Submitted:
16 September 2024
Posted:
17 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
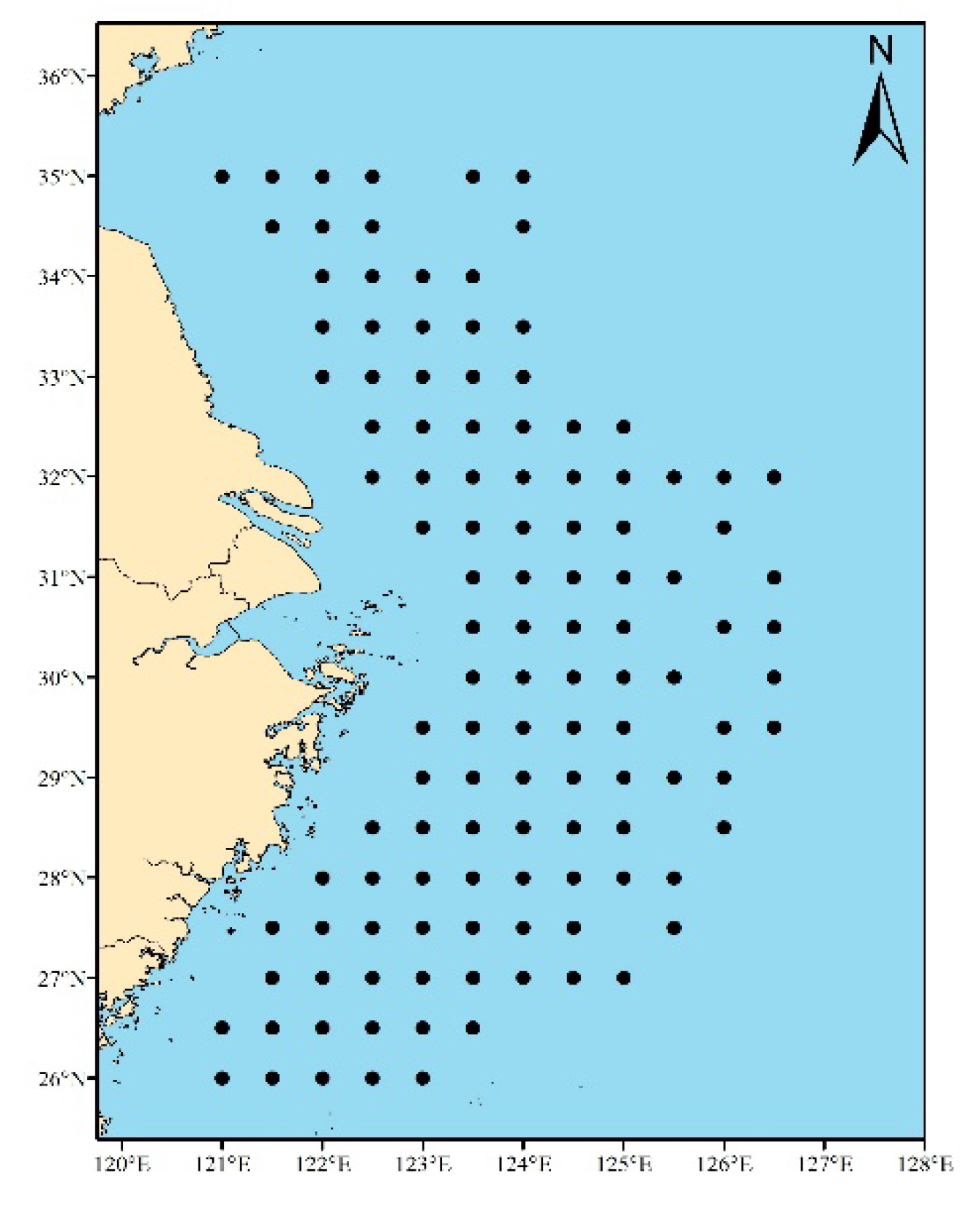
2.1. Data Sources
1.2. Model Construction
1.3. Factor Screening and Model Fitting
1.4. Evaluation of Model Prediction Ability
1.5. Mapping Habitat Distribution Prediction
2. Results and Analysis
2.1. Impact Factor Screening
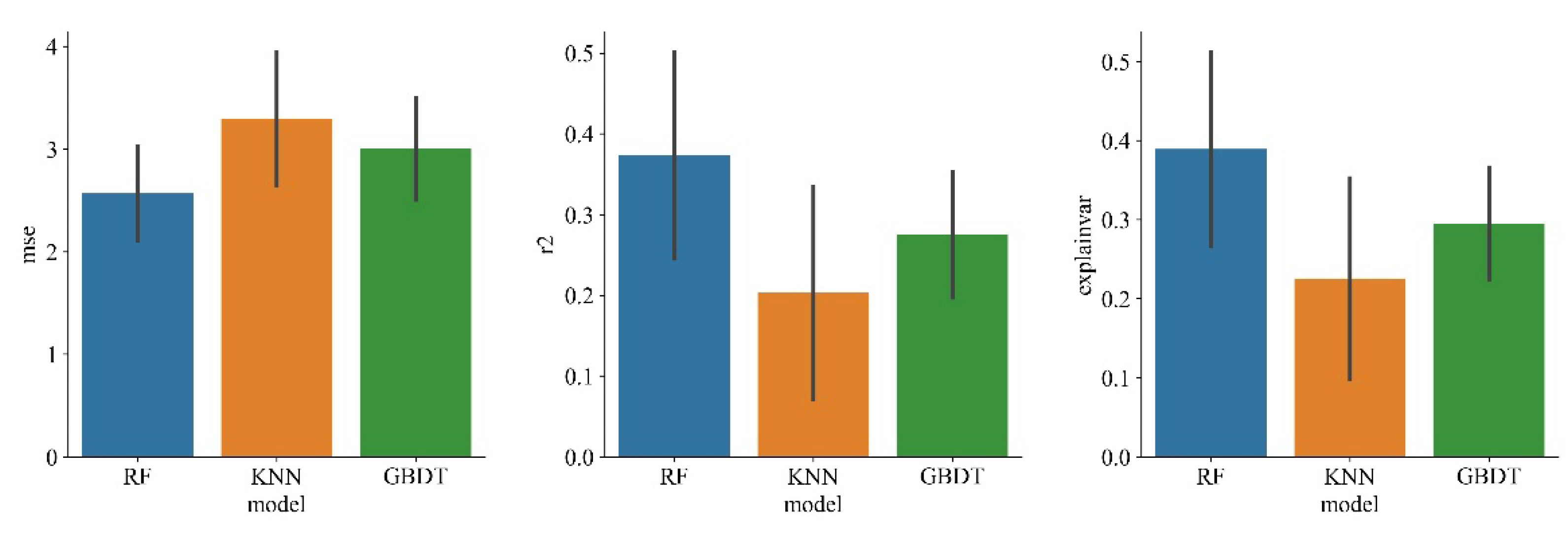
2.2. Model Performance Evaluation
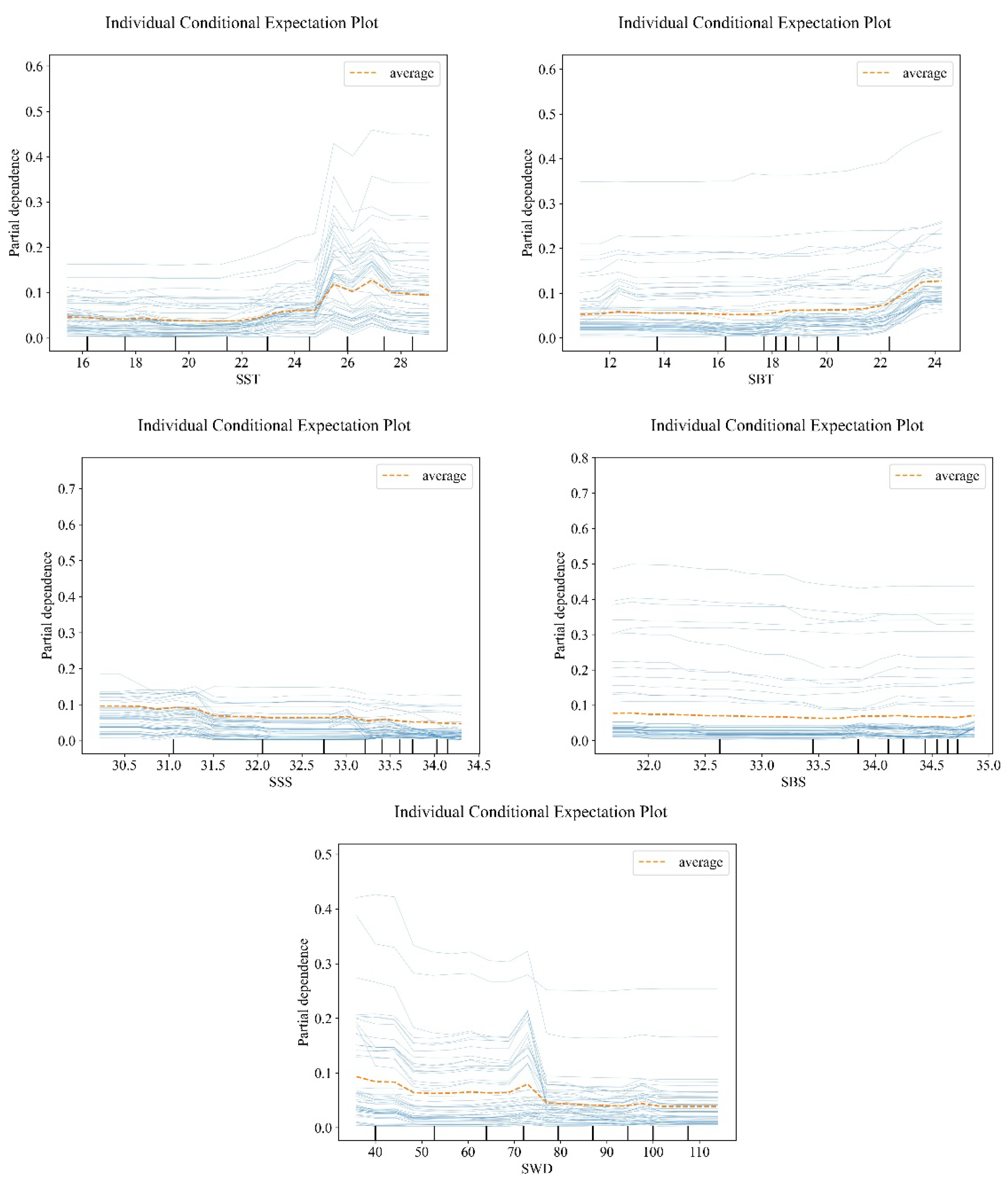
2.3. Importance Ranking of Impact Factors
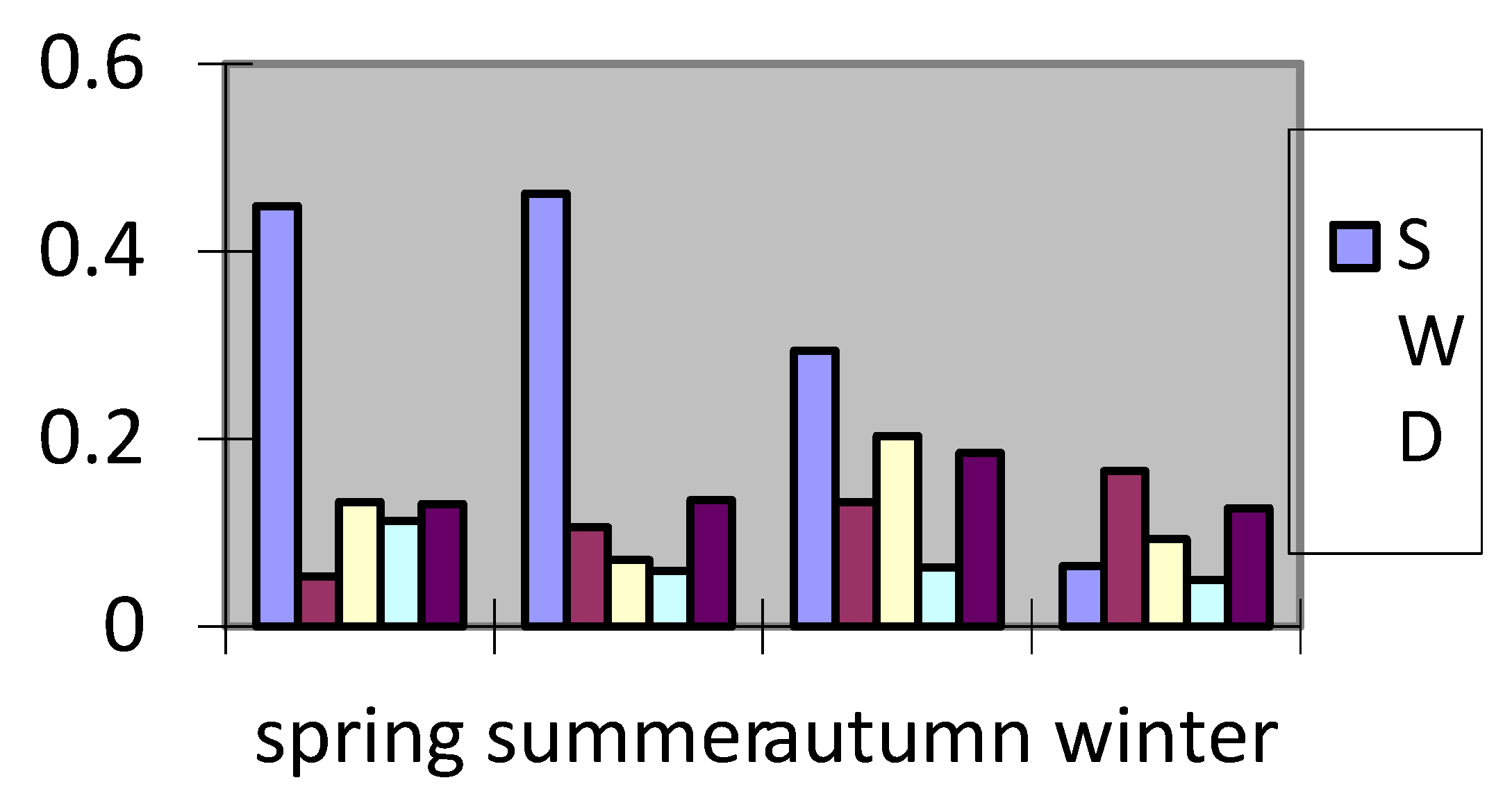
2.4. Relationship between Trichiurus japonicus Distribution and Explanatory Variables
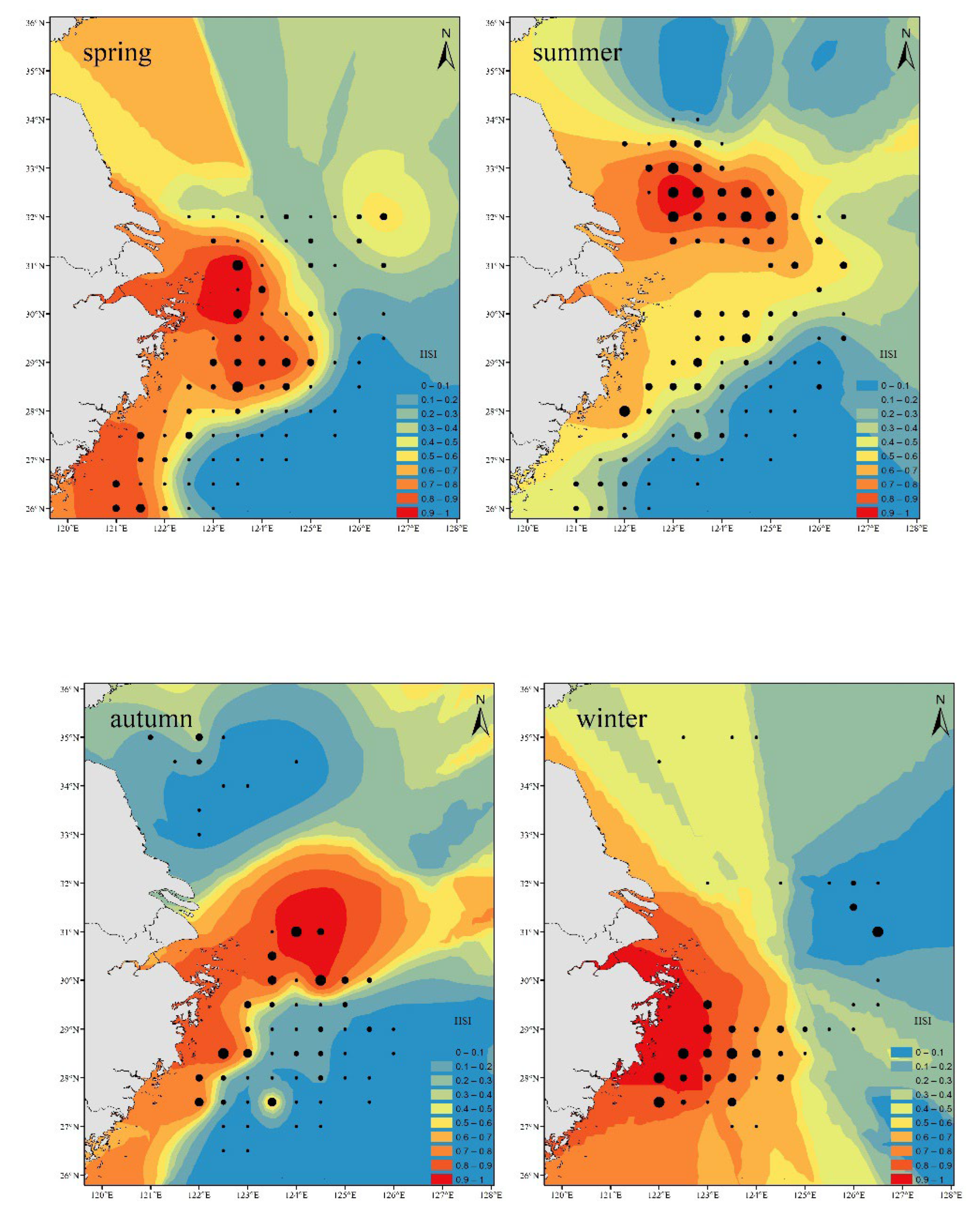
