Submitted:
17 September 2024
Posted:
18 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
Study Area
2. Materials and Methods
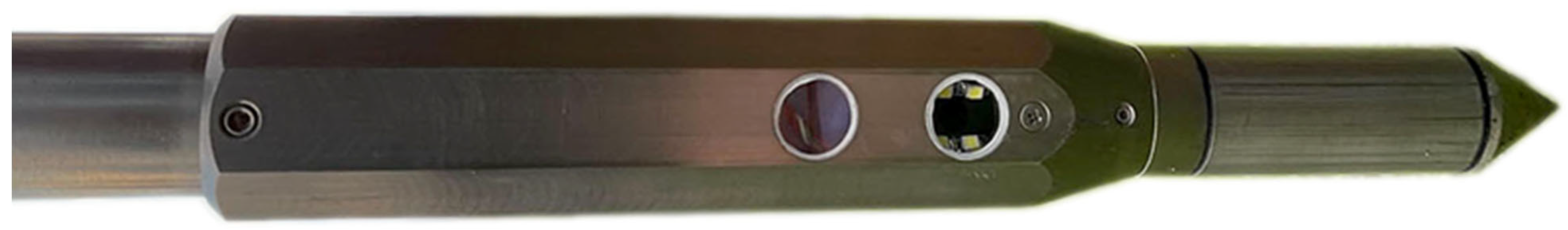
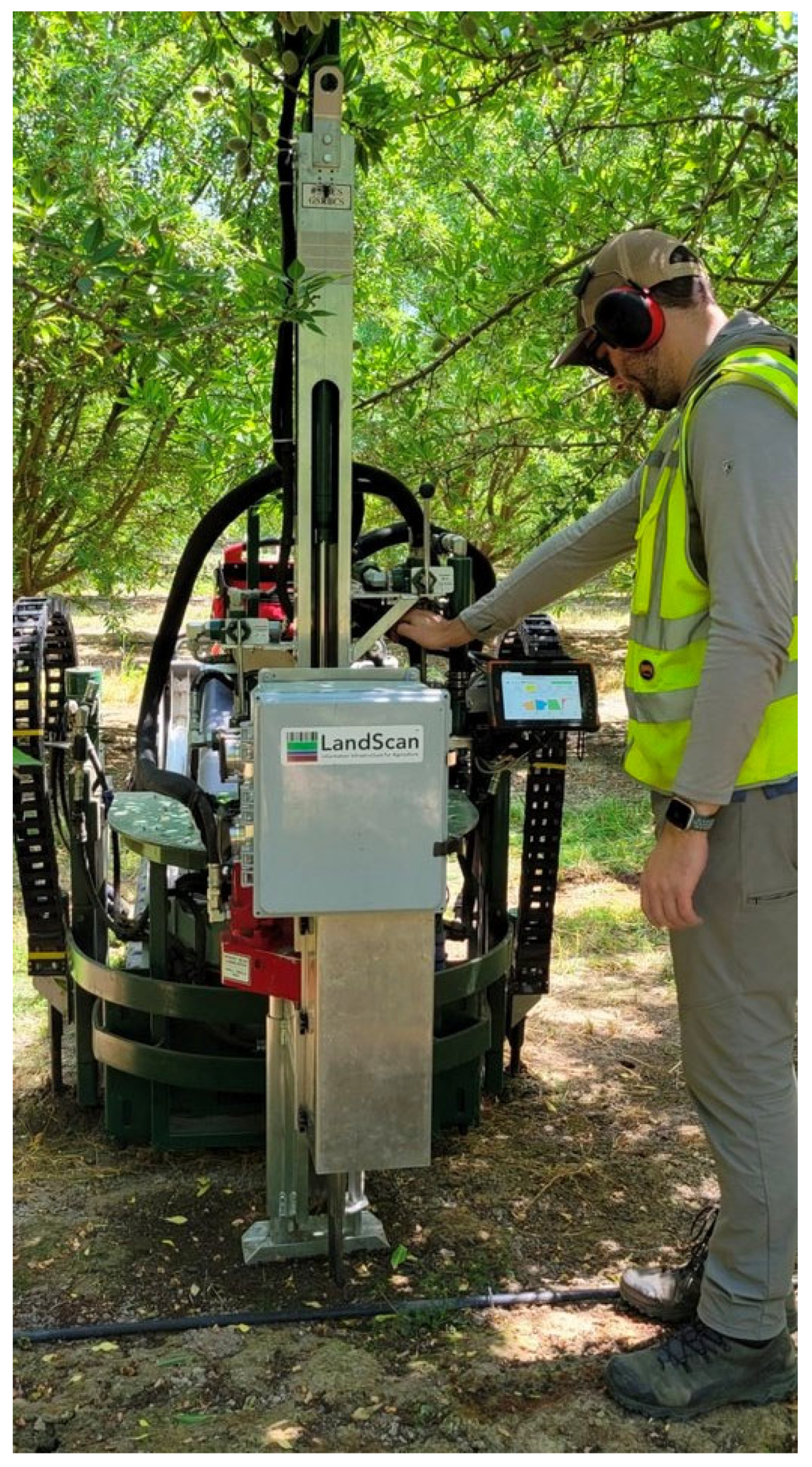
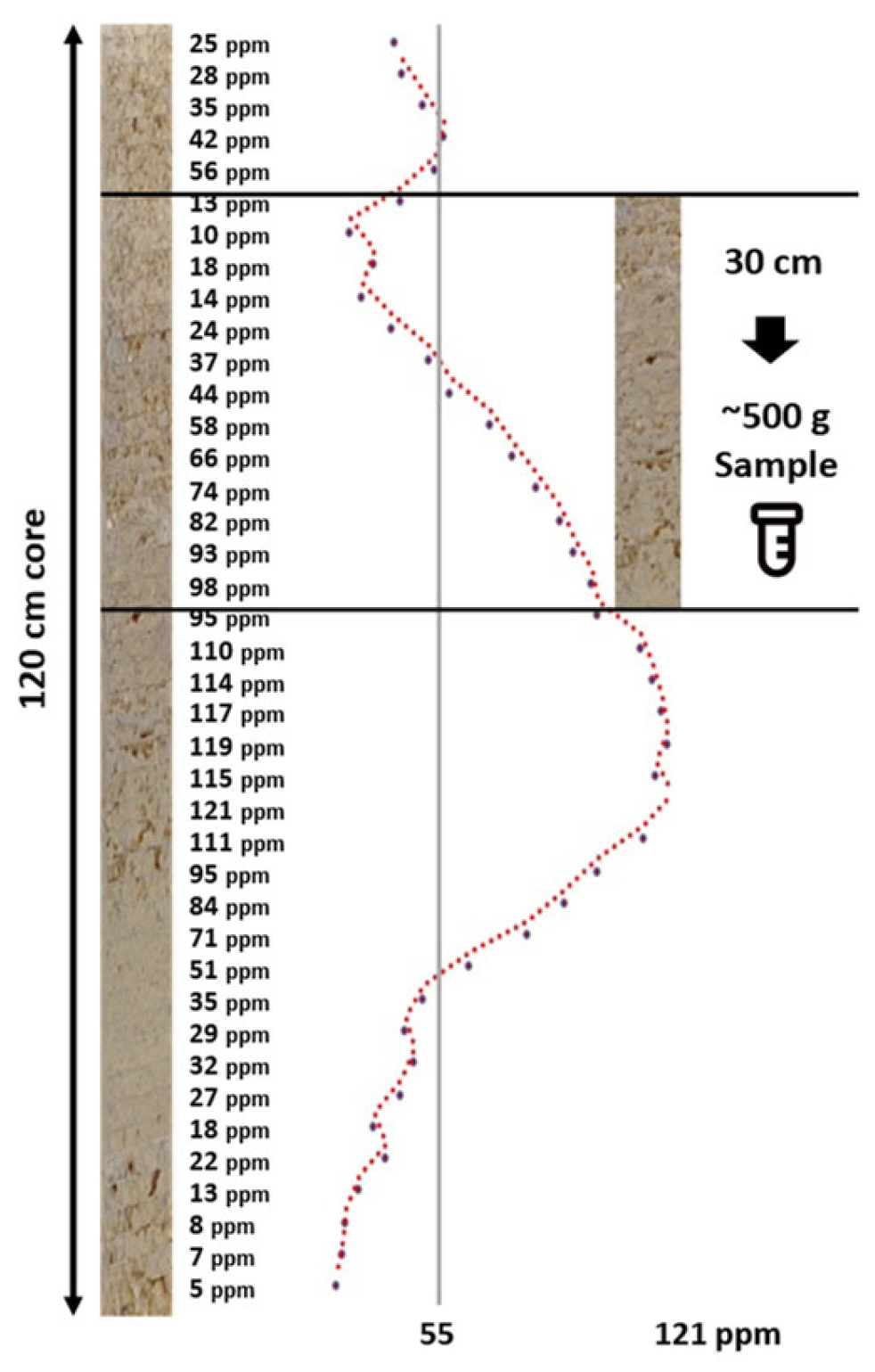
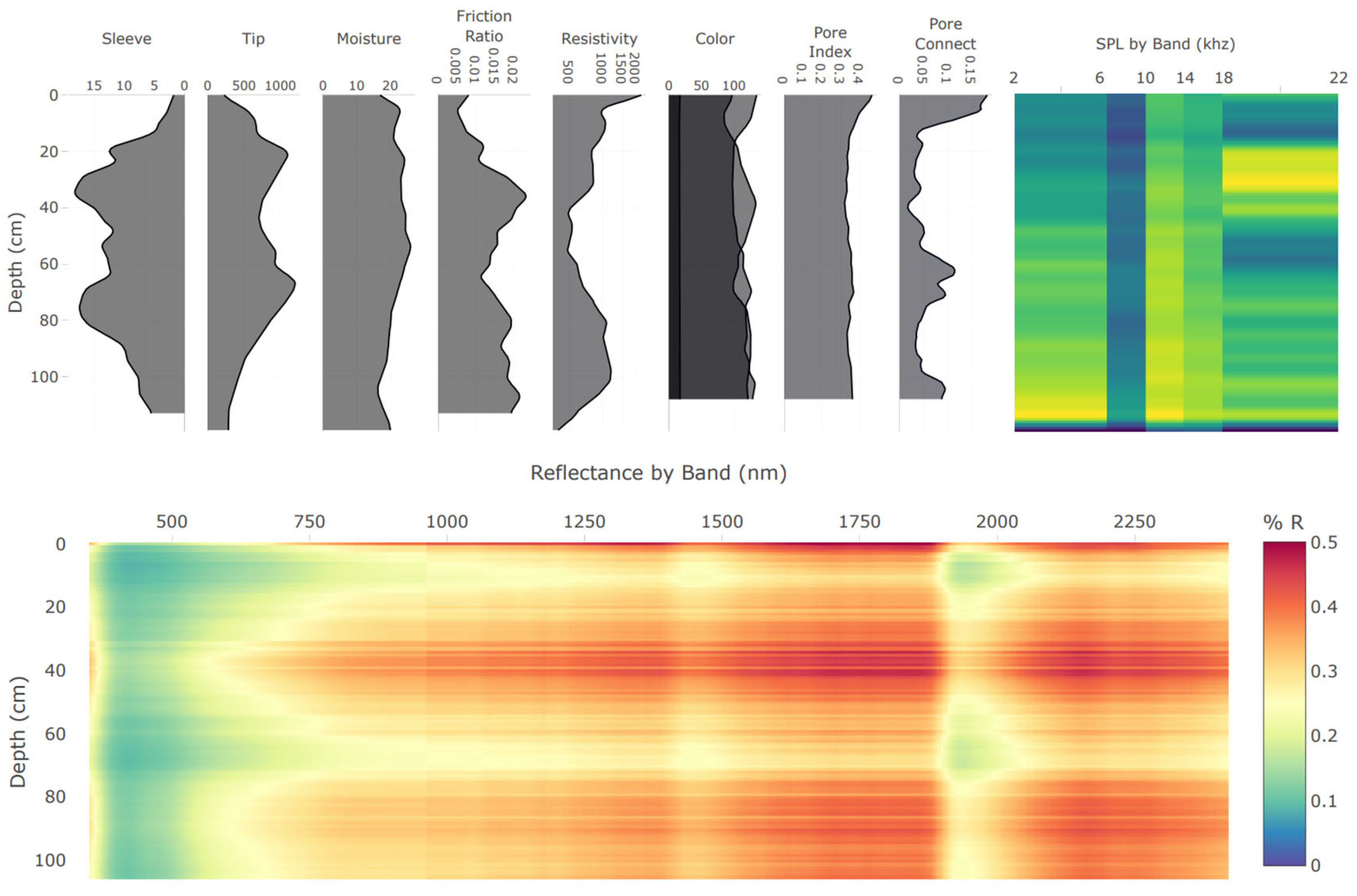
2.1. Digital Soil Core System and Probe
2.2.1. Soil Data Collection
2.2.2. Crop Data Collection
2.3. Data Pre-Processing and Harmonization
2.4. Spectral Data Processing
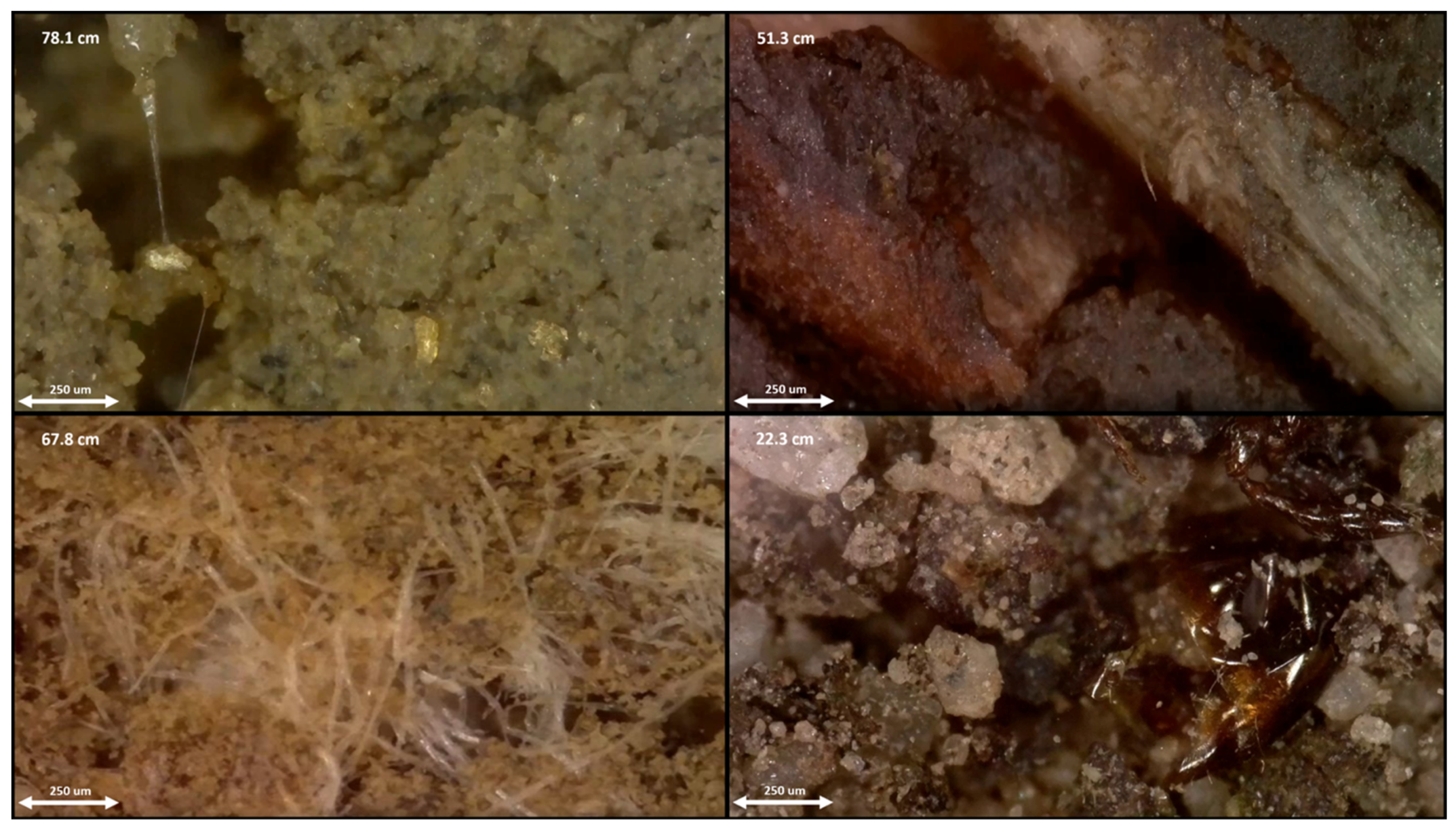
2.5. Processing of Digital Soil Images
2.6. Processing of Audio Data
2.7. Processing of Other Sensor Data
2.8. Data Feature Selection
2.9. Comparison of Training Methods
2.10. Modeling Approach
3. Results
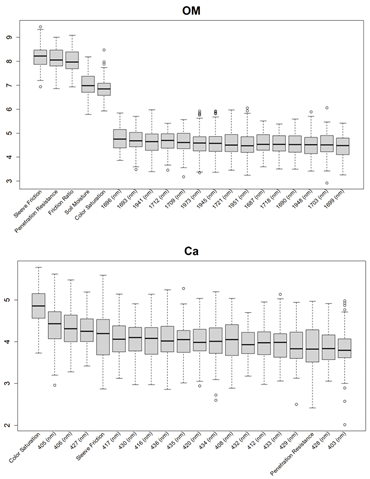
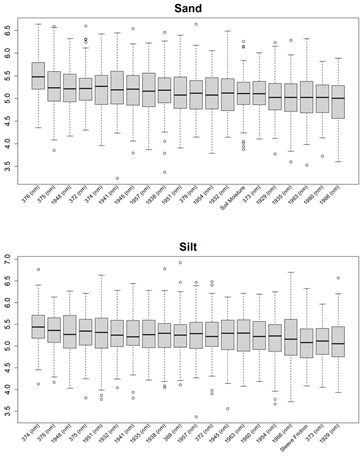
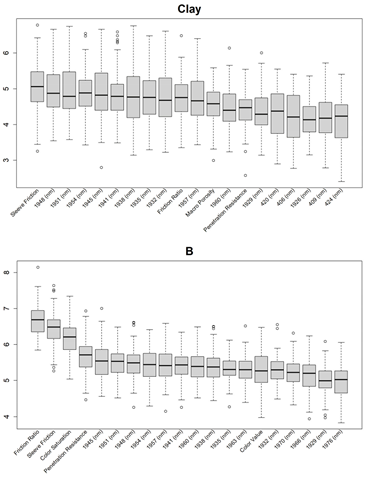
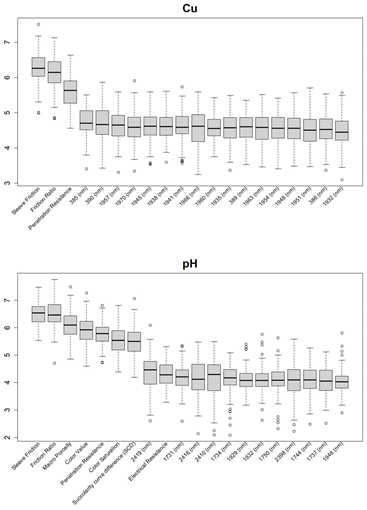
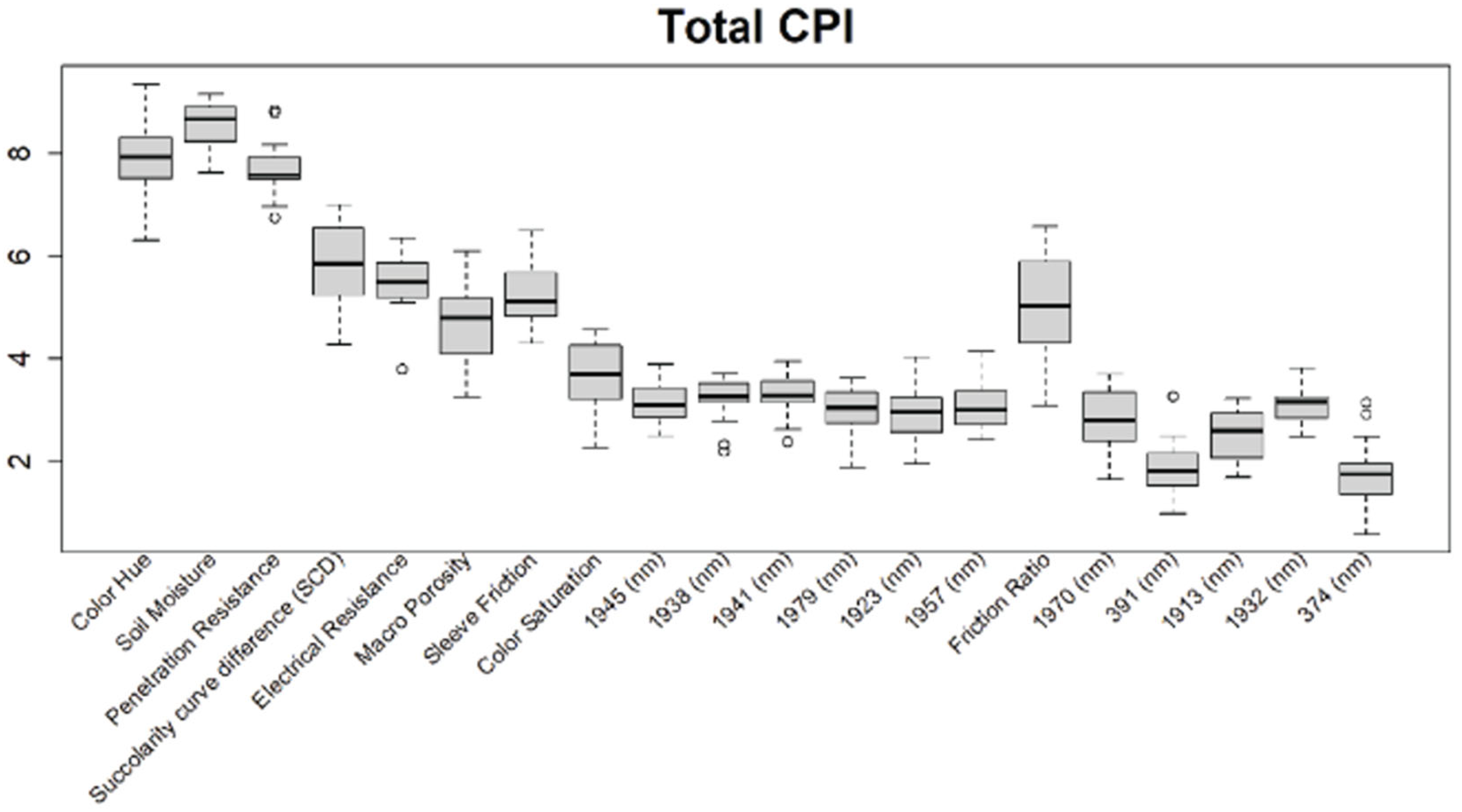
3.1. Feature Selections for Modeling
3.2. Predictive Accuracy of Soil Properties Modeling Methods
3.3. In situ DSC System to Ex situ Laboratory Properties to Digital Crop Performance vs. DSC System to DVS Digital Crop Performance.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Paustian, K., Lehmann, J., Ogle, S., Reay, D., Robertson, G. P., & Smith, P. (2016). Climate-smart soils. Nature, 532(7597). [CrossRef]
- Paustian, K., Larson, E., Kent, J., Marx, E., & Swan, A. (2019). Soil C sequestration as a biological negative emission strategy. Frontiers in Climate, 1, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Verdouw, C., Tekinerdogan, B., Beulens, A., & Wolfert, S. (2021). Digital twins in smart farming. Agricultural Systems, 189, 103046. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E., Heller, D., & Chudnovsky, A. (2008). A novel method of classifying soil profiles in the field using optical means. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 72, 1113–1123. [CrossRef]
- Rooney, D., & Lowery, B. (2000). A profile cone penetrometer for mapping soil horizons. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 64, 2136–2139. [CrossRef]
- Rooney, D. J., Norman, J., & Grunwald, S. (2001). Soil imaging penetrometer: A tool for obtaining real-time-in-situ soil images. In ASAE Annual Meeting, Sacramento, CA. 29 July–1 Aug. 2001. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers.
- Poggio, M., Brown, D. J., & Bricklemyer, R. S. (2015). Laboratory-based evaluation of optical performance for a new soil penetrometer visible and near-infrared (VisNIR) foreoptic. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 115, 12–20. [CrossRef]
