1. Introduction
Stroke is the most common cerebrovascular disease leading to sudden neurological dysfunction caused by a disturbance in the cerebral blood flow due to cerebral ischaemia or haemorrhage.
An early and accurate stroke diagnosis is extremely important to reach a good outcome and improve functional recovery. However, early stroke diagnosis can be challenging as it is dependent on specialist clinical examination together with expensive and time-consuming neuroimaging techniques.
The use of specific circulatory biomarkers related to stroke-associated brain injuries could significantly improve the diagnosis and treatment of stroke patients and post-stroke outcomes and complement the neuroimaging modalities for the diagnosis of stroke [
1]. The circulatory biomarkers could be significant in patients with transient neurological symptoms or those who cannot be easily diagnosed by imaging. Moreover, the blood biomarker assessment could be performed during an initial triage, avoiding delays in transporting stroke patients to appropriate care centres with imaging facilities allowing rapid and proper treatments for high-risk patients [
1].
Stroke leads to neurons, astrocytes, and the blood-brain barrier (BBB) alterations that are reflected through proteins released into the blood [
2]. Recently, different blood-based biomarkers have been investigated in human stroke [
1,
3,
4].
NSE, a neuron-specific biomarker found mainly in the neuronal cytoplasm [
5], has been used in multiple studies to investigate its role in stroke [
6]. Neuronal damage assessed by Neurofilament light chain (NfL), a neurone-specific cytoskeletal protein, is reflected in clinical and imaging measurements of illness across different neurological diseases [
7].
Numerous studies focused on the role of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in differentiating intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) and ischaemic stroke (IS) suggesting that GFAP may be a potential biomarker for an early prediction of ICH [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12]. A recent study also reported a positive correlation between serum GFAP level and the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score in acute IS [
13].
Rapid loss of Occludin (OCLN), a BBB tight junctional (TJ) protein in the cerebral microvessels has been observed in a rat IS model induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) [
14]. Pan
et al. (2017) found that OCLN levels in blood increased significantly 4.5 hours after MCAO and the increase in blood OCLN levels positively correlated with the extent of BBB damage [
15].
Disarrangement of Zonula occludens 1 (ZO-1), another BBB TJ component [
16], has been shown to reduce BBB integrity indicating BBB damage [
17]. In contrast, Claudin-5, a key TJ component selectively reduce the permeability to ions [
18], did not change significantly after cerebral ischaemia in the rat MCAO model [
15,
19].
Despite intense efforts in the search for blood-based biomarkers, there is no single circulating biomarker that can be used in hospitals to differentiate between stroke patients and stroke mimics. Most of the studies had a small sample size and very few have compared the biomarker levels in stroke patients with that of stroke mimics (SM) [
9,
10,
20,
21,
22]. Also, very few studies have assessed biomarker levels in combination with NIHSS scores, which might improve diagnostic accuracy. A recent study by Gaude
et al. (2021) has shown that a novel combination of GFAP and D-dimer with NIHSS scores can facilitate the detection of large vessel occlusion [
23].
Hence, the main aim of this exploratory study is to assess the ability of blood-based biomarkers (specific to neurones, astrocytes, and BBB damage) in combination with NIHSS scores to distinguish between IS patients and SM. This study has been reported according to the Standards for Reporting Diagnostic Accuracy (STARD) guidelines [
24].
2. Methods
2.1. Method Design
This prospective study included suspected IS patients (N=90) admitted to the stroke unit from the Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust emergency room at the Leeds General Infirmary (LGI), UK. The study was approved by the Yorkshire & The Humber-Leeds East Research Ethics Committee Patient selection (NHS-REC reference 19/YH/0232, IRAS reference No: 50831). A flow diagram of the study's design and the patient’s routine clinical pathways is shown in
Figure S1 (Supplemental material).
2.2. Patient Selection
Patients included in this study were a) Aged 18+ years, and b) suspected of acute IS when admitted to the hospital.
The exclusion criteria were a) The patient had capacity but refused consent, b) The patient lacked capacity and informed consent from the consultee could not be obtained. All the patients were recruited randomly between 2021-2022.
2.3. Recruitment Procedures
Researchers who trained in good clinical practice (GCP) took informed consent from the patients. Patients with acute stroke not infrequently lose capacity but it is important to include this group to minimise bias. Therefore, consent was also permissible from a relative. All in-patient populations with suspected IS were approached. Patients in the research were not included if it was impossible to obtain a patient informed consent or consultee declaration from a relative. Patient information was retrieved from NHS Trust paper and electronic medical health records (Patient Pathway Manager PPM+). All patient-identifiable data was stored on a password-protected database on the NHS Trust network drive. Data taken offsite to the University for analysis were in a pseudo-anonymised format. The data collected at baseline were: Demographic information (age, gender, ethnicity, and occupation), Height, weight, waist circumference, blood pressure, comorbidities, vital signs, NIHSS score on arrival, and medication on admission. Based on the NIHSS score on arrival, IS patients were classified as mild stroke (NIHSS ≤7) and moderate to severe (NIHSS >7).