2.5. Prediction of Habitat Distribution of Trichiurus japonicus in Central and Southern East China Sea and Yellow Sea
3. Discussion
3.1. Model Analysis
3.2. The Influence of Environmental Factors on the Distribution of Trichiurus japonicus
3.3. Habitat Distribution Characteristics of Trichiurus japonicus
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang,Q.H.; Cheng, J.H.; Xu,H.X..Fishery Resources and Their Sustainable Utilization in The East China Sea. Shanghai:Fudan University Press. 2007,147-169.
- Cheng,J,H.; Yan,L.P.; Lin,L.S. Analyses on the fishery ecological effect of summer close season in the East China Sea region. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China. 1999, 4, 81-85.
- Luan,J.; Zhang;C.L.; Xu,B.D. Relationship between catch distribution of Portunid crab (Charybdis bimaculata)and environmental factors based on three species distribution models in Haizhou Bay.Journal of Fisheries of China. 2018, 42, 889-901.
- Jiang,Y.; Zhang,Y.L.; Pang,Z.W. Spatial distribution characteristics of sepia esculenta in haizhou bay and adjacent waters and their relationship with environmental factors. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica. 2024, 48, 617-624.
- Planque B, Loots C, Petitgas P, et al. Understanding what controls the spatial distribution of fish populations using a multi-model approach. Fisheries Oceanography. 