- Grunwald, S. (2022). Artificial intelligence and soil carbon modeling demystified: Power, potentials, and perils. Carbon Footprints, 1(5), 1–23. [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R. A., Adamchuk, V. I., Sudduth, K. A., McKenzie, N. J., & Lobsey, C. (2011). Proximal soil sensing: An effective approach for soil measurements in space and time. In Advances in Agronomy (Vol. 113, pp. 243–291). Elsevier. Available online: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780123864734000051.
- Brown, D. J., Shepherd, K. D., Walsh, M. G., Mays, M. D., & Reinsch, T. G. (2006). Global soil characterization with VNIR diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Geoderma, 132(3–4), 273–290. [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R. A., Behrens, T., Ben-Dor, E., Brown, D. J., Demattê, J. A. M., Shepherd, K. D., Shi, Z., Stenberg, B., Stevens, A., Adamchuk, V., Aïchi, H., Barthès, B. G., Bartholomeus, H. M., Bayer, A. D., Bernoux, M., Böttcher, K., Brodský, L., Du, C. W., Chappell, A., ... Ji, W. (2016). A global spectral library to characterize the world’s soil. Earth-Science Reviews, 155, 198–230. [CrossRef]
- Knox, N. M., Grunwald, S., McDowell, M. L., Bruland, G. L., Myers, D. B., & Harris, W. G. (2015). Modelling soil carbon fractions with visible near-infrared (VNIR) and mid-infrared (MIR) spectroscopy. Geoderma, 239–240, 229–239. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X., Zhao, D., Wang, J., & Triantafilis, J. (2022). Soil organic carbon (SOC) prediction in Australian sugarcane fields using Vis–NIR spectroscopy with different model setting approaches. Geoderma Regional, 30(e00566), 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Clingensmith, C. M., & Grunwald, S. (2022). Predicting soil properties and interpreting Vis-NIR models from across continental United States. Sensors, 22(3187), 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Ng, W., Minasny, B., Montazerolghaem, M., Padarian, J., Ferguson, R., Bailey, S., & McBratney, A. B. (2019). Convolutional neural network for simultaneous prediction of several soil properties using visible/near-infrared, mid-infrared, and their combined spectra. Geoderma, 352, 251–267. [CrossRef]
- Demattê, J. A. M., Paiva, A. F. S., Poppiel, R. R., Rosin, N. A., Ruiz, L. F. C., Mello, F. A. O., Minasny, B., Grunwald, S., Ge, Y., Ben Dor, E., Gholizadeh, A., Gomez, C., Chabrillat, S., Francos, N., Ayoubi, S., Fiantis, D., Biney, J. K. M., Wang, C., Belal, A., Silvero, N. E. Q. (2022). The Brazilian Soil Spectral Service (BraSpecS): A user-friendly system for global soil spectra communication. Remote Sensing, 14(740), 1–28. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z., Wang, Q. L., Peng, J., Ji, W., Liu, H., Li, X., & Viscarra Rossel, R. A. (2014). Development of a national VNIR soil-spectral library for soil classification and prediction of organic matter concentrations. Science China Earth Sciences, 57(7), 1671–1680. [CrossRef]