2.4. Blood Sample Collection
Blood samples from 90 suspected stroke patients (66 were diagnosed as IS patients and 24 as SM following clinical evaluation) were collected to measure the concentration of biomarkers. For the serum sample, 5 ml of blood was collected in a gel clot active tube (Gold Hemogard closure) and allowed to clot by leaving it undisturbed at room temperature for 30 minutes. The clot was then removed by centrifuging at 1500 x g for 10 minutes at 40 C. The supernatant (serum) was aliquoted into a 1ml sterile vial labelled with the patient’s ID, date of blood collection and time of collection. The samples were flash-frozen using liquid nitrogen and stored at – 80 0C until analysis.
2.5. Analysis and Measurement of Blood Biomarkers
The ELISA technique was used to quantitatively assess biomarkers following the manufacturer’s protocol. The following ELISA Kits were used: human GFAP (Fine test, EH0410, sensitivity: 0.188 ng/ml), human ZO-1 (Fine test, EH15434, sensitivity: 0.094 ng/ml), human OCLN (Fine test, EH1674, sensitivity: 18.75 pg/ml), human Claudin-5 (Fine test, EH2839, sensitivity: 0.094 ng/ml), human NSE (R&D Systems, DENL20, sensitivity:0.038 ng/ml), human NfL (Abbexa, abx152468, sensitivity:< 5.7 pg/ml). All assays were done blind to the clinical characteristics of the patients.
2.6. Clinical Phenotyping
Routine NHS care was followed in the stroke unit. When the diagnosis of stroke or mimic was uncertain after brain CT, a clinical brain MRI was requested (23% of total participants, IS patients=9, SM=13). All clinical information and radiology were subsequently reviewed by a vascular neurologist blind to the laboratory data. Patients were given a final binary classification of IS or SM by a vascular neurologist using all the available clinical and radiological data, blind to the biomarker data. The clinical data was received up to the point of discharge from the hospital and this was blind to the biomarker data.
2.7. Statistical Analyses
Means and standard deviations were used to summarise numerical variables and frequencies and percentages for categorical variables. The comparison of clinical variables between IS patients and SM was assessed by student t-tests for numerical variables and chi-squared tests for categorical variables. The Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare the blood biomarker levels between IS patients and SM. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic performance of biomarkers in combination with NIHSS score to differentiate between IS patients and SM.
The diagnostic accuracy of the biomarkers was assessed using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity with a 95% confidence interval (CI). The likelihood ratio (LR) test and Akaike information criterion (AIC) were used to compare nested models of NIHSS score and a combination of biomarkers to select the optimal panel of blood biomarkers (GFAP and BBB proteins) that differentiate IS patients from SM. The cut-off value was selected by equalising the sensitivity and specificity. Data analysis was performed with Stata 17 MP software. GraphPad Prism 9 software (GraphPad, San Diego, California) was used for biomarker quantification or analysis and graph presentation. Statistical significance was determined at p≤0.05.
