Submitted:
13 September 2024
Posted:
16 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
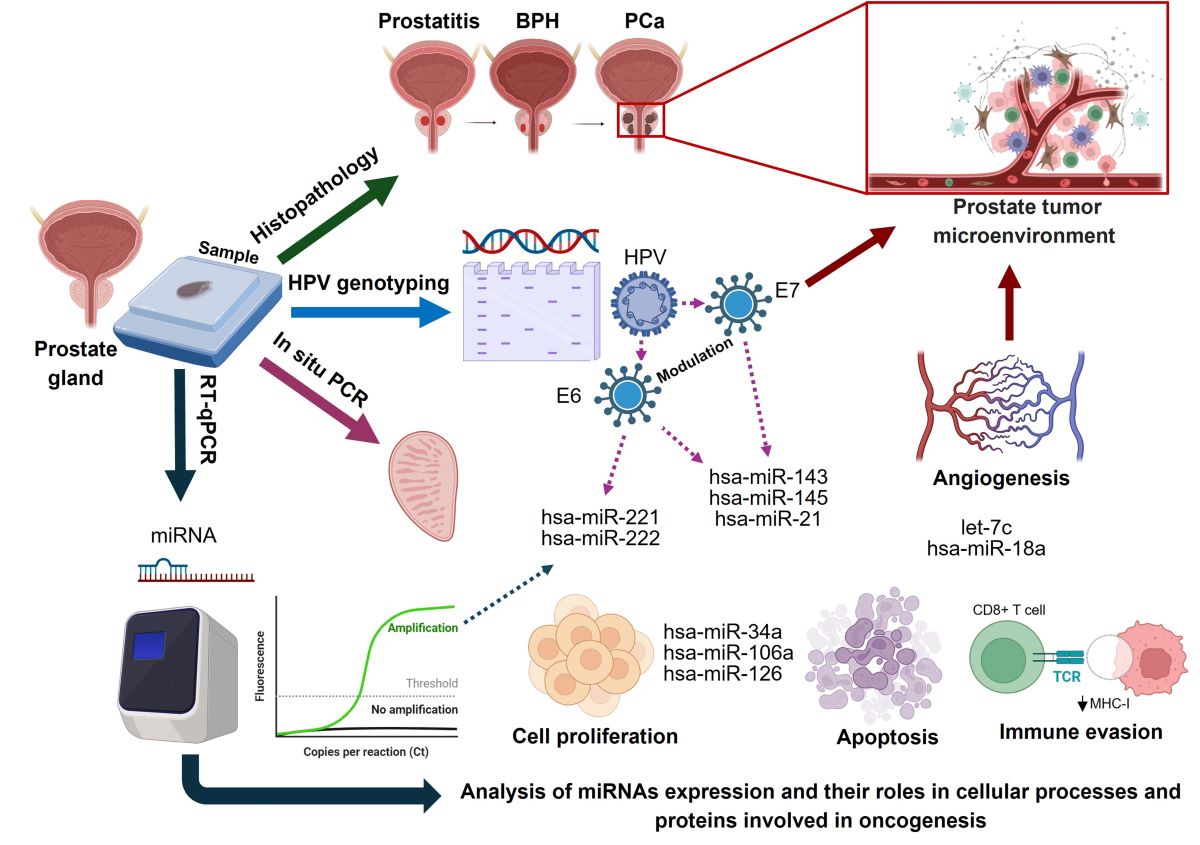
1. Introduction
2. Results
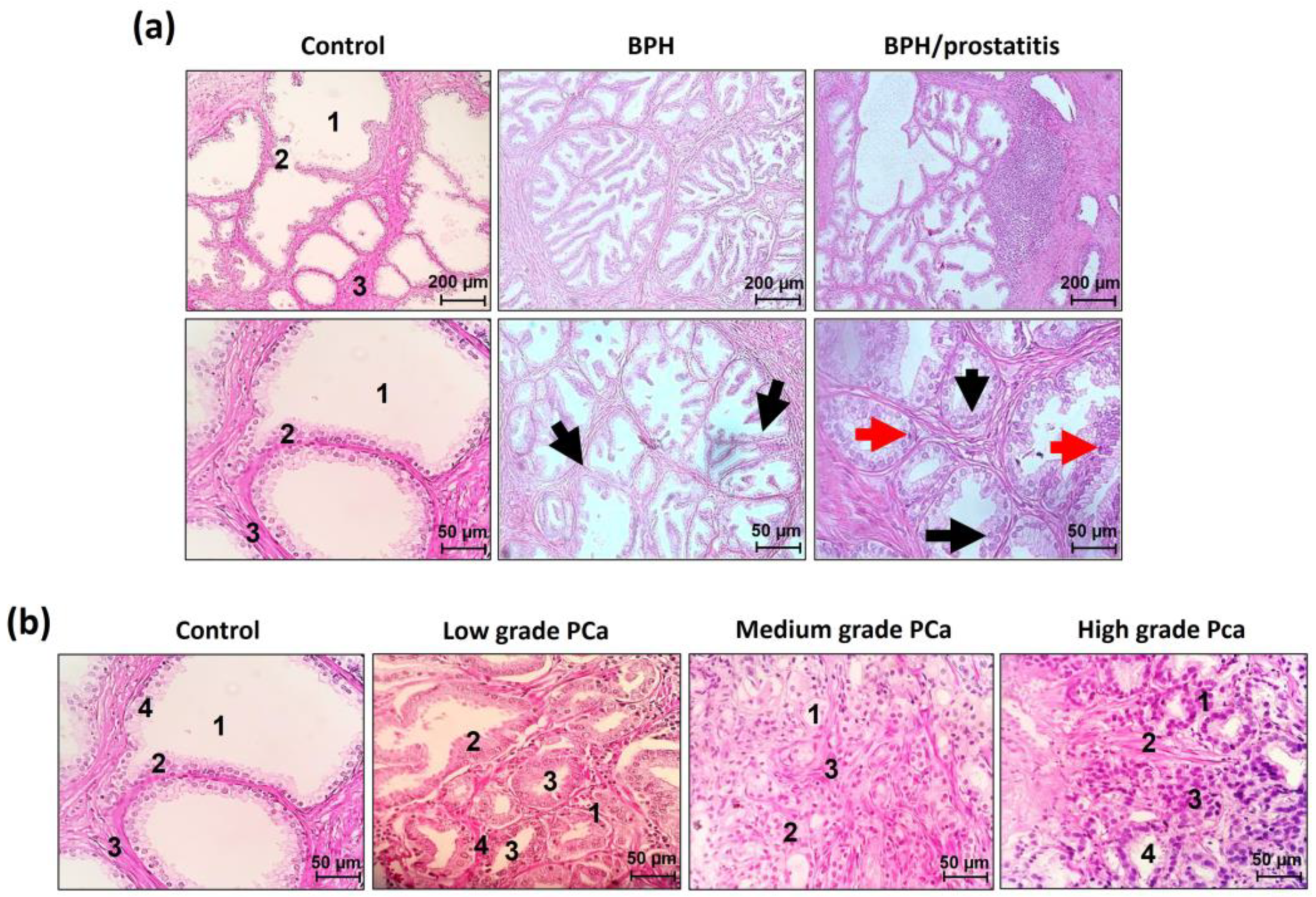
2.1. Histopathological Analysis of Pre-Malignant Lesions and Prostate Cancer
2.2. Histological Identification of Koilocytes and In Situ Molecular Detection of HPV Sequences
2.3. Multiplex Amplification
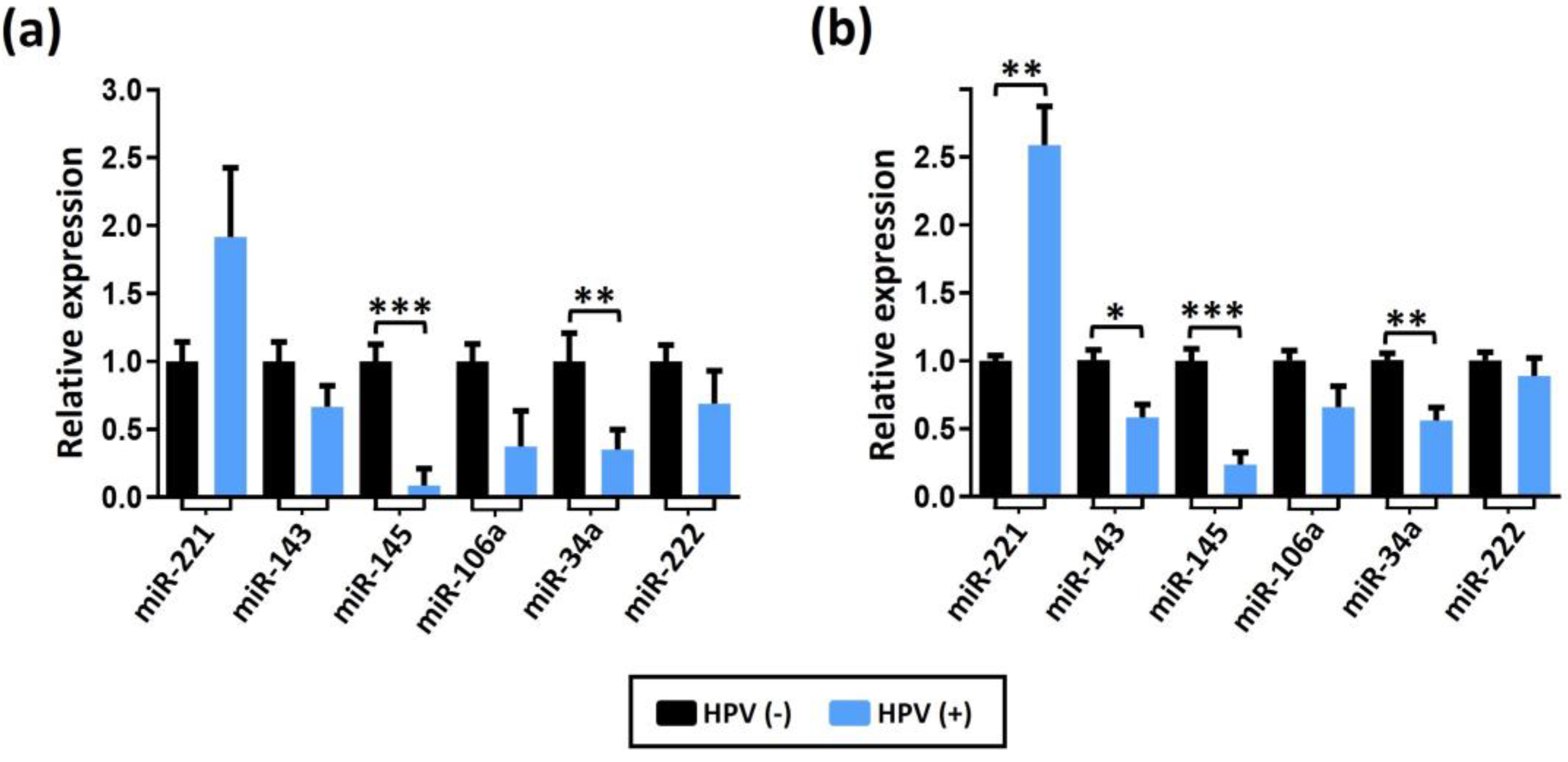
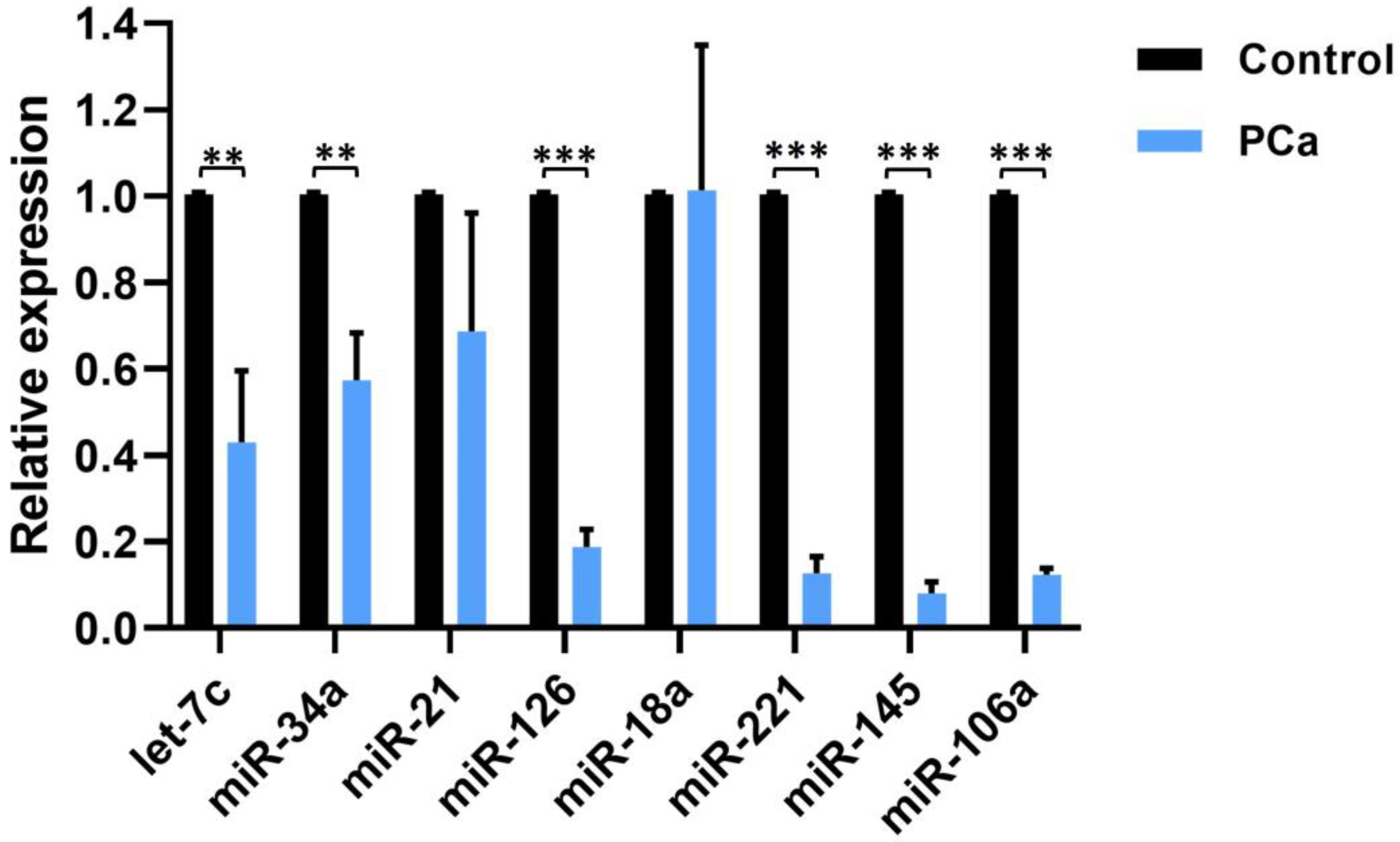
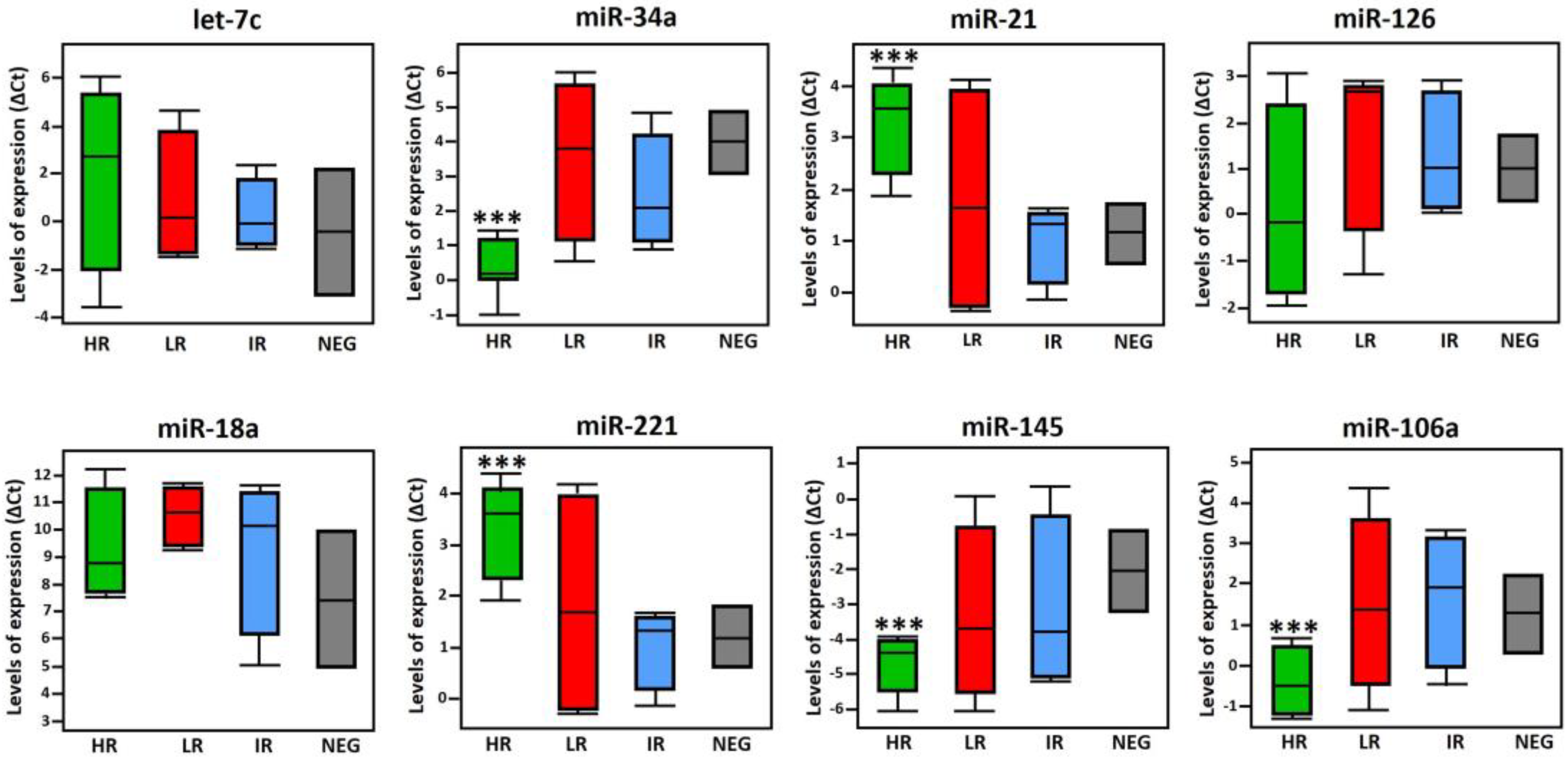
2.4. Expression Levels of miRNA in BPH and BPH/Prostatitis Samples
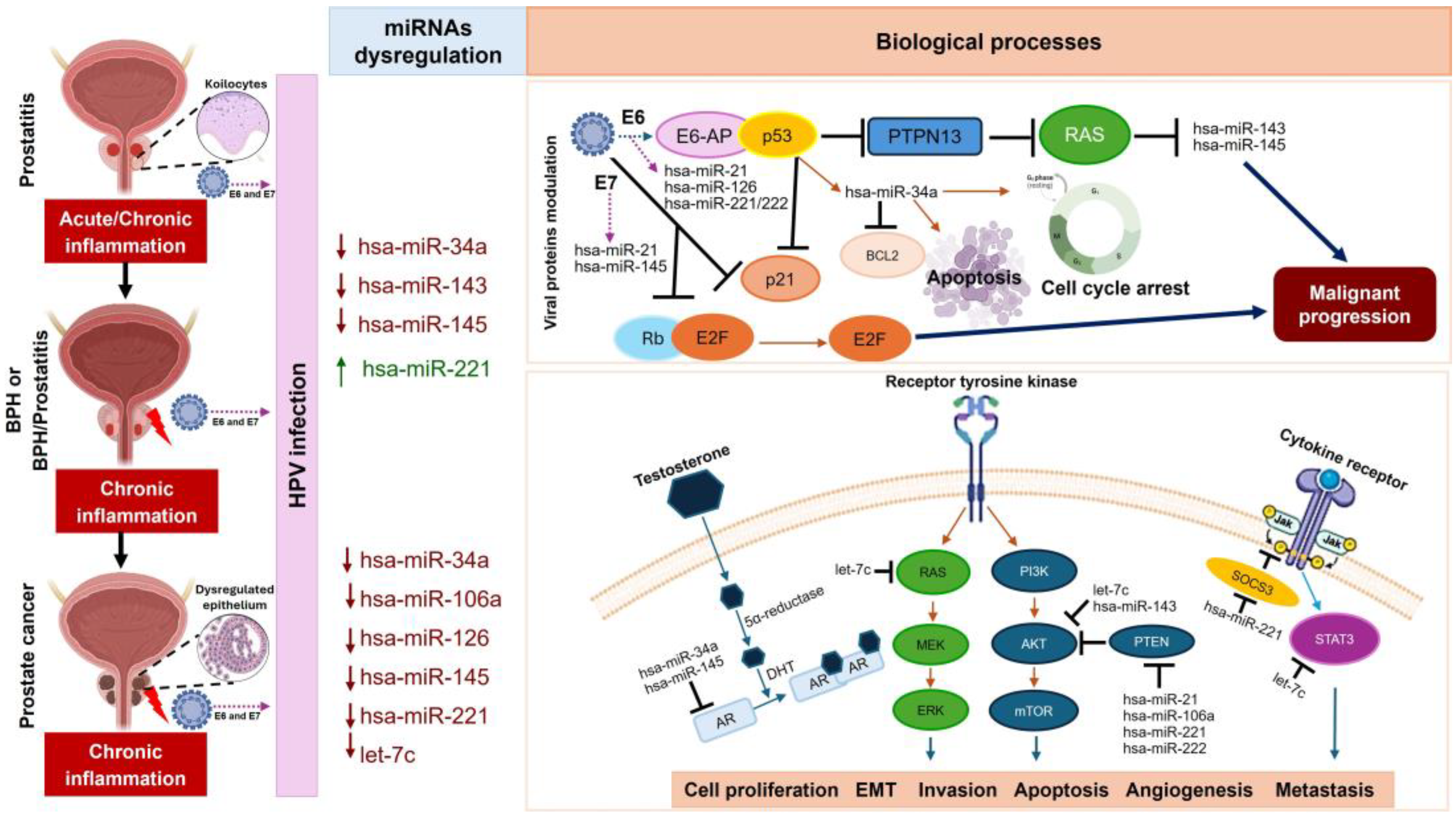
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Samples
4.2. Histopathological Analyses and DNA Extraction
4.3. HPV Detection by Multiplex PCR
4.4. In Situ PCR
4.5. Sequence Detection of In Situ PCR Products
4.6. Digital Analysis and Relative Semi-Quantification of In Situ Positive Signal
4.7. RT-qPCR for miRNAs
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, X.; Fang, X.; Ma, Y.; Xianyu, J. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and the Risk of Prostate Cancer and Bladder Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e3493. [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Sun, G.; Zhao, P.; Dai, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, J.; Tao, R.; Yang, J.; et al. MicroRNA-106a Suppresses Prostate Cancer Proliferation, Migration and Invasion by Targeting Tumor-Derived IL-8. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 3507–3517. [CrossRef]
- Shiau, M.-Y.; Fan, L.-C.; Yang, S.-C.; Tsao, C.-H.; Lee, H.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Lai, L.-C.; Chang, Y.-H. Human Papillomavirus Up-Regulates MMP-2 and MMP-9 Expression and Activity by Inducing Interleukin-8 in Lung Adenocarcinomas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54423. [CrossRef]
