1. Introduction
Wheat is one of the most important staple crops in temperate areas worldwide and is an important source of nutrients for millions of people [
1]. A large variety of baked products can be made from wheat flour because of its ability to form viscoelastic dough [
2]. This is primarily attributed to the gluten proteins [
3]. These are among the most complex proteins in nature owing to their various components and sizes, ranging from dimers to polymers, with molecular weights exceeding one million kDa. Their variability is caused by genotype variants, growth conditions, and technological processes [
4]. Gluten proteins play a key role in determining the unique rheological dough properties and baking quality of wheat [
3,
5,
6].
Gliadins and glutenins are the two main classes of gluten protein that determine the technological characteristics of wheat flour [
3]. They are classified according to their solubility, molecular weight and electrophoretic mobility. Gliadins are monomeric proteins that are soluble in alcohol. They are categorized into α, β, γ, ω-gliadin, sulfur rich or poor (S-rich or S-poor) gliadins, with molecular weights ranging from 30 to 74 kDa [
4]. Glutenins are polymeric proteins and are classified according to their molecular weight into high (HMW-GS) (80–160 kDa) and low molecular weight (LMW-GS) (30–51 kDa), and genotype (x or y). There are 7 to 16 different LMW-GS, in each genotype and can be classified according to their N-terminal amino acids such as i-, s- and m-LMW-GS (isoleucine, serine, and methionine, respectively) [
4]. The quantity of HMW-GS is strongly correlated with dough properties and bread quality [
7,
8].
The unique structure of the gluten network is due mainly to covalent (disulfide) and noncovalent (hydrogen, ionic, and hydrophobic) bonds owing to their amino acid composition which have a high amount of glutamine and proline as well as a low levels of charged amino acids [
2,
9].
Treating wheat with processes involving temperature and pressure can change its protein structure. Heat processing can affect technological properties and reduce allergenicity to wheat flours and breads to varying extents [
10]. Protein degradation occurs with increasing temperature and mainly involves cysteine and lysine amino acids [
9]. During dough preparation and baking, competitive redox reactions occur in the glutenin polymer network: (1) oxidation of free SH groups which support polymerization; (2) chain ‘terminators’ that stop polymerization, and (3) SH/SS interchange reactions between glutenins and thiol compounds such as glutathione that depolymerize polymers [
2,
11]. Another important production process is extrusion, in which high temperature, pressure, screw speed, shear, die geometry, and moisture content result in various low-density products, such as meat analogs, breakfast cereals, snacks, starches, and baby foods [
12].
Immune-mediated diseases triggered by gluten consumption include celiac disease (CD), gluten ataxia, and dermatitis herpetiformis [
13]. The primary trigger of the immune response in celiac disease (CD) are specific gluten protein epitopes that are resistant to digestion. The most common symptoms of CD include malnutrition, diarrhea, growth retardation, anemia, and fatigue [
14] resulting from inflammatory injury to the small intestine mucosa after gluten consumption [
15]. Different gliadin types (α/β-type, ω-type and γ-type gliadins) as well as glutenins [
16,
17] have been shown to have important and variable roles in the disease pathogenesis, and inflammatory response [
15,
18]. Some researchers have theorized that heat treatment can affect the toxicity and chemical characteristics of gluten [
19,
20,
21,
22]. Therefore, this study aimed to provide a better understanding of the possible processing-induced changes in gluten proteins. We investigated how processing (extrusion, oven and microwave) affects gluten protein network solubility, secondary protein structure and microstructure of the flour, and whether any treatment tested affected protein digestibility or celiac disease epitopes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Processing
All chemicals and reagents were of analytical grade, and all sample treatments and analyses were performed in triplicate. Brazilian commercial fortified white wheat flour (Triticum aestivum) was obtained from Cooperativa Agrária Agroindustrial (Guarapuava, Paraná, Brazil) and was analyzed before and after the following treatments:
Extrusion: Pilot-scale extrusion was performed under optimal operating conditions using a single-screw MX40 pilot extruder (Inbramaq, Ribeirão Preto, SP, Brazil). The extrusion conditions were modified based upon previous experience as follows: the temperature of the barrel head was 120 °C, there was a water addition of 30% (w/v) in relation to flour, and the screw speed was 220 rpm. The flow rate was approximately 20% of the nominal capacity and amounted to 50 kg/h. The L/D ratio was 2.3:1, the screw diameter was 92.5 mm and the processing barrel length was 210 mm. The diameter of the ten circular nozzles was 3 mm. The dough feed rate to the screw and the barrel were 40 and 50 %, respectively.
Dry heat oven: Dough was made by mixing 200 g of flour with sufficient water, as previously described [
23]. The dough was hand knead until pass to windowpane test, and approximately 40 g of dough was rolled to uniform thickness (3.0 mm) and placed in an oven at 250°C for 5 min [
24].
Microwave: Wheat flour was suspended in water 90 % (w/v) and exposed to microwave radiation in a laboratory microwave for 5 min at 500 W [
19].
After all treatments, the samples were lyophilized, ground with IKA (A 11 basic Analytical mill, IKA Works, Inc., USA) to 0.5 mm sieve then stored at -5 °C before conducting further analysis.
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
The individual samples were mounted on stubs and secured using carbon tape, coated with a 350 Å gold layer and examined in a JEOL JSM-6390LV scanning electron microscope (JEOL USA, Peabody, MA, USA). The working distance was set at 15 mm with a voltage of 10 kV.
2.3. Determination of Total Protein (%TP) – LECO
All samples were analyzed by nitrogen combustion using a Leco FP-428 nitrogen determinator (Leco St. Joseph, MI USA) according to the AACC method 46-30.01 [
25]. A factor of N=5.7 was used for protein determination.
2.4. Determination of Percentage of Insoluble Polymeric Protein (%IPP) and Monomeric and Soluble Polymeric Protein (%SPP)
Proteins were extracted according to the method described [
26]. The extracted proteins were lyophilized, and protein content was determined as described above. SPP (%) was determined by Equation 1:
2.5. Determination of Monomeric and Polymeric Distribution - Size Exclusion HPLC
To determine the monomeric and polymeric distributions of wheat proteins, size exclusion high-performance liquid chromatography (SEC-HPLC) was carried out, as previously described [
27].
Total polymeric protein (TPP), extractable polymeric protein (EPP), and unextractable polymeric protein (UPP) were extracted as described [
27,
28].
After extraction, analyses were performed using an Agilent 1100 HPLC instrument (Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, USA). The protein extract (20 µL) was injected into a BioSep-SEC s4000 analytical column (300 mm length × 7.8 mm ID, 5 um particle size, 500 Å pore size) (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA) and run for 30 min on an isocratic gradient of 50 % water containing 0.1 % trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) and 50 % acetonitrile containing 0.1 % of TFA at a constant flow rate of 0.5 mL/min with a column temperature of 30 ºC. Post run lasted 10 min. Absorbance was measured at 210 nm using a variable wavelength detector. The relative molecular weight distributions of polymeric proteins were obtained based on the method described [
27].
2.6. Gliadin and Glutenin Profile - Reverse Phase HPLC (RP-HPLC)
Gliadin and glutenin were extracted as described by [
29]. After extraction, the glutenins and gliadins were analyzed by RP-HPLC using an Agilent Technologies 1260 Infinity HPLC system (Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, USA). Extracts (20 µL injection) were analyzed using a Jupiter C18 analytical column 5 µm particle size and 300 Å pore size (250 mm length × 4.6 mm ID) (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA), and the eluent absorbance was measured using a UV detector at 210 nm.
For gliadins, proteins were eluted using the following solvents: (A) water containing 0.1 % TFA, and (B) acetonitrile containing 0.05 % TFA in a 25 % to 50 % linear gradient of B over 80 min at a constant flow rate of 1 mL/min. The column temperature was set to 70 ºC with a 10 min post run.
