Submitted:
16 September 2024
Posted:
16 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
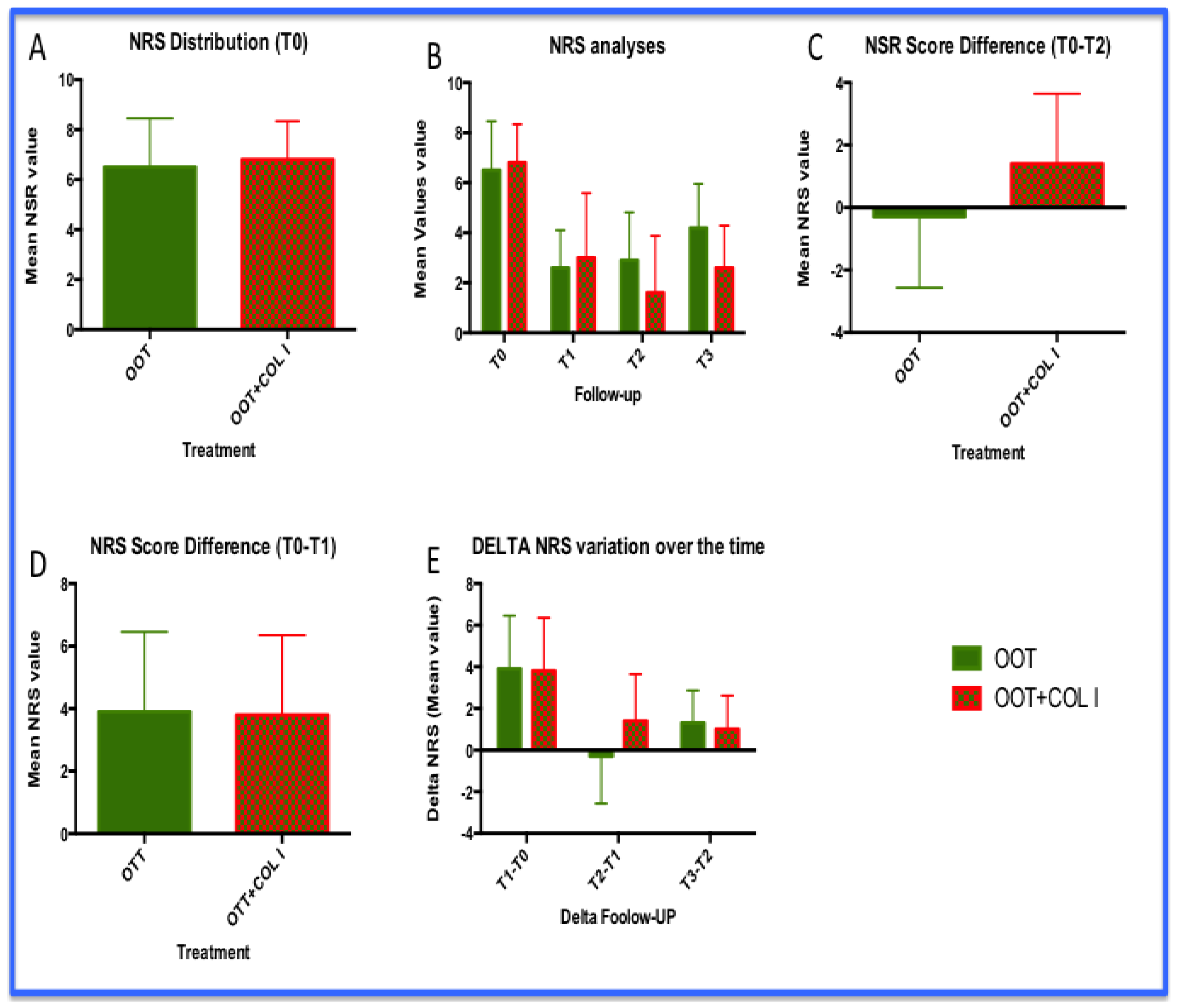
3.1. NRS Analysis
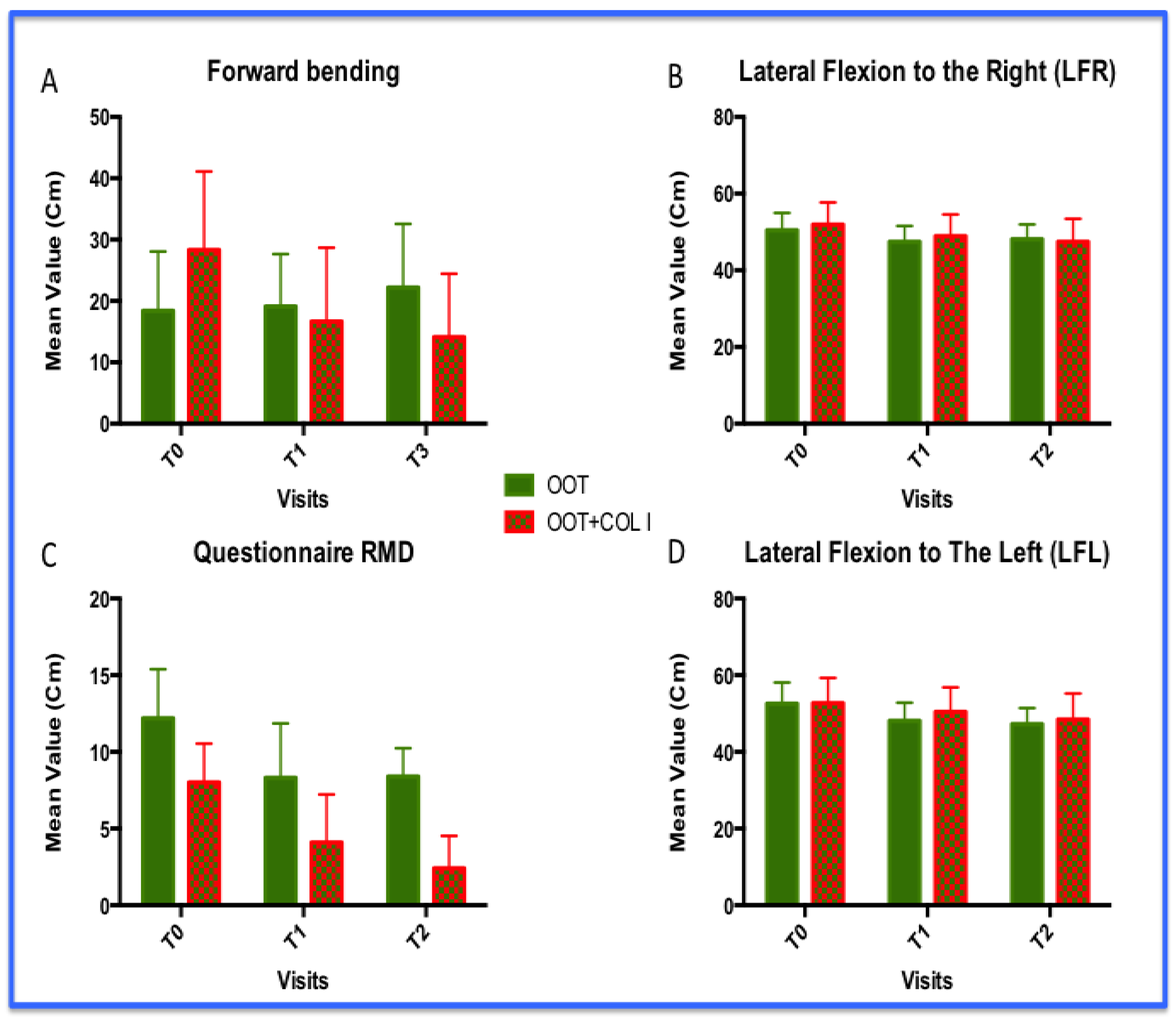
3.2. Functional Improvements: Forward Bending, Lateral Flexions (LF) and Level Disability (Roland and Morris Questionnaire)
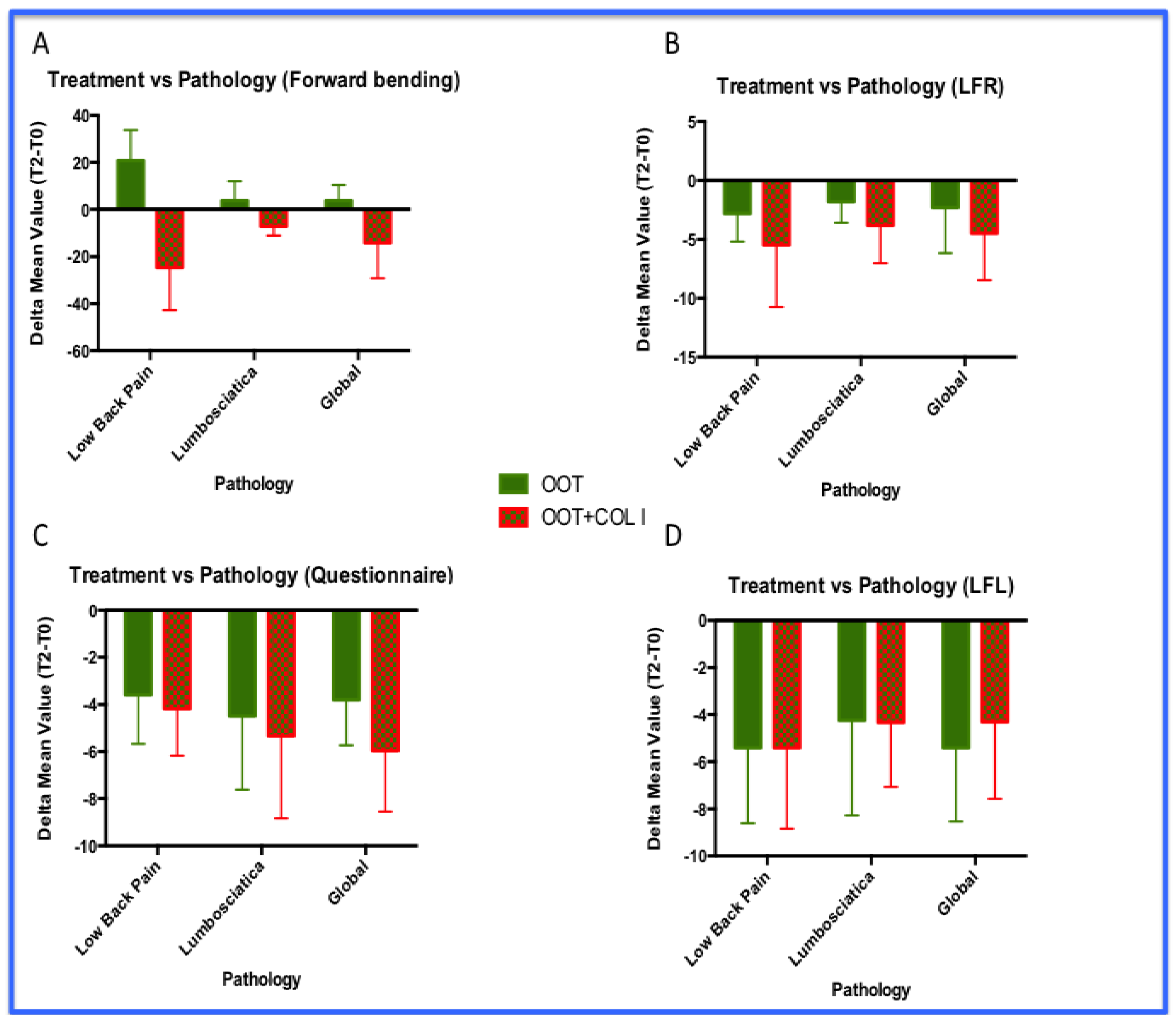
3.3. Functional Improvements: Analyses by Pathologies
- The OOT+COL I treatments increased forward flexion in patients with LBP compared to those with lumbosciatica. Furthemere, OOT+COL I treatment improved forward flexion in both pathologies (p<0.001).
- The OOT+COL I treatments improved better disability condition level in patients with lumbosciatica compared to those with LBP. Again, OOT+COL I treatment improved disability in both pathologies (p<0.01).
- No statistically significant differences were observed in lateral flexion analyses . However, the LFR results analyzed returned a probability value very close to significance (p=0.0606).
- So far, even in these analyses, non-inferiority levels have been achieved for both pathologies investigated. Indeed, in our personal impression the combined approach (OOT+COL I) acts as booster improving the clinical condition of both LBP and lumbosciatica patients.
