Submitted:
18 September 2024
Posted:
19 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Subjects
2.2. Clinical and Biochemical Data
2.3. MRI / MR Spectroscopic Imaging
2.3.1. MR Spectroscopic Imaging of Calf Muscles
2.3.2. Abdominal Fat Imaging
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
2.4.1. Spectroscopic Data Processing
2.4.2. Abdominal Fat Segmentation
2.4.3. Liver and Pancreatic Fat
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Calf Muscle MRS (YHC vs. AMHC)
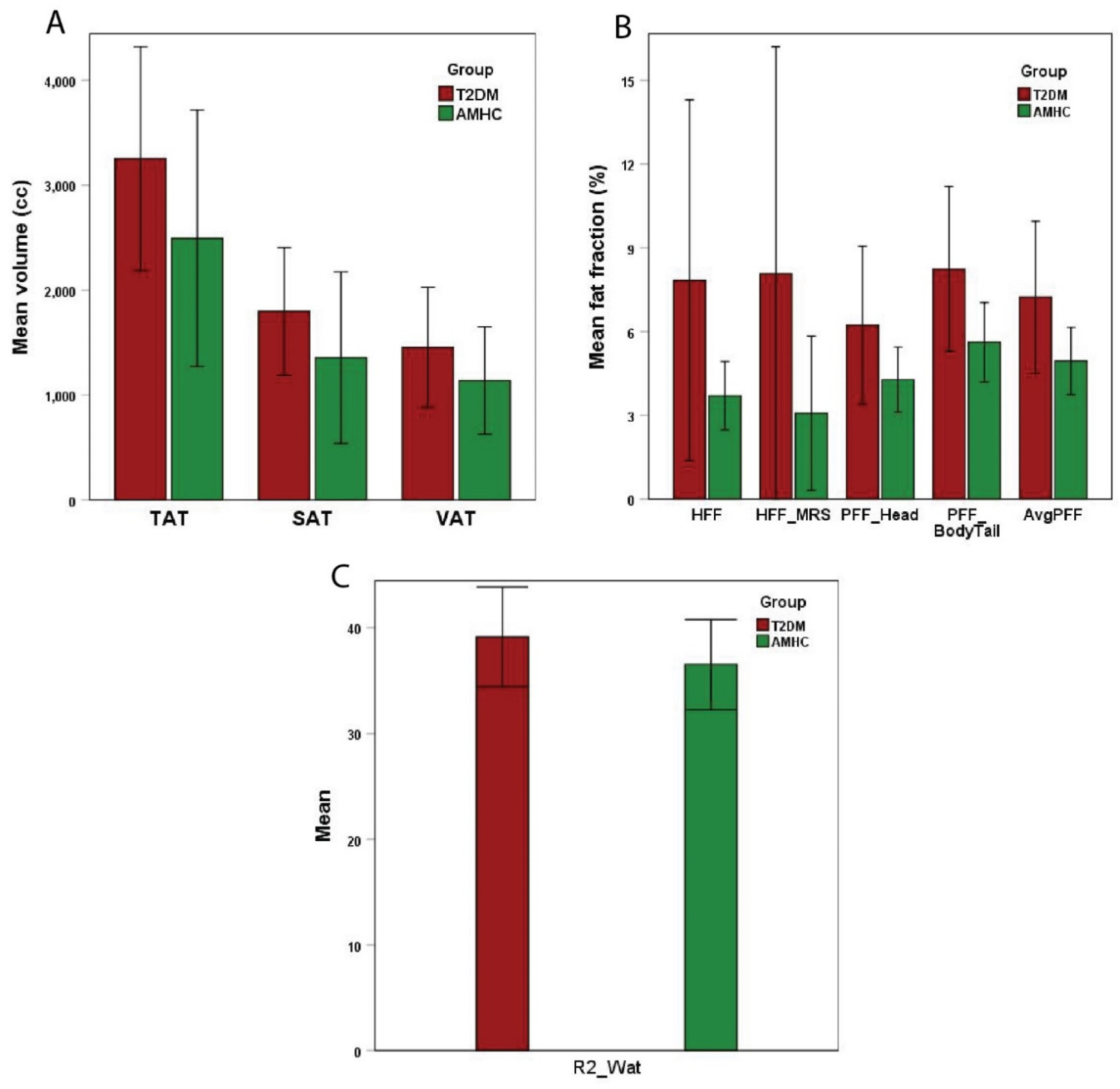
3.2. Calf Muscle MRS and Abdominal MRI (T2DM vs AMHC)
3.3. Association between MRS and MRI Fat Measures in T2DM,
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merz, K.E. and D.C. Thurmond, Role of skeletal muscle in insulin resistance and glucose uptake. Comprehensive Physiology, 2011. 10(3): p. 785-809. [CrossRef]
- Rivas, D.A., et al., Diminished anabolic signaling response to insulin induced by intramuscular lipid accumulation is associated with inflammation in aging but not obesity. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 2016. 310(7): p. R561-R569. [CrossRef]
- Roden, M., Muscle triglycerides and mitochondrial function: possible mechanisms for the development of type 2 diabetes. International journal of obesity, 2005. 29(2): p. S111-S115. [CrossRef]
- Correa-de-Araujo, R., et al., Myosteatosis in the context of skeletal muscle function deficit: an interdisciplinary workshop at the National Institute on Aging. Frontiers in physiology, 2020. 11: p. 963. [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, S. and N.R.F. Collaboration, Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: pooled analysis of 751 population-based measurement studies with over 4.4 million participants. The Lancet, 2016. 387(10027). [CrossRef]
- Reaven, G.M., Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes, 1988. 37(12): p. 1595-1607. [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K., Clinical characteristics of OGTT-derived hepatic-and muscle insulin resistance in healthy young men. Journal of exercise nutrition & biochemistry, 2014. 18(4): p. 385. [CrossRef]
- Meshkani, R. and K. Adeli, Hepatic insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Clinical biochemistry, 2009. 42(13-14): p. 1331-1346. [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.F. and G.I. Shulman, Etiology of insulin resistance. The American journal of medicine, 2006. 119(5): p. S10-S16. [CrossRef]
- Cusi, K., The role of adipose tissue and lipotoxicity in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Current diabetes reports, 2010. 10: p. 306-315. [CrossRef]
- Mantatzis, M., et al., Abdominal adipose tissue distribution on MRI and diabetes. Academic Radiology, 2014. 21(5): p. 667-674. [CrossRef]
