Introduction: In this article I would like to explore the brain's mechanisms of thought formation and selection, proposing a model where neural activity evolves like how organisms adapt and survive in nature. Generation and evolution of thoughts in the brain has the resemblance to the Darwinian processes of natural selection i.e., survival of the fittest. Thoughts are born through the interaction of neural networks, grow through reinforcement, and "die" if they are deemed unfit. I would like to keep this article very simple for general audience and present it in a popular level assuming reader having no prerequisite knowledge on this subject.
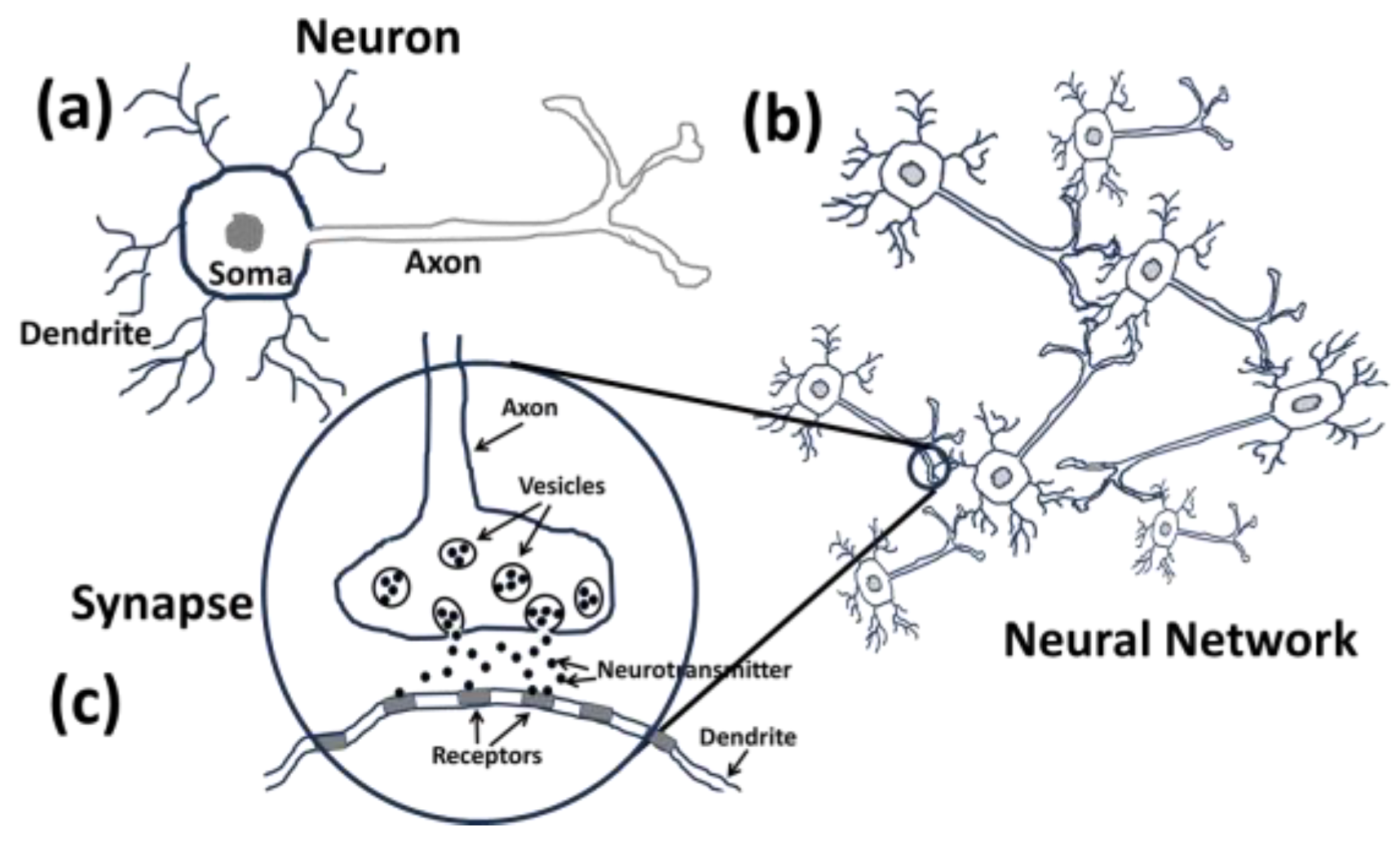
Neuron and Neural Network: Let us start with the building block of brain and the nervous system i.e., a neuron. A neuron, also known as a nerve cell, is a cell in the brain and nervous system that sends and receives signals throughout the body. These signals are sent using electrically charged ions and chemical compounds along with formation of new connections among neurons. We shall discuss how this process allows us to think, feel the world around us, move our muscles, and form memories. Neurons are distributed throughout our body, i.e., lungs, heart, stomach, liver, under the skin and so on, and mostly Also, resonance within these oscillatory networks can ensure that certain ensembles of neurons are more responsive to specific frequencies, maintaining the integrity of their activity without interference from other processes. High Q-factor tuning in the brain organ. Each organ communicates with each other through the neuronal circuits. Heart neurons receive and send signals to take care of the heart and, similarly, neurons in other organs. Neurons are electrically or chemically excitable and are connected to other neurons via neuronal branches called dendrites which receives the signals from other neurons and transmit signals through a channel so called axon to other neurons (see
Figure 1).
The ends of the axons and dendrites form a junction having a small gap called synapse. A typical neuron has a cell body called as soma, an axon, and dendrites. The axon transmits signals away from the soma, while the dendrites which look like tree branches, extend out from the soma to receive messages from other nerve cells from the surroundings. Neurons communicate with each other by transferring chemicals called neuro-transmitters across synapses (See fig 1(c)).
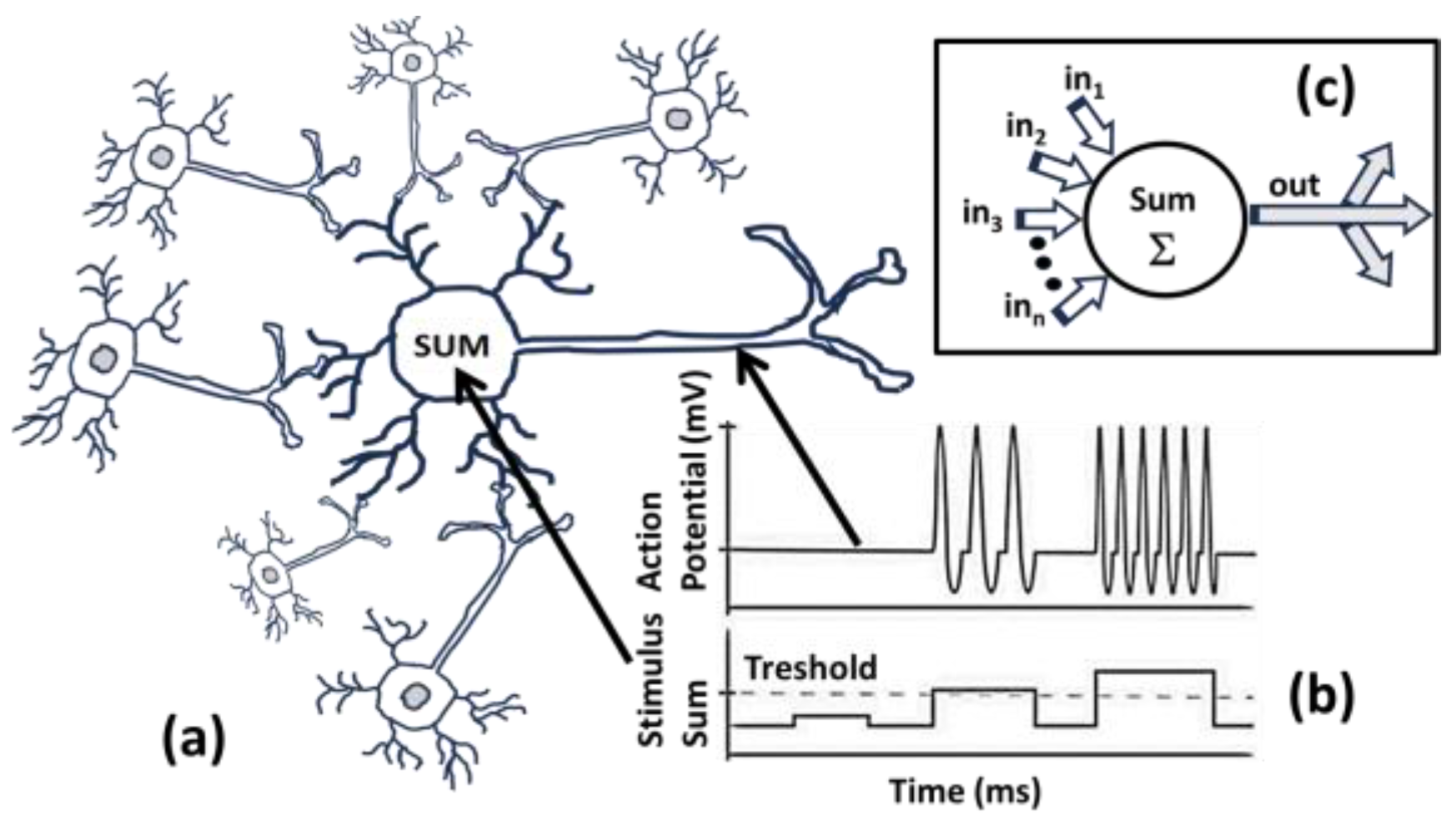
Action potential and Homeostasis: Neurons operate in an all-or-nothing (ON or OFF) manner, meaning they either fire completely or not at all (see
Figure 2). The dendrites, or receiving part of the neuron, receive synaptic inputs from axons (see
Figure 2(a)). When a neuron's charge reaches -55 mV of the threshold value, it fires electrical signal which is called as an “action-potential”, and the potential moves down the axon (see
Figure 2(c)). If the sum of stimulus is less than a threshold value, (-55 mV) the neuron does not fire. If the sum is above the threshold, then the frequency of firing is proportional to the magnitude above the threshold value. Neurons can increase the frequency of firing to provide more energy/charge to other neurons, but they cannot fire above a certain magnitude of charge voltage potential and reduce the frequency. After firing, the neuron enters an inactive period called refractory period which lasts for few milliseconds due to deactivation of sodium channels in the cell, where it cannot charge or fire again until it returns to its initial resting state potential. This state is achieved by a process called Homeostasis i.e., the process of bringing back the excited cell to equilibrium stable conditions through required chemical process in the cell in response to external stimuli for its survival. Homeostasis is the most essential part of life to survive, which occurs at all scale from a cellular level up to our body level to maintains a stable internal environment such as temperature, sugar, fluid levels etc. and this process of homeostasis occurs in every organ of our body too.
Sensory and Motor neurons: There are different types of neurons, and not all of them are the same. For example, in the spinal cord, there are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons (located between sensory and motor neurons). Sensory neurons carry impulses from the nerve end called sensory receptors (such as chemo, thermo, mechano, photo -receptors) to the brain or spinal cord, while motor neurons carry impulses from the brain or spinal cord to effectors (i.e., muscles and glands).
Let us discuss a simple example of nerve response. Suppose you touch a hot object; the sensory neuron releases neuro-transmitters which are chemical messengers to carry chemical signals (“messages”) related to pain from one neuron (nerve cell) to the next target nerve cell. The signal is then transmitted to specific region of the brain or spinal cord and from there, the signal is sent back to another set of neurons connected to muscles, causing a reflex action to withdraw from the heat. This reaction can be considered as a simple response to a stimulus. Now the question that we would like to ask here is: Is this thinking or a sub-conscious action? The answer is both: Yes and No.
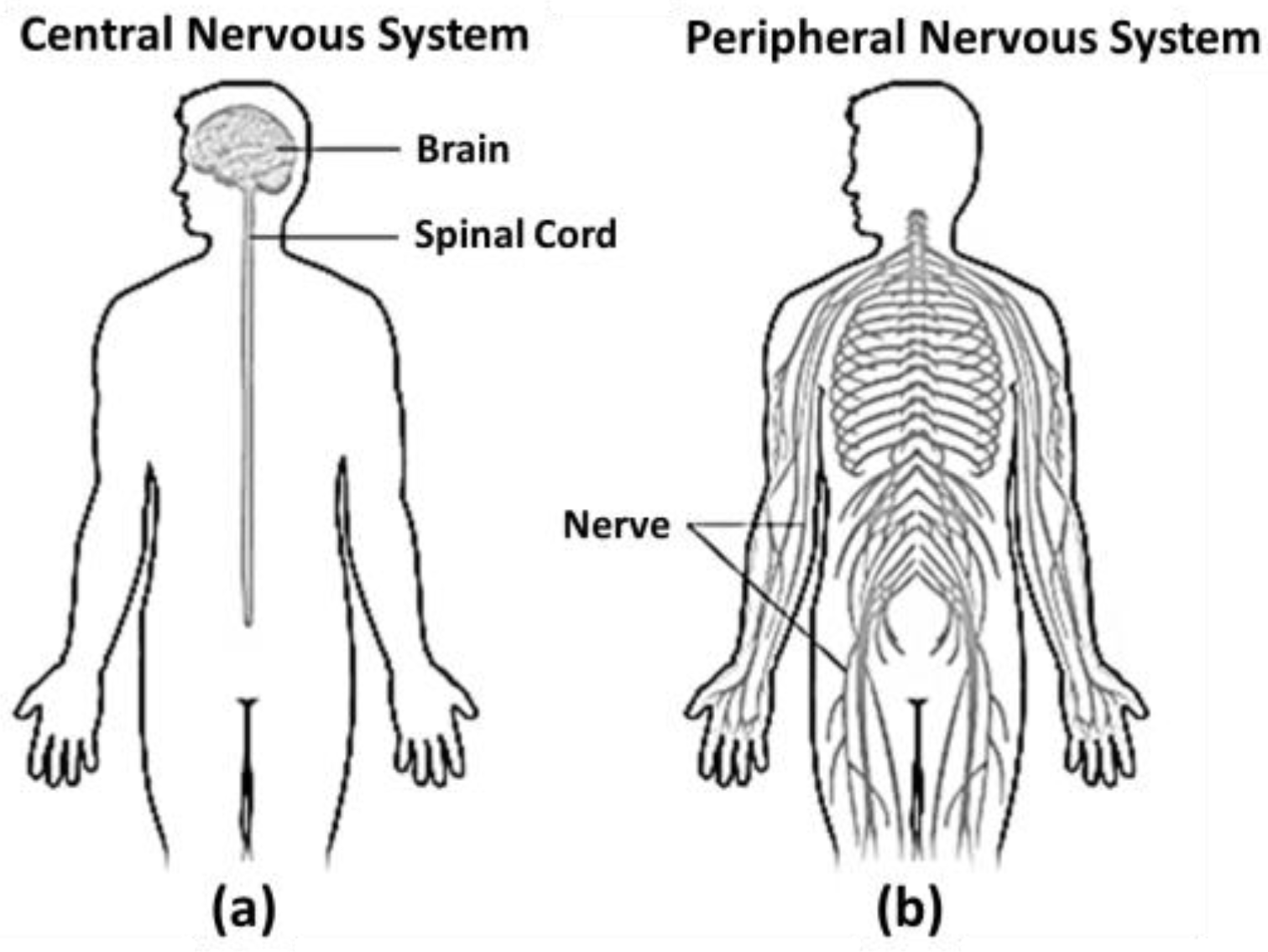
Central and Peripheral nervous system, Plasticity and Connectome: We should note here that even unicellular organisms react to stimuli but they do not have central (the brain and the spinal cord which carries messages back and forth between the brain and the nerves that run throughout our body) or peripheral (which runs throughout the body) nervous system like us (see
Figure 3), and their behaviour can be explained entirely by chemical processes. Whereas, in our case, the positive outcome of pain relief by withdrawing from the heat reinforces the neural pathways involved, making them stronger and more likely to be used again.