2011, 20, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Chen,X.J. Fishery Resources and Fishery Oceanograghy. Beijing:China Ocean Press. 2014, 152-161.
- Guo,Y.L.; Zhao,Z.F.; Qiao,H.J. Challenges and development trend of species distribution model. Advances in EarthScience. 2020, 35, 1292−1305.
- Zhu,W,B.; Zhu,H.C.; Zhang,Y.Z. Quantitative distribution of juvenile Engraulis japonicus and the relationship with environmental factors along the Zhejiang coast. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China. 2021, 28, 1175-1183.
- Feng,B.; Chen,X.J.; Xu,L.X. Catch rate analysis of yellowfin tuna from longline fishery using generalized linear model in the Indian Ocean. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China. 2009, 16, 282-288.
- LI,Z.G.; WAN, R.; YE,Z.J. Use of random forests and support vector machines to improve annual egg production estimation. Fisheries Science. 2017, 83, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- HARALABOUS J; GEORGAKARAKOS S. Artificial neural networks as a tool for species identification of fish schools. ICES Journal of Marine Science. 1996, 53, 173-180. [CrossRef]
- Yang,S.L.; Zhang,Y.; Zhang,H. Comparison and analysis of different model algorithms for CPUE standardization in fishery. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering. 2015, 31, 259-264.
