1. Introduction
Metallothionein (MT) is a superfamily of proteins widely distributed among both eukaryotic [
1] and prokaryotic [
2] organisms. They are distinguished by their exceptional affinity for heavy metal ions and metal binding capacity, attributed primarily to a unique content of reduced cysteine residues (20-35%) in the primary structure, giving rise to metal-tetrathiolate clusters [
3].
Native purified MTs typically bind Zn(II) and Cu(I) ions, particularly under physiological conditions [
4]. However, their binding affinities extend to other metals in vivo, including Cd(II) and Hg(II) [
5]. Furthermore, monosubstituted derivative MTs, originating from the metal-free, known as MT apo form, can accommodate various metals such as Fe(II), an essential metal, along with Pb(II), Bi(III), Sn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Tc(III), In(III), and Sb(III) [
6]. These forms are practically artificial and do not occur in natural systems. Traditionally designated as reservoirs/buffers for physiological heavy metal ions and scavengers for toxic species like Cd, Cu and Hg [
5], MTs have been often perceived to have an elusive primary function [
7]. Knockout studies in fruit flies, in fact, revealed that MTs are non-essential for organismal development and survival [
8]. Nevertheless, they confer significant advantages in coping with stressful situations, including exposure to heavy metals, low Zn conditions, infection, and various oxidative stress-related processes [
9]. Moreover, beyond their metal ion affinity and binding capacity, MTs exhibit a substantial redox capacity, playing a pivotal role in diverse stress response processes, such as inflammation [
10], gamma rays [
11] or UVB irradiation [
12], and challenges from xenobiotics triggering the formation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROSs) [
13]. Additionally, MT genes display transcriptional responsiveness to other non-physiological and physiological non-metal stimuli including glucocorticoids, and/or several polypeptide hormones [
14]. Despite these broad functional capacities, no role in iron homeostasis has been attributed to MTs so far.
Tetrahymena spp. are ciliated protozoa that express multiple metallothionein genes, which fall into two discrete subfamilies, 7a and 7b, differing in their structural and evolutionary traits [
15].
Tetrahymena MT genes coordinate expression with distinctive functions and respond diversely to environmental stressors. In
T. thermophila, MTT1 (protein encoded by the Mtt1 gene) binds and responds preferentially to Cd(II), aiding in noxious metal homeostasis and detoxification. Nearly identical, Mtt2 and Mtt4 genes encode copper-MTs with the highest binding preference for Cu(I) [
16]. Among its five metallothionein genes, the cadmium metallothionein Mtt5 gene is deemed essential [
17]. The transcriptional regulation of MT genes in
Tetrahymena has been a subject of investigation owing to its significance in understanding cellular responses to metal stress and environmental adaptation. Two seminal studies demonstrated the robust inducibility-repressibility of the Cd-inducible Mtt1 [
18] and Cu-inducible Mtt2 [
19] genes in
T. thermophila. These studies revealed that Mtt1 or Mtt2 mRNA expression is tightly regulated by cadmium or copper ion concentration respectively, with rapid induction upon metal exposure and subsequent downregulation upon withdrawal. Moreover, both promoters were shown to be highly efficient in driving conditional expression of heterologous genes, under control of fully sub-toxic metal levels, offering a valuable tool for genetic manipulation and functional studies in
T. thermophila, but also demonstrating definitively that Mtt1 and Mtt2 are primarily controlled by inducible promoters. Mt genes are transcriptionally regulated through multiple cis-acting elements known as Metal Responsive Elements (MRE) [
14].
Tetrahymena MT promoters don’t appear to contain genuine MREs. Insights into the transcriptional regulation of
Tetrahymena MT genes emerged from the work of Formigari et al., [
20] showing the involvement of a proximal composite GATA cis-acting element in Cd inducibility of Mtt5 and those of Diaz et al., [
15] and de Francisco et al., [
21] who identified multiple Metallothionein Conserved Motif 1 (MTCM1) resembling AP-1 antioxidant responsive elements, suggesting a potential role for AP-1 (bZIP) transcription factors in regulation of Mtt gene expression. AP-1 binding sites have been identified in several MT vertebrate promoters, where they are part of a complex cis-acting element setting [
22,
23,
24].
