1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
In the context of globalisation and rapid urbanisation, the construction industry is facing unprecedented challenges, which include improving resource efficiency, reducing environmental impacts, and responding to social and governance pressures. For example, the increasing demand for urban infrastructure has led to significant resource depletion, with global construction accounting for 39% of energy-related carbon dioxide emissions [
1]. Additionally, issues such as waste management and labour rights have become critical, particularly in developing countries where rapid urban expansion often leads to inadequate governance structures [
2]. These challenges are compounded by the growing need for compliance with environmental regulations and the implementation of sustainable development practices [
3].
Building Information Modelling (BIM), as an advanced digital technology, provides the construction industry with a new and efficient method for managing the entire lifecycle of a building project—from design and construction to maintenance and operations. This technology enhances collaboration among stakeholders and improves project outcomes by facilitating real-time information sharing and decision-making [
4].
The concept of Building Information Modelling (BIM) was first introduced by Charles M. Eastman in the 1970s. Eastman pioneered the idea of using digital technologies to manage building data comprehensively, going beyond traditional design methods. Initially rooted in computer-aided design (CAD), which focused on creating 2D and 3D models, BIM integrates detailed information about building components, processes, and lifecycle management, enabling a more holistic approach to construction projects [
5].The main purpose of BIM is to facilitate information sharing and collaboration by creating a virtual model that contains building geometry, spatial relationships, geographic information and the number of building components [
4].
Today, BIM is widely used in the construction industry to help improve the efficiency, quality, and sustainability of projects, as it enables better information management, collaboration, and decision-making throughout the project lifecycle [
6,
7].
In recent years, there has been a growing global focus on sustainable development.In 2015, the United Nations adopted 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which have become an important framework for guiding the development of various industries around the world.These goals, as outlined by the United Nations in 2015, cover multiple aspects such as eradicating poverty (SDG 1), combating climate change (SDG 13), and promoting peace and justice (SDG 16). They also address key dimensions such as health (SDG 3), education (SDG 4), gender equality (SDG 5), and clean energy (SDG 7), aiming to achieve economically, socially, and environmentally sustainable development[
8].
Through these goals, the United Nations calls on governments, businesses, and all sectors of society to work together to achieve these goals by 2030 in order to address global challenges such as climate change, resource depletion, and social inequality.
Meanwhile, Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) criteria have citation in recent years as an important indicator of corporate social responsibility and sustainability practices[
9]. As early as 2013, researchers began to emphasise the importance of ESG criteria in corporate valuation, noting that ESG provides investors with a framework for assessing a company's performance in managing environmental risks, being socially responsible, and maintaining good corporate governance [
10]. Friede et al. (2015), by integrating more than 2,000 empirical studies, found that firms that value ESG criteria typically achieve higher financial performance over the long term, which not only reflects their leadership in sustainability practices but also demonstrates their commitment to environmental and social responsibility[
11].
It can be seen that in the construction industry, ESG is particularly relevant as companies face increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, reduce carbon emissions, and ensure fair labour conditions. [
12].
The integration of BIM with ESG facilitates more effective management of environmental impacts through efficient resource use and enhances transparency in governance by promoting data sharing and collaboration among stakeholders [
13]. This is especially important in the context of BIM implementation, as BIM technology enables construction firms to achieve ESG goals by improving resource efficiency, minimizing waste, and ensuring compliance with sustainability standards. Moreover, aligning BIM with ESG practices can bolster a company's reputation, attract investors, and ultimately lead to improved financial performance.
In addition,integrating SDGs with ESG criteria provides companies a unified approach to achieving both economic efficiency and sustainability[
14]. BIM plays a key role in this by optimizing resource use, improving transparency, and supporting sustainable construction practices[
15].
1.2. The Necessity of Integrating BIM with ESG and SDGs
BIM as a collaborative tool, not only improves the efficiency of building design and construction, but also can promote better resource utilisation and waste reduction in life cycle management[
6,
7].
Although BIM technology can significantly improve efficiency and sustainability in the construction industry, several pressing issues must be addressed when integrating it into ESG and SDGs contexts for implementation [
16,
17].
These challenges include how to effectively integrate BIM with ESG and SDG requirements, such as optimizing energy use, reducing carbon emissions, and enhancing stakeholder collaboration. Additionally, there are challenges in assessing and accurately reporting the long-term environmental, social, and economic impacts of BIM across the entire project lifecycle [
18,
19]. Further barriers include data management issues, such as ensuring interoperability between different software platforms and efficiently handling large datasets [
20]. Moreover, the lack of standardization in BIM processes and coordination difficulties among stakeholders—such as misaligned project goals and communication gaps—complicate the integration of BIM with broader sustainability goals and corporate social responsibility [
21,
22].
In the context of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG), BIM technologies can contribute to environmental sustainability by improving the energy efficiency of buildings and reducing their carbon footprint. For example, BIM enables energy simulations during the design phase, allowing for the optimization of building orientation, insulation, and material choices, which can significantly reduce energy consumption. Additionally, BIM facilitates the use of renewable energy systems by integrating photovoltaic panels and energy-efficient HVAC systems into building designs [
23,
24].
In addition, BIM can enhance social sustainability by facilitating better safety management and increasing project transparency. For example, BIM allows for the simulation of construction sequences and hazard identification, enabling the early detection of potential safety risks and the implementation of preventive measures. Furthermore, BIM increases transparency by providing a shared digital platform where all stakeholders can access up-to-date project information, fostering clearer communication and more informed decision-making, which in turn improves labour conditions and encourages community participation[
25].
In terms of governance, BIM can enhance accountability mechanisms in project management through transparency of data and optimisation of information flows [
26,
27]. Alreshidi et al. (2017) highlight the potential of BIM in promoting sustainability in the construction industry, especially when combined with ESG criteria that can enhance the assessment of environmental impacts and social benefits. Their study showed that BIM integration with ESG can bring greater transparency and better governance structures to projects, leading to improved decision-making processes[
28].
At the same time, BIM technology has shown great potential in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). For example, BIM can support the construction of sustainable cities and communities (SDG 11) by optimising resource allocation through intelligent planning and design [
29]. Furthermore, BIM plays a key role in supporting responsible consumption and production (SDG 12) by optimising material use and reducing construction waste[
30,
31]. Further research has shown that BIM can support SDG 7 (clean energy) and SDG 13 (climate action) goals by effectively managing resources and energy consumption throughout the building lifecycle [
16].
In a study on the integration of BIM with ESG and SDGs, Sætra (2021) proposes the adoption of SDGs to systematically assess AI-related ESG impacts. This framework, although focused on AI, offers valuable insights for BIM integration, as both technologies share common challenges in managing large datasets, ensuring transparency, and addressing sustainability goals[
32]. Like AI, BIM can benefit from a structured assessment framework to evaluate its contributions to environmental, social, and governance criteria, particularly in optimizing resource use and enhancing stakeholder engagement.
Such an integrated framework could help companies to assess and disclose the contribution of their building projects to sustainable development in a more structured way, especially when considering environmental impacts, social responsibility and quality of governance[
32], and Mohammed (2022 )found through their analysis that BIM is increasingly instrumental in driving green building certification[
33]. However, there is still a research gap on how to closely integrate these certification criteria with ESG and SDGs frameworks.
Although existing studies have revealed the potential benefits of integrating BIM with ESG and SDGs, there remains a lack of research focusing on several critical aspects of the systematic integration of BIM into the implementation process. For instance, limited attention has been given to how BIM can support decision-making aligned with ESG and SDGs, particularly in the areas of stakeholder engagement, supply chain management, and lifecycle impact assessment. Additionally, the development of standardized metrics for assessing the long-term sustainability and governance impacts of BIM projects remains underexplored. Wong and Zhou (2015) discussed BIM implementation challenges, such as technological complexity and organizational change, but did not examine how these challenges could be connected to ESG and SDG integration. Similarly, Jayasinghe & Waldmann's (2020) study focuses on the use of BIM in construction site information management rather than its potential role in driving sustainability initiatives across the entire project lifecycle. Further research is needed to bridge these gaps and develop comprehensive tools that address these under-researched areas[
34,
35].
This lack of systematic assessment limits the potential of BIM in driving overall sustainable development in the construction industry and highlights the need to develop new integration frameworks and methods to better guide the implementation of BIM in the context of ESG and SDGs. For example, future frameworks could incorporate lifecycle sustainability assessment (LCSA) tools that evaluate the environmental, social, and economic impacts of construction projects throughout their entire lifecycle. Additionally, adapting existing frameworks such as the STOPE (Strategy, Technology, Organization, People, Environment) model could offer a multi-dimensional approach to addressing both technical and organizational challenges in integrating BIM with sustainability goals [
23,
28].
In terms of BIM implementation frameworks, existing research tends to focus mainly on a single dimension of BIM technology, and these frameworks tend to focus on specific domains or aspects, such as technical or organisational aspects, rather than addressing a holistic, multidimensional approach. For example, Khalid Bouguerra et al. (2020) focus on the technical aspects of BIM adoption in the Algerian construction industry, while Chen (2015) explores BIM-related organisational change management in Chinese firms.Miceli Junior (2020) proposes a framework for improving decision-making, project outcomes and organisational efficiency in BIM implementation[
36]. Sena & Fabricio (2023) highlight the need for a standardised approach in BIM implementation, proposing a BIM implementation framework specific to Brazilian construction companies[
37]. These studies emphasise the need for comprehensive standards, prioritisation systems, and consideration of factors such as policy, culture and business structure when developing an effective BIM implementation strategy.
While these studies provide valuable insights, they ignore the interdependencies between technical, organisational and environmental factors that are critical for the successful integration of BIM with ESG and SDG. This narrow focus limits the ability of these frameworks to guide holistic implementation strategies that consider sustainability, governance, and stakeholder engagement.
1.3. Research Objectives and Questions
The aim of this research is to identify the key factors affecting the implementation of BIM in the context of ESGs and SDGs, and based on these factors to develop a theoretical framework integrating ESGs and SDGs for the implementation of BIM based on the STOPE (Strategy, Technology, Organisation, People, Environment) framework.
The STOPE framework has been successfully applied in a variety of information security environments, demonstrating its versatility in addressing complex, multidimensional challenges.
Alhogail (2015) developed an integrated information security culture framework based on STOPE that incorporates human factors and change management principles[
38]. Similarly, Alghamdi et al. (2019) used STOPE to create a framework for establishing an information security risk management environment in cloud computing[
39].Saleh et al. (2007) used STOPE to develop a mathematical model for investigating compliance with the international standard for information security management, ISO 17799-2005[
40].
