Submitted:
16 September 2024
Posted:
17 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Animals
2.2. Preparation of Brains for Immunohistochemistry
- Ketamine (10%, 1 ml/kg) and xylazine (2%, 0.5 mL/kg).
- Mini-peristaltic pump for intracardial perfusion of small animals.
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, 10X): 137 mM NaCl, 27 mM KCl, 14 mM Na2HPO4, and 43 mM KH2PO4. Bring total volume to 1 L with deionized water (see Note 1). Adjust pH to 7.4. Sterilize by autoclaving.
- 4% Paraformaldehyde (PFA) in PBS 1X, pH 7.4.
- Cryoprotective solution I (for brains after perfusion): 30% sucrose in PBS 1X.
- N-methylbutane.
- Laboratory dissection tools for brain preparation and extraction.
2.3. Preparation of Slices for IF-IHC
- Cryostat.
- 12-well plates (see Note 2).
- Optimal cutting temperature (OCT) compound to fix brains for cutting in the cryostat.
- Cryoprotective solution II (for slices after cutting): 25% ethylene glycol, 25% glycerol in PBS 1X pre-cooled to -20 °C.
2.4. Immunofluorescent Staining
- 24-well plates.
- Washing buffer: PBS 1X.
- Blocking/permeabilization buffer: PBS 1X, 0.5% Triton X-100 and 5% normal goat serum (NGS).
- Primary antibody buffer solution: PBS 1X, 0.5% Triton X-100 and 5% normal goat serum (see Note 3).
- 1.
- Secondary antibody solution: PBS 1X.
- 2.
-
Primary antibody
- rabbit monoclonal anti-GFAP antibody (1:200, Cell Signaling D1F4Q XP) to label the cytoskeletal structure of astrocytes.
- 3.
-
Secondary antibody
- b.
- goat-anti rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 (1:1000, Invitrogen).
- 4.
- Round-shaped glass plate to mount slices on slides.
- 5.
- Pre-cleaned microscope slides (Superfrost, e.g. Fisher Scientific).
- 6.
- Roti® Mount FluorCare DAPI.
- 7.
- Microscope cover glass (22 × 60 mm, e.g. Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA).
- 8.
- Pipettes, brushes, and other general laboratory equipment.
- 9.
- Horizontal shaker.
- 10.
- Confocal microscope (CLSM, Zeiss LSM 980).
- 11.
- ImageJ Software (http://www.imagescience.org).
3. Methods
3.1. Preparation of Brains for Immunofluorescent-Immunohistochemistry (IF-IHC)
- Following behavioral experiment (2), anaesthetize the animal by administering intraperitoneally (i.p.) a mixture of ketamine and xylazine (see Note 4).
- Transfer the animal on a perfusion tray, fix their four paws with tape or pin so that nothing moves during the procedure.
- From this step on, operate within a fume hood (see Note 5).
- With the help of forceps, hold the skin of the animals above the chest and with scissors open it by cutting a small hole below sternum. Carefully cut laterally just under the diaphragm. Then carefully cut the diaphragm along the entire length of the ribcage. Clamp the sternum with a pair of hemostats and lift it up to fully expose the chest cavity with heart and lung.
- Carefully tear off pericardial sac to enable to have a clear view of the heart.
- Take the apex of the heart with your thumb and fore finger or a good pair of tissue forceps. Insert the perfusion needle into left ventricle and hold it there with a pair of hemostats and make a small incision on the right atrium using fine scissors.
- Let the cold (4 °C) PBS 1X flow at a steady drip of 19ml/min (see Note 6) until the liver turns to a pale colour, which indicates a good flush of arteries/veins from blood with PBS 1X.
- Change the PBS 1X to cold PFA 4% and continue perfusing the animal for 3-4 minutes (see Note 7) until all paws and liver become whitish and blenched, respectively.
- Remove needle and clamps (hemostats) and decapitate the head with a pair of scissors.
- After decapitation, open the skull and remove the brain.
- Place each brain in a 50-ml falcon tube for post-fixation overnight (o.n.) in 4% PFA at 4 °C.
- After one day, transfer the brains to Cryoprotective solution I. Let the brains in this solution at 4 °C until they sink.
- After sinking of brains, wipe them from excess of liquid and flash-frozen N-methylbutane pre-cooled in dry ice before placing them in a piece of aluminium foil (or other foil) labelled with the number of the respective animal.