- Johann, D.J.; Shin, I.J.; Roberge, A.; Laun, S.; Peterson, E.A.; Liu, M.; Steliga, M.A.; Muesse, J.; Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Tangrea, M.A. Effect of Antigen Retrieval on Genomic DNA From Immunodissected Samples. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2022, 70, 643–658. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Z.; Gao, X.; Xing, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, W.; Song, N.; Zhang, W. Correlation between Prostatitis, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 177–189. [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.B. Epidemiology of Clinical Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Asian J. Urol. 2017, 4, 148–151. [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [CrossRef]
- Bergh, J.; Marklund, I.; Gustavsson, C.; Wiklund, F.; Grönberg, H.; Allard, A.; Alexeyev, O.; Elgh, F. No Link between Viral Findings in the Prostate and Subsequent Cancer Development. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 137–139. [CrossRef]
- Adami, H.-O.; Kuper, H.; Andersson, S.-O.; Bergström, R.; Dillner, J. Prostate Cancer Risk and Serologic Evidence of Human Papilloma Virus Infection: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2003, 12, 872–875.
- Effert, P.J.; Frye, R.A.; Neubauer, A.; Liu, E.T.; Walther, P.J. Human Papillomavirus Types 16 and 18 Are Not Involved in Human Prostate Carcinogenesis: Analysis of Archival Human Prostate Cancer Specimens by Differential Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Urol. 1992, 147, 192–196. [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Hussain, S.; Kakkar, N.; Singh, S.K.; Sobti, R.C.; Bharadwaj, M. Implication of High Risk Human Papillomavirus HR-HPV Infection in Prostate Cancer in Indian Population- A Pioneering Case-Control Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7822. [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.I.; Calogero, A.E.; Condorelli, R.A.; Scalia, G.; Morgia, G.; La Vignera, S. Human Papillomavirus and Risk of Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Aging Male 2020, 23, 132–138. [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and Cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [CrossRef]