The STOPE framework is therefore particularly suitable for studying BIM in the context of ESG and SDGs as it involves multiple interrelated dimensions - strategic alignment, technological capabilities, organisational structure, human factors and environmental factors. These dimensions are important to ensure that the implementation of BIM not only meets technical requirements, but also aligns with broader sustainability and governance goals.
Through this research, we expect to be able to provide new insights into the role of BIM in supporting sustainable building practices for both academia and practice, as well as advancing sustainable development in the construction industry.
In order to achieve this objective, the following research questions were formulated for this research::
1.What are the key factors affecting the effective implementation of BIM in the context of ESGs and SDGs?
2.How can the STOPE framework be used to develop a comprehensive theoretical framework for BIM implementation that promotes sustainable development of construction projects?
2. Materials and Methods
This research adopts a Systematic Literature Review (SLR) approach to identify and analyze key factors for the implementation of BIM in the context of ESGs (Environmental, Social, and Governance) and SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals). Originally proposed by Kitchenham (2004) in software engineering, the SLR method is a systematic, transparent, and replicable process that synthesizes and evaluates existing research to identify trends, gaps, and critical factors[
41]. This rigorous approach ensures the quality and relevance of the reviewed literature, providing a solid foundation for understanding current knowledge and guiding future research on the integration of BIM with ESG and SDGs.
In recent years, the use of systematic literature reviews (SLR) in Building Information Modelling (BIM) research has grown substantially. This is due to SLR's ability to systematically synthesize fragmented research across multiple domains, making it particularly useful in addressing the multidisciplinary nature of BIM. For example, Boje et al. (2020) conducted an SLR to explore the integration of BIM with blockchain technology, offering insights into potential synergies and challenges[
42]. Similarly, Darko et al. (2017) used an SLR to investigate BIM's role in green building practices, providing a comprehensive understanding of BIM’s contributions to sustainability[
43]. These cases demonstrate how SLR helps consolidate diverse findings, identify consistent patterns, and highlight critical gaps for future research and practical applications.
Through this approach, this study systematically examines the implementation of BIM in the context of the integration of ESGs and SDGs to provide a comprehensive perspective on the development of the field.
2.1. Data Collection
The researchers began by using Succar's (2009) definition of BIM, emphasising its role in transforming the construction process, focusing on aspects of technology adoption, maturity and capability development[
4]. This directly prompted the researcher to include the search strings ”BIM implementation”, “BIM adoption”, “maturity” and “capability “, terms, whilst Anderson & Ackerman Anderson (2002) highlighted the importance of leadership, change management and human performance to organisational success[
44]. As a result, broader terms related to collaboration and organisational factors were added to the search terms such as “strategy”, “technology”, “organisation”, “people” and “environment”, which is consistent with the STOPE model to capture the multifaceted nature of BIM integration As a basis for this.From this the researchers identified search strings (
Table 1).
Subsequently, these keywords and strings were utilized for searching in Chau (1997) and Ahmad et al. (2018), as well as the suggested list of journals in the categories of Architecture, Building Technology, and Construction Management. Chau's (1997) ranking of construction management journals remains a foundational reference for identifying high-impact publications in the construction field, making it highly relevant for BIM research[
45]. Ahmad et al. (2018) expanded upon this by evaluating journal rankings in terms of their influence and relevance in contemporary architecture and building technology, ensuring that the selected journals align with the study's focus on integrating BIM with ESG and SDGs[
46]. These sources help ensure that the study reviews authoritative, peer-reviewed journals that are central to discussions on technological innovation and sustainable practices in the construction industry.
As part of the methodology, we reviewed 22 journals suggested by Chau (1997) and 61 journals from Ahmad et al. (2018). Only 4 journals from Chau’s list and 3 from Ahmad’s list were relevant to this study’s focus on BIM, ESG, and SDG integration. After accounting for duplicates, 5 unique journals met the criteria for in-depth review.
2.2. Database Identification
In order to ensure the comprehensiveness and diversity of the literature review, the search was conducted using databases such as Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Scopus to capture more interdisciplinary research outputs. These databases were chosen because they cover a broad range of disciplines, including architecture, engineering, environmental science, and social sciences, which are critical for studying the integration of BIM with ESG and SDGs. Google Scholar offers extensive academic coverage across various fields, Web of Science is known for its high-quality, peer-reviewed publications, and Scopus provides access to a wide range of technical and scientific literature. Together, these databases ensure that the literature review incorporates the necessary breadth and depth to address the multidisciplinary aspects of the study.
Searches were conducted in Google Scholar, Web of Science and Scopus using the search strings in Table1 to access literature not in the journals listed in Chau (1997) and Ahmad et al. (2018). Similar to the study by Hansen et al. (2018), the researcher realised that in the field of construction technology and management, conducting a literature review should not be limited to construction technology and construction management journals only[
47].
By drawing on the methodology of Ahmad et al. (2018), the researcher also included publications from other fields related to these topics, such as information management and sustainable building practices. This interdisciplinary approach is crucial for achieving the study's goals because the integration of BIM with ESG and SDGs involves not only technical aspects but also organizational, environmental, and social dimensions. Incorporating literature from various fields ensures a more holistic understanding of how BIM can contribute to sustainability goals and address governance and social challenges. Interdisciplinary research has been shown to offer richer insights and more innovative solutions, particularly in complex fields like construction and sustainability [
48].
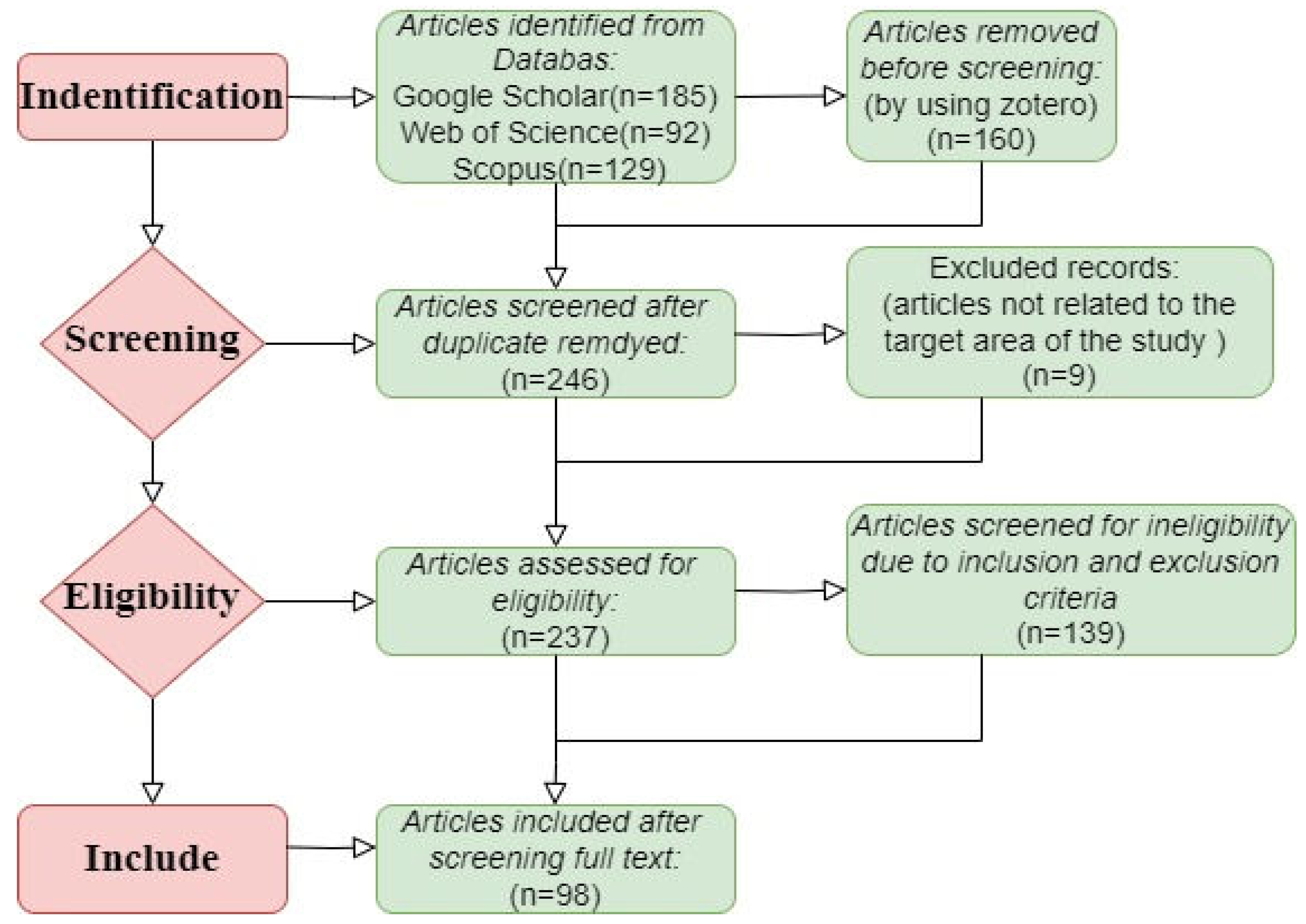
In addition, the researcher collected relevant literature from recognised building technology conference proceedings and industry reports, whilst additional valuable sources were identified and included by examining the citation and reference lists of the reviewed articles. This investigation resulted in an initial number of 406 papers from 20 journals, the number of journals as well as the initial number of papers are shown in Table 3. Subsequently, an Excel spreadsheet containing 406 articles was imported into Zotero Literature Manager with the aim of removing duplicate entries and duplicate studies. As a result 246 papers were saved. Out of these 246 articles there were also 9 articles that were not related to the target area of the study and finally 237 papers were saved for the next step of the study.
2.3. Data Quality Selection Criteria
Further in-depth analyses of the 237 articles were conducted to assess whether they met the research criteria. The researchers developed a set of inclusion and exclusion criteria to ensure that only relevant and high-quality studies were selected. As shown in
Table 2, the inclusion criteria focused on peer-reviewed articles published between 2009 and 2024 that directly addressed the integration of BIM with ESG and SDGs. The selected articles needed to discuss key aspects of BIM implementation, such as technological, organizational, or sustainability issues. Exclusion criteria filtered out non-English articles, non-peer-reviewed publications, and studies that did not specifically relate to the core focus of BIM, ESG, or SDGs integration. This careful screening ensured that the selected literature aligned with the study’s objectives.