- Medina-Gomez, G., S. Gray, and A. Vidal-Puig, Adipogenesis and lipotoxicity: role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) and PPARγcoactivator-1 (PGC1). Public health nutrition, 2007. 10(10A): p. 1132-1137. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-H., et al., Increased intrahepatic triglyceride is associated with peripheral insulin resistance: in vivo MR imaging and spectroscopy studies. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 2007. 293(6): p. E1663-E1669. [CrossRef]
- Gastaldelli, A., et al., Insulin resistance, adipose depots and gut: interactions and pathological implications. Digestive and Liver Disease, 2010. 42(5): p. 310-319. [CrossRef]
- Vessby, B., et al., Desaturation and elongation of fatty acids and insulin action. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2002. 967(1): p. 183-195. [CrossRef]
- Savage, D.B., et al., Accumulation of saturated intramyocellular lipid is associated with insulin resistance [S]. Journal of lipid research, 2019. 60(7): p. 1323-1332. [CrossRef]
- Boesch C., et al. Observation of intramyocellular lipids by 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Ann N.Y. Acad Sci 2000;904:p.25-. [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y. and M. Hattori, Intramyocellular lipids of muscle type in athletes of different sport disciplines. Open Access Journal of Sports Medicine, 2017: p. 161-166. [CrossRef]
- Casey, A., et al., Creatine ingestion favorably affects performance and muscle metabolism during maximal exercise in humans. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 1996. 271(1): p. E31-E37. [CrossRef]
- Greenhaff, P.L., et al., Influence of oral creatine supplementation of muscle torque during repeated bouts of maximal voluntary exercise in man. Clinical Science, 1993. 84(5): p. 565-571. [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.X., et al., Nutritional and dietary interventions for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, in Dietary Interventions in Liver Disease. 2019, Elsevier. p. 357-372. [CrossRef]
- da Costa, K.-A., et al., Elevated serum creatine phosphokinase in choline-deficient humans: mechanistic studies in C2C12 mouse myoblasts. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 2004. 80(1): p. 163-170. [CrossRef]
- Alves, F.M., et al., Choline administration attenuates aspects of the dystrophic pathology in mdx mice. Clinical Nutrition Experimental, 2019. 24: p. 83-91. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D., M.A. Frohman, and J.K. Blusztajn, Generation of choline for acetylcholine synthesis by phospholipase D isoforms. BMC neuroscience, 2001. 2: p. 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Volpe, P., et al., Role of inositol 1, 4, 5--trisphosphate in excitation--contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. FEBS letters, 1986. 197(1-2): p. 1-4. [CrossRef]
- Merckx, C. and B. De Paepe, The role of taurine in skeletal muscle functioning and its potential as a supportive treatment for duchenne muscular dystrophy. Metabolites, 2022. 12(2): p. 193. [CrossRef]