- Baumann, P., Helfenstein, A., Gubler, A., Keller, A., Meuli, R. G., Wächter, D., Lee, J., Viscarra Rossel, R., & Six, J. (2021). Developing the Swiss mid-infrared soil spectral library for local estimation and monitoring. SOIL, 7(2), 525–546. [CrossRef]
- Wijewardane, N. K., Ge, Y., & Morgan, C. L. S. (2016). Prediction of soil organic and inorganic carbon at different moisture contents with dry ground VNIR: A comparative study of different approaches. European Journal of Soil Science, 67(5), 605–615. [CrossRef]
- Karray, E., Elmannai, H., Toumi, E., Gharbia, M. H., Meshoul, S., & Ben Rabah, Z. (2023). Evaluating the potentials of PLSR and SVR models for soil properties prediction using field imaging, laboratory VNIR spectroscopy and their combination. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci, 136, 1399–1425. [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B., McBratney, A. B., Tranter, G., & Murphy, B. W. (2008). Using soil knowledge for the evaluation of mid-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for predicting soil physical and mechanical properties. European Journal of Soil Science, 59(5), 960–971. [CrossRef]
- Tsimpouris, E., Tsakiridis, N. L., & Theocharis, J. B. (2021). Using autoencoders to compress soil VNIR–SWIR spectra for more robust prediction of soil properties. Geoderma, 393, 114967. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N., Hong, J., Song, B., Wu, S., Wei, Y., & Wang, T. (2024). Feature variable selection based on VIS-NIR spectra and soil moisture content prediction model construction. Journal of Spectroscopy, 2024, e8180765. [CrossRef]
- Dangal, S. R. S., Sanderman, J., Wills, S., & Ramirez-Lopez, L. (2019). Accurate and precise prediction of soil properties from a large mid-infrared spectral library. Soil Systems, 3(1), Article 1. [CrossRef]
- Davari, M., Karimi, S. A., Bahrami, H. A., Hammond, S. M., & Fahmideh, S. (2021). Simultaneous prediction of several soil properties related to engineering uses based on laboratory Vis-NIR reflectance spectroscopy. CATENA, 197, 104987. [CrossRef]
- Grunwald, S., Rooney, D. J., McSweeney, K., & Lowery, B. (2001). Development of pedotransfer functions for a profile cone penetrometer. Geoderma, 100(1–2), 25–47. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P., Mondal, S., Roy, D., Meena, M., Aggarwal, B., Sharma, A., Behera, U., Das, T., Jatav, R., & Chakraborty, D. (2020). Exploring the relationships between penetration resistance, bulk density, and water content in cultivated soils. Journal of Agricultural Physics, 20(1), 22.
