Introduction
Recently, there has been an increasing interest in biologically active compounds obtained from natural sources. Plant extracts are utilized in the food industry as preservatives and antioxidants, in cooking as flavoring agents, in cosmetology as components in skin care products, and in traditional medicine for their antidiabetic, antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, wound healing immunomodulatory or hemostatic. In addition, certain plant extracts are utilized in the biological hemostatic manufacturing of cellulose nanofibers, silver nanoparticles, and copper and zinc oxides as reducing or stabilizing agents [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Ginger, a rhizome of the Zingiber officinale plant, has been used for centuries in traditional medicine for its potential health benefits, such as assisting digestion and alleviating symptoms of stomach distress, including diarrhea and nausea. Additionally, it may be utilized to treat conditions such as arthritis, colic, and heart disorders [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. In recent years, researchers have investigated Ginger’s antibacterial properties [
10], as well as its phytochemical profile and GC-MS analysis [
11], to assess its potential as a natural remedy and alternative to conventional antibiotics.
A growing body of evidence suggests Ginger has antibacterial solid properties due to its rich chemical composition. In numerous studies, Ginger has been shown to inhibit the growth of many bacteria, including
Escherichia coli,
Staphylococcus aureus, and
Salmonella enterica. The active compounds in Ginger, such as gingerol, shogaol, and paradol, are believed to be responsible for these antibacterial effects [
12,
13,
14]. These compounds interact with bacterial cell membranes, disrupting their integrity and ultimately leading to cell death. Additionally, Ginger has been found to have a synergistic effect when combined with certain antibiotics, enhancing its efficacy against resistant strains of bacteria [
15].
Ginger is rich in phytochemicals and bioactive compounds found in plants linked to numerous health benefits [
16]. The rhizome contains some bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenolic acids. It has been demonstrated that these phytochemicals have anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and antioxidant qualities and anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties. Based on the Folin-Ciocalteu assay, the total polyphenol content of the Zingiber officinale rhizome extract was measured at 181.41 mg GAE/g of extract, with flavonoids accounting for 7.8% (14.15 mg quercetin/g of extract). [
17]. In addition to its antibacterial properties, Ginger has been found to contain phytochemicals with a wide range of health benefits. These compounds, including flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenolic acids, have been shown to possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties, making Ginger a potential superfood for promoting overall health and well-being.
Turmeric, cardamom, and galangal are other plants in the Zingiberaceae family. These plants share similar botanical characteristics and are widely used for culinary and medicinal purposes [
18]. The present study aims to comprehensively analyze ginger rhizome’s antibacterial, phytochemical, and GC-MS properties and explore its possible applications. The identified ginger phytochemicals have been assessed for their pharmacokinetic properties, binding activities, and molecular interactions with the TyrRS from
S. aureus and the aspartic proteinase from
C. albicans [
19]).
On a global scale, there is enormous concern about the potential decline of antibiotic efficacy due to the increasing prevalence of multi-drug-resistant bacteria. As a result, scientists are actively exploring different alternatives from many sources [
20]. The WHO has published a list of Critical and High-Priority clinical bacteria, including drug-resistant
Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and MRSA, among others, emphasizing the need for urgent action to control the rapid spread of these pathogens [
21,
22].
Regrettably, there is a scarcity of comprehensive data about the pharmacological qualities of Sudanese medicinal plants. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), “The Sudan Atlas of Medicinal Plants” documents more than 2,000 therapeutic plants. However, it is suspected that the current number of medicinal plants in use may exceed [
23]. Plant composition is well known to vary significantly depending on climate conditions [
24]. The climate in central Sudan is tropical, characterized by elevated humidity and precipitation levels.
Nevertheless, further study on Zingiber officinale rhizome is necessary.. Therefore, this study will provide a detailed insight into the various chemical constituents present in ginger rhizome cultivated in Sudan, along with their potential antibacterial effects and possible therapeutic uses using in vitro and computational assay on TyrRS from S. aureus (1JIJ) and aspartic proteinase from C. albicans (2QZW). The findings of this research will contribute to the global understanding of Ginger’s health benefits and support its widespread use in various medical and culinary applications.