For glutenins, proteins were eluted using solvents (A) and (B) in a 23–60 % linear gradient of B over 40 min at a constant flow rate of 1 mL/min. The column temperature was set to 70 ºC with a 10 min post run.
2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
The FTIR analysis was conducted using a Perkin Elmer FTIR with Attenuated Total Reflection (ATR) equipped with a single-bounce diamond crystal and a deuterated triglycine sulfate (DTGS) detector. Spectra were collected at room temperature, 400–4000 cm
-1 range with a resolution of 4 cm
-1, data spacing of 0.482 cm
-1, and 64 scans. Each spectrum was corrected for a linear baseline over five points (ca. 4000, 3990, 2500, 1880, and 700 cm
−1). The secondary protein structures were determined and quantified by deconvoluting the amide I band peak observed between 1600-1700 cm
-1 using the GRAMS/AI software (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, WA) following a second-order derivative approach as described [
30]. Briefly, the second-order derivative of the complex Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra was taken and enhanced using a Savitzky-Golay function, which was followed by a non-linear least squares peak fitting process assuming mixed Lorentzian and Gaussian wave distribution using the Voigt function. A double-subtraction protocol was applied to account for the water contribution. The first subtraction was performed automatically by the instrument to account for any residual water vapor in the air, and the second was performed using a water reference spectrum. The areas under each peak were used for quantification.
2.8. Standard In Vitro Protein Digestibility
The protein digestibility of all samples was determined using protocols previously described [
31,
32]. Undigested proteins were determined by nitrogen combustion (n × 5.7) using LECO. The digestibility was calculated using the following Equation 2:
Where:
Ptotal = Total protein
Pundigest = Undigested protein
2.9. Immunoreactivity by ELISA R5 and G12
Processing effects on immunoreactivity was analyzed by ELISA using R5 and G12 antibodies after gluten extraction. Flours were extracted using the Méndez Cocktail [
33] followed by the addition of 80 % ethanol to a final concentration of 60 % ethanol.
ELISA R5: The extracted samples were analyzed by the R5 Method, as previously described [
34]. Briefly, a Ridascreen Gliadin R5 sandwich ELISA kit (#7001 R-Biopharm Ag, Darmstadt, Germany) was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
ELISA G12: The extracted samples were analyzed using a G12 antibody-based sandwich ELISA test kit (AgraQuant® Gluten G12 ELISA) from Romer Labs (Romer Labs, Union, MO, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Values are expressed as g of gluten/100 g flour.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
The results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Bartlett’s test was used to verify the homogeneity of the variances. Differences in protein levels among the different treatment groups were determined by one-way analysis of variance (ONE-WAY ANOVA). Multiple comparisons were performed using Tukey’s post hoc test, and the criterion for significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
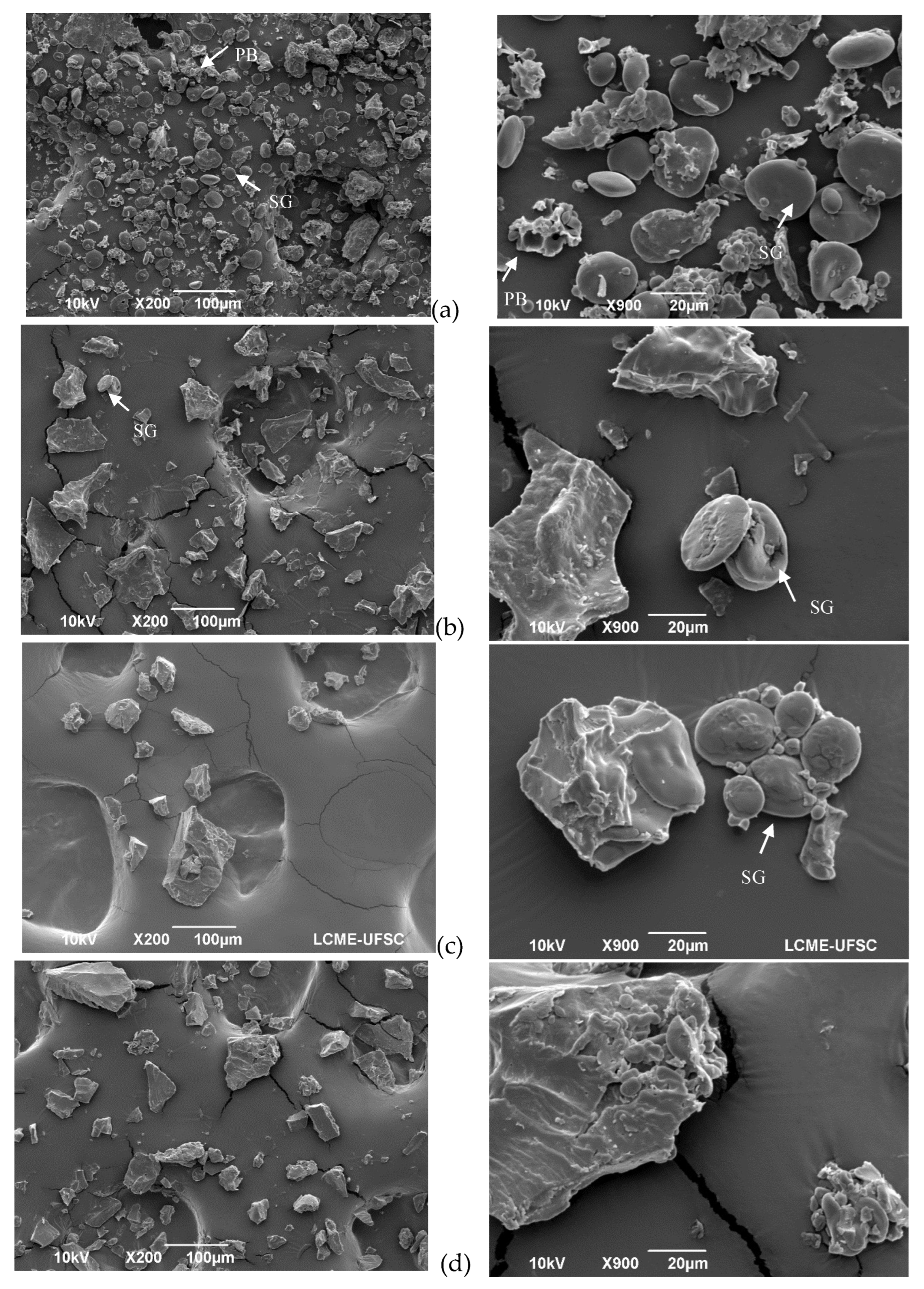
The SEM images in
Figure 1 reveal the influence of the treatments (extrusion, oven and microwave) on flour structure. In the control flour (
Figure 1a) both type A and B starch granules appear with a smooth clean surface and free from the protein matrix. The same results were observed by Scheuer, et al. [
35]. However, after treatment (
Figure 1b-d), the microstructure changed.
After flour extrusion, the starch granules were not easily detected because of starch gelatinization, resulting in a general homogenous and porous structure (
Figure 1d). After microwave irradiation, the microstructure was compact, and the starch appeared to be gelatinized (
Figure 1b). After kneading and oven treatment, the microstructure of the protein network structures was observed (
Figure 1c) as a result of the progressive development of the viscoelastic properties of the dough [
36,
37], which occurs due to changes in the gluten protein polymer structure as both covalent and noncovalent bonds are reorganized, resulting in a complex continuous network that entraps starch and gas molecules [
4].
3.2. Total Protein, Soluble and Insoluble Polymeric Protein
The treatments affected the solubility of the gluten proteins, as determined by the amount of polymeric and monomeric proteins. In all treatments the solubility of proteins decreased; the amount of IPP (insoluble polymeric protein) was higher in the treatment groups than that in the control flour (
Table 1) with a concomitant decrease in SPP (soluble polymeric protein). These treatments involved mechanical work and/or high temperatures. An increase in temperature results in an alteration in protein conformation due to an increase in chemical interactions, including in covalent and non-covalent bonds that stabilize gluten structures, resulting in a decrease in solubility [
38].
