1. Introduction
Block copolymers are considered as a special class of polymers in the large family of soft matter [
1], consisting of at least two fragments of different chemical nature of the polymer, joined together by a junction – type of covalent bond and can be easily synthetized by various polymerization techniques [
2,
3,
4,
5]. The advantage of the block copolymers resides in the coupling of two polymers and combining their divergent properties differing in a single structure. Block copolymers are widely used as self-assembling polymer materials that provide access to a variety of periodic nanoscale morphologies with feature sizes ranging from 5 to 50 nm [
6,
7].
Many works were devoted to block copolymers because of their self-assembly into 2- or 3-dimensional periodic nanostructures, such as spherical, cylindrical, lamellar, gyroid structures [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12], and the crucial interest of the control of their surface structure and uses in many areas of science and technology where surface properties play an important role due to their uniformity, spatial regularity at the nanometric scale [
13], and versatile nanoscale fabrication tool for semiconductor devices and other applications [
14,
15]. The block copolymers have received considerable attention due to their ability to microphase separate into various nanostructures when studied in bulk and/or thin films. The important contribution to their self-assembly results in the immiscibility between the different covalently connected segments and their application towards the fabrication of high-resolution patterns for nanolithography applications. Recent advances in directed self- assembly of block copolymers enable low defect density, extremely minimal dimensions, facile processability, etching selectivity, low-cost and ability to design various patterns [
16,
17]. The periodic ordered microphase separation structures at the molecular chain scale formed by block copolymers, are ideal materials for self-assembly of structured particles and for fabricating polymer particles with adjustable shapes, internal phase structures and surface characteristics [
18,
19].
The block copolymers, due to their high periodicity, feature and precise size, were used in many applications such as optoelectronics, photonics, sensors, field emission, catalysis, membranes, energy conversion, energy storage devices, photolithography, nanomedicine, and biomedical applications for the diagnosis and treatment of a variety of diseases [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34]. They also served as templates for the deposition of inorganic materials [
25]. The solvent-mediated infiltration of different oxidation state metal cations selectively inserted into self-assembled block copolymer nanopatterns formed from polystyrene-
b-poly(4-vinylpyridine) (PS-
b-P4VP) thin films. It was observed that the stability of the as-obtained metal-pyridine complex is highly influenced by the coordination chemistry of the metal ion and the P4VP group and this impacts the formation of metal oxide patterns [
26]. Shevate et al. [
35] used the PS-
b-P4VP copolymer to obtain isoporous block copolymer membranes by non-solvent induced phase separation and showed highly ordered surface layer, high flux and superior separation properties and a strong flux dependence of pH; pores closed at low pH and opened at high pH. A unique perforated lamellar (PL) morphology was observed by Singh et al. [
36] in a mixture of an asymmetric PS-
b-P4VP block copolymer and CdSe–CdS quantum dots (QDs). The PL morphology formed by the PS-
b-P4VP/CdSe–CdS composites consisted of alternating layers of PS and P4VP, where the layer formed by the minority PS block contained cylindrical perforations of the majority P4VP block. The thermal and rheological properties of PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymers were studied by Xue et al. [
37] and Schultze et al [
38] in order to get information about the optimum foaming temperature. PS-b-P4VP was also to identify the constructional details of the polymer thin film morphology [
39].
The important and interesting uses and applications of PS-b-P4VP copolymer, particularly in the field of nanotechnology, nanolithography, nanodevices, and materials science, imply the necessity of the determination of the surface physicochemical properties of PS-b-P4VP copolymer. Because of the important lack in this domain, this research work was devoted to an accurate evaluation of the surface thermodynamic properties of this copolymer, such as the London dispersive surface energy, the free dispersive and polar interaction energy, the Lewis’s acid-base parameters, and the transition temperatures of PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer as a function of the temperature. To do that, the inverse gas chromatography (IGC) technique at infinite dilution [
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52] was used by applying our new methodology based on the thermal hamieh model and the London dispersion interaction that were proved to give more accurate surface parameters of solid surfaces [
53,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Solvents and Materials
All chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Beirut, Lebanon): the non-polar organic solvents such as
n-Hexane,
n-heptane,
n-octane, benzene, and the polar molecules, such as dichloromethane, chloroform, and carbon tetrachloride (Lewis’s acid solvents); ethyl acetate, acetone, and tetrahydrofuran (Lewis’s base solvents); and ethanol and acetonitrile (amphoteric solvents). The polystyrene-
b-poly(4-vinylpyridine) was previously synthetized [
64] through atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) with a number average molecular weight equal to Mn = 41,000 g mol
−1 were from molecular weights of PS and P4VP blocks respectively equal to Mn = 41,000 and 5200 g mol
−1.
2.2. Inverse Gas Chromatography
The net retention time of organic solvents adsorbed on polystyrene-b-poly(4-vinylpyridine) copolymer was determined at different temperatures using inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution with the help of a Focus GC gas chromatograph equipped with a flame ionization detector of high sensitivity (Sigma-Aldrich, France). A mass of 1 g of PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer was packed into a stainless-steel column of length 30 cm and 2 mm internal diameter. Helium was used as carrier gas with a flow rate equal to 25 mL/min. The retention times of the different injected organic solvents, measured at infinite dilution, led to the interactions between the organic molecules and the polymer, supposing that there is no interaction between the probe molecules themselves. The column temperatures varied from 30 to 200 °C. Average retention times and volumes were determined by repeating three times each solvent injection with a standard deviation less than 1% in all chromatographic measurements.
2.3. Thermodynamic Methods
2.3.1. Fundamental Equation of IGC
The fundamental equation of the inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution can be written as follows:
where
is the free energy of adsorption of organic solvents on the solid materials,
the net retention volume,
the absolute temperature,
the perfect constant gas, and
a constant depending on the temperature and the interaction solvents-sorbent.
The IGC experiments allow obtaining the values of of the adsorbed probes at different temperatures and consequently the free energy of interaction.
When non-polar solvents such as n-alkanes are adsorbed on the copolymer,
is only equal to the London dispersive energy
at any temperature, and one writes:
However, by using polar solvents, Equation 3 can be therefore written:
with
the free polar energy of the polar probes.
2.3.2. London Dispersive Surface Energy of Solid Surfaces
In a first attempt, Dorris-Gray [
65] determined the London dispersive component
of the surface energy of the solid material using the Fowkes’s relation [
66]. The obtained relation giving
is the following:
Where
and
are two consecutive n-alkanes,
, the surface area of methylene group with
, independent from the temperature, and the surface energy
of methylene group was given by:
A second method using the same Fowkes concept was proposed in literature [
44] and also led to
of solid surfaces (Equation 6):
Where
is the surface area of an adsorbed molecule (previously supposed constant),
the Avogadro number and
a constant only depending on the temperature and the solid substrate.
A first criticism was addressed to the above methods by hamieh et al. [
50] that proved that the London dispersive surface energy of the solvents
depended on the temperature and proposed several molecular models allowing the determination of the surface areas of molecules and then the surface area of methylene group for each model. The following models were used: geometric model based on the real form of molecules, cylindrical model based on cylindrical form of molecules, spherical model based on spherical form of molecules. Kiselev results, the two-dimensional Van der Waals (VDW) equation, and the two-dimensional Redlich-Kwong (R-K) equation [
50].
The second serious criticism was formulated by the Hamieh thermal model proving in recent works that the surface area of organic solvents strongly depends on the temperature [
53,
54,
55,
56,
59,
60], and this thermal influence effectively modifies the different values of the surface parameters of solid substrates such as
,
and the Lewis acid-base surface energies and variables. New equation giving the variation of the surface area
of polar and non-polar molecules were proposed against the temperature, as well as the expression of surface area of methylene group
[
53,
54,
55,
56,
59,
60]. The linear relations of
of the various were also given.
The surface energetic parameters of PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer were determined using our new thermal model taking into account the variations of and of the probes versus the temperature.
2.3.3. London Dispersive and Polar Free Energies of Adsorption
Several chromatographic methods were used in the literature to determine the London dispersive and polar free energies of solids [
41,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50]. The various methods were based on the use of several reference thermodynamic parameters such as the boiling point
of the solvents [
41], the vapor pressure
of the probes at a fixed temperature [
45,
46]
the dispersive component
of the surface energy of the solvent [
44], the deformation polarizability
[
47], the topological index
of the solvents [
48,
49].
It was proved that these various methods cannot be considered as accurate quantitative methods that allow an accurate separation between the dispersive and polar free energies of adsorption and the only method theoretically well-founded was that based on the deformation polarizability. However, this method was not well-applied, because the authors did some approximations that led to wrong values of the polar contribution of the free energy of interaction between the solvents and the solid materials.
To better determine the two dispersive and polar of the free energies of solvents adsorbed on the PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer, our new methodology [
53,
54,
55,
56,
59,
60] based on the London dispersion interaction energy was applied (Equation 7):
Where is the dielectric constant of vacuum, and the respective deformation polarizabilities of the solid material denoted by S and the organic solvent denoted by X, separated by a distance , and and their corresponding ionization energies.
By combining Equations 1, 3, and 7, one obtained the following relation:
A new chromatographic interaction parameter
was chosen:
In the case of non-polar molecules such as n-alkanes, the variations of
of the solvents were obtained from Equation 10:
where
is the slope of the non-polar straight line which is function of the separation distance between solid surface and organic molecules.