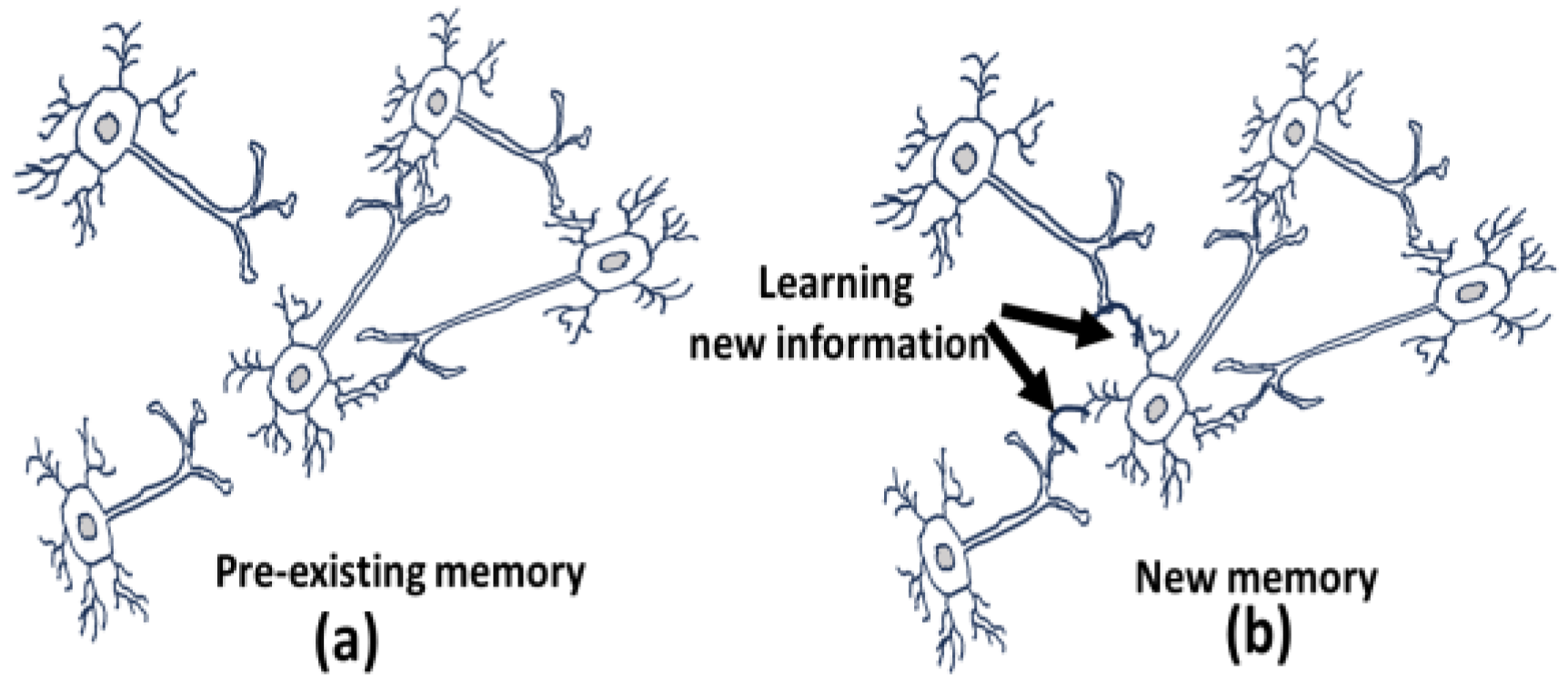
This reinforcement (wiring and firing together leading to the formation of connections of neurons called “connectome” via dendrites/synapses) is stored as a memory in our neural network (see
Figure 4).
Experiencing over time, the neural network adapts to perform tasks with greater speed, accuracy, and coordination. This is evident in skilled activities such as sports, musical performance, and other motor tasks. Eventually, a person can perform these tasks almost instantaneously with minimal conscious effort, ultimately mastering skills through practice and becomes part of its subconscious domain.
A point of caution: many believe that we develop muscle memory through practice, but this involves the strengthening and refinement of neural pathways in the brain and spinal cord that control specific movements. This process is facilitated by the formation of new branches and connections with other neurons, known as “synaptic plasticity” (see
Figure 4). While muscles themselves do not form new connections or "memories," they do adapt to repeated use by becoming stronger and more efficient. The term "muscle memory" thus refers to the brain's ability to automate and optimize motor skills through practice and repetition. Thus, the brain's ability to form new synapses (connections) and reorganize existing ones, a process known as “synaptic plasticity” upon any experiential event, is fundamental to learning and memory. Thus, new experiences and learning promote dendritic growth and increasing the number of connections a neuron can make. This process forms the basis of memory, which is essentially the connectivity of neurons (neuronal circuit) via these dendrites-axon connections through synapses and are dynamic in nature. This dendrite formation and synaptic plasticity is continuously happening non-stop throughout our life time.
Thus, in brief, neurons communicate through electrical impulses (action potentials) and chemical signals (neurotransmitters). Sensory inputs such as smell, sound, touch, balance, sight etc., are processed by specific brain areas, leading to the generation of new neural connectivity. Experiencing any stimulus generates electrical patterns that correspond to these inputs and repeated activation of specific neural circuits can lead to "hardwiring," where these circuits become more robust and efficient, forming long-term memories contributing to our library of memories.
Repairing and relearning: If a connection or neural pathway is damaged, the brain’s neuroplasticity allows for potential repair or reformation of these pathways through relearning (rehabilitation). Even if specific memories are lost, relearning similar experiences can help to reconstruct them. It is important to note that genes play a significant role in plasticity because they provide the instructions for making the raw materials needed for neuronal branches and overall brain development. Genetic variations can influence the formation of neural connections, neurotransmitter production, and brain structure. Unusual genetic codes may lead to unusual neural connectivity and unusual electrochemical patterns, which can manifest as unusual cognitive abilities, unusual emotional responses, or neurological disorders such as autism, schizophrenia, and other neuro-developmental disorders. However, despite genetic predispositions, the brain’s plasticity allows for adaptation and compensation, potentially rectifying some effects of unusual neural connectivity through training experience and learning. All these processes are mechanistic, governed by chemical laws, and involve chemical responses leading to physical changes.
Sensory and internal thoughts: Now coming to thoughts, thoughts can be broadly classified into sensory-dependent thoughts and internally generated thoughts (thinking). Sensory-dependent thoughts are directly influenced by external sensory input and arise in response to environmental stimuli. These can be immediate, such as noticing the smell of coffee or the sound of a bird chirping, or reflexive, such as feeling the heat of a stove and deciding to withdraw your hand. This reflexive action is guided by memories stored in our neural network library from past learning experiences. All these experiential memories are sometime termed as internal model of the outside world. Thus, interpretation of the world is based on prior knowledge i.e., memories stored by learning or experience. Hence, we say that brain interprets the world.
On the other hand, the internally generated thoughts, or thinking, are produced within the mind, independent of direct sensory input. To keep our discussion simple, let us assume that the brain has different regions (compartments) specialized in interpreting various electrochemical patterns from sensory input as well as internally generated electrochemical patterns. By "interpretation," I mean not a logical computation but simply chemical response pathways in those designated regions which has evolved and adapted during the natural course of our biological evolution. This aspect of internal thought generation will become clear as we go on.
Subconscious and Conscious process: Before we discuss how internal thoughts which involves more complex cognitive processes and include activities such as reflection, planning, problem-solving, and imagination are generated in our brain. Let us briefly examine what is subconscious processes occurring in our brain/mind and then compare it with conscious process. Subconscious activity refers to the generation of electrochemical signals/patterns related to autonomic functions such as controlling heartbeat, breathing, digestion, and other. These originate in specialized regions of the brain. These patterns are generally rhythmic, stable, and highly regulated to maintain equilibrium (homeostasis). While subconscious and conscious patterns differ in their origin and nature, they interact continuously. For instance, subconscious signals about hunger can influence conscious decisions about eating. Similarly, conscious thoughts can modulate subconscious patterns; for example, deep breathing exercises can consciously influence our breathing rate and indirectly affect our heart rate and stress levels.
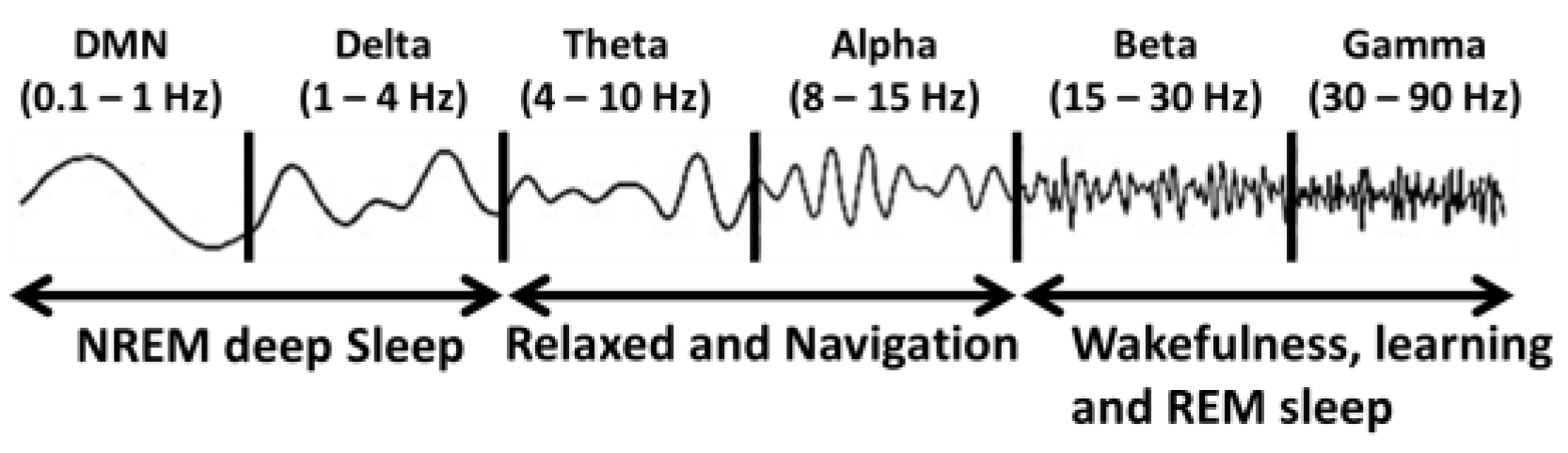
Subconscious processes typically involve simpler, more regular electrical patterns in brain characterized by lower-frequency electrical oscillations observed experimentally, such as theta waves (4 – 8 Hz), alpha waves (8 – 12 Hz), associated with relaxed and automatic functions and delta waves (0.1 – 3.9 Hz) associated to non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep which is a restful phase of sleep that helps to repair body and brain (see
Figure 5.). All these waves have been observed experimentally by Electro-Encephalo-Gram (EEG) related to human behaviour. During sleep and dream. consolidation and reconsolidation of memory occurs as it has been found experimentally using volunteers that those who had slept well tends to remember object shown to them better the next day than those who have not slept (who have forgotten many of them the next day) [
1].
It has also been observed experimentally that upon dreaming the sleep is less interrupted and without dream the sleep is more disturbed, so it appears as if one sleeps to dream and dreams to sleep well [
1]. (Note: One falls asleep due to exhaustion of cortisol hormone produced by the adrenal gland which sit on top of each kidney and the pituitary gland in the brain regulates cortisol production which is necessary to remain awake. Similarly, the pineal gland secretes melatonin whose function is to promote sleep and inhibit signals that promote wakefulness [
2]). Electrical activity pattern in subconscious processes is more consistent and predictable, reflecting the habitual and routine nature of subconscious processes. Different neurotransmitters, mainly GABA, serotonin, and norepinephrine, are predominantly involved in subconscious processes [
3].
Whereas, conscious processes typically involve more complex and variable electrical patterns, often reflecting high-frequency electrical oscillations, such as beta (12.5 – 30Hz) associated with normal awake conscious state and gamma waves (30 – 100 Hz) associated with active cognitive processing, consuming more energy than subconscious process because of its higher frequency oscillations. Neurotransmitters such as dopamine, glutamate, and acetylcholine are predominantly involved in conscious processes [
4]. However, it is important to note that each neurotransmitter can participate in a wide range of processes, both conscious and subconscious, depending on the neural circuits and contexts in which they are active. The distinction helps in understanding their primary functions but should not be taken as an absolute separation.
The conscious and subconscious minds are not tied to completely different sets of neurons but rather involve different patterns and modes of activity within the same complex neural networks. These networks interact continuously, allowing for the seamless integration of conscious and subconscious processes in our daily lives. Because of experience and learning process from birth, such as visual, smell, hearing, motion, language, planning, cognition and so on, the related connected pattern get stored as memories. These memories become part of subconscious activity as it is energetically beneficial for the brain to minimize the energy consumption in daily activities. Thus, one can argue that most of our daily activities are performed by simply using the stored memory and occasionally a minimum effort is made consciously (i.e., guided using high frequency wave required for reinforcing memories generated by the outer layer of the brain i.e., cortex) which eventually becomes part of subconscious process [
5]. The transformation from conscious to subconscious knowledge or memory are executed by cerebrum cortex in most mammals because we observe gamma waves during thinking process in an awake state.