Treatment conditions had no effect on the total protein content (TP) (p < 0.05) (
Table 1). The IPP values agreed with those reported in previous studies on wheat flour [
37]. IPP (insoluble polymeric protein) is a protein quality indicator that correlates better than protein content with bread loaf volume, bake mix time, and mixing tolerance [
26]. In terms of dough quality, higher IPP content increases the retention of CO
2, and bread dough becomes hard and less elastic. However, low IPP content is related to low elasticity and weakening of the gluten network, and high SPP (soluble polymeric protein) content is related to low extensibility strength of the dough [
37].
As reported by Silvas-García et al., [
37] changes in the IPP and SPP content indicate modifications in the gluten polymer chains. Therefore, heat treatment resulted in an increase in the molecular size of gluten polymers.
The hydrophobic interactions that occur during heating promote the formation of aggregates [
39]. These bonds are different from other bonds because their energy increases with increasing temperature, which provides additional stability during baking [
2]. The most important covalent bonds are disulfide, tyrosine, and hydrophobic bonds. Disulfide bonds play a significant role in determining the structure and properties of gluten proteins. Monomeric α/β- γ- and ω-gliadins have three and four intrachain disulfide bonds, respectively, whereas polymeric LMW- and HMW-GS have both intra- and interchain bonds [
2].
As the temperature increased, hydrophobic interactions increased owing to the disruption of the ionic and hydrogen bonds in the gluten protein. These hydrogen bonds primarily contribute to holding the gluten dough together. Temperatures above 60 ºC denature the gluten proteins, causing them to unfold and resulting in free SH groups that are susceptible to oxidation and intra- or intermolecular disulfide bond formation[
39].
3.3. Total, Extractable and Unextractable Polymeric Proteins by Size Exclusion HLPC
SEC-HPLC is useful for obtaining information on the solubility of protein fractions induced by heat treatment and protein aggregation and help to better understand the gluten network arrangement [
40].
Results showed a significant increase and decrease in the extractability of monomeric and polymeric proteins, respectively. Overmixing dough decreases the HMW-GS and gliadin extractability [
41]. Ionic, S-S, and hydrogen bonds are affected by heat treatment, leading to the unfolding of wheat gluten [
39]. These changes affect the secondary structure of gluten and influence the dough’s rheological properties [
12].
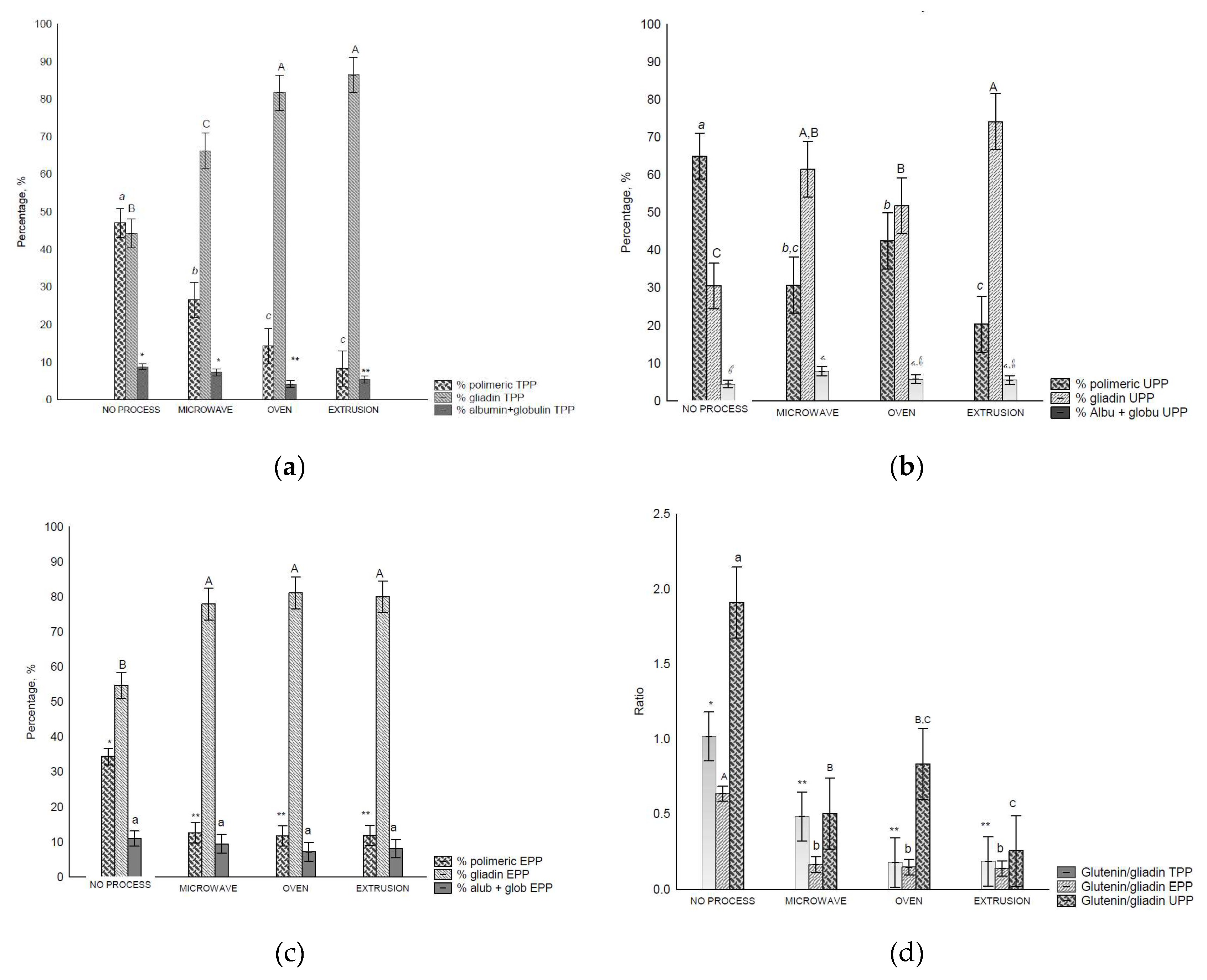
The amount of TPP (total polymeric protein) (
Figure 2-a), UPP (unextractable polymeric protein) (
Figure 2-b), EPP (extractable polymeric protein) (
Figure 2-c), and Glu/Glia ratios (
Figure 2-d) were affected by the treatments. When the TPP of the control flour was extracted, the proportions of polymeric and monomeric gliadins were not significatively different; however, after treatment, they were altered (Figures 2-a, 2-b, 2-c). The amount of polymeric proteins decreased, while that of monomeric proteins increased (p < 0.05), most notably in the oven and extrusion treatments. Consequently, the Glu/Glia ratio (
Figure 2-d) decreased after all treatments.
In the UPP fraction of control flour, polymeric proteins were found in higher amounts than the monomeric proteins owing to their higher complexity and, consequently, lower solubility. A decrease in the polymeric proteins was observed after all treatments (
Figure 2-b), and consequently the Glu/Glia ratios (
Figure 2-d) as the amount of extracted monomeric proteins increased. UPP is comprised of polymeric glutenin protein (> 158 kDa) with the lowest solubility, and therefore, the highest molecular weight [
42,
43]. It is also related to the size and/or complexity of the gluten polymer [
42] and the total number of HMW subunits [
7]. In this study, we observed that the treatments affected the solubility of this fraction.
More monomeric proteins are present in the EPP (extractable polymeric protein)fraction. Nevertheless, after treatment, the proportion of monomeric proteins increased under all conditions (
Figure 2-c). In addition, decreased glutenin levels were observed. In all fractions, the polymeric proteins and Glu/Glia ratio decreased compared with control flour, which suggests poor rheological properties [
12], affecting dough development and stability [
44].