- Viscarra Rossel, R. A., Lobsey, C. R., Sharman, C., Flick, P., & McLachlan, G. (2017). Novel proximal sensing for monitoring soil organic C stocks and condition. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(10), 5630–5641. [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R. A., McBratney, A. B., & Minasny, B. (2010). Proximal soil sensing (Progress in soil science). Springer.
- Pasquini, C. (2018). Near infrared spectroscopy: A mature analytical technique with new perspectives – A review. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1026, 8–36. [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A. Gholizadeh, A., Borůvka, L., Saberioon, M., & Vašát, R. (2013). Visible, near-infrared, and mid-infrared spectroscopy applications for soil assessment with emphasis on soil organic matter content and quality: State-of-the-art and key issues. Applied Spectroscopy, 67(12), 1349–1362. [CrossRef]
- Gubler, A. (2012). Quantitative estimations of soil properties by VNIR spectroscopy: Applications for laboratory and field measurements. Südwestdeutscher Verlag für Hochschulschriften.
- Maia, C. M. B. F., Novotny, E. H., Rittl, T. F., & Hayes, M. H. B. (2013). Soil organic matter: Chemical and physical characteristics and analytical methods. A review. Current Organic Chemistry, 17(24), 2985–2990. [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, B., Viscarra Rossel, R. A., Mouazen, A. M., & Wetterlind, J. (2010). Chapter five—Visible and near infrared spectroscopy in soil science. In D. L. Sparks (Ed.), Advances in Agronomy (Vol. 107, pp. 163–215). Academic Press. [CrossRef]
- Bowers, S. A., & Hanks, R. J. (1965). Reflection of radiant energy from soils. Soil Science, 100(2), 130–138. [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G. R., & Vincent, R. K. (1968). The behavior of spectral features in the infrared emission from particulate surfaces of various grain sizes. Journal of Geophysical Research, 73(18), 6039–6046. [CrossRef]
- Bänninger, D., Lehmann, P., & Flühler, H. (2006). Modelling the effect of particle size, shape and orientation of light transfer through porous media. European Journal of Soil Science, 57(6), 906–915. [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M., Babaeian, E., Tuller, M., & Jones, S. B. (2018). Particle size effects on soil reflectance explained by an analytical radiative transfer model. Remote Sensing of Environment, 210, 375–386. [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, S., Sadeghi, M., Liaghat, A., Tuller, M., Jones, S. B., & Ebrahimian, H. (2021). Information depth of NIR/SWIR soil reflectance spectroscopy. Remote Sensing of Environment, 256, 112315. [CrossRef]
- Cierniewski, J., Gdala, T., & Karnieli, A. (2004). A hemispherical–directional reflectance model as a tool for understanding image distinctions between cultivated and uncultivated bare surfaces. Remote Sensing of Environment, 90(4), 505-523. [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. Y., Jacobson, A. R., Laba, M., & Baveye, P. C. (2009). Alleviating moisture content effects on the visible near-infrared diffuse-reflectance sensing of soils. Soil Science, 174(8), 456. [CrossRef]
- Piekarczyk, J., Kaźmierowski, C., Królewicz, S., & Cierniewski, J. (2016). Effects of soil surface roughness on soil reflectance measured in laboratory and outdoor conditions. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 9(2), 827-834. [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, T., Balafoutis, A., Zalidis, G., & Bochtis, D. (2020). From laboratory to proximal sensing spectroscopy for soil organic carbon estimation—A review. Sustainability, 12(443), Article 2. [CrossRef]
- Hedley, C., Roudier, P., & Maddi, L. (2015). VNIR soil spectroscopy for field soil analysis. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 46(sup1), 104–121. [CrossRef]
- Chang, C. W., Laird, D. A., & Hurburgh, C. R. J. (2005). Influence of soil moisture on near-infrared reflectance spectroscopic measurement of soil properties. Soil Science, 170(4), 244. [CrossRef]
- Rienzi, E. A., Mijatovic, B., Mueller, T. G., Matocha, C. J., Sikora, F. J., & Castrignanò, A. M. (2014). Prediction of soil organic carbon under varying moisture levels using reflectance spectroscopy. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 78(3), 958–967. [CrossRef]
- Seidel, M., Vohland, M., Greenberg, I., Ludwig, B., Ortner, M., Thiele-Bruhn, S., & Hutengs, C. (2022). Soil moisture effects on predictive VNIR and MIR modeling of soil organic carbon and clay content. Geoderma, 427, 116103. [CrossRef]
- Knadel, M., Castaldi, F., Barbetti, R., Ben-Dor, E., Gholizadeh, A., & Lorenzetti, R. (2023). Mathematical techniques to remove moisture effects from visible–near-infrared–shortwave-infrared soil spectra—Review. Applied Spectroscopy Reviews, 58(9), 629–662. [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D. B., & Asner, G. P. (2002). Moisture effects on soil reflectance. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 66(3), 722–727. [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y., Jiang, Q., Yu, L., Liu, H., & Zhang, B. (2021). Reducing the moisture effect and improving the prediction of soil organic matter with VIS-NIR spectroscopy in black soil area. IEEE Access, 9, 5895–5905. [CrossRef]
- Cambou, A., Allory, V., Cardinael, R., Vieira, L. C., & Barthes, B. G. (2021). Comparison of soil organic carbon stocks predicted using visible and near infrared reflectance (VNIR) spectra acquired in situ vs. on sieved dried samples: Synthesis of different studies. Soil Security, 5, 100024. [CrossRef]
- Dhawale, N. M., Adamchuk, V. I., Prasher, S. O., & Viscarra Rossel, R. A. (2021). Evaluating the precision and accuracy of proximal soil vis–NIR sensors for estimating soil organic matter and texture. Soil Systems, 5(3), 48. [CrossRef]
- Hutengs, C., Ludwig, B., Jung, A., Eisele, A., & Vohland, M. (2018). Comparison of portable and bench-top spectrometers for mid-infrared diffuse reflectance measurements of soils. Sensors, 18(4), 993. [CrossRef]
- Hutengs, C., Seidel, M., Oertel, F., Ludwig, B., & Vohland, M. (2019). In situ and laboratory soil spectroscopy with portable visible-to-near-infrared and mid-infrared instruments for the assessment of organic carbon in soils. Geoderma, 355, 113900. [CrossRef]
- Hutengs, C., Eisenhauer, N., Schaedler, M., Lochner, A., Seidel, M., & Vohland, M. (2021). VNIR and MIR spectroscopy of PLFA-derived soil microbial properties and associated soil physicochemical characteristics in an experimental plant diversity gradient. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 160, 108319. [CrossRef]
- Semella, S., Hutengs, C., Seidel, M., Ulrich, M., Schneider, B., Ortner, M., Thiele-Bruhn, S., Ludwig, B., & Vohland, M. (2022). Accuracy and reproducibility of laboratory diffuse reflectance measurements with portable VNIR and MIR spectrometers for predictive soil organic carbon modeling. Sensors, 22(7), 2749. [CrossRef]
- Sharififar, A., Sarmadian, F., Malone, B. P., & Minasny, B. (2019). Addressing the issue of digital mapping of soil classes with imbalanced class observations. Geoderma, 350, 84–92. [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, D. J., Kane, D. A., Dhakal, K., Covey, K. R., Bettigole, C., Hanle, J., Ortega-S, J. A., Perotto-Baldivieso, H. L., Fox, W. E., & Tolleson, D. R. (2022). Can low-cost, handheld spectroscopy tools coupled with remote sensing accurately estimate soil organic carbon in semi-arid grazing lands? Soil Systems, 6(2), 38. [CrossRef]