- Oseni, S.O.; Naar, C.; Pavlović, M.; Asghar, W.; Hartmann, J.X.; Fields, G.B.; Esiobu, N.; Kumi-Diaka, J. The Molecular Basis and Clinical Consequences of Chronic Inflammation in Prostatic Diseases: Prostatitis, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, and Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 3110. [CrossRef]
- Naiyila, X.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhu, M.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, L.; Ai, J.; Wei, Q.; et al. A Novel Insight into the Immune-Related Interaction of Inflammatory Cytokines in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1821. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Chen, Y.; Singla, R.K.; Cao, D.; Shen, B. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and CXC Chemokines as Game-Changer in Age-Associated Prostate Cancer and Ovarian Cancer: Insights from Preclinical and Clinical Studies’ Outcomes. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 204, 107213. [CrossRef]
- Hatano, K.; Fujita, K.; Nonomura, N. Application of Anti-Inflammatory Agents in Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2680. [CrossRef]
- Coradduzza, D.; Solinas, T.; Balzano, F.; Culeddu, N.; Rossi, N.; Cruciani, S.; Azara, E.; Maioli, M.; Zinellu, A.; De Miglio, M.R.; et al. miRNAs as Molecular Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer. J. Mol. Diagn. 2022, 24, 1171–1180. [CrossRef]
- Smolarz, B.; Durczyński, A.; Romanowicz, H.; Szyłło, K.; Hogendorf, P. miRNAs in Cancer (Review of Literature). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2805. [CrossRef]
- Pekarek, L.; Torres-Carranza, D.; Fraile-Martinez, O.; García-Montero, C.; Pekarek, T.; Saez, M.A.; Rueda-Correa, F.; Pimentel-Martinez, C.; Guijarro, L.G.; Diaz-Pedrero, R.; et al. An Overview of the Role of MicroRNAs on Carcinogenesis: A Focus on Cell Cycle, Angiogenesis and Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7268. [CrossRef]
- Vanacore, D.; Boccellino, M.; Rossetti, S.; Cavaliere, C.; D’Aniello, C.; Di Franco, R.; Romano, F.J.; Montanari, M.; La Mantia, E.; Piscitelli, R.; et al. Micrornas in Prostate Cancer: An Overview. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 50240–50251. [CrossRef]