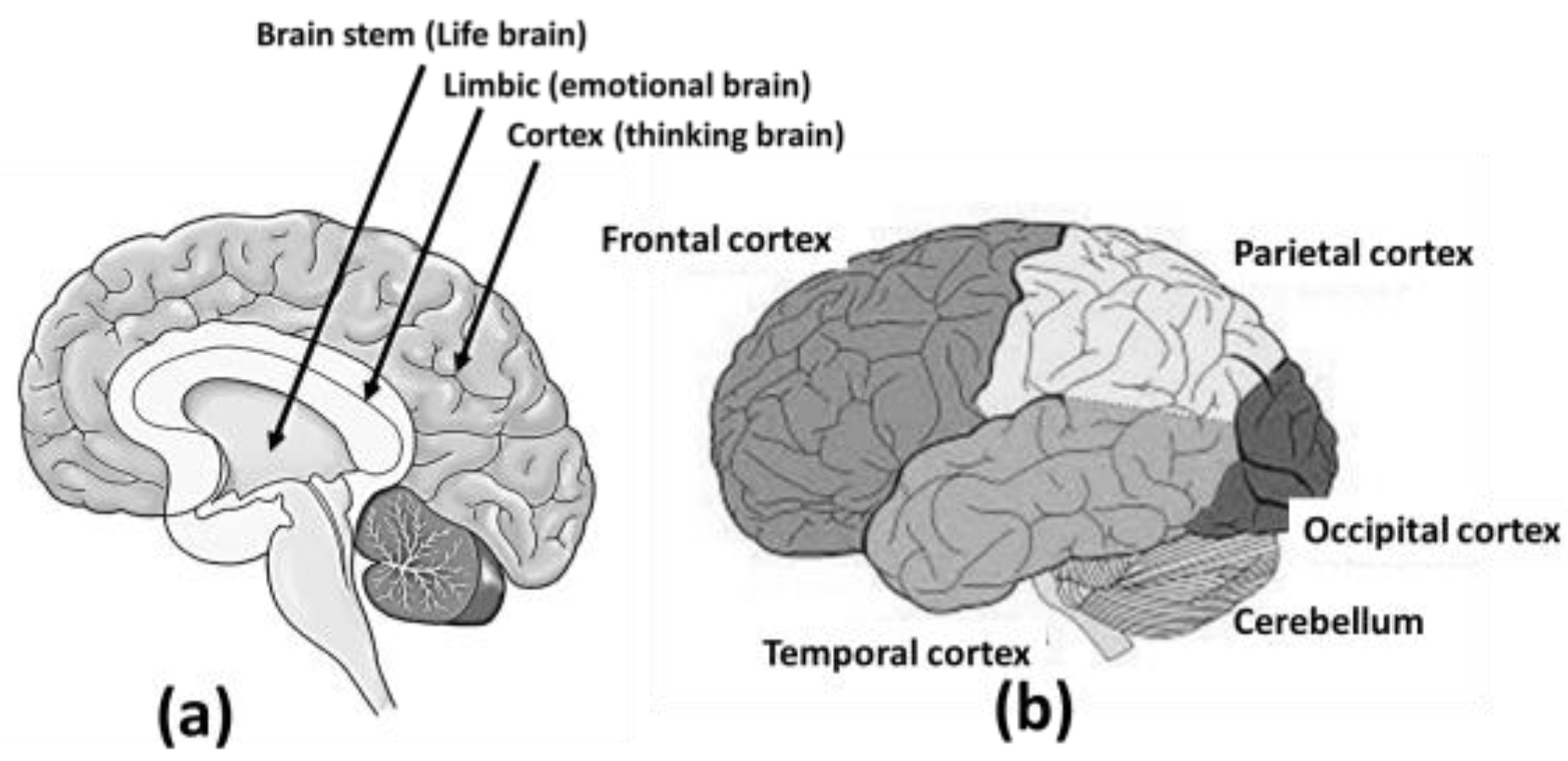
The three layered brain: The human brain is generally considered to have three layers (see
Figure 6) and they are, “cortex” the outer most layer which is active during wakefulness, “limbic”, the middle layer- involved in the formation of new memories and the retrieval of existing memories by interacting with cortex to store and retrieve information and “brain stem”, the inner most layer (sometimes called as reptilian brain) which controls vital subconscious functions necessary for survival, such as heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, and arousal, and each of these layers are further separated into regions for specialised functions.
Since, humans are having a large cerebrum cortex layer compared to other animals, the extra working space in the cortex region helps in holding short-term memories which eventually with continuous stimulus and through propagation of electrical patterns get reinforced and incorporated as a long-term memory in limbic region and becomes part of subconscious information memory library. A best example of short-term memory is about vision where the world remains stationary despite movements of the eyes, head and body, the short-term memory builds the model of the world in brain and whether or not they are in the field of view, we can point or turn to objects in the surroundings. The internal model thus contains an abstract representation of both the surroundings and the motions of the head and body leading to a stable representation of space and orientation. As we know that even in dark, we can to a certain extent move around and if practiced repeatedly the subconscious region of the brain takes over. Thus, we can say that most of our daily activities are performed by subconscious process. Sleepwalking is strong evidence of a subconscious process, where the subject is not in active conscious state, affecting up to 17% of children between the ages of 8–12.
Homeostasis at play: The fundamental aspect of how the nervous system operates is to maintain homeostasis of neurons and each neuron respond to changes in the environment. Here is how this process works: Sensory receptors in various parts of the body, including in the tip of your toe, detect changes in the environment, such as temperature, pressure, or pain. These sensory receptors send electrical signals through sensory neurons to the brain, where they are felt (some consider it as processing and interpreting). The specialised brain regions receive and integrates these sensory signals, as if understanding the current state of the body and environment. Based on this information, these regions of the brain react (it appears as if it makes decisions about how to respond. This can involve conscious awareness (e.g., deciding to move your body away from something hot) or subconscious processes (e.g., automatic reflexes which is most often the case)). The brain sends electrical signals through motor neurons to appropriate muscles or organs to initiate a response. For example, if you touch something hot, the brain sends signals to the muscles to withdraw. This chain of response pathway is evolutionary designed to protect the body or maintain homeostasis by correcting the detected imbalance. Thus, the overall goal of these responses is to maintain homeostasis, which is the neuronal cell’s (also the body’s) ability to keep internal conditions stable despite external changes. For instance, if you touch something hot, the withdrawal response helps prevent damage and maintain a safe body temperature. This mechanism underlies both reflexive actions and more complex neural activities, “appearing like conscious decisions”, ensuring that the body can adapt to and manage various challenges and changes in its environment.
In gist, the main essence is, neurons communicate via electrical impulses (action potentials) and chemical signals (neurotransmitters). These signals travel through neural circuits, influencing other neurons and leading to responses and further signalling. Although individual neurons might only respond to specific inputs, the interaction among millions of neurons creates complex electrical patterns and can be perceived as performing computations. This is not computation in the classical sense (like in a computer), but rather a responsive property of neural interactions.
Interaction among different regions in brain: Different regions of the brain are specialized for various functions. For example, the visual cortex processes visual information, while the prefrontal cortex helps in formation of memory and hence learning, decision-making and so on. These areas do not operate in isolation but work together, integrating neural activities in such a way that resembles complex processing. Through processes like synaptic plasticity, the neural circuits adapt and learn from experiences. This adaptation is driven by changes in the patterns of synaptic connections, which allows for flexible responses and decision-making. Thus, the brain activities are dynamic patterns of electrical and chemical signalling continuously, based on experience, context, and goals. This dynamic aspect appears as “computation” of an ongoing process of adjustment and integration. The “illusion” of computation might be a matter of perspective, but it reflects the complex nature of how the different region of brain interacts and responds to a stimulus i.e., information.
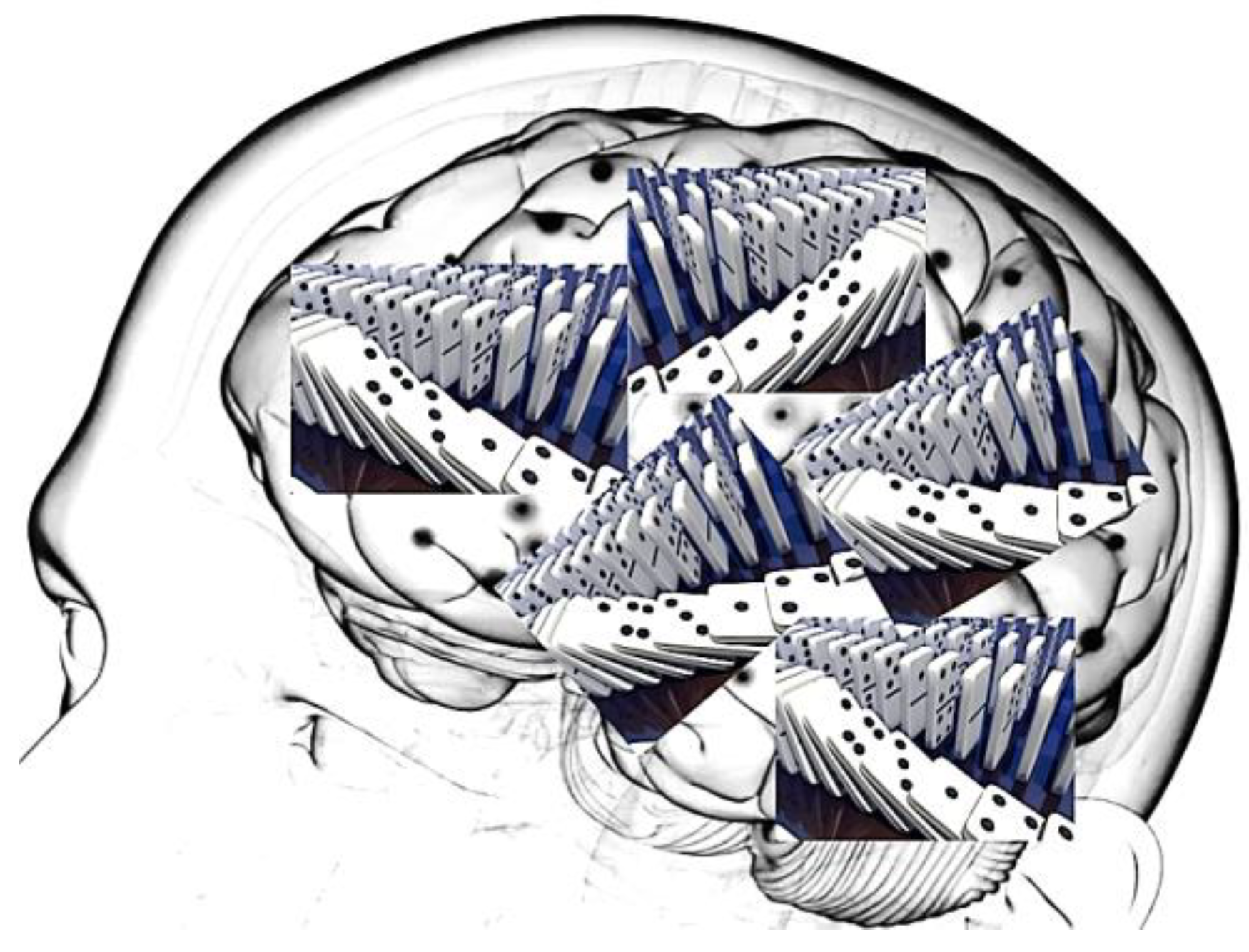
Attractor and domino effect: When one neuron is activated, it can trigger a cascade of activities in the connected neurons, akin to a “domino effect” (see
Figure 7) following along the reinforced path or creates a new path if it is a new experience. This is how information propagates through the network. In simpler organisms, the neural networks are less complex, but the fundamental principles are similar.
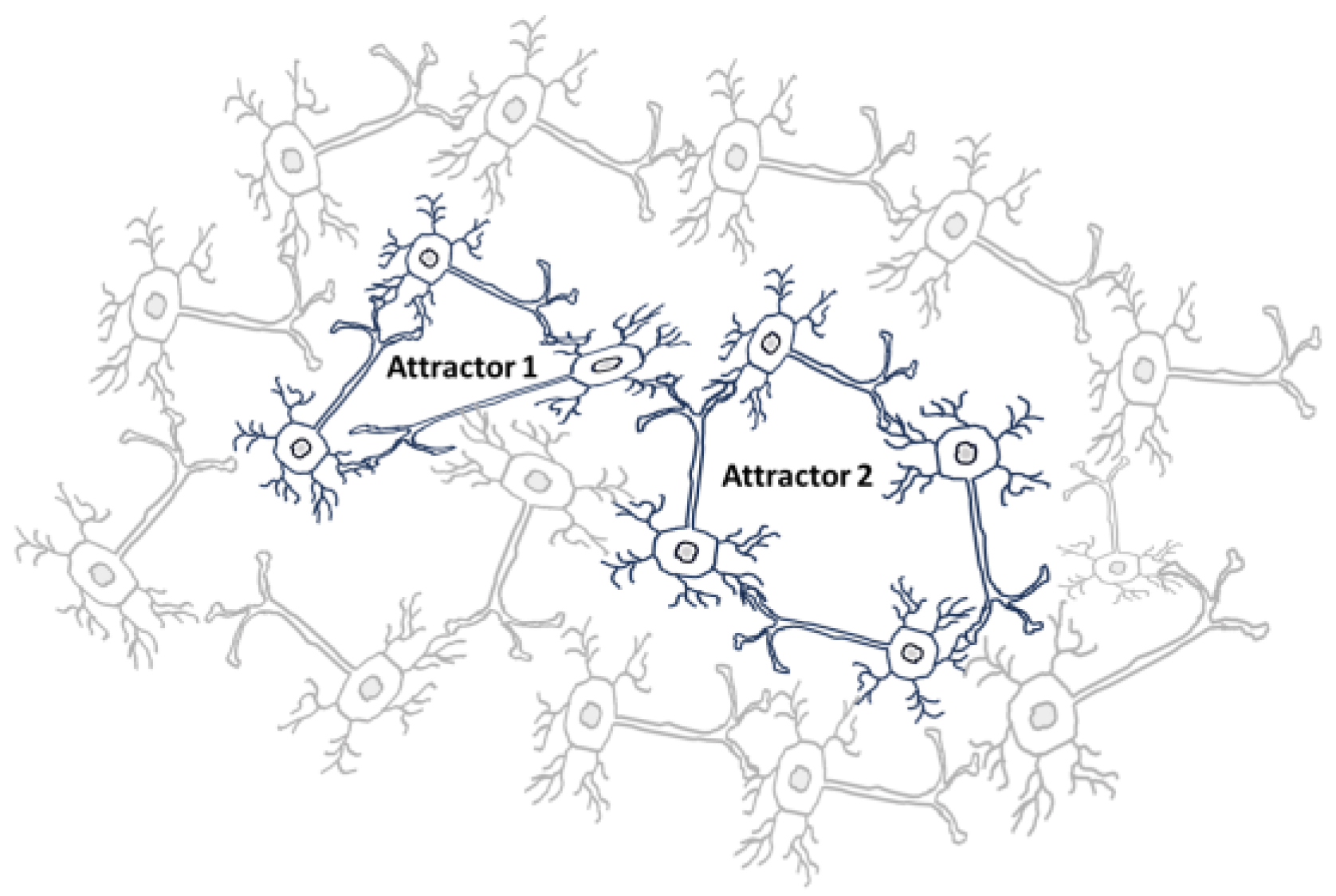
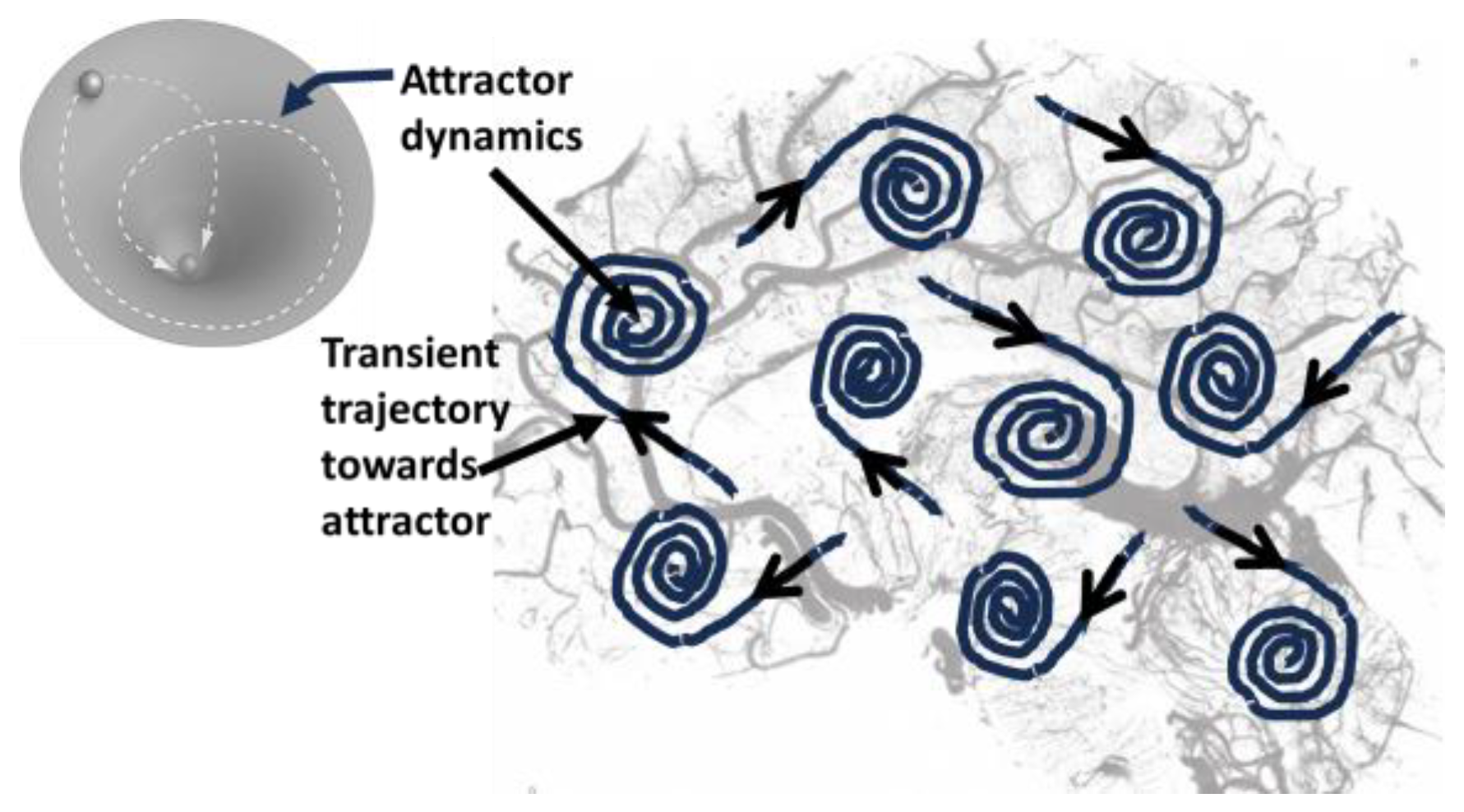
As organisms evolved, their neural networks become more intricate and increased in complexity, supporting a broader range of functions and more sophisticated behaviours. The objective of neural communication and coordination are fundamental to maintaining life and enabling adaptive behaviour for survival. The brain consists of vast networks of neurons (one hundred billion) that interact through synapses. When you learn or feel something, certain patterns of neural activity become more stable and easier to activate. These patterns can be thought of as “attractor” states (see
Figure 8). An attractor is a state towards which the pattern tends to evolve, from both external or internal stimuli. In the brain, these attractors represent stable patterns of neural activity in a stable neural circuit unit that correspond to particular memories, concepts, or knowledge.
