Submitted:
20 September 2024
Posted:
20 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Selection Process and Descriptive Analysis
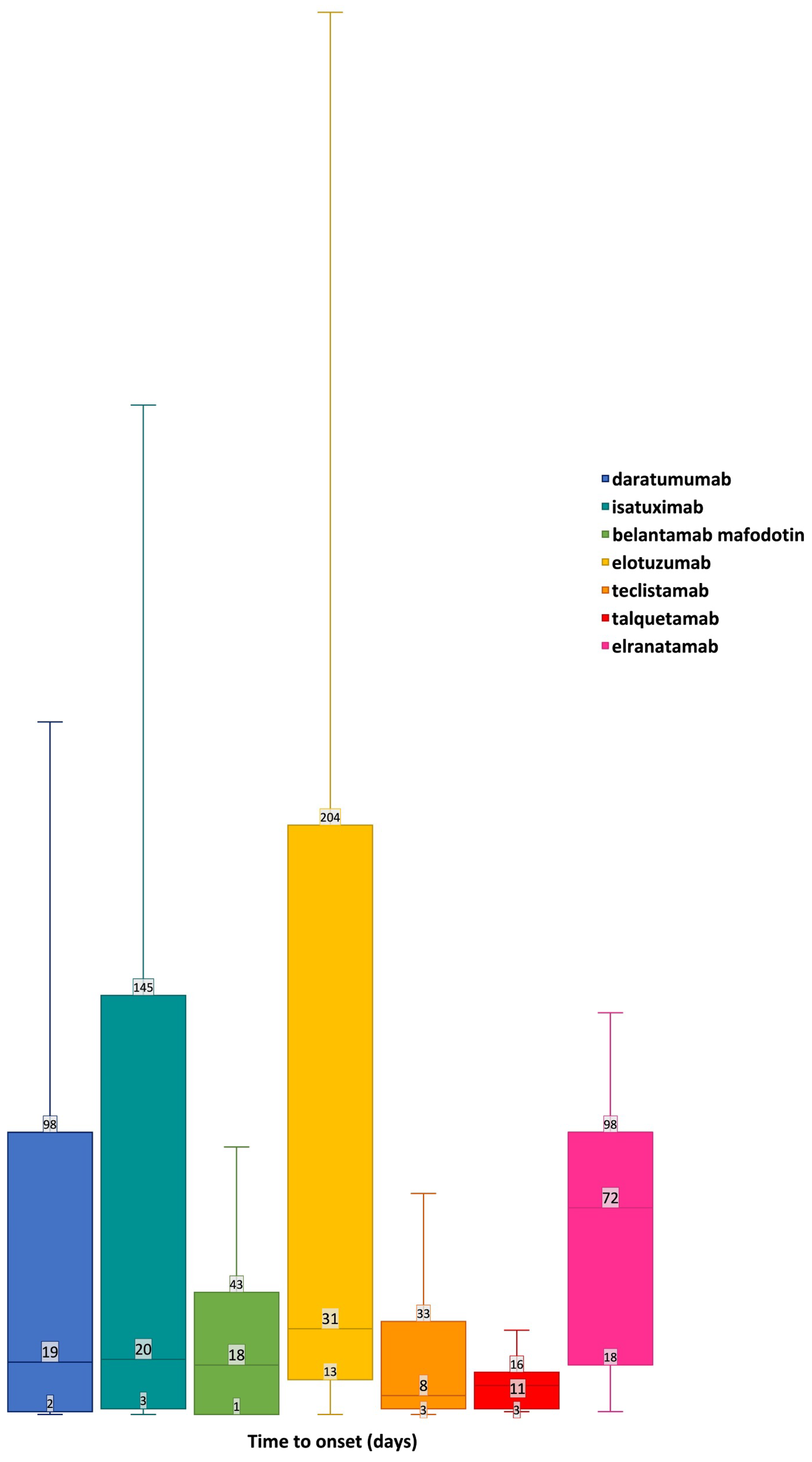
2.2. Disproportionality Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Strengths and Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Selection of Cases
4.3. Data Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix – List of Abbreviations
References
- Rajkumar, S.V.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Palumbo, A.; Blade, J.; Merlini, G.; Mateos, M.-V.; Kumar, S.; Hillengass, J.; Kastritis, E.; Richardson, P.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group Updated Criteria for the Diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma. Lancet Oncol 2014, 15, e538–e548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapietra, G.; Fazio, F.; Petrucci, M.T. Race for the Cure: From the Oldest to the Newest Monoclonal Antibodies for Multiple Myeloma Treatment. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wudhikarn, K.; Wills, B.; Lesokhin, A.M. Monoclonal Antibodies in Multiple Myeloma: Current and Emerging Targets and Mechanisms of Action. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2020, 33, 101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Pawlyn, C.; Yong, K.L. Multiple Myeloma. Lancet 2021, 397, 410–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Oriol, A.; Nahi, H.; San-Miguel, J.; Bahlis, N.J.; Usmani, S.Z.; Rabin, N.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Suzuki, K.; Plesner, T.; et al. Overall Survival with Daratumumab, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone in Previously Treated Multiple Myeloma (POLLUX): A Randomized, Open-Label, Phase III Trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2023, 41, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonial, S.; Dimopoulos, M.; Palumbo, A.; White, D.; Grosicki, S.; Spicka, I.; Walter-Croneck, A.; Moreau, P.; Mateos, M.-V.; Magen, H.; et al. Elotuzumab Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N Engl J Med 2015, 373, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, P.; Garfall, A.L.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Nahi, H.; San-Miguel, J.F.; Oriol, A.; Nooka, A.K.; Martin, T.; Rosinol, L.; Chari, A.; et al. Teclistamab in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N Engl J Med 2022, 387, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Storti, P.; Marchica, V.; Scandura, G.; Notarfranchi, L.; Craviotto, L.; Di Raimondo, F.; Giuliani, N. Mechanisms of Action of the New Antibodies in Use in Multiple Myeloma. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 684561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration Full Prescribing Information Talvey® (Talquetamab-Tgvs) Available online:. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/761342s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- US Food and Drug Administration Full Prescribing Information Elrexfio TM® (Elranatamab Bcmm) Available online:. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/761345Orig1s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- US Food and Drug Administration Full Prescribing Information Texvayli® (Teclistamab-Cqyv) Available online:. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/761291s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- US Food and Drug Administration Full Prescribing Information Blenrep® (Belantamab Mafodotin-Blmf). Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/761158s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- US Food and Drug Administration Full Prescribing Information Empliciti® (Elotuzumab) Available online:. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/761035s015lbl.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- US Food and Drug Administration Full Prescribing Information Sarclisa® (Isatuximab-Irfc) Available online:. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/761113s009lbl.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- US Food and Drug Administration Full Prescribing Information Darzalex® (Daratumumab) Available online:. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/761036s044lbl.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- Kareem, S.S.; Viswanathan, N.; Sahebjam, S.; Tran, N.D.; Gatewood, T.; Tobon, K.; Baz, R.; Piña, Y.; Shain, K.H.; Mokhtari, S. Leukoencephalopathy During Daratumumab-Based Therapy: A Case Series of Two Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Onco Targets Ther 2022, 15, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smets, I.; Titulaer, M.J. Antibody Therapies in Autoimmune Encephalitis. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratuszny, D.; Skripuletz, T.; Wegner, F.; Gro?, M.; Falk, C.; Jacobs, R.; Ruschulte, H.; Stangel, M.; S?hs, K.