The data showed that the treatments modified the size and/or complexity of gluten proteins, resulting in more insoluble protein.
It was expected that post all treatments, polymeric glutenins would be the predominant protein group in the UPP fraction. However, this was not the case because of external heating, shear, pressure, and radiation applied. Notably, monomeric gliadins were more abundant in EPP and TPP compared with the control flour.
During extrusion, the high temperature applied to proteins exposes the hydrophobic groups on the protein surface, resulting in interactions with other food components, causing a decrease in protein solubility [
45]. The main structural changes during polymerization occur owing to isopeptide aggregation, Maillard reactions, and free-radical-initiated cross-linking, creating an anisotropic product that resembles meat-like textures, which may be desirable in some products. This is a direct result of aggregation and degradation, which promote modifications in the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of the protein [
45].
3.4. Glutenin and Gliadin Protein Characterization by RP-HPLC
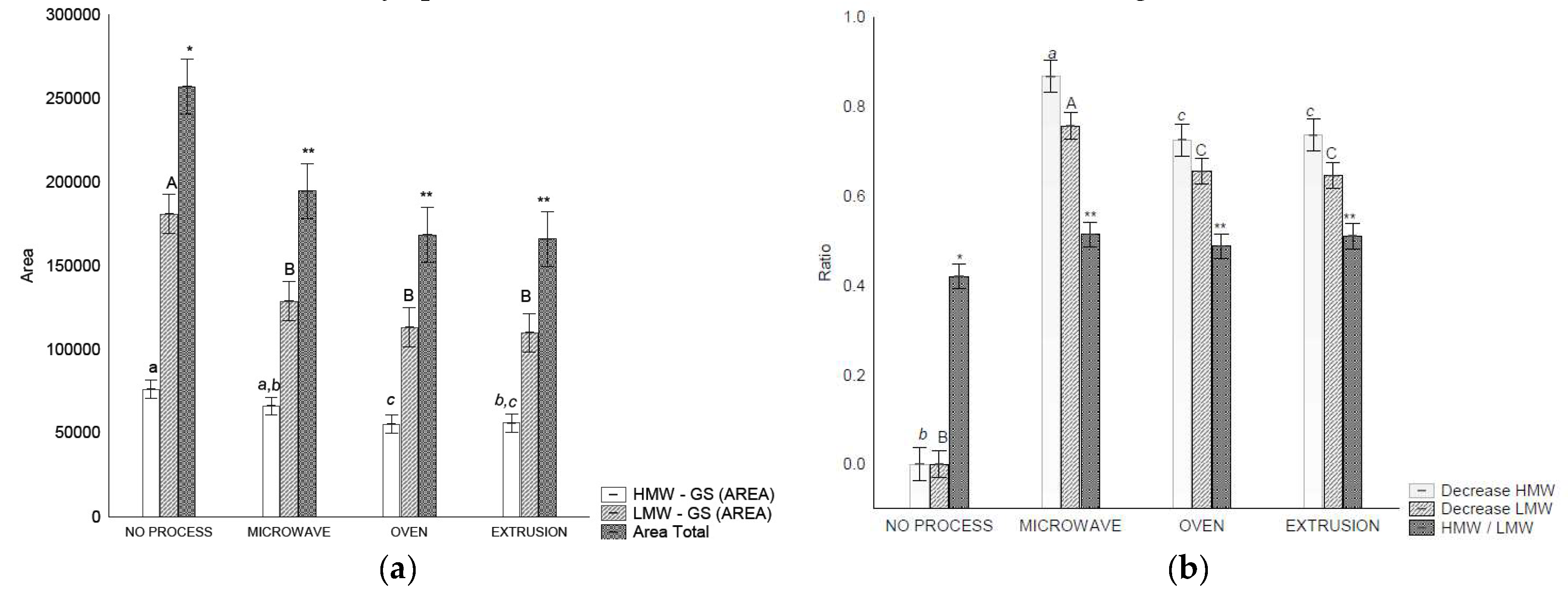
3.4.1. Glutenins
RP-HPLC glutenins can be classified into HMW-GS and LWM-GS. Based on these, they can be characterized by an HMW-GS/LMW-GS ratio, whereby changes in the fractions (increase or decrease in extractability after treatment) can be measured.
The extractability of HMW-GS decreased after oven and extrusion treatments compared to that of the control flour and microwave treatment (
Figure 3-a). For LMW-GSs and total glutenin, a decreased extractability (p<0.05) was observed after all the treatments (
Figure 3-b).
HMW-GSs are directly related to the technological applications of wheat as they are major determinants of dough elasticity [
46]. In addition, HMW-GSs are required for glutenin formation, and affect the internal structure of glutenin [
7].
The HMW-GS/LMW-GS ratio changed after all treatments, indicating an increase in glutenin size and complexity. These results are in accordance with those of [
7] who observed that an alteration in the HMW/LMW-GS ratio is indicative of alterations in glutenin particle size.
During heat and mechanical treatments, the gluten protein unfolds, and protein crosslinking increases because of the exposure of hydrophobic regions and free SH groups that interact with each other. This leads to irreversible protein aggregation and the formation of a three-dimensional network of high-molecular-weight and viscous wheat gluten aggregates [
39,
47]. In addition, an increase in pressure and temperature leads to a significant reduction in the solubility and thiol content of gluten, gliadin, and glutenin, strengthening them [
45].
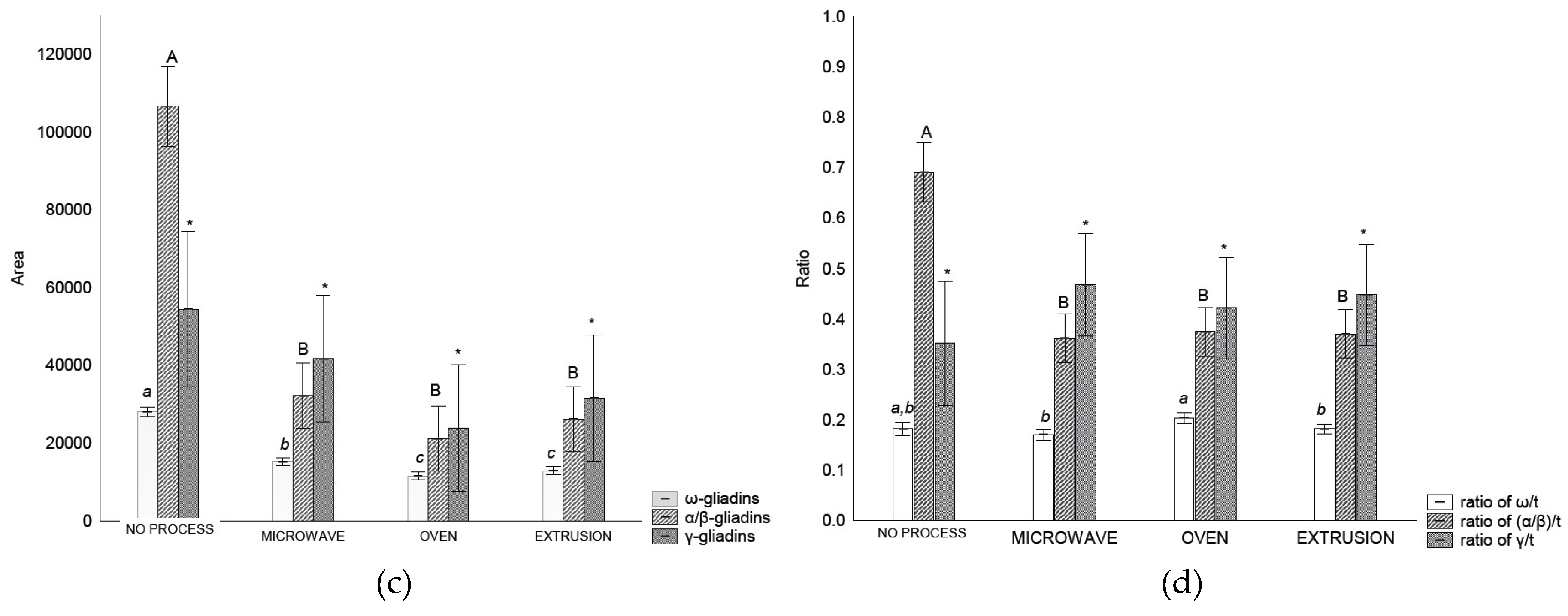
3.4.2. Gliadins
Gliadin distribution measured by RP-HPLC in wheat flour before and after treatment varied depending on the treatment (
Figure 3-c). It was possible to separate the gliadins into ω-, α/β- and γ-gliadin. The amount of ω-gliadin and α/β- gliadins extracted decreased (p < 0.05) after all treatments in comparison with control flour. However, the γ- gliadins were not affected (p > 0.05) by any treatment (
Figure 3-c). In relation to gliadin ratios, treatments affected the α/β-/t ratios that decreased after treatment (p < 0.05) (
Figure 3-d).
