Submitted:
19 September 2024
Posted:
20 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fortington, L.V.; Donaldson, A.; Finch, C.F. Self-reported worst injuries in women's Australian football identify lower limb injuries as a prevention priority. BMJ Open Sport—Exercise Medicine 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardern, C.L.; Webster, K.E.; Taylor, N.F.; Feller, J.A. Return to sport following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the state of play. British journal of sports medicine 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, L.Y.; Agel, J.; Albohm, M.J.; Arendt, E.A.; Dick, R.W.; Garrett, W.E.; Garrick, J.G.; Hewett, T.E.; Huston, L.; Ireland, M.L. Noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injuries: risk factors and prevention strategies. JAAOS-Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2000, 8, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renstrom, P.; Ljungqvist, A.; Arendt, E.; Beynnon, B.; Fukubayashi, T.; Garrett, W.; Georgoulis, T.; Hewett, T.E.; Johnson, R.; Krosshaug, T. Non-contact ACL injuries in female athletes: an International Olympic Committee current concepts statement. British journal of sports medicine 2008, 42, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, B.P.; Sheehan, F.T. Mechanism of non-contact ACL injury: OREF Clinical Research Award 2021. Journal of Orthopaedic Research® 2022, 40, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjaminse, A.; Webster, K.E.; Kimp, A.; Meijer, M.; Gokeler, A. Revised approach to the role of fatigue in anterior cruciate ligament injury prevention: a systematic review with meta-analyses. Sports medicine 2019, 49, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, A.; Vanrenterghem, J.; Staes, F.; Vandenneucker, H.; Claes, S.; Verschueren, S. Are ACL reconstructed athletes more vulnerable to fatigue than uninjured athletes? Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2020, 52, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernozek, T.W.; Torry, M.R.; Iwasaki, M. Gender differences in lower extremity landing mechanics caused by neuromuscular fatigue. The American journal of sports medicine 2008, 36, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjaminse, A.; Habu, A.; Sell, T.C.; Abt, J.P.; Fu, F.H.; Myers, J.B.; Lephart, S.M. Fatigue alters lower extremity kinematics during a single-leg stop-jump task. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy 2008, 16, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhou, H.; Quan, W.; Gusztav, F.; Wang, M.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. Accurately and effectively predict the ACL force: Utilizing biomechanical landing pattern before and after-fatigue. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2023, 241, 107761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Lin, C.-F.; Garrett, W.E. Lower extremity biomechanics during the landing of a stop-jump task. Clinical biomechanics 2006, 21, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMorat, G.; Weinhold, P.; Blackburn, T.; Chudik, S.; Garrett, W. Aggressive quadriceps loading can induce noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injury. The American journal of sports medicine 2004, 32, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, T.; Sell, T.C.; House, A.J.; Abt, J.P.; Lephart, S.M. Knee proprioception and strength and landing kinematics during a single-leg stop-jump task. Journal of athletic training 2013, 48, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.J.; Kulas, A.S.; Perrin, D.H.; Riemann, B.L.; Shultz, S.J. Sex differences in lower extremity biomechanics during single leg landings. Clinical biomechanics 2007, 22, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtys, E.M.; Beaulieu, M.L.; Ashton-Miller, J.A. New perspectives on ACL injury: on the role of repetitive sub-maximal knee loading in causing ACL fatigue failure. Journal of Orthopaedic Research® 2016, 34, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristianslund, E.; Faul, O.; Bahr, R.; Myklebust, G.; Krosshaug, T. Sidestep cutting technique and knee abduction loading: implications for ACL prevention exercises. British journal of sports medicine 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, C.; Elliott, B.C.; Ackland, T.R.; Doyle, T.L.; Beiser, T.F.; Finch, C.F.; Cochrane, J.; Dempsey, A.R.; Lloyd, D. An anterior cruciate ligament injury prevention framework: incorporating the recent evidence. Research in sports medicine 2012, 20, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griebert, M.C.; Needle, A.R.; McConnell, J.; Kaminski, T.W. Lower-leg Kinesio tape reduces rate of loading in participants with medial tibial stress syndrome. Physical therapy in sport 2016, 18, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Whatman, C.; Hume, P.A.; Sheerin, K. Kinesio taping in treatment and prevention of sports injuries: a meta-analysis of the evidence for its effectiveness. Sports medicine 2012, 42, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-K.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lai, C.-P.; Wang, H.-P.; Hsieh, T.-H. Dynamic taping improves landing biomechanics in young volleyball athletes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 13716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.