-W.C.R. Daratumumab in a Patient With Severe Refractory Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis. Front Neurol 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohyuddin, G.R.; Banerjee, R.; Alam, Z.; Berger, K.E.; Chakraborty, R. Rethinking Mechanisms of Neurotoxicity with BCMA Directed Therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2021, 166, 103453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, E.P.; McGladrigan, C.G. Differences in Safety Profiles of Newly Approved Medications for Multiple Myeloma in Real-World Settings versus Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of Oncology Pharmacy Practice 2021, 27, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.E.; Ilaghi, M.; Aslani, A.; Yekta, Z.; Nejadghaderi, S.A. A Population-Based Study on Incidence Trends of Myeloma in the United States over 2000–2020. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 20705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, S.; Cairns, D.; Menzies, T.; Boyd, K.; Davies, F.; Cook, G.; Drayson, M.; Gregory, W.; Jenner, M.; Jones, J.; et al. Sex Differences in Multiple Myeloma Biology but Not Clinical Outcomes: Results from 3894 Patients in the Myeloma XI Trial. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2021, 21, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; El-Khoury, H.; Tramontano, A.C.; Alberge, J.-B.; Perry, J.; Davis, M.I.; Horowitz, E.; Redd, R.; Sakrikar, D.; Barnidge, D.; et al. Mass Spectrometry-Detected MGUS Is Associated with Obesity and Other Novel Modifiable Risk Factors in a High-Risk Population. Blood Adv 2024, 8, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Verde, L.; Vetrani, C.; Barrea, L.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. Obesity: A Gender-View. J Endocrinol Invest 2023, 47, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/fact_sheets/adult_data/cig_smoking/index.htm (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A.; Barsouk, A.; Rawla, P.; Vakiti, A.; Kolhe, R.; Kota, V.; Ajebo, G.H. Epidemiology, Staging, and Management of Multiple Myeloma. Medical Sciences 2021, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, E.M.; Legrand, C.; Demarquette, H.; Guidez, S.; Herbaux, C.; Leleu, X.; Facon, T. Treatment of Elderly Patients with Myeloma. In Handbook of Multiple Myeloma; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2015; pp. 41–63. [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo, A.; Oliva, S. Latest Advances in the Management of Elderly Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Int J Hematol Oncol 2013, 2, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, A.; Bringhen, S.; Ludwig, H.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Bladé, J.; Mateos, M.V.; Rosiñol, L.; Boccadoro, M.; Cavo, M.; Lokhorst, H.; et al. Personalized Therapy in Multiple Myeloma According to Patient Age and Vulnerability: A Report of the European Myeloma Network (EMN). Blood 2011, 118, 4519–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Laubach, J.P.; Schlossman, R.L.; Mitsiades, C.; Anderson, K. Complications of Multiple Myeloma Therapy, Part 1: Risk Reduction and Management of Peripheral Neuropathy and Asthenia. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network 2010, 8, S–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzi, S.; Bari, A.; Pecherstorfer, M.; Vallet, S. Management of Adverse Events and Supportive Therapy in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimabukuro-Vornhagen, A.; Gödel, P.; Subklewe, M.; Stemmler, H.J.; Schlößer, H.A.; Schlaak, M.; Kochanek, M.; Böll, B.; von Bergwelt-Baildon, M.S. Cytokine Release Syndrome. J Immunother Cancer 2018, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesokhin, A.M.; Tomasson, M.H.; Arnulf, B.; Bahlis, N.J.; Miles Prince, H.; Niesvizky, R.; Rodrίguez-Otero, P.; Martinez-Lopez, J.; Koehne, G.; Touzeau, C.; et al. Elranatamab in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Phase 2 MagnetisMM-3 Trial Results. Nat Med 2023, 29, 2259–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sborov, D.W.; Baljevic, M.; Reeves, B.; Laubach, J.; Efebera, Y.A.; Rodriguez, C.; Costa, L.J.; Chari, A.; Silbermann, R.; Holstein, S.A.; et al. Daratumumab plus Lenalidomide, Bortezomib and Dexamethasone in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma: Analysis of Vascular Thrombotic Events in the <scp>GRIFFIN</Scp> Study. Br J Haematol 2022, 199, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, P.; Dimopoulos, M.-A.; Mikhael, J.; Yong, K.; Capra, M.; Facon, T.; Hajek, R.; Špička, I.; Baker, R.; Kim, K.; et al. Isatuximab, Carfilzomib, and Dexamethasone in Relapsed Multiple Myeloma (IKEMA): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised Phase 3 Trial. The Lancet 2021, 397, 2361–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, L.; Alhaj Hussen, K.; Thouroude, S.; Mbemba, E.; Cost, H.; Garderet, L.; Elalamy, I.; Larsen, A.; Van Dreden, P.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; et al. Modelization of Blood-Borne Hypercoagulability in Myeloma: A Tissue-Factor-Bearing Microparticle-Driven Process. TH Open 2019, 03, e340–e347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Tong, D.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Zhou, P.; Jin, J.