44% by mass. Although higher fluorination levels can be attained, they begin to damage the carbon nanotube backbone [
23]. Therefore, it is reasonable to expect that these highly fluorinated CNTs are more vulnerable to mild degradation conditions due to the high defect level, and once fluorine atoms are removed over long-term use or storage, some of the recovered carbon sites will remain as bare carbon defect sites.
Re-functionalization is often necessary to restore the properties of carbon nanotubes for reuse. Since defect sites are generally more reactive and can undergo chemical modifications under milder conditions [
24,
25], we hypothesize that QD-FCNTs with more defluorination-induced defects can be functionalized under milder, greener conditions to improve their hydrophilicity for better interaction with hydrogels.
It is well known that introducing hydrophilic hydroxyl or carbonyl groups to the sidewalls of carbon nanotubes increases their hydrophilicity. Conventional methods for achieving this, however, typically require energy-intensive processes and the use of large amounts of environmentally harmful chemicals, such as concentrated nitric acid or piranha solutions [
21]. Given that defluorination often leaves surface defects on the nanotube lattice [
22], we propose a novel approach to treating these defect-containing QD-FCNTs using
N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-
p-phenylenediamine (TMPD), a strong organic electron donor. This treatment, carried out at room temperature with no energy input, enhances the hydrophilicity of the QD-FCNTs and their interactions with PAAm microgels. TMPD, being polar and slightly water-soluble, allows us to use only a small amount to reduce environmental impact. Instead of soaking the CNTs in bulk quantities of strong acids, we simply add milligram-level amounts of TMPD and allow them to treat QD-FCNTs overnight at room temperature. Considering its lower environmental and energy footprint and for shorter abbreviation, the TMPD-treated QD-FCNTs are referred to as Eco-friendly Treated QD-FCNTs (ET-QD-FCNTs) in this paper.
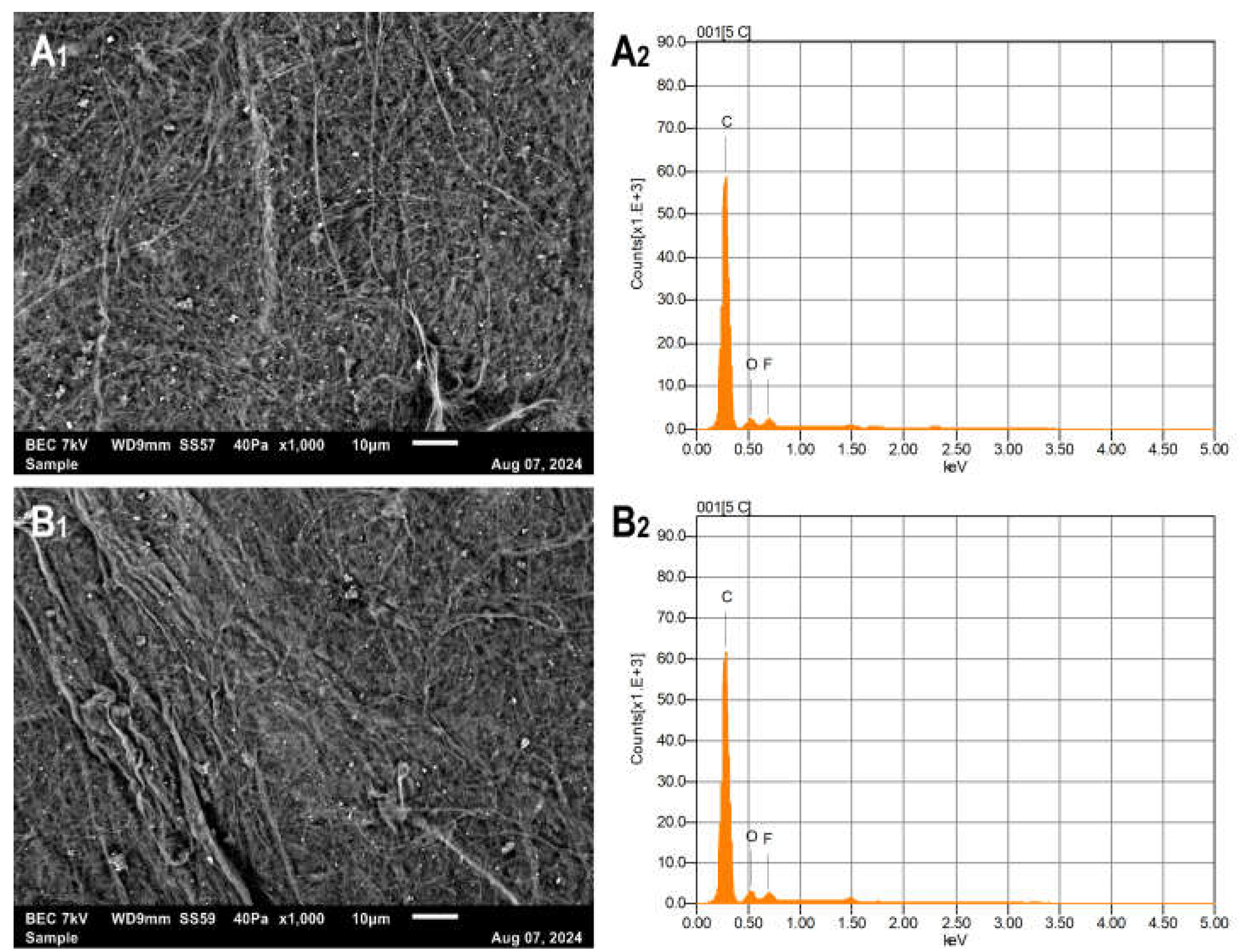
Figure 1 shows SEM images and EDX elemental analysis of the QD-FCNTs before and after TMPD treatment. Both the untreated QD-FCNT control sample (
Figure 1, A1) and the TMPD-treated sample (
Figure 1, B1) exhibit compact nanotube networks composed of FCNT bundles. The observed bundle lengths vary up to 80 µm. EDX elemental analysis (
Figure 1, A2 and B2) shows a slight increase in oxygen content after TMPD treatment. As listed in
Table 1, the fluorine content decreased by only 0.2%, indicating that the remaining fluorine content after long-term storage is relatively stable. The observed increase in oxygen content, though small, is notably higher than the decrease in fluorine content, suggesting additional oxygen was bonded to the nanotubes during the TMPD treatment. This is further supported by the water contact angle change of thin films prepared from QD-FCNTs (
Table 1), which decreased from 150° (untreated) to 120° after TMPD-treatment, indicating that even a slight increase in oxygen content via eco-friendly mild treatment can significantly improve the hydrophilicity of the CNT surface.