The free polar energy
of polar molecules adsorbed on the diblock copolymer were then obtained as a function of the temperature using Equation 11:
2.3.4. Lewis’s Acid-Base Parameters of PS-b-P4VP Diblock Copolymer
The experimental determination of
was used to obtain the values of polar enthalpy
and entropy
of polar probes adsorbed on the PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer. The relation 12 was used when the linearity of
is satisfied.
However, in many cases of the interaction between polymers and organic solvents, the linearity was not insured. The values of
and
were then determined from the following thermodynamic equations:
The classic relations 14 were used to determine the variations of the Lewis’s acid-base parameters of PS-
b-P4VP copolymer as a function of the temperature. Their enthalpic (
KA,
KD) and entropic (
,
) acid-base parameters were therefore determined:
where
and
are, respectively, the corrected electron donor and acceptor numbers of the polar molecule [
67,
68].
2.3.4. Lewis’s Acid-Base Surface Energies of PS-b-P4VP Copolymer
The application of the Hamieh thermal model led to the London dispersive surface energy
of PS-
b-P4VP copolymer against the temperature. However, the total surface energy
of a solid surface is given by:
where
represents the polar (or acid-base) contribution of the surface energy.
The determination of
was obtained using Van Oss et al.’s method [
69], it was possible to determine
of PS-
b-P4VP copolymer. The polar surface energy of the copolymer is given by:
where
and
are respectively the Lewis acid and base surface energies of the solid material.
Van Oss et al. [
69] used two solvents such as ethyl acetate (base
B) and dichloromethane (acid
A), characterized by the following parameters:
Knowing that the polar free energy
of the polar solvents are given by:
therefore, the Lewis acid and base surface energies of the copolymer can be obtained from Equations 18:
Equations 18, 15, and 14 led to the values of the polar and total surface energies of the copolymer.
3. Experimental Results
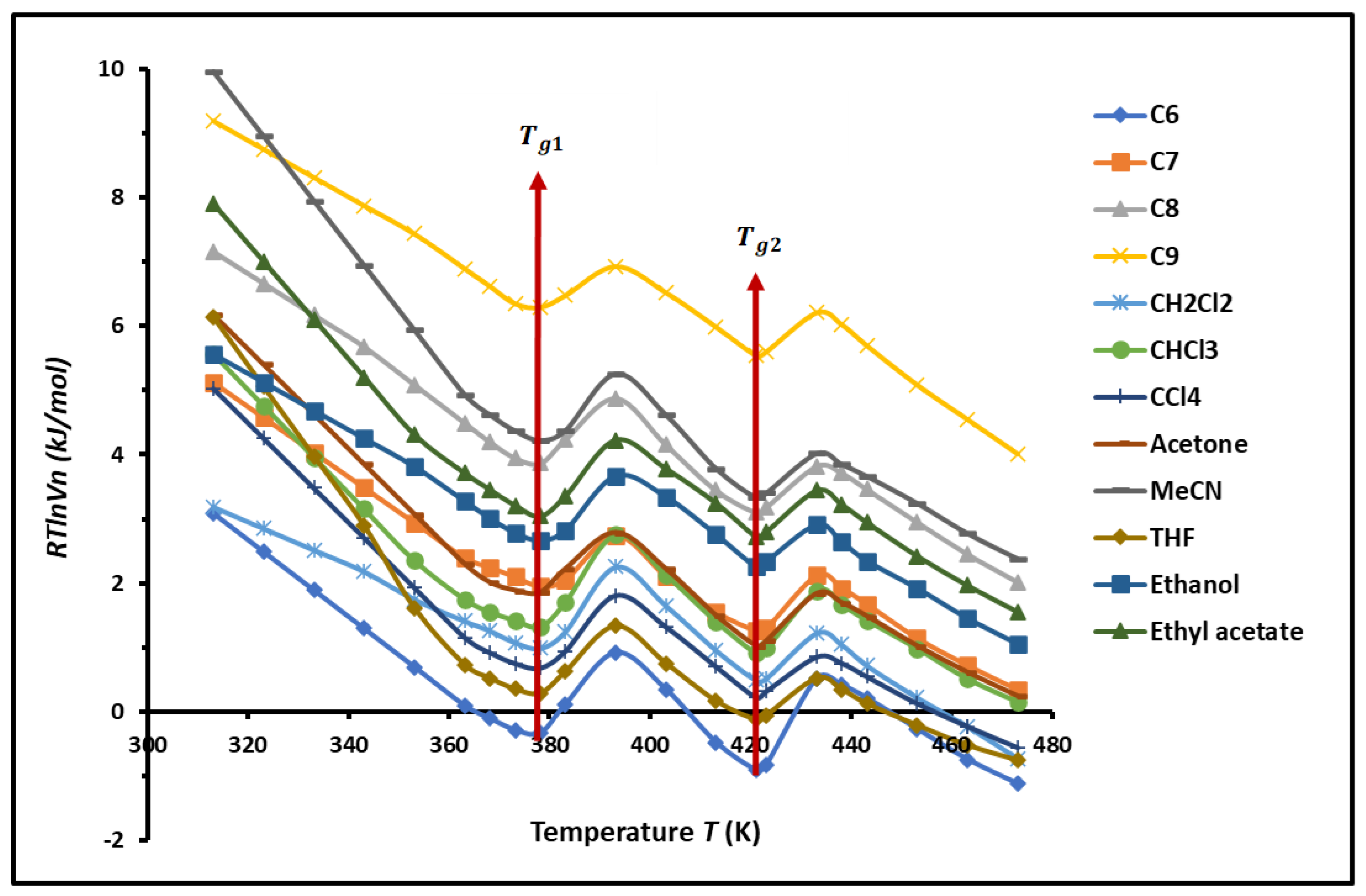
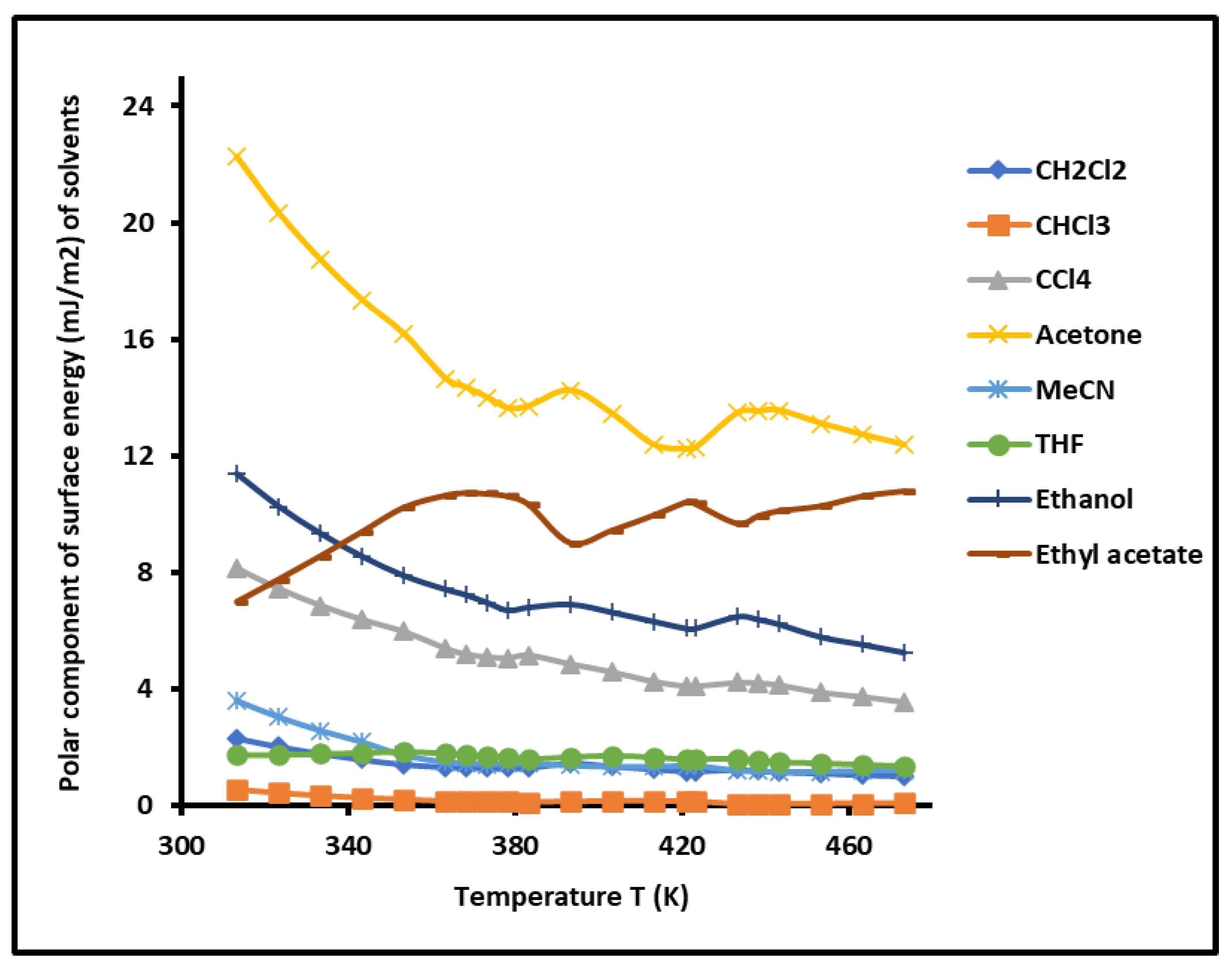
3.1. Variations of of Solvents Adsorbed on PS-b-P4VP Diblock Copolymer
The non-linear evolution of
of the different organic molecules adsorbed on PS-P4VP diblock copolymer against the temperature, drawn in
Figure 1 showed the presence of two minima for all used solvents at the respective temperatures
and
. These two particular temperatures perfectly correspond to the respective transition temperatures of PS and P4VP. This interesting result proved that the block copolymers behave as separated phases.