3. Results
The clinical characteristics of IS patients and SM are reported in
Table 1. In our cohort, we observed significant differences between IS patients and SM in age, gender, and history of hypertension and type 2 diabetes. All SM had alternative neurological conditions which included migraine, seizures, functional neurological disorder, cranial neuropathy, vestibulopathy, head injury, demyelination or paraneoplastic syndrome.
3.1. Distinguishing between Ischaemic Stroke Patients and Stroke Mimics
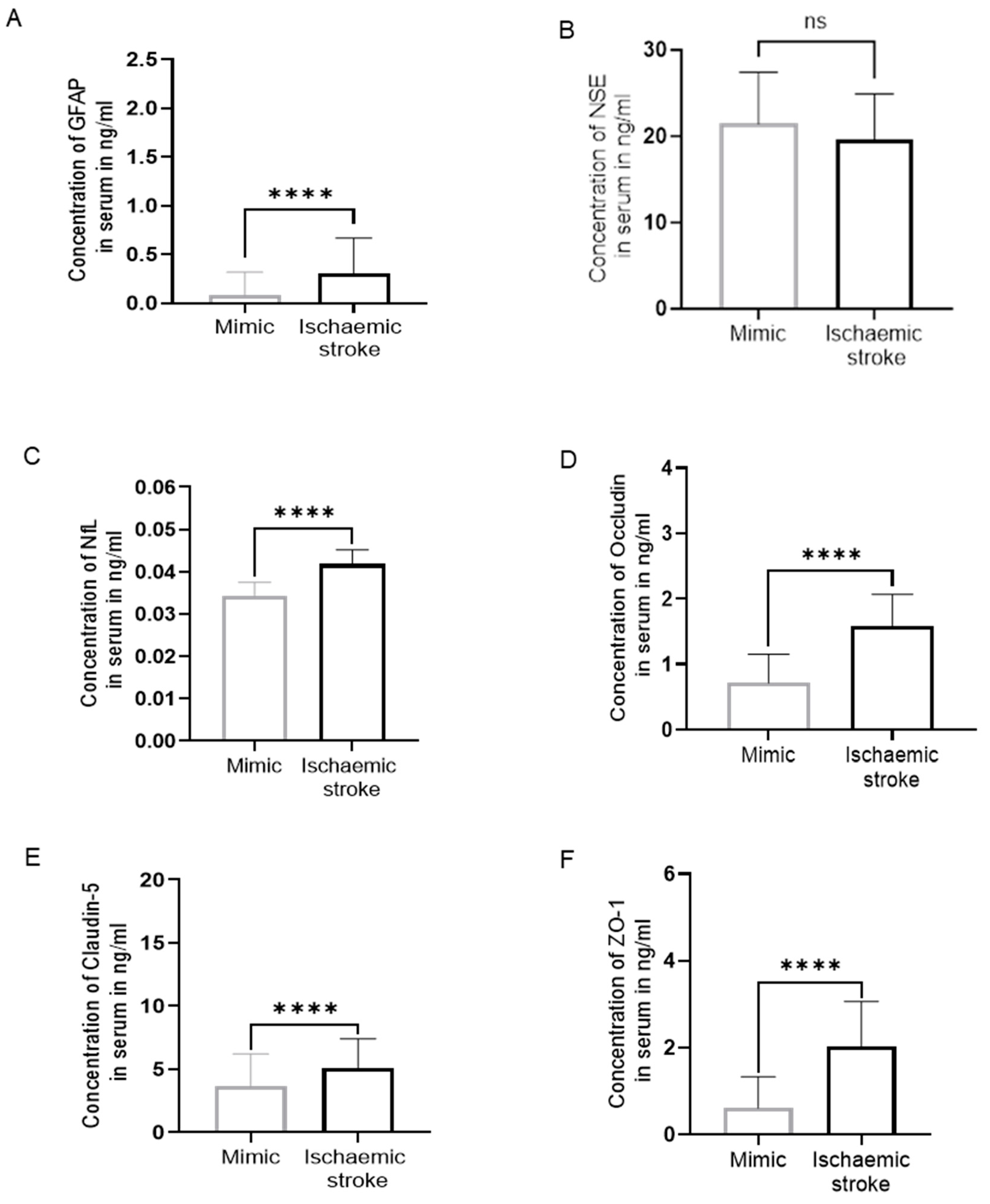
Table 2 shows the range, mean and median of serum GFAP, NSE, NfL, OCLN, Claudin-5, and ZO-1 concentrations in IS patients and SM. The levels of serum GFAP were significantly higher in IS patients as compared to SM with a 4-fold increase (p<0.0001,
Figure 1A) (N=90; IS=66, SM=24). No significant difference was observed between the levels of NSE in the serum of IS patients and SM (p = 0.07,
Figure 1B). Serum NfL concentration was 1.33-fold significantly higher in IS patients compared to SM (p<0.0001,
The range of serum OCLN, Claudin-5, and ZO-1 in IS patients was significantly higher compared to SM (p<0.0001,
As the concentrations of NSE in the serum of IS patients were not significantly different compared to SM, the analysis of NSE was discontinued at N=63; IS=46, SM=17.
3.2. Difference in Biomarker Levels Based on the Severity of Stroke
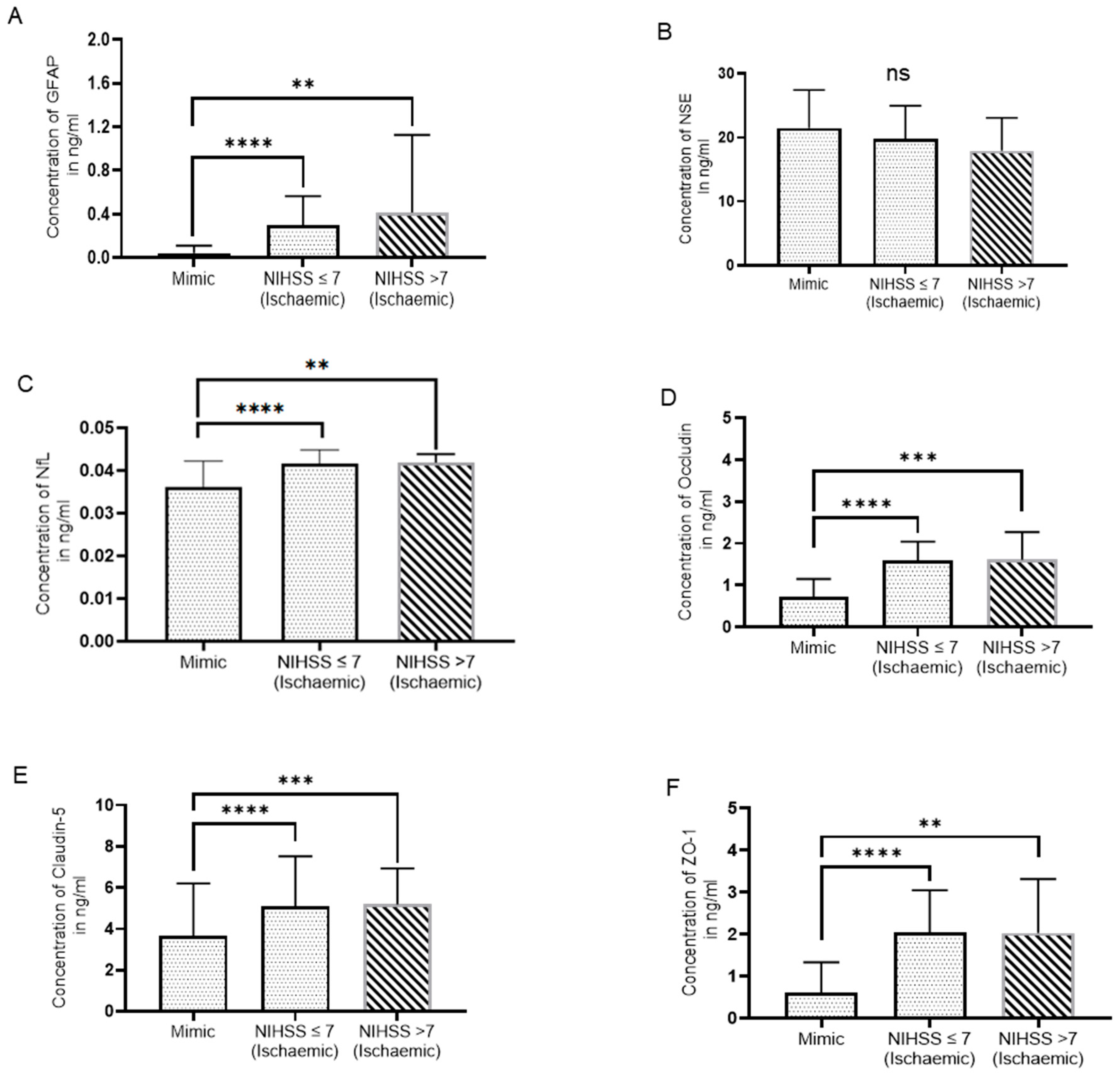
IS patients were classified as mild stroke (NIHSS ≤7) and moderate to severe stroke (NIHSS >7). Out of 66 IS patients, 56 patients had NIHSS score
7 and 10 patients had NIHSS score
7. When comparing the relationship between the IS group and SM group and the severity of a stroke, we found that IS patients had significantly higher serum GFAP, NFL, OCLN, Claudin-5, and ZO-1 levels in both groups as compared to SM (
Figure 2A, C, D, E). IS patients with NIHSS scores
7 (N=38) and NIHSS scores >7 (N=8) had non-significant changes in serum NSE levels as compared to SM (N=17) (p=0.285 and p=0.158, respectively) (
Figure 2B).
3.3. Combination of Blood Biomarkers with NIHSS
The multivariable logistic regression models that were fitted to determine the optimal panel of biomarkers to differentiate IS patients with SM are shown in
Table 3 and
Table 4. Adding biomarkers (GFAP and BBB proteins) to a model with NIHSS score resulted in a significant reduction in AIC suggesting a better model fit and an increase in AUC from 50 to greater than 90 showing better discrimination. The combination of selected biomarkers with NIHSS score has significant LR test
p-values (
p ≤ 0.05 has been considered statistically significant) showing a significant improvement compared to a model with NIHSS score only.