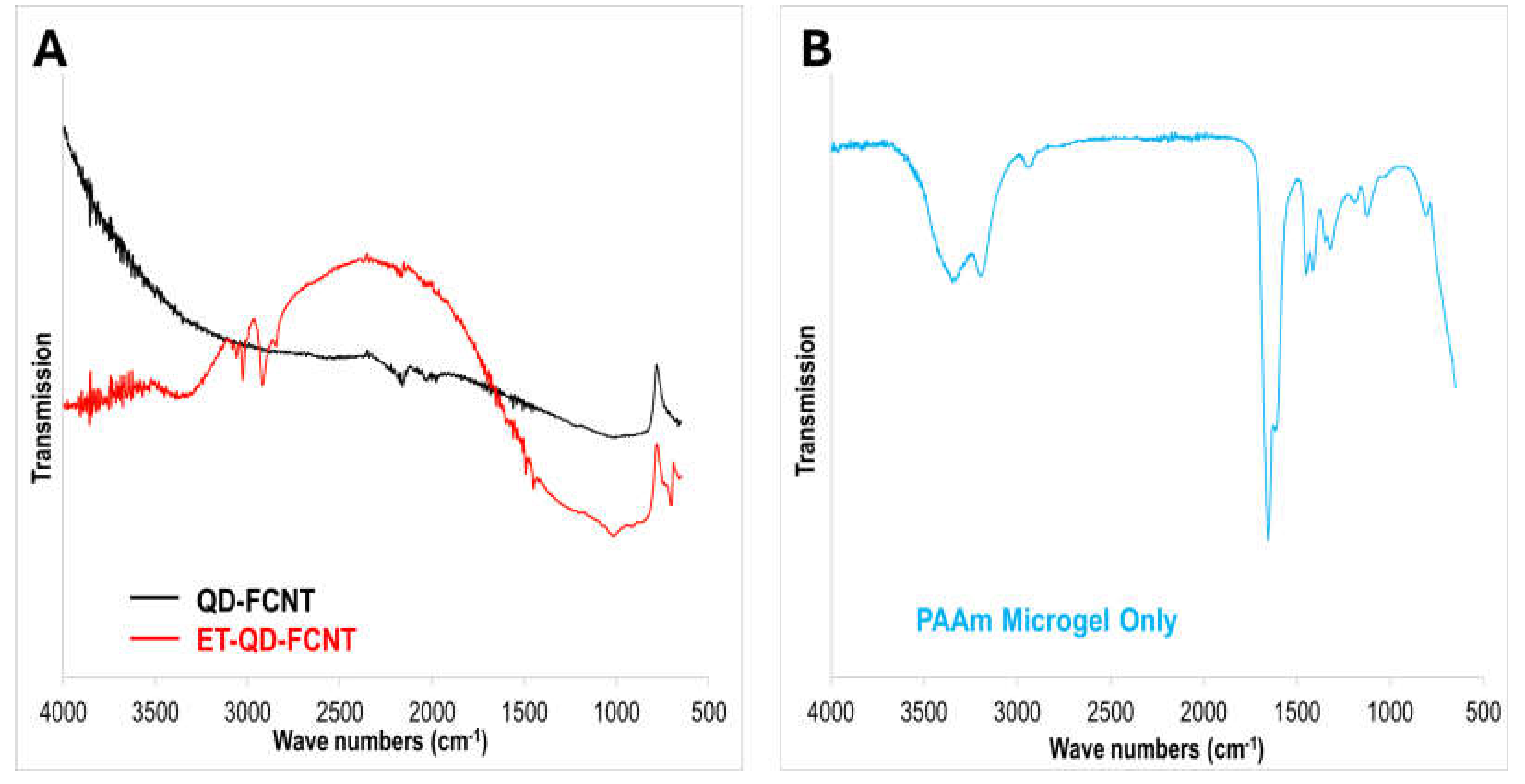
To investigate surface chemical changes due to TMPD treatment, we collected ATR-FTIR spectra of the QD-FCNTs (
Figure 2A). The untreated QD-FCNTs show a small peak at 1210 cm⁻¹, corresponding to the C-F bond stretching vibration, with no other significant peaks. After TMPD treatment, no peak related to the surface adsorption or chemical bonding of TMPD molecules was observed. Instead, a notable peak corresponding to -OH stretching emerged at 3333 cm⁻¹, consistent with the increased oxygen content observed in the EDX analysis. This suggests the formation of hydrophilic hydroxyl groups on the CNT surface, likely due to TMPD’s role in generating reactive species (e.g., TMPD•⁺ radical cations). Forming these radicals donates electrons to CNT defect sites for further reacting with water, leading to the formation of hydroxyl groups at defect sites. Simultaneously, multiple peaks appeared between 2900 – 3100 cm
-1, which can be assigned to the C-H stretching vibration bonds on some reduced defect sites.