- Singh, P., et al., Taurine deficiency as a driver of aging. Science, 2023. 380(6649): p. eabn9257. [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, A. and M. Bizzarri, Inositols in insulin signaling and glucose metabolism. International journal of endocrinology, 2018. 2018(1): p. 1968450. [CrossRef]
- Krššák, M., et al., Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in skeletal muscle: Experts’ consensus recommendations. NMR in Biomedicine, 2021. 34(5): p. e4266. [CrossRef]
- Velan, S.S., et al., Investigation of muscle lipid metabolism by localized one--and two--dimensional MRS techniques using a clinical 3T MRI/MRS scanner. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2007. 25(1): p. 192-199. [CrossRef]
- Velan, S.S., et al., Distinct patterns of fat metabolism in skeletal muscle of normal-weight, overweight, and obese humans. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 2008. 295(4): p. R1060-R1065. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.A., et al., Localized two--dimensional shift correlated MR spectroscopy of human brain. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2001. 46(1): p. 58-67. [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, R., et al., Assessment of lipid and metabolite changes in obese calf muscle using multi-echo echo-planar correlated spectroscopic imaging. Scientific reports, 2017. 7(1): p. 17338. [CrossRef]
- Machann J., et al., Follow up whole-body assessment of adipose tissue compartments during a lifestyle intervention in a large cohort at increased risk for type 2 diabetes. Radiology 2010;257:p.353-363. [CrossRef]
- Bozzetto, L., et al., Liver fat in obesity: role of type 2 diabetes mellitus and adipose tissue distribution. European journal of clinical investigation, 2011. 41(1): p. 39-44. [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D., et al., Adipose tissue distribution is different in type 2 diabetes. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 2009. 89(3): p. 807-814. [CrossRef]
- Papaetis, G.S., P. Papakyriakou, and T.N. Panagiotou, State of the art paper Central obesity, type 2 diabetes and insulin: exploring a pathway full of thorns. Archives of Medical Science, 2015. 11(3): p. 463-482. [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P., Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. New England Journal of Medicine, 2002. 346(16): p. 1221-1231. [CrossRef]
- Al-Mrabeh, A., et al., Quantification of intrapancreatic fat in type 2 diabetes by MRI. PloS one, 2017. 12(4): p. e0174660. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S., et al., Clinical implications of fatty pancreas: correlations between fatty pancreas and metabolic syndrome. World journal of gastroenterology: WJG, 2009. 15(15): p. 1869. [CrossRef]
- Ou, H.-Y., et al., The association between nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease and diabetes. PloS one, 2013. 8(5): p. e62561. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.E., et al., Correlated spectroscopic imaging of calf muscle in three spatial dimensions using group sparse reconstruction of undersampled single and multichannel data. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 2015. 74(5): p. 1199-1208. [CrossRef]