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; et al. Phosphatidylserine-Exposing Cells Contribute to the Hypercoagulable State in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Int J Oncol 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covut, F.; Sanfilippo, K.M. Mitigating the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Receiving Immunomodulatory-Based Therapy. Hematology 2022, 2022, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.L.; Nielson, C.M.; Park, J.K.; Marongiu, A.; Soff, G.A. The Incidence of Thrombocytopenia in Adult Patients Receiving Chemotherapy for Solid Tumors or Hematologic Malignancies. Eur J Haematol 2021, 106, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Bazou, D.; Santos-Martinez, M.J. Bleeding and Thrombosis in Multiple Myeloma: Platelets as Key Players during Cell Interactions and Potential Use as Drug Delivery Systems. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 15855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiq, N.; Bergstrom, C.; Anderson, L.D.; Nagalla, S. Bleeding Due to Acquired Dysfibrinogenemia as the Initial Presentation of Multiple Myeloma. BMJ Case Rep 2019, 12, e229312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Veeraballi, S.; Chan, K.H.; Shaaban, H.S. Bleeding Diathesis in Multiple Myeloma: A Rare Presentation of a Dreadful Emergency With Management Nightmare. Cureus 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, G.; Farias, A.A.; Ranade, A.; Meisels, I. Altered Mental Status in a Case of Multiple Myeloma Not Related to a Metabolic Cause. Clin Kidney J 2009, 2, 434–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-J.; Kao, T.-W.; Chen, W.-L. Relationship between Peripheral Neuropathy and Cognitive Performance in the Elderly Population. Medicine 2021, 100, e26071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, U.H.; Mir, M.A.; Sivik, J.K.; Raheja, D.; Pandey, M.K.; Talamo, G. Central Neurotoxicity of Immunomodulatory Drugs in Multiple Myeloma. Hematol Rep 2015, 7, 5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fugate, J.E.; Rabinstein, A.A. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome: Clinical and Radiological Manifestations, Pathophysiology, and Outstanding Questions. Lancet Neurol 2015, 14, 914–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, R.; Glaisner, S.; Bobin, A.; Ronchetti, A.-M.; Cereja, S.; Joly, B.; Salanoubat, C.; Fouquet, G. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) and Myeloma. Leuk Res Rep 2024, 21, 100407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonial, S.; Lee, H.C.; Badros, A.; Trudel, S.; Nooka, A.K.; Chari, A.; Abdallah, A.-O.; Callander, N.; Lendvai, N.; Sborov, D.; et al. Belantamab Mafodotin for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (DREAMM-2): A Two-Arm, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 2 Study. Lancet Oncol 2020, 21, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.-T.; de Weers, M.; Li, X.-F.; Song, W.; Nahar, S.; Bakker, J.M.; Vink, T.; Jacobs, D.; Oomen, L.; Bleeker, W.K.; et al. Daratumumab, a Novel Potent Human Anti-CD38 Monoclonal Antibody, Induces Significant Killing of Human Multiple Myeloma Cells: Therapeutic Implication. Blood 2009, 114, 608–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A. Belantamab Mafodotin: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohty, B.; El-Cheikh, J.; Yakoub-Agha, I.; Moreau, P.; Harousseau, J.-L.; Mohty, M. Peripheral Neuropathy and New Treatments for Multiple Myeloma: Background and Practical Recommendations. Haematologica 2010, 95, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Živković, S.A.; Lacomis, D.; Lentzsch, S. Paraproteinemic Neuropathy. Leuk Lymphoma 2009, 50, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahi, H.; Walinder, G.; Patel, V.; Qu, Y.; Levine, A.; Majer, I.; Kutikova, L.; Hellqvist Franck, E.; Svensson, M.K.; Hansson, M. Burden of Treatment-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Multiple Myeloma in Sweden. Acta Haematol 2021, 144, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, P.G.; Delforge, M.; Beksac, M.; Wen, P.; Jongen, J.L.; Sezer, O.; Terpos, E.; Munshi, N.; Palumbo, A.; Rajkumar, S. V; et al. Management of Treatment-Emergent Peripheral Neuropathy in Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2012, 26, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, P.G.; Siegel, D.S.; Vij, R.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Baz, R.; Jagannath, S.; Chen, C.; Lonial, S.; Jakubowiak, A.; Bahlis, N.; et al. Pomalidomide Alone or in Combination with Low-Dose Dexamethasone in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma: A Randomized Phase 2 Study. Blood 2014, 123, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, D.S.; Martin, T.; Wang, M.; Vij, R.; Jakubowiak, A.J.; Lonial, S.; Trudel, S.; Kukreti, V.; Bahlis, N.; Alsina, M.; et al. A Phase 2 Study of Single-Agent Carfilzomib (PX-171-003-A1) in Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2012, 120, 2817–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, B.; Walgaard, C.; Drenthen, J.; Fokke, C.; Jacobs, B.C.; van Doorn, P.A. Guillain–Barré Syndrome: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis. Nat Rev Neurol 2014, 10, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Tejedor, A.; Lorenzo-Mohamed, M.; Puig, N.; García-Sanz, R.; Mateos, M.