The transition temperatures of PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer were studied by several authors using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) [
38,
70,
71,
72,
73,
74,
75]. Zhang et al. [
70] showed that the pure PSb-P4VP copolymer exhibits two glass transition temperatures: one
of PS is 100.88 °C and the other is the
of P4VP at 130.98 °C largely depending on the ratio of the molecular masses of PS on P4VP blocks. Whereas, other values of
of P4VP (
= 138 °C) was showed by Zhao et al. [
71]. The ratio of number molecular weights of PS on P4VP varied between 30% and 50%.
However, the glass transition temperature
of the PS and P4VP of the diblock copolymer was analyzed by Schulze et al. [
38] using DSC technique. They highlighted two glass transitions of approximately 105 °C for polystyrene and 150 °C for poly(4-vinylpyridine). The same values of
were obtained by Rahikkala et al. [
74]. The DSC measurements on the PSb-P4VP block copolymers carried out by Huang et al. [
75] also exhibited two glass transitions, indicating that the resulting block copolymers are phase separated and reporting two
for PS and P4VP blocks in the PSb-P4VP copolymer respectively equal to 100 °C, and 150 °C for a ratio of number molecular weights of PS on P4VP equal to 20%. These two transition temperatures are obviously, quite similar to those of respective homopolymers indicating that the resulting block copolymers are phase separated in condensed state [
75].
The results of
obtained by this work
and
are very close to those obtained by Schulze et al. [
38], Rahikkala et al. [
74], and Huang et al. [
75] with a small deviation not exceeding 5% due to the difference observed in the molecular weight and composition of the blocks.
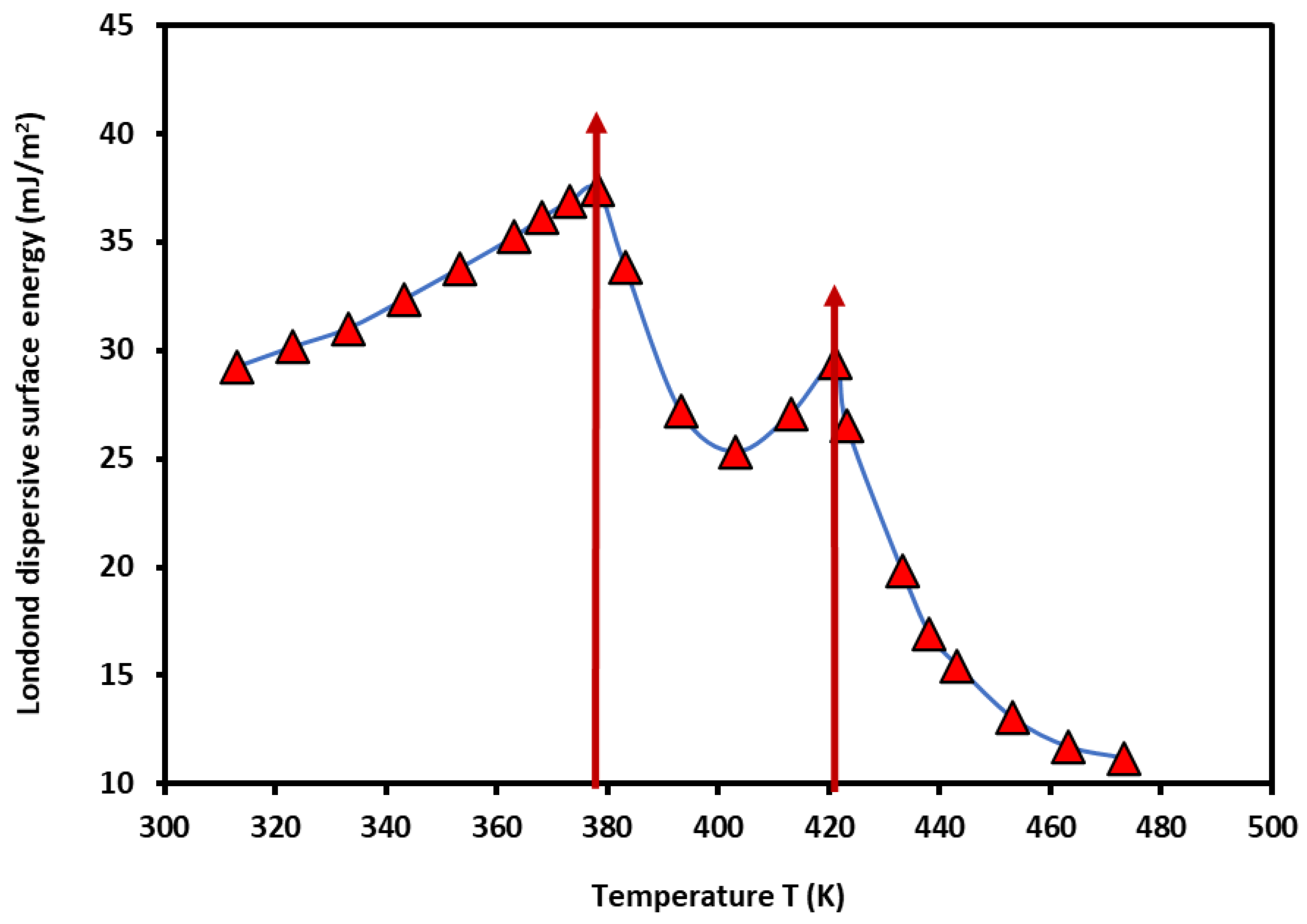
3.2. London Dispersive Surface Energy of PS-b-P4VP Diblock Copolymer
Using the results given in
Tables S1 and S2, and the Hamieh thermal model [
53,
54,
55,
56], it was possible to determine the Londo dispersive surface energy
of PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer as a function of the temperature. The results were given in
Figure 2.
The non-linear variations of the London dispersive surface energy showed two maxima corresponding to the two glass transition temperatures of PS and P4VP blocks in PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer then confirming those previously obtained in
Figure 1:
- -
relative to PS glass transition
- -
relative to P4VP glass transition
In several previous studies [
50,
61,
62,
63], the transition temperatures of some polymers in bulk and adsorbed phases were highlighted by IGC technique. An important effect of the temperature, the polymer tacticity, and the recovery fraction was showed on the values of the second order transition temperatures. The variations of
of PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer are constituted by three parabolic functions given in
Table 1 and represented by the following general equation with an excellent linear regression coefficient (R
2 > 0.99):
The results in
Table 1 confirmed the general tendency of the variations of the London dispersive surface energy of polymers obtained in the case of transition phenomena of Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) [
50,
61,
62,
63]. For the PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer, it was proved that the two glass transition temperatures correspond to those of PS and P4VP separately taken with slight variation. In the case of first order linear interpolation in the considered temperature interval [313.15K - 473.15K], a bad linear correlation, R
2 = 0.6456, was obtained, certainly due to non-linearity of the function
. The corresponding
of PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer is given by the following relation:
The useful information obtained by this large approximation was the determination of the following surface energetic parameters of PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer:
- -
the surface entropy: ,
- -
the London dispersive energy at 0K: ,
- -
the intrinsic temperature .
The above values can be compared to those obtained in other works on PMMA [
61,
62,
63], with smaller surface parameter values of PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer, but higher intrinsic temperature.
3.3. Polar Free Surface Energy of PS-b-P4VP Diblock Copolymer
By applying our new methodology using the London dispersion interaction equation, the results given in
Tables S1 and S2, and the values of the deformation polarizability
and the ionization energies [
76] of the various n-alkanes and polar molecules adsorbed on the PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer, Equation 11 led to the variations of the free polar surface energy (
) of polar solvents adsorbed on the copolymer as a function of the temperature. The values of (
) were given in
Table S3 and the curves were plotted in
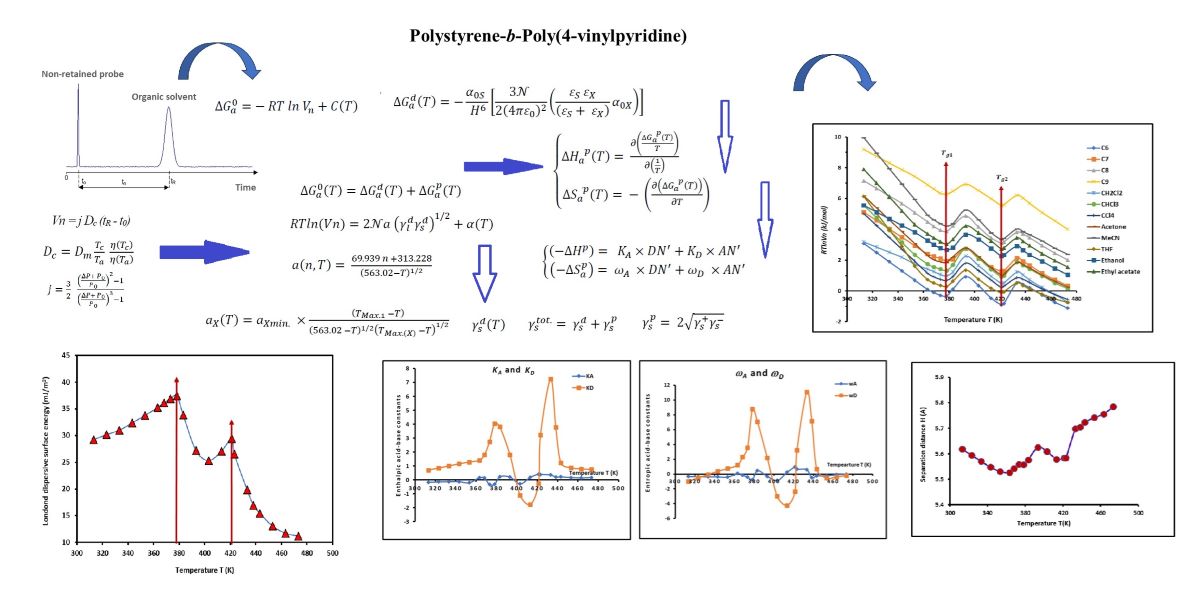
Figure 3. A large difference in the values of the free polar energy was observed with the various polar solvents adsorbed on PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer. The polar probes can be globally classified in increasing order of their polar interaction energy as follows:
CHCl3 < CH2Cl2 < THF < MeCN < CCl4 < ethyl acetate < ethanol < acetone showing the highest polar free energy with Lewis’s base solvents.