In baked products, gliadins are correlated with dough strength, mixing tolerance, and loaf volume [
48]. During mixing and baking, the gliadins interchain S-S bonds start to form at 70 °C [
22]. Heat and mechanical work cause α-, β-, and γ–gliadins (S-rich) to be incorporated into the gluten polymer with intermolecular SS bonds. Notably, ω-gliadins (S-poor) interact with hydrogen or other noncovalent bonds [
4] altering the solubility and extractability of the flour. This results in changes in gliadin and glutenin distributions.
The extractability of gliadins in the control flour was higher than that of the treated samples (
Figure 3-c). Similar results have been reported with flour and bread, with S-S interaction attributed to this higher extractability; α- and γ-gliadins are more affected than are ω-gliadins [
22,
49]. Microwave heating can affect gliadin structure, leading to a decrease of gliadin extractability and an increase of the immunoreactivity by promoting conformational and chemical changes in the gliadin structure according with level of energy applied that result in unsolved high molecular weight product in the chromatograms [
19]. The same authors [
19] reported that after microwave treatment, the content of all gliadin fractions decreased. Notably, we observed these decreases in ω-gliadin and α/β- gliadins. A similar gliadin distribution was noted in wheat from Argentina [
48].
Microwave energy decreases the solubility and emulsifying capacity of gluten proteins, and the quality of baking value during baking tests [
38]. Damage to gluten proteins is caused by an increase in temperature and irradiation, resulting in changes in protein structure and solubility [
38].
A strong decrease in the amount of all gliadin fractions in microwave-irradiated wheat flour with an increase in applied energy was reported [
19]; however, further studies showed a decrease in gliadin extractability [
50].
High-pressure processing, such as extrusion, affects gluten by unfolding the proteins, partially denaturing, and dissociating polymeric structures into subunits due to weakened electrostatic and hydrophobic bonds, ionization of acid groups on amino acid side chains, and aggregation and formation of gel networks or precipitates, resulting in poor rheological properties [
51]. However, in some products, structural changes are desirable; the extrusion products can be flakes or meat-like products depending on the conditions, and this texture is due to the processes of denaturation, dissociation, and fragmentation, allowing the unraveled protein to align in the direction of shear [
45].
3.5. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
FTIR was used to assess changes in protein secondary structure caused by different treatments. The absorption bands represent the functional groups. Specifically, the Amide I band corresponds to the C=O of the peptide bonds, which are determined by the secondary structure (α-helix, β-sheet, etc.). Treatments altered the secondary structure of wheat proteins (
Table 2). In the general spectra, there was a flour-specific peak (not observed with the pure protein) at 1770-1732 cm
-1, possibly determined by the extent of starch-protein interactions.
We observed a decrease (p < 0.05) in α-helix and random structures with treatment as compared to the control (
Table 2). Mahroug et al. (2019) [
52] also reported a decrease in α-helix structures after microwave treatment suggesting that the heat induced to a sulfhydryl-disulfide interchange reaction resulted in a different arrangement of the disulfide bonds. In addition, the data showed an increase in β-sheets, β-turns and other structures (Table 3). The high pressure and temperature of the extrusion process resulted in the largest decrease in the α-helix structure. This corroborates with literature that showed protein aggregation is primarily accompanied by the disappearance of α-helices and increase in antiparallel β-sheets [
45]. This is related to the higher stability of the β-sheet structures than α-helices in high-pressure-denatured proteins [
51,
53]. Compared to glutenin, gliadin is less affected by pressure and heat treatments because of its low thiol content. Meanwhile, compared with ω-gliadins (ω5- and ω1,2-gliadins), α- and γ-gliadins are more sensitive to high pressures, and intrachain disulfide bonds of α- and γ-gliadins are converted to interchain bonds [
54].
Previous studies revealed that high pressure and medium temperature treatment on gluten protein lead to a decrease in the β-sheets (%), antiparallel β-sheets (%), and α-helix (%) structures and an increase in random structures [
55], while microwave treatment could change β-turn structures to random [
52].
Gluten contains large amounts of glycine, proline, glutamine, and leucine, which are the main contributors to hydrophobic interactions [
56]. Most interactions are covalent (disulfide bonds), noncovalent (hydrogen, ionic, and hydrophobic bonds), and other bonds that are susceptible to modification. Among the physical modifications, heating-freezing and extrusion exhibit significant modifications to the gluten structure via the formation and dissociation of covalent bonds and noncovalent interactions [
38].
Heating can induce sulfhydryl-disulfide interchange reactions, which involve the exchange between free thiol (-SH) groups and disulfide bonds (-S-S-) within the protein structure. This exchange can lead to a reorganization of disulfide bonds, potentially altering the protein’s secondary structure [
52].
The increase and/or decrease in the relative abundance of certain secondary structures, such as β-sheets or α-helices, after heat treatment suggests that the protein’s conformation has changed. This rearrangement is evidenced by an observed increase in the relative abundance of specific secondary structures, β-sheets, indicating a shift in the protein’s conformation. In the HMW-GS the main secondary structure was proposed to be β-turn organized in a regular β-spiral structure, and these are closely associated with the elastic behavior of gluten [
57,
58]. In the context of gluten, these structural modifications could impact its functional properties, such as elasticity, viscosity, and dough-forming ability, which are critical in various food applications.
3.6. Protein Digestibility
In addition to the important and fundamental technological qualities of wheat gluten proteins, there are concerns regarding their nutritional aspects, and how these treatments affect digestibility. In this study, only extrusion showed a small yet significant decrease in digestibility (p < 0.05) compared to the control flour (
Table 1). The nutritional value of a protein depends on its quantity, digestibility, and the availability of essential amino acids. The extrusion process was expected to improve the digestibility of proteins by inactivating protease inhibitors and other anti-physiological substances and improve digestibility [
59].
3.7. Immunoreactivity by ELISA R5 and G12 Antibody Tests
The results showed a difference between the epitope availability for R5 and G12 antibodies. Using the R5 antibody, there was no statistically significant difference between control and treatments (
Table 1). When the G12 antibody was used a reduction in recognition was observed in both oven and microwave treatments (
Table 1). Oven and microwave treatments resulted in a 22% and 46% reduction respectively.
The microwave radiation effect on immunoreactivity of gluten was demonstrated by increasing the energy input, but, with same effect that untreated flour after the highest power (500W) and time (5 min) [
19]. The same author also noted that microwave and heat treatment are closely related in regard of changes in immunoreactivity of gluten to celiac antibodies. Which can be explained by the change in protein configurations that result in lower solubility.
Our results presented a decrease in α/β- and ω-gliadin extractability after microwave treatment (
Figure 3-c). It is already reported in literature a positive correlation between ω-gliadins, γ-gliadins, and total gliadin contents and immune reactivity to the R5 ELISA test, and no correlation to α/β-gliadin [
60].