- Place brains at -20 °C or -80 °C until ready for cutting and staining (see Note 8).
3.2. Preparation of Free-Floating Sections for IF-IHC
- Take out brains from the freezer and allow them to equilibrate to the cutting temperature of the cryostat for about 20-30 minutes (see Note 9).
- Prepare a 12-well plate with about 2 ml of cryoprotective solution II at -20 °C per well.
- Prepare the brain holder of the cryostat with a thin layer of OCT compound and immerge the brain into it in a vertical position (olfactory bulbs towards you) (see Note 10), surround it at the base with additional OCT and keep it in this position until the OCT is completely frozen.
- Place the block in the correct position in the cryostat and start cutting at 30-40 µm (see Note 11)
- Collect the slices using a thin brush that has been previously dampened with a small drop of cryoprotective solution II to ease the peeling of the slice (see Note 12). Place the slice into the 12-well plate following the series for each brain region.
- Once the brain has been cut to the desired extent, remove it from the block and put it back into the foil for further cutting, if necessary.
- Put the plate at -20 °C until proceeding with the staining (see Note 13).
- Procedure for the double IF-IHC.
- Remove the plates from the freezer and, using a thin brush, select a series of LS region for staining from each brain.
- Transfer slices in a 24-well plate with about 1 ml of PBS 1X per well and let them wash on a horizontal shaker for 20 minutes at room temperature (RT). Discard the buffer and repeat this step other two times to allow a wash-through of the cryoprotective solution II (see Note 14).
- Remove the buffer and incubate slices in the blocking/permeabilization solution for 1 hour (hr) at RT.
- Remove the blocking solution and incubate slices in the antibody solution containing the primary antibody o.n. on a horizontal shaker at 4 °C (see Note 15).
- Remove the antibody solution and wash slices 3 times with PBS 1X for 20 minutes each, on a horizontal shaker at RT.
- Remove the antibody primary solution (see Note 16) and incubate slices the with secondary antibody solution for 2 hrs on a horizontal shaker at RT (in a closed box or covered with aluminium foil to keep the fluorescent dyes protected from light).
- To keep the fluorescent dyes protected from light, from this step on operate in a dimly lit condition.
- Remove the secondary antibody solution and wash slices for three times with PBS 1X for 20 minutes each at RT (keeping always the plate protected from light).
- Put slices from one series in a glass petri dish filled with PBS 1X and mount them on a slide with the help of a thin brush to gently drift them.
- Let slices to air-dry inside a closed box or under an aluminium foil.
- Put few drops of mounting medium containing DAPI on slides and cover them with a microscope cover glass (see Note 17).
- Keep sections in a refrigerator until microscopic analysis.
3.3. Confocal Microscopy
- Visualize and select the region of interest for image capture with a confocal laser scanning microscopeusing a 20x objective.
- Switch to a 63x oil-immerged objective and capture three z-sections per each brain, each 30 µm-thick, with a 0.5 µm/z section interval, and acquired at 1024 × 1024 resolution.
- Save files in the existing proprietary CZI file format (.czi) file format.
3.4. Morphological Analysis
- To analyze astrocyte morphology open the file using ImageJ Software with the FIJI update.