- Schitcu, V.H.; Raduly, L.; Nutu, A.; Zanoaga, O.; Ciocan, C.; Munteanu, V.C.; Cojocneanu, R.; Petrut, B.; Coman, I.; Braicu, C.; et al. MicroRNA Dysregulation in Prostate Cancer. Pharmacogenomics Pers. Med. 2022, 15, 177–193. [CrossRef]
- Abudoubari, S.; Bu, K.; Mei, Y.; Maimaitiyiming, A.; An, H.; Tao, N. Preliminary Study on miRNA in Prostate Cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 21, 270. [CrossRef]
- Tomaić, V. Functional Roles of E6 and E7 Oncoproteins in HPV-Induced Malignancies at Diverse Anatomical Sites. Cancers 2016, 8, 95. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-M.; Wang, X. Regulation of Cellular miRNA Expression by Human Papillomaviruses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA - Gene Regul. Mech. 2011, 1809, 668–677. [CrossRef]
- Yim, E.-K.; Park, J.-S. The Role of HPV E6 and E7 Oncoproteins in HPV-Associated Cervical Carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. Treat. 2005, 37, 319. [CrossRef]
- Chiantore, M.V.; Mangino, G.; Iuliano, M.; Zangrillo, M.S.; De Lillis, I.; Vaccari, G.; Accardi, R.; Tommasino, M.; Columba Cabezas, S.; Federico, M.; et al. Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7 Oncoproteins Affect the Expression of Cancer-Related microRNAs: Additional Evidence in HPV-Induced Tumorigenesis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 1751–1763. [CrossRef]
- Ali Syeda, Z.; Langden, S.S.S.; Munkhzul, C.; Lee, M.; Song, S.J. Regulatory Mechanism of MicroRNA Expression in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1723. [CrossRef]
- Boulet, G.; Horvath, C.; Broeck, D.V.; Sahebali, S.; Bogers, J. Human Papillomavirus: E6 and E7 Oncogenes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 2006–2011. [CrossRef]
- Swan, D.C.; Tucker, R.A.; Tortolero-Luna, G.; Mitchell, M.F.; Wideroff, L.; Unger, E.R.; Nisenbaum, R.A.; Reeves, W.C.; Icenogle, J.P. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) DNA Copy Number Is Dependent on Grade of Cervical Disease and HPV Type. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 1030–1034.