The aim of this study was to establish a central involvement of metallothioneins in the oxidative stress response within a relatively simpler and well-characterized metallothionein expressing system i.e., the ciliated protozoa
T. thermophila. To achieve this objective, we employed quantitative real-time reverse transcription quantitative PCR (QPCR) in conjunction with multiplexed Taqman hydrolysis probes, allowing for precise assessment of the relative abundance levels of metallothionein mRNAs, specifically Mtt1, Mtt2/4, and Mtt5. In selecting the metallothionein genes Mtt1, Mtt2/4, and Mtt5 for analysis, we aimed to reduce complexity while ensuring a comprehensive understanding of MT gene regulation in
T. thermophila. According to Diaz et al., [
15] the coding sequences and amino acid compositions of Mtt2 and Mtt4 are nearly identical, indicating very close molecular evolution of the 7b Mtt sub-family. Due to the high nucleotide sequence similarity between them, we analyzed Mtt2 and Mtt4 together as a set. On the other hand, Mtt3 is similar to Mtt1, with both genes appearing to have evolved from the same ancestral gene. Although Mtt5 is distinct, it shares an evolutionary origin with Mtt1 and Mtt3 [
15], providing a broader perspective on MT gene regulation for the 7a Mtt sub-family protein. Our investigation into the gene responsiveness of metallothionein involved the influence of superoxide and hydroxyl radicals, achieved through the use of inhibitors for superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT), as well as the introduction of iron to initiate the Fenton [
25] and/or Haber-Weiss [
26] reactions triggering superoxide and hydroxyl radicals’ formation. Unexpectedly, our findings highlighted a pivotal role of iron
per se in modulating gene expression within
T. thermophila metallothionein.
3. Results
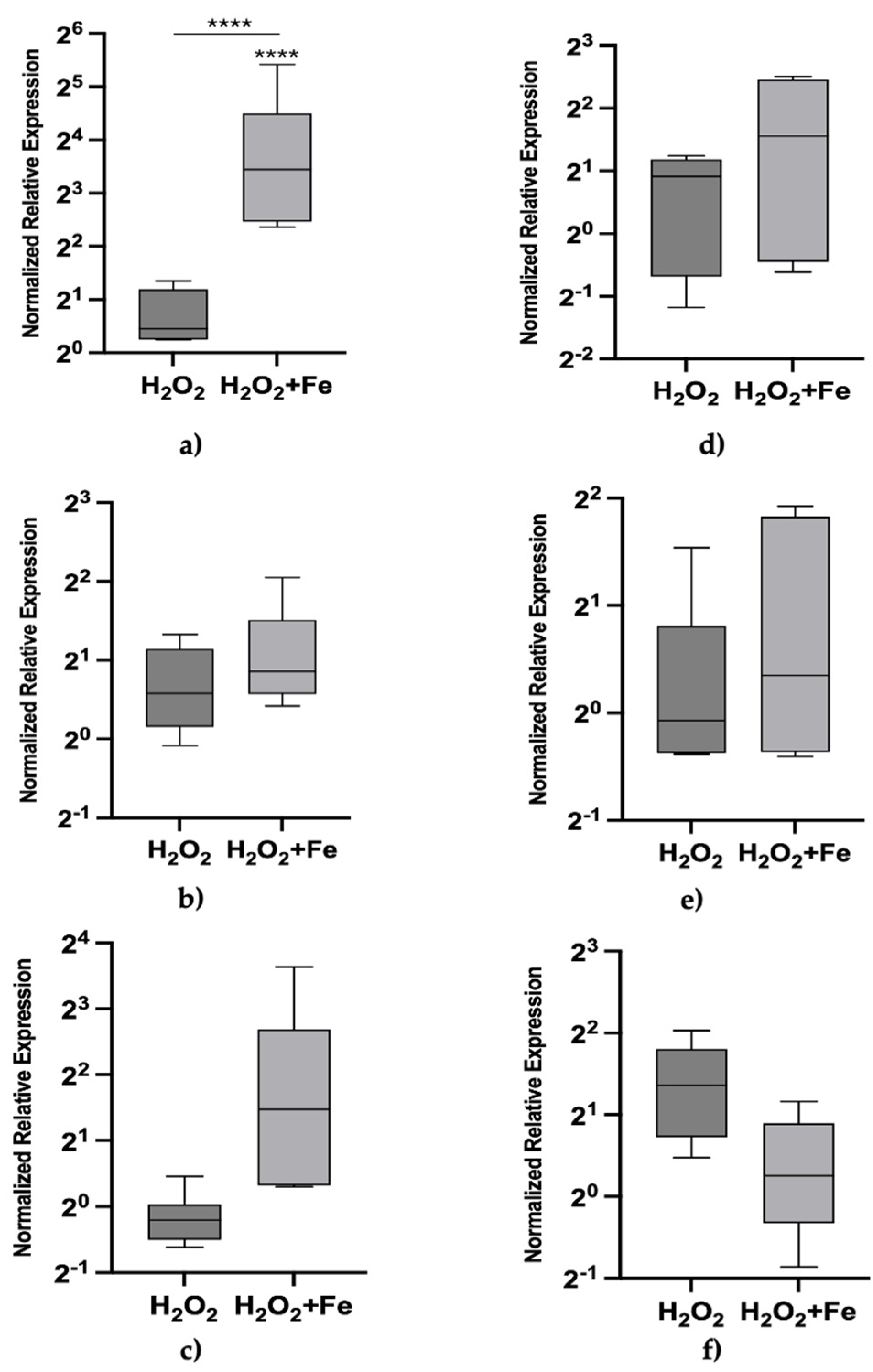
