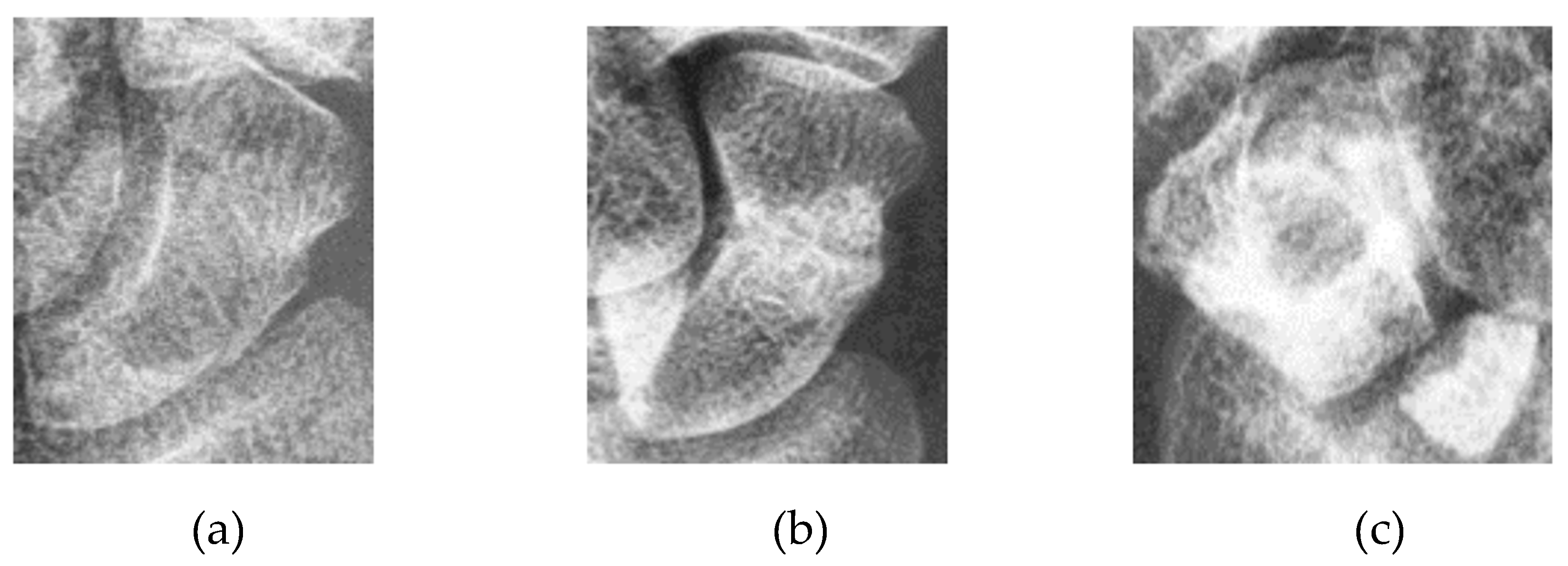
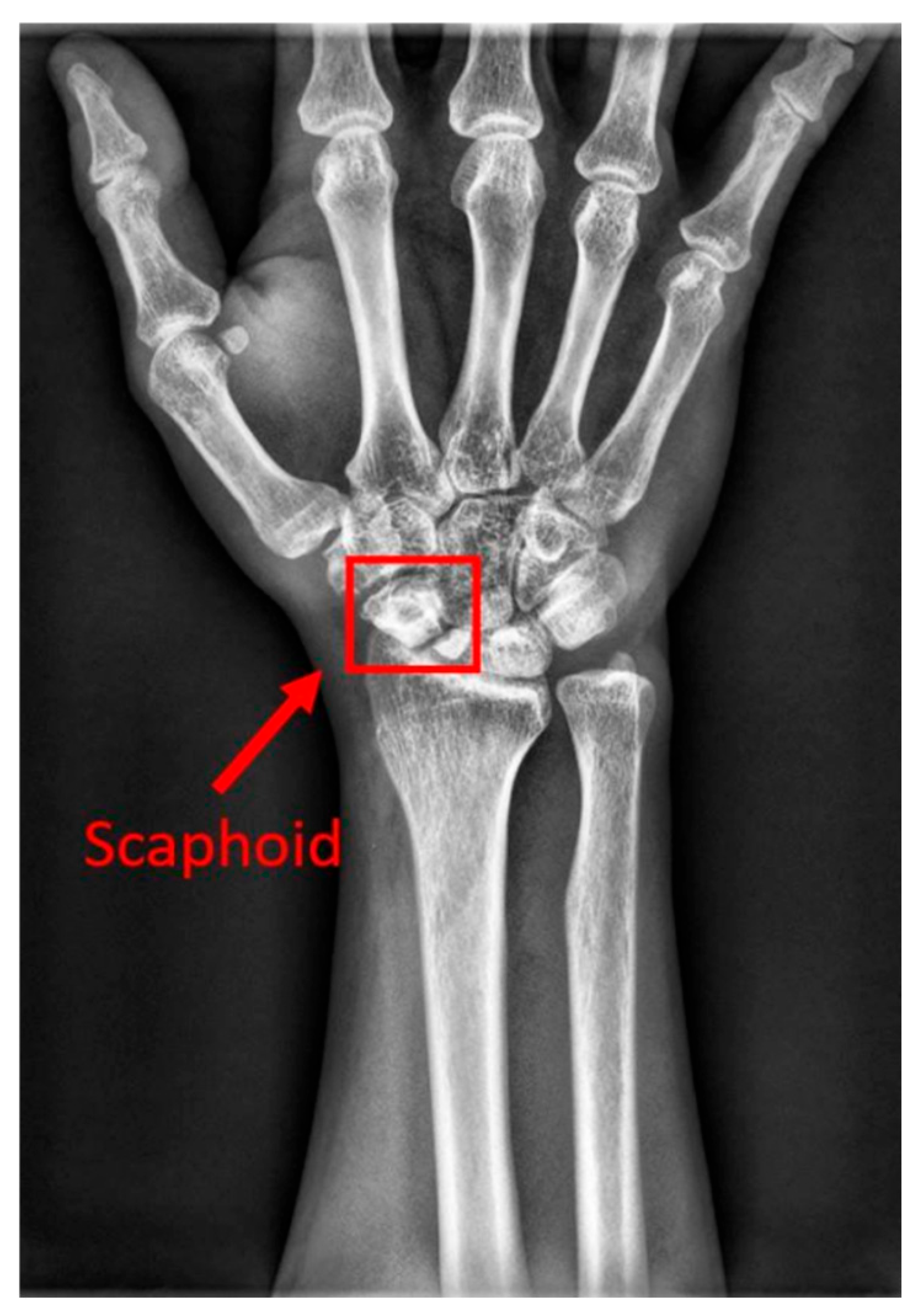
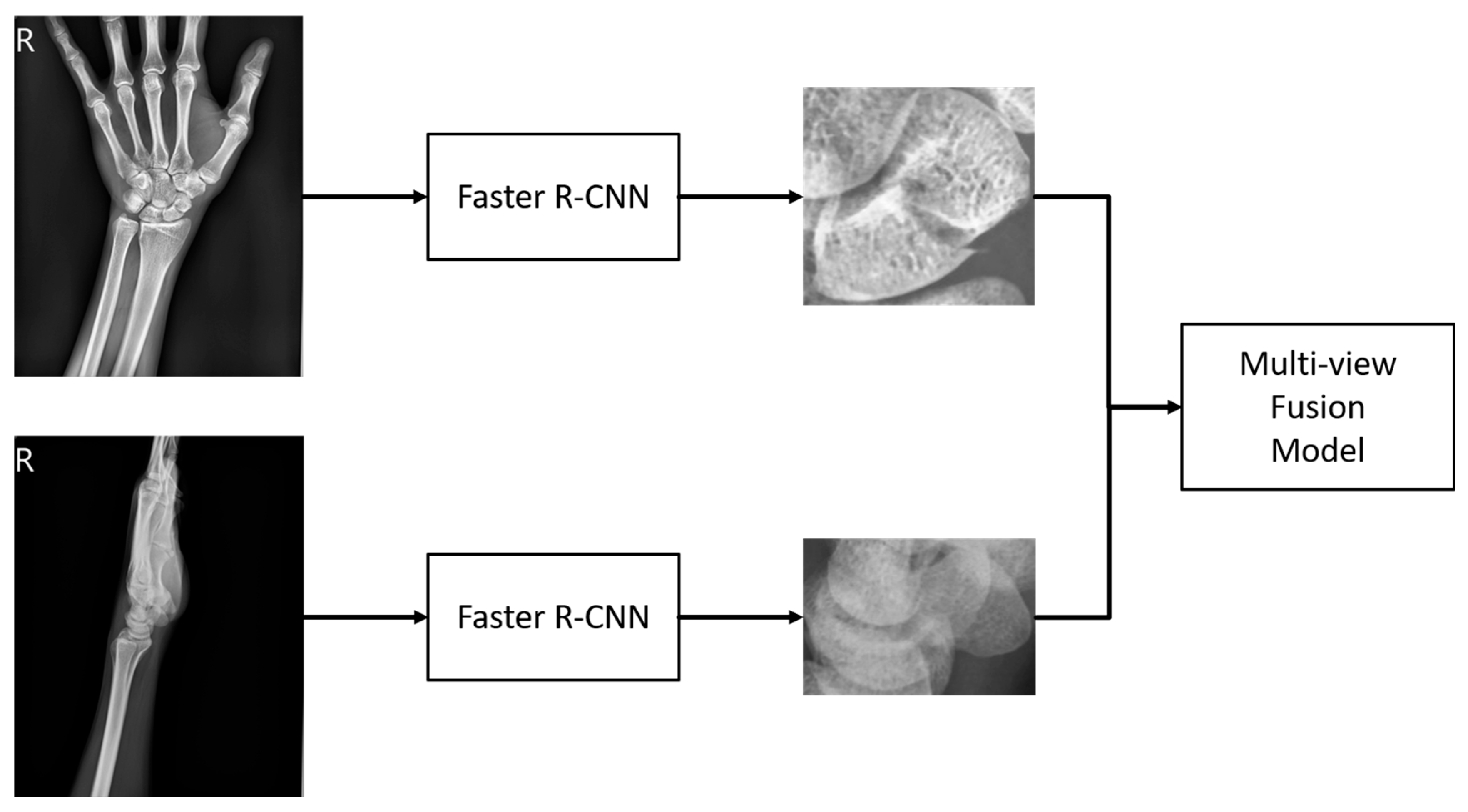
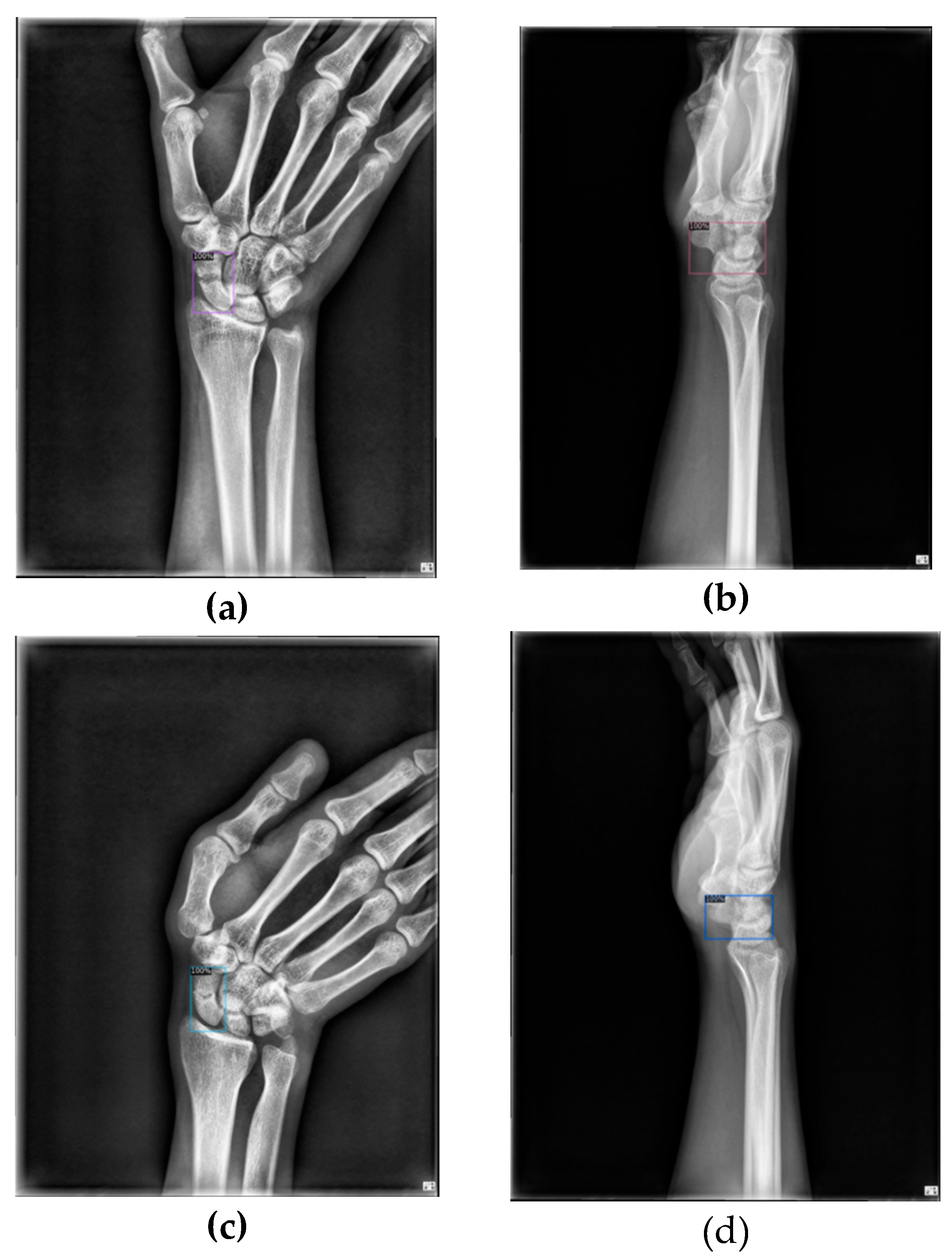
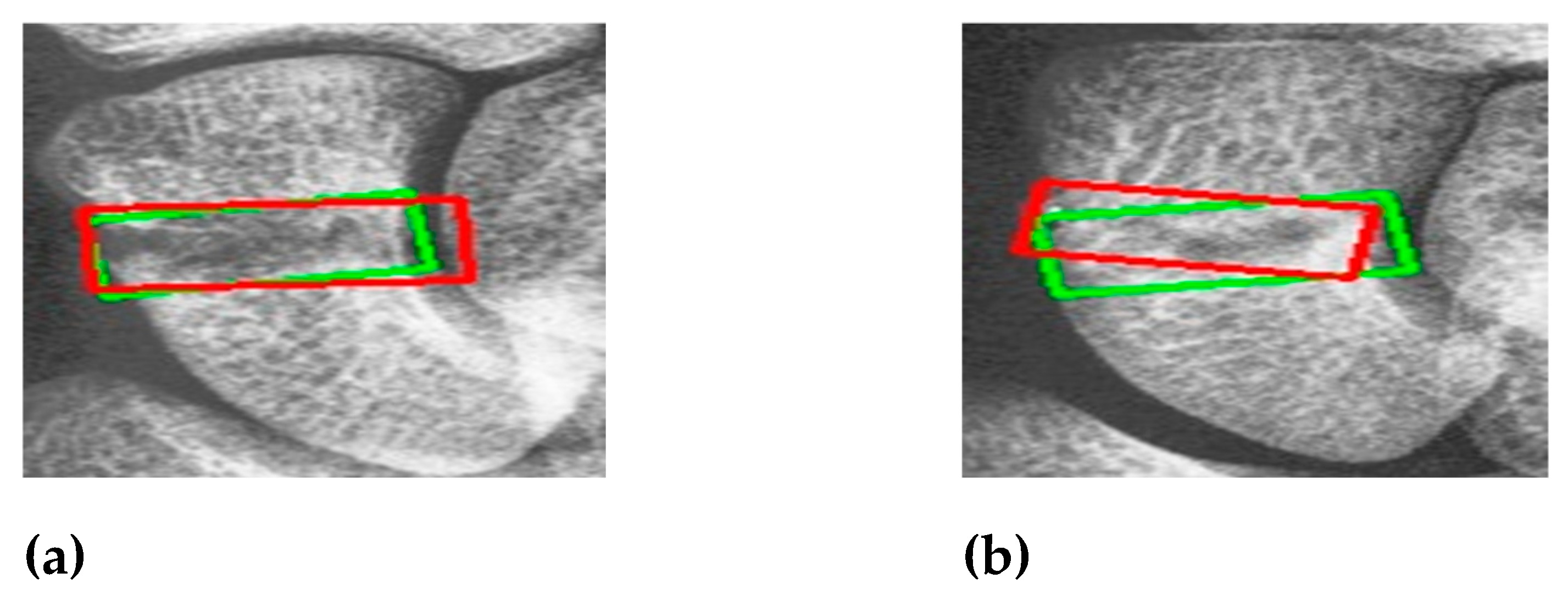
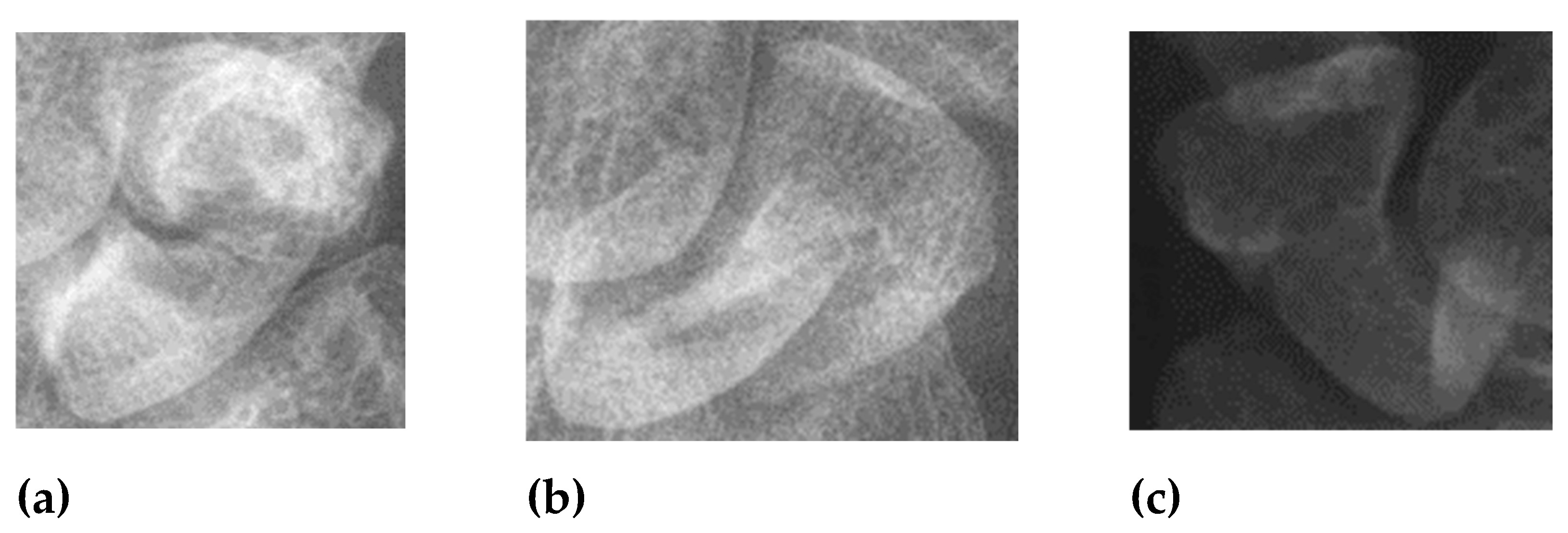