Amongst the combination model of one biomarker with a stroke severity scale, the NIHSS score+OCLN combination has higher accuracy and sensitivity but lower specificity than other combinations. Adding the GFAP biomarker to this model increases the accuracy and specificity but not sensitivity. Similarly, adding Claudin-5 to the NIHSS score+OCLN combination model doesn’t change any parameter. However, adding Claudin-5 to the NIHSS score+ZO-1 combination model increases the specificity of this model. Thus, we combined ZO-1, Claudin-5, and OCLN with NIHSS score which gives an accuracy of 89.41 (95% CI: 80.85-95.04), sensitivity of 87.50 (76.85-95.24), and specificity of 95.24 (76.18-99.88), higher among all the combination of three biomarkers with NIHSS score. We also found that testing BBB markers on their own could help diagnose ischaemic stroke with an accuracy of 86.67 %.
4. Discussion
This novel study for the first time reported a significant difference in circulating BBB TJ proteins (OCLN, ZO-1, and Claudin-5) along with GFAP and NfL but not NSE in IS patients compared to SM.
The multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that a combination of BBB TJ proteins with NIHSS score gives the highest diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity and specificity.
Previous studies have shown that GFAP might be utilised as a blood biomarker to distinguish between IS and ICH in the acute stage [
25,
26]. In the present study, we found that serum GFAP level in IS patients was significantly higher than in SM. Unlike other studies[
27,
28,
29,
30] we did not find that serum NSE concentrations in IS patients were significantly different between IS patients and SM. Serum NfL was significantly higher in IS patients compared to SM confirming previous studies that measured NfL in the blood of IS patients using Simoa [
31,
32,
33,
34].
Previous research has shown that the BBB is disrupted during a stroke, resulting in alterations in the concentrations and distributions of Claudin-5, OCLN, ZO-1, and other BBB building blocks [
14,
18]. Our novel findings showed that these BBB TJ protein levels are significantly higher in IS patients in comparison with SM. This might reflect the early BBB damage, which may not be detected on early CT imaging, hence these biomarkers could potentially have greater sensitivity than imaging strategies routinely available in the Emergency Department (ED).
A study by Gaude
et al. (2021), has shown that a biomarker panel composed of GFAP and D-dimer combined with clinical stroke severity scales can be a valuable tool for the identification of patients with large vessel occlusion (LVO) [
23]. Also, a recent study by Jæger et al. (2023) has shown that GFAP combined with the Prehospital stroke scale (PreSS) can identify stroke and stroke subtypes [
35]. Herein, we have demonstrated that a biomarker panel of TJ proteins (OCLN, Claudin-5, and ZO-1) combined with a stroke severity scale, NIHSS, can be a good prediction model to differentiate between IS patients and SM. To our knowledge, no study has established the role of TJ proteins and NIHSS scores in distinguishing between IS patients and SM. Even for clinicians who are not NIHSS trained, testing the BBB markers in isolation could reliably help with the diagnosis of IS based purely on clinical suspicion from the history and/or more limited examination e.g., the FAST test.