Figure 1 illustrates the effects of exogenous exposure to hydrogen peroxide and hydrogen peroxide with iron at 24 and 72 hours. We intentionally selected a concentration of hydrogen peroxide (Table 2) that was ineffective on its own to specifically evaluate its combined effect with iron on Mtt transcriptional activation under the current experimental conditions. When combined with iron, Mtt1 showed significant activation while a mild trend of activation was observed for Mtt5 and Mtt2 at 24 hours. No significant effects were seen at 72 hours.
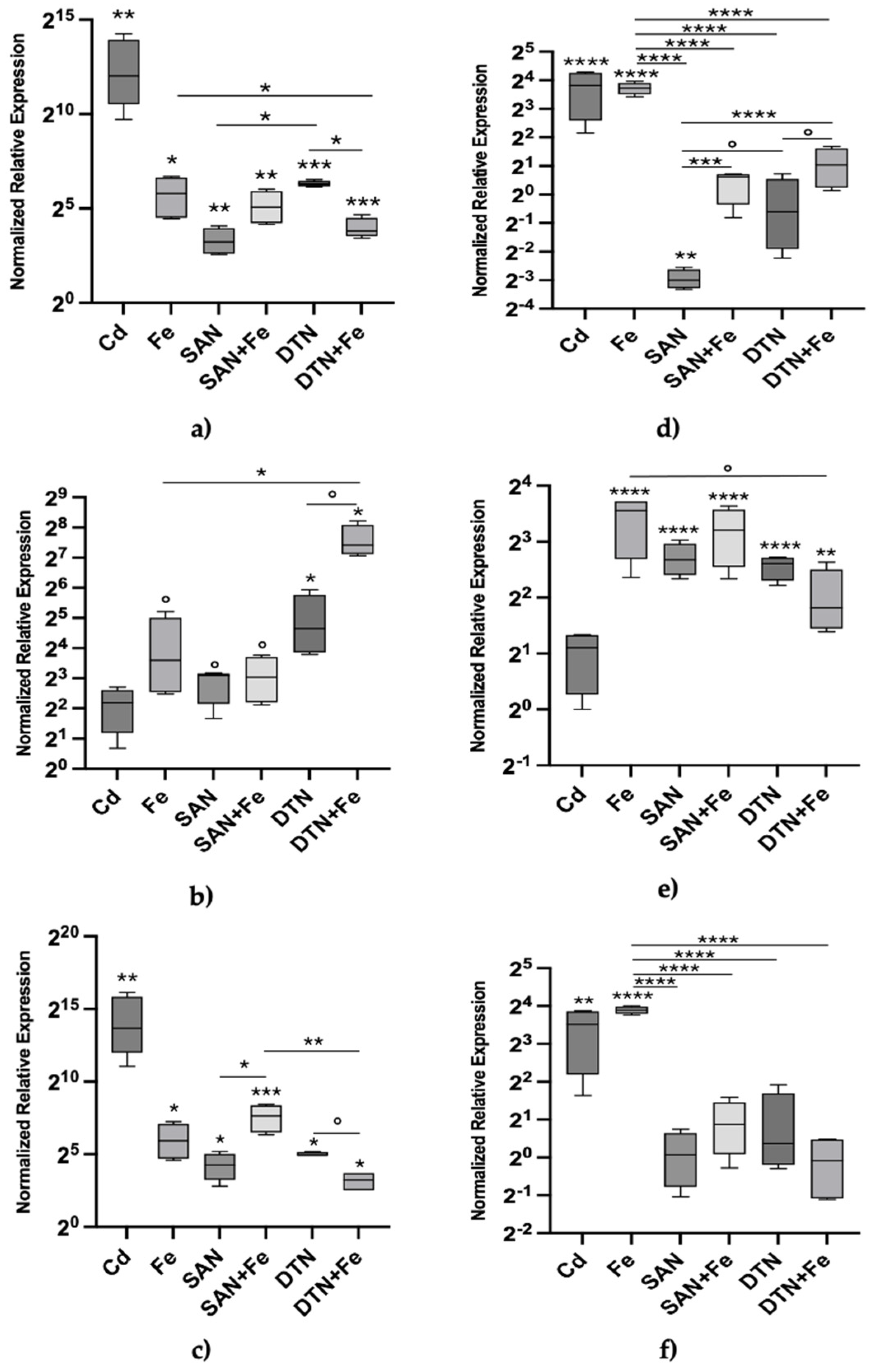
The relative expression levels of Mtt1, Mtt2/4, and Mtt5 were, then, measured after 24 hours of exposure to various stressors (Table 2), including Cd (II) as a positive control, Fe (III), sodium azide, sodium diethyldithiocarbamate, and combinations of each inhibitor with iron (
Figure 2a–c). Cadmium exposure resulted in the highest expression of the Mtt1 gene. Iron also induced Mtt1 expression (
Figure 2a), though to a lesser extent. The inhibitors sodium azide and sodium diethyldithiocarbamate caused a significant effect on Mtt1 expression (
Figure 2a). Interestingly, sodium azide plus Fe resulted in a trend of higher expression than sodium azide alone which, however, seemed to be driven by Fe, while diethyldithiocarbamate plus Fe showed a statistically significant lower expression level than diethyldithiocarbamate itself.
For Mtt2/4, (
Figure 2b) iron exposure alone yielded substantial gene expression, relatively higher than that induced by cadmium, but generally lower than Mtt1, with differences from control values being only marginally statistically significant (p < 0.1). Sodium azide and diethyldithiocarbamate also elicited a marginal trend of Mtt2/4 induction similar to iron. Their combination with iron led to varied effects: sodium azide plus iron showed no additional effect, whereas diethyldithiocarbamate plus iron caused a sharp increase compared to diethyldithiocarbamate or iron alone.
Similar to Mtt1, cadmium exposure resulted in the highest expression of Mtt5 (