Non-linear variations of (
) of the different polar molecules were also observed due to the reorganization of the surface groups of the copolymer blocks and highlighted the two glass transition temperatures of PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer with small fluctuations of the polar interaction energy as a function of the temperature (
Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy (kJ/mol) of different polar solvents adsorbed on PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer.
Figure 3.
Evolution of the polar free interaction energy (kJ/mol) of different polar solvents adsorbed on PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer.
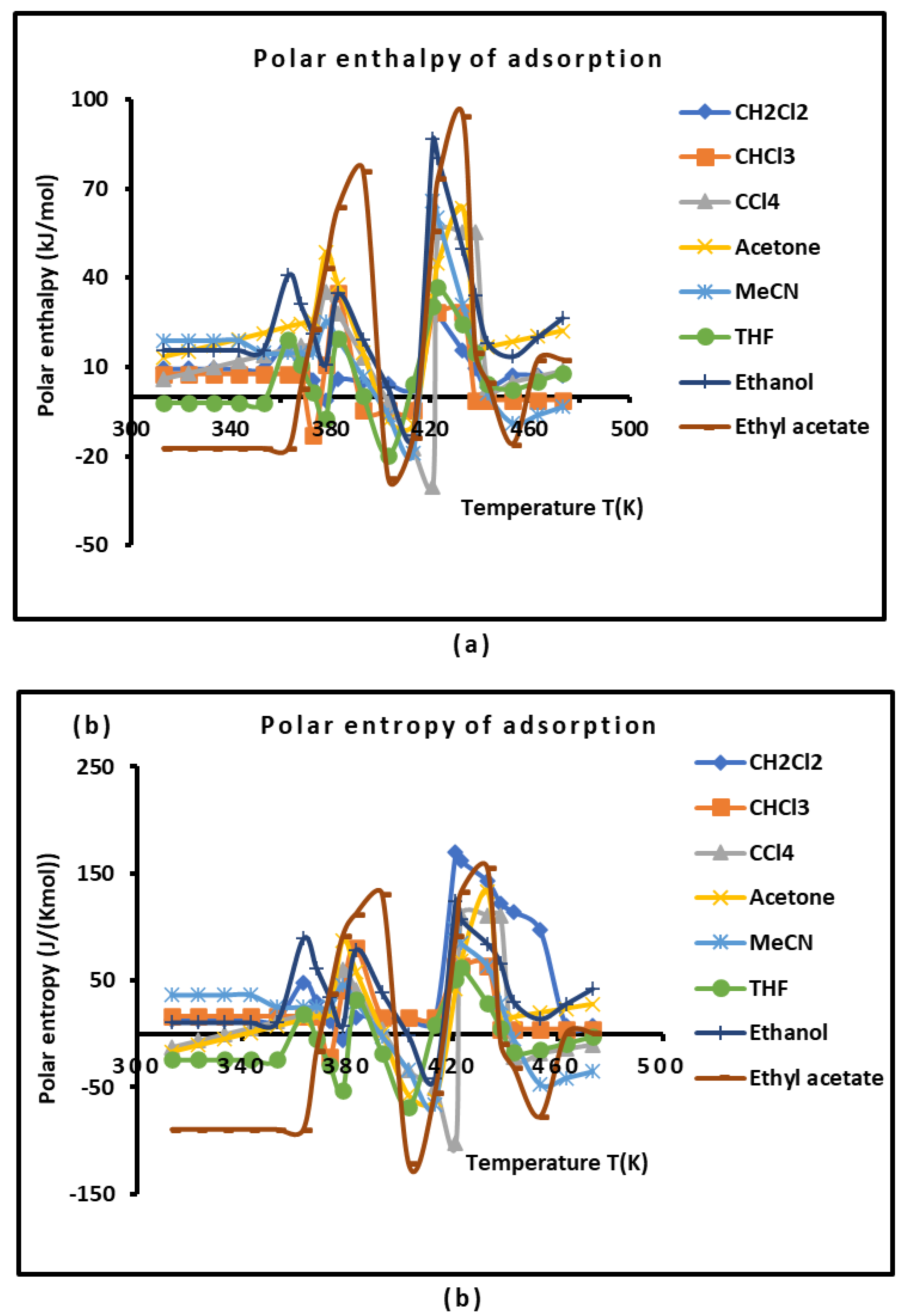
3.4. Polar Enthalpy and Entropy of Adsorption
The results presented in
Table S3 giving the non-linear variations of (
of adsorbed solvents on PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer and the Equations 13 allowed determining the values of the polar enthalpy
(
Table S4) and entropy
(
Table S5) of adsorption of polar probes on the copolymer as a function of the temperature. The results were plotted in
Figure 4. The variations of
showed the adsorption and desorption phenomena of the polar molecules on the copolymer surface with a stronger tendency to the adsorption and sever and non-linear fluctuations as a function of the temperature due to the presence of the glass transition affecting the group reorganization and rearrangement when the temperature is very close to the transition phenomena. Whereas, brutal variations of the polar entropy change
of the adsorbed with a certain disorder near the transition temperatures and more ordered and organized surface of the copolymer far from these transition temperatures. Some solvents such THF and ethyl acetate showed higher disorder of interaction with the PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer. The maximum of disorder was observed at the two transition temperatures for all polar molecules.
The non-linearity variations of
and
of the different adsorbed solvents observed as a function of temperature led to important variations of the Lewis’s acid-base properties of the PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer against the temperature. However, the calculations of the average values
and
of the various polar molecules allowed obtaining the results in
Table 2.
The results in
Table 2 showed that the linear regression coefficients are generally very bad because of the extreme non-linearity previously observed in
Figure 3 and
Figure 4.
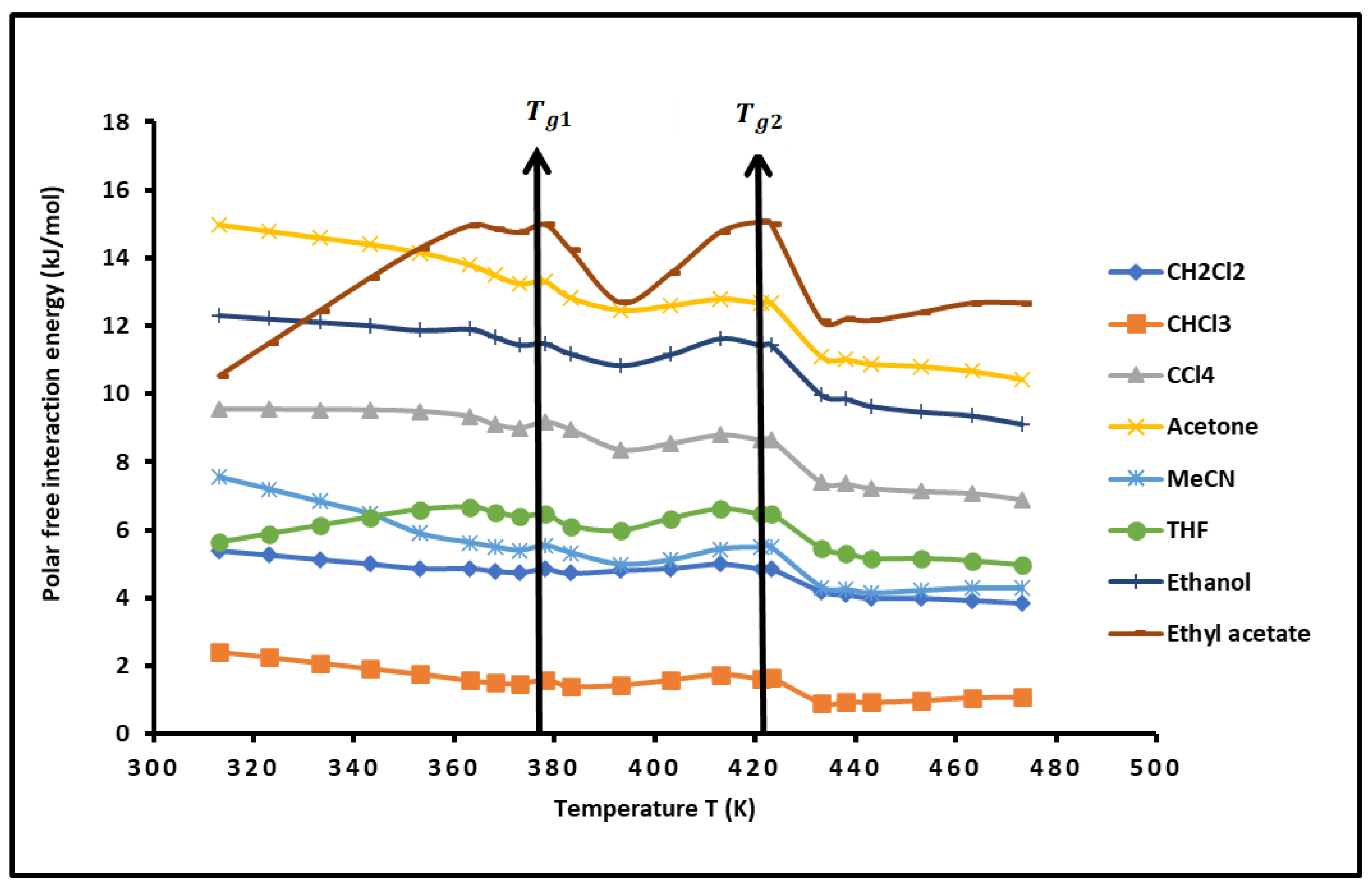
3.5. Temperature Effect on the Lewis’s Acid-Base Parameters of the Copolymer
Using equations 14 and the values of
and
given in
Tables S4 and S5, one determined the Lewis enthalpic acid base parameters
and
and the entropic acid base parameters
and
of the PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer as a function of the temperature. The evolution of the various enthalpic and entropic acid-base parameters of the PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer as a function of the temperature was plotted in
Figure 5. It was showed that the diblock copolymer exhibited very stronger Lewis’s base character reaching at certain temperatures 20 times higher than its Lewis acidity. The basicity of the copolymer was proved to be maximum at the glass transition. An important non-linearity of the different Lewis’s acid-base parameters the PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer was observed (
Figure 5) when the temperature varied. This is essentially due to the presence of the glass transitions that participate to the acid and base group reorganization controlling at the same time the variations of the acid-base properties of the copolymer.