Recent attention has focused on the Italian patented product GlutenFriendly
TM technology [
21] that uses microwave radiation to generate safe celiac flour that retains functionality. A recent report [
50] demonstrated that, although the microwave process abolishes the recognition of epitopes by the R5 antibody, this is due to the protein insolubility and does not affect the immunological response to enzymatically digested microwave-treated gluten. Our results are consistent with those previously reported.
The commercial antibodies used herein bind to gluten-responsive DQ2/DQ8 T cell epitopes in celiacs [
61,
62]. The R5 monoclonal antibody recognizes the QQPFP repetitive pentapeptide epitope [
62] and is recommended by the Codex Alimentarius. The G12 monoclonal antibody recognizes the QPQLPY repetitive hexapeptide epitopes primarily present in alpha gliadin [
61].
In autoimmune diseases triggered by gluten, such as in celiac disease, gluten ataxia, and dermatitis herpetiformis, different epitopes are responsible different presentations [
63]. There are more than 50 T cell–stimulatory peptides in gluten proteins, with varying degree of similarities, such as hydrophobic residues at specific positions and higher toxicity of ω-gliadin [
16], as well as in HMW-GS and LMW-GS [
64].
It was observed that in vitro immunoreactivity against R5 and G12 antibodies showed a change based on the changes in glutenin and gliadin profiles (HMW-GS, LMW-GS, γ-, α/β-, and ω-gliadin) (
Table 1). The observed changes in solubility and protein profiles suggest that the treatments modified the structure/complexity of gluten proteins, probably by masking epitopes and/or domains of glutenins and gliadins, leading to decreased binding of G12 antibodies. Antibodies bind to specific protein sequences that are affected by new covalent and non-covalent interactions (i.e., hydrophobicity) induced by flour treatments.
The manner in which gluten proteins are presented to individuals may be related to disease development. Further research could clarify whether, together with genetic conditions, the way in which gluten protein reaches the gut defines how and if an autoimmune disease will manifest.
Gliadins are primarily detected as toxic to celiacs, and there has been an increase in the development of methods for detecting traces of gliadin in heat-treated and non-heat-treated foods. The current market includes several ELISA kits for antibodies directed against the epitopes of gliadin, which are toxic to celiac people. It should also be noted that, except for HMW- GS, disulfide, tryptophan, and tyrosine bonds may also exist in gliadins and/or LMW-GSs, which may affect dough properties [
12].
5. Conclusions
The effects of different processing conditions on the gluten network extractability, digestibility secondary structure and antibody recognition were investigated in this study. The results indicate a decrease in solubility of the polymeric and monomeric proteins. In addition, the treatments affected the glutenin and gliadin profiles; glutenins become less extractable while an increase in gliadin extractability. These changes, are the result of the rearrangement of proteins during the treatments, resulting in a more complex, less soluble structure. FTIR analysis revealed that changes in protein secondary structure are involved in the observed changes in extractability with significant increases of the intermolecular β-sheet and β-turns with a decrease in α-helix were observed for all treated samples compared to the control flour. Protein digestibility remained unchanged except for the extruded sample which showed a small but significant decrease in digestibility, most likely due to the high temperature and pressure conditions. The potential celiac disease immune stimulatory epitopes were measured and found to be decreased in oven and microwave treatment by the G12 ELISA, however no change was observed using the R5 antibody. These findings illustrate the structural and physicochemical changes of wheat proteins during heating and microwaving. Understanding the effects of various flour treatments might be beneficial to the production of specific modified flours to develop improved wheat-based foods.
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, B.M., A.F. and M.T.; methodology, B.M. and M.T; formal analysis, B.M., U.Y. and M.T; investigation, B.M., A.F. and M.T.; resources, M.T; data curation, B.M.; writing—original draft preparation, B.M. and P.S.; writing—review and editing, B.M., P.S., N.P., M.T, U.Y., D.W. and A.F.; visualization, B.M., A.F. and M.T; supervision, A.F., N.P., D.W. and M.T; project administration, M.T; funding acquisition, B.M., A.F. and M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
This research was funded by CAPES Foundation, Ministry of Education of Brazil, Brasília grant number 99999.009381/2014-07 and USDA CRIS Project No. 3020-44000-027-000D. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely to provide specific information but does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Data Availability Statement
Public data will be added to the USDA-NAL Ag Data Commons data repository.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Sushma Prakash for excellent technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors Bruna Mattioni, Michael Tilley, Patricia Matos Scheuer, Umut Yucel, Donghai Wang, Alicia de Francisco declare no conflict of interest. Author Dr. Paulino was employed by the company Medical LEX. He participated as joint-advisor in the study. The role of the company was CEO. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest”.
References
- Shewry, P.R.; Hey, S.J. Do We Need to Worry about Eating Wheat? Nutr Bull 2016, 41, 6–13, doi:10.1111/nbu.12186. [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H. Chemistry of Gluten Proteins. Food Microbiol 2007, 24, 115–119, doi:10.1016/j.fm.2006.07.004. [CrossRef]
- Hamer, R.J. Chapter IV Gluten. In; 2003; pp. 87–131.
- Johansson, E.; Malik, A.H.; Hussain, A.; Rasheed, F.; Newson, W.R.; Plivelic, T.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Gällstedt, M.; Kuktaite, R. Wheat Gluten Polymer Structures: The Impact of Genotype, Environment, and Processing on Their Functionality in Various Applications. Cereal Chem 2013, 90, 367–376, doi:10.1094/CCHEM-08-12-0105-FI. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Kontogiorgos, V.; Kasapis, S.; Douglas Goff, H. Rheological Investigation and Molecular Architecture of Highly Hydrated Gluten Networks at Subzero Temperatures. J Food Eng 2008, 89, 42–48, doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2008.04.001. [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R.; Halford, N.G. Cereal Seed Storage Proteins: Structures, Properties and Role in Grain Utilization. J Exp Bot 2002, 53, 947–958, doi:10.1093/jexbot/53.370.947. [CrossRef]
- Don, C.; Mann, G.; Bekes, F.; Hamer, R.J. HMW-GS Affect the Properties of Glutenin Particles in GMP and Thus Flour Quality. J Cereal Sci 2006, 44, 127–136, doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2006.02.005. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, C.-Y.; Lv, D.-W.; Zhen, S.-M.; Li, X.-H.; Yan, Y.-M. Comparative Phosphoproteome Analysis of the Developing Grains in Bread Wheat ( Triticum Aestivum L.) under Well-Watered and Water-Deficit Conditions. J Proteome Res 2014, 13, 4281–4297, doi:10.1021/pr500400t. [CrossRef]
- Rombouts, I.; Lagrain, B.; Delcour, J.A. Heat-Induced Cross-Linking and Degradation of Wheat Gluten, Serum Albumin, and Mixtures Thereof. J Agric Food Chem 2012, 60, 10133–10140, doi:10.1021/jf3024672. [CrossRef]
- Sudha, M.L.; Soumya, C.; Prabhasankar, P. Use of Dry-Moist Heat Effects to Improve the Functionality, Immunogenicity of Whole Wheat Flour and Its Application in Bread Making. J Cereal Sci 2016, 69, 313–320, doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2016.04.010. [CrossRef]
- Keck, B.; Köhler, P.; Wieser, H. Disulphide Bonds in Wheat Gluten: Cystine Peptides Derived from Gluten Proteins Following Peptic and Thermolytic Digestion. Z Lebensm Unters Forsch 1995, 200, 432–439, doi:10.1007/BF01193253. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, T.; Song, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Gao, X. Influence of High-Molecular-Weight Glutenin Subunit Composition at Glu-A1 and Glu-D1 Loci on Secondary and Micro Structures of Gluten in Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.). Food Chem 2016, 213, 728–734, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.043. [CrossRef]
- Sapone, A.; Bai, J.C.; Ciacci, C.; Dolinsek, J.; Green, P.H.R.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Kaukinen, K.; Rostami, K.; Sanders, D.S.; Schumann, M.; et al. Spectrum of Gluten-Related Disorders: Consensus on New Nomenclature and Classification. BMC Med 2012, 10, 13, doi:10.1186/1741-7015-10-13. [CrossRef]
- Cosnes, J.; Cellier, C.; Viola, S.; Colombel, J.; Michaud, L.; Sarles, J.; Hugot, J.; Ginies, J.; Dabadie, A.; Mouterde, O. Incidence of Autoimmune Diseases in Celiac Disease: Protective Effect of the Gluten-Free Diet. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2008, 6, 753–758, doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2007.12.022. [CrossRef]
- Farrel, R.J.; Kelly, C.P. Celiac Sprue. N Engl J Med 2002, 346, 180–188.