4. Discussion
- (1)
- The self-diffusion capacity of the medical device (MD-LUMBAR) highlights the ability of collagen molecules to enrich the site of interest, where, the EUS-guided injection could be a non-mandatory approach, but remain still recommended.
- (2)
- The combined action of OOT+COL I maximises the effect of the therapy, as a booster, in patients affected by LBP and lumbosciatica.
- (3)
- At the same time, the regenerative properties of porcine collagen type 1 could lead to this treatment being included within the branch of regenerative medicine.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, T.; Linhares, D.; Ribeiro da Silva, M.; Neves, N. Ozone Therapy for Low Back Pain. A Systematic Review. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2018, 43, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, M.; Poorfarokh, M.; Mohajerani, S.A.; Jalili, P.; Akhyani, V.; Barikani, A.; Farivar, F. Injection of Intradiscal O2-O3 to Reduce Pain and Disability of Patients With Low Back Pain Due to Prolapsed Lumbar Disk. Anesthesiol. Pain Med. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoloni, M.; Di Sante, L.; Cacchio, A.; Apuzzo, D.; Marotta, S.; Razzano, M.; Franzini, M.; Santilli, V. Intramuscular Oxygen-Ozone Therapy in the Treatment of Acute Back Pain With Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Clinical Trial of Active and Simulated Lumbar Paravertebral Injection. Spine 2009, 34, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonetti, M.; Zambello, A.; Leonardi, M.; Princiotta, C. Herniated Disks Unchanged over Time: Size Reduced after Oxygen–Ozone Therapy. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2016, 22, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Sun, R.; Zhang, S.-D.; Wu, X.-T. Comparison of Thoracolumbar versus Non-Thoracolumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in Risk Factors, Vertebral Compression Degree and Pre-Hospital Back Pain. J. Orthop. Surg. 2023, 18, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gu, M.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Mao, S.; Zhou, W. Effects of Exercise Therapy on Disability, Mobility, and Quality of Life in the Elderly with Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Orthop. Surg. 2023, 18, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, D.; Grider, J.; Strand, N.; Hagedorn, J.M.; Falowski, S.; Lam, C.M.; Tieppo Francio, V.; Beall, D.P.; Tomycz, N.D.; Davanzo, J.R.; et al. The American Society of Pain and Neuroscience (ASPN) Evidence-Based Clinical Guideline of Interventional Treatments for Low Back Pain. J. Pain Res. 2022, 15, 3729–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derby, R.; Lee, S.-H.; Date, E.S.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, C.-H. Size and Aggregation of Corticosteroids Used for Epidural Injections. Pain Med. 2008, 9, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantele, F.; Tognolo, L.; Caneva, F.; Formaggio, E.; Copetti, V.; Venturin, A.; Caregnato, A.; Masiero, S. Influence of Pain-Related Psychological Factors on Therapeutic Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain after Oxygen-Ozone Treatment: A Case-Series. Eur. J. Transl. Myol. 2021, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazzo, A.; Corriero, A.S.; Confalonieri, N. Intramuscular