- Sarma, M.K., et al., Noninvasive assessment of abdominal adipose tissues and quantification of hepatic and pancreatic fat fractions in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Magnetic resonance imaging, 2020. 72: p. 95-102. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H., et al., Resolution of creatine and phosphocreatine 1H signals in isolated human skeletal muscle using HR--MAS 1H NMR. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2008. 59(6): p. 1221-1224. [CrossRef]
- Srikanthan, P., et al., Characterization of intra-myocellular lipids using 2D localized correlated spectroscopy and abdominal fat using MRI in type 2 diabetes. Magnetic resonance insights, 2012. 5: p. MRI. S10489. [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, D., et al., Impact of different ectopic fat depots on cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Journal of cellular physiology, 2019. 234(12): p. 21630-21641. [CrossRef]
- Vermathen, P., et al., Skeletal muscle 1H MRSI before and after prolonged exercise. I. muscle specific depletion of intramyocellular lipids. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 2012. 68(5): p. 1357-1367. [CrossRef]
- Brumbaugh, D.E., et al., Intramyocellular lipid is associated with visceral adiposity, markers of insulin resistance, and cardiovascular risk in prepubertal children: the EPOCH study. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2012. 97(7): p. E1099-E1105. [CrossRef]

| Metabolites ↓ | Muscle | T2DM Mean ± SD |
AMHC Mean ± SD |
YHC Mean ± SD |
P value T2DM vs. AMHC |
P value AMHC vs. YHC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ch_d | GAS SOL TA |
1.15 ± 0.28 1.00 ± 0.32 1.13 ± 0.91 |
1.02 ± 0.13 1.21 ± 0.54 0.58 ± 0.22 |
0.63 ± 0.36 0.43 ± 0.30 1.26 ± 1.01 |
0.274 0.280 0.097 |
0.013 0.001 0.066 |
| EMCL1 | GAS SOL TA |
0.07 ± 0.05 0.11 ± 0.06 0.12 ± 0.07 |
0.07 ± 0.05 0.08 ± 0.06 0.12 ± 0.07 |
0.09 ± 0.08 0.04 ± 0.02 0.15 ± 0.14 |
0.910 0.368 0.994 |
0.524 0.049 0.660 |
| EMCL2 | GAS SOL TA |
0.12 ± 0.09 0.15 ± 0.09 0.20 ± 0.12 |
0.11 ± 0.05 0.14 ± 0.09 0.21 ± 0.13 |
0.16 ± 0.12 0.10 ± 0.07 0.28 ± 0.26 |
0.815 0.735 0.926 |
0.296 0.294 0.497 |
| Avg EMCL | GAS SOL TA |
0.09 ± 0.07 0.13 ± 0.07 0.16 ± 0.08 |
0.09 ± 0.05 0.11 ± 0.07 0.17 ± 0.10 |
0.12 ± 0.09 0.07 ± 0.05 0.22 ± 0.20 |
0.847 0.549 0.940 |
0.367 0.141 0.550 |
| EMCL UI | GAS SOL TA |
1.68 ± 0.68 1.59 ± 0.91 1.36 ± 0.41 |
1.72 ± 0.52 1.89 ± 0.85 1.51 ± 0.53 |
1.87 ± 0.48 2.49 ± 0.75 2.00 ± 0.59 |
0.895 0.452 0.478 |
0.580 0.119 0.076 |
| IMCL1 | GAS SOL TA |
0.02 ± 0.02 0.02 ± 0.02 0.01 ± 0.01 |
0.01 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.01 |
0.01 ± 0.00 0.01 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.02 |
0.410 0.248 0.817 |
0.111 0.106 0.191 |
| IMCL2 | GAS SOL TA |
0.02 ± 0.03 0.04 ± 0.03 0.02 ± 0.01 |