Results
2.1. The Antibacterial Properties of Ginger Rhizome
The results of the antibacterial activity using the disc-diffusion method are shown in
Table 1; the In vitro testing revealed that the Sudanese Ginger aqueous extract exhibited moderate antibacterial activity against several bacteria, including
S. aureus, weak activity against
Sal. typhi and
K. Pneumoniae. The results indicated that the mean inhibition zone at the higher concentration of the extract (30 µg/disc) averaged 14.5±0.0 mm to 12.87±0.11 mm, while at the lower concentration, it averaged 11.0±0.1 mm to 6.33±0.33 mm. The evaluation of the sizes of inhibition zones was conducted based on the disc-diffusion test for bacteria, using the following criteria for assessing inhibitory zones: A diameter of 10 mm or less suggests low activity, a diameter between 10 and 15 mm represents moderate activity, and a diameter beyond 15 mm reflects vigorous activity [
25]
. Furthermore, the data showed that
S. aureus was the most highly inhibited bacteria by the Ginger extract.
S. aureus (Gram-positive) shows higher inhibition zones than other bacteria (Gram-negative) due to its thicker but more permeable peptidoglycan layer. In contrast, the gram-negative bacteria have an outer membrane that acts as an additional barrier, reducing antibacterial penetration and effectiveness [
26,
27]. Our results corroborate previous studies; it was reported that the aqueous extract of ginger rhizome has antibacterial activity against
E. coli and
Bacillus subtilis [
28]. It was reported that antibacterial effects were still observed after mixing soybean oil extract and ginger extract. This combination showed acceptable activity against 24 bacterial isolates belonging to six distinct types of foodborne pathogens:
E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus, Klebsiella spp.,
Vibrio cholerae, and
Salmonella spp. The range of inhibitory zones varied from 11.67±1.53 mm to 8.0±1.73 mm [
29]. Interestingly, the essential oils of the Ginger were reported to have high antibacterial activity, as was the diameter of the zone of inhibition against
S. aureus recorded 17.10 mm [
30].
The M.I.C. and M.B.C. results, crucial in determining the potency of the ginger extract, are presented in (
Table 2). These results align with the findings of the disc-diffusion test. Notably, the most susceptible bacterium was
S. typhyi (M.I.C.= 6.25 µg/mL, M.B.C.= 25 µg/mL), Possibly due to the unique bioactive compounds in the ginger extract that are particularly effective against cellular structures or metabolic processes. A previous study suggested that the antibacterial properties of Ginger are linked to the presence of bioactive compounds [
31].
S. aureus recorded (M.I.C.=6.25 µg/mL, M.B.C.= 50 µg/mL), Indicating that while the extract effectively inhibits bacterial growth at lower concentrations, higher concentrations are needed for bactericidal effects. The thicker peptidoglycan layer of Gram-positive bacteria like
S. aureus may necessitate a higher extract concentration for complete bacterial eradication [
32].
P. aeruginosa, E. coli, and K. pneumoniae exhibited similar levels of susceptibility with an M.I.C. of 25 µg/mL and an M.B.C. of 25 µg/mL. These Gram-negative bacteria have an outer membrane that provides an extra barrier to the extract, which could explain the higher M.I.C. and M.B.C. values compared to
S. aureus. However, as M.B.C. equals the M.I.C. for these bacteria, it suggests that the extract is equally effective at inhibiting and killing these pathogens once the threshold concentration is reached. The M.B.C./M.I.C. ratio, calculated for the time-kill assay, suggests that Ginger extract has bacteriostatic effects on
S. aureus and bactericidal effects on the other tested bacteria. This conclusion is drawn from the fact that the effect is classified as bactericidal if the ratio of M.B.C./M.I.C. is less than or equal to 4. Conversely, if the ratio was more significant than 4, the impact was categorized as bacteriostatic [
33]. Genetic Variation and Environmental Adaptation may influence this phenomenon.
2.2. Phytochemical Analysis
The provided excerpt presents the results of a phytochemical screening of ginger rhizome in
Table 3. The screening revealed the presence of various compounds in the ginger rhizome, specifically flavonoids, saponins, glycosides, alkaloids, and terpenoids. Interestingly, tannins were not found in the ginger rhizome. This information indicates the diverse array of phytochemicals in these plant parts, which could have implications for their potential uses in various applications such as traditional medicine or food science.