- Wu, Y.; Godoy, A.; Azzouni, F.; Wilton, J.H.; Ip, C.; Mohler, J.L. Prostate Cancer Cells Differ in Testosterone Accumulation, Dihydrotestosterone Conversion, and Androgen Receptor Signaling Response to Steroid 5α-Reductase Inhibitors. The Prostate 2013, 73, 1470–1482. [CrossRef]
- García Lozano, T.; García García, E.; González Monsalve, J.A.; Illueca Ballester, C.; Aznar Oroval, E.; San Juan Gadea, M.C.; Navarro Gallego, M.T.; Almenar Medina, S. Análisis de las coinfecciones mixtas por el virus del papiloma humano (VPH) de alto y bajo riesgo en lesiones de significado incierto. Clínica E Investig. En Ginecol. Obstet. 2015, 42, 18–24. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Ngezahayo, A.; Murua Escobar, H.; Nolte, I. Role of miRNA Let-7 and Its Major Targets in Prostate Cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, E.J.; Green, W.P.; Buckley, N.E.; McCarthy, H.O. Exploring the Potential of MicroRNA Let-7c as a Therapeutic for Prostate Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 927–937. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shen, N.; Wicha, M.S.; Luo, M. The Roles of the Let-7 Family of MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Cancer Stemness. Cells 2021, 10, 2415. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-T.; Zhang, G.-X.; Gao, S.-S. The Potential Diagnostic Accuracy of Let-7 Family for Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211033061. [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Meng, P.; Wang, T.; Qin, W.; Qin, W.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, A.; Wang, H. MicroRNA Let-7a Inhibits Proliferation of Human Prostate Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo by Targeting E2F2 and CCND2. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10147. [CrossRef]
- Alwhaibi, A.; Parvathagiri, V.; Verma, A.; Artham, S.; Adil, M.S.; Somanath, P.R. Regulation of Let-7a-5p and miR-199a-5p Expression by Akt1 Modulates Prostate Cancer Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via the Transforming Growth Factor-β Pathway. Cancers 2022, 14, 1625. [CrossRef]