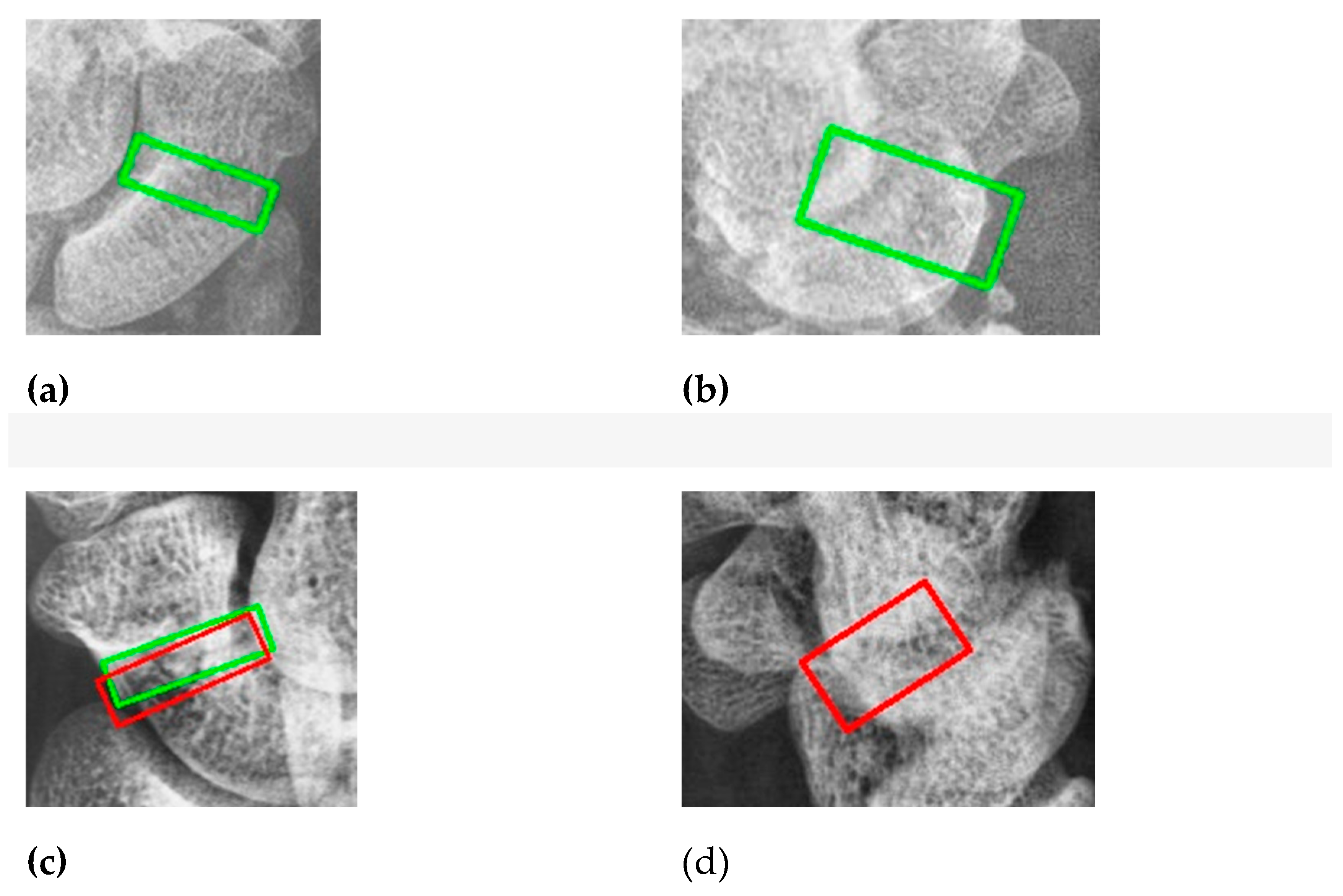
The main objective of this article is to locate the scaphoid bone in X-ray images and assist doctors in determining whether it is fractured, as well as in identifying the fracture area. Displaced fractures are typically easy to detect in X-ray images, allowing doctors to quickly diagnose them. In contrast, non-displaced and occult fractures are more challenging to identify due to X-ray projection shadowing and variations in bone density among patients. Additionally, discrepancies in interpretation between radiologists and orthopedic surgeons are common. For fractures not visible in the anterior-posterior view, doctors must examine the scaphoid bone for discontinuities, making the diagnosis time-consuming and demanding a thorough understanding of the scaphoid.