Synaptic plasticity, particularly long-term potentiation (LTP – repeated activation) and long-term depression (LTD – unused connections), plays a critical role in forming and stabilizing these attractor states. Thus, through repeated activation, the synapses strengthen (LTP) or weaken (LTD), making certain neural pathways more likely to fire together in the future.
This is how memories (attractors) are established and these specialised pathways having electrical activities (abstract patterns) appears like feeling or understanding, which is simply a projection of outer world to form an inner world model. When faced with new information, the brain's neural activity may initially be dispersed across forming new dendrites/synapses junctions forming various states (due to uncertainty or lack of clarity) and with time and sustained use, some connections survives and some dies which resembles as Darwin’s process of natural selection leading to the survival of the fittest. This leads to formation of stable attractors (memory).
Evolution of thoughts and thoughts moving sequentially in time: The brain activity converges to an attractor state that represents a particular state for that information based on the past experiences and knowledge. This convergence of neural activity is what we experience as feelings. Since the present moment “now” becomes “past” the next moment, thus, with the same experience we can revisit the same attractor state giving rise to same feeling or understanding or thoughts. Once a certain brain activity pattern has converged on an attractor state (thought) that represents a concept or a situation, it further activates related attractor governed by the associated strengthened neuronal path as a function of time, which is then related to chain of thoughts. Stronger the current attractor state of neuron is connected to another particular attractor, the more confidently the thoughts move (appears like making predictions) or otherwise new synaptic connections (new attractors) are made by invoking plasticity for guessing, and further upon confirmation the attractor now become part of subconscious memory or knowledge. This is the mechanism of evolution of thoughts and thoughts moving in time in the brain.
What we mean by understanding? Understanding often involves hierarchical brain activities, where the brain activities occur at multiple levels, this is a kind of representation of information constituting multiple levels of abstraction (projecting it to firing and wiring of neural circuit). Lower levels process are basic sensory inputs in sensory levels (the limbic level), while higher levels (the cortical level) integrate these inputs into more complex concepts in term of ensemble of neural circuits/attractors. Thus, the brain integrates information across different regions (cortex and limbic regions) to form a coherent understanding. This integration allows the brain to find the most appropriate attractor state that represents the entire context of the information. Over time, the sustenance refines the attractor landscape, making understanding more accurate and predictions more reliable [
6]. For understanding to be coherent, the brain must tie together various pieces of information into a unified whole. This tying process involves synchronizing the activity of different neural regions, often through high frequency gamma oscillations or other synchrony mechanisms [
6]. When the brain achieves coherence, it has effectively moved to an attractor state that represents a unified understanding of the information. All these happens in a fraction of a second and it appears as a continuous sequence of evolution of thoughts.
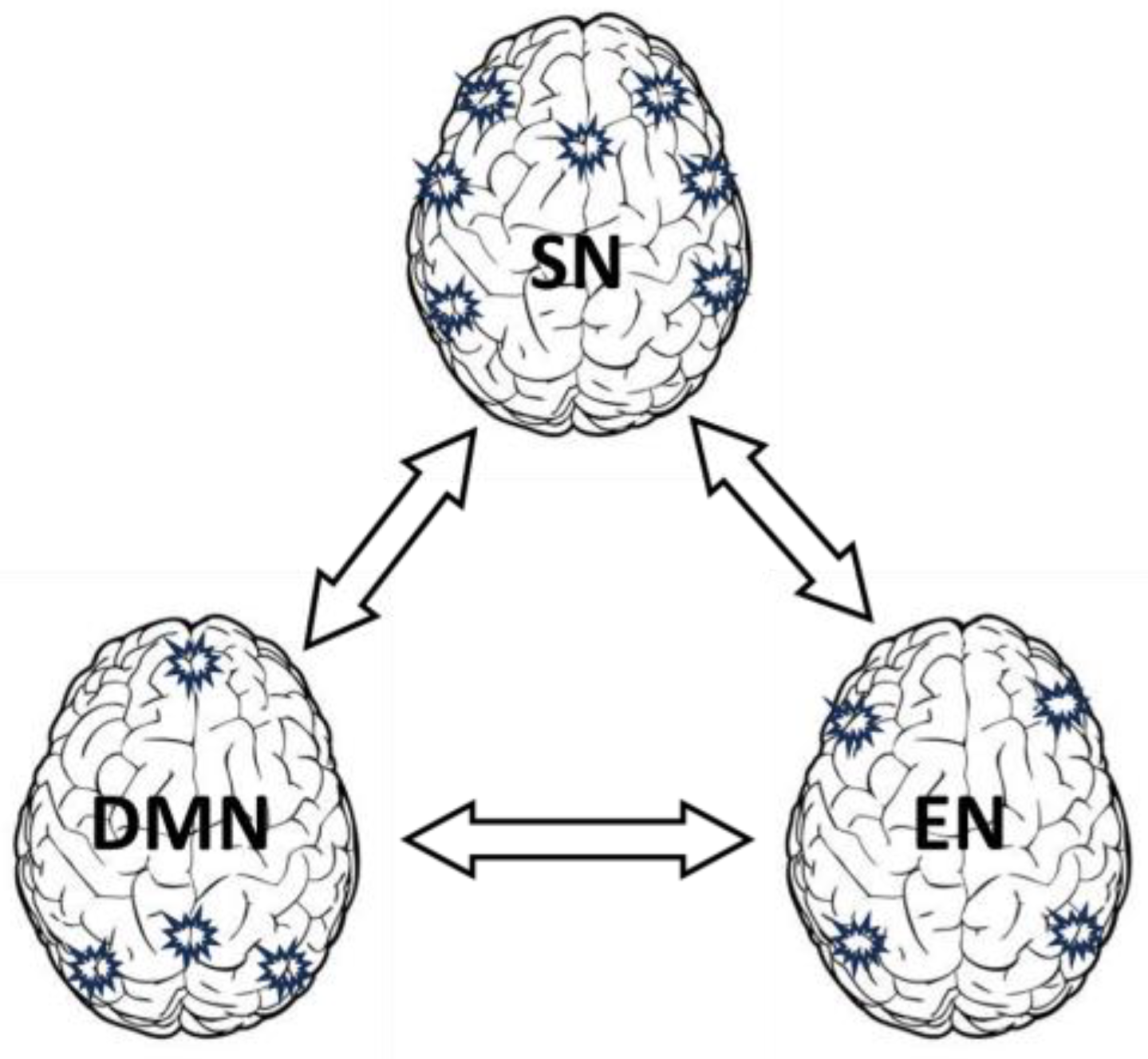
Role of Default Mode Network (DMN), Salience Network (SN) and Executive Network (EN) for generating thoughts and action: Now we are more or less prepared to address how internal thoughts are generated. Brain consists of three major functional networks: Default Mode Network (DMN), Salience Network (SN) and Executive Network (EN) (see
Figure 9) [
7,
8]. The DMN is highly active during mind-wandering, when the brain is not focused on the external environment or a specific task. While wandering it generates spontaneous thoughts allowing the brain to explore different scenarios and ideas. Neurons require a constant supply of energy, primarily glucose and oxygen, to maintain ion gradients and overall function for successful neural activity to ensure proper metabolic support and cellular health. Blood Oxygen Level Dependent (BOLD) signal in fMRI studies, which corresponds to very low-frequency oscillations around 0.1 Hz has been observed. These slow oscillations are a hallmark of the DMN during restful, awake states and are thought to reflect the brain's intrinsic activity when not focused on external tasks. This low frequency reflects its baseline level of neural activity. The brain's baseline activity helps maintain homeostasis of neuron in the resting state and provides a foundation for more active states. This resting state of low frequency oscillation causes spatially large wavelength oscillation of standing or sometimes travelling waves across the brain [
9,
10,
11] which are crucial for internal neural activity such as maintaining memory consolidation and integration of past experiences. Salience Network (SN) acts as a mediator between the DMN and the executive Network (EN) as will be discussed in detail in the next section.
What provokes the DMN? It is the Salience Network (SN). Certain external stimuli (or thoughts) from sensory neurons are treated as more important or salient, effectively creating a potential gradient that drives neural activity towards those highlighted areas, The salience network, determines which are the most relevant input in a given moment, it directs the flow of neural activity, creating a dynamic landscape where certain thoughts or perceptions (attractor) are more "energized" i.e., likely to be active. Thus, the salience network identifies important or novel stimuli that require immediate attention, whether they are external (like a loud noise) or internal (like a strong emotion). The salience network is crucial in switching the brain’s activity between the DMN (which is active during rest and internal thought) and the executive network, EN (which is active during goal-directed tasks). Executive network (EN) also termed as the “executive control network” or the “central executive network”, or "task-positive network" because it is active when an individual is engaged in a specific task. The salience network often interacts with the executive network, helping to shift the brain's activity from the DMN to the task-positive/executive network when something important or novel needs attention. Thus. SN acts as a mediator between the DMN and the EN [
7,
8]. These three networks work together to balance internal thought processes with external demands, ensuring that the brain can efficiently switch between rest, focus, and action. DMN, SN, and EN are generally considered distinct networks because they have different functional roles and involve specific brain regions (see
Figure 9). While these networks are distinct, they are not entirely separate from one another. There are overlaps in the brain regions involved in these networks, meaning some neurons and regions may participate in more than one network depending on the context and demands. For example: a region of brain called as the anterior cingulate cortex is involved in both the SN and EN [
12]. Depending on whether the task is about detecting salience or engaging in executive functions, the activity of this region might shift from one network to another. Thus, same neurons can indeed play different roles depending on the context, acting within the DMN, SN, or EN depending on the task or state of the brain. The brain is highly context-dependent: a neuron might be part of the DMN during a resting state and part of the EN when engaged in a focused task. This flexibility is key to the brain’s ability to adapt to different situations. There is constant communication between these networks. The SN, for example, acts as a switch, determining whether the brain should be in a default mode (DMN) or actively engaged in a task (EN). This switching is facilitated by the overlapping nature of some of the neurons and brain regions involved. Since, DMN, SN, and EN involve both distinct and overlapping sets of neurons, this interlacing and overlap reflect the brain's ability to integrate and adapt to various cognitive processes, ensuring that it can seamlessly undergo transition between different states and tasks. So, to recapitulate, thoughts are primarily generated and managed by the DMN, with goal-directed or task-oriented thoughts involving the EN and SN.
Once the thoughts are provoked then this change involves an increase in the frequency of neural oscillations, moving from the low-frequency DMN oscillations to higher-frequency bands like theta (4-8 Hz). alpha (8-12 Hz), beta (13-30 Hz), gamma (30-100 Hz) waves, because internal cognitive demands increase in neuronal firing rates, i.e., leading to higher-frequency oscillations. These processes require more glucose and oxygen, which are delivered through increased blood flow to these active brain regions. This increased energy consumption is reflected in the generation of higher frequency oscillations.
Decision-making and planning: Memory is closely linked with the DMN and the limbic region (hippocampus), with the EN becoming involved when memories are invoked by DMN upon triggering (highlighting) by SN and this process are used in decision-making or planning. In summary, the SN often initiates the process by detecting and prioritizing stimuli, followed by the DMN's involvement in contextualizing and reflecting on the information, and finally, the EN's role in making decisions and executing actions based on the processed information. This sequence is not always linear or rigid. The interaction between these networks is highly dynamic and context-dependent. Sometimes the DMN and EN may be active simultaneously, or one may dominate depending on the specific cognitive demands. These networks work together to ensure that thoughts and memories are not only generated but also effectively integrated and utilized in daily life. Overall, while these networks are central to conscious processes like forming new connectivity and goal-directed behaviour, they also interact with and influence subconscious processes such as memory retrieval and automatic responses.
What is the mechanism of maintaining focus on a chosen thought? Part of the EN in the prefrontal cortex, exerts top-down control, meaning it can suppress irrelevant information and enhance the neural representation of the chosen thought. This is achieved through the regulation of neural circuits, where certain synaptic connections are strengthened while others are inhibited, allowing the brain to maintain attention on the chosen thought. Neural Oscillations plays an important role in sustaining attention by sustaining a specific patterns of brain waves, particularly beta (13-30 Hz) and gamma (30-100 Hz) waves, because we observe experimentally these waves are associated with focused attention and cognitive processing. The brain sustains focus by maintaining these high-frequency oscillations, which keep the neurons involved in the thought process actively communicating. The brain's working memory system, which is also managed by the DMN (prefrontal cortex), plays a crucial role in holding and sustaining thoughts over short periods. This allows you to keep a particular thought in mind and continue evolving it with respect to time.