2.3. GC-MS Result
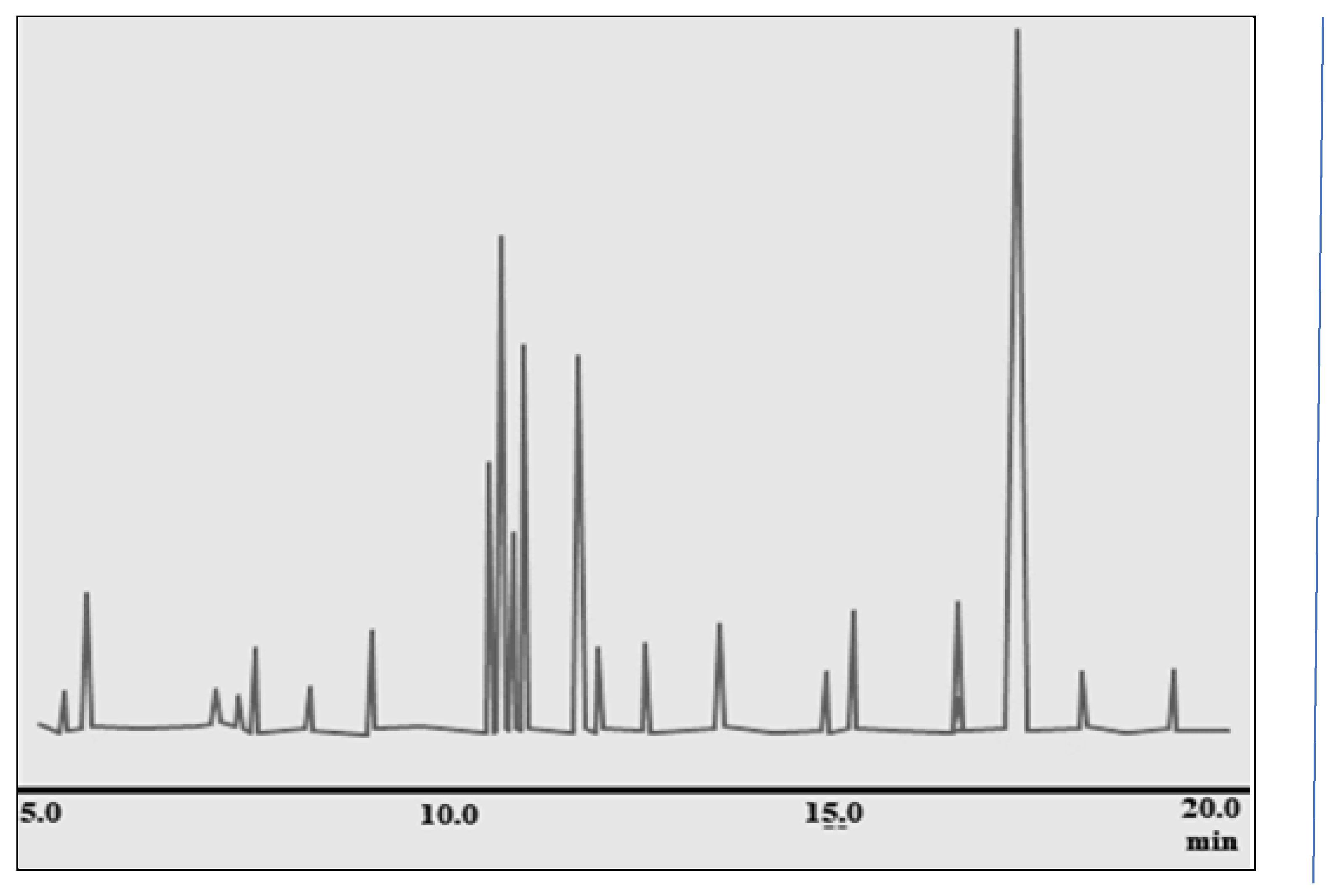
The GC-MS analysis of ginger rhizome revealed the presence of 22 different compounds, with gingerol being the most abundant at 41.30% concentration. Other significant compounds identified include Zingiberene (14.04%), β-D-glucopyranose, 4-O-beta-D-galactose (7.96%), Cyclohexane, 3-(1,5-dimethyl-4-hexenyl)- (6.69%), 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid (4.65%), β-bisabolene (3.44%), and Exo-2,7,7-trimethyl bicyclo [1,2] heptane-2-ol (2.39%). These compounds were distributed within a retention time range of 5.106 – 19.351 minutes, providing a comprehensive chemical profile of the ginger rhizome.