-V.; Garayoa, M.; Paíno, T. Immune System Alterations in Multiple Myeloma: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies to Reverse Immunosuppression. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, B.; Decker, M.; Ryan, R.; Kaczmarczyk, K.; Jandir, P.; Waykole, T.; Ashkar, R.; Harmon, G.; Mathur, A.; Levitt, M. Multiple Myeloma: A Review of the Literature and a Case Report Highlighting the Immunocompromised State of Myeloma Patients. World J Oncol 2024, 15, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Zhou, B.; Pak, A.; Yang, N.; Barmettler, S. Hypogammaglobulinemia and Risk of Infection Following Daratumumab in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2024, 153, AB231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilopoulos, S.; Vassilopoulos, A.; Kalligeros, M.; Shehadeh, F.; Mylonakis, E. Cumulative Incidence and Relative Risk of Infection in Patients With Multiple Myeloma Treated With Anti-CD38 Monoclonal Antibody-Based Regimens: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Open Forum Infect Dis 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, M.A.; Sorbara, E.E.; Cicala, G.; Santoro, V.; Cutroneo, P.M.; Franchina, T.; Spina, E. Adverse Drug Reactions with HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Treatment: An Analysis from the Italian Pharmacovigilance Database. Drugs Real World Outcomes 2022, 9, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, M.A.; Sorbara, E.E.; Cicala, G.; Santoro, V.; Cutroneo, P.M.; Franchina, T.; Santarpia, M.; Silvestris, N.; Spina, E. Safety Profile of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Used in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Analysis from the Italian Pharmacovigilance Database. Front Oncol 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celi, L.A.; Moseley, E.; Moses, C.; Ryan, P.; Somai, M.; Stone, D.; Tang, K. From Pharmacovigilance to Clinical Care Optimization. Big Data 2014, 2, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montastruc, J.; Sommet, A.; Bagheri, H.; Lapeyre-Mestre, M. Benefits and Strengths of the Disproportionality Analysis for Identification of Adverse Drug Reactions in a Pharmacovigilance Database. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2011, 72, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicala, G.; de Filippis, R.; Barbieri, M.A.; Cutroneo, P.M.; De Fazio, P.; Schoretsanitis, G.; Spina, E. Tolerability Profile of Paliperidone Palmitate Formulations: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis of the EUDRAVigilance Database. Front Psychiatry 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozsgai, K.; Szűcs, G.; Kőnig-Péter, A.; Balázs, O.; Vajda, P.; Botz, L.; Vida, R.G. Analysis of Pharmacovigilance Databases for Spontaneous Reports of Adverse Drug Reactions Related to Substandard and Falsified Medical Products: A Descriptive Study. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaroli, M.; Giunchi, V.; Battini, V.; Puligheddu, S.; Khouri, C.; Carnovale, C.; Raschi, E.; Poluzzi, E. Enhancing Transparency in Defining Studied Drugs: The Open-Source Living DiAna Dictionary for Standardizing Drug Names in the FAERS. Drug Saf 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.A.; Russo, G.; Sorbara, E.E.; Cicala, G.; Franchina, T.; Santarpia, M.; Speranza, D.; Spina, E.; Silvestris, N. Neuropsychiatric Adverse Drug Reactions with Oral Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An Analysis from the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System. Front Oncol 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Barbieri, M.A.; Sorbara, E.E.; Cicala, G.; Franchina, T.; Santarpia, M.; Silvestris, N.; Spina, E. Renal Disorders with Oral Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An Analysis from the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicala, G.; Barbieri, M.A.; Russo, G.; Salvo, F.; Spina, E. Safety of Dual Orexin Receptor Antagonist Daridorexant: A Disproportionality Analysis of Publicly Available FAERS Data. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raschi, E.; Fusaroli, M.; Giunchi, V.; Repaci, A.; Pelusi, C.; Mollica, V.; Massari, F.; Ardizzoni, A.; Poluzzi, E.; Pagotto, U.; et al. Adrenal Insufficiency with Anticancer Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor: Analysis of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14, 4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, E.G.; Wood, L.; Wood, S. The Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA). Drug Saf 1999, 20, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaleel, M.A.; Khan, A.H.; Ghadzi, S.M.S.; Adnan, A.S.; Abdallah, Q.M. A Standardized Dataset of a Spontaneous Adverse Event Reporting System. Healthcare 2022, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RStudio Team RStudio: Integrated Development for R 2019.
- Foundation for Statistical Computing, R. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing Available online: https://www.R-project.org/.