Raman spectroscopy is a powerful tool for characterizing various carbon allotropes by analyzing the rotational and vibrational spectral signatures of carbon atoms within their lattice structures [
26]. In this study, we used Raman spectroscopy with a 1 mW, 785 nm laser to investigate both QD-FCNTs and ET-QD-FCNTs. Typically, Raman spectra of SWNTs exhibit three key bands: the Radial Breathing Mode (RBM) bands, D-band, and G-band. The RBM band, observed in the low-frequency range (100-300 cm⁻¹), is related to nanotube diameter and provides insights into their size and chirality. The D-band, centered around 1300 cm⁻¹, indicates defects and disorder within the carbon lattice, with higher intensity reflecting a greater presence of sp³-hybridized (diamond-like) carbon atoms. The G-band, near 1590 cm⁻¹, corresponds to the tangential stretching mode of carbon-carbon bonds in the sp²-hybridized graphene-like lattice of CNTs [
27].
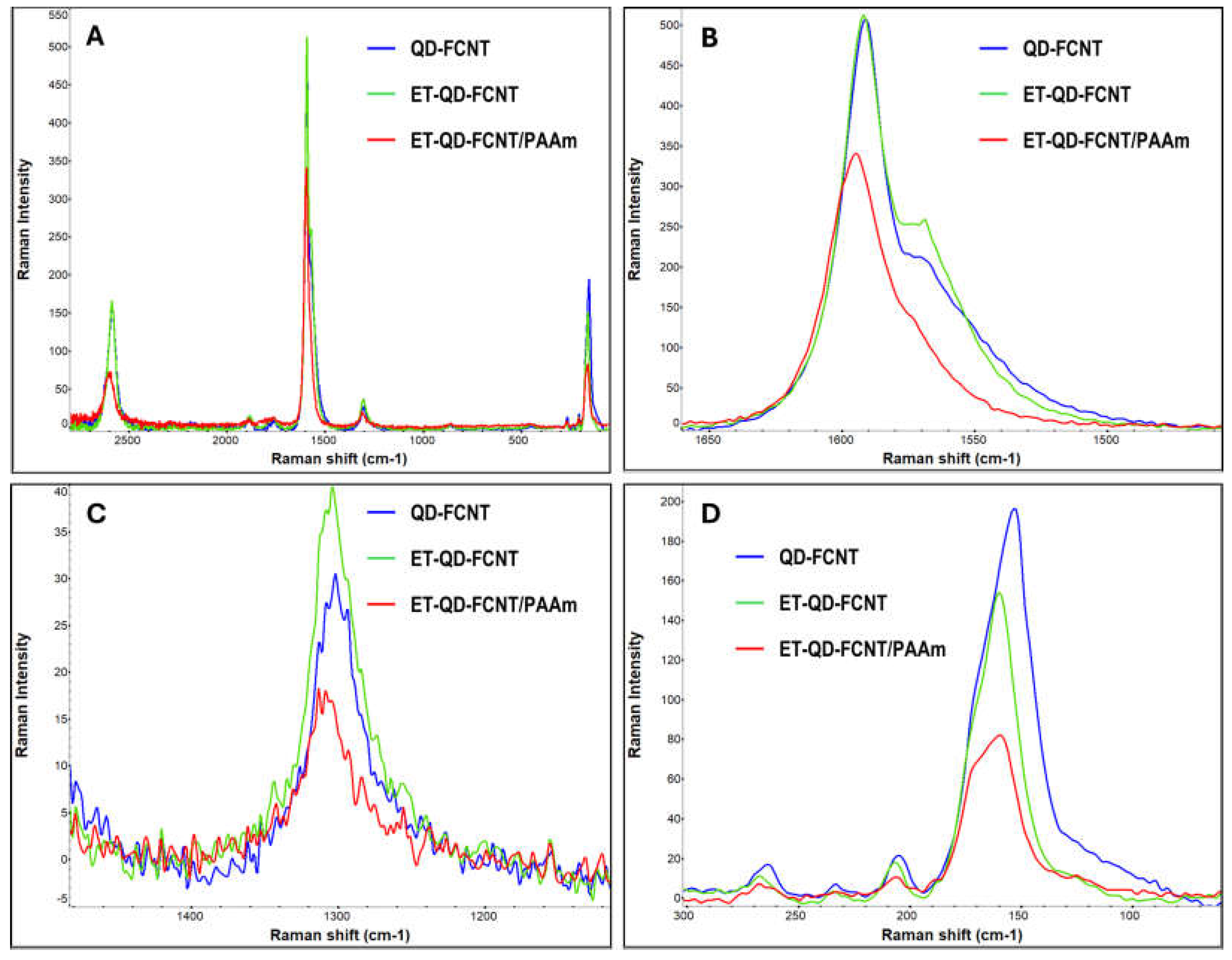
Our Raman analysis revealed that the untreated QD-FCNT samples displayed the typical spectral features of SWNTs, with a strong G-band at 1591.2 cm⁻¹ and a weak D-band at 1301.8 cm⁻¹ (
Figure 3A). The low D-band intensity supports the significant loss of fluorine from the FCNTs and partial recovery toward pristine CNTs. After the echo-friendly TMPD-treatment, the ET-QD-FCNTs kept the same G-band intensity as that of the untreated QD-FCNTs (
Figure 3B), however,the amplified D-bands shown in
Figure 3C demonstrated that the intensity of the disorder-representing D-band of the ET-QD-FCNTs increased comparing to the untreated QD-FCNTs, which agrees with the FT-IR analysis in
Figure 2A and EDX analysis in
Table 1. The G-band in
Figure 3B has a downshifted shoulder around 1570 cm⁻¹. In fact, the G-band can be split into two sub-peaks called the G
+ peak and the G
− peak[
28]. G
+ peak originates from LO (longitudinal optical) phonons, which involves vibrations where the carbon atoms move parallel to the axis of the nanotubes, whereas G
− peak originates from TO (transverse optical) phonons and involves vibrations where the carbon atoms move perpendicular to the axis of the nanotube. The increase of G
− peak after TMPD treatment (ET-QD-FCNTs in
Figure 3B) comparing to that of the untreated (QD-FCNTs in
Figure 3B) is due to the treatment caused hydroxyl functionalization, which introduced more sp³ hybridization and increased disorder in the carbon lattice, enhancing the transverse optical phonon modes. Such hydroxyl functionalization also caused adownshift of the G
− band from 1570.6 to 1568.8 cm⁻¹ due to the weakening of the carbon-carbon bonds near the functionalized sites.