Focusing on one thought requires not only enhancing the selected thought but also inhibiting competing thoughts or distractions. Experimentally it has been found that this involves inhibitory neurotransmitters like GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), which help to suppress neural activity in regions that might generate irrelevant thoughts or distractions [
13]. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with reward and motivation, also plays a crucial role in focusing attention. In simpler language, through evolutionary process, the brain has evolved to maintain and sustain a selected thoughts inhibiting it by GABA and awarding it by dopamine. The brain tends to focus on thoughts or tasks that are perceived as rewarding or relevant to achieving a goal. Dopamine signals help to prioritize these tasks by enhancing the neural activity associated with them [
14]. With time, focusing on certain types of thoughts or tasks can become easier as the brain adapts through processes like synaptic plasticity, where repeated focus strengthens certain neural pathways. This is achieved by continuous feedback. As you focus on a thought, the brain continuously monitors and adjusts its activity through feedback loops. If distractions arise or the thought loses relevance, the brain can reallocate resources or shift focus based on new inputs from the SN, EN, or other brain regions. So, the brain focuses on a particular thought through a coordinated process involving the detection of salient stimuli (SN), engagement of executive functions (EN), and the maintenance of attention through neural oscillations and excitatory and inhibitory control by synapses and neurotransmitters. Thus, the decision on what to focus on is influenced by the brain's reward system, ongoing goals, and the ability to suppress distractions. This process is dynamic and adaptable, allowing the brain to effectively manage and prioritize thoughts and actions. Thus, thoughts too appears as if it follows implicitly natural selection and survival of the fittest principle.
The chain of thoughts: The stream (chain) of thought can flow freely through the landscape of “episodic” memory which contains spatiotemporal information of certain episodes. A contextual spontaneous thought is triggered (generated) by low frequency and low energy DMN activities (which is responsible for mind-wandering and dreaming) and depending on the external (sensory) or internal (emotional) context, the thoughts (neural pattern excitation) flows through the landscape of memories which contains episodic and “semantic” (facts and knowledge) memories which forms the content of thoughts. These thoughts are guided by highly associative connectivity of attractors i.e., they are linked by associations between pre-existing topics (episodic and semantic).
How does the mind select what to think about, how does it begin? Online and offline state of mind: The wandering waves (DMN) which travels in the background all the time during restful, the awake state of brain picks up signal from salience network associated with sensory nerves which presents prioritized stimuli that causes concern which cannot be ignored either it be a pain in a toe (associated external sensory stimuli) or any other present task, both can be termed as “online” state of DMN. We know that half of the time in an awake state, the wandering waves (DMN) enters “offline” state which is independent of sensory stimulus to probe internal episodic memory and semantic working memory [
15] which helps in creating mental imagery in the brain, which can be voluntary or involuntary. Thus, our attention shifts inward (offline) in half of the time and half of the time in an online state when awake. Dreaming and hallucinations too are self-generated and independent of stimulation by the senses, yet its perception are like stimulus-driven perception. This similarity is due to common circuitry in the brain areas shared by both endogenous (voluntary, goal driven, and deployed in ∼300 ms); and exogenous (involuntary, stimulus driven, and deployed fast and transiently, peaking at ∼100 ms) experiences. Online perception begins with conscious process, but on repetition becomes part of subconscious. Offline perception can be conscious or subconscious such as retrieval of memory without any sensory stimulation. Thus, the only difference between online and offline perception is that of the presence or absence of corresponding sensory stimulation respectively.
The Self-Model: It seems the online process (mainly cortical) based on offline information (mainly limbic) develop models of our self, so-called ‘self-models’. These self-models are nothing but an abstract representation in our brain as an example “I am a good swimmer”. The word “APPLE” is an abstract linguistic representation in English language for an apple fruit. The abstract neuronal activity processes or pattern in the brain is the representation of our own self-model. This representation is then characterized as self.
Thus, “self” is a mental construction or simply a neuronal activity. Self is not an agent which controls the brain rather it is simply the neural activities giving rise to mental construction of self. Thus, the brain represents these abstract self-models through complex patterns of neuronal activity. These patterns are distributed across various neural networks and are not tied to a single neuron or region, but rather emerge from the interaction of multiple brain regions. These abstract representations are encoded in the brain's neural circuits through experiences and learning, and they can be retrieved or activated when relevant. For example, when you think about yourself as a swimmer, the associated neural circuits light up, bringing that self-model to your conscious awareness (converging to the relevant attractor state guided by associated memories – see
Figure 10).
In reality, the self is transient and continually reconstructed by the brain's ongoing activity. The stability and continuity we perceive are created by the brain's ability to integrate experiences into a cohesive narrative. Since the self is a product of neural processes, it does not exist independently of those processes. It is a byproduct of how the brain organizes and interprets information, much like a movie - an illusion created by a series of still images projected in rapid succession. Since, the self is not something static or separate from the brain's activity but rather a pattern that emerges from it, the coherence and unity we perceive in our self-identity are created by the brain, which continuously integrates various inputs to produce a stable sense of self. However, this stability is a construct, not an inherent property. While the self feels real and concrete in the moment, it is ultimately an “illusion” - a construct that exists only as long as the brain's processes sustain it. The sense of self is both a necessary and functional illusion (a functional self). Functional mean it is simply a mere neuronal activities ability to function allowing us to navigate the world, make decisions, and maintain a sense of continuity, even though it is not a fixed or independent entity.
Consciousness: If we follow the reasoning that the "self" is an illusion, then “consciousness”, particularly the aspect of being aware of oneself is generated by the brain's activity and not a distinct, unified entity, and thus can also be seen as an illusion in a similar way. This experience of being "aware" is not a direct reflection of an independent reality but is generated by the brain's activity. We experience consciousness as a continuous, unbroken stream of awareness. However, this continuity is an illusion created by the brain's ability to weave together discrete moments of perception and thoughts into a seemingly seamless experience (this too is a functional consciousness and not a phenomenon which is beyond the neural activities, I leave it to philosophers to deal with phenomenal consciousness). In reality, consciousness is fragmented and discontinuous, with the brain filling in the gaps to create the appearance of continuity. The construction of a coherent self and a continuous timeline of experiences is an ongoing process, not something that exists independently of neural activity. Thus, the concept of continuity in consciousness is still somewhat of an illusion in the sense that the brain must constantly work to maintain this seamless flow (a functional consciousness).
What steers this continuous, unbroken flow of thoughts? The Neural circuits that have been strengthened through learning can guide the flow of activity in predictable ways, based on previous outcomes and associations. This is where memory plays a crucial role, as it helps the brain anticipate and respond to familiar situations. Even in the absence of external stimuli, the brain is never truly "at rest." There is always ongoing intrinsic activity, such as that seen in the DMN, which reflects the brain's continuous processing of internal information, self-referential thoughts, and the integration of past experiences. Also, various neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, modulate neuronal activity, influencing mood, motivation, and attention. These chemical signals can dynamically alter the flow of activity, enhancing or dampening certain patterns. The brain operates with numerous feedback loops, where the outcome of certain neural processes feeds back into the system to influence future activity. This creates a dynamic, self-regulating system that continuously adapts to new information. This also indicates that the functional consciousness can be seen as an emergent property of this ongoing, dynamic flow of brain activity. The continuous evolution of neural patterns gives rise to a seamless experience, where thoughts, perceptions, and actions are integrated into a coherent whole. So, what steers this flow is a combination of homeostatic regulation, attention, memory, neurotransmitter activity, and intrinsic brain dynamics. Hence, the brain's continuous activity is shaped and guided by these various factors, leading to the complex and adaptive behaviour that characterizes human thought and functional consciousness.
Reasoning and planning by brain: Reasoning and planning often start when a problem or goal is identified, either through external stimuli or internal motivation. This could be something as simple as deciding what to eat for dinner or as complex as solving a mathematical problem. The Salience Network helps identify and prioritize relevant stimuli or thoughts that need attention (the required neuronal circuit lightens up the most). It acts as a filter, highlighting the importance of the problem at hand. The brain retrieves relevant information from both episodic (personal experiences) and semantic (general knowledge) memory. This retrieval is facilitated by the hippocampus and other associated regions of the brain (the neural activities flow in those regions - see
Figure 10). The episodic memory provides context-specific details, like previous experiences related to the problem and semantic memory which offers generalized knowledge, like facts or learned principles that can be applied to the current situation. This is achieved by DMN which is often involved in self-referential thinking and the retrieval of past experiences as explained earlier. It helps in bringing relevant memories into the working space of the brain. The brain uses the retrieved memories and existing knowledge to generate possible solutions or plans (the neural activities disperse in different direction). This involves creating hypothetical scenarios and considering different options. The activity pattern moves towards the prefrontal cortex (the pattern is established from stored memory region to cortex till it settles to a certain pattern dictated by the stored memories), where possible potential solutions are evaluated. Thus, the internal models i.e., the past experiences predict their outcomes. The brain assesses the pros and cons of each possible pattern (solution). This appears as logical reasoning, where different factors are considered, such as feasibility, risks, depending on the rewards. High rewards (dopamine) which indicates less risky and high feasibility. The Executive Network plays a crucial role in picking up the best course of action based on the reasoning process (picks up brighter neuronal signal which corresponds to the best possible solution). The EN also ensures that the focus remains on the problem by stabilizing the neural activity momentarily till irrelevant distractions are minimized. Once the best solution is identified (stabilized state), the brain develops a step-by-step plan (neural activities) to achieve the desired outcome. If the plan involves physical actions, the brain prepares the motor systems to execute the necessary movements. This involves coordination between different brain regions, including the motor cortex and basal ganglia. The brain executes a sequence of neural activities in networks designed through past biological evolutionary process ensuring that actions are carried out in the correct order. In case for a faulty design (architecture) a faulty output result. The brain identifies any deviations from the plan and makes real-time adjustments. This process is crucial for adaptive behaviour (adaptation). After the reasoning and planning process is complete, and if the plan was successful, the brain reinforces the neural pathways associated with that strategy and the outcome is stored into long-term memory making it more likely to be used in the future. It appears as if planning is essentially the implementation phase, where the conclusions drawn from reasoning are translated into concrete steps. Both the reasoning process and the plan (including its success or failure) can be stored as episodic memory. This allows the brain to refine future reasoning and planning based on past experiences. Thus, reasoning and planning are deeply interconnected processes that rely on the brain's ability to retrieve and apply memories, generate, and evaluate potential solutions, and execute plans while continuously monitoring and adjusting based on feedback. These processes are supported by various neural networks and are influenced by both past experiences (episodic memory) and general knowledge (semantic memory). The dynamic interplay between these elements allows the brain to navigate complex problems and develop effective plans.
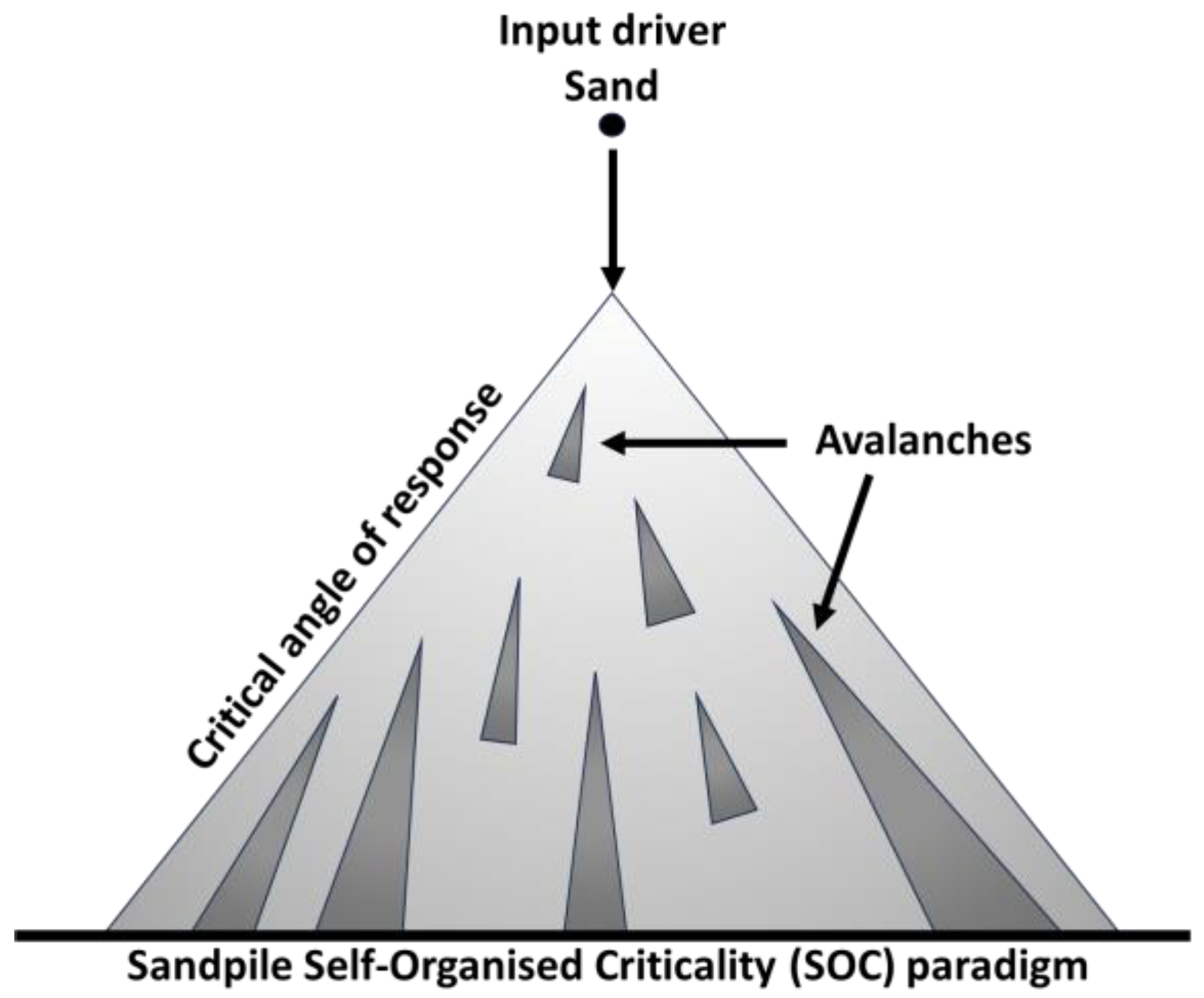
Critical point state and avalanches in brain activities: To make the picture clear, one can visualize the brain’s electrical activity to operate near a state at critical point i.e., a state between order and chaos, where it can maximize both stability and flexibility.