The dominance of gingerol in the composition of ginger rhizome is noteworthy, as it is a bioactive compound associated with various health benefits. Additionally, the presence of Zingiberene, β-D-glucopyranose, 4-O-beta-D-galactose, Cyclohexaene, 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, β-bisabolene, and Exo-2,7,7-trimethylbicyclo [1,2] heptan-2-ol contributes to the overall chemical complexity and potential pharmacological properties of Ginger. This analysis provides valuable insight into the chemical composition of ginger rhizome, offering a foundation for further research into its medicinal and culinary uses.
Figure 2.
GC-MS chromatogram of ginger (Z. officinale) rhizome.
Figure 2.
GC-MS chromatogram of ginger (Z. officinale) rhizome.
Table 4.
GC-MS of ginger (Z. officinale) rhizome.
Table 4.
GC-MS of ginger (Z. officinale) rhizome.
| Peak |
R. time |
Area% |
Compound name |
Mol. form. |
| 1 |
5.106 |
0.69 |
Dihydrocarvyl acetate |
C12H20O2
|
| 2 |
5.421 |
2.39 |
Exo-2,7,7-trimethylbicyclo [1,2]heptan-2-ol |
C10H18O |
| 3 |
7.079 |
1.62 |
isoborneol |
C10H18O |
| 4 |
7.335 |
0.57 |
Alpha-terpineol |
C10H18O |
| 5 |
7.516 |
1.41 |
Butanedioic acid, 2,3-bis(acetyloxy)-[R-(R |
C8H10O8
|
| 6 |
8.237 |
0.76 |
Benzeneethanamine, 2,5-dimethoxy- |
C11H17NO2
|
| 7 |
9.075 |
1.74 |
Phenol, 2-methoxy-3-(2-propenyl)- |
C10H12O2
|
| 8 |
10.546 |
4.65 |
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
C7H6O3
|
| 9 |
10.711 |
14.04 |
Zingiberene |
C15H24
|
| 10 |
10.860 |
3.44 |
β-bisabolene |
C15H24
|
| 11 |
11.001 |
6.69 |
Cyclohexaene, 3-(1,5-dimethyl-4-hexenyl)- |
C15H24
|
| 12 |
11.704 |
7.96 |
β-D-glucopyranose, 4-O-beta-D-galactose |