- Tye-Din, J. a; Stewart, J. a; Dromey, J. a; Beissbarth, T.; van Heel, D. a; Tatham, A.; Henderson, K.; Mannering, S.I.; Gianfrani, C.; Jewell, D.P.; et al. Comprehensive, Quantitative Mapping of T Cell Epitopes in Gluten in Celiac Disease. Sci Transl Med 2010, 2, 41ra51-41ra51, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3001012. [CrossRef]
- Mamone, G.; Di Stasio, L.; Vitale, S.; Gianfrani, C. Wheat Gluten Proteins: From Taxonomy to Toxic Epitopes. In Pediatric and Adult Celiac Disease; Elsevier, 2024; pp. 13–23.
- Catassi, C.; Fabiani, E.; Iacono, G.; D’Agate, C.; Francavilla, R.; Biagi, F.; Volta, U.; Accomando, S.; Picarelli, A.; De Vitis, I.; et al. A Prospective, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial to Establish a Safe Gluten Threshold for Patients with Celiac Disease. Am J Clin Nutr 2007, 85, 160–166, doi:85/1/160 [pii].
- Leszczynska, J.; Ła̧cka, A.; Szemraj, J.; Lukamowicz, J.; Zegota, H. The Influence of Gamma Irradiation on the Immunoreactivity of Gliadin and Wheat Flour. European Food Research and Technology 2003, 217, 143–147, doi:10.1007/s00217-003-0714-3. [CrossRef]
- Panozzo, A.; Manzocco, L.; Lippe, G.; Nicoli, M.C. Effect of Pulsed Light on Structure and Immunoreactivity of Gluten. Food Chem 2016, 194, 366–372, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.042. [CrossRef]
- Lamacchia, C.; Landriscina, L.; Severini, C.; Caporizzi, R.; Derossi, A. Characterizing the Rheological and Bread-Making Properties of Wheat Flour Treated by “Gluten FriendlyTM” Technology. Foods 2021, 10, 751, doi:10.3390/foods10040751. [CrossRef]
- Lamacchia, C.; Landriscina, L.; D’Agnello, P. Changes in Wheat Kernel Proteins Induced by Microwave Treatment. Food Chem 2016, 197, 634–640, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.11.016. [CrossRef]
- Scheuer, P.M.; Mattioni, B.; Barreto, P.L.M.; Montenegro, F.M.; Gomes-Ruffi, C.R.; Biondi, S.; Kilpp, M.; Francisco, A. de Effects of Fat Replacement on Properties of Whole Wheat Bread. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2014, 50, 703–712, doi:10.1590/S1984-82502014000400005. [CrossRef]
- Saxena, D.C.; Prasada Rao, U.J.S.; Rao, P.H. Indian Wheat Cultivars: Correlation between Quality of Gluten Proteins, Rheological Characteristics of Dough and Tandoori Roti Quality. J Sci Food Agric 1997, 74, 265–272, doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0010(199706)74:2<265::AID-JSFA795>3.0.CO;2-1. [CrossRef]
- AACC Method 46-30.01 - Crude Protein-Combustion Method. In AACC International Approved Methods; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, U.S.A, 2009 ISBN 978-1-891127-68-2.
- Bean, S.R.; Lyne, R.K.; Tilley, K. a.; Chung, O.K.; Lookhart, G.L. A Rapid Method for Quantitation of Insoluble Polymeric Proteins in Flour. Cereal Chem 1998, 75, 374–379, doi:10.1094/CCHEM.1998.75.3.374. [CrossRef]
- Larroque, O.R.; Gianibelli, M.C.; Gomez Sanchez, M.; MacRitchie, F. Procedure for Obtaining Stable Protein Extracts of Cereal Flour and Whole Meal for Size-Exclusion Hplc Analysis. Cereal Chem 2000, 77, 448–450, doi:10.1094/CCHEM.2000.77.4.448. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.B.; Khan, K.; Macritchie, F. Biochemical Basis of Flour Properties in Bread Wheats. I. Effects of Variation in the Quantity and Size Distribution of Polymeric Protein. J Cereal Sci 1993, 18, 23–41, doi:10.1006/jcrs.1993.1031. [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.X.; Kovacs, M.I.P. Research Note: Rapid Single-Step Procedure for Isolating Total Glutenin Proteins of Wheat Flour. J Cereal Sci 1999, 29, 113–116, doi:10.1006/jcrs.1998.0225. [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, S.; Kong, J.; Dong, A.; Yu, S. Obtaining Information about Protein Secondary Structures in Aqueous Solution Using Fourier Transform IR Spectroscopy. Nat Protoc 2015, 10, 382–396, doi:10.1038/nprot.2015.024. [CrossRef]
- Mertz, E.T.; Hassen, M.M.; Cairns-Whittern, C.; Kirleis, a W.; Tu, L.; Axtell, J.D. Pepsin Digestibility of Proteins in Sorghum and Other Major Cereals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1984, 81, 1–2, doi:10.1073/pnas.81.1.1. [CrossRef]
- Aboubacar, A.; Axtell, J.D.; Huang, C.; Hamaker, B.R. A Rapid Protein Digestibility Assay for Identifying Highly Digestible Sorghum Lines. Cereal Chem 2001, 78, 160–165, doi:10.1094/CCHEM.2001.78.2.160. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.; Llorente, M.; Hernando, A.; Kieffer, R.; Wieser, H.; Mendez, E. Development of a General Procedure for Complete Extraction of Gliadins for Heat Processed and Unheated Foods. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005, 17, 529–539, doi:10.1097/00042737-200505000-00010. [CrossRef]
- Valdés, I.; García, E.; Llorente, M.; Méndez, E. Innovative Approach to Low-Level Gluten Determination in Foods Using a Novel Sandwich Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Protocol. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2003, 15, 465–474, doi:10.1097/01.meg.0000059119.41030.df. [CrossRef]
- Scheuer, P.M.; Francisco, A. De; Miranda, M.Z. De; Ogliari, P.J.; Torres, G.; Limberger, V.; Montenegro, F.M.; Ruffi, C.R.; Biondi, S.; de Francisco, A.; et al. Characterization of Brazilian Wheat Cultivars for Specific Technological Applications. Ciencia E Tecnologia De Alimentos 2011, 31, 816–825, doi:10.1590/S0101-20612011000300041. [CrossRef]
- Lásztity, R. Recent Results in the Investigation of the Structure of the Gluten Complex. Nahrung 1986, 30, 235–244.