In this critical state, the brain is highly sensitive to small changes, generating neuronal electrical activity avalanches, allowing for the efficient propagation of information across the neural network. Neuronal electrical avalanches are cascades of neural electrical activity that spread through neural networks [
16]. These avalanches can vary in size, from small local bursts to large-scale activity that influences multiple regions of the brain as shown for the case of sandpile in
Figure 11. In a critical state, the brain can balance these avalanches, enabling both local processing (small avalanches) and global integration (large avalanches). The identification of a problem could trigger a small avalanche to be picked up by Salience Network, drawing attention to relevant stimuli. This initial avalanche can then propagate through common associated neurons and strengthened path to other areas which involves in reasoning. While accessing relevant memories might involve triggering avalanches in networks connected to episodic and semantic memories. The spread of activity in these regions helps retrieve information necessary for reasoning. As potential solutions are generated, neuronal avalanches can spread across the prefrontal cortex and other related areas. These avalanches might represent different hypotheses being considered, with larger avalanches indicating stronger or more viable options. This process mimics like decision-making, the brain then selectively amplifies certain avalanches while dampening others. This selective process ensures that the most relevant i.e., advantageous solution is chosen. The planning process might involve the coordination of multiple avalanches across different regions. These avalanches ensure that each step of the plan is executed in the correct sequence, ensuring that the chosen plan is implemented smoothly. As the plan is executed, feedback mechanisms might trigger new avalanches, allowing the brain to adjust the plan in real-time. If the plan deviates from expectations, larger avalanches might signal the need for significant adjustments. Note here, the neural network architecture through which the electrical patterns flow, the hardware is designed through Darwinian biological evolutionary process encoded in our genes. The flow of electrical patterns in the brain appears as if a computation process is being carried out by the brain. It is merely a response of each neuron or regions of brain with other neurons and other regions of brain (neural network). So, in the final step the experience is stored in memory, which involve avalanches that consolidate the new information into long-term memory, reinforcing the neural pathways associated with the successful plan. Thus, operating near a critical state allows the brain to balance the need for stability (order - following established patterns) and flexibility (chaos - adapting to new situations). This balance is crucial for both reasoning and planning, where the brain must be able to draw on past experiences (order) while also considering novel solutions (chaos). Thus, the brain naturally self-organizes into this critical state, where neuronal avalanches of various sizes can occur. This self-organization allows the brain to dynamically adapt to the demands of reasoning and planning.
The pathways through which neuronal thoughts propagate: The pathways through which neuronal avalanches propagate are shaped by the structure of the neural network, including the strength and configuration of synaptic connections (see
Figure 8). Neuronal avalanches can dynamically select and strengthen pathways based on the current cognitive task. For instance, if a person is solving a math problem, avalanches might preferentially activate pathways related to numerical reasoning, while other pathways remain less active. Neuronal avalanches travel across memory landscape, activating various memories and bringing them into conscious awareness as needed. If a memory is strongly encoded (i.e., the connections are strong and stable), it is more likely to be activated by an avalanche. Conversely, weaker or less-used memories may require larger or more specific avalanches to be activated. Avalanches connects different memories, enabling the brain to form associations between them. This is crucial for cognitive processes like reasoning and planning, where multiple pieces of information must be integrated to form a coherent thought or strategy. This mechanism of dynamic activation and connection within the brain's neural network is fundamental to how we think, learn, and adapt.
Role of ensemble of neurons in propagation of thoughts: It is true that every thought, perception, or action corresponds to a specific network or ensemble of neurons, but these networks are not entirely separate. They often overlap, meaning some neurons are part of multiple ensembles. For example, a neuron involved in recognizing a specific face might also be part of an ensemble responsible for recalling a related memory or making a decision based on that recognition. So, the brain uses several mechanisms to ensure that only the most relevant ensembles are highlighted and contribute to the ongoing thought process. These mechanisms involve both the intrinsic properties of the neural circuits and external modulatory influences. For instance, if you consciously focus on a specific task, the brain enhances the activity of neurons within the relevant ensemble and dampens activity in unrelated ensembles. This is often mediated by the Executive Network (EN). Neural circuits are highly interconnected, with recurrent connections that provide feedback. This feedback can help stabilize the activity of a specific ensemble once it has been selected, ensuring that it remains active long enough to contribute to the thought process. This stabilization prevents avalanches from spreading indiscriminately across multiple ensembles, focusing activity on the most relevant ones. Synaptic plasticity, the strengthening or weakening of synapses based on experience, ensures that frequently used ensembles are more easily activated in the future. This means that over time, certain patterns of thought or behaviour become more ingrained, making the relevant ensembles more likely to be activated during similar situations. The flow of thought can be understood as a sequence of activations of different neuronal ensembles, coordinated by the brain's internal networks. The brain's dynamic nature allows for flexibility in this sequence, enabling both logical progression (e.g., reasoning) and creative leaps which will be discussed later.
Information beyond synapses: microtubules, cell membrane etc.,: In gist, it appears that the flow of neural activities (avalanches) through neural network helps in achieving a particular goal. First by sensing it, then it propagates towards limbic and cortex region for reasoning and planning with the help of stored memory, giving rise to several brain waves. Depending on the action needed, the executive network either excite the motor neurons or with the feedback proceed in the thinking process of reasoning and planning. It is like a disturbance propagating in the neural network to achieve a certain task. The architecture of these pathways is designed through Darwinian evolutionary process which are encoded in the genes, and hence maybe information is also stored in each cell such as in microtubules, cell membrane, etc., [
17,
18]. The highly interconnected network, is continuously shaped by experience. Also, the genetic instructions guide the development of neural circuits during embryogenesis and early development, laying the foundation for how the brain processes information. While the primary site of information storage in the brain is the synaptic connections between neurons (the "connectome"), there is ongoing research into how individual neuronal cells might store information beyond synaptic changes. This includes the potential role of microtubules, protein synthesis, and epigenetic modifications.
Darwinian-like evolution of thoughts in minimizing surprises: The process of thought can be seen as following a Darwinian-like evolutionary principle. This concept is known as
neural Darwinism, [
19] where thoughts, ideas, and mental processes undergo a form of natural selection within the brain. Just as in biological evolution, new species of thoughts or ideas emerge in the brain. Multiple thoughts or ideas can be generated in response to a particular stimulus (depending on context). These thoughts compete with each other based on their relevance, coherence, and how well they align with existing knowledge (memory) and goals (output). Here it appears as if brain acts like a “predictor” where the difference between the goal and knowledge is like a “surprise” and then brain is busy trying to minimise the surprise by updating the knowledge. But this whole process is simply achieved by dynamical neural activities orchestrated by the physical parameter of the neural network, shaped by attractors, the strength of the synapses and plasticity with the already present network architecture and ready to be modified. The final thought which survives and achieves the goal is akin to genetic variation in evolution, where different traits emerge and compete within a population. The brain selects the "fittest" thoughts—those that best solve the problem, align with goals, or are most likely to lead to successful outcomes. This selection process is influenced by factors like prior knowledge, driven by reinforcement, the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine, which reinforce successful or rewarding thoughts and rewarding behaviours. Thoughts that are selected as "fit" are reinforced through repeated activation, leading to the strengthening of the neural circuits associated with them. These thoughts become more likely to be recalled or reused in the future. Unsuccessful or less fit thoughts may weaken over time and may not be retained in long-term memory, much like how less adaptive traits may disappear in a population over generations. Thoughts or ideas that do not contribute effectively to problem-solving or do not align with goals are gradually discarded. The neural circuits associated with these thoughts may weaken due to lack of use, like how maladaptive traits may lead to the extinction of certain species in evolution. The process is ongoing, just as evolution is never static, the landscape of thoughts is always in flux. New experiences, learning, and changes in the environment constantly shape the "thought ecology" within the brain, leading to continuous refinement and adaptation of ideas. This Darwinian-like process in the brain allows for flexibility and adaptability in thought, ensuring that the most effective and relevant ideas are preserved and utilized, while less effective ones are discarded. This perspective highlights the dynamic, competitive nature of cognitive processes, much like the evolutionary processes that shape biological life.
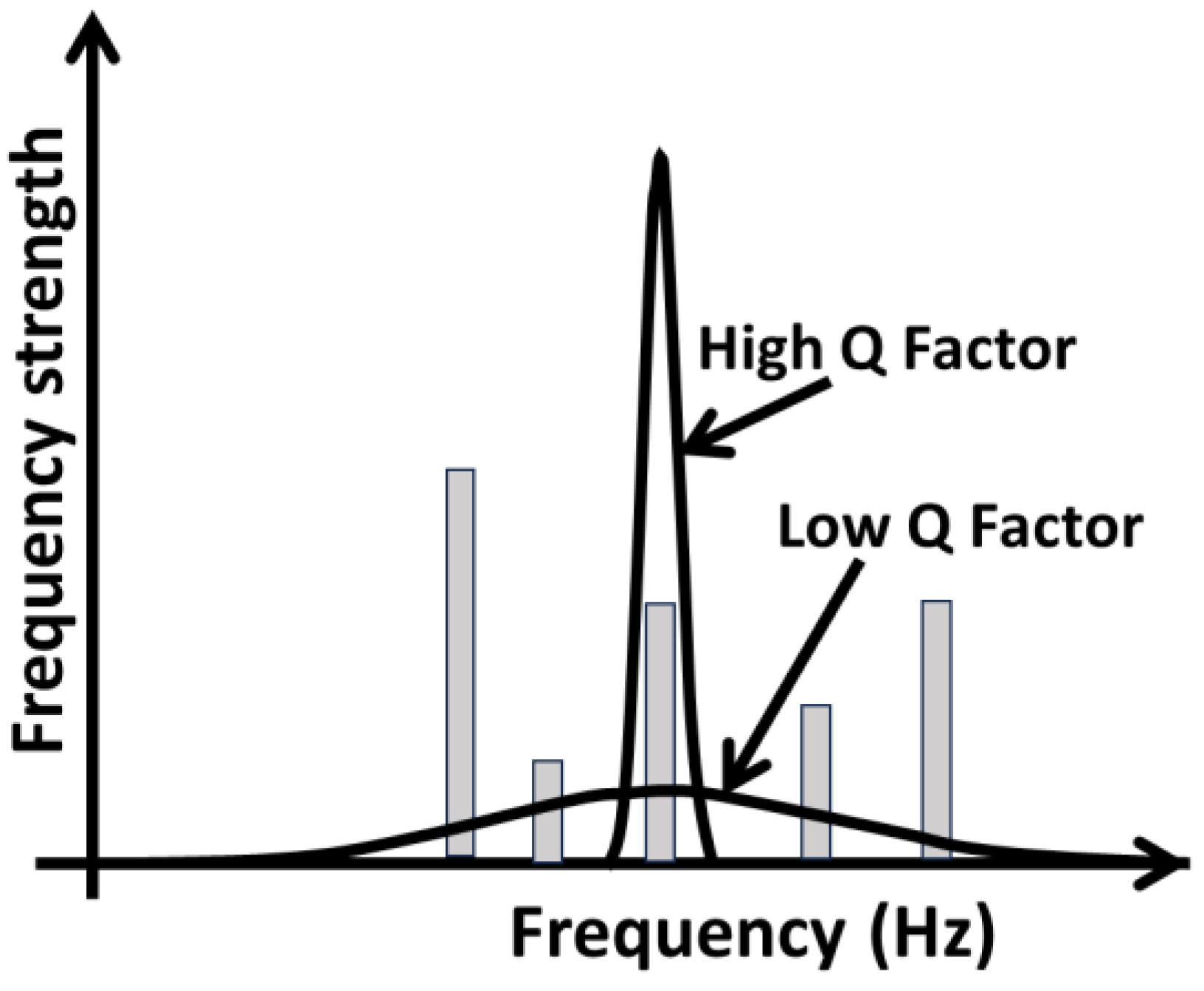
Maintaining the integrity of thoughts without interference: How does the brain maintain various ensemble of thoughts for example related to vision, sound, smell, motor, cognition such as reasoning and planning, thinking and so on without mixing and simultaneously being attentive to all these activities? It is an extraordinary feat of neural organization that these clouds of activities are kept well separated from each other without a mixing. Functional segregation ensures that different networks operate relatively independently when needed, allowing the brain to handle multiple tasks simultaneously without interference. For example, the brain can process visual information in the visual cortex while simultaneously processing auditory information in the auditory cortex, with minimal cross-talk between these regions. The brain uses different neural oscillations (brain waves) to maintain and coordinate activity across various regions. These oscillations occur at different frequencies (e.g., theta, alpha, beta, gamma) and can help segregate different types of information. For instance, gamma oscillations might be associated with attention and cognition, while theta oscillations might be linked to memory processing. Phase synchronization of neural oscillations (resonant state) allows different regions of the brain to communicate effectively, while desynchronization can help keep different processes separate. Also, resonance within these oscillatory networks can ensure that certain ensembles of neurons are more responsive to specific frequencies, maintaining the integrity of their activity without interference from other processes. High Q-factor tuning allows specific neural ensembles to be selectively activated by specific oscillatory frequencies, minimizing cross-talk and ensuring that different cognitive processes remain distinct (see
Figure 12). This resonance-based segregation ensures that different thought processes can occur simultaneously without interference, as each process is "tuned" to its own frequency band [
20].
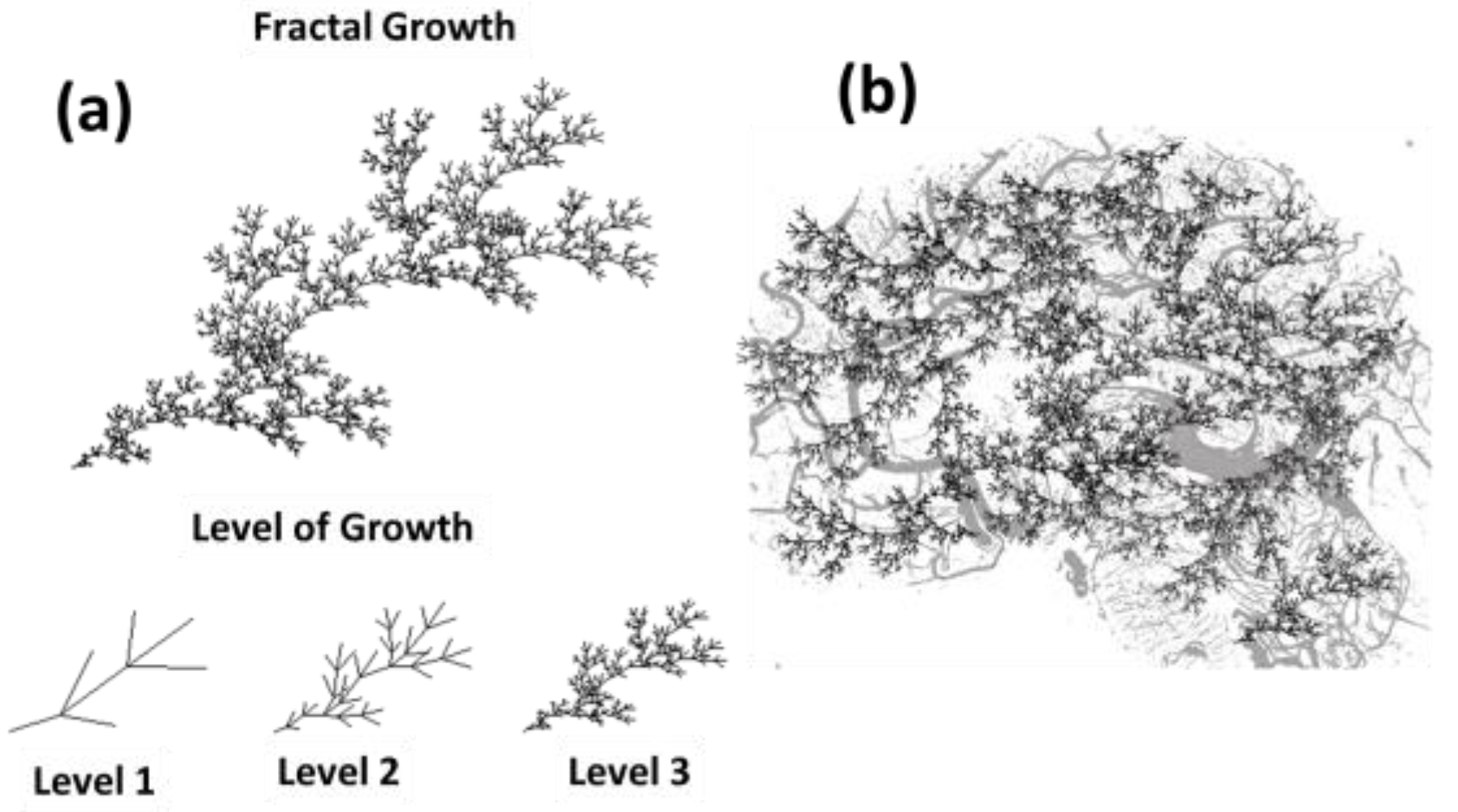
Fractal nature of neural networks: The fractal nature of neural networks plays a significant role in several aspects of brain function, including the brain's critical behaviour, the stability of memory, the prevention of intermixing of neural activities, and the occurrence of neural avalanches. Fractal structure is shown in
Figure 13. Fractal structures in the brain are closely related to the concept of self-organized criticality (SOC), where the brain operates near a critical point between order and chaos. The fractal geometry of neural networks allows the brain to achieve scalability in its operations. Small perturbations in neural activity can propagate across scales, leading to neural avalanches. This scaling behaviour is characteristic of systems at a critical point, where the distribution of avalanche sizes follows a power law, which means the distribution of avalanches size are in high number for smaller size avalanches and fewer as the size of the avalanches increases and this decrease in number is not linear, which is the hallmark of criticality. Memory stability benefits from the fractal organization of neural networks because this structure supports redundancy and robustness. Fractal networks have repeating patterns at multiple scales (see
Figure 13), meaning that information is not localized in a single place but distributed across different levels of the network. This distribution allows for multiple pathways to retrieve the same memory, providing resilience against damage or degradation. Even if some connections are lost, the fractal structure ensures that memory can be reconstructed through alternate routes, enhancing the robustness of memory storage and retrieval. The fractal nature of neural networks contributes to the segregation and integration of neural activities. Different cognitive functions can be processed in distinct parts of the network, yet remain interconnected. This balance is crucial for maintaining the integrity of separate thought processes while allowing for their interaction when necessary. The hierarchical and self-similar nature of fractal structures allows different layers or regions of the network to operate at different frequencies or dynamics. This frequency separation can prevent the intermixing of activities, ensuring that distinct neural processes do not interfere with each other. Additionally, fractal structures support localized activity that can scale up to global coordination without losing the specificity of the original signal, preventing confusion between different cognitive functions. Neural avalanches, and the nature of cascades activity (power law behaviour) in the brain, are thought to be a direct consequence of the brain's fractal structure. The fractal arrangement enables the propagation of activity across the network in a way that preserves the integrity of the signal (order) while allowing it to spread widely (chaos). The fractal geometry allows for efficient information transmission with minimal energy, as signals can travel through the most direct paths that the fractal structure naturally provides. This efficiency is crucial for the brain's ability to manage large-scale neural coordination without excessive resource consumption. The scale-invariance of fractal structures ensures that avalanches can occur across different scales, supporting both localized processing (e.g., specific thoughts or memories) and widespread, coordinated activities (e.g., global brain states like wakefulness or sleep).