Figure 2c). In general, the pattern of Mtt5 was very similar to that of Mtt1, with the same effect of iron on the co-exposure with each inhibitor but this time the difference between sodium azide and sodium azide plus Fe was statistically significant due to a lower uncertainty.
Table 2.
Substances tested for the effects on Mtt gene expression.
Table 2.
Substances tested for the effects on Mtt gene expression.
| Treatment |
NOEC |
| Sodium azide (SAN) |
200 μM |
| Sodium diethyldithiocarbamate (DTN) |
100 μM |
| Cadmium chloride (Cd) |
20 μM |
| Ferric chloride (Fe) |
200 μM |
| Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) |
100 μM |
After 72 h of exposure, the expression patterns of Mtt1 (
Figure 2d), Mtt2/4 (
Figure 2e), and Mtt5 (
Figure 2f) genes were assessed under the same conditions as the 24h exposure. Relative mRNA abundances of Mtt1 fairly declined to new steady state levels, including with cadmium treatment, but remained substantial with iron whose level was significantly higher than any other analyzed condition. The treatments with sodium azide (and marginally diethyldithiocarbamate) rendered negative expression levels respect to control which may suggest repression of Mtt1 transcription. When combined with iron, the expression levels of Mtt1 with sodium azide or diethyldithiocarbamate treatments were significantly higher than the those of the individual inhibitors alone but lower than that of iron itself.
At 72 hours, iron exposure continued to induce substantial Mtt2/4 expression (
Figure 2e), similar to the effects observed with sodium azide and diethyldithiocarbamate treatments. Combining these treatments with iron did not produce any notable additional effects, but a significant reduction for diethyldithiocarbamate plus iron below the 24h level and also below the 72h iron level. These findings suggest an interaction between iron and diethyldithiocarbamate and in same time an adaptive response of Mtt2 in this scenario.