Additional evidence was found in the RBM region (100-300 cm⁻¹), which is characteristic of radial vibrations in perfectly cylindrical nanotubes. The RBM band frequency of SWNTs (
ωRBM) is inversely proportional to their diameter (
dt), following the relation
ωRBM = 248/
dt[
29]. In
Figure 3D, the RBM peaks at 153.3, 205.1, and 263.8 cm⁻¹ correspond to nanotube diameters of 1.62 nm, 1.21 nm, and 0.94 nm, respectively. According to the Kataura plot, which relates SWNT diameter to electronic properties and chirality [
30], under 785 nm laser excitation (1.58 eV), RBM peaks below 162 cm⁻¹ (
dt > 1.53 nm) indicate metallic nanotubes, while those above 200 cm⁻¹ (
dt < 1.24 nm) are from semiconducting tubes. Fluorination generally disrupts the cylindrical structure of SWNTs by introducing sp³ hybridization, causing the RBM bands to disappear, but they can reappear when defluorination occurs [
31]. In this study of QD-FCNTs, the reappearance of the prominent RBM band at 153.3 cm⁻¹ after long-term storage suggests a substantial recovery of metallic SWNTs, while the weaker RBM bands at 205.1 cm⁻¹ and 263.8 cm⁻¹ indicate less recovery of pristine semiconducting SWNTs, despite significant defluorination. Since as-synthesized SWNTs typically consist of approximately 2/3 semiconducting and 1/3 metallic nanotubes, and achieving perfect chirality control is difficult due to the similar structures and formation energies of the two types [
32], the dominant intensity of metallic SWNT RBM bands over semiconducting ones suggests that metallic tubes are more favorably recovered during the long-term natural defluorination. The discrepancy in recovery between metallic and semiconducting nanotubes can be attributed to their differing electronic structures. Metallic CNTs have delocalized π-electrons across their lattice, which tend to preserve nanotube integrity. In contrast, semiconducting CNTs have a more localized electron density and a bandgap, making them more vulnerable to reactions with species such as OH free radicals [
33]. Thus, the RBM bands from the semiconducting nanotubes may be continuously suppressed due to reactions with reactive species in the environment during the quality downgrading process of FSWNTs.