Oxygen-Ozone Therapy in the Treatment of Low Back Pain. Acta Bio Medica Atenei Parm. 2018, 89, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sconza, C.; Leonardi, G.; Kon, E.; Respizzi, S.; Massazza, G.; Marcacci, M.; Di Matteo, B. Oxygen-Ozone Therapy for the Treatment of Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 6034–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, J.; Greiner-Perth, R.; Boehm, H.; Mahlfeld, K.; Grasshoff, H.; Allam, Y.; Awiszus, F. Comparison of a Minimally Invasive Procedure versus Standard Microscopic Discotomy: A Prospective Randomised Controlled Clinical Trial. Eur. Spine J. 2009, 18, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Deer, T.; Sayed, D.; Chopra, P.; Wahezi, S.; Jassal, N.; Weisbein, J.; Jameson, J.; Malinowski, M.; Golovac, S. Minimally Invasive Lumbar Decompression: A Review of Indications, Techniques, Efficacy and Safety. Pain Manag. 2020, 10, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, D.; Grider, J.; Strand, N.; Hagedorn, J.M.; Falowski, S.; Lam, C.M.; Tieppo Francio, V.; Beall, D.P.; Tomycz, N.D.; Davanzo, J.R.; et al. The American Society of Pain and Neuroscience (ASPN) Evidence-Based Clinical Guideline of Interventional Treatments for Low Back Pain. J. Pain Res. 2022, 15, 3729–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akeda, K.; Ohishi, K.; Masuda, K.; Bae, W.C.; Takegami, N.; Yamada, J.; Nakamura, T.; Sakakibara, T.; Kasai, Y.; Sudo, A. Intradiscal Injection of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Releasate to Treat Discogenic Low Back Pain: A Preliminary Clinical Trial. Asian Spine J. 2017, 11, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, D.; Horn, S.; Tyszko, S.; Levin, J.; Hecht-Leavitt, C.; Walko, E. Intradiscal Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection for Chronic Discogenic Low Back Pain: Preliminary Results from a Prospective Trial. Pain Med. 2015, pnv053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galica, R.J.; Hayek, S.M.; Veizi, E.; McEwan, M.T.; Katta, S.; Ali, O.; Aziz, N.; Sondhi, N. Intrathecal Trialing of Continuous Infusion Combination Therapy With Hydromorphone and Bupivacaine in Failed Back Surgery Patients. Neuromodulation Technol. Neural Interface 2018, 21, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrills, P.; Mitchell, B.; Vivian, D.; Sinclair, C. Peripheral Nerve Stimulation: A Treatment for Chronic Low Back Pain and Failed Back Surgery Syndrome? Neuromodulation Technol. Neural Interface 2009, 12, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreula, C.F.; Simonetti, L.; De Santis, F.; Agati, R.; Ricci, R.; Leonardi, M. Minimally Invasive Oxygen-Ozone Therapy for Lumbar Disk Herniation. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2003, 24, 996–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi-Movaghar, V.; Eslami, V. The Major Efficient Mechanisms of Ozone Therapy Are Obtained in Intradiscal Procedures. Pain Physician 2012, 15, E1007–E1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rome, Consensus Conference Italian Guidelines and Good Practices in Oxygen-Ozone Therapy 2024.
- Leo, B.M.; Walker, M.H.; Anderson, D.G. The Molecular Basis of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. In Progress in Neurological Surgery; Freese, A., Simeone, F.A., Leone, P., Janson, C., Eds.; KARGER: Basel, 2005; pp. 5–29. ISBN 978-3-8055-7784-7. [Google Scholar]