- Mitu, S. M., Smith, C., Sanderman, J., Ferguson, R. R., Shepherd, K., & Ge, Y. (2023). Evaluating consistency across multiple NeoSpectra (compact Fourier transform near-infrared) spectrometers for estimating common soil properties. Soil Science Society of America Journal, Nov. 2023, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Murad, M. O. F., Ackerson, J., Tolles, C., Meissner, K., Morgan, C. L. S., & Ge, Y. (2023). Estimating soil organic carbon content at variable moisture contents using a low-cost spectrometer. Geoderma, 440, 116723. [CrossRef]
- Murad, M. O. F., Jones, E. J., Minasny, B., McBratney, A. B., Wijewardane, N., & Ge, Y. (2022). Assessing a VisNIR penetrometer system for in-situ estimation of soil organic carbon under variable soil moisture conditions. Biosystems Engineering, 224, 197–212. [CrossRef]
- Grunwald, S., Vasques, G. M., & Rivero, R. G. (2015). Fusion of soil and remote sensing data to model soil properties. Advances in Agronomy, 131, 1–109. [CrossRef]
- Farzamian, M., Paz, M. C., Paz, A. M., Castanheira, N. L., Gonçalves, M. C., Monteiro Santos, F. A., & Triantafilis, J. (2019). Mapping soil salinity using electromagnetic conductivity imaging—A comparison of regional and location-specific calibrations. Land Degradation & Development, 30(12), 1393–1406. [CrossRef]
- Tavares, T. R., Nunes, L. C., Alves, E. E. N., Almeida, E., Maldaner, L. F., Krug, F. J., Carvalho, H. W. P., & Molin, J. P. (2019). Simplifying sample preparation for soil fertility analysis by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Sensors, 19(23), Article 5066. [CrossRef]
- Schmidinger, J., Barkov, V., Tavakoli, H., Correa, J. E., Ostermann, M., Atzmueller, M., Gebbers, R., & Vogel, S. (2024). Which and how many soil sensors are ideal to predict key soil properties: A case study with seven sensors. SSRN Scholarly Paper, 4844780. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y., Gao, S., Jones, E. J., & Singh, B. (2021). Prediction of soil clay content and cation exchange capacity using visible near-infrared spectroscopy, portable X-ray fluorescence, and X-ray diffraction techniques. Environmental Science & Technology, 55(8), 4629–4637. [CrossRef]
- Tavares, T. R., Molin, J. P., Nunes, L. C., Wei, M. C. F., Krug, F. J., de Carvalho, H. W. P., & Mouazen, A. M. (2021). Multi-sensor approach for tropical soil fertility analysis: Comparison of individual and combined performance of VNIR, XRF, and LIBS spectroscopies. Agronomy, 11(6), Article 6. [CrossRef]
- Xu, D., Zhao, R., Li, S., Chen, S., Jiang, Q., Zhou, L., & Shi, Z. (2019). Multi-sensor fusion for the determination of several soil properties in the Yangtze River Delta, China. European Journal of Soil Science, 70(1), 162–173. [CrossRef]
- Vasques, G. M., Rodrigues, H. M., Coelho, M. R., Baca, J. F. M., Dart, R. O., Oliveira, R. P., Teixeira, W. G., & Ceddia, M. B. (2020). Field proximal soil sensor fusion for improving high-resolution soil property maps. Soil Systems, 4(3), 52. [CrossRef]
- Yurui, S., Schulze Lammers, P., Daokun, M., Jianhui, L., & Qingmeng, Z. (2008). Determining soil physical properties by multi-sensor technique. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 147(1), 352–357. [CrossRef]
- Milella, A., Reina, G., & Nielsen, M. (2019). A multi-sensor robotic platform for ground mapping and estimation beyond the visible spectrum. Precision Agriculture, 20(2), 423–444. [CrossRef]
- Balan, T., Dumitru, C., Dudnik, G., Alessi, E., Lesecq, S., Correvon, M., Passaniti, F., & Licciardello, A. (2020). Smart multi-sensor platform for analytics and social decision support in agriculture. Sensors, 20(15), Article 15. [CrossRef]
- Van Wyck, N., Anderson, G., Farrington, S., Rooney, D., & Wallace, W. (2023). In-Situ Near Infrared Sensor Unit and Method of Making the Same. US Patent # 11,686,676. Issued June 2023.
- Topp, G. C., Davis, J. L., & Annan, A. P. (1980). Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: Measurements in coaxial transmission lines. Water Resources Research, 16(3), 574–582. [CrossRef]
- Ledieu, J., Ridder, P. D., Clerck, P. D., & Dautrebande, S. (1986). A method of measuring soil moisture by time-domain reflectometry. Journal of Hydrology, 88(3), 319-328. [CrossRef]
- Ferré, P. A., Rudolph, D. L., & Kachanoski, R. G. (1996). Spatial averaging of water content by time domain reflectometry: Implications for twin rod probes with and without dielectric coatings. Water Resources Research, 32(2), 271-279. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J. K., Villet, W. C. B., Tringale, P. T., & Chan, C. K. (1983). Acoustic penetrometer for subsoil investigation. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 74(3), 1095–1095. [CrossRef]
- Goktepe, A. B., Altun, S., & Sezer, A. (2005). Soil clustering by fuzzy c-means algorithm. Advances in Engineering Software, 36(10), 691–698. [CrossRef]
- Houlsby, G. T., & Ruck, B. M. (1998). Interpretation of signals from an acoustic cone penetrometer. In R. & M. (Eds.), Geotechnical Site Characterization (pp. 1-10). Rotterdam: Balkema.
- Paris, J., Unverferth, M., Farrington, S., Hull, M., Horton, R., & Rooney, D. (2023). Systems and Methods for Multispectral Landscape Mapping. US Patent # 11,800,246. Issued October 2023.
- Rooney, D., Dlott, J., Farrington, S., & Wallace, W. (2024). Precision site characterization using digital twin. US Patent # 12,092,625. Issued September 2024.
- Zhang, X., Pourreza, A., Cheung, K. H., Zuniga-Ramirez, G., Lampinen, B. D., & Shackel, K. A. (2021). Estimation of fractional photosynthetically active radiation from a canopy 3D model: Case study—Almond yield prediction. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12, 715361. [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A., & Golay, M. J. E. (1964). Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Analytical Chemistry, 36(8), 1627-1639. [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R. J., Dhanoa, M. S., & Lister, S. J. (1989). Standard normal variate transformation and de-trending of near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra. Applied Spectroscopy, 43(5), 772–777.
- de Melo, R. H. C., & Conci, A. (2008). Succolarity: Defining a method to calculate this fractal measure. 2008 15th International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing, 291–294. [CrossRef]
- de Melo, R. H. C., & Conci, A. (2013). How Succolarity could be used as another fractal measure in image analysis. Telecommunication Systems, 52(3), 1643–1655. [CrossRef]
- Leavitt, B., Pearce, A., Van Wyck, N., Kwayu, K., Courville, Z. R., Melendy, T. D., & Farrington, S. (2021). Use of a stable surrogate material and microscopy in the inference of bulk microstructural and strength properties of packed snow. Unpublished manuscript.
- Barrena-González, J., Gabourel-Landaverde, V. A., Mora, J., Contador, J. F. L., & Fernández, M. P. (2023). Exploring soil property spatial patterns in a small grazed catchment using machine learning. Earth Science Informatics, 16(4), 3811–3838. [CrossRef]
- Guindo, M. L., Kabir, M. H., Chen, R., & Liu, F. (2021). Potential of Vis-NIR to measure heavy metals in different varieties of organic-fertilizers using Boruta and deep belief network. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 228, 112996. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y., Wang, T., Xie, S., Liu, Z., Lin, C., Hu, Y., Wang, J., & Mao, X. (2023). Estimation of soil cations based on visible and near-infrared spectroscopy and machine learning. Agriculture, 13(6), 1237. [CrossRef]
- Kursa, M. B., & Rudnicki, W. R. (2010). Feature selection with the Boruta package. Journal of Statistical Software, 36, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J. H., & Friedman, J. H. (2009). The elements of statistical learning: Data mining, inference, and prediction (Vol. 2, pp. 1-758). New York: Springer.