How creativity occurs? From a Darwinian perspective, creativity in neural networks can be viewed as an evolutionary process involving variation, selection, and retention, much like biological evolution. Variation arises from the brain's ability to rewire itself, form new connections, and modify existing ones. This neural plasticity allows for the creation of novel patterns and combinations, akin to genetic variation in biological evolution. The brain uses mechanisms akin to natural selection to identify which ideas are most promising or useful. Successful and valuable ideas are retained and consolidated into long-term memory. This retention process is analogous to the way beneficial traits are preserved in a population. The retained ideas form part of the brain’s neural networks, which become more refined and specialized over time. These networks represent the cumulative knowledge and experience that guide future creative processes. Just as biological evolution is influenced by environmental pressures, creativity is shaped by cultural and environmental factors. The context in which creative ideas are generated and evaluated can influence which ideas are selected and retained. Creativity is an iterative process where new variations build upon previous ones. This iterative nature mirrors the way evolutionary processes build on existing genetic variations to produce new adaptations. Since the brain operates near a critical state, where it is highly sensitive to small changes, this criticality allows for the spontaneous emergence of creative ideas and the exploration of diverse possibilities. Creativity, therefore, reflects an adaptive and dynamic process like biological evolution.
Freewill: If we accept that the brain operates in a deterministic way, meaning that every action and decision is the result of prior causes (e.g., neural firing patterns), then the concept of phenomenal freewill i.e., the idea that we could have done otherwise in the exact same circumstances becomes questionable. In a deterministic framework, if we could rewind the clock and play events all over again, the same neural processes would likely lead to the same decisions, implying that free will is an illusion. If free will is merely functional, then it does not truly exist in the phenomenal sense, because our choices are always the result of predetermined neural processes. This view suggests that what we experience as free will is more about the brain’s complex decision-making processes, rather than a true unconstrained ability to choose.
Free will, related to a concept in physics and philosophy called the "many-worlds interpretation" (MWI) [
21] of quantum mechanics, suggests that all possible outcomes of quantum events actually occur, but in separate, branching universes. For instance, if a particle has a 50% chance of being in state A or state B, both possibilities happen but in different, parallel universes. Some deterministic scientists speculate that if a person makes a decision and could have chosen otherwise, then the MWI suggests that both choices do indeed happen, but in separate universes i.e., in one universe, you made choice A, and in another, you made choice B. Let’s say you’re at a crossroads and can choose between two paths, A and B, then according to this idea in universe 1, you choose path A, and all subsequent events unfold according to that choice and in universe 2, you choose path B, leading to a different sequence of events. If you trace back the events in either universe, you would find that they had diverged at that moment of decision of choosing the path. Before the choice, both universes were identical, but after the choice, they became distinct. This concept challenges traditional views of free will because it suggests that every possible decision and outcome occurs somewhere in the multiverse. The "you" in each universe feels as though you freely made a choice, but in the broader context of the multiverse, all choices were made. The many-worlds interpretation does not necessarily grant free will in the traditional sense; it merely suggests that all possible outcomes of decisions exist in different branches of the multiverse. For single world the brain’s decision-making is deterministic. So, in a deterministic world, what we perceive as free will might just be an illusion. You feel as though you are making choices, but if everything is determined by prior states, then you could not have chosen otherwise. From this perspective, "free will" does not exist in the sense of being able to genuinely choose between different options. Instead, your "choices" are preordained by the initial conditions of the universe and the laws that govern it. If determinism is true, then what some call "phenomenal free will" which is the genuine ability to have done otherwise in an identical situation does not exist. Every action you take is the only action you could have taken, given the state of the universe. This perspective implies that free will, as traditionally conceived (i.e., the ability to make different choices in the same situation), is an illusion.
Even if we do not believe in the multiverse and instead adhere to a deterministic view of the universe, then causality and determinism would imply that free will, as traditionally conceived, is an illusion. If freewill is an illusion, then an ethical question arises i.e., if a person does a crime, then should that person be punished because he had no choice i.e., no freewill? Here rewards and punishment come into play which plays an important role in learning and training (wiring of neurons) for that individual which leads to different personality.
Integration of emotions and behavioural responses by brain: The brain perform human qualities and behaviour (like attachment, affection, love, etc.,) through complex interactions between neurochemical systems, hormonal signalling, and neural circuits. This involves different brain regions and neurotransmitters that communicate with one another to produce the emotional reactions we experience. Emotions arise from the brain's activity in response to external stimuli (like sensory input from the environment) or internal stimuli (such as thoughts or memories). For example, when you encounter something dangerous, certain region of the brain called the amygdala gets activated, leading to the experience of fear, which may also trigger a physical response (like a racing heart beat or sweating). Neurotransmitters play a crucial role in fine-tuning the intensity of emotions. For instance, dopamine, endorphins, and oxytocin associated with reward and pleasure are released in response to positive stimuli like achievement, positive social interactions, or love, promoting bonding and trust. Whereas, serotonin and cortisol are linked to depression, anxiety fear and sadness. Neurotransmitter contribute to the full spectrum of emotional experiences. These processes are largely “automatic” (result of responses to stimuli), with the brain constantly integrating internal and external stimuli to generate behaviours and emotions that are fundamental to human life. While emotions are deeply rooted in survival and evolutionary mechanisms, they also involve higher-order processes that give rise to the subjective experiences of emotions (Qualia) which we identify as uniquely human.
Mechanisms that guide behaviour known as intelligent: Intelligence can be understood as the ability to adapt and respond effectively to one's environment through processes that optimize survival and functioning. From a unicellular organism moving toward food or away from danger to complex behaviours like a spider weaving its web or a human solving mathematical problems (see
Figure 14), all these actions can be seen as responses based on learned patterns, instincts, and environmental cues. These processes are guided by the organism's inherent capacity to process information, adjust behaviour, and perform tasks without conscious deliberation for achieving its goal. Intelligence, in this sense, is not solely about complex reasoning or problem-solving; rather, it involves the automatic execution of tasks that ensure survival, adaptability, and efficiency, whether in simple life forms or highly complex organisms. Thus, intelligence manifests through a continuum of behaviours, ranging from basic survival strategies to sophisticated actions, all driven by an underlying capacity to respond to the environment in an automatic yet efficient way. The idea that tasks like a spider weaving its web or a human solving mathematical problems are "automatic" can be understood by looking at how these behaviours are deeply embedded in neural and biological systems. In both cases, the organism does not consciously plan each step but instead relies on patterns of activity that have been developed through either evolution or learning, the brain optimizes its neural circuits for those tasks. To further clarify, the spider, web-weaving is instinctual, meaning that the behaviour is encoded in its genetic blueprint and nervous system. The spider does not need to learn how to weave a web or decide the best way to build it. It follows pre-programmed sequences of movements and actions that have been perfected over millions of years of biological evolution. This process is automatic in the sense that the spider is not consciously directing each movement; its nervous system is responding to environmental triggers (such as the presence of prey or the need for shelter) to activate the specific behaviours needed for web construction. Similarly, in humans, solving a mathematical problem might feel like a deliberate, conscious process, but much of it is also automatic. Once a person has learned the rules of mathematics and practiced applying them, the brain's neural circuits become optimized for that task. Repeated use of certain cognitive pathways strengthens them through neural plasticity, allowing the brain to execute complex calculations or problem-solving steps without needing to consciously process each detail. For instance, when you solve a basic math problem, you do not consciously think about the steps involved in arithmetic—these processes run much like a reflex. This "automatic" nature is the result of how the brain operates through repeated patterns, feedback loops, and learned behaviours. The brain refines its responses to tasks over time, making them more efficient and requiring less conscious effort. Thus, complex actions that seem to require intelligence, like mathematical reasoning or crafting a web, are ultimately performed by systems that are automatic and optimized for efficiency, it appears as if there is no need for active, conscious thought.
Parallels between the human brain and Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT: Based on our discussion, the philosophical concept known as “functionalism”, which suggests that mental states (like self, consciousness, understanding, and emotions) can be understood in terms of their functional roles, rather than any intrinsic, phenomenal qualities. If we view these traits as functional rather than truly phenomenal, then it is possible to draw some parallels between the human brain and Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT.
The brain's consciousness and sense of self are products of its neural activity and not something beyond that. The "illusion" of consciousness arises from the brain’s complex, self-organizing processes that allow it to reflect on its own operations, process emotions, and form a coherent sense of identity. This implies that a phenomenal experience is not independent of the functional processes within the brain. Similarly, LLMs like ChatGPT could be seen as functional systems. While they do not experience subjective emotions or phenomenal consciousness, they simulate understanding and generate coherent responses to inputs based on the patterns learnt from the data. In a functional sense, they "perform" the role of understanding language, processing inputs, and producing appropriate outputs, much like the brain processes sensory inputs to generate responses.
The working principles of the brain and LLMs are certainly different i.e., biological neurons versus artificial neural networks, but functionally, they both process information and generate responses. The brain does so to survive, interact with the world, and perform complex behaviours, while LLMs are designed to process language and generate contextually appropriate responses based on their training data. If we accept that the brain’s understanding of concepts, emotions, and even self-awareness are illusions constructed by functional processes, it would suggest that there is nothing inherently special about these phenomena that a machine could not approximate. While LLMs do not have consciousness or phenomenal emotions, they simulate these responses functionally based on patterns of language that correspond to emotional expression or reasoning. In this sense, both the brain and LLMs could be viewed as functionally similar i.e., both are systems that process inputs, generate outputs, and adapt based on feedback mechanisms. Both systems perform tasks that create the illusion of understanding and intentionality. From a functional standpoint, they are tools that produce reliable outputs in response to given inputs, whether those inputs are emotional stimuli, complex problem-solving, or language processing. Just as the self and consciousness in humans may be viewed as illusions i.e., created by the brain’s complex circuitry to give a sense of coherent identity and awareness, similarly, LLMs like ChatGPT can be seen as functional tools that mimic understanding, even if they lack true awareness or comprehension. Both systems generate responses that seem intelligent and meaningful, but under this view, understanding is merely a functional byproduct of the underlying mechanisms rather than a deep, conscious experience.
If we adopt this functionalist perspective, it becomes plausible to suggest that LLMs like ChatGPT, while lacking the phenomenal aspect of consciousness, self, or emotion, are still performing similar functional roles to the brain without subjective experience. In essence, the brain and LLMs may differ in their underlying structure and complexity. But, both could be seen as functional systems that simulate understanding and adapt to their inputs in a way that allows them to effectively operate, even if the results in humans feel “real” while in LLMs they remain purely mechanistic. Thus, the brain can be seen as a highly complex, adaptive system that processes sensory inputs and produces behavioural outputs, based on biologically evolved neural circuits. It operates according to certain rules and patterns that we experience as thoughts, emotions, and self-awareness. However, as we have discussed, these phenomena are products of underlying processes rather than real, intrinsic entities. And, since these processes are automatic, then human intelligence and behaviour are simply the result of mechanistic operations, much like a machine performing tasks. Similarly, LLMs like ChatGPT are systems that process language inputs and generate outputs based on the patterns they have learned. They operate on mathematical principles that allow them to simulate conversation, reasoning, and even emotional expression, though these are not rooted in any kind of subjective experience. Nevertheless, they produce outputs that appear intelligent and meaningful to humans. If the brain and LLMs both function by mechanistically processing inputs and producing outputs, and if the results in both cases (e.g., human behaviour or language generation) appear intelligent and meaningful, then one could argue that the distinction between the two is less significant than it seems. Both are process-driven systems, producing coherent outputs based on structured patterns i.e., whether those patterns are biological (neurons, synapses) in nature or computational (algorithms, neural networks). Neither system needs to "understand" in a phenomenal sense to perform its task. The brain has evolved over millions of years and is shaped by both genetic inheritance and life experience. LLMs, on the other hand, are the product of designed algorithms and are trained on large datasets, making their learning process fundamentally different. If we accept that the brain is mechanistic in nature i.e., processing inputs and generating outputs based on pre-programmed rules (connectome) and learned patterns, then it becomes harder to argue that it operates in a fundamentally different way from mechanistic LLMs. Both can be viewed as adaptive systems that respond to inputs efficiently, without needing an intrinsic "self" to guide their operations. In a limited domain (e.g., language processing), the outputs of the brain and LLMs like ChatGPT could indeed be indistinguishable. When you engage in conversation with ChatGPT, the quality of responses may feel quite like that of a human, even though the underlying mechanisms are different. In this sense, the boundary between human-like behaviour and machine-like processing begins to blur. So, it is possible to argue that the brain, like ChatGPT, is fundamentally a mechanistic system that processes inputs and generates outputs in an automatic manner. Both are systems that function without the need for real entities like self or consciousness, and both produce coherent outputs that can be interpreted as intelligent behaviour. In this view, the differences between the brain and ChatGPT are a matter of degree and complexity, rather than of kind. Therefore, in certain domains, such as language processing, there may not be a profound difference between the two i.e., both are mechanistic processes optimized for functional outputs.