- Cui,Y.H.; Liu,S.D.; Zhang,Y.L. Habitat characteristics of Octopus ocellatus and their relationship with environmental factors during spring in Haizhou Bay, China.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology. 2022, 33, 1686-1692. [CrossRef]
- Xu,M.Z.; Zhang,C.L.; Xue,Y. Relationship between species diversity and environmental factors in the fishery community of Shandong coastal waters. Journal of Fisheries of China. 2022, 46, 1008-1017.
- Chen,X.Z.; Fan,W.; Cui,X.S. Fishing ground forecasting of Thunnus alalung in Indian Ocean based on random forest. Acta Oceanologica Sinica(in Chinese). 2013, 35, 158-164.
- Hou,J.; Zhou,W.F.; Fan,W. Research on fishing grounds forecasting models of albacore tuna based on ensemble learning in South Pacific. South China Fisheries Science. 2020, 16, 42-50.
- Gao,F. Fishing ground forecasting of chub mackerel in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea using boosted regression trees.Shanghai Ocean University. 2016.
- Song,L.M.; Ren,S.Y.; Zhang,M. Fishing ground forecasting of bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) in the tropical waters of Atlantic Ocean based on ensemble learning. Journal of Fisheries of China. 2023, 47, 64-76.
- General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. Specification for Marine survey-Part 6:Marine biological survey. Beijing: Standards Press of China. 2008.
- Breiman L. Random forests. Machine Learning. 2001, 45, 5-32.
- Fang,K.N.; Wu,J.B.; Zhu,J.P. A Review of Technologies on Random Forests. Statistics & Information Forum. 2011, 26, 32-38.
- Dong.S.S.; Huang,Z.X. A brief theoretical overview of Random Forests. Journal of integration technology. 2013, 2, 1-7.
- Zhang,D. Vehicle logo recognition based on Convolutional Neural Network and K-Nearest Neighbor. Xidian University. 2015.
- Li,X.; Zhang,C.L. Analysis of LocalLDtree classification model based on K proximity algorithm.Silicon Valley. 2013, 6, 33+146.
- Ming,Y.S. Using clustering to improve the KNN-based classifiers for online anomaly network traffic identification. Journal of network and computer applications. 2011, 34, 722-730.
- Malunoud,M.; Chokri,B.A. Classification improvement of local feature vectors over the KNN algorithm. Multimedia tools and applications. 2013, 64, 197-218.
- Jagan,S.; Hanan,S.; Amitabh,V. A fast all nearest neighbor algorithm for applications involving large point clouds. Computers & amp; graphics. 2007, 31, 157-174.
- Friedman,J.H. Greedy functionapproximation:A gradient boosting machine. Annals of Statistics. 2001, 29, 1189-1232.
- Gao,J.X.; Zhang,W.; Gao,M. Material calculation time prediction model based on gradient boosting decision trees. Software Guide. 2024,23, 15-20.
- Zhu,Y.L.; Feng,X.Y.; Yan,Q.G. Spatial distribution and main controlling factors of soil organic carbon under cultivated land based on GBDT model in black soil region of Northeast China. China Environmental Science. 2024, 44, 1407-1417. [CrossRef]
- Kabacoff,R. R in Action:Data Analysis and Graphics with R. Greenwich: Manning Publications. 2011, 8, 126-131.
- Hyndman,R.J.; Koehler,A.B. Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. International Journal of Forecasting. 2006, 22, 679-688. [CrossRef]
- Li,J.W.; Chen,C.H.; Sun,Y. Total partial regression sum of squares method for variable selection in multiple linear regression models. Journal of Mathematical Medicine. 2007, 126-127.
- Xu,B.D.; Zhang,C.L.; Xue,Y. Optimization of sampling effort for a fishery-independent survey with multiple goals. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. 2015, 187,252.
- Shim,J.S.; Kim,R.K.; Yoon,K.B. A basic research for the development of habitat suitability index model of Pelophylax chosenicus. Journal of the Korean Society of Environmental Restoration Technology. 2020, 23. 49 -62.
- Tian,S.Q.; Chen,X.J.; Chen,Y. Evaluating habitatsuitability indices derived from CPUE and fishing effortdata for Ommatrephes bratramii in the northwesternPacific Ocean. Fisheries Research. 2009, 95, 181-188.
- Gong,C.X.; Chen,X.J.; Gao,F. Review on habitat suitability index in fishery science. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University. 2011, 20, 260-269.