After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria and screening for eligibility98 papers relevant to the purpose of this study were finally obtained from 246 articles, the steps of screening papers using the systematic literature review method are shown in
Figure 1.
The final results after screening based on the systematic literature review method are presented in
Table 3.
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of #
A systematic literature review was used to derive
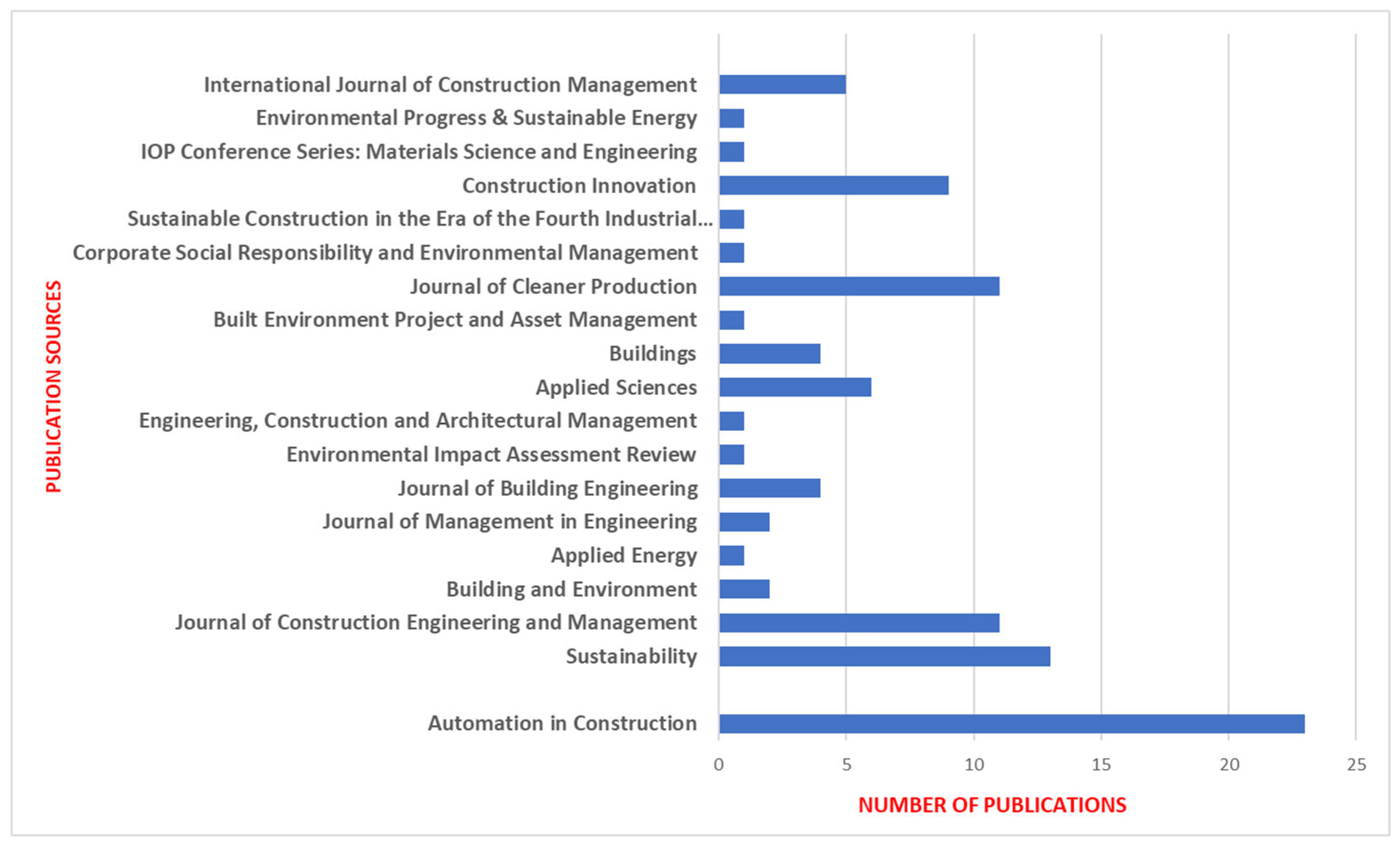
Table 3, which shows that Automation in Construction is the leading source journal in the field of BIM implementation and application, with a total of 84 initial papers, and ultimately 23 were included in the study (
Figure 2).
This suggests that the journal has a significant influence in the BIM research field, especially in the intersection of automation and building information modelling.Sustainability and Journal of Construction Engineering and Management follow closely behind with 42 initial papers (13 eventually included) and 68 initial papers (11 final inclusion). These two journals reflect research on the application of BIM to sustainable building practices as well as construction management.The Journal of Cleaner Production also provided significant literature support with 48 initial articles and 11 final inclusions. This shows the interest in the application of BIM in cleaner production and sustainability management.
Journals such as Building and Environment, Applied Energy and Journal of Building Engineering provided a small but significant amount of literature support reflecting research on BIM in environmental impact assessment and energy efficiency.
3.2. ESG and SDG Integration
According to relevant studies, the integration of ESG and SDGs not only provides strategic advantages for companies, but also contributes positively to the process of global sustainable development.ESG criteria are often used to measure corporate performance in environmental protection, social responsibility and corporate governance, while SDGs provide a set of globally recognised goals aimed at addressing social, economic and environmental challenges[
133].By combining the two, companies can develop and implement strategies that take into account both the global development goals and their own sustainability standards, leading to more holistic responsible management [
10,
11].
By combining ESGs and SDGs, businesses can drive co-operation on a global scale to achieve the wider Sustainable Development Goals [
134].
This involves not only cooperation between businesses, but also collaboration with governments, NGOs and international organisations. By working together, businesses can contribute to the realisation of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) proposed by the United Nations, such as eradicating poverty, combating climate change, and promoting gender equality[
8].
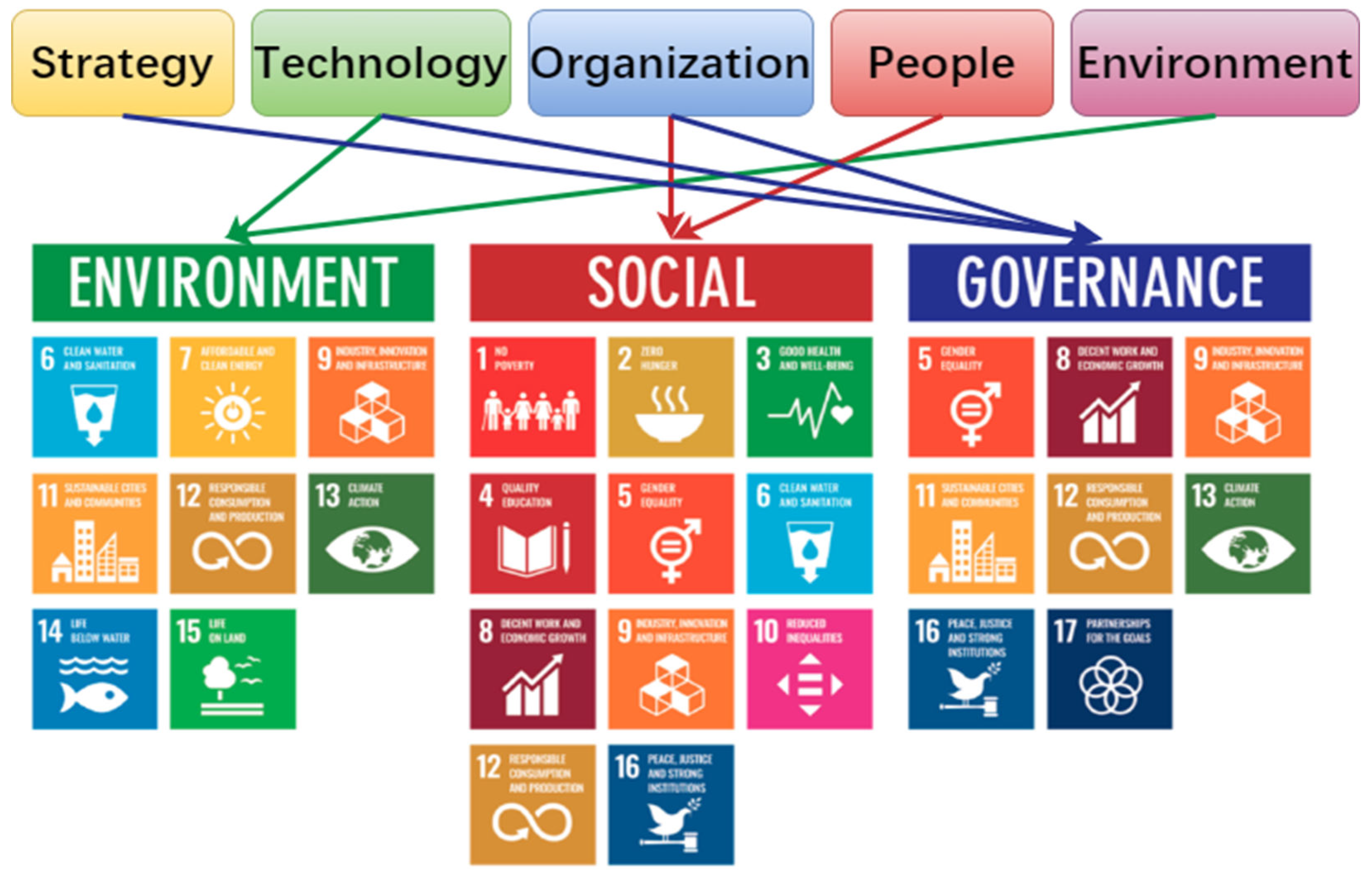
Inspired by Berenberg (2018), the researchers produced a framework integrating ESG and SDG in order to carry out the identification of BIM implementation factors in the context of ESG and SDG integration[
135], and systematically categorise these factors into the STOPE (Strategy, Technology, Organization, People, Environment) framework (
Figure 3).
The STOPE framework was chosen for classification because it provides a systematic, multidimensional approach to analysis that comprehensively covers a wide range of key factors in the BIM implementation process[
40]. Research has shown that the use of a multidimensional framework can be effective in identifying and understanding the interactions between different factors in the technology implementation process[
136].