- García-Cosamalón, J.; Del Valle, M.E.; Calavia, M.G.; García-Suárez, O.; López-Muñiz, A.; Otero, J.; Vega, J.A. Intervertebral Disc, Sensory Nerves and Neurotrophins: Who Is Who in Discogenic Pain? J. Anat. 2010, 217, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langevin, H.M.; Fox, J.R.; Koptiuch, C.; Badger, G.J.; Greenan- Naumann, A.C.; Bouffard, N.A.; Konofagou, E.E.; Lee, W.-N.; Triano, J.J.; Henry, S.M. Reduced Thoracolumbar Fascia Shear Strain in Human Chronic Low Back Pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2011, 12, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, H.M.; Stevens-Tuttle, D.; Fox, J.R.; Badger, G.J.; Bouffard, N.A.; Krag, M.H.; Wu, J.; Henry, S.M. Ultrasound Evidence of Altered Lumbar Connective Tissue Structure in Human Subjects with Chronic Low Back Pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2009, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannus, P. Structure of the Tendon Connective Tissue. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2000, 10, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjær, M. Role of Extracellular Matrix in Adaptation of Tendon and Skeletal Muscle to Mechanical Loading. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 649–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, G.P.; Harrall, R.L.; Constant, C.R.; Chard, M.D.; Cawston, T.E.; Hazleman, B.L. Glycosaminoglycans of Human Rotator Cuff Tendons: Changes with Age and in Chronic Rotator Cuff Tendinitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1994, 53, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randelli, F.; Menon, A.; Giai Via, A.; Mazzoleni, M.; Sciancalepore, F.; Brioschi, M.; Gagliano, N. Effect of a Collagen-Based Compound on Morpho-Functional Properties of Cultured Human Tenocytes. Cells 2018, 7, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randelli, F.; Sartori, P.; Carlomagno, C.; Bedoni, M.; Menon, A.; Vezzoli, E.; Sommariva, M.; Gagliano, N. The Collagen-Based Medical Device MD-Tissue Acts as a Mechanical Scaffold Influencing Morpho-Functional Properties of Cultured Human Tenocytes. Cells 2020, 9, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godek, P. Collagen Therapy in Lumbar Spondylosis – a Pilot Study. Does the Route of Administration Matter? Ortop. Traumatol. Rehabil. 2019, 21, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelka, K.; Jarosova, H.; Milani, L.; Prochazka, Z.; Kostiuk, P.; Kotlarova, L.; Meroni, A.M.; Sliva, J. Efficacy and Tolerability of Injectable Collagen-Containing Products in Comparison to Trimecaine in Patients With Acute Lumbar Spine Pain (Study FUTURE-MD-Back Pain). Physiol. Res. 2019, S65–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, C.E. Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injections. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 29, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Tulder, M.; Koes, B.; Bombardier, C. Low Back Pain. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2002, 16, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Boxem, K.; Cheng, J.; Patijn, J.; Van Kleef, M.; Lataster, A.; Mekhail, N.; Van Zundert, J. 11. Lumbosacral Radicular Pain. Pain Pract. 