-Y.; Hu, M.-T.; Yen, Y.-Y.; Lan, S.-J.; Lee, S.-D. Kinesio Taping Relieves Pain and Improves Isokinetic Not Isometric Muscle Strength in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18, 10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.S.; Smedley, K.; Riegel, H.; Christensen, B.; Lyman, K. EFFECT OF TWO KINESIO TAPE TECHNIQUES ON KNEE KINEMATICS DURING A DROP JUMP TEST. ISBS Proceedings Archive 2022, 40, 126. [Google Scholar]
- Yam, M.L.; Yang, Z.; Zee, B.C.-Y.; Chong, K.C. Effects of Kinesio tape on lower limb muscle strength, hop test, and vertical jump performances: a meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2019, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, R.; Guo, C. Kinesio taping improves pain and function in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. International Journal of Surgery 2018, 59, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, K.Y.; Li, S.M.; Roper, M.; Wong, M.; Wong, O.; Cheung, R. Kinesiology tape does not facilitate muscle performance: A deceptive controlled trial. Manual therapy 2015, 20, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csapo, R.; Alegre, L.M. Effects of Kinesio® taping on skeletal muscle strength—A meta-analysis of current evidence. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport 2015, 18, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boobphachart, D.; Manimmanakorn, N.; Manimmanakorn, A.; Thuwakum, W.; Hamlin, M.J. Effects of elastic taping, non-elastic taping and static stretching on recovery after intensive eccentric exercise. Research in Sports Medicine 2017, 25, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G* Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior research methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, C.; Komi, P.; Tihanyi, J.; Fekete, G.; Apor, P. Mechanical power test and fiber composition of human leg extensor muscles. European journal of applied physiology and occupational physiology 1983, 51, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G. Psychophysical scaling with applications in physical work and the perception of exertion. Scandinavian journal of work, environment & health 1990, 55-58.
- Yu, B.; Gabriel, D.; Noble, L.; An, K.-N. Estimate of the optimum cutoff frequency for the Butterworth low-pass digital filter. Journal of Applied Biomechanics 1999, 15, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, W.T. Space requirements of the seated operator: geometrical, kinematic, and mechanical aspects of the body with special reference to the limbs; Wright Air Development Center Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio: 1955; Volume 159.
- Cohen, J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences; Academic press: 2013.
- Yu, P.; Gong, Z.; Meng, Y.; Baker, J.S.; István, B.; Gu, Y. The acute influence of running-induced fatigue on the performance and biomechanics of a countermovement jump. Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhi, B.; Letafatkar, A.; Hogg, J.; Naseri-Mobaraki, E. The influence of kinesio taping on trunk and lower extremity motions during different landing tasks: implications for anterior cruciate ligament injury. Journal of Experimental Orthopaedics 2021, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, A.; Zaki, S.; Alam, M.F.; Sharma, S.; Aysha, T.; Khiyami, A.T.; Althobaiti, A.J.; Alnefaie, H.A.; Nuhmani, S. Effects of facilitatory and inhibitory Kinesio taping on lateral gastrocnemius muscle activity, motor neuron excitability, and countermovement jump height in university athletes from multiple sports: A randomized controlled trial. Heliyon 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