The calculations of the average values of
and
of the adsorbed polar molecules by applying Equations 14 gave in
Table 3 the following average values of the acid base constants independently from the temperature.
Table 3 showed that the PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer exhibits then a stronger Lewis base character which is globally 7.5 times more basic than acidic. The evolution of the Lewis acid-base of the copolymer also highlighted the presence of the two glass transition temperatures.
Figure 5.
Variations of the various enthalpic and entropic acid-base parameters of the PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer as a function of the temperature: (a): and , (b): and , (c): / and ; (d): / and . The values of and given in the figures were multiplied by 103.
Figure 5.
Variations of the various enthalpic and entropic acid-base parameters of the PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer as a function of the temperature: (a): and , (b): and , (c): / and ; (d): / and . The values of and given in the figures were multiplied by 103.
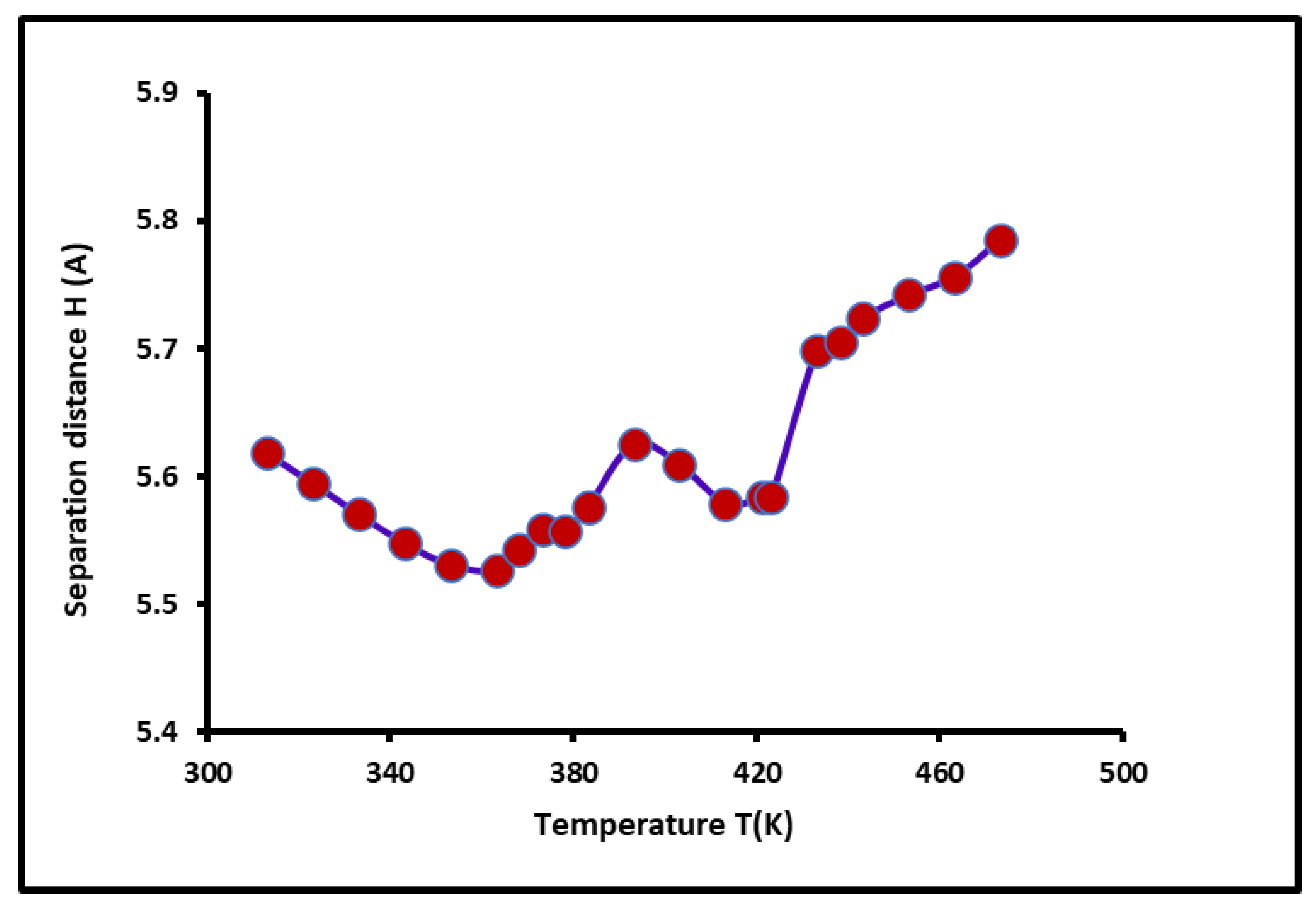
3.6. Separation Distance, Lewis Acid-Base Surface Energies of PS-b-P4VP Copolymer, and and Polar Surface Energy of Solvents
The values of the average separation distance
between the solvents adsorbed on the copolymer surface were determining using Equations 10. The variations of the separation distance
were plotted in
Figure 6 as a function of the temperature. Even if these variations are limited between 5.5 and 6.0 Å, however, it was shown in
Figure 6 that the non-linear evolution of
decreased before reaching each glass transition of the PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer and then increased for larger temperatures.
Furthermore, the Lewis acid
and base
surface energies of the PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer were determined using Equations 20, whereas, the polar acid-base surface energy
of the copolymer was obtained from Equation 15. While the value of the Lifshitz – Van der Waals (LW) surface energy
(or total surface energy of the copolymer) was deduced using equation 14. This led to determine the variations of the various polar acid and base surface energies
,
,
, and
of the copolymer (
Table 4).