- Beniston, J. W., Lal, R., & Mercer, K. L. (2016). Assessing and managing soil quality for urban agriculture in a degraded vacant lot soil. Land Degradation & Development, 27(4), 996–1006. [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.-P., Carrillo, Y., Pino, V., Minasny, B., & McBratney, A. B. (2018). Soil properties drive microbial community structure in a large-scale transect in South Eastern Australia. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 11725. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D., Arshad, M., Li, N., & Triantafilis, J. (2021). Predicting soil physical and chemical properties using vis-NIR in Australian cotton areas. CATENA, 196, 104938. [CrossRef]
- Wijewardane, N. K., Ge, Y., Wills, S., & Loecke, T. (2016). Prediction of soil carbon in the conterminous United States: Visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy analysis of the Rapid Carbon Assessment Project. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 80, 973–982. [CrossRef]
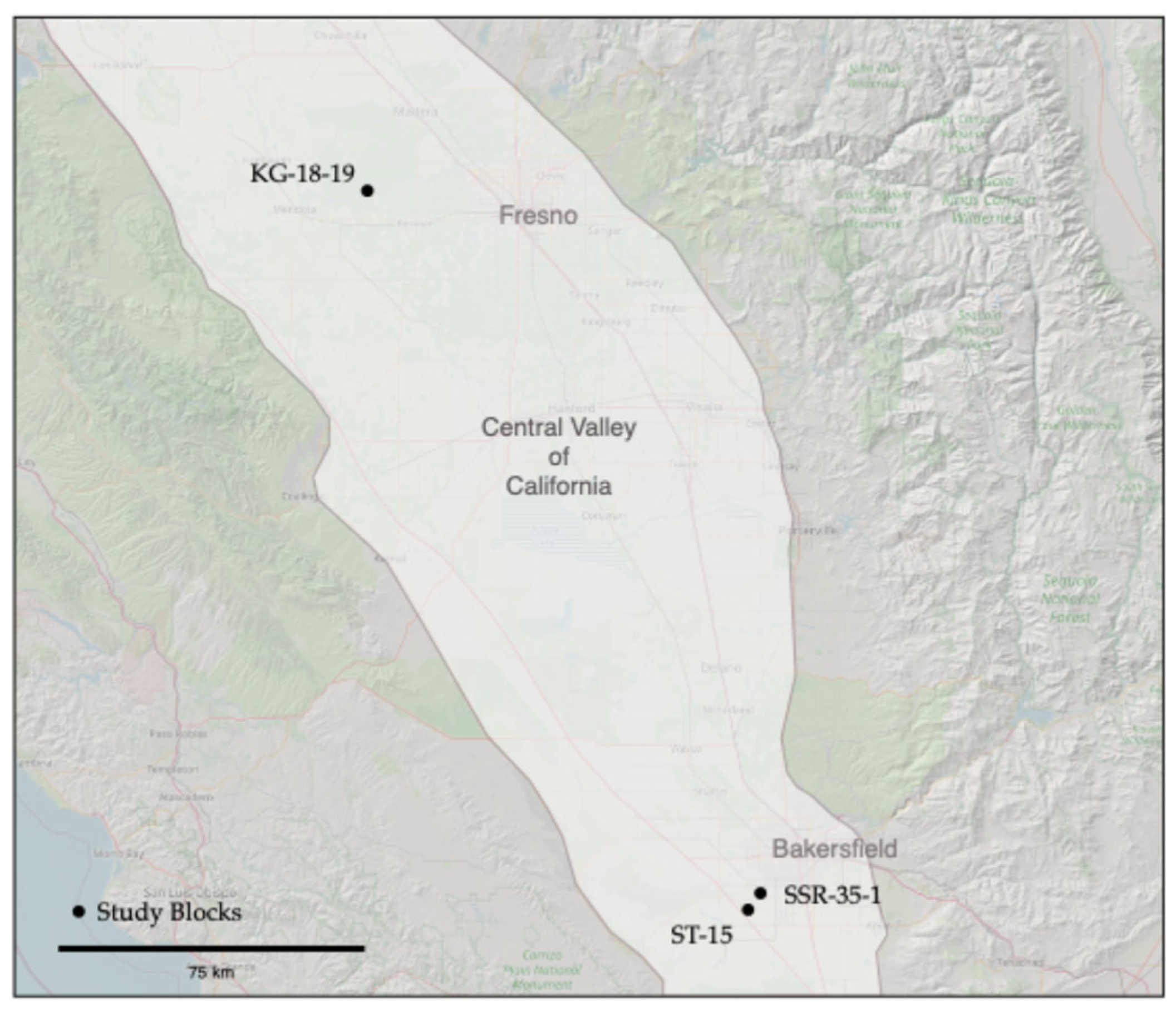



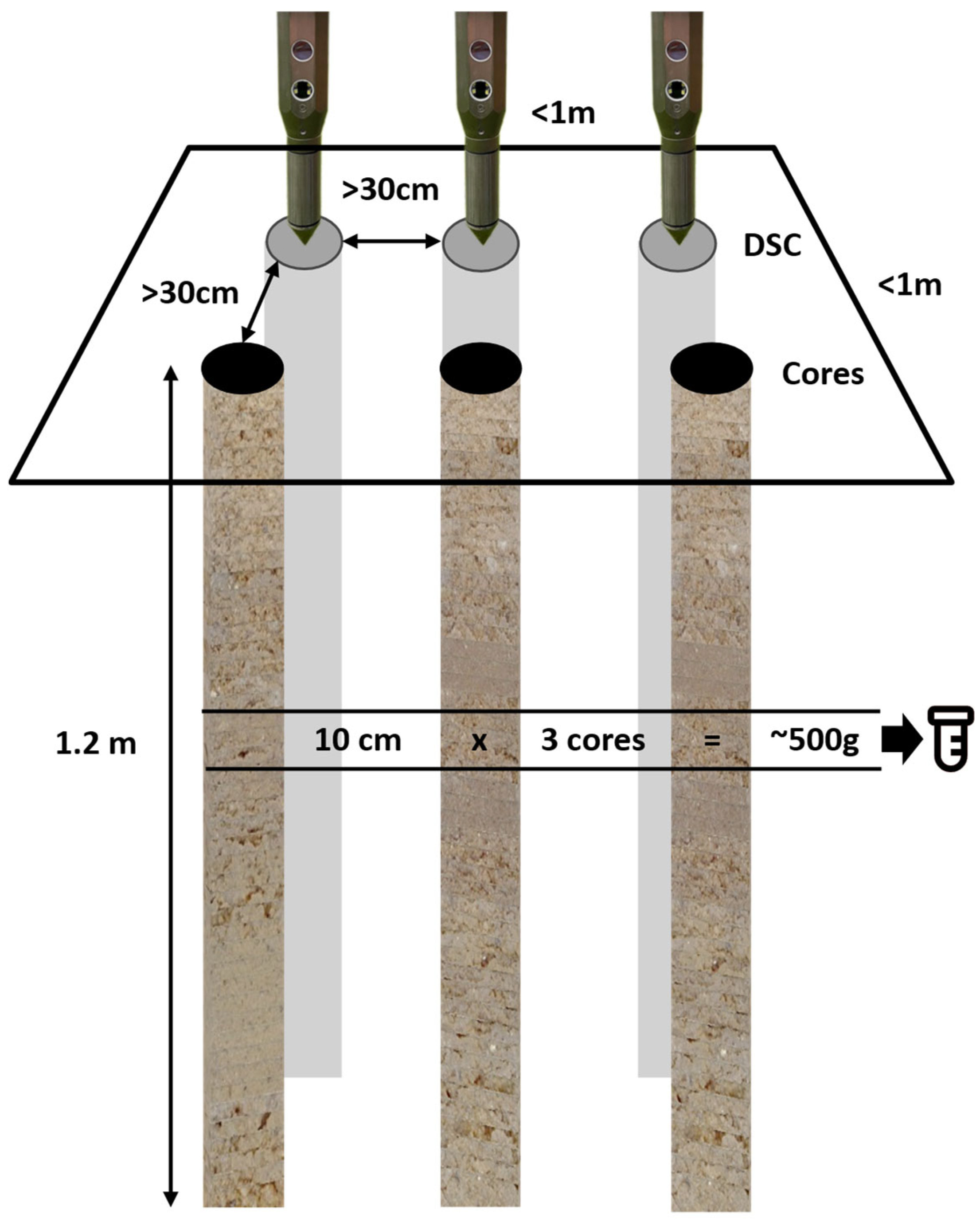
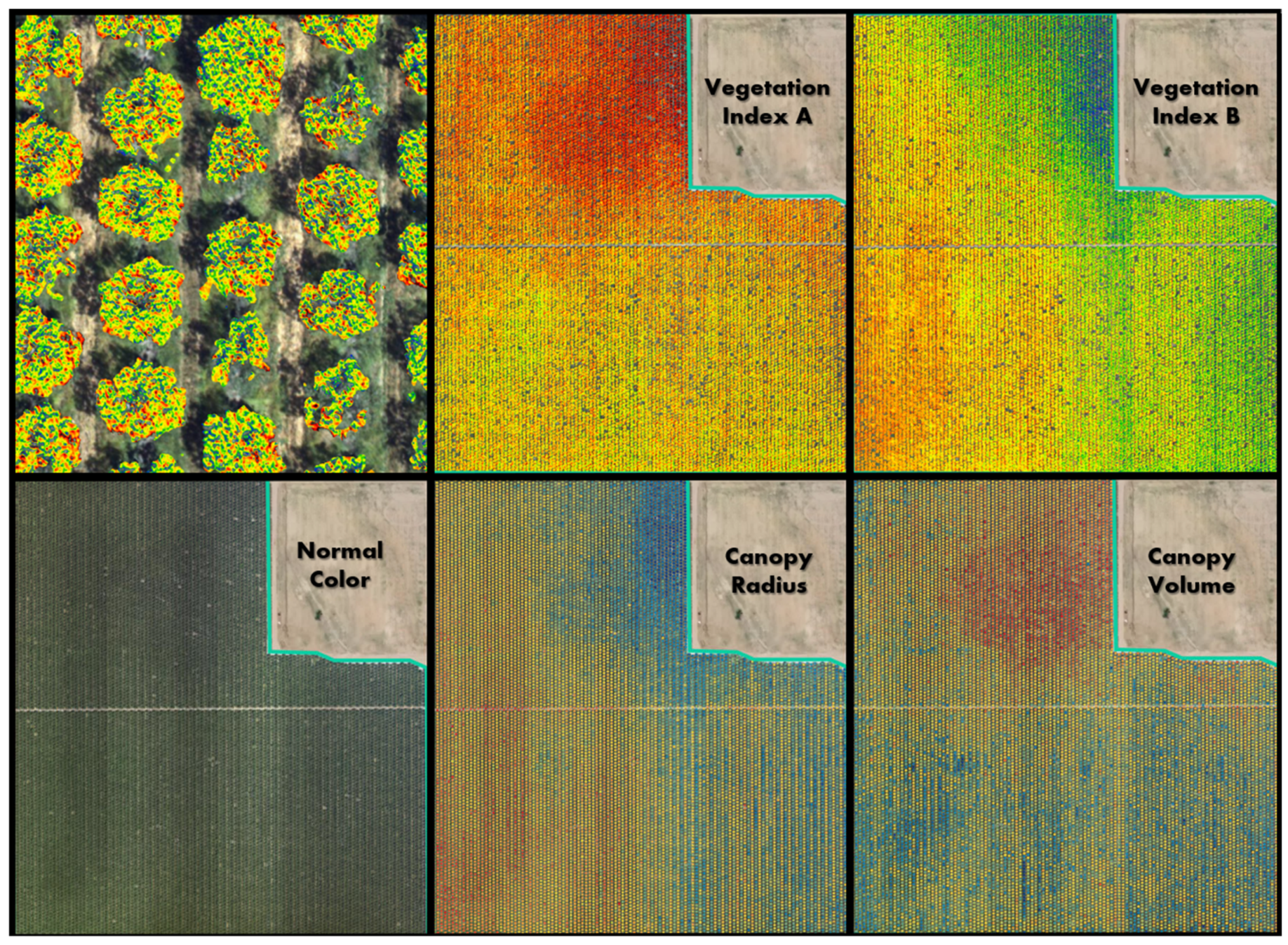
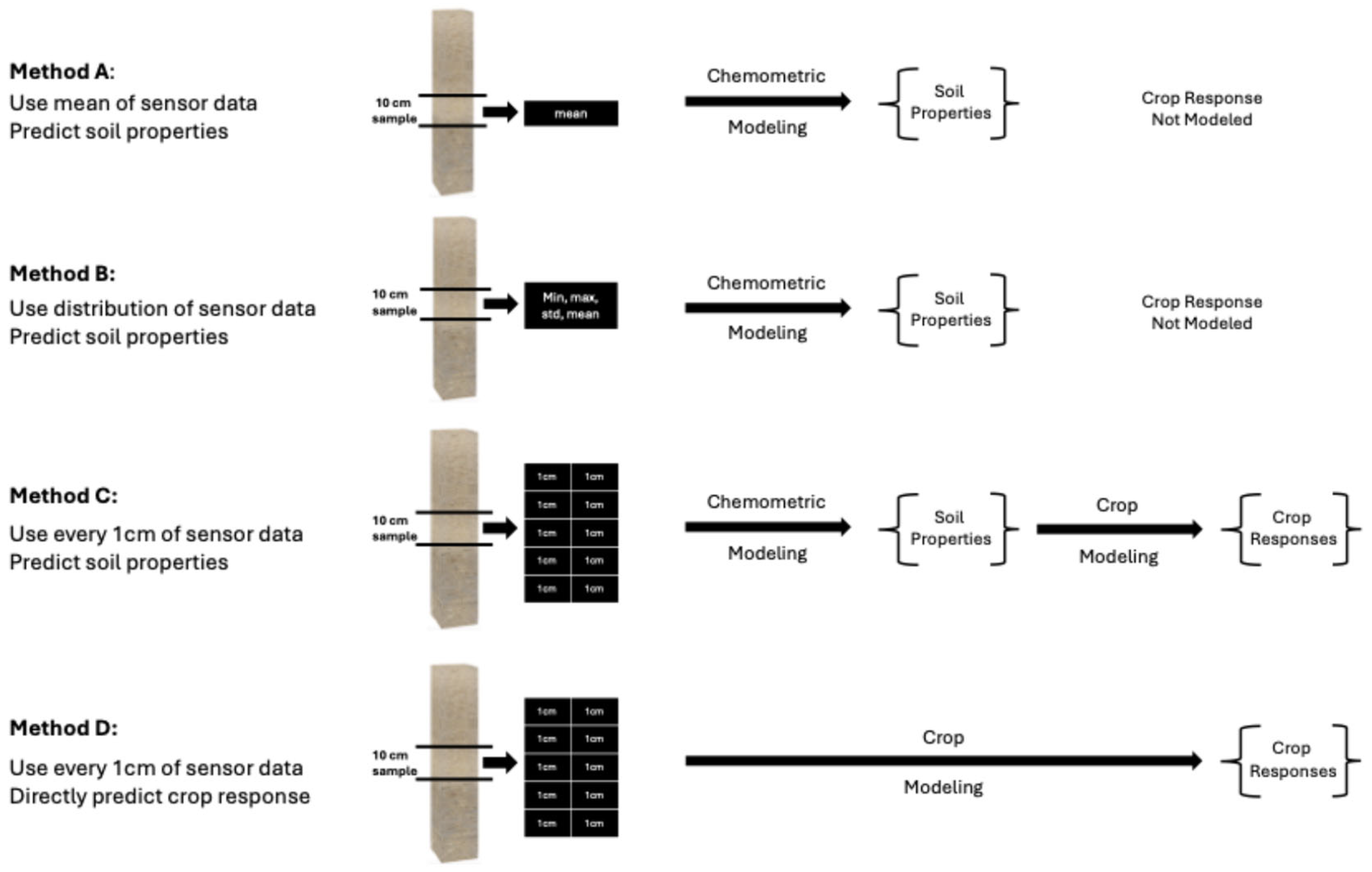
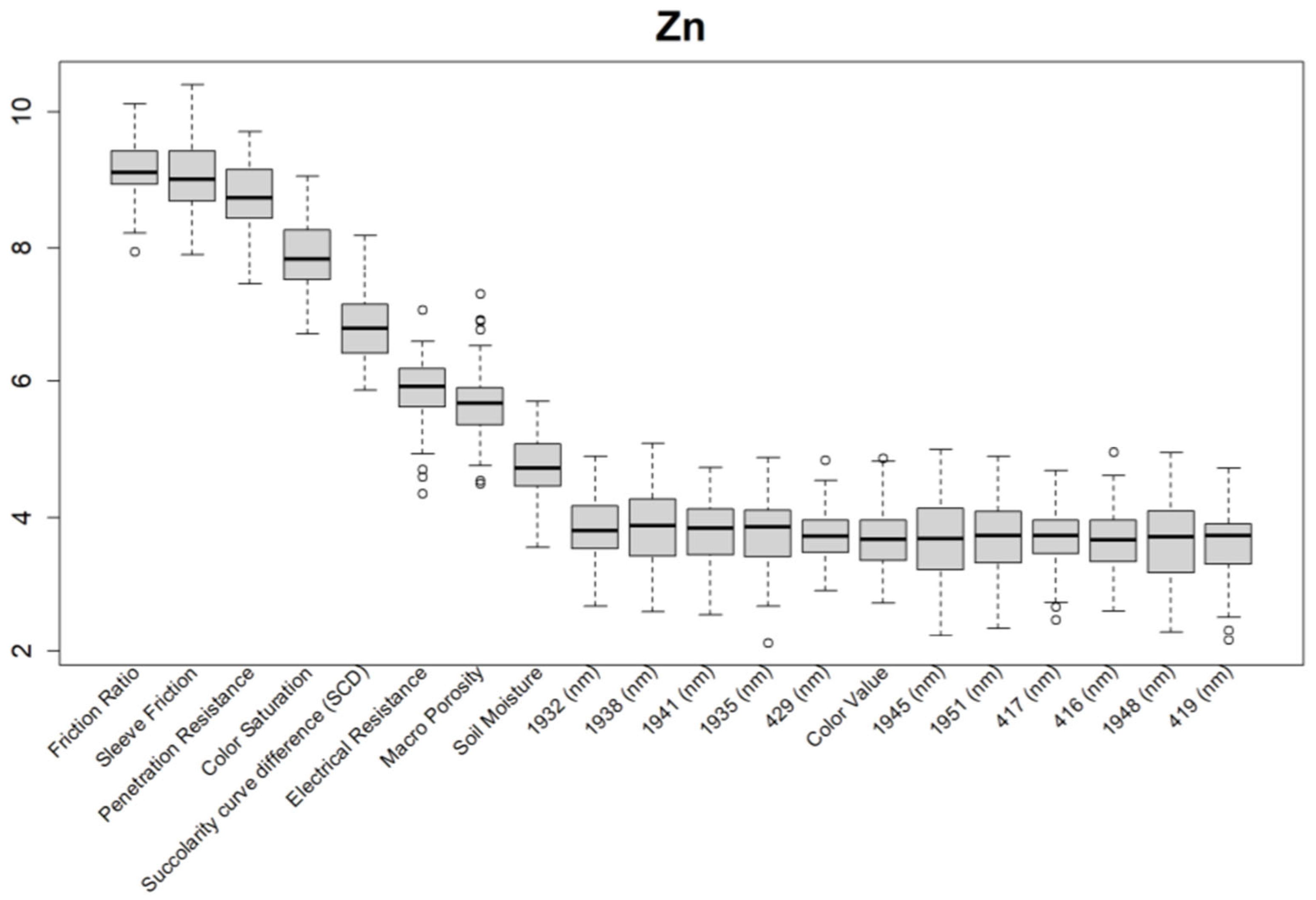
| Block | Location | Description | Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| KG-18-19 | About 20 km southwest of Madera and less than one mile north of the San Joquin River in Madera County, California | 35.2 ha almond orchard, planted in 2017. Double line drip irrigation. Soil map units are El Peco-Dinuba fine sandy loams and Grangeville sandy loam, 0-1 percent slopes (levelled during planting). | 78 samples Dec 2023 |
| SSR-35-1 | About 8 km southwest of Bakersfield in Kern County, California | 25.5 ha almond orchard, planted in 2012. Micro sprinkler irrigation. Soil map units are primarily Kimberlina fine sandy loam with a small section of Granoso loamy sand adjacent to canal. 0-2 percent slopes (levelled during planting). | 36 samples Oct 2023 |
| ST-15 | About 18 km southwest of Bakersfield in Kern County, California, and about 3 mi south of SSR-35-1 | 31.2 ha almond orchard, planted in 2016. Double line drip irrigation. Soil map units include Garces loam, Kimberlina fine sandy loam, Millox clay loam, and Tennco fine sandy loam. Field is split into two sections by field road. The Western section is adjacent to a canal. | 34 samples Oct 2023 |
| Property | Abbrev. | NAPT Method | Units | Method Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Matter | OM | S9.20 | % | Loss on ignition |
| Sand | Sand | S14.10 | % | Hydrometer |
| Silt | Silt | S14.10 | % | Hydrometer |
| Clay | Clay | S14.10 | % | Hydrometer |
| Boron | B | S1.50 | mg/l | Saturated Paste |
| Calcium | Ca | S5.10 | mg/kg | AA Extraction |
| Copper | Cu | S6.10 | mg/kg | DTPA Extraction |
| Zinc | Zn | S6.10 | mg/kg | DTPA Extraction |