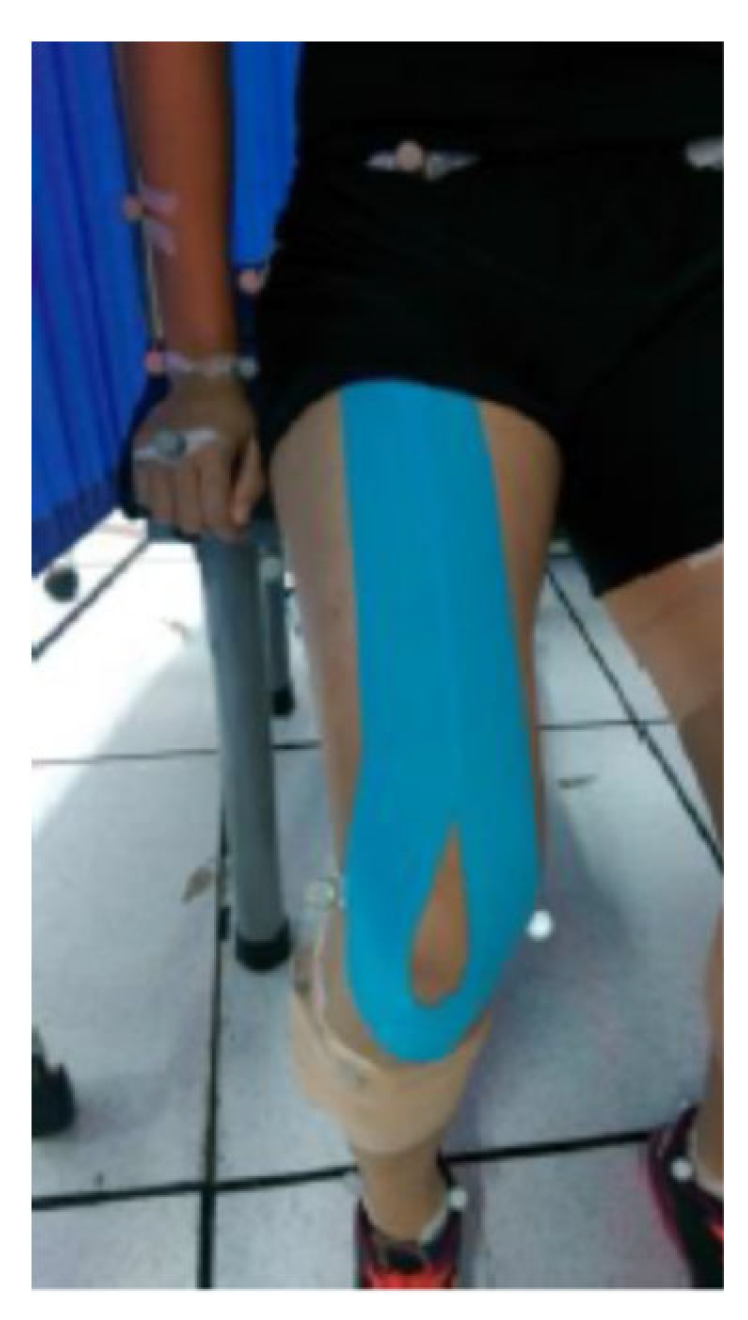
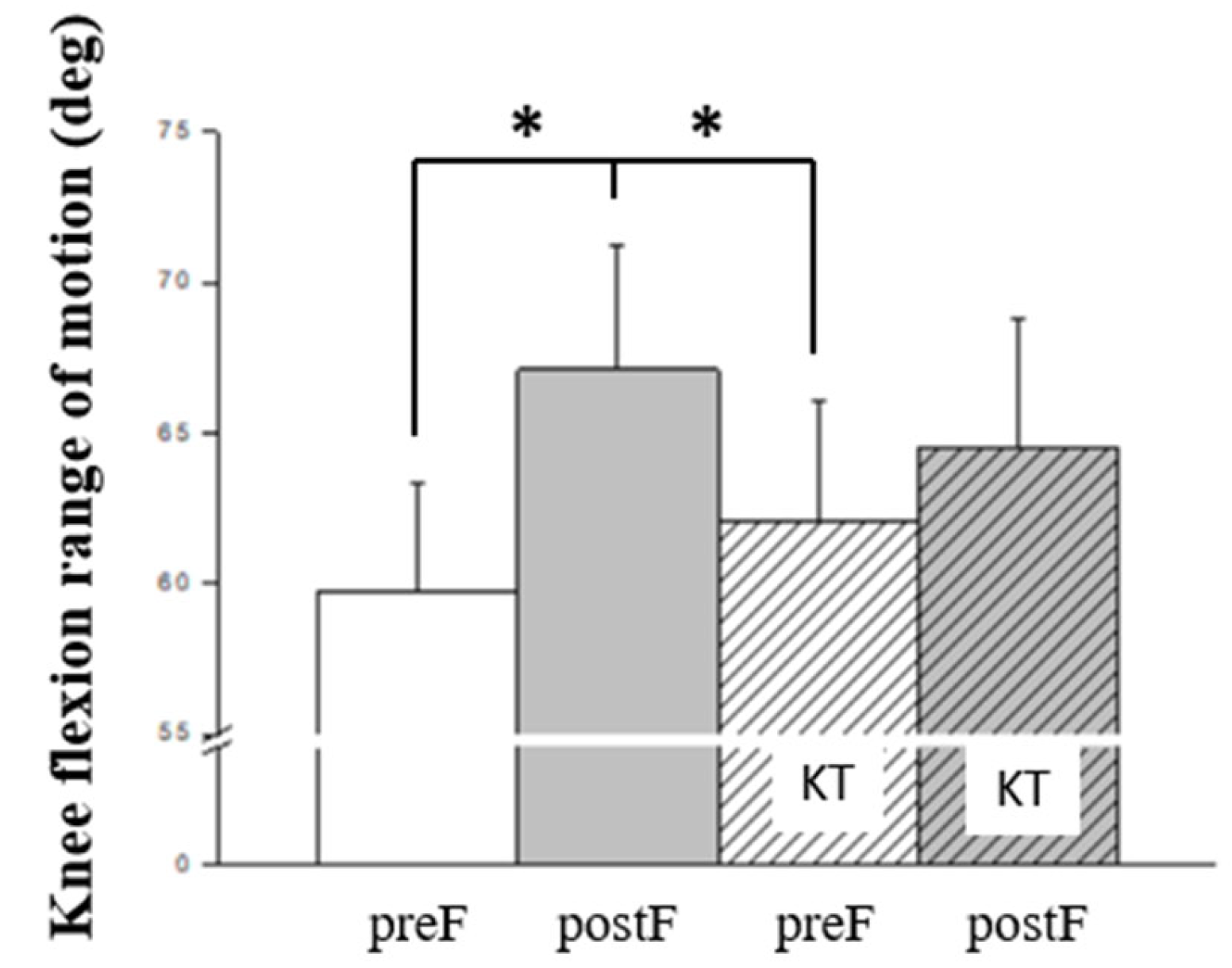
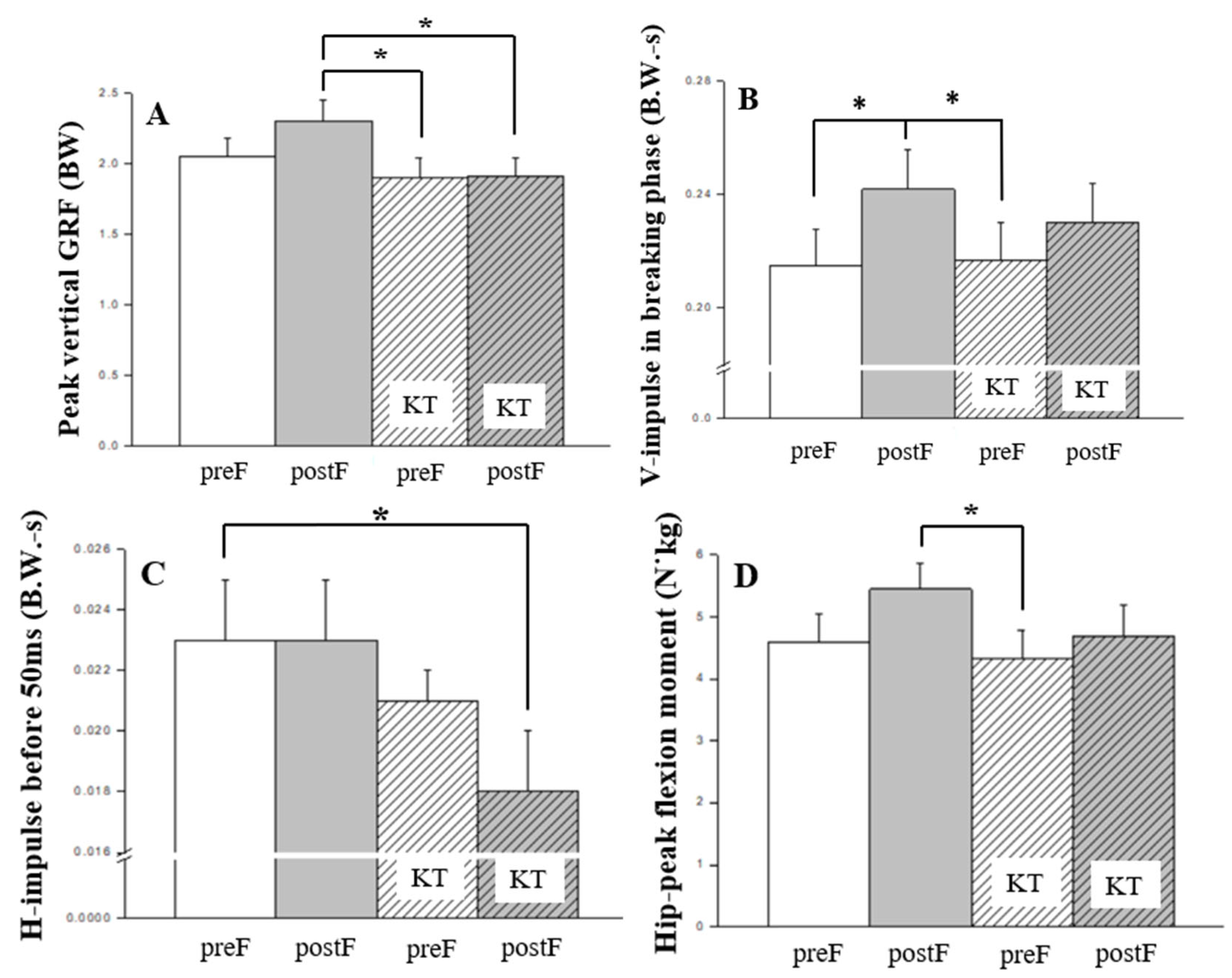
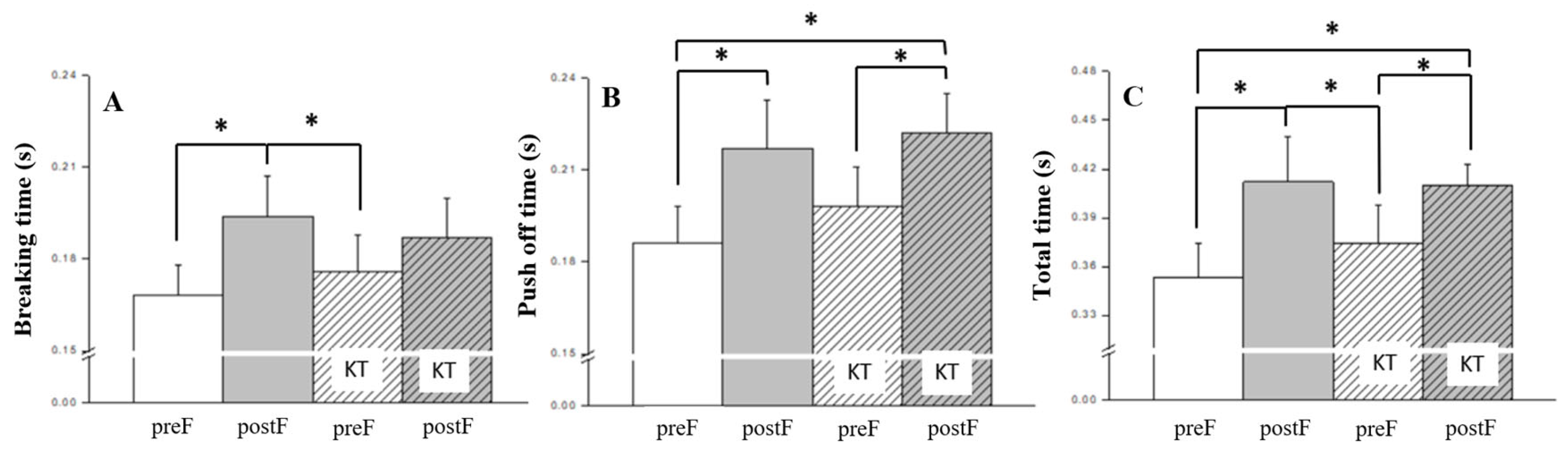
| Major biomechanical variables | main effects | interaction | |||
| p | η2 | p | η2 | ||
| kinematics | Hip- flexion angle at IC (deg) | 0.111 | 0.123 | 0.266 | 0.075 |
| Knee- flexion angle at IC (deg) | 0.223 | 0.084 | 0.352 | 0.060 | |
| Hip-peak flexion angle (deg) | 0.312 | 0.065 | 0.347 | 0.060 | |
| Knee-peak flexion angle (deg) | 0.085 | 0.121 | 0.287 | 0.071 | |
| Knee flexion range of motion (deg)* | 0.015 | 0.184 | 0.735 | 0.024 | |
| Knee Valgus range of motion (deg) | 0.395 | 0.056 | 0.959 | 0.006 | |
| Knee internal rotation range of motion (deg) | 0.419 | 0.049 | 0.438 | 0.047 | |
| Hip-flexion velocity at IC (deg/s) | 0.394 | 0.056 | 0.979 | 0.004 | |
| Knee-flexion velocity at IC (deg/s) | 0.649 | 0.031 | 0.696 | 0.028 | |
| Hip-peak flexion velocity (deg/s) | 0.422 | 0.053 | 0.379 | 0.058 | |
| Knee-peak flexion velocity (deg/s) | 0.921 | 0.009 | 0.744 | 0.042 | |
| kinetics | Hip-peak flexion moment (N/kg)* | 0.017 | 0.179 | 0.179 | 0.091 |
| Knee-peak flexion moment (N/kg) | 0.219 | 0.087 | 0.831 | 0.007 | |
| Peak knee anterior force (N/kg) | 0.067 | 0.161 | 0.667 | 0.019 | |
| Horizontal impulse in the first 50 ms after IC (BW/s)* | 0.046 | 0.162 | 0.803 | 0.014 | |
| Vertical impulse in the first 50 ms after IC (BW/s) | 0.060 | 0.134 | 0.699 | 0.027 | |
| Horizontal impulse in breaking phsae (BW/s) | 0.251 | 0.352 | 0.781 | 0.116 | |