2.2.1. Scaphoid Bone Area Detection
As mentioned earlier, the first stage aims to extract the scaphoid bone from the entire wrist X-ray image. For this purpose, we use the Faster R-CNN model combined with a Feature Pyramid Network (FPN). Faster R-CNN is a renowned two-stage detector that incorporates a Region Proposal Network (RPN), which enhances the speed of the detector by replacing the traditional algorithmic approach used in the initial stage. The Feature Pyramid Network improves the utilization of feature maps at various scales, addressing the issue that deeper networks might lose small objects.
In our research, if the first stage fails to accurately locate the scaphoid bone, subsequent fracture detection cannot proceed effectively. Therefore, we employ the two-stage Faster R-CNN model with FPN at this stage, despite its slightly slower processing time, due to its improved accuracy. Unlike the original Faster R-CNN model, which uses a single-level feature map to generate candidate boxes, the FPN integrates feature maps from multiple levels. This approach helps retain small objects that might otherwise be lost during pooling, thereby enhancing detection performance for small and medium-sized objects.
Considering that a typical wrist X-ray image measures approximately 2000 × 1600 pixels and the scaphoid bone region is around 150 × 150 pixels, the scaphoid falls into the category of small and medium-sized objects. To address this, we use the Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) which upsamples and enlarges deep features to match the size of previous layers, then integrates them using a convolutional layer. Specifically, after incorporating the FPN, a 1×1 convolutional layer adjusts the channel number to 256, and deep features are upsampled and combined with the previous layer’s features. A final 3×3 convolutional layer refines the feature map. This multi-layer approach, with varied anchor box sizes and aspect ratios, enhances overall detection performance.