| pH | pH | S1.10 | pH units | Saturated Paste |
| Methods | A | B | C | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Field | Metrics | SSR 35-1 | St-15 | KG-18-19 | Mean | SSR 35-1 | St-15 | KG-18-19 | Mean | SSR 35-1 | St-15 | KG-18-19 | Mean |
| OM | R2 | 0.48 | 0.54 | 0.64 | 0.55 | 0.48 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.62 | 0.73 | 0.69 | 0.76 | 0.73 |
| RMSE | 0.4 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.27 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.17 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.20 | |
| bias | -0.03 | 0 | 0 | -0.01 | -0.03 | 0.01 | 0 | -0.01 | -0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| RPIQ | 1.28 | 1.17 | 1.72 | 1.39 | 1.28 | 2.12 | 2.06 | 1.82 | 1.91 | 1.95 | 2.47 | 2.11 | |
| Sand | R2 | 0.41 | 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.49 | 0.41 | 0.66 | 0.62 | 0.56 | 0.57 | 0.59 | 0.73 | 0.63 |
| RMSE | 8.37 | 9.06 | 6.47 | 7.97 | 8.37c | 7.47 | 6.15 | 7.33 | 7.01 | 8.41 | 5.22 | 6.88 | |
| bias | 0.14 | 0.3 | -0.13 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.21 | -0.08 | 0.09 | 0.24 | -0.37 | -0.21 | -0.11 | |
| RPIQ | 1.46 | 1.25 | 1.47 | 1.39 | 1.46 | 2.5 | 1.9 | 1.95 | 1.95 | 2.45 | 2.37 | 2.26 | |
| Clay | R2 | 0.43 | 0.68 | 0.6 | 0.57 | 0.39 | 0.69 | 0.66 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.72 | 0.73 | 0.68 |
| RMSE | 3.47 | 3.49 | 1.61 | 2.86 | 3.59 | 3.41 | 1.48 | 2.83 | 3.08 | 3.26 | 1.36 | 2.57 | |
| bias | -0.04 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | -0.04 | -0.24 | 0.02 | -0.09 | -0.19 | -0.06 | 0.01 | -0.08 | |
| RPIQ | 1.2 | 2.07 | 1.57 | 1.61 | 0.98 | 1.83 | 1.96 | 1.59 | 1.28 | 2.26 | 2.5 | 2.01 | |
| Silt | R2 | 0.59 | 0.49 | 0.48 | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.61 | 0.6 | 0.69 | 0.63 |
| RMSE | 6.16 | 6.62 | 5.7 | 6.16 | 6.64 | 6.07 | 5.49 | 6.07 | 6.12 | 5.85 | 4.53 | 5.50 | |
| bias | -0.13 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.05 | -0.03 | -0.16 | 0.07 | -0.04 | 0.1 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.15 | |
| RPIQ | 1.85 | 1.7 | 1.14 | 1.56 | 1.75 | 1.39 | 1.65 | 1.60 | 2.11 | 1.98 | 2.29 | 2.13 | |
| B | R2 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.25 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.53 | 0.35 | 0.46 | 0.81 | 0.7 | 0.49 | 0.67 |
| RMSE | 0.16 | 1.24 | 0.13 | 0.51 | 0.22 | 1.4 | 0.12 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 1.09 | 0.11 | 0.44 | |
| bias | 0 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| RPIQ | 2.25 | 1.29 | 0.8 | 1.45 | 1.63 | 1.42 | 1.27 | 1.44 | 2.82 | 1.59 | 1.54 | 1.98 | |
| Ca | R2 | 0.42 | 0.47 | 0.54 | 0.48 | 0.32 | 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.46 | 0.72 | 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.67 |