- Khatami, A.; Nahand, J.S.; Kiani, S.J.; Khoshmirsafa, M.; Moghoofei, M.; Khanaliha, K.; Tavakoli, A.; Emtiazi, N.; Bokharaei-Salim, F. Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) and Prostate Cancer (PCa): The Potential Role of HPV Gene Expression and Selected Cellular MiRNAs in PCa Development. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 166, 105503. [CrossRef]
- Lajer, C.B.; Garnæs, E.; Friis-Hansen, L.; Norrild, B.; Therkildsen, M.H.; Glud, M.; Rossing, M.; Lajer, H.; Svane, D.; Skotte, L.; et al. The Role of miRNAs in Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)-Associated Cancers: Bridging between HPV-Related Head and Neck Cancer and Cervical Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1526–1534. [CrossRef]
- Bañuelos-Villegas, E.G.; Pérez-yPérez, M.F.; Alvarez-Salas, L.M. Cervical Cancer, Papillomavirus, and miRNA Dysfunction. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 758337. [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.L.; Davis, J.W.; Taylor, K.H.; Johnson, J.; Shi, Z.; Williams, R.; Atasoy, U.; Lewis, J.S.; Stack, M.S. Identification of a Human Papillomavirus–Associated Oncogenic miRNA Panel in Human Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Validated by Bioinformatics Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 679–692. [CrossRef]
- DUAN, K.; GE, Y.-C.; ZHANG, X.-P.; WU, S.-Y.; FENG, J.-S.; CHEN, S.-L.; ZHANG, L.; YUAN, Z.-H.; FU, C.-H. miR-34a Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Prostate Cancer by Downregulation of SIRT1 Expression. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 3223–3227. [CrossRef]
- Slabáková, E.; Culig, Z.; Remšík, J.; Souček, K. Correction Alternative Mechanisms of miR-34a Regulation in Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 783. [CrossRef]
- Slabáková, E.; Culig, Z.; Remšík, J.; Souček, K. Alternative Mechanisms of miR-34a Regulation in Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3100–e3100. [CrossRef]
- Li, W. (Jess); Liu, X.; Dougherty, E.M.; Tang, D.G. MicroRNA-34a, Prostate Cancer Stem Cells, and Therapeutic Development. Cancers 2022, 14, 4538. [CrossRef]
- Mekhail, S.M.; Yousef, P.G.; Jackinsky, S.W.; Pasic, M.; Yousef, G.M. miRNA in Prostate Cancer: New Prospects for Old Challenges. EJIFCC 2014, 25, 79–98.