Additionally, the Faster R-CNN model in this study uses RoI Align to generate feature maps of consistent dimensions for different proposals. RoI Align addresses the limitations of RoI Pooling by avoiding rounding issues associated with dividing regions into smaller blocks. Instead, RoI Align performs bilinear interpolation on these blocks, yielding more accurate feature maps and improving detection results.
To handle multiple bounding boxes that may overlap, Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) is applied to retain the most accurate boxes. NMS starts by selecting the bounding box with the highest score and storing the remaining boxes in an output list. It then calculates the Intersection over Union (IoU) between the selected box and the remaining boxes. If the IoU exceeds a predefined threshold, the overlapping box is removed from the list. This process repeats until only the boxes with the highest scores remain, effectively representing the detected objects.
2.2.2. Fracture Classification and Detection
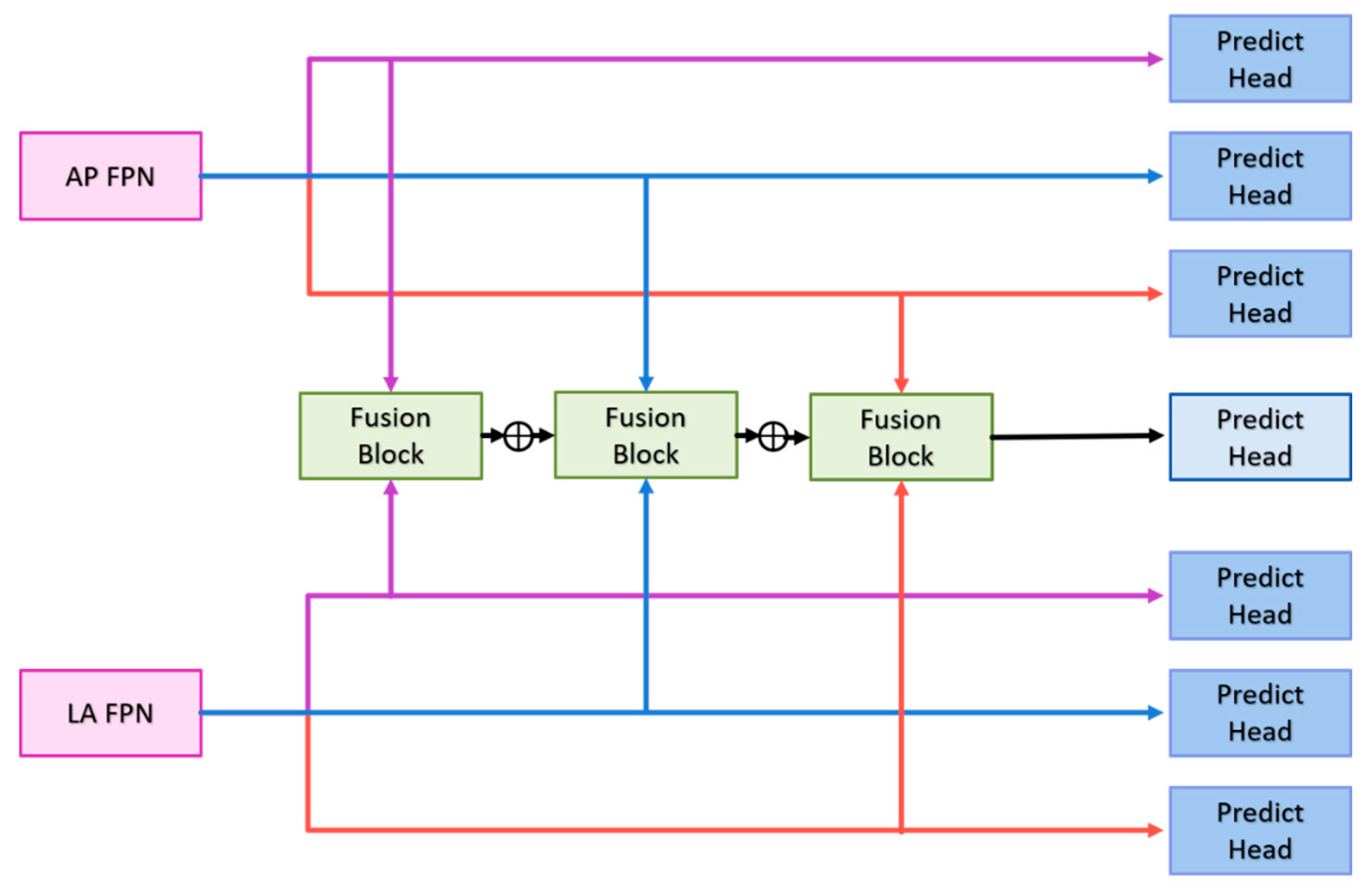
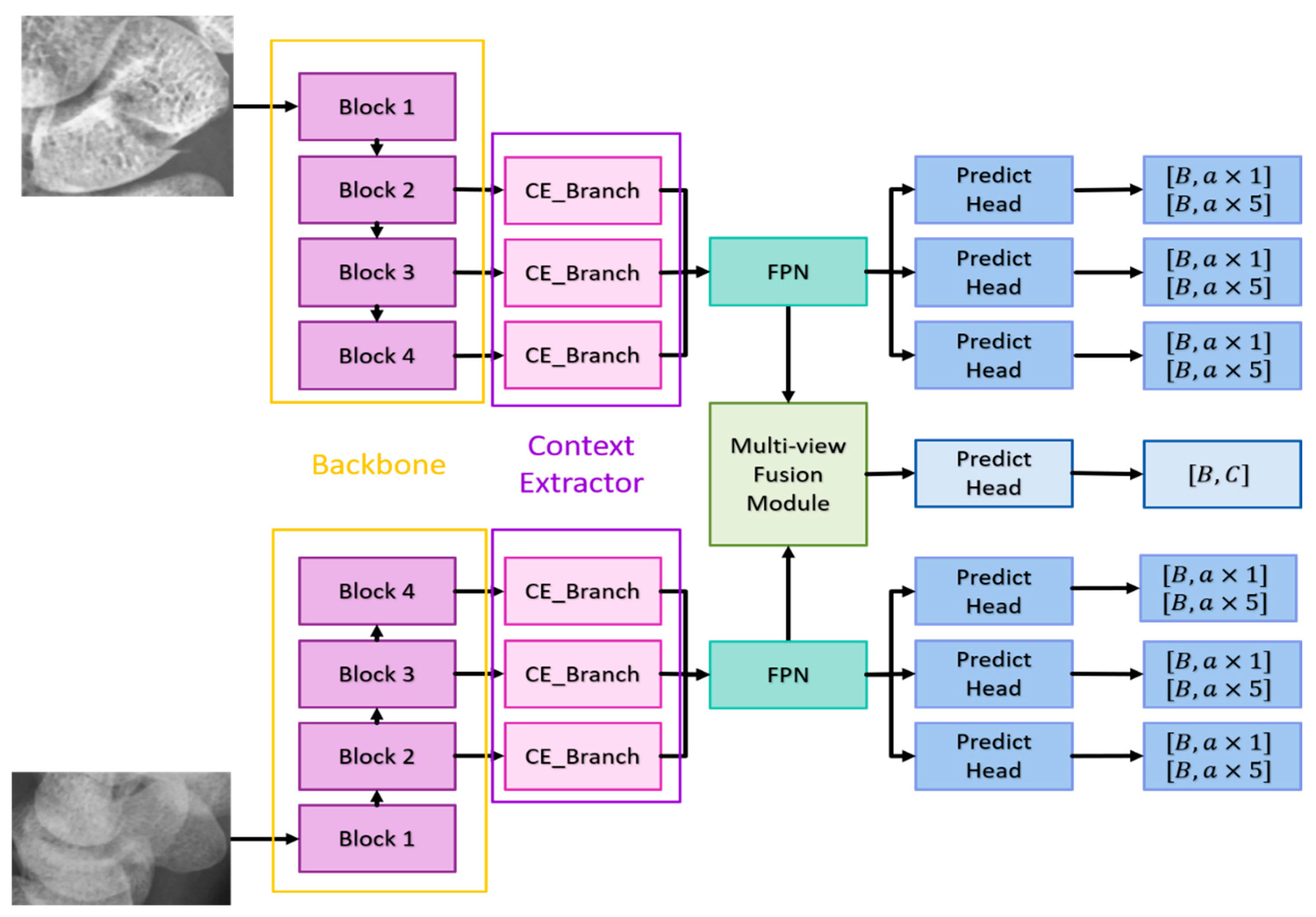
The following sections will detail the multi-view fusion model proposed in this article. Multi-view image techniques have shown promise in enhancing classification capabilities, particularly in clinical settings where accurately locating fractures is crucial. Effective fusion of multi-view data is essential to improving fracture detection beyond what can be achieved with 2D projection images alone. The model presented consists of four key components: the backbone network, the context extractor, the Feature Pyramid Network (FPN), and the multi-view fusion module, as illustrated in
Figure 4.