| Vertical impulse in breaking phsae (BW/s)* | 0.002 | 0.246 | 0.990 | 0.002 | |
| Peak horizontal GRF (BW) | 0.106 | 0.128 | 0.863 | 0.007 | |
| Peak vertical GRF (BW)* | 0.000 | 0.352 | 0.862 | 0.094 | |
| performance | Time to peak proximal tibia anterior shear force (s) | 0.133 | 0.111 | 0.203 | 0.089 |
| Time to peak knee extension moment (s) | 0.838 | 0.415 | 0.399 | 0.049 | |
| Breaking time (s)* | 0.001 | 0.325 | 0.780 | 0.021 | |
| Push off time (s)* | 0.002 | 0.294 | 0.217 | 0.085 | |
| Total time (s)* | 0.001 | 0.354 | 0.392 | 0.054 | |
| Jump height (m)* | 0.000 | 0.618 | 0.908 | 0.004 | |
| Major biomechanical variables | trained | novice | F | p | η2 | power | |
| Kinematics | Hip flexion angle at IC (deg) | 61.75 ± 4.25 | 49.65 ± 4.03 | 4.279 | 0.054 | 0.201 | 0.497 |
| Knee flexion angle at IC (deg) | 36.25 ± 3.16 | 30.69 ± 3.00 | 1.628 | 0.219 | 0.087 | 0.226 | |
| Hip peak flexion angle (deg) | 82.03 ± 5.81 | 69.90 ± 5.51 | 2.298 | 0.148 | 0.119 | 0.299 | |
| Knee peak flexion angle (deg) | 103.08 ± 7.72 | 93.10 ± 7.33 | 0.880 | 0.361 | 0.049 | 0.144 | |
| Knee flexion range of motion (deg) | 64.28 ± 5.42 | 62.44 ± 5.14 | 0.061 | 0.809 | 0.004 | 0.056 | |
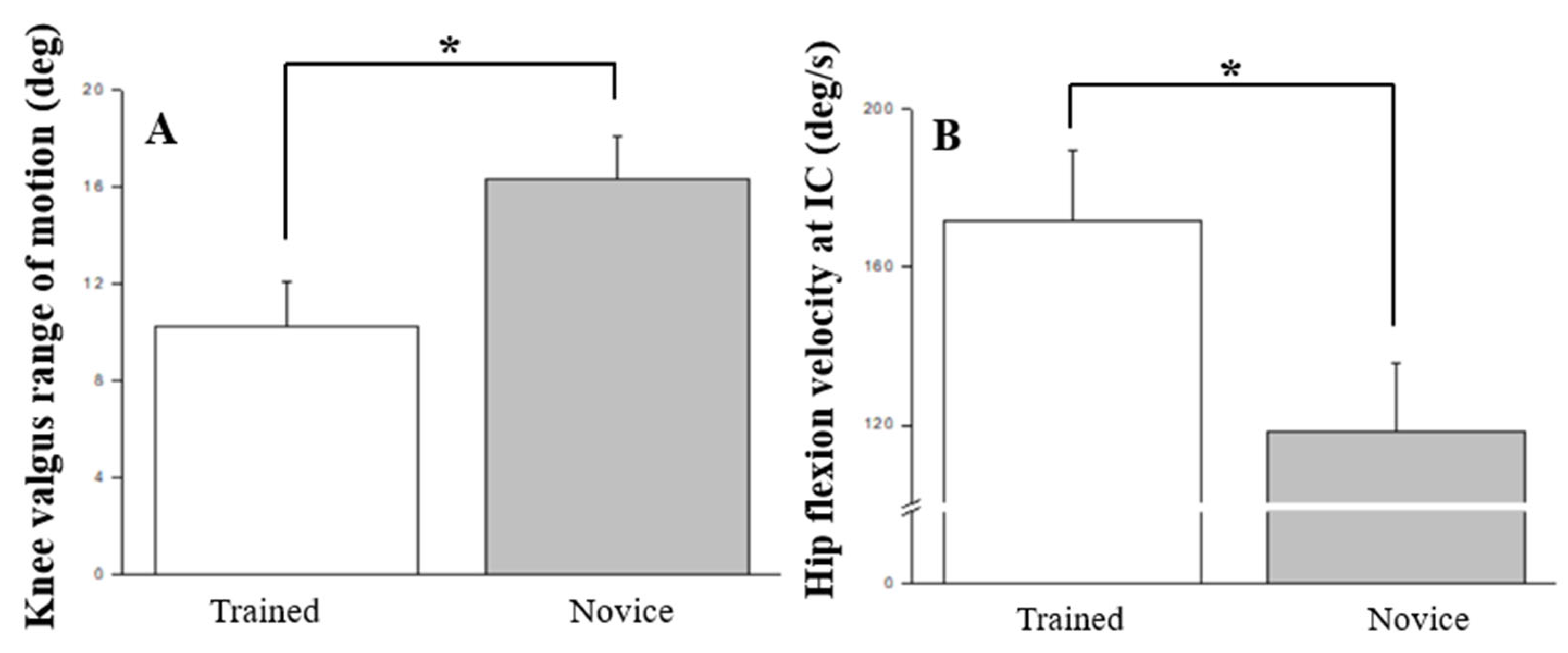
| Knee valgus range of motion (deg) * | 10.24 ± 1.83 | 16.35 ± 1.73 | 5.888 | 0.027 | 0.257 | 0.629 | |
| Knee internal rotation range of motion (deg) | 19.06 ± 2.85 | 23.85 ± 2.71 | 1.488 | 0.239 | 0.080 | 0.210 | |
| Hip flexion velocity at IC (deg/s) * | 171.52 ± 18.23 | 118.47 ± 17.29 | 4.459 | 0.050 | 0.208 | 0.513 | |
| Knee flexion velocity at IC (deg/s) | 330.91 ± 34.98 | 273.23 ± 33.18 | 1.431 | 0.248 | 0.078 | 0.204 | |
| Hip peak flexion velocity (deg/s) | 330.29 ± 37.26 | 350.77 ± 35.35 | 0.159 | 0.695 | 0.009 | 0.066 | |