- Li, B.; Guo, X.; Li, N.; Chen, Q.; Shen, J.; Huang, X.; Huang, G.; Wang, F. WNT1, a Target of miR-34a, Promotes Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma Proliferation and Invasion by Induction of an E-P Cadherin Switch via the WNT/β-Catenin Pathway. Cell. Oncol. Dordr. 2020, 43, 489–503. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Su, J.; Xue, S.-L.; Yang, H.; Ju, L.-L.; Ji, Y.; Wu, K.-H.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Hu, J.-F.; et al. HPV E6/P53 Mediated down-Regulation of miR-34a Inhibits Warburg Effect through Targeting LDHA in Cervical Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 312–320.
- Feng, Y.-H.; Tsao, C.-J. Emerging Role of microRNA-21 in Cancer. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 395–402. [CrossRef]
- Stafford, M.Y.C.; Willoughby, C.E.; Walsh, C.P.; McKenna, D.J. Prognostic Value of miR-21 for Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20211972. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, L. MicroRNA-126: A New and Promising Player in Lung Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 35. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Ye, S.; Wang, H.; Tan, W.; Tian, T.; Qiu, Y.; Luo, H. Down-Regulation of miR-126 Is Associated with Colorectal Cancer Cells Proliferation, Migration and Invasion by Targeting IRS-1 via the AKT and ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81203. [CrossRef]
- Jalil, A.T.; Abdulhadi, M.A.; Al-Ameer, L.R.; Abbas, H.A.; Merza, Muna.S.; Zabibah, R.S.; Fadhil, A.A. The Emerging Role of microRNA-126 as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Pathol. - Res. Pract. 2023, 248, 154631. [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Lu, J.; Fan, B.; Sun, L. MicroRNA-126-5p Inhibits the Migration of Breast Cancer Cells by Directly Targeting CNOT7. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 153303382097754. [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Gu, X. MicroRNA-221 Inhibits Human Papillomavirus 16 E1-E2 Mediated DNA Replication through Activating SOCS1/Type I IFN Signaling Pathway.
- Di Martino, M.T.; Arbitrio, M.; Caracciolo, D.; Cordua, A.; Cuomo, O.; Grillone, K.; Riillo, C.; Caridà, G.; Scionti, F.; Labanca, C.; et al. miR-221/222 as Biomarkers and Targets for Therapeutic Intervention on Cancer and Other Diseases: A Systematic Review. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 27, 1191–1224. [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Zhong, L.; Ye, X.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Yi, H. miR-221-3p and miR-222-3p Regulate the SOCS3/STAT3 Signaling Pathway to Downregulate the Expression of NIS and Reduce Radiosensitivity in Thyroid Cancer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 652. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Deng, J.J.; Gowda, P.S.; Rao, M.K.; Lin, C.-L.; Chen, C.L.; Huang, T.; Sun, L.-Z. Androgen Receptor and MicroRNA-21 Axis down-Regulates Transforming Growth Factor Beta Receptor II (TGFBR2) Expression in Prostate Cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4097–4106. [CrossRef]
- Kneitz, B.; Krebs, M.; Kalogirou, C.; Schubert, M.; Joniau, S.; Van Poppel, H.; Lerut, E.; Kneitz, S.; Scholz, C.J.; Ströbel, P.; et al. Survival in Patients with High-Risk Prostate Cancer Is Predicted by miR-221, Which Regulates Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Invasion of Prostate Cancer Cells by Inhibiting IRF2 and SOCS3. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2591–2603. [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.-Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, L.-B. MicroRNA-145: A Potent Tumour Suppressor That Regulates Multiple Cellular Pathways. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 1913–1926. [CrossRef]
- Hart, M.; Wach, S.; Nolte, E.; Szczyrba, J.; Menon, R.; Taubert, H.; Hartmann, A.; Stoehr, R.; Wieland, W.; Grässer, F.A.; et al. The Proto-oncogene ERG Is a Target of Micro RNA miR-145 in Prostate Cancer. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 2105–2116. [CrossRef]
- Tahamtan, A.; Teymoori-Rad, M.; Nakstad, B.; Salimi, V. Anti-Inflammatory MicroRNAs and Their Potential for Inflammatory Diseases Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1377. [CrossRef]
- Gunasekharan, V.; Laimins, L.A. Human Papillomaviruses Modulate MicroRNA 145 Expression To Directly Control Genome Amplification. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6037–6043. [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Sun, G.; Zhao, P.; Dai, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, J.; Tao, R.; Yang, J.; et al. MicroRNA-106a Suppresses Prostate Cancer Proliferation, Migration and Invasion by Targeting Tumor-Derived IL-8. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9. [CrossRef]