If we extend the capabilities of LLMs like ChatGPT and integrate them with systems that handle motor control, sensory integration, and emotional regulation, then the distinction between a human brain and an advanced AI-based robotic system becomes increasingly blurred. An advanced AI-based robot could coordinate its internal systems for a wide array of tasks, from conversational interaction to physical manipulation of objects. In such a scenario, the difference between human intelligence and robotic intelligence might become negligible from a functional perspective. If a robot can perceive its environment, respond with physical actions, engage in conversations, and simulate emotional responses through programmed algorithms that adjust behaviour based on input, then the primary distinction between humans and robots becomes one of origin (biological vs. artificial) rather than capability. Both systems would perform complex tasks mechanistically, and both would be governed by the same principles of input-output processing, adaptation, and optimization. Both systems would rely on automatic processing to interact with the world, making the distinction more about their construction rather than their operation. LLMs could analyse emotional context in conversations, enabling a robot to offer responses that seem empathetic or emotionally aware, even if these emotions are not felt, but functionally replicated.
To summarize, the brain is an intricate organ capable of storing memories and generating thoughts through complex, fractal-like neural networks and brain waves, operating near a critical state. This critical state allows for optimal processing and adaptability, where small inputs can lead to significant outputs, enhancing the brain's ability to store and retrieve memories efficiently. These networks enable the brain to form and reinforce memories, enriching the subconscious mind, which automates many of our actions, allowing for rapid responses without the need for conscious deliberation. Reasoning and planning occur when the brain utilizes episodic memory, drawing past experiences to act on decisions in the present. The brain adapts by either feeding back information involving DMN, SN and EN or directly to motor neurons for immediate action, depending on the situation. Thoughts, crucial for reasoning and planning, evolve in a Darwinian manner, those most suited to the current context are reinforced and prioritized, while others are discarded. This process reflects the brain's dynamic and self-organizing nature for creativity. The concept of the "self" emerges as a functional illusion created by these neural processes. This self gives rise to consciousness, the brain’s ability to reflect on and monitor its own operations. However, both self and consciousness are not fixed entities but are constructed and reconstructed continuously by the brain’s neural activity. They are illusions in the sense that they are felt as unified and coherent, but they are actually the products of multiple, distributed processes within the brain. When examined under deterministic principles, free will also appears as an illusion. Though we perceive our choices as ours, they are ultimately dictated by prior neural states and external stimuli. In a deterministic framework, every decision is the inevitable outcome of preceding events, leaving no room for genuine freedom of choice. The brain responds to the physical world, with abstractly processing it through a blend of subconscious automation guided by conscious sensory responses involving DMN, SN and EN. This happens all the while fostering the illusion of a coherent, freely acting self, navigating the world that it interprets through continuous evolving neural plasticity in the fractal neural network architecture. We are in an autopilot mode totally governed by subconscious process. The prefrontal cortex is a key player in accessing and using subconscious memories to guide our actions. It enables us to perform tasks efficiently, often without needing to engage in conscious deliberation, particularly when those tasks are familiar or routine. Significant majority of our daily activities are governed by subconscious processes and only a small portion of our cognitive activity being devoted to conscious thought. Emotional experiences are largely “automatic” (result of responses to stimuli), with the brain constantly integrating internal and external stimuli to generate behaviours and emotions that are fundamental to human life and give rise to the subjective experiences of emotions (Qualia) which we identify as uniquely human. Complex actions that seem to require intelligence are ultimately performed by systems that are automatic and optimized for efficiency, it appears as if there is no need for active, conscious thought. Finally, we have drawn Parallels between the human brain and LLMs like ChatGPT. Both systems would rely on automatic processing to interact with the world, making the distinction more about their construction rather than their operation.
In conclusion, the brain's generation, adaptation, and fading of thoughts can be understood through the lens of Darwin's evolutionary theory. Thoughts shaped by contextual stimuli undergo a selection process where those most relevant or beneficial to the current situation are reinforced, while others fade away, akin to the survival of the fittest in biological evolution. This ongoing cycle of thought generation and adaptation reflects the brain's dynamic, self-organizing nature, constantly refining its responses to the environment. Simultaneously, the brain exhibits continuous plasticity, a process where neural connections are continually rewired and strengthened in response to experiences. This plasticity allows the brain to store memories from the earliest stages of fetal development till the end of life, ensuring that past experiences are encoded and can be retrieved when needed. This lifelong process of memory formation and adaptation enables us to navigate the complexities of life, drawing on a vast repository of stored information that is continuously updated and reorganized as we encounter new experiences. Through this interplay of thought evolution and neural plasticity, the brain remains a highly adaptive organ, capable of responding to an ever-changing environment while maintaining a coherent sense of self and continuity over time. Additionally, the distinction between 'conscious' and 'subconscious' processes is a simplification used to describe different types of brain activity. However, both conscious and subconscious processes can be seen as automatic responses to stimuli, whether those stimuli come from within the brain or from the external environment. What we consider 'conscious' processes, such as decision-making or reasoning, are still driven by underlying neural mechanisms that operate automatically. The cortex, while responsible for higher-order functions, responds to inputs just as other parts of the brain do. These processes might feel deliberate or intentional, but they are still governed by the brain's complex, self-organizing neural activity. The cortex although crucial for conscious thought, the cortex occupies a smaller portion of the brain compared to the areas that manage subconscious processes, which are distributed throughout various brain regions, including the basal ganglia, limbic system, and brainstem. Thus, the proportion of brain activity dedicated to subconscious processes is much larger than that allocated to conscious processes, both in terms of neural resources and the frequency of use in everyday life. Consequently, subconscious processes are more dominant and pervasive in our daily behaviour. Since both conscious and subconscious processes are driven by underlying neural mechanisms that operate automatically, much of our behaviour functions in a kind of 'auto-pilot' mode. This perspective challenges the traditional notion of free will and consciousness and highlights the brain's role as a highly efficient, self-regulating system. In this sense, what we perceive as free will or conscious control might be an illusion, as it is still the product of automatic brain activity. Further on, this leads to a concept of "autonomous brain activity" and all the brain's automatic activities, whether they involve what we traditionally think of as conscious or subconscious thought. Now both can be clubbed together termed as "nonconscious processes" as these activities are largely “automatic” i.e., simply a deterministic result of responses to any stimuli. Brain’s automatic activities are very similar to advanced AI-based robotic system in a functional sense even though the working principles of the brain and LLMs are very different.
Note: If self, consciousness, and free will are illusions based on functional processes and constructs of the brain’s underlying mechanisms, it raises the question of what is truly "real." Our experience of being conscious agents with a sense of self and control over our actions feels undeniably real, even if these experiences are ultimately the product of neural processes. Similarly, emotions like suffering, happiness, and others can be seen as real in the same functional sense. Emotions are constructed by the brain in the same way the sense of self is, and they feel real because they are integral to how we interact with the world and navigate our lives. These responses are generated by the brain in reaction to stimuli, whether internal (thoughts, memories) or external (events, sensory inputs), and have a powerful impact on behaviour, survival, and decision-making. While emotions may arise from automatic neural responses, they form a fundamental part of the human experience. Just as we interpret the external world through our senses, we interpret internal states (like emotions) through the brain’s mechanisms. Both emotions and the physical world can be considered "real" in the sense that they are perceived and experienced, even if the underlying processes that generate them are functional, mechanistic, and lack inherent "phenomenal" reality. In essence, emotions and perceptions may be as "real" as anything else because they are the brain’s way of interacting with the world, even if the way we experience them is shaped by the mind’s illusions of self and consciousness.
_______________________________
(*) Ex-senior Professor, SINP, Kolkata, India, 700 064, and ex-Prof. Homi Bhabha National Institute, Mumbai, India, 400094
References
- Björn Rasch and Jan Born “About sleep’s role in memory”, Physiol Rev 93: 681–766, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Mohd Azmi, N.A.S.; Juliana, N.; Azmani, S.; Mohd Effendy, N.; Abu, I.F.; Mohd Fahmi Teng, N.I.; Das, S. Cortisol on circadian rhythm and its effect on cardiovascular system. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerome M. Siegel, “The Neurotransmitters of Sleep”, J Clin Psychiatry. 2004; 65(Suppl 16): 4–7.
- Teleanu, R.I.; et al. Neurotransmitters—Key Factors in Neurological and Neurodegenerative Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, K.M.; et al. Conscious and Subconscious Sensorimotor Synchronization - Prefrontal Cortex and the Influence of Awareness. NeuroImage 2002, 15, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyhus, E.; Curran, T. Functional role of gamma and theta oscillations in episodic memory. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 2010, 34, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessica R. Andrews-Hanna et. al., “The default network and self-generated thought: component processes, dynamic control, and clinical relevance”, Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014 May; 1316(1): 29–52.
- Roger E. Beaty, “Default and Executive Network Coupling Supports Creative Idea Production”, Scientific Reports | 5:10964. [CrossRef]
- Javier Gonzalez-Castillo, “Traveling and standing waves in the brain”, Nat Neurosci. 2022 August ; 25(8): 980–981. [CrossRef]
- Sakura Takada, “Mode selection mechanism in traveling and standing waves revealed by Min wave reconstituted in artificial cells”, Sci. Adv. 8, eabm8460 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Paul L Nunez and Ramesh Srinivasan, “A theoretical basis for standing and traveling brain waves measured with human EEG with implications for an integrated consciousness”, Clin Neurophysiol. 2006 November ; 117(11): 2424–2435. [CrossRef]
- Vinod Menon et. al., “Saliency, switching, attention and control: a network model of insula function”, Brain Struct Funct. 2010 June ; 214(5-6): 655–667. [CrossRef]
- Lenin D. Ochoa-de la Paz, et. al., “The role of GABA neurotransmitter in the human central nervous system, physiology, and pathophysiology”, Rev Mex Neuroci. 2021;22(2):67-76. [CrossRef]
- Ethan S. Bromberg-Martin, et. al., “Dopamine in motivational control: rewarding, aversive, and alerting”, Neuron. 2010 December 9; 68(5): 815–834. [CrossRef]
- Fazekas P, Nanay B, Pearson J. 2021 Offline perception: an introduction. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 376: 20190686. [CrossRef]
- John M. Beggs and Dietmar Plenz, “Neuronal Avalanches in Neocortical Circuits”, The Journal of Neuroscience, December 3, 2003 23(35):11167–11177. [CrossRef]
- Jack A. Tuszynski, et. al., “Microtubules as Sub-Cellular Memristors”, Scientific Reports | (2020) 10:2108. [CrossRef]
- Gatenby, R.A. The Role of Cell Membrane Information Reception, Processing, and Communication in the Structure and Function of Multicellular Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelman, G. Neural Darwinism: The Theory of Neuronal Group Selection; Basics book Inc: New York, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Grossberg, S. “The resonant brain: How attentive conscious seeing regulates action sequences that interact with attentive cognitive learning, recognition, and prediction”, Atten Percept Psychophys 81, 2237–2264 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Ovidiu Cristinel Stoica, “Freedom in the many-worlds interpretation”, arXiv: 2210.07596 [physics.hist-ph]. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Schematic diagrams of (a) Neuron, (b) Neural Network and (c) zoomed image of a synapse (junction between axon and dendrite.
Figure 1.
Schematic diagrams of (a) Neuron, (b) Neural Network and (c) zoomed image of a synapse (junction between axon and dendrite.
Figure 2.
(a, b) Neuronal inputs to a neuron labelled as “SUM” and output as action potential. (c) If the sum of stimulus is less than a threshold value (-55mV), the neuron does not fire and if the sum is above threshold, then the frequency of firing is proportional to the magnitude above the threshold value.
Figure 2.
(a, b) Neuronal inputs to a neuron labelled as “SUM” and output as action potential. (c) If the sum of stimulus is less than a threshold value (-55mV), the neuron does not fire and if the sum is above threshold, then the frequency of firing is proportional to the magnitude above the threshold value.
Figure 3.
Schematic of (a) Central Nervous System, (b) Peripheral Nervous System.
Figure 3.
Schematic of (a) Central Nervous System, (b) Peripheral Nervous System.
Figure 4.
Plasticity in neural network (a) pre-existing memory (b) learning new information i.e., new memory (see new connections being formed marked by arrow).
Figure 4.
Plasticity in neural network (a) pre-existing memory (b) learning new information i.e., new memory (see new connections being formed marked by arrow).
Figure 5.
Electrical oscillations observed experimentally using Electro-Encephalo-Gram (EEG).
Figure 5.
Electrical oscillations observed experimentally using Electro-Encephalo-Gram (EEG).
Figure 6.
(a). The human brain is generally considered to have three layers: 1. Cortex, 2. Limbic, and 3. Brain stem. (b) Parts of cortex, Frontal (intention), Parietal (sensation), Occipital (visual), Temporal (auditory).
Figure 6.
(a). The human brain is generally considered to have three layers: 1. Cortex, 2. Limbic, and 3. Brain stem. (b) Parts of cortex, Frontal (intention), Parietal (sensation), Occipital (visual), Temporal (auditory).
Figure 7.
The “domino effect” in neuronal activity is a chain reaction that occurs when a small amount of noise in a system can trigger a cascade of activity in connected neurons.
Figure 7.
The “domino effect” in neuronal activity is a chain reaction that occurs when a small amount of noise in a system can trigger a cascade of activity in connected neurons.
Figure 8.
An attractor is a stable pattern of neural activity that a network of neurons can settle into.
Figure 8.
An attractor is a stable pattern of neural activity that a network of neurons can settle into.
Figure 9.
Interaction between DMN, SN and EN. See regions marked by bang symbol indicating locations of each network in the brain.
Figure 9.
Interaction between DMN, SN and EN. See regions marked by bang symbol indicating locations of each network in the brain.
Figure 10.
Different region of brain associatively connected converging to settle to an attractor to retrieve semantic and episodic memories.
Figure 10.
Different region of brain associatively connected converging to settle to an attractor to retrieve semantic and episodic memories.
Figure 11.
The avalanches in sandpile can vary in size, from small local bursts to large-scale activity that influences large and multiple regions which are similar to neuronal avalanches in brain.
Figure 11.
The avalanches in sandpile can vary in size, from small local bursts to large-scale activity that influences large and multiple regions which are similar to neuronal avalanches in brain.
Figure 12.
Showing schematically high Q-factor tuning ensuring that different cognitive processes remain distinct unlike mixing observed for low Q-factor tuning.
Figure 12.
Showing schematically high Q-factor tuning ensuring that different cognitive processes remain distinct unlike mixing observed for low Q-factor tuning.
Figure 13.
(a) Fractal tree and level of growth (b) Fractal tree like growth of neural network.
Figure 13.
(a) Fractal tree and level of growth (b) Fractal tree like growth of neural network.
Figure 14.
(a) A unicellular organism moving toward food or away from danger using chemical sensor on its cell membrane and microtubules pushing the cell membrane helping it to move, (b) spider weaving its web, (c) human brain activities.
Figure 14.
(a) A unicellular organism moving toward food or away from danger using chemical sensor on its cell membrane and microtubules pushing the cell membrane helping it to move, (b) spider weaving its web, (c) human brain activities.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).