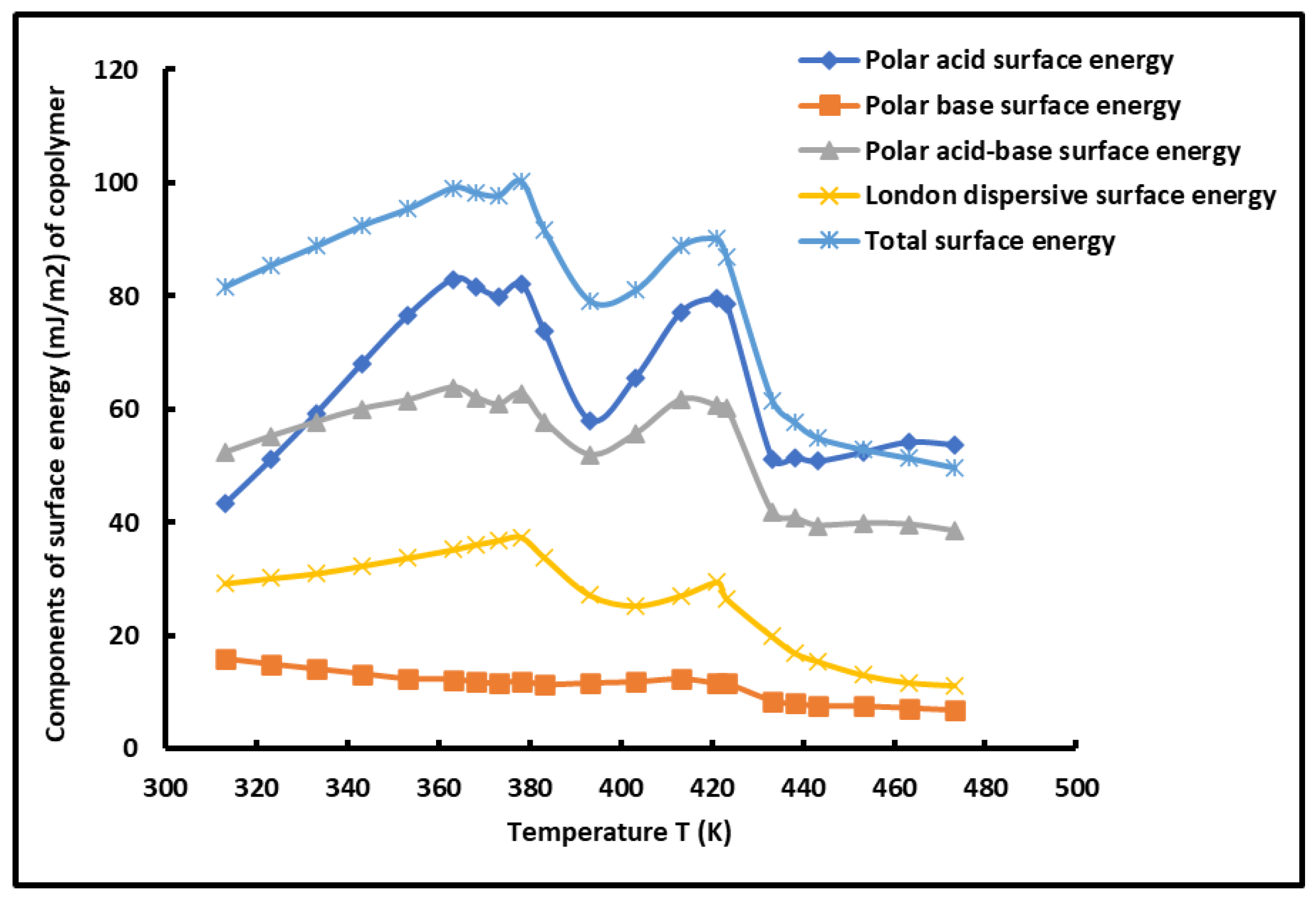
The comparison between the different surface energy components of the copolymer showed the highest values of polar acid surface energy due to the highest basic character of the surface groups of the copolymer blocks. The results in
Table 4 showed that the London dispersive surface energy is equivalent to the half of the polar surface energy of the PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer, whereas, the lowest surface energy was obtained for the basic surface energy component, because of the weaker acid force of the surface groups of the copolymer.
The variations of the various surface energy components plotted in
Figure 7.
The curves of the different components of the surface energy of the copolymer shown in
Figure 7 also confirmed the presence of the two glass transition temperatures of the PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer. The same conclusions were observed in several previous studies [
61,
62,
63,
77].
On the other hand, the experimental results previously obtained allowed determining the polar free energy
of a polar molecule denoted by
having a surface area
and a polar component of the surface energy
, given by Equation 21:
Knowing the polar surface energy
of the PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer, the polar surface energy of the organic molecules was determined by Equation 22:
By varying the temperature, the
of the various polar solvents adsorbed on the copolymer was determined versus the temperature. The results were plotted in
Figure 8. The highest polar contribution of the surface energy of polar molecules was obtained by acetone, respectively followed by ethyl acetate, ethanol, and carbon tetrachloride. A decrease in the values of the
of the various adsorbed polar solvents was observed when the temperature increased with some variations near the glass temperatures of the copolymer. The curves of
Figure 8 highlighted the highest polar surface energy of acetone, certainly due to the highest polarity of this polar solvent.
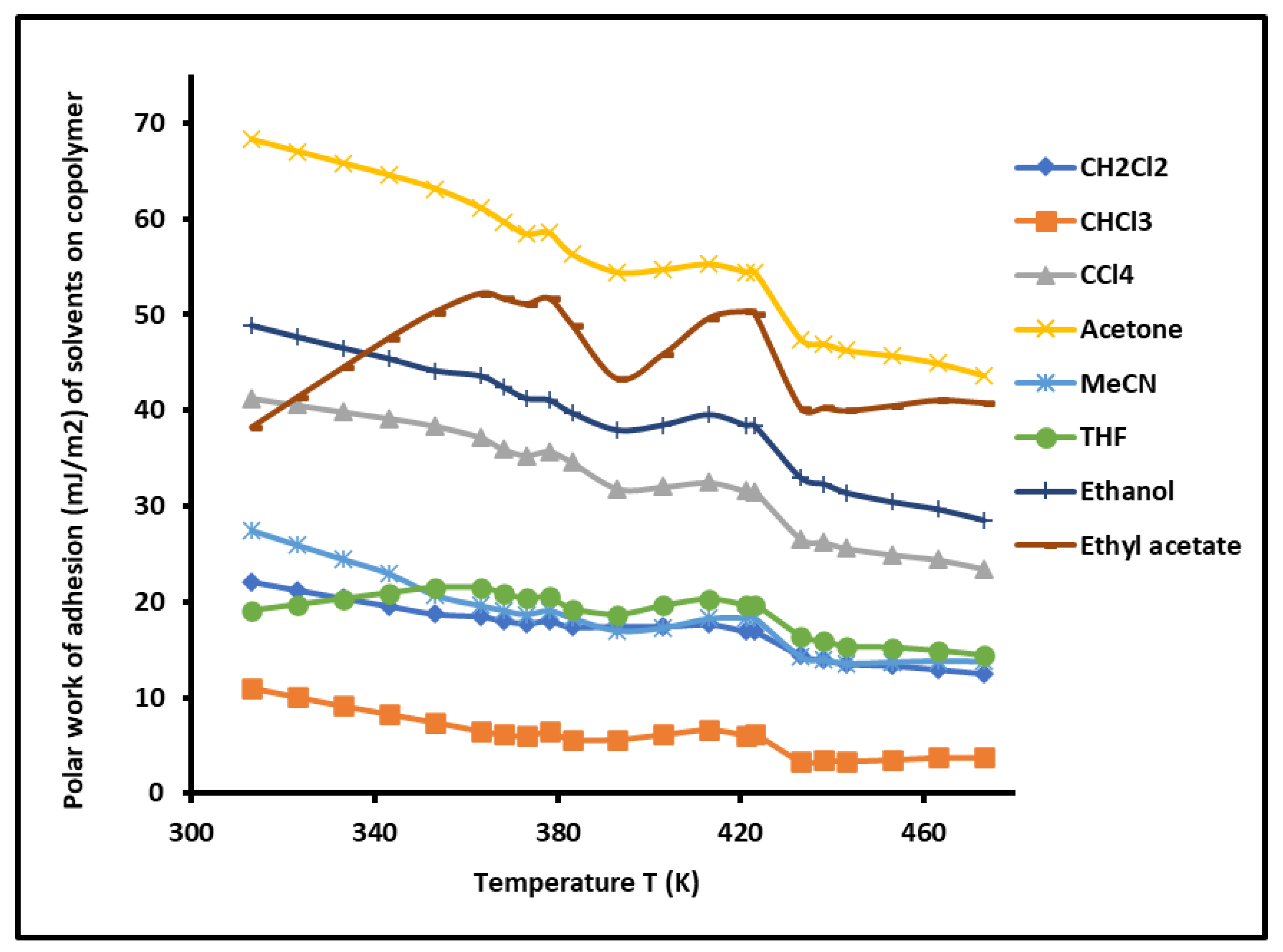
3.7. Work of Adhesion of Solvents on the PS-b-P4VP Copolymer against the Temperature
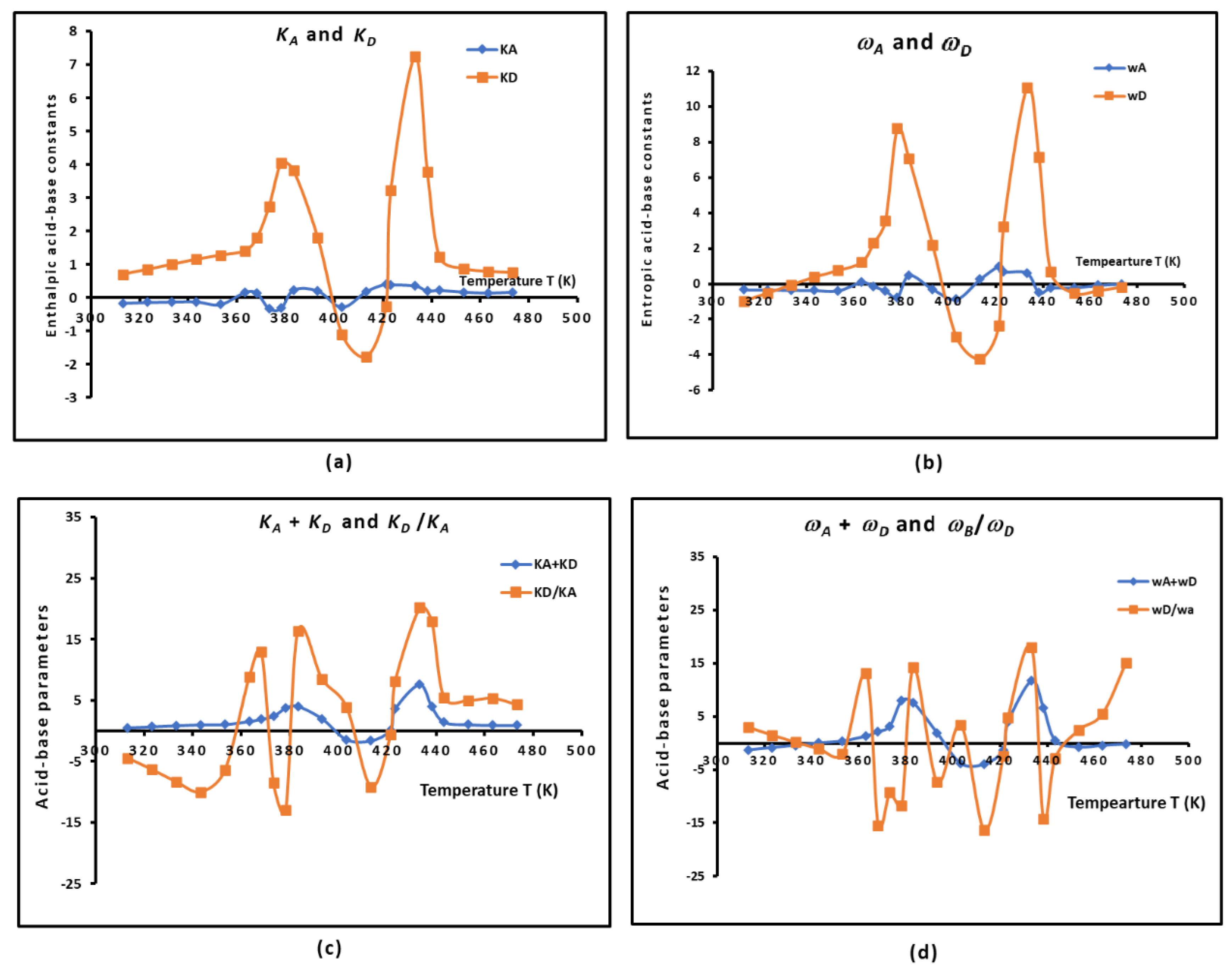
To determine the polar work of adhesion
of the polar organic molecule
adsorbed on the copolymer, the following relation was used: is given by relation 23:
The variations of
versus the temperature were plotted in
Figure 9. The plotted curves showed non-linear variations of the polar work of adhesion with the presence of two maxima at two particular temperatures corresponding to the two glass temperatures of the PS-
b-P4VP diblock copolymer.