- Chen,F.; Li,N.; Fang,Z. Habitat distribution change pattern of Uroteuthis edulis during spring and summer in the coastal waters of Zhejiang Province. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University. 2021, 30, 847-855.
- Tanaka,K.; Chen,Y. Spatiotemporal variability of suitablehabitat for American lobster(Homarus americanus)Long Island Sound. Jpurnal of Shellfish Research. 2015. 34, 531-543.
- Zhang,M.; Wang,X.H.; Cai,Y.C. Spatial aggregation and dispersion characteristics of Trichiurus haumela in the Beibu Gulf, northern South China Sea. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China. 2022, 29, 1647-1658.
- Liu,X.Y. Study on the impacts of climate change on the potential suitable habitat of major commercial fish in offshore China. Zhejiang Ocean University. 2022.
- Liu,J.C.; Jia,M.X.; Feng,W.D. SpatialTemporal Distribution of Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba)Resource and lts Association with Environment FactorsRevealed with RF and GAM Models. Periodical of Ocean University of China(Natural science edition). 2021, 51, 20-29.
- Prchalova,M.; Kubecka,J.; Vašek,M. Distribution patterns of fishes in a canyon shaped reservoir. Journal of Fish Biology. 2008, 73:54-78. [CrossRef]
- Zou,Y.Y.; Xue,Y.; Ma,Q.Y. Spatial distribution of Larimichthys polyactis in Haizhou BayBased on Habitat Suitability Index. Periodical of Ocean University of China(Natural science edition). 2016, 46, 54-63.
- Wang,Y.Z.; Jia,X.P.; Lin,Z.J. Responses of Trichiurus japonicus catches to fishing and climate variability in the East China Sea. Journal of Fisheries of China. 2011, 35, 1881-1889.
- Wang,Y.Z.; Qiu,Y.S. An analysis of interannual variations of hairtail catches in East China Sea. South China Fisheries Science. 2006, 16-24.
- Yuan,X.W.; Liu,Z.L.; Jin,Y. Inter-decadal variation of spatial aggregation of Trichiurus japonicus in East China Sea based on spatial autocorrelation analysis. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology. 2017, 28, 3409-3416(in Chinese).
- You,H.B.; Xu,R. Relationship between central fishing ground and water temperature and salinity in summer season. Marine Fisheries. 1984, 165-167.
- Dai,L.B.; Chen,J.H.; Tian,S.Q. Prediction of fish species richness in the Yangtze River estuary using CART algorithm. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China. 2018, 25, 1082-1090. [CrossRef]
- Zhu,D.K.; Yu,C.G. The relation on the environment of fishing groundwith the occurrence of hairtail in winter offthe middle part of Zhejiang. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China. 1987, 195-203.
- Wang,T.Z.; Han,Q.; Luo,N.J. Catches of several major demersal fish species catches inhabiting Zhejiangsea area and their relationships with main influencing factors. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology. 2021, 43, 77-85.
- Azevedo,M.; Araújo,F.; Cruz-Filho,A.; Pessanha,A.; Silva,M.; Guedes,A. Demersal fishes in a tropical bay in southeastern Brazil:Partitioning the spatial, temporal and environmental components of ecological variation. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 75, 468-480.
- Hu,C.L.; Zhang,H.L.; Zhang,Y.Z. Fish community structure and its relationship with environmentalfactors in the Nature Reserve of Trichiurus japonicus. Journal of Fisheries of China. 2018, 42, 694-703.
- Zhang,Y.Q. Environmental impact on the fish assemblage structure s dissertation submitted to in Adjacent Sea area of the Yangtze River estuary.Graduate School of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. 2012.
- Yan,L.P.; Liu,Z.L.; Li,S.F. Effects of new summer close season of traw l fisheries onfishery ecology and resource enhanca ent in East China Sea. Marine Fisheries. 2010, 32, 186-191.
| Inspection method | Statistical parameters | RF | KNN | GBDT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model fitting | MSE | 0.348 | 2.120 | 2.445 |
| R2 | 0.919 | 0.506 | 0.431 | |
| Cross validation | SE | 2.566±1.734 | 3.295±2.161 | 3.004±1.264 |
| R2 | 0.373±0.563 | 0.203±0.385 | 0.275±0.255 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