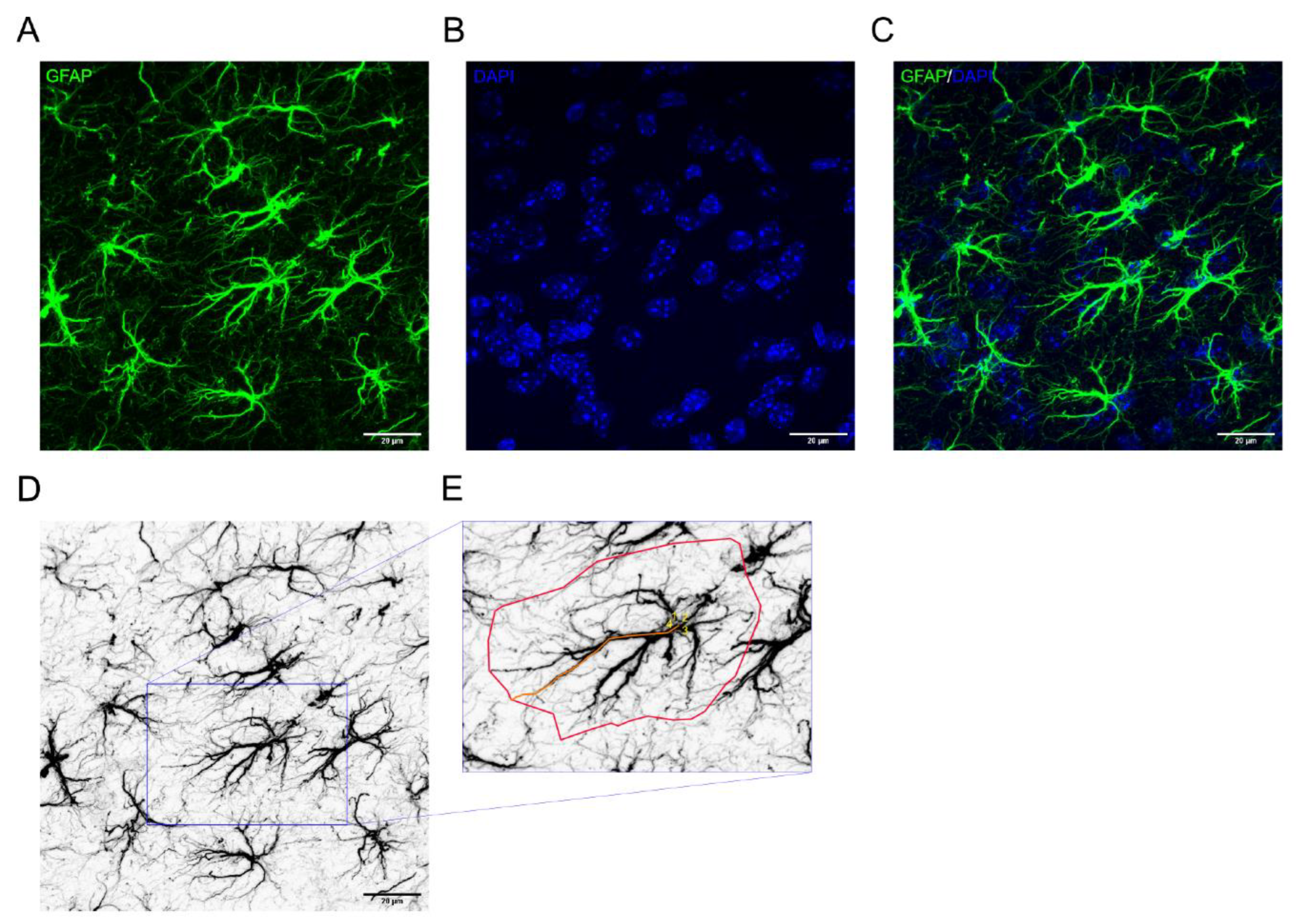
- Emphasize details within the stack, by “flattening” the 3D stack through Z-projection at maximum intensity.
- To facilitate visualization of the astrocyte soma, generate a merge channel with GFAP and DAPI, represented in green and blue, respectively.
- Within the picture frame, select astrocytes whose structure is fully captured. Analyze the number of primary processes, the length of the longest process, and the area covered by each astrocyte (see Note 18).
- To do this, first visualize the soma of the astrocyte, and count the number of primary processes. Then, use the segmented line tool to measure the length of one of the longest processes. Finally, measure the total area covered by each astrocyte using the polygon selection tool.
- The measurements of the length and the area coverage is expressed as arbitrary units (a.u.).
3.5. Statistical Analysis
- For each brain (animal) and parameter considered, calculate the average among the three pictures. Perform a normality test using Shapiro-Wilk test to ensure the data follows a normal distribution.
- If the data is normally distributed, use an unpaired t-Test of the two groups of interest. Use the Mann-Whitney test if the data is not normally distributed.
Notes
- All solutions are prepared in deionized water.
- Cutting in a three-series step-size is ideal for a complete representation of the lateral septum along the rostral-caudal axis.
- Ideally the serum used for the blocking or dilution should come from the same species in which the secondary antibody is raised. This ensures compatibility, reduces the risk of non-specific binding and improves the reliability of the IF-IHC assay.
- Allow a few minutes for the mouse to reach a surgical plane of anesthesia, then test for the loss of response by gently pinching the tail or toe.