Backbone Network: The anterior-posterior (AP) and lateral (LA) views are first processed through the backbone network to extract features. The backbone network must have a sufficiently large receptive field to capture meaningful features. Deeper networks like ResNet, which use residual connections to mitigate issues like gradient vanishing, are ideal. ResNet-152 was found to be the most effective in our experiments among ResNet-50, ResNet-101, and ResNet-152. It provides deep, high-quality features, with the last three blocks of ResNet-152 feeding into the context extractors.
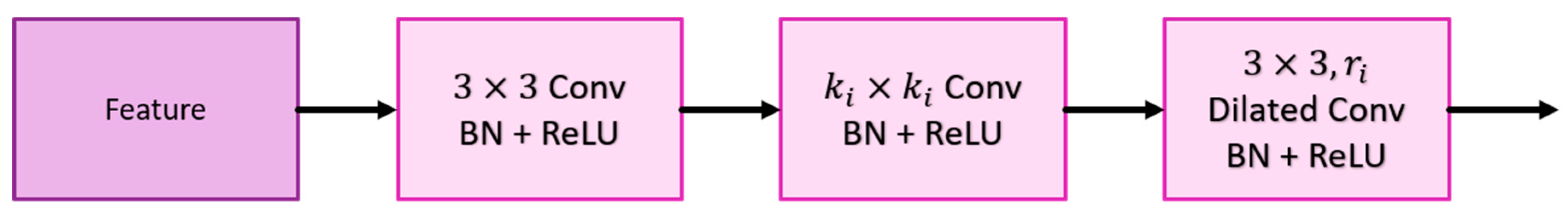
Context Extractor: To address the challenge of detecting occult or non-displaced fractures, which can be camouflaged due to lighting or bone density variations, the context extractor expands the receptive field without pooling, using dilated convolutions. This approach, as demonstrated by Mei et al. [34], helps in extracting rich semantic features across a broader context. The context extractor is designed with four branches (as shown in
Figure 5):
Each context extractor contains four context extraction branches, as shown in
Figure 5. First, the
convolution compresses the number of channels to
of the original and then uses the
convolution and the
dilated convolution with a dilation rate of
to extract context-aware features; where
represents the context extraction branch of
. Each convolutional layer is followed by a set of batch normalization layers and a ReLU. The output of
is added with the output of
to stack the different ranges of receptive fields together. Finally, the outputs of the four context extraction branches are concatenated together and use
convolution to integrate all features. Such a design enables the context extractor to obtain a wide range of rich perceptual features, enabling the model to have contextual reasoning capabilities and to see finer differences in feature maps.
Feature Pyramid Network (FPN): The FPN enhances the feature maps extracted from different scales by combining deep and shallow features, improving detection of small and medium-sized objects like the scaphoid bone.
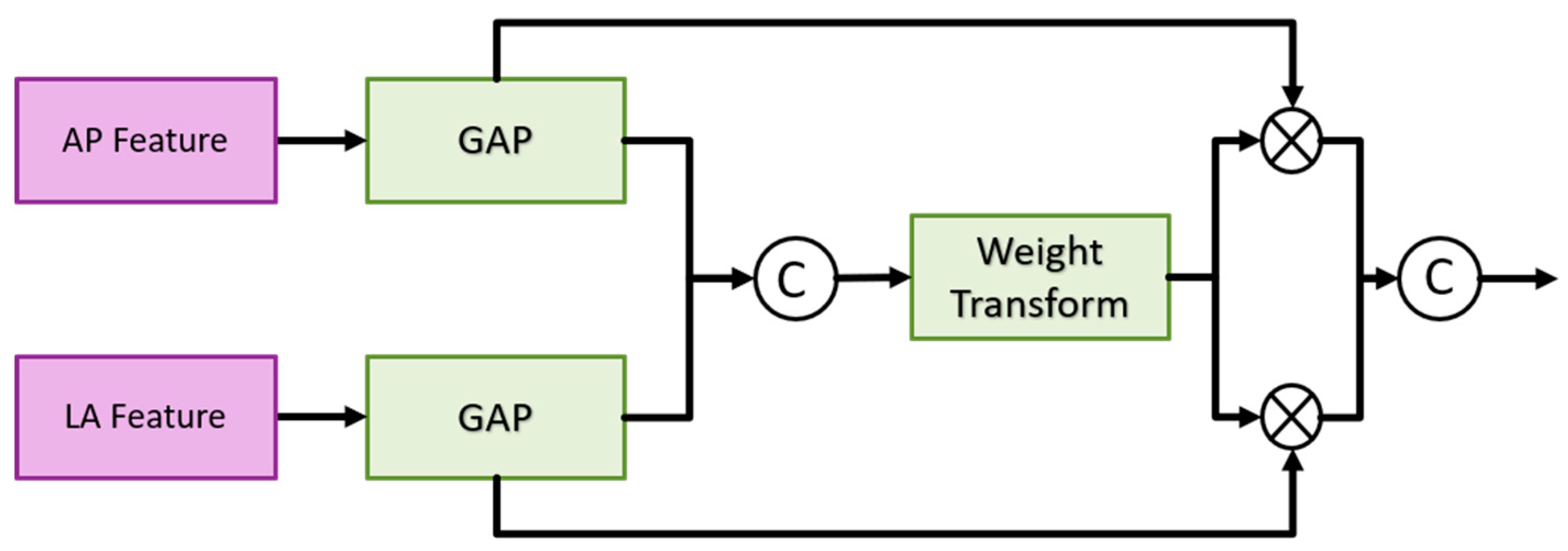
Multi-View Fusion Module: After feature extraction and context enhancement, the FPN outputs from the AP and LA views are fed into the multi-view fusion module. This module integrates features from both views to enhance fracture classification and detection accuracy. The multi-view fusion module uses the FPN features from the AP views and LA views for fusion, and the feature maps of the corresponding layers are input into the fusion block, as shown in
Figure 6. The fusion block first performs global average pooling on the feature maps of the two views and outputs [B, C, 1, 1] to flatten the feature maps and concatenate them. Then the weight transform designed calculates the common important information of the two views, and then multiply this weight back to the respective views. Finally, the features of the two views are concatenated together for the final classification. The goal is to find as much of the fractured scaphoid region as possible, we add the output of
to the output of
, where
represents the
ith fusion block. First use the global average pooling layer to flatten and concatenate the corresponding feature pyramid layers of two different views, then use the weight transform layer to calculate the common information of different views, and finally multiply the weights back to the features of different views and concatenate them.