It was observed that the highest polar work of adhesion corresponded to the adhesion of acetone on the copolymer, followed by ethyl acetate, ethanol and CCl4.
Figure 9.
Evolution of (mJ/m2) of polar molecules adsorbed on the PS-b-P4VP copolymer.
Figure 9.
Evolution of (mJ/m2) of polar molecules adsorbed on the PS-b-P4VP copolymer.
4. Conclusions
The surface thermodynamic properties of the PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer were determined as a function of the temperature using the inverse gas chromatography technique at infinite dilution and applying the new methodology based on the Hamieh thermal model consisting in the accurate determination of the London dispersive surface energy of the copolymer, and on the London dispersion interaction equation allowing the separation between the Dispersive and polar free energies of adsorption of organic solvents on the PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer. An important effect of the temperature on the Lewis’s acid-base properties of the copolymer was showed. Two glass transition temperatures of the copolymer were highlighted, the first one at 105 °C corresponding to the glass transition of PS polymer blocks and the second one at 148 °C relative to that of P4VP blocks.
The variations of the free energy of adsorption, the London dispersive surface energy and the Lewis’s acid and base surface energies of the copolymer as a function of the temperature all showed the presence of the two glass transition temperatures.
It was also showed that the variations of the different Lewis’s acid-base parameters were non-linear with the presence of two maxima at the transition temperatures. An important basic character of the copolymer was observed and varying with the temperature. The calculations of the average values of the Lewis’s acid-base parameters showed a copolymer surface 7.5 times more basic than acidic.
The separation distance between the organic molecules and the PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer was determined and non-linear variations were also noticed with two minima observed at the glass transitions. An average value of the separation distance equal to 5.5 Å was obtained. Our new methodology allowed obtaining the variations of the acid and base surface energies, the polar acid-base surface energy , the London dispersive surface energy , and the Lifshitz – Van der Waals surface energy (mJ/m2) of the PS-b-P4VP diblock copolymer as well as the polar surface energy of the solvents and their work of adhesion as a function of temperature.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Table S1. Values of (kJ/mol) of n-alkanes adsorbed on PS-P4VP copolymer as a function of temperature. Table S2. Values of (kJ/mol) of polar solvents adsorbed on PS-P4VP copolymer as a function of temperature. Table S3. Values of (kJ/mol) of polar solvents adsorbed on PS-P4VP copolymer as a function of temperature. Table S4. Values of (kJ/mol) of polar solvents adsorbed on PS-P4VP copolymer as a function of temperature. Table S5. Values of (J.mol-1.K-1) of polar solvents adsorbed on PS-P4VP copolymer as a function of temperature.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant.
Data Availability Statement
There is no additional data.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Sunil, K.; Varshney, X.; Zhong, Y.; Eisenberg, A. Anionic homopolymerization and block copolymerization of 4-vinylpyridine and its investigation by high-temperature size exclusion chromatography in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Eisenberg, A. A model of micellization for block copolymers in solutions. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 7353–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Urhig, D.; Mays, J.W. Living anionic polymerization. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science 1999, 120, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebdon, J.R.; Eastmond, G.C. New methods of polymer synthesis, Chap 2. Blackie Academic and Professional: Glasgow, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F.; Kuo, S.W.; Chen, J.K.; Chan, F.C. Synthesis and characterization of polystyrene-b-poly (4-vinyl pyridine) block copolymers by atom transfer radical polymerization. Journal of Polymer Research 2005, 12, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Huh, J.; Hwang, J.; Kim, H.-C.; Kim, S.H.; Sohn, B.-H.; Park, C. Ordered arrays of PS-b-P4VP micelles by fusion and fission process upon solvent annealing. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 6688–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamley, I.W. Ordering in thin films of block copolymers: fundamentals to potential applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 1161–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Narita, C.; Xu, X.; Honma, H.; Himeda, Y.; Yamada, K. Controlling the ordered transition of PS-b-P4VP block copolymer ultrathin films by solvent annealing. Materials Chemistry and Physics 2020, 239, 122072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Hashimoto, T. Morphology of block copolymers and mixtures of block copolymers at free surfaces. Polymer 1992, 33, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Cho, H.; Yoo, S.; Park, S. Ordering evolution of block copolymer thin films upon solvent-annealing process. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 383, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Wang, Y. Reversible switch between the nanoporous and the nonporous state of amphiphilic block copolymer films regulated by selective swelling. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 6927–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsudin, S.A.; Mikihito, T.; Hirokazu, H. Controlling ordered structures of PS-b-P2VP block copolymer thin film by tuning solvent evaporation rate. Macromol. Symp. 2017, 371, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, W.; Han, C.D.; Lee, D.H.; Han, S.H.; Kim, J.K.; Kang, J.H.; Park, C. Origin of the difference in Order−Disorder transition temperature between polystyrene-block-poly(2-vinylpyridine) and polystyrene-block-poly(4-vinylpyridine) copolymers. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 2109–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.G.; Choi, H.J.; Han, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.W.; Jung, E.I.; et al. Block copolymer nanopatterning for non-semiconductor device applications. ACS Appl Mater Inter 2022, 14, 12011–12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, B.H.; Moon, H.S.; Kim, S.O. Directed self-assembly of block copolymers for next generation nanolithography. Mater Today 2013, 16, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, P.P.; Moutsios, I.; Manesi, G.M.; Ivanov, D.A.; Sakellariou, G.; Avgeropoulos, A. Designing high χ copolymer materials for nanotechnology applications: A systematic bulk vs. thin films approach. Progress in Polymer Science 2022, 135, 101625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, C.; Pino, G.; Mantione, D.; Fleury, G. Engineering block copolymer materials for patterning ultra-low dimensions. Mol Syst Des Eng 2020, 5, 1642–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F.; Kuo, S.W.; Chen, J.K.; Chang, C.F. Synthesis and Characterization of Polystyrene-b-Poly(4-vinyl pyridine) Block Copolymers by Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. Journal of Polymer Research 2015, 12, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Xia, D.; Wang, Y.; Ding, S.; Xu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Du, B. Fabrication of poly(4-vinylpyridine)-b-polystyrene-b-poly(4-vinylpyridine) triblock copolymer particles via three-dimensional soft confined self-assembly. Polym. Chem. 2024, 15, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Ghoshal, T.; Prochukhan, N.; Fernandez, A.A.; Vasquez, J.F.B.; Yadav, P.; Padmanabhan, S.C.; Morris, M.A. Morphology Engineering of the Asymmetric PS-b-P4VP Block Copolymer: From Porous to Nanodot Oxide Structures. ACS Applied Polymer Materials 2023, 5, 9612–9619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altug, H.; Oh, S.-H.; Maier, S.A.; Homola, J. Advances and Applications of Nanophotonic Biosensors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, L.; Meierhofer, F.; Gorny, S.; Leis, S.; Splith, D.; Zhang, Z.; von Wenckstern, H.; Grundmann, M.; Wang, X.; Hartmann, J.; et al. Toward Three-Dimensional Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Optoelectronics Based on GaN/OCVD-PEDOT Structures. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Shin, H.; Choi, B.; Rhim, W.-K.; Na, K.; Keun Han, D. Advanced Hybrid Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 114, 100686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D.; Shevchenko, E. Design of Functional Composite and All-Inorganic Nanostructured Materials via Infiltration of Polymer Templates with Inorganic Precursors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 10604–10627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Vasquez, J.F.B.; Perova, T.S.; Morris, M.A. Fabrication of metal-oxide arrays: mechanism of solvent-mediated metal infiltration into block copolymer nanopatterns. Clean Techn Environ Policy 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Bando, Y.; Gautam, U.K.; Ye, C.; Golberg, D. Inorganic Semiconductor Nanostructures and Their Field-Emission Applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, F.; Wang, Y. Transition Metal Oxide Nanostructures: Premeditated Fabrication and Applications in Electronic and Photonic Devices. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 4334–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmeraldo Paiva, A.; Baez Vasquez, J.F.; Selkirk, A.; Prochukhan, N.; Medeiros Borsagli, F.G.L.; Morris, M. Highly Ordered Porous Inorganic Structures via Block Copolymer Lithography: An Application of the Versatile and Selective Infiltration of the “Inverse” P2VP-b-PS System. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 35265–35275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.-H.; Han, W.B.; Il Ryu, H.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Choi, N.; Kang, J.Y.; Yu, Y.G.; Kim, T.S. Tunable and Scalable Fabrication of Block Copolymer-Based 3D Polymorphic Artificial Cell Membrane Array. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, T.; Shaw, M.T.; Bolger, C.T.; Holmes, J.D.; Morris, M.A. A General Method for Controlled Nanopatterning of Oxide Dots: A Microphase Separated Block Copolymer Platform. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.; Jeong, U.; Ryu, D.Y.; Russell, T.P.; Hawker, C.J. Block Copolymer Nanolithography: Translation of Molecular Level Control to Nanoscale Patterns. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4769–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, C.M.; Maher, M.J.; Janes, D.W.; Ellison, C.J.; Willson, C.G. Block Copolymer Lithography. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Gwyther, J.; Manners, I.; Chaikin, P.M.; Register, R.A. Metal-Containing Block Copolymer Thin Films Yield Wire Grid Polarizers with High Aspect Ratio. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoshal, T.; Prochukhan, N.; Morris, M.A. Sub-25 Nm Inorganic and Dielectric Nanopattern Arrays on Substrates: A Block Copolymer-Assisted Lithography. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 35738–35744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevate, R.; Karunakaran, M.; Kumar, M.; Peinemann, K.-V. Polyanionic pH-responsive polystyrene-b-poly(4-vinyl pyridine-N-oxide) isoporous membranes. Journal of Membrane Science 2016, 501, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Horechyy, A.; Yadav, S.; Formanek, P.; Hübner, R.; Srivastava, R.K.; Sapra, S.; Fery, A.; Nandan, B. Nanoparticle Stabilized Perforated Lamellar Morphology in Block Copolymer/Quantum Dot, Hybrids. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Li, H.; An, L.; Jiang, S. Constructional details of polystyrene-block-poly(4-vinylpyridine) ordered thin film morphology. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2013, 399, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, M.; Handge, U.A.; Rangou, S.; Lillepärg, J.; Abetz, V. Thermal properties, rheology and foams of polystyrene-block-poly(4-vinylpyridine) diblock copolymers. Polymer 2015, 70, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-Q.; Chen, G.-D.; Pan, C.-Y.; Luan, B.; Hong, C.-Y. Preparation, characterization, and thermal properties of polystyrene-block-quaternized poly(4-vinylpyridine)/Montmorillonite nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.R.; Young, C.L. Physical measurements by gas chromatography. John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, New York, 1979; 632 pages. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, D.T.; Brookman, D.J. Thermodynamically based gas chromatographic retention index for organic molecules using salt-modified aluminas and porous silica beads. Anal. Chem. 1968, 40, 1847–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorris, G.M.; Gray, D.G. Adsorption of n-alkanes at zero surface coverage on cellulose paper and wood fibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1980, 77, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowkes, F.M. Surface and interfacial aspects of biomedical polymers; Andrade, J.D., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, 1985; Vol. I, pp. 337–372. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, J.; Lavielle, L.; Martin, C. The role of the interface in carbon fibre-epoxy composites. J. Adhes. 1987, 23, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Flour, C.; Papirer, E. Gas-solid chromatography. A method of measuring surface free energy characteristics of short glass fibers. 1. Through adsorption isotherms. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1982, 21, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Flour, C.; Papirer, E. Gas-solid chromatography: method of measuring surface free energy characteristics of short fibers. 2. Through retention volumes measured near zero surface coverage. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1982, 21, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnet, J.-B.; Park, S.; Balard, H. Evaluation of specific interactions of solid surfaces by inverse gas chromatography. Chromatographia 1991, 31, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendlé, E.; Papirer, E. A new topological index for molecular probes used in inverse gas chromatography for the surface nanorugosity evaluation, 1. Method of Evaluation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 194, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendlé, E.; Papirer, E. A new topological index for molecular probes used in inverse gas chromatography for the surface nanorugosity evaluation, 2. Application for the Evaluation of the Solid Surface Specific Interaction Potential. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 194, 217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamieh, T.; Schultz, J. New approach to characterize physicochemical properties of solid substrates by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. Some new methods to determine the surface areas of some molecules adsorbed on solid surfaces. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 969, 17–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelkel, A. Inverse gas chromatography: Characterization of polymers, fibers, modified silicas, and surfactants. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1991, 22, 411–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, S.K.; Panayiotou, C. Assessment of the thermodynamic properties of poly(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl methacrylate) by inverse gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1324, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. Study of the temperature effect on the surface area of model organic molecules, the dispersive surface energy and the surface properties of solids by inverse gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1627, 461372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. New methodology to study the dispersive component of the surface energy and acid–base properties of silica particles by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2022, 60, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamieh, T.; Ahmad, A.A.; Roques-Carmes, T.; Toufaily, J. New approach to determine the surface and interface thermodynamic properties of H-β-zeolite/rhodium catalysts by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. Some Irregularities in the Evaluation of Surface Parameters of Solid Materials by Inverse Gas Chromatography. Langmuir 2023, 39, 17059–17070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. New physicochemical methodology for the determination of the surface thermodynamic properties of solid particles. Appl. Chem. 2023, 3, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. New Progress on London Dispersive Energy, Polar Surface Interactions, and Lewis’s Acid–Base Properties of Solid Surfaces. Molecules 2024, 29, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. London Dispersive and Lewis Acid-Base Surface Energy of 2D Single-Crystalline and Polycrystalline Covalent Organic Frameworks. Crystals 2024, 14, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. Inverse Gas Chromatography to Characterize the Surface Properties of Solid Materials. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 2231–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. Effect of Tacticity on London Dispersive Surface Energy, Polar Free Energy and Lewis Acid-Base Surface Energies of Poly Methyl Methacrylate by Inverse Gas Chromatography. Macromol 2024, 4, 356–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. The Effect of Temperature on the London Dispersive and Lewis Acid-Base Surface Energies of Polymethyl Methacrylate Adsorbed on Silica by Inverse Gas Chromatography. Thermo 2024, 4, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. Temperature Dependence of the Polar and Lewis Acid–Base Properties of Poly Methyl Methacrylate Adsorbed on Silica via Inverse Gas Chromatography. Molecules 2024, 29, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajab, M.; Hamieh, T.; Airoudj, A.; Mougin, K.; Hariri, K.; Rammal, W.; Mortada, H.; Akil, M.; Kassas, A.; Toufaily, J. Synthesis by ATRP of Polystyrene-b-Poly(4-vinylpyridine) and Characterization by Inverse Gas Chromatography. Journal of Research Updates in Polymer Science 2017, 6, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorris, G.M.; Gray, D.G. Adsorption of n-alkanes at zero surface coverage on cellulose paper and wood fibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1980, 77, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowkes, F.M. Surface and interfacial aspects of biomedical polymers. Andrade, J.D., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, 1985; Vol. I, pp. 337–372. [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann, V. The Donor-Acceptor Approach to Molecular Interactions. Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Riddle, F.L.; Fowkes, F.M. Spectral shifts in acid-base chemistry. Van der Waals contributions to acceptor numbers, Spectral shifts in acid-base chemistry. 1. van der Waals contributions to acceptor numbers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 3259–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oss, C.J.; Good, R.J.; Chaudhury, M.K. Additive and nonadditive surface tension components and the interpretation of contact angles. Langmuir 1988, 4, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-Q.; Chen, G.-D.; Pan, C.-Y.; Luan, B.; Hong, C.-Y. Preparation, Characterization, and Thermal Properties of Polystyrene-block-Quaternized Poly(4 vinylpyridine)/Montmorillonite Nanocomposites. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2006, 102, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tian, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S.; Ji, X.; An, L.; Jiang, B. Nanoscopic surface patterns of diblock copolymer thin films. Eur. Phys. J. E 2005, 16, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Rangou, S.; Abetz, C.; Filiz, V.; Abetz, V. Isoporous Membranes from Novel Polystyrene-b-poly(4-vinylpyridine)-b-poly(solketal methacrylate) (PS-b-P4VP-b-PSMA) Triblock Terpolymers and Their Post-Modification. Polymers 2020, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Li, H.; An, L.; Jiang, S. Constructional details of polystyrene-block-poly(4-vinylpyridine) ordered thin film morphology. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2013, 399, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahikkala, A.; Soininen, A.; Ruokolainen, J.; Mezzenga, R.; Raula, J.; Kauppinen, E. Self-assembly of PS-b-P4VP block copolymers of varying architectures in aerosol nanospheres. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-F.; Kuo, S.-W.; Chen, J.K.; Chang, F.C. Synthesis and Characterization of Polystyrene-b-Poly(4-vinyl pyridine) Block Copolymers by Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. Journal of Polymer Research 2005, 12, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, R.L. (Ed.) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Internet Version 2007, 87th ed.; Taylor and Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; Available online: http://www.hbcpnetbase.com (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Hamieh, T. Surface Thermodynamic Properties of Poly Lactic Acid by Inverse Gas Chromatography. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).