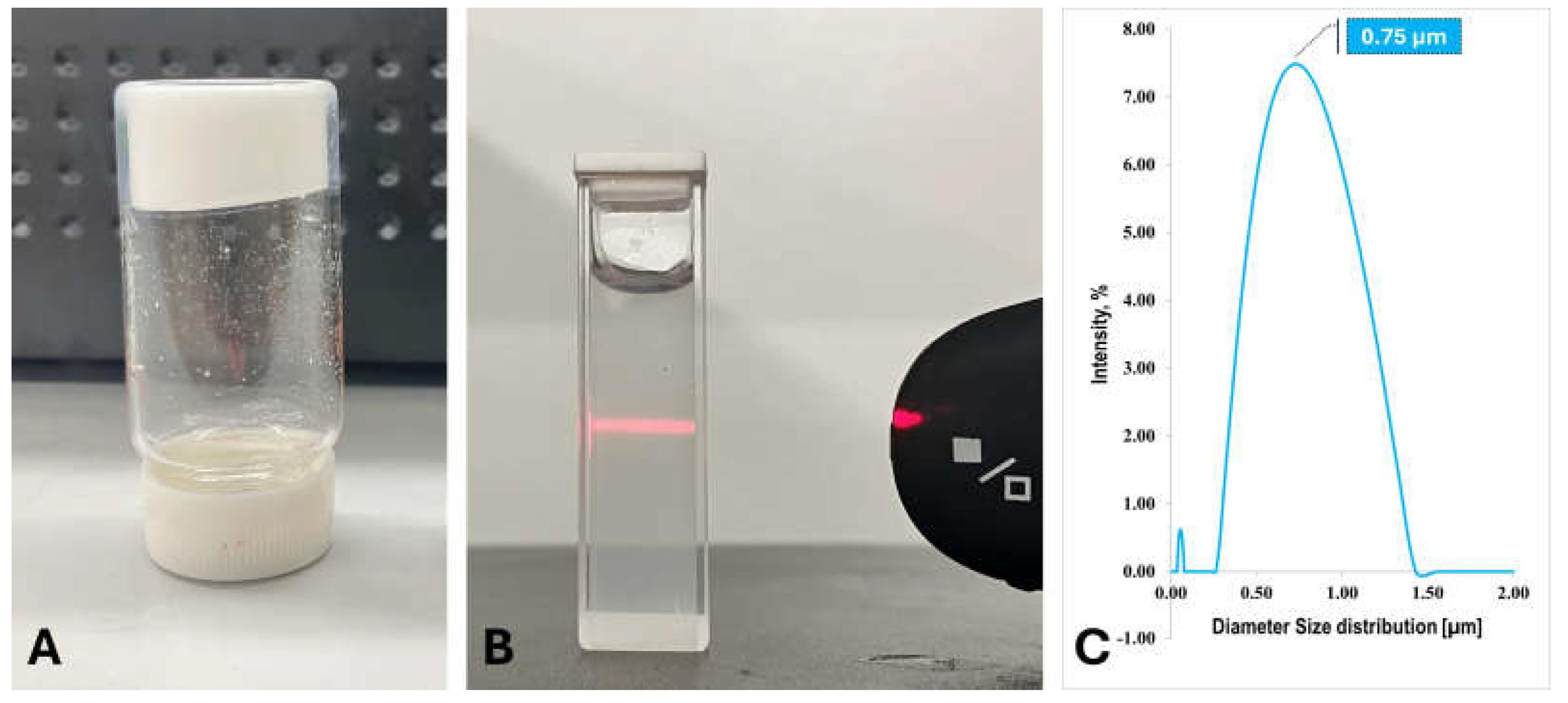
To prepare hydrogel used for incorporating with carbon nanotubes, we need a low energy cost synthesis method as well. Synthesizing hydrogels in an aqueous system typically results in uniform, macroscopic hydrogels. However, when using an alcohol system—commonly employed for the precipitation and purification of polyacrylamide polymers—the growth of PAAm hydrogels is limited. Instead of forming macroscopic networks, the hydrogels synthesized in alcohol remain as microgels, ceasing growth once they reach certain sizes. As shown in
Figure 4A, the microgels formed in ethanol are visible as low-density white powders. When these microgels are dispersed in D.I. water, they produce a cloudy, milky colloidal suspension. The Tyndall effect is clearly observed when a red laser beam passes through the suspension, with the light path being visible from a direction perpendicular to the beam (
Figure 4B). This phenomenon confirms the microgel nature of the suspension, indicating that the particles are both small and well-dispersed. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements revealed an average particle size of approximately 0.75 micrometers, as shown in
Figure 4C. The FT-IR spectrum of PAAm microgels (
Figure 2B) shows two distinct stretching vibration peaks located at 1550 and 1650 cm
-1 for amide II and amide I, respectively. Additionally, the peak aroused at 1450 cm
-1 is attributed to the C-N bond, while the peak at 3340 cm
-1 is assigned to the N-H bonds.
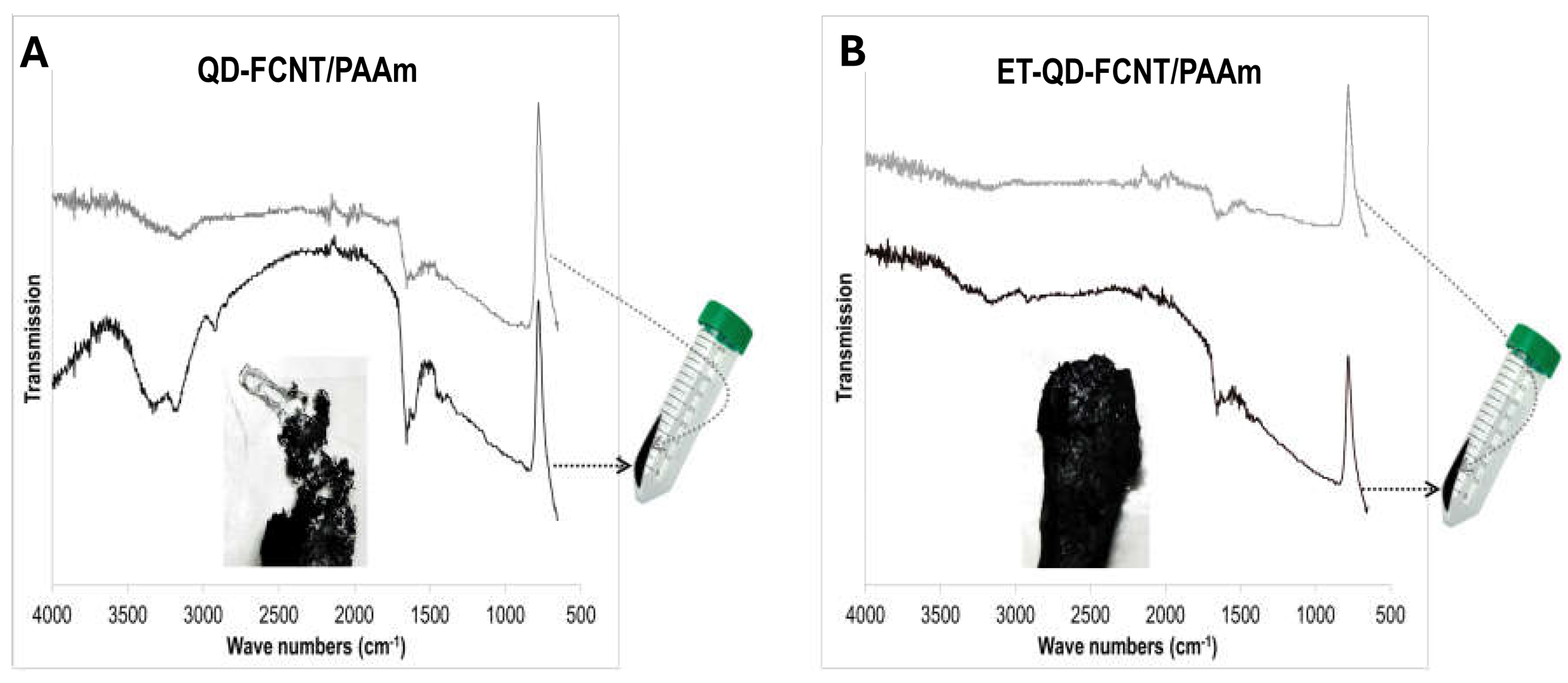
To prepare the CNT/microgel composites, a selected amount of dried PAAm microgels was dispersed in deionized water and sonicated together with either QD-FCNTs or ET-QD-FCNTs at a mass ratio of approximately 5% to the dried microgel. The resulting black dispersion was centrifuged to separate the composite materials from the solution. After drying to remove the absorbed water, the composite surfaces, those facing the center of the centrifuge tube and those facing the tube wall, were analyzed using ATR-FTIR, respectively (
Figure 5).