0.01 ± 0.00 0.02 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 |
0.02 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 |
0.385 0.275 0.888 |
0.591 0.027 0.172 |
| Avg IMCL | GAS SOL TA |
0.02 ± 0.02 0.03 ± 0.03 0.02 ± 0.01 |
0.01 ± 0.00 0.02 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.01 |
0.01 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 |
0.386 0.252 0.832 |
0.835 0.037 0.121 |
| IMCL UI | GAS SOL TA |
1.31 ± 0.46 1.52 ± 0.53 1.48 ± 0.68 |
1.34 ± 0.49 1.79 ± 0.81 1.66 ± 1.18 |
2.16 ± 1.10 1.85 ± 0.66 1.76 ± 1.23 |
0.902 0.369 0.684 |
0.074 0.856 0.859 |
| Car | GAS SOL TA |
0.01 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.02 |
0.01 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.02 |
0.01 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 |
0.894 0.597 0.938 |
0.345 0.077 0.300 |
| Tau | GAS SOL TA |
0.19 ± 0.24 0.16 ± 0.09 0.33 ± 0.79 |
0.13 ± 0.06 0.14 ± 0.06 0.11 ± 0.11 |
0.10 ± 0.09 0.16 ± 0.07 0.34 ± 0.33 |
0.538 0.570 0.430 |
0.371 0.451 0.061 |
| mI | GAS SOL TA |
0.06 ± 0.03 0.07 ± 0.02 0.10 ± 0.10 |
0.05 ± 0.02 0.05 ± 0.02 0.06 ± 0.05 |
0.03 ± 0.02 0.07 ± 0.07 0.25 ± 0.26 |
0.257 0.067 0.336 |
0.009 0.501 0.049 |
| Cr_3.9 | GAS SOL TA |
0.37 ± 0.13 0.29 ± 0.07 0.46 ± 0.48 |
0.30 ± 0.08 0.29 ± 0.06 0.27 ± 0.23 |
0.21 ± 0.10 0.43 ± 0.30 0.82 ± 0.64 |
0.233 0.941 0.292 |
0.060 0.170 0.026 |
| TGFR1 | GAS SOL TA |
0.03 ± 0.02 0.07 ± 0.06 0.14 ± 0.09 |
0.03 ± 0.03 0.11 ± 0.16 0.22 ± 0.18 |
0.16 ± 0.17 0.06 ± 0.08 0.29 ± 0.35 |
0.989 0.400 0.211 |
0.062 0.407 0.633 |
| TGFR2 | GAS SOL TA |
0.02 ± 0.02 0.01 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 |
0.02 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.01 0.03 ± 0.01 |
0.03 ± 0.03 0.02 ± 0.02 0.04 ± 0.03 |
0.941 0.622 0.030 |
0.142 0.754 0.252 |
| FAT_1.4 | GAS SOL TA |
11.85 ± 5.62 15.11 ± 6.69 15.77 ± 6.15 |
11.10 ± 5.36 10.76 ± 4.35 18.54 ± 5.85 |
9.63 ± 5.45 11.11 ± 9.34 21.84 ± 11.39 |
0.790 0.107 0.310 |
0.594 0.920 0.447 |
| FAT_5.4 | GAS SOL TA |
0.86 ± 0.46 1.17 ± 0.45 1.22 ± 0.44 |
0.73 ± 0.35 0.96 ± 0.41 1.81 ± 0.80 |
0.563 0.282 0.043 |
| IMCL_UI | Carnosine | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAS r, p value |
SOL r, p value |
TA r, p value |
GAS r, p value |
SOL r, p value |
TA r, p value |
|
| SAT | -0.36, p=0.379 | 0.15, p=0.705 | -0.06, p=0.886 | 0.75, p=0.034 | 0.44, p=0.234 | 0.40, p=0.281 |
| VAT | 0.11, p=0.797 | 0.29, p=0.449 | -0.16, p=0.705 | 0.83, p=0.012 | 0.71, p=0.033 | 0.69, p=0.041 |
| TAT | -0.13, p=0.755 | 0.24, p=0.535 | -0.12, p=0.775 | 0.85, p=0.007 | 0.63, p=0.068 | 0.60, p=0.089 |
| HFF | 0.07, p=0.872 | 0.45, p=0.230 | 0.35, p=0.395 | 0.44, p=0.274 | 0.30, p=0.44 | 0.05, p=0.901 |
| PFFHead | 0.63, p=0.129 | 0.25, p=0.559 | 0.57, p=0.179 | 0.10, p=0.838 | 0.12, p=0.774 | -0.16, p=0.7 |
| PFFBody+Tail | 0.30, p=0.508 | 0.64, p=0.086 | 0.58, p=0.177 | 0.54, p=0.213 | 0.57, p=0.136 | 0.20, p=0.635 |
| AvgPFF | 0.50, p=0.252 | 0.48, p=0.234 | 0.61, p=0.143 | 0.34, p=0.457 | 0.38, p=0.36 | 0.02, p=0.955 |