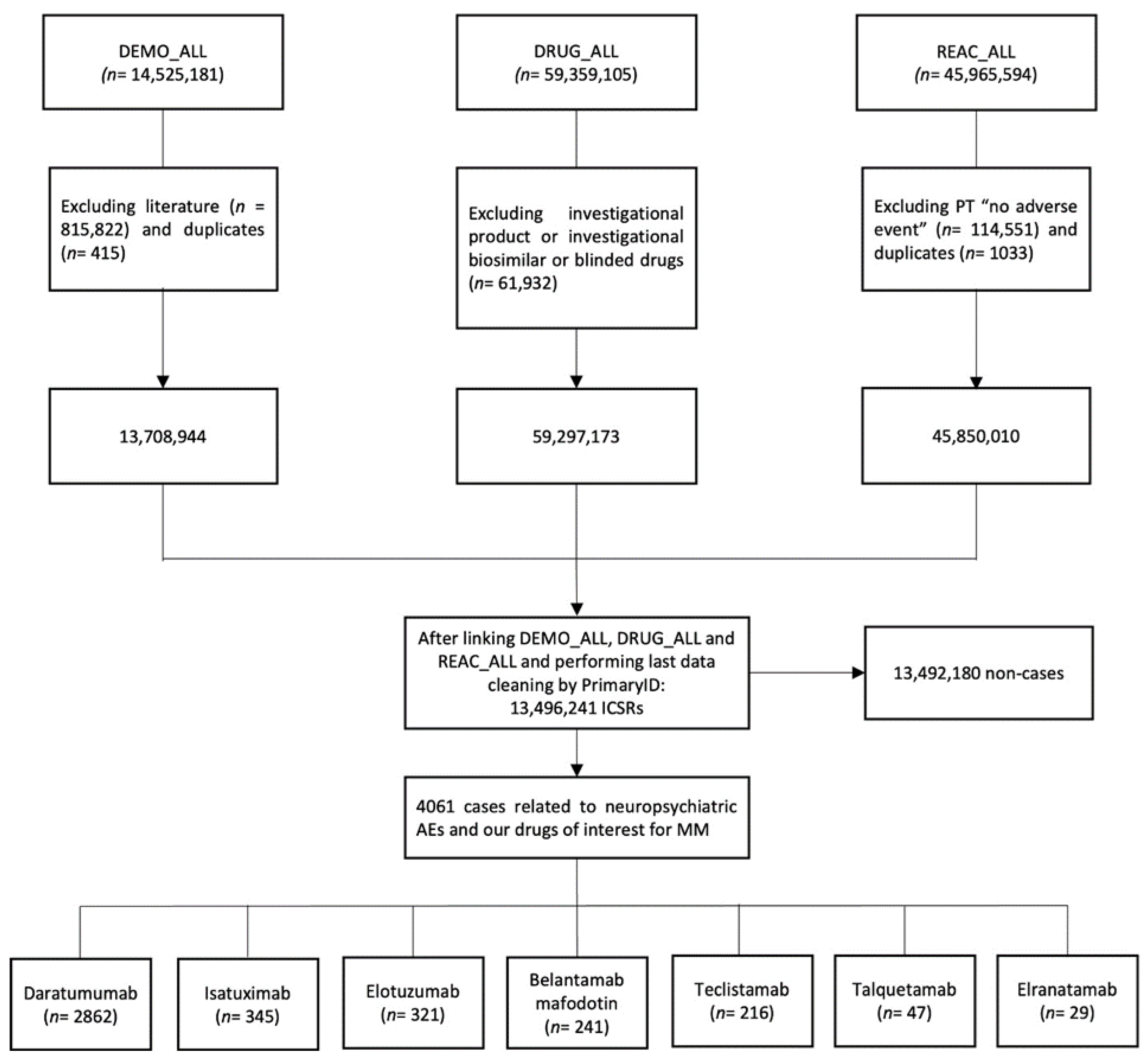
| Characteristic | Neuropsychiatric cases (n= 4061) |
Non-cases (n= 13,492,180) |
Total (n=13,496,241) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age group, n (%) | |||
| Neonate | 3 (<0.1%) | 39,379 (0.3%) | 39,382 (0.3%) |
| Infants | 15,400 (0.1%) | 15,400 (0.1%) | |
| Child | 7 (0.2%) | 150,436 (1.1%) | 150,443 (1.1%) |
| Adolescent | 10 (0.3%) | 196,410 (1.5%) | 196,420 (1.5%) |
| Adult | 1006 (24.8%) | 4,157,969 (30.8%) | 4,158,975 (30.8%) |
| Elderly | 1947 (47.9%) | 2,895,017 (21.5%) | 2,896,964 (21.5%) |
| Not available | 1088 (26.8%) | 6,037,569 (44.8%) | 6,038,657 (44.7%) |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Female | 1588 (39.1%) | 7,145,404 (53.0%) | 7,146,992 (53.0%) |
| Male | 1849 (45.5%) | 4,670,150 (34.6%) | 4,671,999 (34.6%) |
| Not available | 624 (15.4%) | 1,676,626 (12.4%) | 1,677,250 (12.4%) |
| Primary source qualification, n (%) | |||
| Consumers | 580 (14.3%) | 6,659,308 (49.4%) | 6,659,888 (49.4%) |
| Health professional | 685 (16.9%) | 1,185,741 (8.8%) | 1,186,426 (8.8%) |
| Physician | 2114 (52.1%) | 2,801,856 (20.8%) | 2,803,970 (20.8%) |
| Other health-professional | 352 (8.7%) | 1,140,098 (8.5%) | 1,140,450 (8.5%) |
| Pharmacist | 312 (7.7%) | 884,427 (6.6%) | 884,739 (6.6%) |
| Lawyer | 502,463 (3.7%) | 502,463 (3.7%) | |
| Not available | 18 (0.4%) | 318,287 (2.4%) | 318,305 (2.4%) |
| Outcome codification, n (%) | |||
| Death | 351 (8.6%) | 780,158 (5.8%) | 780,509 (5.8%) |
| Disability | 69 (1.7%) | 147,322 (1.1%) | 147,391 (1.1%) |
| Hospitalization - Initial or prolonged | 1397 (34.4%) | 2,090,657 (15.5%) | 2,092,054 (15.5%) |
| Life-threatening | 112 (2.8%) | 143,135 (1.1%) | 143,247 (1.1%) |
| Other serious (Important Medical Event) | 1801 (44.4%) | 4,233,022 (31.4%) | 4,234,823 (31.4%) |
| Required intervention to prevent permanent impairment/damage | 5 (0.1%) | 12,674 (0.1%) | 12,679 (0.1%) |
| Congenital anomaly | 21,535 (0.2%) | 21,535 (0.2%) | |
| Not available | 326 (8.0%) | 6,063,677 (44.9%) | 6,064,003 (44.9%) |
| Reporter Country, n (%) | |||
| Africa | 19 (0.5%) | 37,622 (0.3%) | 37,641 (0.3%) |
| Asia | 635 (15.6%) | 667,858 (5.0%) | 668,493 (5.0%) |
| Central America | 18 (0.4%) | 28,633 (0.2%) | 28,651 (0.2%) |
| Europe | 1668 (41.1%) | 1,749,620 (13.0%) | 1,751,288 (13.0%) |
| North America | 1414 (34.8%) | 10,100,868 (74.9%) | 10,102,282 (74.9%) |
| Oceania | 77 (1.9%) | 95,927 (0.7%) | 96,004 (0.7%) |
| South America | 172 (4.2%) | 227,114 (1.7%) | 227,286 (1.7%) |
| Not available | 58 (1.4%) | 584,538 (4.3%) | 584,596 (4.3%) |
| Year of reporting, n (%) | |||
| 2015 | 17 (0.4%) | 1,239,483 (9.2%) | 1,239,500 (9.2%) |
| 2016 | 251 (6.2%) | 1,300,142 (9.6%) | 1,300,393 (9.6%) |
| 2017 | 250 (6.2%) | 1,356,259 (10.1%) | 1,356,509 (10.1%) |
| 2018 | 414 (10.2%) | 1,616,069 (12.0%) | 1,616,483 (12.0%) |
| 2019 | 471 (11.6%) | 1,628,852 (12.1%) | 1,629,323 (12.1%) |
| 2020 | 469 (11.6%) | 1,681,724 (12.5%) | 1,682,193 (12.5%) |
| 2021 | 535 (13.2%) | 1,706,194 (12.7%) | 1,706,729 (12.7%) |
| 2022 | 748 (18.4%) | 1,628,953 (12.1%) | 1,629,701 (12.1%) |