The pattern for Mtt5 after 72 hours mirrored that of Mtt1, with significant relative mRNA abundances observed only with cadmium and iron exposures. Moreover, the effects of the two inhibitors were fully compensated, which may suggest faster adaptive kinetics for Mtt5 compared to Mtt1.
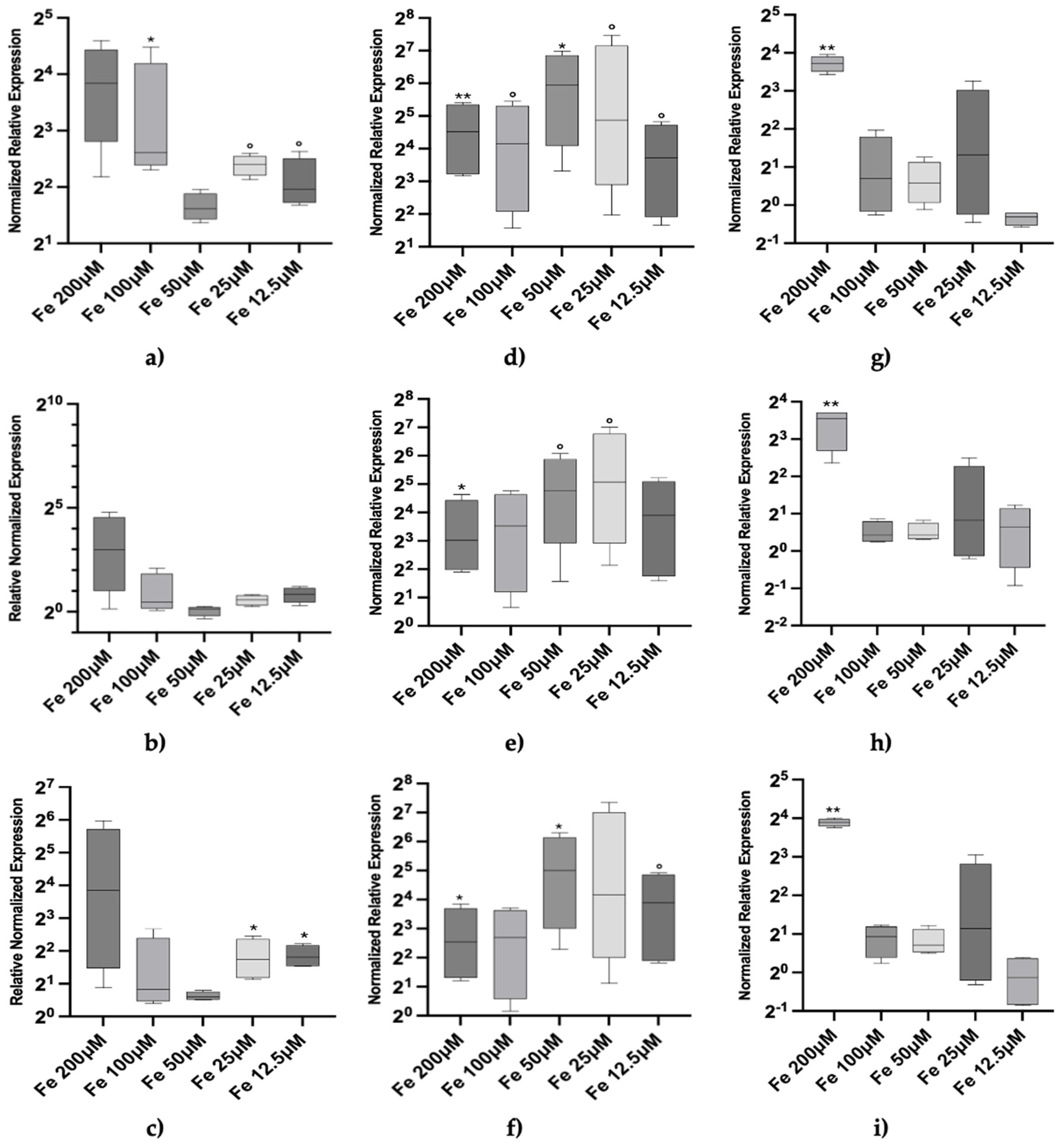
We, then, directed our focus towards solely iron as a potential novel Mtt inducer, examining dose-dependent effects ranging from 12.5 μM to 200 μM and kinetic responses spanning from 2h to 72h (
Figure 3).