4. Discussion
With the growing global focus on sustainability, integrating BIM technologies with ESG and SDG goals has become a key way to drive green transformation in the construction industry [
21,
125]. Identifying BIM implementation factors in the context of ESG and SDG integration can help construction firms and related stakeholders better understand the broader implications of BIM implementation and develop strategies that meet sustainability requirements[
22,
58].
The researcher will focus on filtering and extracting key factors related to BIM implementation from the literature identified in table3. And systematically categorise these factors into the STOPE (Strategy, Technology, Organization, People, Environment) framework. In this study, a literature analysis matrix will be constructed and keyword co-occurrence analysis will be performed using VOSviewer. These methods enable the researcher to distil the most influential themes and concepts from a large body of literature. The goal of this step is to identify the core factors that influence the success or failure of BIM technology in its application process
4.1. Strategic Dimension for BIM Implementation Factors
As
Table 4 shows, in the strategy dimension, the key factors to focus on include: Top management support for ESG and SDGs, ESG integration, stakeholder engagement, sustainability risk management, green building policy integration, BIM policy, long-term cost-benefit analyses, and alignment of SDG targets.
The results show that top management support for ESG and SDGs, ESG integration and SDG goal alignment are the most important factors in BIM implementation.
One of the key drivers to ensure successful BIM implementation is top management support for ESG and SDGs for ESG and SDGs, which is mentioned 23 times in the literature analysis matrix. This is because it directly influences the allocation of resources and the direction of strategic decisions [
55,
59]. When top management commits to supporting BIM implementation, organisations tend to be more willing to invest in the necessary technological infrastructure, training and resources to create the conditions for effective BIM deployment [
22,
105]. For example, Lu et al. (2017) showed that with top management support for ESG and SDGs, organisations are better able to cope with challenges in BIM implementation, such as technology integration and process changes, thus improving project success.
ESG integration is also a key factor, which appears 16 times in the literature analysis matrix because it enables the application of BIM technology to be aligned with the organisation's environmental, social and governance objectives.ESG integration emphasises that BIM is not only a technical tool, but also a strategic tool to achieve sustainable development[
17,
55]. For example, Zhao & Taib (2022) point out that by integrating ESG standards into BIM implementation, the market competitiveness and reputation of firms can be enhanced by better meeting the environmental and social responsibility expectations of clients and investors. This integration can drive firms to be more conscious of their environmental impacts during the design and construction phases and to adopt green building materials and technologies, thereby reducing carbon emissions and resource wastage.
SDG goal alignment is also an important factor in BIM implementation and it appears 14 times in the literature analysis matrix. This is because it provides organisations with a clear direction for sustainable development and motivates them to consider the SDGs globally in project planning and execution[
22,
58]. Alignment with the SDGs ensures that BIM projects contribute to broader societal goals, such as climate action and sustainable cities, which are increasingly becoming important benchmarks for assessing project success [
53,
132]. By aligning with the SDG goals, companies can more effectively achieve long-term sustainable development goals and gain more recognition and support in international markets.
In contrast, while stakeholder engagement, sustainability risk management, and green building policy integration are also important strategic factors, their impact usually depends on top management support for ESG and SDGs and the effectiveness of ESG integration. For example, without explicit support from top management, stakeholder engagement may not be organised and managed effectively [
82,
113]. Similarly, the successful implementation of green building policies usually relies on the support of overall corporate strategy and the promotion of ESG objectives [
118].
Overall, top management support for ESG and SDGs, ESG integration, and SDG goal alignment take centre stage in BIM implementation strategies. Together, they provide a clear strategic direction and the necessary resource support to ensure that BIM implementation is not just a technology upgrade, but part of the organisation's sustainability goals. Through this comprehensive and systematic strategic framework, organisations can more effectively address the challenges of the construction industry and achieve long-term success and growth.
4.2. Technology Dimension for BIM Implementation Factors
As
Table 5 shows,in the technology dimension, the key factors of interest include: BIM hardware, data standardisation, innovative applications, blockchain , technical support and BIM software.
The results show that BIM hardware and software provide the necessary infrastructure and tools, data standardisation ensures compatibility between different systems, innovative applications expand the functionality of BIM, blockchain technology enhances data security and transparency, and technical support ensures that teams can apply these technologies effectively.
Technical support is considered to be a core element in ensuring BIM implementation, and it appears 19 times in the literature analysis matrix. This is because it has a direct impact on staff training and technical competence enhancement. Technical support includes continuous training of team members, providing technical guidance, and solving problems encountered during BIM implementation [
27,
42]. For example, Boje et al. (2020) emphasise that adequate technical support in the early stages of BIM implementation can be effective in reducing errors due to technical unskill, thereby improving the overall efficiency and accuracy of the project. Jung & Joo (2011) further state that by providing continuous technical support, organisations can ensure that employees are proficient in the operation of the BIM tools, thereby maximise the potential of these tools. In addition, technical support can help the team to quickly adapt to changes in new technology and maintain the project's technological leadership and competitiveness [
74].Tam et al. (2022), on the other hand, emphasise that by establishing an effective technical support system, the team can be helped to quickly respond to the challenges posed by technological updates, thus ensuring that the project's schedule and quality are not compromised.
BIM software is also a key factor who appears 18 times in the literature analysis matrix. Because it determines the functionality and performance of a BIM system, high-quality BIM software is able to support complex data processing, provide accurate 3D modelling, and collaborative features[
50,
57]. For example, Miettinen & Paavola (2014) state that choosing the appropriate BIM software can greatly improve the efficiency of information management, allowing for smoother cross-departmental and cross-team collaboration. This collaborative nature is particularly important for complex construction projects and can effectively reduce project delays and cost overruns due to information asymmetry or miscommunication [
87].
BIM hardware is also an important factor which appears 16 times in the literature analysis matrix. This is because the performance of the hardware directly affects the operational efficiency of the BIM software and the ability to process project data.BIM hardware includes high-performance computers, servers, and other related equipment that can support the creation and real-time modification of large BIM models [
42,
56]. For example, research by Boje et al. (2020) suggests that with the support of high-performance hardware, BIM software is able to process and present complex building data more quickly, ensuring that project teams are able to make timely decisions and reduce design errors and construction changes.
In contrast, while data standardisation, innovative applications and blockchain are also important technological factors, data standardisation plays a key role in ensuring data interoperability between different systems when without strong BIM software support and appropriate technical guidance, the implementation of data standardisation may face difficulties[
7,
53]. Innovative applications such as virtual reality and augmented reality can enhance the functionality and user experience of BIM, but the success of these applications relies on the stability of the underlying technology and hardware compatibility [
49,
87]. Blockchain technology provides secure data sharing and storage solutions, but the breadth and effectiveness of its applications still rely heavily on the need for technical support and software integration capabilities [
20,
64].
Overall, technical support, BIM hardware and BIM software have a central role in the technological dimension of BIM implementation. They provide the necessary infrastructure and support for a successful BIM implementation, ensuring that the project team is able to manage and process building information efficiently and securely. While data standardisation, innovative applications and blockchain technology are important, their success often relies on a solid foundation of the aforementioned key technology factors. By prioritising these core technology needs, organisations are better able to address the technical challenges of BIM implementation and achieve successful project delivery and sustainability.
4.3. Organization Dimension for BIM Implementation Factors
As
Table 6 shows, in the Organisational Dimension, the key factors of interest are: Structural adjustment & collaboration, organisational culture, capacity building, change management, performance measurement and resource allocation.
The results show that Structural Adjustment & Collaboration, capacity building and change management are the most important factors in BIM implementation.
Structural Adjustment & Collaborationis considered a core driver for successful BIM implementation, appearing 22 times in the literature analysis matrix. This is because it facilitates cross-departmental communication and collaboration, which leads to more efficient information sharing and overall project coordination[
42,
57]. When organisational structures are adapted to support the implementation of BIM, firms are better able to break down traditional departmental barriers and ensure that information flows smoothly between different disciplines[
76,
118]. For example, Boje et al. (2020) showed that project delays and resource wastage due to information silos can be effectively reduced through structural adjustment and the establishment of collaborative mechanisms, thereby increasing project success rates. At the same time, restructuring can also facilitate external collaboration, enabling firms to communicate and collaborate more effectively with external stakeholders such as customers, suppliers and partners.Halder & Batra (2024) state that by establishing cross-organisational collaboration mechanisms, firms can ensure that all relevant parties are involved in the decision-making process and sharing of information and knowledge during a BIM project, thus enhancing the overall synergy and transparency of the project.Eadie et al. (2013) further support this view by arguing that through restructuring, firms can make better use of external resources and expertise, enhancing the innovation and adaptability of the project.
Capacity building is also a key factor which appears 18 times in the literature analysis matrix. This is because the application of BIM technology requires specific skills and knowledge. Capacity building focuses on providing continuous training and learning opportunities for employees to master and apply the latest BIM technologies[
27,
118]. For example, Yoon & Pishdad-Bozorgi (2021) state that through a systematic capacity building programme, organisations can ensure that employees remain efficient and equipped to cope with various technological challenges during BIM implementation. Capacity building involves not only technical training, but also the development of teamwork and problem solving skills, which are key to success in a BIM environment[
81,
96].
Change management is also an important factor in BIM implementation, and it appears 14 times in the literature analysis matrix. This is because BIM adoption is often accompanied by changes in processes and culture within the organisation. Effective change management can help organisations overcome the resistance and challenges encountered in adopting new technologies [
27,
51]. For example, Linderoth (2010) highlights that the implementation of BIM requires organisations to have the ability to adapt to change, and through active change management, organisations can reduce employee resistance to new technologies and increase acceptance of BIM systems. Furthermore, Herrera et al. (2021) state that change management can help organisations to develop a clear transition strategy that ensures a smooth transition during BIM implementation and reduces productivity decline during the transition.
In contrast, while organisational culture, performance measurement and resource allocation are also important organisational factors, their impact usually depends on the effectiveness of structural alignment and collaboration, capacity building and change management. For example, without effective structural alignment and collaboration mechanisms, support for innovation and collaboration in organisational culture may not actually translate into concrete actions and outcomes[
118,
124]. Similarly, the effectiveness of performance measurement often relies on a clear strategy for change management to ensure that project progress and success can be accurately tracked and evaluated during BIM implementation [
122]. Optimisation of resource allocation also requires capacity building support and a clear organisational strategy to ensure that resources are effectively channelled to the areas of greatest need [
73,
76].