| RMSE | 738.46 | 875.83 | 838.52 | 817.60 | 776.29 | 857.52 | 832.42 | 822.08 | 483.76 | 705.47 | 764.21 | 651.15 | |
| bias | -27.78 | -21.28 | -7.15 | -18.74 | 11.06 | -35.92 | -7.16 | -10.67 | -0.97 | -8.79 | 5.83 | -1.31 | |
| RPIQ | 1.23 | 1.4 | 1.67 | 1.43 | 0.9 | 1.21 | 1.56 | 1.22 | 1.77 | 1.93 | 2.26 | 1.99 | |
| Cu | R2 | 0.24 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.38 | 0.06 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.35 | 0.74 | 0.53 | 0.56 | 0.61 |
| RMSE | 0.35 | 1.03 | 0.1 | 0.49 | 0.36 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.49 | 0.19 | 0.95 | 0.09 | 0.41 | |
| bias | -0.02 | 0.04 | 0 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.03 | -0.01 | -0.01 | 0 | -0.01 | |
| RPIQ | 0.87 | 1.33 | 1.36 | 1.19 | 0.39 | 1.38 | 1.61 | 1.13 | 2.48 | 1.7 | 1.86 | 2.01 | |
| Zn | R2 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 0.56 | 0.51 | 0.42 | 0.41 | 0.64 | 0.49 | 0.72 | 0.6 | 0.71 | 0.68 |
| RMSE | 2.59 | 1.43 | 0.72 | 1.58 | 2.84 | 1.46 | 0.65 | 1.65 | 1.86 | 1.23 | 0.59 | 1.23 | |
| bias | -0.09 | 0.05 | 0 | -0.01 | -0.07 | 0 | 0 | -0.02 | -0.02 | 0.01 | -0.01 | -0.01 | |
| RPIQ | 1.02 | 1.34 | 1.54 | 1.30 | 0.91 | 1.29 | 1.98 | 1.39 | 1.23 | 1.73 | 2.03 | 1.66 | |
| pH | R2 | 0.32 | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.56 | 0.6 | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.70 | 0.81 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.79 |
| RMSE | 0.23 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.44 | 0.21 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 0.40 | 0.12 | 0.53 | 0.4 | 0.35 | |
| bias | -0.01 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.01 | -0.03 | 0 | -0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| RPIQ | 1.18 | 2.11 | 2.41 | 1.90 | 1.69 | 2.46 | 2.91 | 2.35 | 3.37 | 2.45 | 3.01 | 2.94 | |
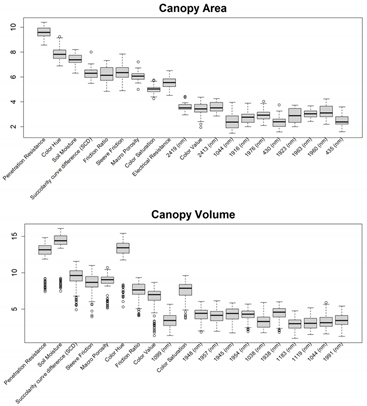
| Method C | ||||||||||||
| CPI | Canopy Area (m2) | Canopy Volume (m3) | ||||||||||
| Fields | R2 | RMSE | Bias | RPIQ | R2 | RMSE | Bias | RPIQ | R2 | RMSE | Bias | RPIQ |
| St-15 | 0.67 | 6.34 | -0.07 | 0.63 | 0.67 | 4.79 | -0.15 | 0.58 | 0.68 | 14.56 | -0.06 | 0.7 |
| SSR-35-1 | 0.66 | 20.97 | -0.47 | 0.75 | 0.58 | 3.73 | 0.02 | 0.65 | 0.63 | 25.35 | -0.16 | 0.81 |
| KG-18-19 | 0.54 | 10.32 | -0.01 | 0.85 | 0.44 | 2.13 | 0 | 0.58 | 0.48 | 15.74 | -0.06 | 0.68 |
| Method D | ||||||||||||
| CPI | Canopy Area (m2) | Canopy Volume (m3) | ||||||||||
| Fields | R2 | RMSE | Bias | Fields | R2 | RMSE | Bias | Fields | R2 | RMSE | Bias | Fields |
| St-15 | 0.75 | 5.09 | -0.09 | 1.13 | 0.76 | 3.65 | -0.18 | 1.03 | 0.76 | 11.51 | -0.19 | 1.16 |
| SSR-35-1 | 0.74 | 17.93 | -0.41 | 1.27 | 0.72 | 2.94 | 0.01 | 1.06 | 0.73 | 21.2 | -0.15 | 1.21 |
| KG-18-19 | 0.72 | 8.15 | -0.08 | 1.64 | 0.65 | 1.72 | -0.01 | 1.33 | 0.70 | 12.23 | -0.11 | 1.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