- Shiau, M.-Y.; Fan, L.-C.; Yang, S.-C.; Tsao, C.-H.; Lee, H.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Lai, L.-C.; Chang, Y.-H. Human Papillomavirus Up-Regulates MMP-2 and MMP-9 Expression and Activity by Inducing Interleukin-8 in Lung Adenocarcinomas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54423. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Mora, S.; Ocampo-López, J.; Gómez-García, M.D.C.; Pérez-Ishiwara, D.G. BFNB Enhances Hair Growth in C57BL/6 Mice through the Induction of EGF and FGF7 Factors and the PI3K-AKT-β-Catenin Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12110. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Cuazitl, A.; Gómez-García, M.D.C.; Pérez-Mora, S.; Rojas-López, M.; Delgado-Macuil, R.J.; Ocampo-López, J.; Vázquez-Zapién, G.J.; Mata-Miranda, M.M.; Pérez-Ishiwara, D.G. Polyphenolic Compounds Nanostructurated with Gold Nanoparticles Enhance Wound Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17138. [CrossRef]
- Johann, D.J.; Shin, I.J.; Roberge, A.; Laun, S.; Peterson, E.A.; Liu, M.; Steliga, M.A.; Muesse, J.; Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Tangrea, M.A. Effect of Antigen Retrieval on Genomic DNA From Immunodissected Samples. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2022, 70, 643–658. [CrossRef]
- Zandnia, F.; Doosti, A.; Mokhtari-Farsani, A.; Kardi, M.T.; Movafagh, A. Application of Multiplex PCR for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Human Papillomaviruses in Cervical Cancer. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 32, 444–447. [CrossRef]
- Williamson, A.; Rybicki, E.P. Detection of Genital Human Papillomaviruses by Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification with Degenerate Nested Primers. J. Med. Virol. 1991, 33, 165–171. [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.F.; Adamson, C.S.; Simmons-Arnold, L.; Cooper, K. Touchdown General Primer (GP5+/GP6+) PCR and Optimized Sample DNA Concentration Support the Sensitive Detection of Human Papillomavirus. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2005, 5, 10. [CrossRef]
- Ocadiz-Delgado, R.; Castañeda-Saucedo, E.; Indra, A.K.; Hernandez-Pando, R.; Flores-Guizar, P.; Cruz-Colin, J.L.; Recillas-Targa, F.; Perez-Ishiwara, G.; Covarrubias, L.; Gariglio, P. RXRα Deletion and E6E7 Oncogene Expression Are Sufficient to Induce Cervical Malignant Lesions in Vivo. Cancer Lett. 2012, 317, 226–236. [CrossRef]
- Kato, I. Simultaneous Detection and Typing of Genital Human papiHomavirus DNA Using the Polymerase Chain Reaction.
- Ocadiz-Delgado, R.; Lizcano-Meneses, S.; Trejo-Vazquez, J.; Conde-Perezprina, J.; Garrido-Palmas, F.; Alvarez-Rios, E.; García-Villa, E.; Ruiz, G.; Illades-Aguiar, B.; Leyva-Vázquez, M.A.; et al. Circulating miR-15b, miR-34a and miR-218 as Promising Novel Early Low-invasive Biomarkers of Cervical Carcinogenesis. APMIS 2021, 129, 70–79. [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [CrossRef]

| Histopathological diagnosis | Number of samples | |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy tissues (HPV-negative tissue biopsy) |
14 | |
| BPH | 13 | |
| BPH / Prostatitis | 37 | |
| PCa | 33 | |
| Gleason (8-10) (High degree of malignancy) |
21 | |
| Gleason (7) (Intermediate degree of malignancy) |
3 | |
| Gleason <6 (Low degree of malignancy) |
9 | |
| Type of injury | HPV positivity frequency (%) | Predominant HPV genotypes | Coinfection [1] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign lesions | 67.2 | 6, 11 | |
| Malignant lesions | 93.4 | 16, 18, 31,33, 52, 58 | |
| HPV genotypes in benign lesions group | |||
| BPH | LR: 62.5 | 6,11 | ND |
| IR: 25.0 | 52,58 | 6,11 | |
| HR: 12.5 | 16,18 | 6, 11, 33 | |
| BPH/Prostatitis | LR:74 | 6, 11 | ND |
| IR: 21.7 | 52,58 | 6,11 | |
| HR: 4.3 | 16, 18 | 6,11,33 | |
| HPV genotypes in PCa group | |||
| Low risk cancer | 29.7 | 6, 11 | |
| Intermediate risk cancer | 9.1 | 31, 33, 52, 58 | |
| High risk cancer | 61.2 | 16, 18 | |
| HPV genotypes depending on PCa Gleason stratification | |||
| Grade Gleason score < 6 |
LR-HPV: 55.5 | 6, 11 | 58, 52[1] |
| IR-HPV: 11.1 | 52 | 16 | |
| HR-HPV: 33.3 | 16 | ND | |
| Grade Gleason 7 |
LR-HPV: ND | ND | ND |
| IR-HPV: 66.67 | 31,58 | 16 | |
| HR-HPV: 33.33 | 18 | ND | |
| Grade Gleason 8 - 9 |
LR-HPV: 10.6 | 6, 11 | 31, 52 |
| IR-HPV: 47.3 | 33, 31, 52 | 18 | |
| HR-HPV: 42.10 | 16, 18 | 6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