- To minimize inhalation of formaldehyde vapor, operate always within fume a hood and wear a suitable protective equipment.
- In order to utilize the circulatory system effectively, the flow should be adjusted to the physiological pressure of the species.
- Efficient perfusion is crucial for obtaining high-quality tissue suitable for morphological analysis, with reduced background staining and improved clarity of the images. When brains are well perfused and fixed, they show a whitish color, without any evident blood vessels on the surface.
- If you intend to store the brains at -80 °C, it would be ideal to transfer them to -20 °C the day before slicing. This gradual thawing process ensures a smother slicing procedure.
- Based on our experience, we have found that for obtaining slices with a thickness of 30-40 µm, a cryostat temperature -20 °C is ideal for soft tissues such as the adult animal brain tissue.
- To guarantee uniform and accurate slicing, consider making a straight cut through the cerebellum and positioning the brain on the holder without any angle.
- To ensure the preservation of morphology as much as possible during sectioning, it is ideal to use a minimum of slice size of 30 µm. This allows for a greater possibility of analyzing extensive branching processes and structure within the same section.
- Ensure that the bristle of the brush are not damaged, as this could potentially harm the tissue quality.
- Since section will float above the solution and potentially become stuck at the walls of well, make sure they are fully immersed in the cryoprotective solution before placing them in the freezer.
- During the change of solutions, slices should never get dried. Additionally, handle the process gently, avoiding any pressure on the slices to prevent damage to the tissue.
- Once again, before placing the plate on the shaker, ensure the slices are fully immersed in the solution and that the agitation is not too strong.
- You may store the antibody primary solution at -20 °C for future use, typically for 1-2 additional times.
- Take care of avoid forming bubbles in the mounting medium, as they may interfere with imaging on the confocal microscope. If bubbles do form, gently remove them using a pipette tip pressed against the cover slip.
- For easier analysis, you might opt to keep the GFAP channel grayscale and invert the colors to depict the astrocyte cytoskeleton in black (see Figure 1 D, E).
Acknowledgments
References
- Menon, R.; Süß, T.; Oliveira, V.E.d.M.; et al. Neurobiology of the lateral septum: regulation of social behavior. Trends Neurosci 2022, 45, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, I.; Neumann, I.D.; Slattery, D.A. Social fear conditioning: a novel and specific animal model to study social anxiety disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzi-Wise, C.A.; Wang, D.V. Putting Together Pieces of the Lateral Septum: Multifaceted Functions and Its Neural Pathways. eNeuro 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirtshafter, H.S.; Wilson, M.A. Lateral septum as a nexus for mood, motivation, and movement. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2021, 126, 544–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.C.; Wang, L.; D'Amour, J.A.; et al. Effective Modulation of Male Aggression through Lateral Septum to Medial Hypothalamus Projection. Curr Biol 2016, 26, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, R.; Grund, T.; Zoicas, I.; et al. Oxytocin Signaling in the Lateral Septum Prevents Social Fear during Lactation. Curr Biol 2018, 28, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carus-Cadavieco, M.; Gorbati, M.; Ye, L.; et al. Gamma oscillations organize top-down signalling to hypothalamus and enable food seeking. Nature 2017, 542, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Nedergaard, M. Physiology of Astroglia. Physiol Rev 2018, 98, 239–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigetomi, E.; Koizumi, S. The role of astrocytes in behaviors related to emotion and motivation. Neurosci Res 2023, 187, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofuji, P.; Araque, A. Astrocytes and Behavior. Annu Rev Neurosci 2021, 44, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Nagai, J.; Khakh, B.S. Improved tools to study astrocytes. Nat Rev Neurosci 2020, 21, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Zuo, Y.-X.; Jiang, R.-T. Astrocyte morphology: Diversity, plasticity, and role in neurological diseases. CNS Neurosci Ther 2019, 25, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banasr, M.; Duman, R.S. Glial loss in the prefrontal cortex is sufficient to induce depressive-like behaviors. Biol Psychiatry 2008, 64, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkowska, G.; Hughes, J.; Stockmeier, C.A.; et al. Coverage of blood vessels by astrocytic endfeet is reduced in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2013, 73, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel-Hidalgo, J.J.; Baucom, C.; Dilley, G.; et al. Glial fibrillary acidic protein immunoreactivity in the prefrontal cortex distinguishes younger from older adults in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2000, 48, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