In the case of the composites without TMPD treatment (QD-FCNTs/PAAm,
Figure 5A), the wall-facing side showed more intense PAAm adsorption bands (PAAm control in
Figure 2C) than the center-facing side. This difference could be attributed to the slippage of PAAm microgels from the QD-FCNT networks under the centrifugal force, or incomplete incorporation of the hydrogel with the QD-FCNTs. By contrast, in the composites made of PAAm microgels and ET-QD-FCNTs, the FTIR adsorption band intensities were nearly identical on both the wall-facing and center-facing sides after centrifugation (
Figure 5B). This suggests that the ET-QD-FCNTs enhanced the bonding interaction between the PAAm microgels and the nanotubes, likely due to the additional -OH functional groups formed after TMPD treatment (
Scheme 1), resulting in stronger and more stable composites. The centrifugal force was insufficient to separate the microgel and CNT phases with enhanced interfacial interaction, thus preventing slippage and producing a more stable composite material, as confirmed by the digital photograph inset in
Figure 5.
The ET-QD-FCNT/PAAm microgel composite was further characterized using Raman spectroscopy (
Figure 3, red traces). The presence of the microgel diluted the CNT fraction in the sample, leading to a decrease in the peak intensities of the G-band (
Figure 3B, red trace), D-band (
Figure 3C, red trace), and RBM bands (
Figure 3D, red trace). However, all Raman bands exhibited upshifts in band frequency compared to CNT samples without the PAAm microgel (
Figure 3, green and blue traces). This upshift is attributed to the compressive strain exerted on the CNTs by the shrinking of the PAAm microgels after the drying process, which leads to a more rigid carbon lattice and increases the vibrational frequencies.
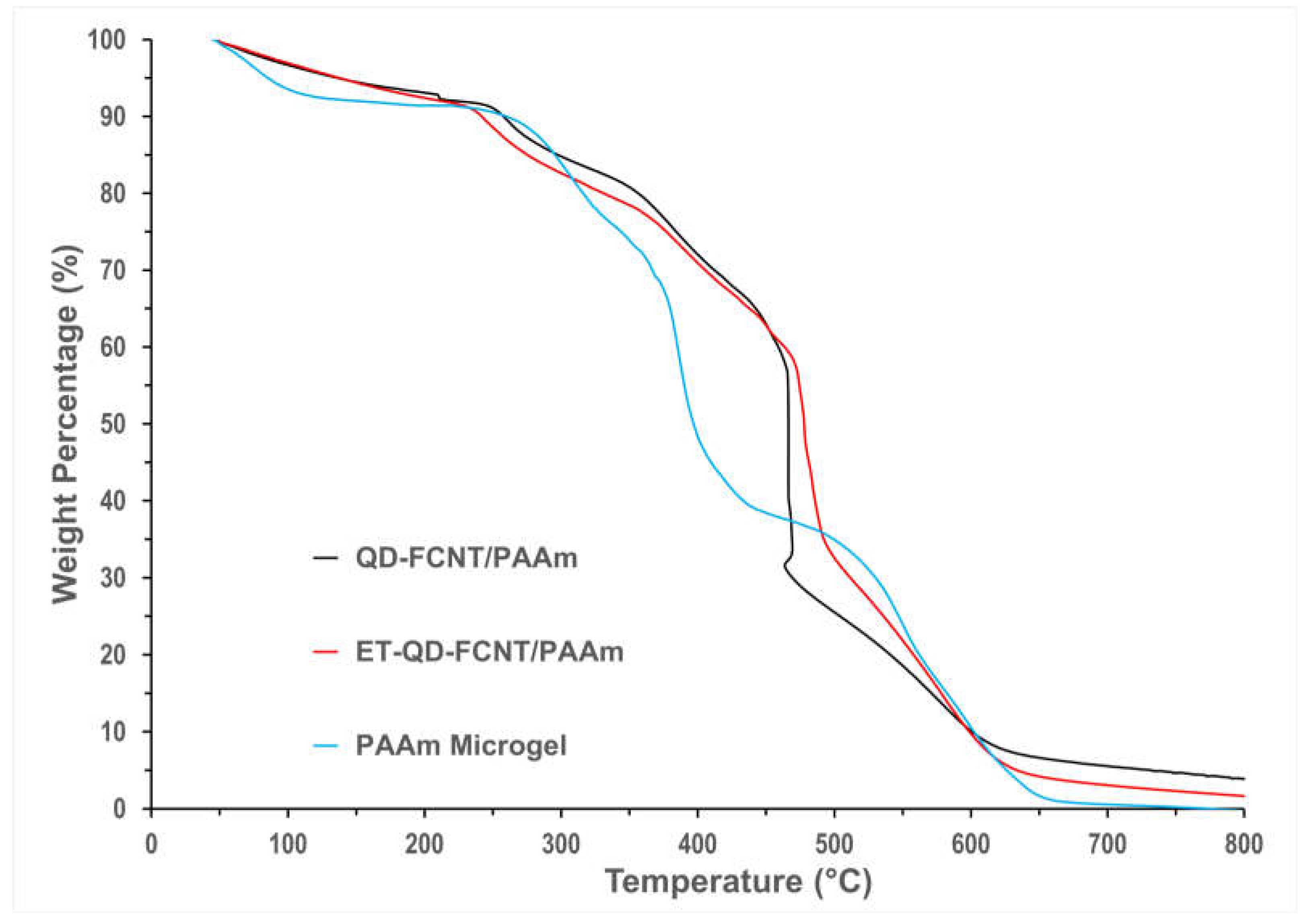