Although blood-based diagnostic tests for cardiac illnesses are often utilised (e.g., troponin I for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction) [
36], the use of biomarkers to diagnose stroke is still in its early stages. Blood biomarkers may help physicians make an accurate fast diagnosis of IS, which may be crucial in emergencies where therapies need to be started as soon as possible to enhance patient outcomes. On the other hand, some patients with neurological symptoms that mimic stroke might receive unnecessary interventions. To quickly distinguish and improve the therapeutic care of both IS patients and SM may also help in the pre-hospital setting to determine whether to transfer patients quickly to a stroke centre. However, in this study, we focused on the ability of selected blood-based biomarkers to distinguish between IS patients and SM in a population of patients possibly to have IS by ED staff based on clinical triage and brain CT alone.
Potential limitations of this study are that due to COVID-19 restrictions in the ED, we were not able to recruit hyperacute stroke patients and further studies are needed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of these biomarkers in the first few hours after stroke. Mild strokes were over-represented in this study as they were more likely to be recruited due to easier consent. However, this remains an important group to study as they usually reflect lacunar or posterior circulation events which can easily be missed or overdiagnosed in the ED.
Another limitation is that some SM may have been excluded based on imaging. However, the recruited population is likely to be representative of a population that poses a challenge in the ED and is often referred to stroke teams for further investigations or acute management. Although we controlled for potential confounding factors in multivariable logistic regression, we cannot completely exclude chance effects. Bias is unlikely as the phenotyping was done completely blind to the laboratory assays.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, our exploratory data suggests that circulating serum BBB TJ proteins combined with the NIHSS score can differentiate between IS patients and SM who have been admitted to the hospital from the ED for suspected stroke. Further prospective studies are required to determine the accuracy of these biomarkers in the hyperacute phase of stroke to maximise the clinical impact of a biomarker diagnostic strategy.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org. Figure S1: Flow diagram.
Author Contributions
PK: Methodology, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, MA: Methodology, Data curation, Formal analysis. Writing – original draft, TK: Methodology, TM: Validation, LM: Methodology, KK: Methodology, Ethics application, AH: Methodology, Clinical Phenotyping, Writing – review & editing, and SS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
This research is supported by the Medical Research Council, UK Developmental Pathway Gap Fund (MR/Y503460/1). This research is also part of a PhD project supported by the "Research Center of the Female Scientific and Medical Colleges", Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia.
Ethics statement
The study was approved by Yorkshire & The Humber - Leeds East Research Ethics Committee Patient selection (NHS REC reference 19/YH/0232, IRAS reference No: 50831).
Informed consent statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data availability statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to privacy or ethical reasons.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the patients who donated blood for the research, the Leeds-NHS Trust stroke unit staff for their support and help in collecting blood and the patient public involvement group that has approved the research in this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
- Glushakova, O.Y., et al., Biomarkers for acute diagnosis and management of stroke in neurointensive care units. Brain circulation, 2016. 2(1): p. 28. [CrossRef]
- Kamtchum-Tatuene, J. and G.C. Jickling, Blood biomarkers for stroke diagnosis and management. Neuromolecular medicine, 2019. 21(4): p. 344-368. [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N., et al., Towards the identification of blood biomarkers for acute stroke in humans: a comprehensive systematic review. British journal of clinical pharmacology, 2012. 74(2): p. 230-240. [CrossRef]
- Whiteley, W., M.-C. Tseng, and P. Sandercock, Blood biomarkers in the diagnosis of ischemic stroke: a systematic review. Stroke, 2008. 39(10): p. 2902-2909. [CrossRef]
- Anand, N. and L.G. Stead, Neuron-specific enolase as a marker for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review. Cerebrovascular diseases, 2005. 20(4): p. 213-219. [CrossRef]
- Bharosay, A., et al., Correlation of brain biomarker neuron specific enolase (NSE) with degree of disability and neurological worsening in cerebrovascular stroke. Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry, 2012. 27: p. 186-190. [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M., et al., Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders. Nature Reviews Neurology, 2018. 14(10): p. 577-589. [CrossRef]
- Foerch, C., et al., Serum glial fibrillary acidic protein as a biomarker for intracerebral haemorrhage in patients with acute stroke. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 2006. 77(2): p. 181-184. [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, A.H., et al., Plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein in the differential diagnosis of intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke, 2017. 48(9): p. 2586-2588. [CrossRef]
- Luger, S., et al., Glial fibrillary acidic protein serum levels distinguish between intracerebral hemorrhage and cerebral ischemia in the early phase of stroke. Clinical chemistry, 2017. 63(1): p. 377-385. [CrossRef]