Overall, restructuring and collaboration, capacity building and change management occupy a central place in the organisational dimensions of BIM implementation. Together, they provide the necessary organisational support and management strategies to ensure that BIM implementation is not just a technological change, but a comprehensive transformation of processes and culture within the organisation. Through this multi-dimensional organisational framework, companies are able to more effectively address the challenges of BIM implementation and achieve their organisational goals and long-term sustainability.
4.4. People Dimension for BIM Implementation Factors
As
Table 7 shows,in the people dimension, the key factors of concern include: education training and development, knowledge sharing & management, roles & responsibilities, team Collaboration, skills and attitude, sustainability Commitment, and Incentive mechanism.
The results show that education training and development, skills and attitudes, and incentive mechanism are the most important factors in BIM implementation.
Skills and attitudes are considered to be a key driver in ensuring the successful implementation of BIM, and it is mentioned 18 times in the literature analysis matrix. Skills and attitudes not only influence how employees use BIM tools, but also their ability to accept and adapt to new technologies [
61,
67]. Research has shown that employees with positive attitudes and high levels of skills are more likely to quickly master BIM technology for effective use in projects[
82,
87]. For example, Linderoth (2010) noted that when employees had a positive attitude towards BIM and possessed the relevant skills, they were more confident and efficient in facing technical challenges in projects. Wu et al. (2018) also found that employees' skill levels and work attitudes had a direct impact on the effectiveness of BIM implementation, and that high levels of skills and positive attitudes could significantly reduce project error rates and cost overruns.This is further supported by Fargnoli & Lombardi's (2020) research, which suggests that employees with BIM skills are better able to understand project requirements and provide innovative solutions that drive project success.
Education training and development is also a key factor which appears 14 times in the literature analysis matrix. This is because it ensures that employees acquire the necessary knowledge and skills to effectively apply BIM technology. Educational training not only helps employees to understand and use BIM tools, but also improves their ability to solve practical problems [
66,
125]. For example, Ahmed & Kassem (2018) state that through continuous education and training programmes, organisations can ensure that their employees are up-to-date with the latest BIM technologies and industry standards, which can improve the success and skill level of their projects. Such training helps employees to reduce the learning curve and increase productivity when faced with new BIM tools [
85,
96].
Incentive mechanism are also an important factor in BIM implementation, and it appears 13 times in the literature analysis matrix. This is because incentive mechanism can increase employee engagement and motivation, thus better promoting BIM adoption. By setting rewards and incentives, organisations can encourage their employees to actively participate in BIM training and application and promote the diffusion and use of the technology[
42,
82]. For example, a study by Bynum et al. (2012) showed that implementing effective incentives can stimulate employees' interest and commitment to BIM technology, which can lead to increased innovation and efficiency in projects.Wu et al. (2018) also noted that incentives can help organisations to attract and retain talented people with BIM skills, creating a competitive advantage.
Roles and responsibilities is another key factor in ensuring the success of BIM implementation and was mentioned 11 times in the literature analysis matrix. A clear definition of roles and responsibilities ensures that each team member understands his or her specific tasks and objectives, thereby reducing misunderstandings and duplication of work and increasing productivity [
56,
76]. For example, Manzoor et al. (2021b) state that in BIM projects, clear role assignments help to co-ordinate work between team members and ensure that tasks are carried out effectively. In addition, Halder & Batra (2024) showed that with clear role definitions, teams are able to better manage tasks and responsibilities, reduce conflicts and problems in projects, and thus improve overall project performance.
In contrast, while knowledge sharing and management, teamwork, and sustainability commitment are also important people factors, their impact usually depends on the effectiveness of education and training, skills and attitudes, roles and responsibilities, and incentive mechanism. For example, without systematic education and training and clear role definitions, knowledge sharing and management may be much less effective because employees may lack the necessary background knowledge and a clear sense of responsibility for understanding and applying shared information[
20,
51]. Similarly, the effectiveness of teamwork often relies on employees having the necessary BIM skills and willingness to collaborate, and if these conditions are not met, teamwork will struggle to succeed [
52,
81]. And while sustainability commitments play an important role in promoting long-term environmental and social responsibility, their actual impact often depends on the level of employee skills, clear role assignments, and the presence of incentive mechanism [
75,
101]. If employees lack sufficient BIM skills and knowledge, even if there is a commitment to sustainability, it will be difficult to implement it effectively in real projects. In addition, the lack of clear responsibilities and incentive mechanism may lead to a lack of initiative and motivation among employees in driving sustainability goals [
22,
88]. Therefore, the effectiveness of sustainability commitment relies on the solid support of the previous four key factors to ensure that employees truly understand and practice the concept of sustainability during BIM implementation.
Overall, education, training and development, roles and responsibilities, skills and attitudes, and incentive mechanism take centre stage in the people dimension of BIM implementation. Together they provide the necessary knowledge, skills and motivation to ensure that BIM implementation is not just about the introduction of technology, but also about organisational capability and staff development. Through this comprehensive and systematic people development framework, companies are able to drive the adoption of BIM technology more effectively, achieving project success and long-term organisational growth.
4.5. Environment Dimension for BIM Implementation Factors
As
Table 8 shows,in the Environment dimension, the key factors of concern include: Green certifications and standards, sustainable construction practices, resource efficiency, environmental impact assessment, climate resilience, policies and regulations, and biodiversity conservation.
The results show that sustainable construction practices, policies and regulations, and resource efficiency are the most important factors in BIM implementation.
Sustainable construction practice is considered as a core element for the successful implementation of BIM, and it appears 22 times in the literature matrix. Sustainable construction practices emphasise the use of environmentally friendly methods and materials throughout the building lifecycle to reduce negative environmental impacts [
17,
58]. Research has shown that by integrating sustainable construction practices, BIM can effectively reduce material waste and energy consumption and enhance the eco-efficiency of projects [
66,
73]. For example, Sepasgozar et al. (2021) state that projects that adopt sustainable construction practices not only perform well environmentally, but also reduce construction costs by conserving resources and reducing waste.Wen et al. (2021) found that BIM technology can help construction teams to monitor and optimise the use of resources in real time, ensuring that the design and construction phases always adopt the best sustainable solutions. In addition, research by Huang et al. (2021) further shows that by integrating sustainable construction practices in the early stages of a project, organisations can better anticipate and manage environmental risks, thereby avoiding potential environmental penalties and project delays. Not only do sustainable construction practices comply with global requirements for environmental protection, they can also significantly enhance a company's social responsibility image and market competitiveness [
69,
125]. All these studies show that sustainable construction practices play a key role in reducing environmental impacts, lowering project costs, and improving resource efficiency, and are one of the core drivers for successful BIM implementation.
Policies and regulations are also a key factor, which appears 16 times in the literature matrix. Policies and regulations provide the necessary guidance and enforcement to ensure that construction projects comply with legal requirements for environmental protection[
19,
113]. Strict environmental regulations can drive firms to adopt higher environmental standards and BIM technologies to ensure project compliance and reduce environmental impacts[
61,
68]. For example, stringent policies and regulations can facilitate the promotion of green building certifications, allowing companies to enhance their social responsibility image and market competitiveness while remaining legally compliant [
125].
Resource efficiency also plays an important role in BIM implementation and it appears 14 times in the literature matrix. Resource efficiency is concerned with the efficient use of materials and energy in the construction process to reduce waste and environmental burden [
22,
128]. Improving resource efficiency can help firms save money during the construction process while minimising the consumption of natural resources [
20,
111]. For example, Ansah et al. (2021) showed that optimising the use of resources not only reduces the carbon footprint of a construction project, but also improves the economic efficiency of the project and generates sustainable business returns for the firm.
In contrast, while green certifications and standards, environmental impact assessments, and climate resilience are also important environmental factors, their impact usually depends on the effectiveness of sustainable construction practices, policies and regulations, and resource efficiency. For example, green certifications and standards may be difficult to popularise and widely accepted if they are not supported by rigorous policies and regulations [
73,
128]. Similarly, the effectiveness of environmental impact assessment often relies on the application of sustainable construction practices to ensure that the results are translated into practical environmental actions[
111,
113]. Climate resilience, on the other hand, requires a combination of resource efficiency and policy requirements in building design and construction to address the challenges of climate change [
19,
93].
Overall, sustainable construction practices, policies and regulations, and resource efficiency occupy a central place in the environmental dimension of BIM implementation. Together, they provide the necessary environmental guidance and support for building projects, ensuring that projects continue to reduce negative environmental impacts while pursuing economic efficiency. By prioritising these core environmental factors, organisations are better able to address environmental challenges in construction projects and achieve sustainable construction goals and long-term growth.