2010, 10, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, L.T.; Rodrigues, C.F.D.S.; Andrade, R.R.D.; Barbosa, F.T. The Effectiveness of Percutaneous Injections of Ozonotherapy in Low Back Pain. Rev. Assoc. Médica Bras. 2020, 66, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavo, B.; Robaina, F.; Urrutia, G.; Bisshopp, S.; Ramallo, Y.; Szolna, A.; Caramés, M.A.; Fiuza, M.D.; Linertová, R. Ozone Therapy versus Surgery for Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2021, 59, 102724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elawamy, A.; Kamel, E.Z.; Hassanien, M.; Wahba, O.M.; Amin, S.E. Implication of Two Different Doses of Intradiscal Ozone-Oxygen Injection upon the Pain Alleviation in Patients with Low Back Pain: A Randomized, Single-Blind Study. Pain Physician 2018, 21, E25–E31. [Google Scholar]
- Davidovic, K.; Cotofana, S.; Heisinger, S.; Savic, S.; Alfertshofer, M.; Antonić, T.; Jovanović, S.; Ercegovac, M.; Muto, M.; Jeremić, D.; et al. Percutaneous Computed Tomography-Guided Oxygen-Ozone (O2O3) Injection Therapy in Patients with Lower Back Pain—An Interventional Two-Year Follow-Up Study of 321 Patients. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, D.C.; Ângelos, J.S.D.; Macena, G.M.J.D.; Magalhães, F.N.D.O.; Fonoff, E.T. Effects of Ozone on the Pain and Disability in Patients with Failed Back Surgery Syndrome. Rev. Assoc. Médica Bras. 2017, 63, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sire, A.; Agostini, F.; Lippi, L.; Mangone, M.; Marchese, S.; Cisari, C.; Bernetti, A.; Invernizzi, M. Oxygen–Ozone Therapy in the Rehabilitation Field:State of the Art on Mechanisms of Action, Safety andEffectiveness in Patients with Musculoskeletal Disorders. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sire, A.; Marotta, N.; Ferrillo, M.; Agostini, F.; Sconza, C.; Lippi, L.; Respizzi, S.; Giudice, A.; Invernizzi, M.; Ammendolia, A. Oxygen-Ozone Therapy for Reducing Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Serum Levels in Musculoskeletal and Temporomandibular Disorders: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stochkendahl, M.J.; Kjaer, P.; Hartvigsen, J.; Kongsted, A.; Aaboe, J.; Andersen, M.; Andersen, M.Ø.; Fournier, G.; Højgaard, B.; Jensen, M.B.; et al. National Clinical Guidelines for Non-Surgical Treatment of Patients with Recent Onset Low Back Pain or Lumbar Radiculopathy. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavo, B.; Martínez-Sánchez, G.; Rodríguez-Esparragón, F.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Galván, S.; Aguiar-Bujanda, D.; Díaz-Garrido, J.A.; Cañas, S.; Torres-Mata, L.B.; Fabelo, H.; et al. Modulation by Ozone Therapy of Oxidative Stress in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: The Background for a Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.-B.; Tang, W.-J.; Wang, K.; Zou, K.; Che, B. Expressions of IL-1α and MMP-9 in Degenerated Lumbar Disc Tissues and Their Clinical Significance. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 4007–4013. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
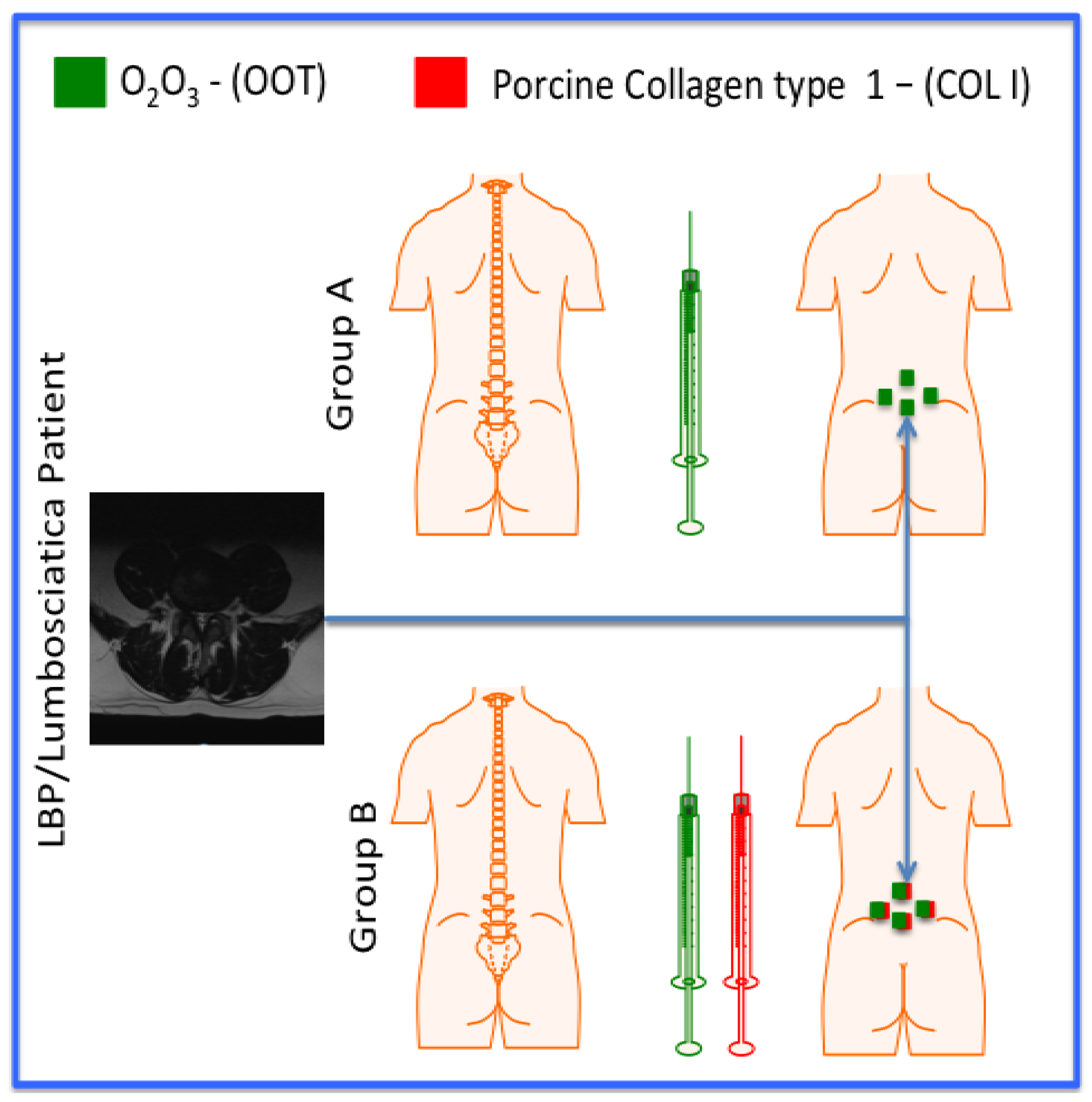
| Gruop | Treatment | Volume | Number of treatments |
|---|---|---|---|
| A (10; 5M and 5F) | O2O3 | 20 ml | 8 |
| B (10; 5M and 5F) | O2O3 + MD-LUMBAR | 20 ml + 2 ml | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