- Ren, C., et al., Assessment of serum UCH-L1 and GFAP in acute stroke patients. Scientific reports, 2016. 6(1): p. 24588. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L., et al., The use of serum glial fibrillary acidic protein test as a promising tool for intracerebral hemorrhage diagnosis in Chinese patients and prediction of the short-term functional outcomes. Neurological sciences, 2015. 36: p. 2081-2087. [CrossRef]
- Amalia, L., Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP): Neuroinflammation biomarker in acute ischemic stroke. Journal of Inflammation Research, 2021. 14: p. 7501. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J., et al., Matrix metalloproteinase-2-mediated occludin degradation and caveolin-1-mediated claudin-5 redistribution contribute to blood–brain barrier damage in early ischemic stroke stage. Journal of neuroscience, 2012. 32(9): p. 3044-3057. [CrossRef]
- Pan, R., et al., Blood occludin level as a potential biomarker for early blood brain barrier damage following ischemic stroke. Scientific reports, 2017. 7(1): p. 40331. [CrossRef]
- Itoh, M. and M.J. Bissell, The organization of tight junctions in epithelia: implications for mammary gland biology and breast tumorigenesis. Journal of mammary gland biology and neoplasia, 2003. 8: p. 449-462. [CrossRef]
- Petty, M. and J. Wettstein, Elements of cerebral microvascular ischaemia. Brain Research Reviews, 2001. 36(1): p. 23-34. [CrossRef]
- Jia, W., et al., The role of claudin-5 in blood-brain barrier (BBB) and brain metastases. Molecular medicine reports, 2014. 9(3): p. 779-785. [CrossRef]
- Shi, S., et al., Normobaric hyperoxia reduces blood occludin fragments in rats and patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke, 2017. 48(10): p. 2848-2854. [CrossRef]
- Purrucker, J.C., et al., Serum protein S100β is a diagnostic biomarker for distinguishing posterior circulation stroke from vertigo of nonvascular causes. European Neurology, 2014. 72(5-6): p. 278-284. [CrossRef]
- Dambinova, S.A., et al., Diagnostic potential of the NMDA receptor peptide assay for acute ischemic stroke. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Montaner, J., et al., Etiologic diagnosis of ischemic stroke subtypes with plasma biomarkers. Stroke, 2008. 39(8): p. 2280-2287. [CrossRef]
- Gaude, E., et al., A novel combination of blood biomarkers and clinical stroke scales facilitates detection of large vessel occlusion ischemic strokes. Diagnostics, 2021. 11(7): p. 1137. [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, P.M., et al., STARD 2015: an updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies. Radiology, 2015. 277(3): p. 826-832. [CrossRef]
- Foerch, C., S. Luger, and B.F.S. Group, Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) plasma levels distinguish intracerebral hemorrhage from cerebral ischemia in the early phase of acute stroke. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 2015. 357: p. e430. [CrossRef]
- Luger, S., et al., Diagnostic accuracy of glial fibrillary acidic protein and ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase-L1 serum concentrations for differentiating acute intracerebral hemorrhage from ischemic stroke. Neurocritical care, 2020. 33: p. 39-48. [CrossRef]
- Missler, U., et al., S-100 protein and neuron-specific enolase concentrations in blood as indicators of infarction volume and prognosis in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke, 1997. 28(10): p. 1956-1960. [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.V., et al., Prognostic value of neuron specific enolase and IL-10 in ischemic stroke and its correlation with degree of neurological deficit. Clinica chimica acta, 2013. 419: p. 136-138. [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, M.T., et al., Neuron-specific enolase and tau protein as neurobiochemical markers of neuronal damage are related to early clinical course and long-term outcome in acute ischemic stroke. Clinical neurology and neurosurgery, 2006. 108(6): p. 558-563. [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, M.T., C.-W. Wallesch, and M. Goertler, Release of neurobiochemical markers of brain damage is related to the neurovascular status on admission and the site of arterial occlusion in acute ischemic stroke. Journal of the neurological sciences, 2004. 227(1): p. 49-53. [CrossRef]
- Gendron, T.F., et al., Plasma neurofilament light predicts mortality in patients with stroke. Science translational medicine, 2020. 12(569): p. eaay1913. [CrossRef]
- Onatsu, J., et al., Serum neurofilament light chain concentration correlates with infarct volume but not prognosis in acute ischemic stroke. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 2019. 28(8): p. 2242-2249. [CrossRef]
- Uphaus, T., et al., NfL (neurofilament light chain) levels as a predictive marker for long-term outcome after ischemic stroke. Stroke, 2019. 50(11): p. 3077-3084. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., et al., Plasma neurofilament light chain as a predictive biomarker for post-stroke cognitive impairment: a prospective cohort study. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 2021. 13: p. 631738. [CrossRef]
- Jæger, H.S., et al., Diagnostic performance of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein and Prehospital Stroke Scale for identification of stroke and stroke subtypes in an unselected patient cohort with symptom onset< 4.5 h. Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine, 2023. 31(1): p. 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Panteghini, M., Role and importance of biochemical markers in clinical cardiology. European heart journal, 2004. 25(14): p. 1187-1196. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Biomarker levels in serum. (A) GFAP, (B) NSE, (C) NfL, (D) Occludin, (E) Claudin-5, and (F) ZO-1 in ischaemic patients (N=66) compared to mimics(N=24). There was a significant increase in the concentration of biomarkers in an ischaemic group compared to mimics except NSE (46 ischaemic patients, 17 mimics). (Mann-Whitney U test, p>0.05: ns, p≤0.05: *, p≤0.01: **, p≤0.001: ***, p≤0.0001: ****).
Figure 1.