4.6. Network Visualisation
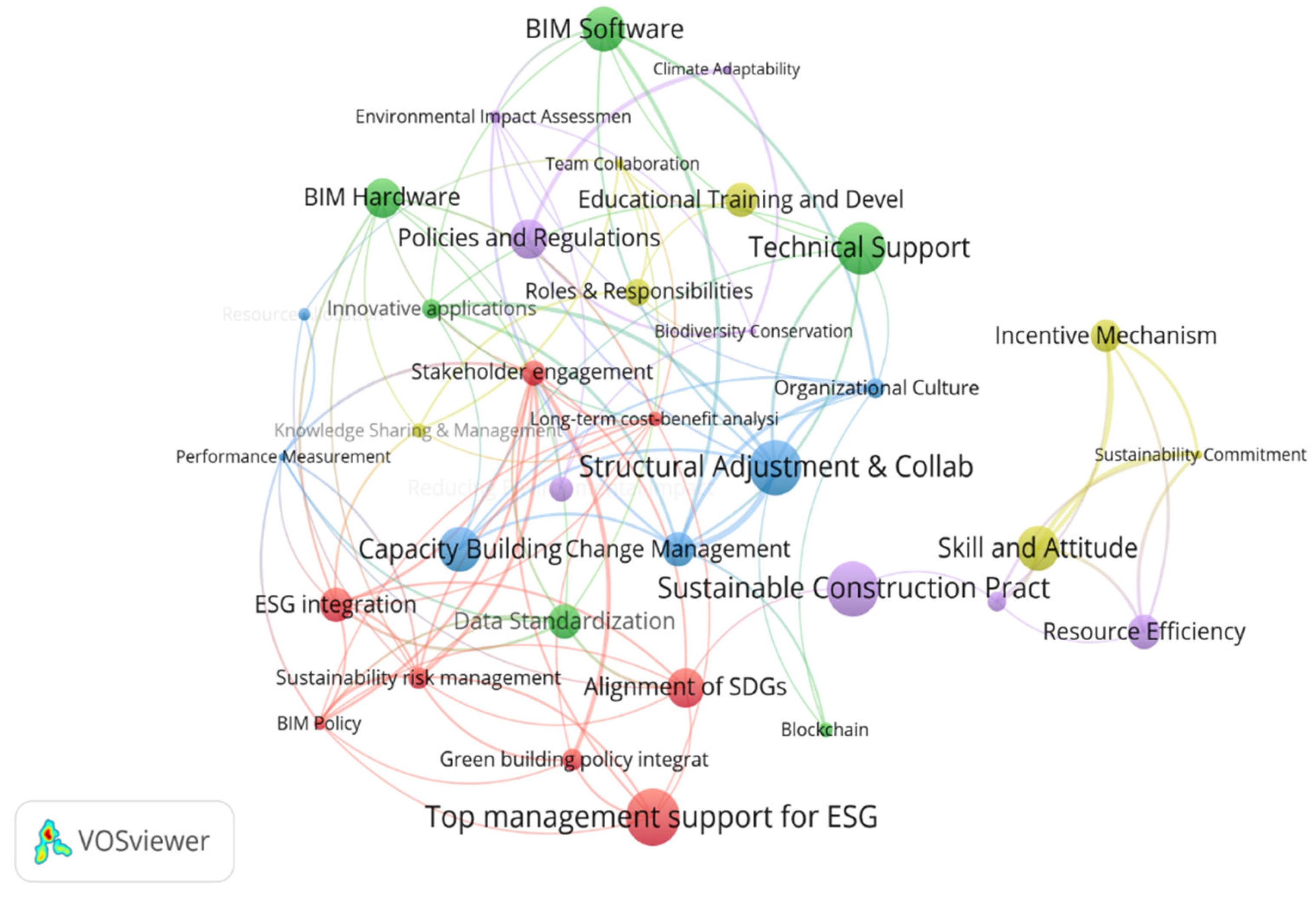
The above data were imported into the VOSviewer software for keyword co-occurrence analysis and a cluster diagram was generated using the VOS clustering algorithm (
Figure 4), which is a tool for constructing and visualising the structure of scientific knowledge and is widely used in bibliometric studies[
137].
As shown in
Figure 4, the red clusters represent the strategic dimension, the green clusters represent the technical dimension, the blue clusters represent the organisational dimension, the yellow clusters represent the people dimension, and the purple dimension represents the environmental dimension. Core concepts and themes related to BIM implementation are visualised by constructing co-occurrence diagrams. These diagrams demonstrate the relationships between keywords that appear with high frequency in the literature, enabling the study to identify the most relevant key factors for BIM implementation in the context of ESG and SDG.
4.7. Theoretical Framework for BIM Implementation
The theoretical framework (
Table 9) for BIM implementation proposed in this study is constructed based on the STOPE framework (Strategy, Technology, Organisation, People, Environment), which aims to integrate ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) and SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) principles.The STOPE framework provides a multi-dimensional perspective for the study and enables a comprehensive analysis of the implementation of BIM in the construction industry.
During the data collection and analysis process, a coding methodology was used to categorise and summarise the textual data. The coding process consisted of systematically labelling specific concepts and themes mentioned in the literature and categorising them into the five dimensions of the STOPE framework. This process helped the researcher to distil the most representative key factors.For example,”top management support for ESG and SDGs” was frequently mentioned as a core driver for successful implementation of BIM projects [
22,
59].
In addition, the exploration of readiness criteria is based on an in-depth analysis of case studies and empirical research in the literature. By analysing the practical application of different BIM projects, this study develops specific readiness criteria for each key factor. These criteria provide a self-assessment tool for organisations to ensure that they have the necessary conditions in place to implement BIM. For example, the readiness criterion of ‘technical support’ requires organisations to have high-performance computing resources and compatible BIM software to meet the technical needs of the project [
53,
74]. With such a standard, firms can more effectively evaluate and improve their BIM implementation strategies to ensure compliance with ESG and SDG requirements [
16,
125].
Through the combination of the STOPE framework and data coding, this study successfully constructed a multidimensional theoretical framework that provides systematic guidance for BIM implementation in the context of ESG and SDG. The framework not only contributes to the deepening of academic research, but also supports the sustainable development goals of the construction industry in practical applications.
5. Conclusions
The aim of this research is to identify the key factors affecting the effective implementation of BIM (Building Information Modelling) in the context of ESG (Environment, Society, Governance) and SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) and to develop an integrated theoretical framework for BIM implementation using the STOPE framework as a basis for sustainable development of construction projects. Through a systematic literature review approach, 16 key factors affecting the implementation of BIM (Building Information Modelling) in the context of ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) and SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) integration were identified.
These factors are incorporated into the STOPE (Strategy, Technology, Organisation, People, Environment) framework to form a comprehensive theoretical framework, and by constructing this theoretical framework, this research fills the theoretical gap in the application of BIM in the field of sustainability and provides a structured guide to the application of BIM in the context of sustainable development. The findings of the research show that successful BIM implementation needs to span across strategic, technological, organisational, people and environmental dimensions, ensuring full integration and coordination across these dimensions.
Through this study, stakeholders in the construction industry can more effectively identify and manage the key elements of BIM implementation, thereby enhancing the sustainability and overall performance of projects and achieving broader environmental and social responsibility goals.
5. Future Research
This research provides a theoretical framework for BIM implementation based on the integration of ESG and SDG, but there are still many areas that can be further explored to enrich and extend the current findings. Future research could explore the following areas in depth:
Impact of regional and cultural differences: future research could examine the applicability and performance of these key factors in different geographical and cultural contexts. Different countries and regions have differences in environmental regulations, social norms, and governance structures, which may affect the effectiveness of BIM implementation. Research can compare these differences and explore how BIM implementation strategies can be optimised in different cultural and policy environments.
Dynamic changes in the time dimension: key factors in BIM implementation may change as technology advances and policies change. Future research could take a longitudinal approach to continuously track the evolution of these factors over time to understand how BIM implementation strategies can be dynamically adapted to new environmental requirements and technological advances.
Conceptual framework development: future research can validate the influence and importance of these factors through qualitative analyses, quantitative analyses, or mixed research methods. A conceptual framework can be proposed by quantifying the contribution of each factor to the success of BIM implementation through questionnaires, case studies and structured interviews to further consolidate the practicality of the theoretical framework.
Impact of emerging technologies: with the development of emerging technologies such as AI, IoT and blockchain, the application scenarios of BIM technology will continue to expand. Future research should focus on how these new technologies can be combined with BIM to further promote the sustainable development of the construction industry, and assess their impact on the existing BIM implementation framework.
Through these extended studies, the BIM implementation framework can be further validated and improved to better adapt to the changing technological and market environments, and provide continuous support for the sustainable development of the construction industry. This will not only enhance the depth of the theory, but also its guiding value in practical application, providing a strong reference for construction practice worldwide.
References
- Environment, U.N. UN Environment Annual Report 2017 | UNEP - UN Environment Programme. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/un-environment-annual-report-2017 (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Open Knowledge Repository. Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/34406/9781464816192.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Ghaffarianhoseini, A.; Tookey, J.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A.; Naismith, N.; Azhar, S.; Efimova, O.; Raahemifar, K. Building Information Modelling (BIM) Uptake: Clear Benefits, Understanding Its Implementation, Risks and Challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 75, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Succar, B. Building Information Modelling Framework: A Research and Delivery Foundation for Industry Stakeholders. Autom. Constr. 2009, 18, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, C.; Others, A. An Outline of the Building Description System. Research Report No. 50; 1974;
- Azhar, S. Building Information Modeling (BIM): Trends, Benefits, Risks, and Challenges for the AEC Industry. Leadersh. Manag. Eng. 2011, 11, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, R.; Stengel, J.; Schultmann, F. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Existing Buildings — Literature Review and Future Needs. Autom. Constr. 2014, 38, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- THE 17 GOALS | Sustainable Development. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/zh/goals (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Sabirali, K.P. Environmental Social Governance (ESG) Practices: A Systematic Literature Review. South Asian J. Soc. Stud. Econ. 2024, 21, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, R.G.; Serafeim, G. A Tale of Two Stories: Sustainability and the Quarterly Earnings Call. J. Appl. Corp. Finance 2013, 25, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friede, G.; Busch, T.; Bassen, A. ESG and Financial Performance: Aggregated Evidence from More than 2000 Empirical Studies. J. Sustain. Finance Invest. 2015, 5, 210–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roukoz, K.; Ersenkal, D. Environmental, Social and Governance-Related Challenges in the Construction Industry (CIC 2023). 2023.
- Markopoulos, E.; Markopoulos, P.; Nandi, A.; Wu, T.; Zhao, K.; Samkova, M.; Huang, M. Using the UN SDGs and the ESG Index Towards the Development of a Unified Building Information Modelling Language and Culture for Sustainable Construction. Sustain. Constr. Era Fourth Ind. Revolut. 2024, 149, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, S.; Moolearambil Sukumaran Nair, M.; Datta, A. Role of Environmental, Social, and Governance in Achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals: A Special Focus on India. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2023, 42, e14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqar, A.; Qureshi, A.H.; Alaloul, W.S. Barriers to Building Information Modeling (BIM) Deployment in Small Construction Projects: Malaysian Construction Industry. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowafy, N.; El Zayat, M.; Marzouk, M. Parametric BIM-Based Life Cycle Assessment Framework for Optimal Sustainable Design. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 75, 106898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, C.; Jin, X.; Zhou, X.; Shi, X. A Performance Data Integrated BIM Framework for Building Life-Cycle Energy Efficiency and Environmental Optimization Design. Autom. Constr. 2021, 127, 103712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarneh, S.T. BIM-Based Information Exchange Framework to Support Facilities Management Systems. PhD Thesis, University of Portsmouth, 2019.