At 2 hours there was a positive transcriptional response of Mtt1 and Mtt5 at both high and low concentrations, although high uncertainty levels affected some conditions (
Figure 3a–c). The gene Mtt2/4 showed only a trend of activation at 200 µM Fe. We analyzed the effects of same concentrations at 24h (
Figure 3d–f) and 72 hours (
Figure 3g–i), revealing that: no clear dose response pattern is seen for any Mtt genes; the response is adaptive peaking at 24h; the highest iron concentration (200 µM) is not compensated after 72h. The lack of a clear dose-response effect and the adaptive response observed over time may suggest that intracellular iron concentration is regulated in
T. thermophila with a possible role for Mtt genes.
4. Discussion
Our initial hypothesis centered around confirming Tetrahymena Mtt’s involvement in ROS scavenging activity. Consequently, we utilized hydrogen peroxide and a combination of hydrogen peroxide with iron as exogenous sources of ROSs. Furthermore, we used inhibitors targeting key antioxidant enzymes, specifically sodium azide [
30] and sodium diethyldithiocarbamate [
31], to inhibit catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities, respectively, thereby promoting the intracellular formation of ROS. Previous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of this strategy to raise levels of hydrogen peroxide [
32] or superoxide ion [
33] using micromolar levels of the same inhibitors employed in this work. To intensify this effect, we included iron as an additional treatment with the aim of stimulating the Fenton [
25] and/or Haber-Weiss [
26] reactions known to generate hydroxyl and/or hydroperoxyl radicals from hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) or superoxide (O₂⁻). Thus, we gathered and assessed the transcriptional modulation of the Mtt genes using QPCR quantifying relative abundances of
T. thermophila metallothionein mRNAs (Mtt1, Mtt2/4, Mtt5).
Sodium azide was used due to its ability to inhibit catalase [
30]. This enzyme is responsible for the conversion of hydrogen peroxide into molecular oxygen and water [
34]. This is a fundamental defense mechanism that all organisms use to detoxify endogenous H
2O
2, and if this molecule is not taken care of, it reacts and degrade proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. Sodium diethyldithiocarbamate was used because it is a known inhibitor of Super Oxide Dismutase (SOD) [
31]. This enzyme is responsible for the dismutation reaction of the superoxide anion (O
2-) into two different compounds (H
2O
2 and O
2) [
35]. SOD is a key enzyme in the cell’s defense against superoxide anion, a ROS species, which causes the inactivation of iron/sulphur clusters present in many enzymes and proteins that play a key role in metabolic processes.
In addition to exacerbating the intracellular oxidation we paired the two inhibitors with iron, therefore, three new treatments were obtained i.e., sodium azide plus iron, sodium diethyldithiocarbamate plus iron and H
2O
2 plus iron. Iron, in fact, must be tightly regulated intracellularly as it is the starting point of several reactions that create oxidative stress (sensu the Fenton [
25] or Haber-Weiss reactions [
26]). Previous data based on comparative QPCR analyses and protein-DNA interaction experiments supported the involvement of AP-1 transcription factors in mediating MT gene expression responses to metal stress in
T. thermophila [
21]. The latter finding is quite relevant in the context of gene expression results of our study since AP-1 transcription factors are responsible for the transcriptional control of oxidative stress related genes through the Antioxidant Response genetic Elements (AREs). In mammalian cells, these factors can bind to specific cis-acting elements rendering numerous cellular processes, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, development, but also triggering response to stress induced by exposure to UV or cytotoxic agents (e.g. cycloheximide, 4-nitroquinoline), iron-chelating complexes, oxidizing agents and several heavy metals including iron [
36,
37]. AP-1 transcription factors seem to be universal mediators as they are also relevant for abiotic stress response in yeast [
38] and plants [
39], moreover they have been already mapped in MT promoters of vertebrates [
22,
23,
24]. In addition to transcription factors, epigenetic mechanisms such as microRNAs (miRNAs) have been implicated in post-transcriptional regulation of genes involved in metal stress responses. Amaro et al. [
40] isolated and characterized miRNAs involved in the post-transcriptional regulation of transcripts linked to the response to cadmium stress in
T. thermophila. These studies highlight the regulatory complexity underlying the cellular response to metals in modulating gene expression in
Tetrahymena, even in a relatively simpler model organism. They also emphasize the inevitable interplay between heavy metal and oxidative stress responses, as has been previously described in vertebrates.