Biomarker levels in serum. (A) GFAP, (B) NSE, (C) NfL, (D) Occludin, (E) Claudin-5, and (F) ZO-1 in ischaemic patients (N=66) compared to mimics(N=24). There was a significant increase in the concentration of biomarkers in an ischaemic group compared to mimics except NSE (46 ischaemic patients, 17 mimics). (Mann-Whitney U test, p>0.05: ns, p≤0.05: *, p≤0.01: **, p≤0.001: ***, p≤0.0001: ****).
Figure 2.
Serum biomarker levels based on NIHSS score. (A) GFAP, (B) NSE, (C) NFL, (D) Occludin (E) Claudin-5, and (F) ZO-1 (Mann-Whitney U test, p>0.05: ns, p≤0.05: *, p≤0.01: **, p≤0.001: ***, p≤0.0001: ****), (NIHSS >7: N=10, 8 for NSE, NIHSS 7: N=56, 38 for NSE and mimics: N=24, 17 for NSE).
Figure 2.
Serum biomarker levels based on NIHSS score. (A) GFAP, (B) NSE, (C) NFL, (D) Occludin (E) Claudin-5, and (F) ZO-1 (Mann-Whitney U test, p>0.05: ns, p≤0.05: *, p≤0.01: **, p≤0.001: ***, p≤0.0001: ****), (NIHSS >7: N=10, 8 for NSE, NIHSS 7: N=56, 38 for NSE and mimics: N=24, 17 for NSE).
Table 1.
Univariate analysis of clinical variables in ischaemic stroke patients and stroke mimics.
Table 1.
Univariate analysis of clinical variables in ischaemic stroke patients and stroke mimics.
| Clinical Variables |
Ischaemic stroke patients
Mean (SD*) |
Stroke mimics
Mean (SD) |
p-value |
| Gender (M/F) |
50/16 |
15/9 |
<0.001 |
| Age |
65.8(10.9) |
54.2(16.9) |
<0.001 |
| Systolic BP† |
154.6(32.1) |
149.8(28.2) |
0.53 |
| Diastolic BP |
85.8(18.5) |
89.2(11.4) |
0.41 |
| Hypertension (% Yes) |
54.5 |
41.6 |
<0.001 |
| Diabetes(%Yes) |
36.4 |
33.3 |
<0.001 |
| APTT‡ |
30.2(2.8) |
31.2(3.1) |
0.20 |
| Prothrombin time (sec) |
12.0(2.4) |
11.9(0.9) |
0.90 |
| Platelet count |
256.2(64.1) |
244.0(60.3) |
0.42 |
| Red blood count |
4.75(0.51) |
4.79(0.57) |
0.74 |
| NIHSS score |
3.6(3.4) |
3.0(2.4) |
0.47 |
| OBT §(days) |
3.1(2.7) |
3.3(2.3) |
0.77 |
| Posterior/Anterior Ischaemia |
21/45 |
NA |
|
Table 2.
The range, mean (SD), and median of serum GFAP, NSE, NfL, OCLN, ZO-1, and Claudin-5 concentrations in the ischaemic stroke group (N=66 for all biomarkers; N = 46 for NSE) and mimics group (N=24 for all biomarkers; N = 17 for NSE).
Table 2.
The range, mean (SD), and median of serum GFAP, NSE, NfL, OCLN, ZO-1, and Claudin-5 concentrations in the ischaemic stroke group (N=66 for all biomarkers; N = 46 for NSE) and mimics group (N=24 for all biomarkers; N = 17 for NSE).
| Biomarker |
Ischaemic stroke
(ng/ml) |
Stroke mimics
(ng/ml) |
p-value |
| GFAP |
Mean(SD*) |
0.31(0.36) |
0.08(0.24) |
<0.0001 |
| Minimum |
0.02 |
0.01 |
|
| Maximum |
2.41 |
1.20 |
|
| Median |
0.26 |
0.02 |
|
| NSE |
Mean (SD) |
19.64(5.24) |
21.47(5.95) |
0.07 |
| Minimum |
9.29 |
12.38 |
|
| Maximum |
28.42 |
27.43 |
|
| Median |
20.54 |
23.66 |
|
| Claudin-5 |
Mean (SD) |
5.09(2.32) |
3.65(2.55) |
<0.0001 |
| Minimum |
0.57 |
0.74 |
|
| Maximum |
17.10 |
14.99 |
|
| Median |
5.51 |
2.96 |
|
| OCLN |
Mean (SD) |
1.59(0.48) |
0.71(0.44) |
<0.0001 |
| Minimum |
0.19 |
0.25 |
|
| Maximum |
3.18 |
1.66 |
|
| Median |
1.64 |
0.62 |
|
| ZO-1 |
Mean (SD) |
2.02(1.04) |
0.61(0.72) |
<0.0001 |
| Minimum |
0.01 |
0.07 |
|
| Maximum |
5.12 |
3.70 |
|
| Median |
2.57 |
0.42 |
|
| NfL |
Mean (SD) |
0.040(0.003) |
0.030(0.003) |
<0.0001 |
| Minimum |
0.03 |
0.03 |
|
| Maximum |
0.05 |
0.04 |
|
| Median |
0.04 |
0.03 |
|
Table 3.
Different comparison models of biomarkers with NIHSS.