| 2023 | 906 (22.3%) | 1,334,504 (9.9%) | 1,335,410 (9.9%) |
| Median age (Q1–Q3), years | 69 (61 - 75) | 60 (44 - 71) | 60 (44 - 71) |
| Median weights (Q1–Q3), Kgs | 70 (60 - 85) | 73 (60 - 88) | 73 (60 - 88) |
| Daratumumab | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOC | PT | N | ROR (95%CI) | IC (IC025-IC075) | Expected in FDA Prescribing Information |
| Nervous system disorders | Neuropathy peripheral | 533 | 5.89 (5.4-6.42) | 2.64 (2.49-2.74) | Uk (peripheral sensory neuropathy) |
| Polyneuropathy | 189 | 17.74 (15.34-20.5) | 4.15 (3.91-4.32) | Uk (peripheral sensory neuropathy) | |
| Syncope | 145 | 1.66 (1.41-1.95) | 1.11 (0.83-1.31) | Yes | |
| Encephalopathy | 71 | 5.07 (4.01-6.41) | 2.48 (2.08-2.76) | Uk (posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome) | |
| Peripheral sensory neuropathy | 45 | 10.49 (7.81-14.08) | 3.45 (2.96-3.81) | Yes | |
| Cerebral infarction | 45 | 2.39 (1.79-3.21) | 1.54 (1.05-1.9) | No | |
| Depressed level of consciousness | 42 | 1.65 (1.22-2.24) | 1.12 (0.6-1.48) | No | |
| Ischaemic stroke | 33 | 2.24 (1.59-3.15) | 1.47 (0.89-1.88) | No | |
| Altered state of consciousness | 32 | 1.97 (1.39-2.78) | 1.32 (0.73-1.74) | No | |
| Presyncope | 32 | 1.42 (1-2.01) | 0.96 (0.37-1.37) | Yes | |
| Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome | 29 | 6.13 (4.25-8.84) | 2.74 (2.12-3.18) | Yes | |
| Nervous system disorder | 28 | 1.69 (1.16-2.45) | 1.15 (0.52-1.59) | Yes | |
| Partial seizures | 27 | 6.77 (4.63-9.89) | 2.87 (2.23-3.33) | No | |
| Leukoencephalopathy | 26 | 14.8 (10.04-21.84) | 3.93 (3.28-4.4) | Uk (posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome) | |
| Spinal cord compression | 23 | 6.48 (4.29-9.77) | 2.82 (2.12-3.31) | No | |
| Guillain-Barre syndrome | 23 | 6.42 (4.26-9.69) | 2.81 (2.11-3.3) | No | |
| Brain oedema | 20 | 2.51 (1.62-3.9) | 1.62 (0.87-2.14) | Uk (peripheral oedema) | |
| Facial paralysis | 19 | 1.6 (1.02-2.52) | 1.1 (0.33-1.64) | Uk (peripheral sensory neuropathy) | |
| Peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy | 18 | 22.42 (14.02-35.85) | 4.51 (3.72-5.07) | Uk (peripheral sensory neuropathy) | |
| ICANS | 18 | 5.36 (3.37-8.53) | 2.58 (1.79-3.13) | No | |
| Neurotoxicity | 17 | 1.69 (1.05-2.72) | 1.16 (0.35-1.73) | No | |
| Peripheral motor neuropathy | 14 | 14.48 (8.53-24.58) | 3.93 (3.02-4.55) | Uk (peripheral sensory neuropathy) | |
| Incoherent | 12 | 2.61 (1.48-4.61) | 1.68 (0.71-2.35) | No | |
| Orthostatic intolerance | 10 | 12.54 (6.71-23.43) | 3.75 (2.67-4.48) | No | |
| Stupor | 8 | 4.48 (2.23-8.98) | 2.39 (1.18-3.19) | No | |
| Senile dementia | 6 | 10.24 (4.57-22.93) | 3.52 (2.1-4.43) | No | |
| Intracranial mass | 6 | 4.61 (2.07-10.3) | 2.45 (1.04-3.36) | No | |
| Cytotoxic oedema | 5 | 41.17 (16.71-101.45) | 5.44 (3.88-6.42) | Uk (peripheral oedema) | |
| Allodynia | 5 | 8.64 (3.57-20.86) | 3.31 (1.74-4.29) | Uk (nerve damage causing tingling, numbness or pain) | |
| Hyperammonaemic encephalopathy | 5 | 7.57 (3.13-18.26) | 3.13 (1.57-4.11) | Uk (posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome) | |