- Madkhali, A.; Sithole, S.T.M. Exploring the Role of Information Technology in Supporting Sustainability Efforts in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepasgozar, S.M.E.; Hui, F.K.P.; Shirowzhan, S.; Foroozanfar, M.; Yang, L.; Aye, L. Lean Practices Using Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Digital Twinning for Sustainable Construction. Sustainability 2021, 13, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Taib, N. Cloud-Based Building Information Modelling (Cloud-BIM): Systematic Literature Review and Bibliometric-Qualitative Analysis. Autom. Constr. 2022, 142, 104468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.; Sheikhkhoshkar, M.; Pour Rahimian, F.; El Haouzi, H.B.; Najafi, M.; Talebi, S. Sustainability and Building Information Modelling: Integration, Research Gaps, and Future Directions. Autom. Constr. 2024, 163, 105420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarneh, S.T.; Danso-Amoako, M.; Al-Bizri, S.; Gaterell, M.; Matarneh, R. Building Information Modeling for Facilities Management: A Literature Review and Future Research Directions. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 24, 100755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibert, C.J. Sustainable Construction: Green Building Design and Delivery; John Wiley & Sons, 2016;
- Jalaei, F.; Jrade, A. Integrating Building Information Modeling (BIM) and LEED System at the Conceptual Design Stage of Sustainable Buildings. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 18, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Succar, B.; Kassem, M. Macro-BIM Adoption: Conceptual Structures. Autom. Constr. 2015, 57, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.L.; Kassem, M. A Unified BIM Adoption Taxonomy: Conceptual Development, Empirical Validation and Application. Autom. Constr. 2018, 96, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alreshidi, E.; Mourshed, M.; Rezgui, Y. Factors for Effective BIM Governance. J. Build. Eng. 2017, 10, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, G.Q.; Xue, X. Critical Review of the Research on the Management of Prefabricated Construction. Habitat Int. 2014, 43, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Meng, X. BIM-Supported Knowledge Management: Potentials and Expectations. J. Manag. Eng. 2021, 37, 04021032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Zuo, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Key Factors for the BIM Adoption by Architects: A China Study. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2015, 22, 732–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sætra, H.S. A Framework for Evaluating and Disclosing the ESG Related Impacts of AI with the SDGs. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.B. Applying BIM to Achieve Sustainability throughout a Building Life Cycle towards a Sustainable BIM Model. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2022, 22, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.W.; Zhou, J. Enhancing Environmental Sustainability over Building Life Cycles through Green BIM: A Review. Autom. Constr. 2015, 57, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, L.B.; Waldmann, D. Development of a BIM-Based Web Tool as a Material and Component Bank for a Sustainable Construction Industry. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, G.; Ribeiro, N.; Pellanda, P.; Reis, M. Implementation Framework for BIM Adoption and Project Management in Public Organizations. J. Civ. Eng. Archit. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, T.C. de; Fabricio, M.M. Framework Proposal for BIM Implementation in Brazilian Construction and Development Companies. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 30, 2101–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlHogail, A. Design and Validation of Information Security Culture Framework. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 49, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, B.S.; Elnamaky, M.; Arafah, M.A.; Alsabaan, M.; Bakry, S.H. A Context Establishment Framework for Cloud Computing Information Security Risk Management Based on the STOPE View. Int J Netw Secur 2019, 21, 166–176. [Google Scholar]
- Saad Saleh, M.; Alrabiah, A.; Haj Bakry, S. A STOPE Model for the Investigation of Compliance with ISO 17799-2005. Inf. Manag. Comput. Secur. 2007, 15, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchenham, B. Procedures for Performing Systematic Reviews. Keele UK Keele Univ. 2004, 33, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Boje, C.; Guerriero, A.; Kubicki, S.; Rezgui, Y. Towards a Semantic Construction Digital Twin: Directions for Future Research. Autom. Constr. 2020, 114, 103179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Zhang, C.; Chan, A.P. Drivers for Green Building: A Review of Empirical Studies. Habitat Int. 2017, 60, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.A.; Anderson, D. The Change Leader’s Roadmap: How to Navigate Your Organization’s Transformation; John Wiley & Sons, 2010;
- Wing_1997_The Ranking of Construction Management Journals.Pdf.
- Ahmad, S.; Sohail, M.; Waris, A.; Elginaid, A.; Abdel-Magid, I.M. SCImago, Eigenfactor Score, and H5 Index Journal Rank Indicator: A Study of Journals in the Area of Construction and Building Technologies. DESIDOC J. Libr. Inf. Technol. 2018, 38, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.; Too, E.; Le, T. Retrospective Look on Front-End Planning in the Construction Industry: A Literature Review of 30 Years of Research. Int. J. Constr. Supply Chain Manag. 2018, 8, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, S.L. Assessing the Perception of Drones in the Construction Industry. B.S. thesis, University of Twente, 2015.
- Love, P.E.D.; Matthews, J.; Simpson, I.; Hill, A.; Olatunji, O.A. A Benefits Realization Management Building Information Modeling Framework for Asset Owners. Autom. Constr. 2014, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, R.; Paavola, S. Beyond the BIM Utopia: Approaches to the Development and Implementation of Building Information Modeling. Autom. Constr. 2014, 43, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linderoth, H.C.J. Understanding Adoption and Use of BIM as the Creation of Actor Networks. Autom. Constr. 2010, 19, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Teizer, J.; Lee, J.-K.; Eastman, C.M.; Venugopal, M. Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Safety: Automatic Safety Checking of Construction Models and Schedules. Autom. Constr. 2013, 29, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, N.; London, K. Understanding and Facilitating BIM Adoption in the AEC Industry. Autom. Constr. 2010, 19, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eadie, R.; Browne, M.; Odeyinka, H.; McKeown, C.; McNiff, S. BIM Implementation throughout the UK Construction Project Lifecycle: An Analysis. Autom. Constr. 2013, 36, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Costa, A.A.; Silvestre, J.D.; Pyl, L. Informetric Analysis and Review of Literature on the Role of BIM in Sustainable Construction. Autom. Constr. 2019, 103, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Solihin, W.; Eastman, C.M. The Mechanism and Challenges of Validating a Building Information Model Regarding Data Exchange Standards. Autom. Constr. 2019, 100, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isikdag, U.; Underwood, J. Two Design Patterns for Facilitating Building Information Model-Based Synchronous Collaboration. Autom. Constr. 2010, 19, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, H.-M. Integration of Building Information Modeling and Project Management in Construction Project Life Cycle. Autom. Constr. 2023, 150, 104832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chang, R.; Li, Y. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Green Buildings: A Critical Review and Future Directions. Autom. Constr. 2017, 83, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Pan, Y.; Luo, X. Integration of BIM and GIS in Sustainable Built Environment: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Autom. Constr. 2019, 103, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.-J.; Ren, Z.-J.; Lu, H.; Wu, J.-F. The Progress and Trend of BIM Research: A Bibliometrics-Based Visualization Analysis. Autom. Constr. 2021, 124, 103558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Joo, M. Building Information Modelling (BIM) Framework for Practical Implementation. Autom. Constr. 2011, 20, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porwal, A.; Hewage, K.N. Building Information Modeling (BIM) Partnering Framework for Public Construction Projects. Autom. Constr. 2013, 31, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawab, M.; Kineber, A.F.; Chileshe, N.; Abanda, H.; Ali, A.H.; Almukhtar, A. Building Information Modelling Implementation Model for Sustainable Building Projects in Developing Countries: A PLS-SEM Approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.D.; Tayeh, B.A.; Hakeem, I.Y.; Abu Aisheh, Y.I. Benefits and Barriers of Implementing Building Information Modeling Techniques for Sustainable Practices in the Construction Industry—A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirdöğen, G.; Diren, N.S.; Aladağ, H.; Işık, Z. Lean Based Maturity Framework Integrating Value, BIM and Big Data Analytics: Evidence from AEC Industry. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cidik, M.S.; Boyd, D.; Thurairajah, N.; Hill, S. BIM and Conceptual Design Sustainability Analysis: An Information Categorization Framework. 2014.