Table 3.
Different comparison models of biomarkers with NIHSS.
| Model |
AIC* |
AUC†
|
LR‡, p-value |
| NIHSS |
98.47 |
52.3(38.3-66.4) |
- |
| NIHSS+GFAP |
81.46 |
89.5(80.0-99.0) |
19.01, <0.001 |
| NIHSS+ZO-1 |
66.07 |
88.7(78.8-98.6) |
34.40, <0.001 |
| NIHSS+OCLN |
63.85 |
90.6(83.1-98.1) |
36.61, <0.001 |
| NIHSS+CLAUDIN-5 |
90.38 |
86.1(75.6-96.7) |
10.09, 0.006 |
| NIHSS+GFAP+ZO-1 |
67.66 |
89.2(79.3-99.0) |
34.81, <0.001 |
| NIHSS+GFAP+OCLN |
64.84 |
90.1(80.6-99.6) |
37.62, <0.001 |
| NIHSS+GFAP+CLAUDIN-5 |
81.53 |
91.7(82.1-100) |
20.94, <0.001 |
| NIHSS+ZO-1+OCLN |
63.15 |
90.3(81.1-99.6) |
39.32, <0.001 |
| NIHSS+ZO-1+CLAUDIN-5 |
66.64 |
90.6(83.1-98.1) |
35.83, <0.001 |
| NIHSS+OCLN+CLAUDIN-5 |
65.62 |
91.4(84.9-97.8) |
36.85, <0.001 |
| NIHSS+GFAP+ZO-1+OCLN |
65.07 |
90.3(81.1-99.6) |
39.40, <0.001 |
| NIHSS+GFAP+ZO-1+CLAUDIN-5 |
68.41 |
90.5(81.8-99.1) |
36.06, <0.001 |
| NIHSS+GFAP+OCLN+CLAUDIN-5 |
65.05 |
91.4(84.5-98.1) |
39.42, <0.001 |
| NIHSS+ZO-1+OCLN+CLAUDIN-5 |
62.54 |
92.1(86.1-98.1) |
41.92, <0.001 |
| NIHSS+GFAP+ZO-1+OCLN+CLAUDIN-5 |
64.36 |
92.2(86.3-98.0) |
42.11, <0.001 |
| ZO-1+OCLN+CLAUDIN-5 |
65.85 |
93.0(87.7-98.3) |
- |
Table 4.
Accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity values of different combinations of biomarkers with NIHSS.
Table 4.
Accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity values of different combinations of biomarkers with NIHSS.
| Model |
Accuracy |
Sensitivity |
Specificity |
| NIHSS |
47.06(36.13-58.19) |
43.19(29.94-55.18) |
61.90(38.44-81.89) |
| NIHSS+GFAP |
83.53(73.91-90.69) |
79.69(67.77-88.72) |
95.24(76.18-99.88) |
| NIHSS+ZO-1 |
85.88(76.64-92.49) |
83.81(71.32-91.10) |
95.24(76.18-99.88) |
| NIHSS+OCLN |
87.06(78.02-93.36) |
89.06(78.75-95.49) |
80.95(58.09-94.55) |
| NIHSS+CLAUDIN-5 |
77.65(67.31-85.97) |
71.88(59.24-82.40) |
95.24(76.18-99.88) |
| NIHSS+GFAP+ZO-1 |
87.06(78.02-93.36) |
84.38(73.14-92.24) |
95.24(76.18-99.88) |
| NIHSS+GFAP+OCLN |
89.41(80.85-95.04) |
89.06(78.75-95.49) |
90.48(69.62-98.83) |
| NIHSS+GFAP+CLAUDIN-5 |
84.71(75.27-91.60) |
81.25(69.54-89.92) |
95.24(76.18-99.88) |
| NIHSS+ZO-1+OCLN |
88.24(79.43-94.21) |
85.94(74.98-93.36) |
95.24(76.18-99.88) |
| NIHSS+ZO-1+CLAUDIN-5 |
85.88(76.64-92.49) |
82.81(71.32-91.10) |
95.24(76.18-99.88) |
| NIHSS+OCLN+CLAUDIN-5 |
87.06(78.02-93.36) |
89.06(78.75-95.49) |
80.95(58.09- 94.55) |
| NIHSS+GFAP+ZO-1+OCLN |
88.24(79.43-94.21) |
85.94(74.98-93.36) |
95.24(76.18-99.88) |
| NIHSS+GFAP+ZO-1+CLAUDIN-5 |
85.88(76.64-92.49) |
82.81(71.32-91.10) |
95.24(76.18-99.88) |
| NIHSS+GFAP+OCLN+CLAUDIN-5 |
88.24(79.43-94.21) |
87.50(76.85-94.45) |
90.48(69.62-98.83) |
| NIHSS+ZO-1+OCLN+CLAUDIN-5 |
89.41(80.85-95.04) |
87.50(76.85-94.45) |
95.24(76.18-99.88) |
| NIHSS+GFAP+ZO-1+OCLN+CLAUDIN-5 |
89.41(80.85-95.04) |
87.50(76.85-94.45) |
95.24(76.18-99.88) |
| ZO-1+OCLN+CLAUDIN-5 |
86.67(77.87-92.92) |
83.33(72.13-95.38) |
95.83(78.88-99.89) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).