| Paraparesis | 5 | 3.69 (1.53-8.89) | 2.18 (0.62-3.17) | Uk (peripheral sensory neuropathy) | |
| Pleocytosis | 4 | 11.42 (4.25-30.68) | 3.72 (1.95-4.8) | No | |
| VIth nerve paralysis | 4 | 6.48 (2.42-17.35) | 2.95 (1.19-4.03) | Uk (nerve damage causing tingling, numbness or pain) | |
| Cerebellar haemorrhage | 4 | 3.04 (1.14-8.11) | 1.97 (0.2-3.04) | No | |
| Loss of proprioception | 3 | 12.5 (3.99-39.14) | 3.89 (1.82-5.1) | No | |
| Cerebellar haematoma | 3 | 11.42 (3.65-35.74) | 3.77 (1.7-4.98) | No | |
| Toxic neuropathy | 3 | 10.67 (3.41-33.38) | 3.68 (1.61-4.88) | Uk (peripheral sensory neuropathy) | |
| Autonomic neuropathy | 3 | 3.93 (1.26-12.21) | 2.34 (0.27-3.55) | Uk (peripheral sensory neuropathy) | |
| Psychiatric disorders | Delirium | 54 | 2.29 (1.75-2.99) | 1.49 (1.04-1.81) | No |
| Mental status changes | 40 | 2.66 (1.95-3.63) | 1.67 (1.14-2.04) | No | |
| Body dysmorphic disorder | 15 | 58.08 (34.3-98.33) | 5.81 (4.94-6.41) | No | |
| Anxiety disorder | 12 | 3.6 (2.04-6.35) | 2.08 (1.1-2.75) | Yes | |
| Belantamab Mafodotin | |||||
| SOC | PT | N | ROR (95%CI) | IC (IC025-IC075) | Expected in FDA Prescribing Information |
| Nervous system disorders | Neuropathy peripheral | 38 | 2.62 (1.9-3.61) | 1.65 (1.11-2.03) | No |
| Altered state of consciousness | 6 | 2.35 (1.05-5.23) | 1.6 (0.19-2.52) | No | |
| Muscle tone disorder | 4 | 59.56 (22.19-159.81) | 6.06 (4.29-7.14) | No | |
| Bell's palsy | 3 | 12.77 (4.11-39.68) | 3.94 (1.87-5.15) | No | |
| Neurological decompensation | 3 | 12.49 (4.02-38.8) | 3.91 (1.84-5.12) | No | |
| Psychiatric disorders | Mental status changes | 10 | 4.23 (2.28-7.88) | 2.3 (1.22-3.03) | No |
| Elranatamab | |||||
| SOC | PT | N | ROR (95%CI) | IC (IC025-IC075) | Expected in FDA Prescribing Information |
| Nervous system disorders | Altered state of consciousness | 3 | 20.7 (6.61-64.83) | 4.6 (2.53-5.81) | Yes |
| Syncope | 3 | 3.82 (1.22-11.98) | 2.29 (0.22-3.5) | Uk (depressed level of consciousness) | |
| Neuropathy peripheral | 3 | 3.6 (1.15-11.28) | 2.22 (0.15-3.42) | Yes | |
| Isatuximab | |||||
| SOC | PT | N | ROR (95%CI) | IC (IC025-IC075) | Expected in FDA Prescribing Information |
| Nervous system disorders | Polyneuropathy | 21 | 9.26 (6.03-14.22) | 3.31 (2.58-3.82) | No |
| Transient ischaemic attack | 17 | 3.37 (2.09-5.42) | 1.98 (1.17-2.55) | No | |
| Ischaemic stroke | 14 | 4.59 (2.71-7.75) | 2.39 (1.48-3.01) | No | |
| Peripheral sensory neuropathy | 11 | 12.23 (6.76-22.13) | 3.72 (2.7-4.42) | No | |
| Cerebral infarction | 10 | 2.56 (1.38-4.76) | 1.67 (0.59-2.4) | No | |
| Cerebral ischaemia | 9 | 12.64 (6.56-24.34) | 3.78 (2.64-4.54) | No | |
| Guillain-Barre syndrome | 8 | 10.72 (5.35-21.48) | 3.57 (2.35-4.37) | No | |
| Haemorrhage intracranial | 7 | 2.76 (1.31-5.79) | 1.79 (0.48-2.64) | No | |
| Basal ganglia infarction | 6 | 132.39 (58.54-299.42) | 7.11 (5.7-8.02) | No | |
| Peripheral motor neuropathy | 6 | 29.61 (13.25-66.18) | 5.01 (3.6-5.92) | No | |
| Subarachnoid haemorrhage | 5 | 2.95 (1.23-7.09) | 1.9 (0.34-2.89) | No | |