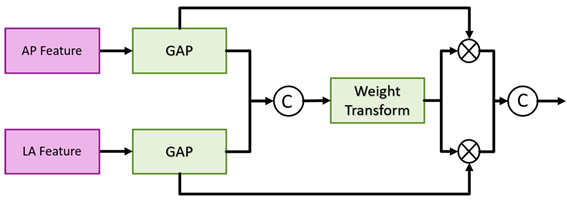
Figure 6.
Multi-view fusion module architecture.
Figure 6.
Multi-view fusion module architecture.
Algorithm:
1) Feature Extraction: Both AP and LA views are processed through the backbone network to extract initial features.
2) Contextual Information: The context extractor refines these features by expanding the receptive field and integrating contextual information.
3) Feature Fusion: The FPN combines features from multiple scales to improve detection performance.
4) Final Classification and Detection: The multi-view fusion module combines features from both views to classify fractures and re-evaluate detection boxes for precise localization.
The model aims to improve the accuracy of fracture detection, particularly for occult and non-displaced fractures, by leveraging comprehensive multi-view information and advanced feature extraction techniques.
Most of the detection methods, regardless of one-stage or two-stage methods, only use a single scale for prediction. However. in order to extract better features, the depth of the model is often very deep that the loss of information on small objects. FPN can well combine the deep and shallow information, so that the feature map of each scale can be better used, and greatly improve the detection results of small objects. The ground-truth of the fractures in this article also belong to small objects, so a FPN is added after the context extractor. The structure here is the same as Faster R-CNN. First, the convolution layer is used to adjust the number of channels of the input feature map to , and then the feature map is upsampled and added with feature maps, and finally the information is integrated through a convolution.
Figure 7.
Fusion block architecture in the multi-view fusion module.
Figure 7.
Fusion block architecture in the multi-view fusion module.
Weight transform is mainly used to combine information from AP views and LA views. It is too rough to classify the features directly after merging as mentioned above. In general, the importance of the AP view is higher than that of the LA view. Therefore, classification after direct concatenation may cause all the weights to be pulled away by the AP views and results in the loss of the features of the LA views. Therefore, we design a weight transform, which combines the features of the AP views and the LA views, calculates the common important information of the two views, and then multiplies them back to their respective views. In this way, the information of the LA views is preserved and avoided its weight being completely discarded. Equations (1) and (2) show the module construction by different feature map AP
i and LP
i of scale
i.
where
represents the number of layers of the feature pyramid;
represents the fully connection layer;
represents the concatenation, and the number of channels output by the two fully connected layers is
of the number of input channels.
The architecture of the detection branch in the second stage is a fully convolutional network. The classification of the detection branch and the prediction head of the detection is the same that consists of
convolutional layers, batch normalization layer, ReLU, and
convolutional layers. The number of output channels of the classification branch is
, and the number of channels of the detection branch is
.
and
represent the number of anchor boxes and categories, respectively, and
represents
, representing the center point coordinates, width, high, and angle of the prediction box [
22]. Each layer of the FPN has its prediction head, and finally, the results of each layer are merged to unify match with ground-truth and calculate the loss. The multi-view fusion classification branch consists of a fully connected layer, ReLU and a fully connected layer. The first fully connection layer input the refined features by the multi-view fusion module, and the output channel is half of the number of inputs. The output of the second fully connection layer is 2, indicating the probability of fracture and non-fracture.
To pass information to fracture detection in two different views through this classification branch, the classification results are re-scored the prediction boxes in the final prediction stage. In the most perfect case, both the classification score and the predicted box score will be close to 1, so when both branch predictions are at their highest, the sum is 2 and the smallest is 0. We take 0.5 as the threshold of the classification branch to keep the classification score greater than or equal to the threshold and set the classification score to 0 if it is smaller than the threshold. The purpose of this is to give priority to the classification results. Because the classification branch is directly using the multi-view feature, it can better distinguish whether the scaphoid is fractured or not. The formula of rescore is shown as Equation (3).
The model in the second stage consists of three parts, namely the detector for AP views, the detector for LA views, and the classifier for multi-view fusion. The following will describe their loss functions respectively. The detector part is similar to Faster R-CNN, but regression an additional angle. First encode the ground truth box
and prediction box
as
and
, anchor box is expressed as
.
and
are defined as Equations (4) and (5):
And use the
loss to regress the positive samples, the
loss is defined in Equation (6):
The classification prediction head of the detection branch uses the Binary Cross Entropy loss as Equations (7) and (8):
Since the number of negative samples is much larger than that of positive samples, we divide the number of positive samples rather than the total number of samples to take the average, which can avoid the classifier from being affected by too many negative samples and can better solve the problem of sample imbalance. problems to improve the effectiveness of training.
represents the number of total samples, and
represents the number of positive samples. The loss function of multi-view fusion classification is the same as that of Faster R-CNN, and both use the Cross Entropy loss. The total loss is defined as Equation (9):