The activation of
T. thermophila metallothionein genes by oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide is well-documented in the literature [
41,
42]. Our study, however, provides new insights into the response of metallothioneins to abiotic stimuli. Based on the hypothesis that the repression of catalase and SOD enzyme activities could increase the levels of H
2O
2 and superoxide radicals, we conducted a pioneering investigation into the influence of iron on metallothionein gene expression, focusing specifically on the
T. thermophila Mtt system.
Our work represents a significant advancement in the understanding of the molecular regulation of metallothionein genes. By targeting key antioxidant enzymes with specific inhibitors and co-exposing protozoa to iron, the study aimed to simulate endogenous oxidative stress conditions conducive to MT gene induction. This innovative approach allowed us to explore the direct impact of reactive oxygen species (ROS) on MT gene expression. A key question is whether the two inhibitors could activate Mtt gene transcription, and this study provides clear evidence supporting that. This activation may result from either a direct effect of increased endogenous ROS levels or from indirect effects of ROS on intracellular metal levels (and their oxidation state). Another significant finding is that iron itself effectively modulated Mtt gene expression. The combination of iron with sodium azide or hydrogen peroxide never exceeded the effects of iron alone, suggesting non-significant interactions, at least by 24 hours (
Figure 2a–c). Indeed, at 72 hours (
Figure 2d–f), the effects of iron combined with sodium azide were significantly lower than those of iron alone for Mtt1 and Mtt5, but not for Mtt2/4. This finding suggests differential regulation between the 7a and 7b groups of Mtt genes, indicating that Mtt2/4 might have a unique regulatory mechanism compared to Mtt1 and Mtt5. Comprehensive mechanistic explanations for this behavior cannot be determined from gene expression data alone, necessitating further studies. However, for the combined effects of exogenous hydrogen peroxide and iron at 72 h a possible explanation can be drawn from an analogy with
S. cerevisiae, where iron uptake involves a membrane-bound ferrireductase to reduce Fe(III) to Fe(II) and a ferrous transporter (Ftr1p) to import Fe(II) into the cell [
43,
44]. Exogenous hydrogen peroxide may reduce Fe(III) to Fe(II), interfering with iron’s availability to enter the cell and modulate Mtt gene expression. Simultaneously, the interaction between endogenously formed hydrogen peroxide, due to catalase inhibition by sodium azide, might alter the oxidation state of iron over time, affecting its ability to regulate Mtt1 and Mtt5 expression. This suggests that the observed effects at 72 hours are the result of a time-dependent process that requires further investigation to fully understand the underlying mechanisms.
A consistent pattern of iron inducibility was observed across all Mtt genes (
Figure 3), characterized by an adaptive response that lowered its intensity over time, except at high, non-permissive levels (200 µM), where gene expression remained substantial throughout. Unlike Cd and Cu exposures, iron did not show dose dependency in Mtt gene transcriptional activity, likely due to the tight regulation of free iron intracellular concentrations [
45].
Our results open up the intriguing hypothesis that the Mtt system participates in iron homeostasis. Despite a native Fe-bound metallothionein (MT) never being isolated so far, it is interesting to note that hepcidin binds one Fe(III) ion through a tetrahedral thiolate cluster [
46], similar to how metallothionein binds multiple Cd/Cu atoms. Hepcidin, a liver hormone, is the overarching governor of iron homeostasis in the plasma of mammals [
47]. Very little is known about iron homeostasis in ciliates; therefore, further research is essential to understand the potential roles and mechanisms involved.
Examining the effects of diethyldithiocarbamate, a superoxide dismutase (SOD) inhibitor, combined with iron (
Figure 2), we observed a discordant pattern between the Mtt1/Mtt5 pair and Mtt2/4. Mtt1 and Mtt5 are phylogenetically related, with consistently aligned transcriptional patterns in our study. In contrast, diethyldithiocarbamate plus iron exhibited an antagonistic effect on Mtt1/Mtt5 expression while having an additive, if not cooperative, effect on Mtt2/4. This suggests that in co-exposures, iron alone can account for the transcriptional activation of Mtt1/Mtt5 but not Mtt2/4. The response observed indicates that either iron, or superoxide ions whose levels are elevated by SOD inhibition, have distinct modes of action on the Mtt2/4 promoter. Alternatively, this interaction may generate new effector(s), possibly through the Haber-Weiss reaction, which are more effective in activating Mtt2/4, i.e. the hydroperoxyl (HO₂•) and hydroxyl radical (OH•) are possible candidates.