Figure 6 presents the thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) curves for the pure PAAm microgel, QD-FCNT/PAAm, and ET-QD-FCNT/PAAm microgel composites. Below 100 °C, all samples exhibit a slight weight loss, attributed to the evaporation of loosely bound or absorbed moisture. Up to 240 °C, the weight loss remains minimal (around 9%) across all samples, demonstrating that the materials are thermally stable within this range. The decomposition of the pure PAAm microgel accelerates at approximately 360 °C, whereas the QD-FCNT/PAAm and ET-QD-FCNT/PAAm composites show a delayed onset of decomposition, starting around 460 °C. This indicates that incorporating CNTs significantly enhances the thermal stability of the PAAm microgels. Although both QD-FCNT/PAAm and ET-QD-FCNT/PAAm composites exhibit similar decomposition temperatures, the ET-QD-FCNT/PAAm composite shows a less steep decomposition curve, suggesting a more gradual weight loss compared to the untreated QD-FCNT/PAAm composite.The steeper decomposition of the untreated QD-FCNT/PAAm is likely due to insufficient interaction between the QD-FCNTs and the PAAm microgels, which limits the contact area and reduces the thermal stabilization effect provided by the CNTs. Weaker CNT-microgel interactions also result in larger microgel domains that, when decomposed, create larger pores through which volatile components can escape, leading to a faster and more pronounced mass decrease.In contrast, the TMPD-treated ET-QD-FCNTs form more uniform interactions with the PAAm microgel via the newly introduced hydroxyl groups. This increases the contact surface area and reduces the size of the microgel domains, which slows down the decomposition process.
Upon heating to 800 °C, approximately 3.8% of the original weight of the ET-QD-FCNT/PAAm composite and 1.6% of the QD-FCNT/PAAm composite remain as residues. In contrast, the pure PAAm microgels fully decompose by 700 °C. The lower percentage of residue in the ET-QD-FCNT/PAAm composite is likely due to the stronger interactions between the CNTs and the polymer, resulting in more uniform dispersion of individual nanotubes. In the case of the untreated QD-FCNT/PAAm composite, weaker interactions may cause some CNTs to remain bundled, leading to higher residual mass after heating, as the dense nanotubes packing in these bundles reduces the evaporation of volatile components.