| HFF_MRS | 0.03, p=0.944 | 0.40, p=0.282 | 0.22, p=0.598 | 0.57, p=0.141 | 0.39, p=0.296 | 0.21, p=0.582 |
| R2_WAT | -0.09, p=0.831 | -0.53, p=0.141 | -0.59, p=0.127 | 0.10, p=0.823 | 0.04, p=0.91 | 0.31, p=0.416 |
| Taurine (Tau) | Myo-inositol (mI) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAS r, p value |
SOL r, p value |
TA r, p value |
GAS r, p value |
SOL r, p value |
TA r, p value |
|
| SAT | -0.22, p=0.601 | -0.14, p=0.722 | -0.38, p=0.311 | 0.07, p=0.864 | -0.12, p=0.762 | 0.04, p=0.921 |
| VAT | -0.23, p=0.582 | 0.24, p=0.540 | 0.03, p=0.944 | 0.34, p=0.411 | 0.02, p=0.969 | 0.17, p=0.656 |
| TAT | -0.25, p=0.559 | 0.05, p=0.902 | -0.20, p=0.601 | 0.23, p=0.590 | -0.06, p=0.880 | 0.12, p=0.768 |
| HFF | -0.18, p=0.678 | -0.05, p=0.904 | -0.16, p=0.687 | 0.64, p=0.087 | -0.22, p=0.575 | -0.22, p=0.567 |
| PFFHead | -0.22, p=0.637 | -0.23, p=0.593 | -0.30, p=0.476 | 0.57, p=0.184 | -0.33, p=0.422 | -0.46, p=0.253 |
| PFFBody+Tail | -0.18, p=0.705 | 0.24, p=0.576 | -0.41, p=0.319 | 0.85, p=0.016 | 0.21, p=0.615 | -0.42, p=0.300 |
| AvgPFF | -0.21, p=0.649 | 0.01, p=0.980 | -0.37, p=0.361 | 0.76, p=0.048 | -0.06, p=0.892 | -0.47, p=0.244 |
| HFF_MRS | -0.23, p=0.585 | -0.01, p=0.971 | -0.13, p=0.731 | 0.57, p=0.144 | -0.19, p=0.625 | -0.11, p=0.773 |
| R2_WAT | -0.34, p=0.408 | -0.32, p=0.407 | -0.03, p=0.943 | -0.64, p=0.087 | -0.38, p=0.318 | 0.23, p=0.561 |
| Blood chemistry | Lipid/metabolites and body fat | Correlation coefficient (r), p value |
|---|---|---|
| HbA1c | EMCL2 (TA) avgEMCL (TA) EMCLUI (SOL) IMCLUI (TA) Car (SOL) Car (TA) Cr_3.9 (SOL) TGFR1 (TA) R2_WAT |
0.73, p=0.039 0.70, p=0.055 0.64, p=0.065 -0.63, p=0.094 0.59, p=0.098 0.65, p=0.056 0.60, p=0.088 0.77, p=0.015 0.62, p=0.073 |
| Triglycerides | Ch_d (SOL) | 0.59, p=0.096 |
| CHOLDL | Ch_d (GAS) IMCLUI (TA) mI (GAS) Cr_3.9 (GAS) R2_WAT |
-0.62, p=0.098 -0.74, p=0.037 -0.68, p=0.062 -0.72, p=0.045 0.94, p=0.0001 |
| Cre | EMCLUI (GAS) EMCLUI (SOL) avgIMCL (GAS) |
0.77, p=0.071 -0.76, p=0.048 -0.89, p=0.044 |
| Glc | Ch_d (SOL) EMCL1 (TA) IMCLUI (GAS) SAT |
0.70, p=0.082 0.75, p=0.085 0.78, p=0.067 -0.71, p=0.075 |
| CHO | mI (SOL) R2_WAT |
-0.79, p=0.061 0.95, p=0.004 |
| CHOHDL | EMCLUI (TA) Cr_3.9 (SOL) TGFR1 (SOL) SAT TAT |
0.80, p=0.058 -0.96, p=0.003 0.83, p=0.043 0.83, p=0.042 0.84, p=0.037 |
| NHDLCHO | EMCL2 (TA) R2_WAT |
0.85, p=0.068 0.97, p=0.001 |
| AST | EMCL1 (GAS) EMCL1 (SOL) EMCL2 (GAS) avgEMCL (GAS) IMCLUI (TA) Car (SOL) Tau (GAS) TGFR1 (GAS) FAT_1.4 (SOL) |
-0.91, p=0.095 -0.82, p=0.09 -0.94, p=0.063 -0.95, p=0.055 0.86, p=0.06 0.90, p=0.036 0.93, p=0.066 -0.92, p=0.084 -0.89, p=0.042 |
| ALT | EMCLUI (GAS) IMCL2 (TA) VAT HFF HFF_MRS |
0.93, p=0.066 -0.97, p=0.033 0.96, p=0.011 0.88, p=0.049 0.90, p=0.038 |
| AP | TGFR1 (TA) R2_WAT |
0.92, p=0.028 0.91, p=0.034 |
| TB | EMCLUI (SOL) IMCL2 (GAS) Cr_3.9 (SOL) |
-0.87, p=0.057 -0.99, p=0.083 -0.84, p=0.076 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