| Knee-peak flexion velocity (deg/s) | 800.68 ± 67.92 | 685.13 ± 64.43 | 1.524 | 0.233 | 0.082 | 0.214 | |
| Kinetics | Hip-peak flexion moment (N/kg) | 5.03 ± 0.58 | 4.50 ± 0.55 | 0.440 | 0.516 | 0.025 | 0.096 |
| Knee-peak flexion moment (N/kg) | 2.79 ± 0.34 | 3.24 ± 3.23 | 0.919 | 0.351 | 0.051 | 0.148 | |
| Peak knee anterior force (N/kg) | 12.40 ± 1.38 | 11.98 ± 1.31 | 0.050 | 0.826 | 0.003 | 0.055 | |
| Horizontal impulse before 50ms (BW/s) | 0.021 ± .002 | 0.021 ± .002 | 0.075 | 0.788 | 0.004 | 0.058 | |
| Vertical impulse before 50ms (BW/s) | 0.058 ± 0.01 | 0.055 ± 0.01 | 0.182 | 0.672 | 0.011 | 0.069 | |
| Horizontal impulse in breaking phsae (BW/s) | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.159 | 0.695 | 0.009 | 0.066 | |
| Vertical impulse in breaking phsae (BW/s) | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 0.416 | 0.527 | 0.024 | 0.094 | |
| Peak horizontal GRF (BW) | 0.877 ± 0.082 | 0.809 ± 0.878 | 0.364 | 0.554 | 0.021 | 0.088 | |
| Peak vertical GRF (BW) | 2.077 ± 0.189 | 2.004 ± 0.179 | 0.080 | 0.781 | 0.005 | 0.058 | |
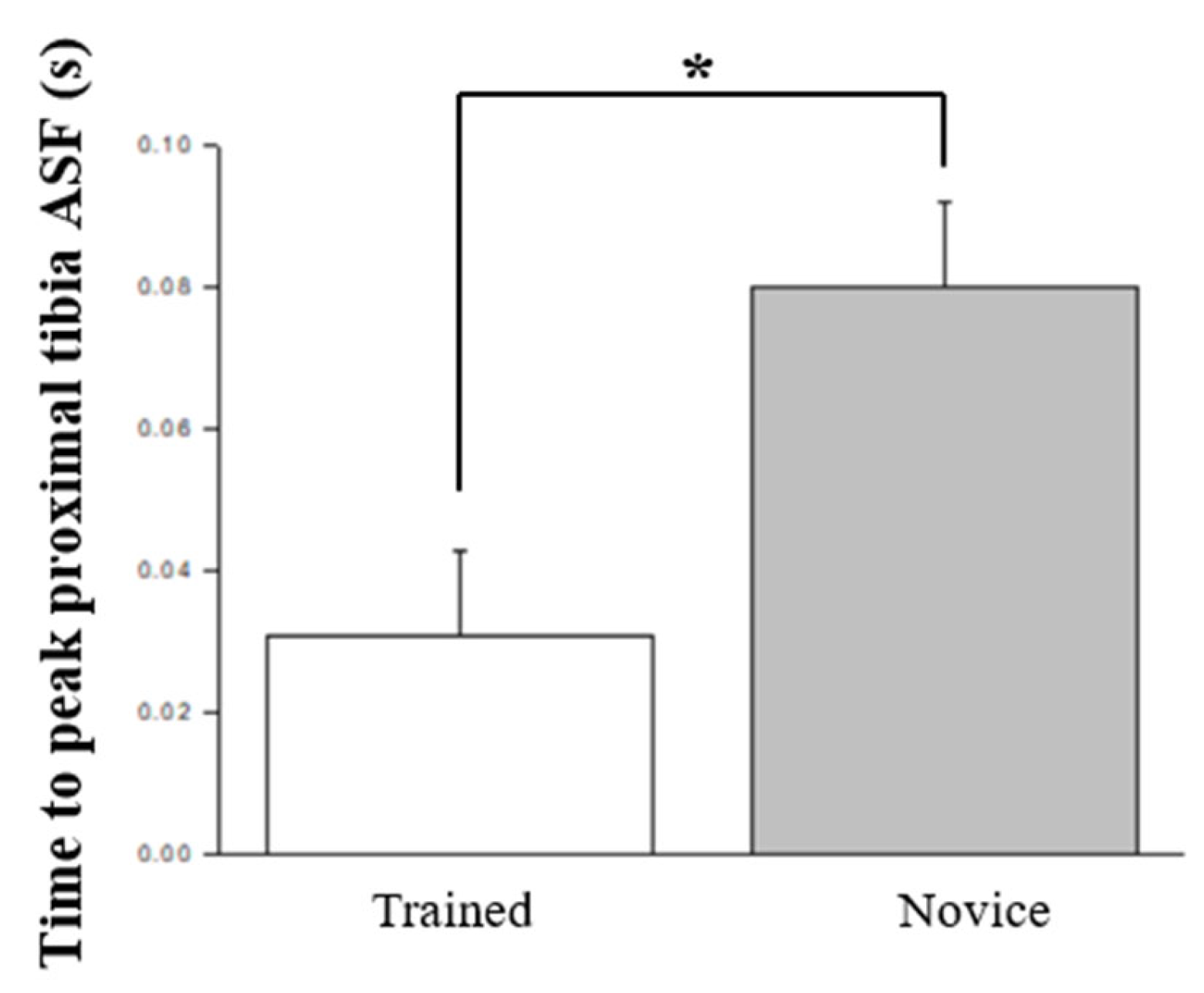
| Performance | Time to peak proximal tibia anterior shear force (s) * | 0.031 ± 0.012 | 0.080 ± 0.012 | 8.286 | 0.010 | 0.328 | 0.774 |
| Time to peak knee extension moment (s) | 0.064 ± 0.009 | 0.075 ± 0.008 | 0.768 | 0.393 | 0.043 | 0.131 | |
| Breaking time (s) | 0.176 ± 0.016 | 0.187 ± 0.016 | 0.198 | 0.662 | 0.011 | 0.070 | |
| Push off time (s) | 0.203 ± 0.20 | 0.208 ± 0.19 | 0.030 | 0.865 | 0.002 | 0.053 | |
| Total time (s) | 0.379 ± 0.035 | 0.395 ± 0.034 | 0.106 | 0.749 | 0.006 | 0.061 | |
| Jump height (m) | 0.468 ± 0.038 | 0.395 ± 0.036 | 1.891 | 0.187 | 0.100 | 0.255 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