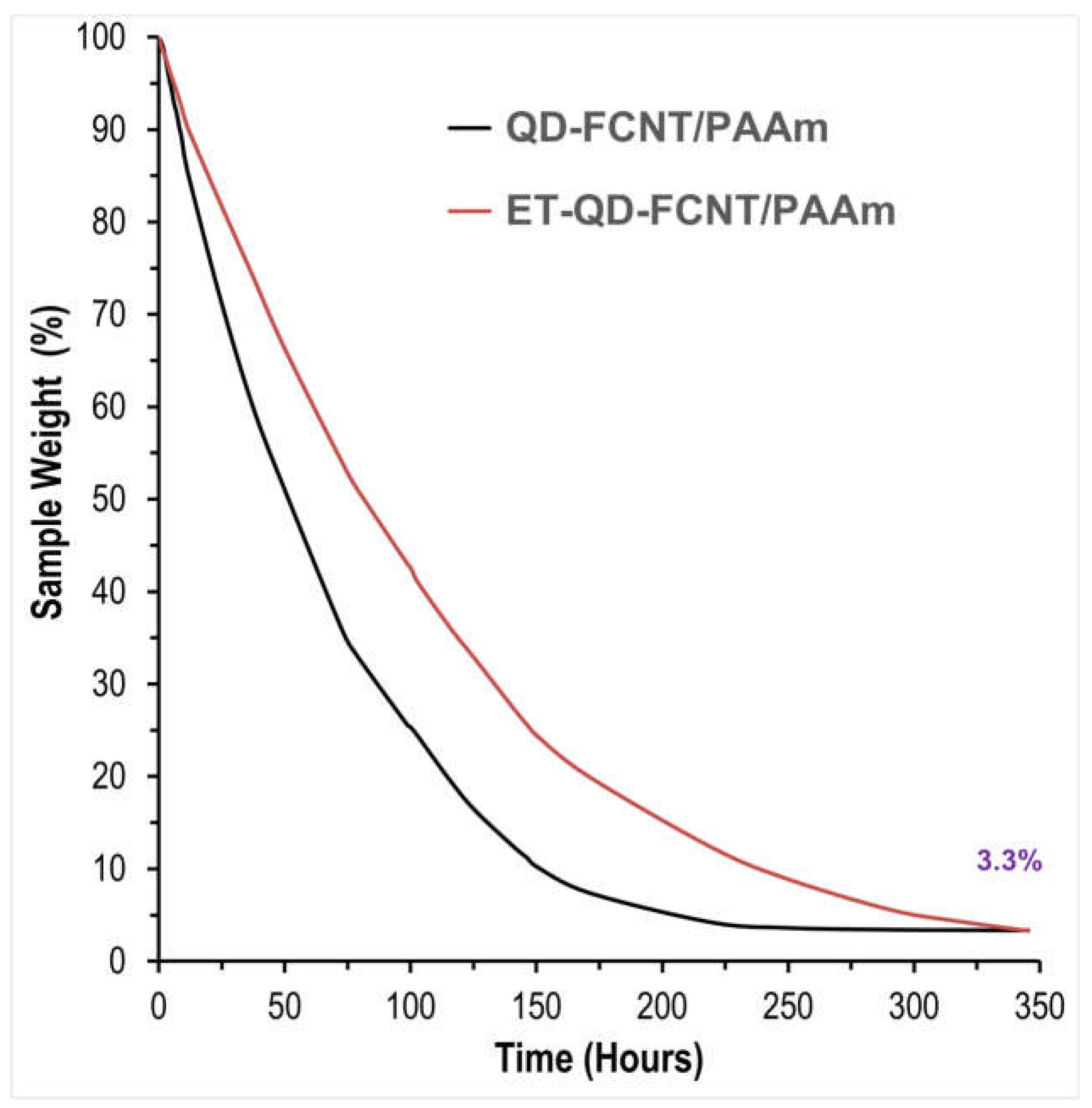
To assess the water retention properties, the prepared composites (without drying) in centrifuge tubes were placed inside a 35 °C incubator with ventilation, simulating the warm conditions of agricultural fields. The controlled water release properties of the QD-FCNT/PAAm and ET-QD-FCNT/PAAm microgel composites were measured by tracking the percentage of water evaporation over a period of 350 hours. As shown in
Figure 7, although both composites initially retain the same amount of water (96.7%), the TMPD-treated ET-QD-FCNT/PAAm microgel composites demonstrate slower water evaporation compared to the untreated QD-FCNT/PAAm composites over an extended period of 300 hours. Specifically, the QD-FCNT/PAAm composites took 142 hours to lose 88% of their weight, while the ET-QD-FCNT/PAAm composites required 220 hours to reach the same weight loss, reflecting a 55% increase in water retention time, just due to the energy-free surface treatment of the QD-FCNTs with low-dosage TMPD. This improved water retention is likely due to the stronger interactions between the ET-QD-FCNTs and the PAAm microgel, creating a more tightly "linked" composite structure through the nanotubes, which effectively locks in water for a longer duration.
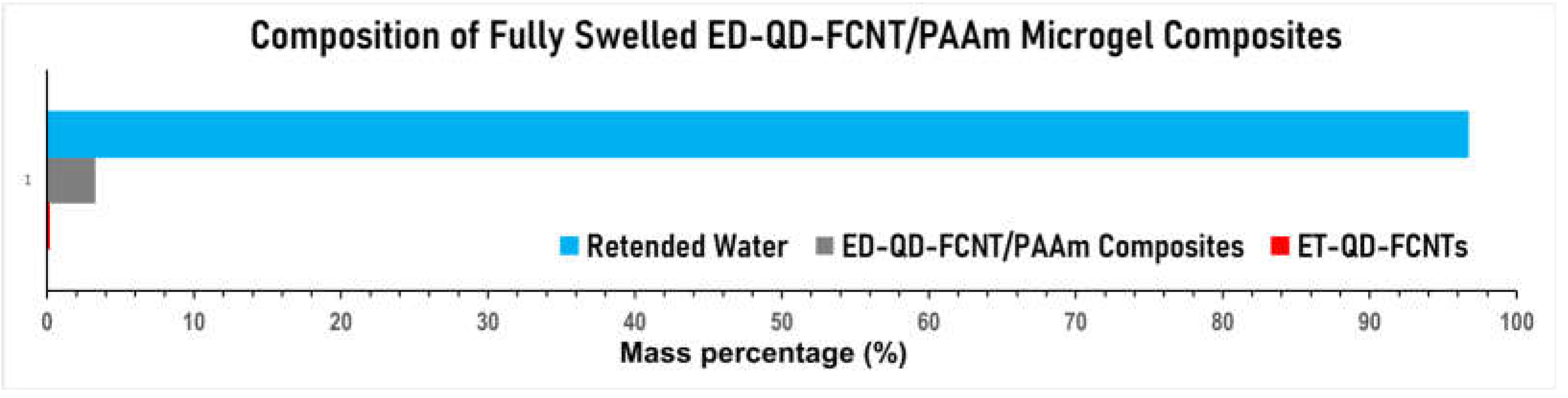
Notably, these composites require only a small fraction of CNTs to achieve the above exceptional functions. We conducted a composition analysis of the ET-QD-FCNT/PAAm composites fully saturated with water, based on the initially added components and the amount of water lost after complete drying. As shown in
Figure 8, water constitutes 96.7% of the composite, PAAm accounts for 3.2%, and the ET-QD-FCNTs represent just 0.1%, demonstrating the exceptional performance of ET-QD-FCNTs as an efficient microgel additive.
The results highlight the effectiveness of the ET-QD-FCNT/PAAm microgel composite in maintaining water retention under thermal stress, underscoring its potential for applications in water management and sustained release environments.