Our findings highlight the complex interplay between iron, ROS, and the regulatory mechanisms governing MT gene expression. The evolution of metallothionein and heavy metal-inducible gene transcription systems is a fascinating topic that intertwines the roles of oxidative stress and heavy metal detoxification. While it is clear that this system is primarily known for its role in metal ion homeostasis and detoxification, we cannot exclude the possibility that oxidative stress response has driven their evolution. This study underscores the importance of considering both direct and indirect effects of oxidative stress and metal ions in understanding the molecular regulation of MT genes. Considering the previously described effects of cadmium and copper, it is evident that ROS alone cannot be regarded as the primary factor for MT gene activation. Metals can promptly induce and repress MT gene transcription, suggesting the involvement of a metal-sensitive transcription factor analogue to the MTF-1 [
48] found in vertebrate systems. Rather than a zinc finger like MTF-1, we speculate the existence of a redox-sensitive transcription factor in
T. thermophila, akin to the
E. coli SoxR protein [
49], or the
S. cerevisiae Yap5 [
50] which are indeed Fe-S (iron-sulfur) protein, known for their essential role in response to oxidative stress. The latter, in particular, is known for regulating iron storage and is a basic leucin zipper (bZIP) protein, the same family of transcription factors putatively identified by de Francisco [
21] in Mtt promoters. This hypothetical factor may function as a redox sensor that recognizes superoxide and/or other ROS, while also being influenced by metal ions with high affinity for sulfur. An important question arises: what has driven the evolution of metallothionein and heavy metal-inducible gene transcription systems? Can we truly exclude the possibility that oxidative stress response mechanisms could have driven the evolution of inducible systems that incidentally respond to heavy metals? The dual functionality of MT in both metal detoxification and oxidative stress response suggests an evolutionary advantage in environments where organisms are exposed to both metals and oxidative stress. However, oxidative stress is a common challenge faced by aerobic organisms, leading to the production of ROS, which are highly reactive and can cause cellular damage. The evolution of MT may have been driven by the need to mitigate this damage. Additionally, MT, by binding metal ions, can reduce the catalytic activity of metals like copper or iron, which participate in Fenton and Haber-Weiss reactions, generating harmful hydroxyl radicals. The ability of MT to scavenge ROS directly provides an additional layer of protection and binding heavy metals may not represent the primary function of MT but rather a structural constraint to keep cysteine residues in a reduced state, acquiring redox potential and scavenging activity against oxidative radicals as already shown [
11]. The incidental responsiveness to heavy metals could be an advantageous byproduct of this primary function. In mammals it has been shown that metals like cadmium and copper as well as ROS or disulfides like oxidized glutathione can displace zinc in MT, leading to changes in MT conformation and, consequently, increase gene transcription through the activation of the proper transcription factors [
51].
In summary, while oxidative stress plays a significant role in Mtt gene activation, the primary regulatory mechanism likely involves a complex interplay between ROS and metal-responsive elements, mediated by specialized transcription factors that respond to both oxidative and metal-induced signals. The evolution of MT and its transcription system may have been driven by the need to protect against oxidative damage, with the incidental benefit of metal detoxification. The Mtt system’s response to iron suggests potential involvement in iron metabolism. Mtt2/4 promptly responded to the interactive effects of superoxide and iron and exhibited prolonged expression in response to elevated endogenous hydrogen peroxide and superoxide levels. Given its earlier molecular evolution [
15] and responsiveness to Cu [
16], we speculate that Mtt2/4 might better represent the antioxidant function of the ancestral MT gene, while the 7a group may have evolved later, acquiring specialized functions related to heavy metal homeostasis, including iron. Indeed, Mtt5, which is an essential gene [
17], appears to be the best candidate for specifically controlling essential metals such as iron. Further research is needed to validate this hypothesis in view also of the limitation of this study (missing data on Mtt3, and no discrimination between Mtt2 and Mtt4 expression), identify the regulatory elements and factors involved, and better understand the evolutionary pressures that shaped these multifunctional proteins. The ciliate
T. thermophila represents an appropriate experimental system for this purpose.