| Acute motor-sensory axonal neuropathy | 4 | 93.02 (34.43-251.26) | 6.68 (4.91-7.76) | No | |
| Meningoradiculitis | 3 | 179.87 (56.31-574.58) | 7.64 (5.57-8.85) | No | |
| Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy | 3 | 11.95 (3.84-37.14) | 3.85 (1.78-5.05) | No | |
| Psychiatric disorders | Acute psychosis | 3 | 8.8 (2.83-27.34) | 3.42 (1.36-4.63) | No |
| Talquetamab | |||||
| SOC | PT | N | ROR (95%CI) | IC (IC025-IC075) | Expected in FDA Prescribing Information |
| Nervous system disorders | Dysgeusia | 13 | 17.71 (10.11-31.02) | 4.16 (3.22-4.8) | Yes |
| ICANS | 7 | 185.55 (87.3-394.35) | 7.59 (6.29-8.44) | Yes | |
| Taste disorder | 7 | 26.81 (12.63-56.93) | 4.82 (3.52-5.68) | Yes | |
| Ageusia | 5 | 18.81 (7.75-45.66) | 4.37 (2.81-5.36) | Yes | |
| Neurotoxicity | 3 | 26.11 (8.35-81.62) | 4.93 (2.86-6.14) | Yes | |
| Teclistamab | |||||
| SOC | PT | N | ROR (95%CI) | IC (IC025-IC075) | Expected in FDA Prescribing Information |
| Nervous system disorders | ICANS | 96 | 450.7 (364.76-556.89) | 8.66 (8.32-8.9) | Yes |
| Neurotoxicity | 22 | 31.49 (20.65-48.02) | 5 (4.29-5.51) | Yes | |
| Polyneuropathy | 5 | 6.45 (2.68-15.53) | 2.92 (1.36-3.91) | Yes | |
| Nervous system disorder | 5 | 4.27 (1.78-10.28) | 2.37 (0.81-3.36) | Yes | |
| Depressed level of consciousness | 5 | 2.79 (1.16-6.71) | 1.83 (0.27-2.82) | Yes | |
| Spinal cord compression | 4 | 15.87 (5.94-42.38) | 4.19 (2.43-5.27) | No | |
| Encephalopathy | 4 | 4.02 (1.51-10.72) | 2.32 (0.56-3.4) | Yes | |
| Unresponsive to stimuli | 4 | 3.44 (1.29-9.19) | 2.13 (0.36-3.21) | Uk (depressed level of consciousness) | |
| Psychiatric disorders | Mental status changes | 5 | 4.7 (1.95-11.31) | 2.5 (0.94-3.48) | Yes |
| Elotuzumab | |||||
| SOC | PT | N | ROR (95%CI) | IC (IC025-IC075) | Expected in FDA Prescribing Information |
| Nervous system disorders | Neuropathy peripheral | 41 | 2.52 (1.85-3.43) | 1.6 (1.08-1.97) | Yes |
| Syncope | 27 | 1.75 (1.2-2.56) | 1.19 (0.55-1.64) | No | |
| Cerebral infarction | 25 | 7.61 (5.13-11.28) | 3.03 (2.37-3.51) | No | |
| Cerebral haemorrhage | 12 | 2.27 (1.29-4) | 1.52 (0.54-2.18) | No | |
| Cerebrovascular disorder | 4 | 16.68 (6.24-44.56) | 4.26 (2.5-5.34) | No | |
| Clumsiness | 4 | 7.82 (2.93-20.86) | 3.21 (1.45-4.29) | Uk (peripheral motor neuropathy) | |
| Orthostatic intolerance | 4 | 28.31 (10.58-75.73) | 5 (3.24-6.08) | No | |
| VIth nerve paralysis | 4 | 36.99 (13.81-99.05) | 5.38 (3.62-6.46) | No | |
| Guillain-Barre syndrome | 3 | 4.74 (1.53-14.7) | 2.59 (0.52-3.8) | No | |
| Intention tremor | 3 | 49.87 (15.97-155.8) | 5.86 (3.79-7.06) | No | |
| Monoplegia | 3 | 4.55 (1.46-14.11) | 2.54 (0.47-3.74) | No | |
| Post herpetic neuralgia | 3 | 11.39 (3.67-35.39) | 3.78 (1.71-4.99) | Uk (herpes zoster) | |
| Spinal cord compression | 3 | 4.78 (1.54-14.83) | 2.6 (0.53-3.81) | No | |
| Toxic encephalopathy | 3 | 6.51 (2.1-20.22) | 3.01 (0.95-4.22) | No | |
| Psychiatric disorders | Delirium | 15 | 3.63 (2.18-6.02) | 2.08 (1.21-2.68) | Uk (mood altered) |
| Listless | 3 | 5.28 (1.7-16.38) | 2.73 (0.66-3.94) | No | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