- Xie, M.; Qiu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G. Policies, Applications, Barriers and Future Trends of Building Information Modeling Technology for Building Sustainability and Informatization in China. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 7107–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouguerra, K.; Yaik-Wah, L.; Ali, K.N. A Preliminary Implementation Framework of Building Information Modelling (BIM) in the Algerian AEC Industry. Int. J. Built Environ. Sustain. 2020, 7, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoli, C.; Iannantuono, M.; Giannakopoulos, V.; Fotopoulou, A.; Ferrante, A.; Garagnani, S. Building Information Modeling as an Effective Process for the Sustainable Re-Shaping of the Built Environment. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pero, M.; Moretto, A.; Bottani, E.; Bigliardi, B. Environmental Collaboration for Sustainability in the Construction Industry: An Exploratory Study in Italy. Sustainability 2017, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famakin, I.O.; Othman, I.; Kineber, A.F.; Oke, A.E.; Olanrewaju, O.I.; Hamed, M.M.; Olayemi, T.M. Building Information Modeling Execution Drivers for Sustainable Building Developments. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khahro, S.H.; Kumar, D.; Siddiqui, F.H.; Ali, T.H.; Raza, M.S.; Khoso, A.R. Optimizing Energy Use, Cost and Carbon Emission through Building Information Modelling and a Sustainability Approach: A Case-Study of a Hospital Building. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bynum, P.; Issa, R.R.A.; Olbina, S. Building Information Modeling in Support of Sustainable Design and Construction. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2013, 139, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Mayo, G.; McCuen, T.L.; Issa, R.R.A.; Smith, D.K. Building Information Modeling Body of Knowledge. I: Background, Framework, and Initial Development. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2018, 144, 04018065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Pishdad-Bozorgi, P. State-of-the-Art Review of Blockchain-Enabled Construction Supply Chain. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2022, 148, 03121008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; He, Q.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G. Peer Effects on Corporate Social Responsibility Engagement of Chinese Construction Firms through Board Interlocking Ties. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2024, 150, 04024064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Fenn, P.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L. Adopting BIM to Facilitate Dispute Management in the Construction Industry: A Conceptual Framework Development. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2023, 149, 03122010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chan, A.P.C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xiong, F. Critical Strategies for Enhancing BIM Implementation in AEC Projects: Perspectives from Chinese Practitioners. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2020, 146, 05019019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, B.A.F.S.; Sotelino, E.D. Constructability and Sustainability Studies in Conceptual Projects: A BIM-Based Approach. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2023, 149, 04023012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, A.; Batra, S. Navigating the Ethical Discourse in Construction: A State-of-the-Art Review of Relevant Literature. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2024, 150, 03124001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, T.F.L.; de Carvalho, M.M.; Vieira, D.R. BIM Critical-Success Factors in the Design Phase and Risk Management: Exploring Knowledge and Maturity Mediating Effect. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2022, 148, 04022104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, R.F.; Mourgues, C.; Alarcón, L.F.; Pellicer, E. Analyzing the Association between Lean Design Management Practices and BIM Uses in the Design of Construction Projects. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2021, 147, 04021010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavallaei, R.; Mashayekhi, A.; Harrison, N.; Talebian, M.; Moser, R. BIM Adoption: A Case of Institutional Pressures and Top Management Support. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2022, 148, 04022084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.WY.; Zhou, Y.; Illankoon, C.; Le, K.N. A Critical Review on BIM and LCA Integration Using the ISO 14040 Framework. Build. Environ. 2022, 213, 108865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Bulle, C.; Lesage, P. Integrating Building Information Modeling and Life Cycle Assessment in the Early and Detailed Building Design Stages. Build. Environ. 2019, 153, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, M.; Figueiredo, K.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Haddad, A. Integrated Optimization with Building Information Modeling and Life Cycle Assessment for Generating Energy Efficient Buildings. Appl. Energy 2019, 250, 1366–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yu, J.; Jeong, D. BIM Acceptance Model in Construction Organizations. J. Manag. Eng. 2015, 31, 04014048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lu, W.; Papadonikolaki, E. Human-Organization-Technology Fit Model for BIM Adoption in Construction Project Organizations: Impact Factor Analysis Using SNA and Comparative Case Study. J. Manag. Eng. 2022, 38, 04022004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soust-Verdaguer, B.; Bernardino Galeana, I.; Llatas, C.; Montes, M.V.; Hoxha, E.; Passer, A. How to Conduct Consistent Environmental, Economic, and Social Assessment during the Building Design Process. A BIM-Based Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment Method. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawumi, T.O.; Chan, D.W.M.; Wong, J.K.W.; Chan, A.P.C. Barriers to the Integration of BIM and Sustainability Practices in Construction Projects: A Delphi Survey of International Experts. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 20, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansah, M.K.; Chen, X.; Yang, H.; Lu, L.; Lam, P.T.I. Developing an Automated BIM-Based Life Cycle Assessment Approach for Modularly Designed High-Rise Buildings. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 90, 106618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Li, X.; Ke, Y.; Xu, W.; Xu, Z.; Skibniewski, M.J. Developing a Building Information Modeling–Based Performance Management System for Public–Private Partnerships. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2020, 27, 1727–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villena-Manzanares, F.; García-Segura, T.; Pellicer, E. Organizational Factors That Drive to BIM Effectiveness: Technological Learning, Collaborative Culture, and Senior Management Support. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, B.; Othman, I.; Gardezi, S.S.S.; Altan, H.; Abdalla, S.B. BIM-Based Research Framework for Sustainable Building Projects: A Strategy for Mitigating BIM Implementation Barriers. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.; Kim, J.-W.; Ju, K.-B.; An, Y.-K. Infrastructure BIM Platform for Lifecycle Management. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kineber, A.F.; Othman, I.; Famakin, I.O.; Oke, A.E.; Hamed, M.M.; Olayemi, T.M. Challenges to the Implementation of Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Sustainable Construction Projects. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.P.; Bragança, L.; Mateus, R. A Systematic Review of the Role of BIM in Building Sustainability Assessment Methods. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, B.; Othman, I.; Kang, J.M.; Geem, Z.W. Influence of Building Information Modeling (BIM) Implementation in High-Rise Buildings towards Sustainability. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghalzadeh Shishehgarkhaneh, M.; Keivani, A.; Moehler, R.C.; Jelodari, N.; Roshdi Laleh, S. Internet of Things (IoT), Building Information Modeling (BIM), and Digital Twin (DT) in Construction Industry: A Review, Bibliometric, and Network Analysis. Buildings 2022, 12, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargnoli, M.; Lombardi, M. Building Information Modelling (BIM) to Enhance Occupational Safety in Construction Activities: Research Trends Emerging from One Decade of Studies. Buildings 2020, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Osmani, M. Integration of Smart Cities and Building Information Modeling (BIM) for a Sustainability Oriented Business Model to Address Sustainable Development Goals. Buildings 2024, 14, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuMoeilak, L.; AlQuraidi, A.; AlZarooni, A.; Beheiry, S. Critical Success Factors for Building Information Modeling Implementation as a Sustainable Construction Practice in the UAE. Buildings 2023, 13, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Kumar, V.R.P. Analyzing the Barriers for Blockchain-Enabled BIM Adoption in Facility Management Using Best-Worst Method Approach. Built Environ. Proj. Asset Manag. 2024, 14, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawumi, T.O.; Chan, D.W.M. A Scientometric Review of Global Research on Sustainability and Sustainable Development. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.S.; Lau, H.; Nakandala, D.; Fan, Y.; Hurriyet, H. Adoption of Green Supply Chain Management Practices through Collaboration Approach in Developing Countries – From Literature Review to Conceptual Framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Kueh, T.-B.; Hou, L.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H. A Bibliometric Analysis of Corporate Social Responsibility in Sustainable Development. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Lei, J.; Ren, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, S.; Lin, Y. Contribution and Obstacle Analysis of Applying BIM in Promoting Green Buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomponi, F.; Moncaster, A. Circular Economy for the Built Environment: A Research Framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagnino, A.; Montanaro, T.; Lazoi, M.; Sergi, I.; Corallo, A.; Patrono, L. Building Information Modeling and Internet of Things Integration for Smart and Sustainable Environments: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Chen, K.; Xue, F.; Lu, W. Barriers to Building Information Modeling (BIM) Implementation in China’s Prefabricated Construction: An Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Wang, B.; Gao, Q. Environment, Social and Governance Research of Infrastructure Investment: A Literature Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 139030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Shen, M.; Peh, L.C. Transition from Building Information Modeling (BIM) to Integrated Digital Delivery (IDD) in Sustainable Building Management: A Knowledge Discovery Approach Based Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.-Y.; Lee, C.-Y.; Wang, X. A Mixed Review of the Adoption of Building Information Modelling (BIM) for Sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 4114–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.F.; Esmanioto, F.; Huber, N.; Loures, E.R.; Canciglieri, O. A Systematic Literature Review of Interoperability in the Green Building Information Modeling Lifecycle. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalis, T.A.; Malamateniou, K.E.; Koulouriotis, D.; Nikolaou, I.E. New Challenges for Corporate Sustainability Reporting: United Nations’ 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020, 27, 1617–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mohammad, M.S.; Haron, A.T.; Esa, M.; Aloko, M.N.; Alhammadi, Y.; Anandh, K.S.; Rahman, R.A. Factors Affecting BIM Implementation: Evidence from Countries with Different Income Levels. Constr. Innov. 2023, 23, 683–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, A.B.; Chan, D.W.M. Profound Barriers to Building Information Modelling (BIM) Adoption in Construction Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs). Constr. Innov. 2020, 20, 261–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylili, A.; Georgali, P.-Z.; Christou, P.; Fokaides, P. An Integrated Building Information Modeling (BIM)-Based Lifecycle-Oriented Framework for Sustainable Building Design. Constr. Innov. 2024, 24, 492–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadou, M.C. An Overview of Benefits and Challenges of Building Information Modelling (BIM) Adoption in UK Residential Projects. Constr. Innov. 2019, 19, 298–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Sormunen, P. Integrating Lean Construction with BIM and Sustainability: A Comparative Study of Challenges, Enablers, Techniques, and Benefits. Constr. Innov. 2024, 24, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olugboyega, O.; Windapo, A.O. Structural Equation Model of the Barriers to Preliminary and Sustained BIM Adoption in a Developing Country. Constr. Innov. 2022, 22, 849–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, J.A.; Arefin, S.; Ahmmed, M.I. Uncovering the Research Tapestry: Bibliometric Insights into BIM and LCA – Exploring Trends, Collaborations and Future Directions. Constr. Innov. 2024, ahead-of-print. [CrossRef]
- Alankarage, S.; Chileshe, N.; Rameezdeen, R.; Edwards, D.J.; Samaraweera, A. Exploring BIM-Triggered Organisational and Professional Culture Change: A Systematic Literature Review. Constr. Innov. 2023, 23, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawumi, T.O.; Chan, D.W.M. An Empirical Survey of the Perceived Benefits of Executing BIM and Sustainability Practices in the Built Environment. Constr. Innov. 2019, 19, 321–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, R.J.; Irfan, M.; Alam, C.N.; Azis, M.A. Level of Readiness of Users of Integrated Information Systems at UIN Sunan Gunung Djati Bandung Using Framework Strategy, Technology, Organization, People, Environment (STOPE). IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1098, 032112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Moolearambil Sukumaran Nair, M.; Datta, A. Role of Environmental, Social, and Governance in Achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals: A Special Focus on India. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2023, 42, e14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C.; Wang, R.; Zhang, B. An Empirical Analysis of Barriers to Building Information Modelling (BIM) Implementation in Construction Projects: Evidence from the Chinese Context. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2022, 22, 3119–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshfetrat, R.; Sarvari, H.; Chan, D.W.M.; Rakhshanifar, M. Critical Risk Factors for Implementing Building Information Modelling (BIM): A Delphi-Based Survey. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2022, 22, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Teo, E.A.L. Managing Critical Drivers for Building Information Modelling Implementation in the Singapore Construction Industry: An Organizational Change Perspective. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2019, 19, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barqawi, M.; Chong, H.-Y.; Lopez, R. Effects of Critical Success Factors, BIM Implementation Strategies, and Barriers on Employer-Initiated Delays. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2023, 23, 2788–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Azhar, S.; Nadeem, A.; Khalfan, M. Using Building Information Modelling to Achieve Lean Principles by Improving Efficiency of Work Teams. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2018, 18, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolo’, G.; Zampone, G.; De Iorio, S.; Sannino, G. Does SDG Disclosure Reflect Corporate Underlying Sustainability Performance? Evidence from UN Global Compact Participants. J. Int. Financ. Manag. Account. 2024, 35, 214–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Global Compact Strategy 2021–2023 | UN Global Compact. Available online: https://unglobalcompact.org/library/5869 (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Berenberg, J. Understanding the SDGs in Sustainable Investing. Joh Berenberg Gossler Co KG N Dec. 2018, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sacks, R.; Eastman, C.; Lee, G.; Teicholz, P. BIM Handbook: A Guide to Building Information Modeling for Owners, Designers, Engineers, Contractors, and Facility Managers; John Wiley & Sons, 2018.
- Kirby, A. Exploratory Bibliometrics: Using VOSviewer as a Preliminary Research Tool. Publications 2023, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).