- Silvas-García, M.I.; Ramírez-Wong, B.; Torres-Chávez, P.I.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Barrón-Hoyos, J.M.; Bello-Pérez, L.A.; Quintero-Ramos, A. Effect of Freezing Rate and Storage Time on Gluten Protein Solubility, and Dough and Bread Properties. J Food Process Eng 2014, 37, 237–247, doi:10.1111/jfpe.12079. [CrossRef]
- Abedi, E.; Pourmohammadi, K. Physical Modifications of Wheat Gluten Protein: An Extensive Review. J Food Process Eng 2021, 44, 1–28, doi:10.1111/jfpe.13619. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-Q.Q.; Luo, S.-Z.Z.; Zhong, X.-Y.Y.; Cai, J.; Jiang, S.-T.T.; Zheng, Z. Changes in Chemical Interactions and Protein Conformation during Heat-Induced Wheat Gluten Gel Formation. Food Chem 2017, 214, 393–399, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.037. [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Wang, N.; Wang, X. Effect of Different Treatment Methods on Protein Aggregation Characteristics in Wheat Flour Maturation. Int J Food Sci Technol 2020, 55, 2011–2019, doi:10.1111/ijfs.14447. [CrossRef]
- Patey, A.L.; Shearer, G.; McWeeny, D.J. A Study of Gluten Extractability from Doughs Made from Fresh and Stored Wheat Flours. J Sci Food Agric 1977, 28, 63–68, doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740280110. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.B.; Khan, K.; Macritchie, F. Biochemical Basis of Flour Properties in Bread Wheats. I. Effects of Variation in the Quantity and Size Distribution of Polymeric Protein. J Cereal Sci 1993, 18, 23–41, doi:10.1006/jcrs.1993.1031. [CrossRef]
- MacRitchie, F. Theories of Glutenin/Dough Systems. J Cereal Sci 2014, 60, 4–6, doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2014.02.010. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.; Dangi, P.; Khatkar, B.S. Evaluation of Molecular Weight Distribution of Unreduced Wheat Gluten Proteins Associated with Noodle Quality. J Food Sci Technol 2016, 53, 2695–2704, doi:10.1007/s13197-016-2241-9. [CrossRef]
- Abedi, E.; Pourmohammadi, K. Chemical Modifications and Their Effects on Gluten Protein: An Extensive Review. Food Chem 2021, 343, 128398, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128398. [CrossRef]
- Konarev, A. V; Beaudoin, F.; Marsh, J.; Vilkova, N. a; Nefedova, L.I.; Sivri, D.; Köksel, H.; Shewry, P.R.; Lovegrove, A. Characterization of a Glutenin-Specific Serine Proteinase of Sunn Bug Eurygaster Integricepts Put. J Agric Food Chem 2011, 59, 2462–2470, doi:10.1021/jf103867g. [CrossRef]
- Chantapet, P.; Kunanopparat, T.; Menut, P.; Siriwattanayotin, S. Extrusion Processing of Wheat Gluten Bioplastic: Effect of the Addition of Kraft Lignin. J Polym Environ 2013, 21, 864–873, doi:10.1007/s10924-012-0557-8. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Rodriguez-Quijano, M.; Nunes, F.M.; Carrillo, J.M.; Branlard, G.; Igrejas, G. New Insights into Wheat Toxicity: Breeding Did Not Seem to Contribute to a Prevalence of Potential Celiac Disease’s Immunostimulatory Epitopes. Food Chem 2016, 213, 8–18, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.06.043. [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H.; Antes, S.; Seilmeier, W. Quantitative Determination of Gluten Protein Types in Wheat Flour by Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Cereal Chem 1998, 75, 644–650, doi:10.1094/CCHEM.1998.75.5.644. [CrossRef]
- Gianfrani, C.; Mamone, G.; la Gatta, B.; Camarca, A.; Di Stasio, L.; Maurano, F.; Picascia, S.; Capozzi, V.; Perna, G.; Picariello, G.; et al. Microwave-Based Treatments of Wheat Kernels Do Not Abolish Gluten Epitopes Implicated in Celiac Disease. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2017, 101, 105–113, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2017.01.010. [CrossRef]
- Vallons, K.J.R.; Arendt, E.K. Understanding High Pressure-Induced Changes in Wheat Flour–Water Suspensions Using Starch–Gluten Mixtures as Model Systems. Food Research International 2010, 43, 893–901, doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2009.12.010. [CrossRef]
- Mahroug, H.; Ribeiro, M.; Rhazi, L.; Bentallah, L.; Zidoune, M.N.; Nunes, F.M.; Igrejas, G. How Microwave Treatment of Gluten Affects Its Toxicity for Celiac Patients? A Study on the Effect of Microwaves on the Structure, Conformation, Functionality and Immunogenicity of Gluten. Food Chem 2019, 297, 124986, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.124986. [CrossRef]
- Schurer, F.; Kieffer, R.; Wieser, H.; Koehler, P. Effect of Hydrostatic Pressure and Temperature on the Chemical and Functional Properties of Wheat Gluten II. Studies on the Influence of Additives. J Cereal Sci 2007, 46, 39–48, doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2006.11.004. [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, R.; Schurer, F.; Köhler, P.; Wieser, H. Effect of Hydrostatic Pressure and Temperature on the Chemical and Functional Properties of Wheat Gluten: Studies on Gluten, Gliadin and Glutenin. J Cereal Sci 2007, 45, 285–292, doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2006.09.008. [CrossRef]
- Abedi, E.; Pourmohammadi, K. The Effect of Redox Agents on Conformation and Structure Characterization of Gluten Protein: An Extensive Review. Food Sci Nutr 2020, 8, 6301–6319, doi:10.1002/fsn3.1937. [CrossRef]
- Angioloni, A.; Collar, C. Nutritional and Functional Added Value of Oat, Kamut ®, Spelt, Rye and Buckwheat versus Common Wheat in Breadmaking. J Sci Food Agric 2011, 91, 1283–1292, doi:10.1002/jsfa.4314. [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R.; Halford, N.G.; Belton, P.S.; Tatham, A.S. The Structure and Properties of Gluten: An Elastic Protein from Wheat Grain. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2002, 357, 133–142, doi:10.1098/rstb.2001.1024. [CrossRef]
- Wellner, N.; Mills, E.N.C.; Brownsey, G.; Wilson, R.H.; Brown, N.; Freeman, J.; Halford, N.G.; Shewry, P.R.; Belton, P.S. Changes in Protein Secondary Structure during Gluten Deformation Studied by Dynamic Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 255–261, doi:10.1021/bm049584d. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gamlath, S.; Wakeling, L. Nutritional Aspects of Food Extrusion: A Review. Int J Food Sci Technol 2007, 42, 916–929, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.2006.01309.x. [CrossRef]
- Pilolli, R.; Gadaleta, A.; Mamone, G.; Nigro, D.; De Angelis, E.; Montemurro, N.; Monaci, L. Scouting for Naturally Low-Toxicity Wheat Genotypes by a Multidisciplinary Approach. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 1646, doi:10.1038/s41598-018-36845-8. [CrossRef]
- Morón, B.; Bethune, M.T.; Comino, I.; Manyani, H.; Ferragud, M.; López, M.C.; Cebolla, Á.; Khosla, C.; Sousa, C. Toward the Assessment of Food Toxicity for Celiac Patients: Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies to a Main Immunogenic Gluten Peptide. PLoS One 2008, 3, e2294–e2294, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002294. [CrossRef]
- Osman, a a; Uhlig, H.H.; Valdes, I.; Amin, M.; Méndez, E.; Mothes, T. A Monoclonal Antibody That Recognizes a Potential Coeliac-Toxic Repetitive Pentapeptide Epitope in Gliadins. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2001, 13, 1189–1193.
- Silano, M.; Vincentini, O.; De Vincenzi, M. Toxic, Immunostimulatory and Antagonist Gluten Peptides in Celiac Disease. Curr Med Chem 2009, 16, 1489–1498, doi:10.2174/092986709787909613. [CrossRef]
- Molberg, Ø.; Flæte, N.S.; Jensen, T.; Lundin, K.E.A.; Arentz-Hansen, H.; Anderson, O.D.; Kjersti Uhlen, A.; Sollid, L.M. Intestinal T-Cell Responses to High-Molecular-Weight Glutenins in Celiac Disease. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 337–344, doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(03)00890-4. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).