C12H22O11
|
| 13 |
11.973 |
1.44 |
Hydroxycinnamic acid |
C9H8O4
|
| 14 |
12.554 |
1.51 |
6,10-Dodecadien-1-yn-3-ol, 3,7,11-trimethyl- |
C15H24O |
| 15 |
13.503 |
1.87 |
Vanillin |
C8H8O4
|
| 16 |
14.894 |
1.02 |
2,4-bis(hydroxyamino)-5-nitropyrimidine |
C6H6N2O2S2
|
| 17 |
15.201 |
2.07 |
Docosanoic acid, ethyl ester |
C24H34O2
|
| 18 |
16.584 |
2.22 |
E-11-hexadecenoic acid, ethyl ester |
C18H34O2
|
| 19 |
16.892 |
0.57 |
1-(5-bicyclo [1,2] heptyl)ethylamine |
C9H17N |
| 20 |
17.309 |
41.30 |
Gingerol |
C17H26O4
|
| 21 |
18.130 |
0.99 |
Salicylic acid |
C7H6O3
|
| 22 |
19.351 |
1.05 |
Kaempferol |
C15H10O6
|
| Total |
100 |
|
|
2.4. Computational Modeling Results
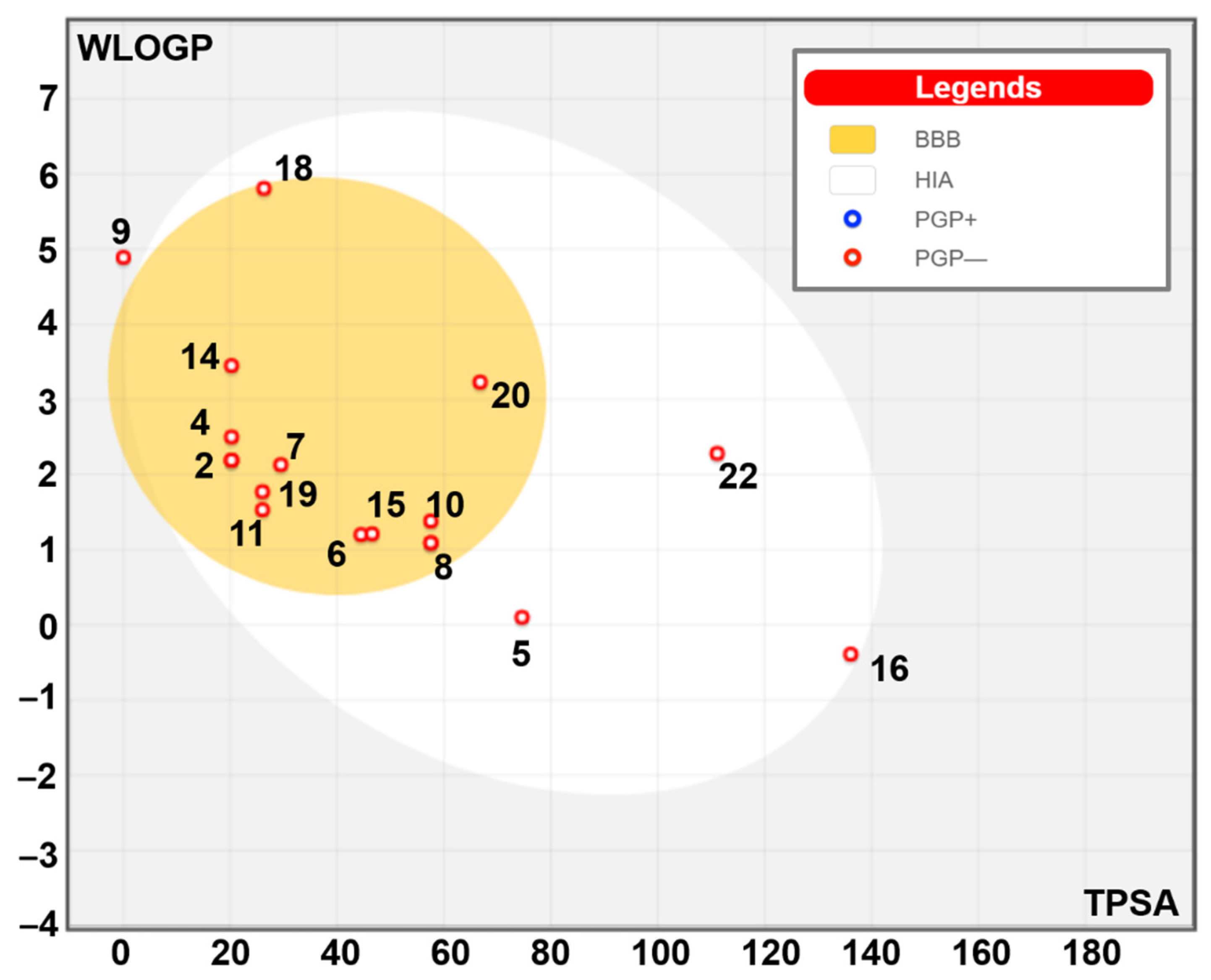
Table 5 shows the identified compounds’ lipophilicity, bioavailability, and pharmacokinetic properties based on the absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) properties. Our findings showed acceptable ADMET properties for most Ginger-identified compounds (
Figure 3). Most of the latter did not inhibit the five assessed cytochrome P450 (C.Y.P.s) isoforms (1A2, 2C19, 2C9, 2D6, and 3A4) and possessed good oral bioavailability. Furthermore, all the Ginger-identified compounds obeyed the Lipinski rule. They were predicted not to be substrates of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), which means there will be no disruption of distribution and metabolism. The synthetic accessibility varied between 1 and 4.81, which indicates that these compounds are easy to synthesize. Ginger compounds bound TyrRS from
S. aureus (1JIJ) and aspartic proteinase from
C. albicans (2QZW) with acceptable affinities (from −4.5 to −9.5 kcal/mol) (
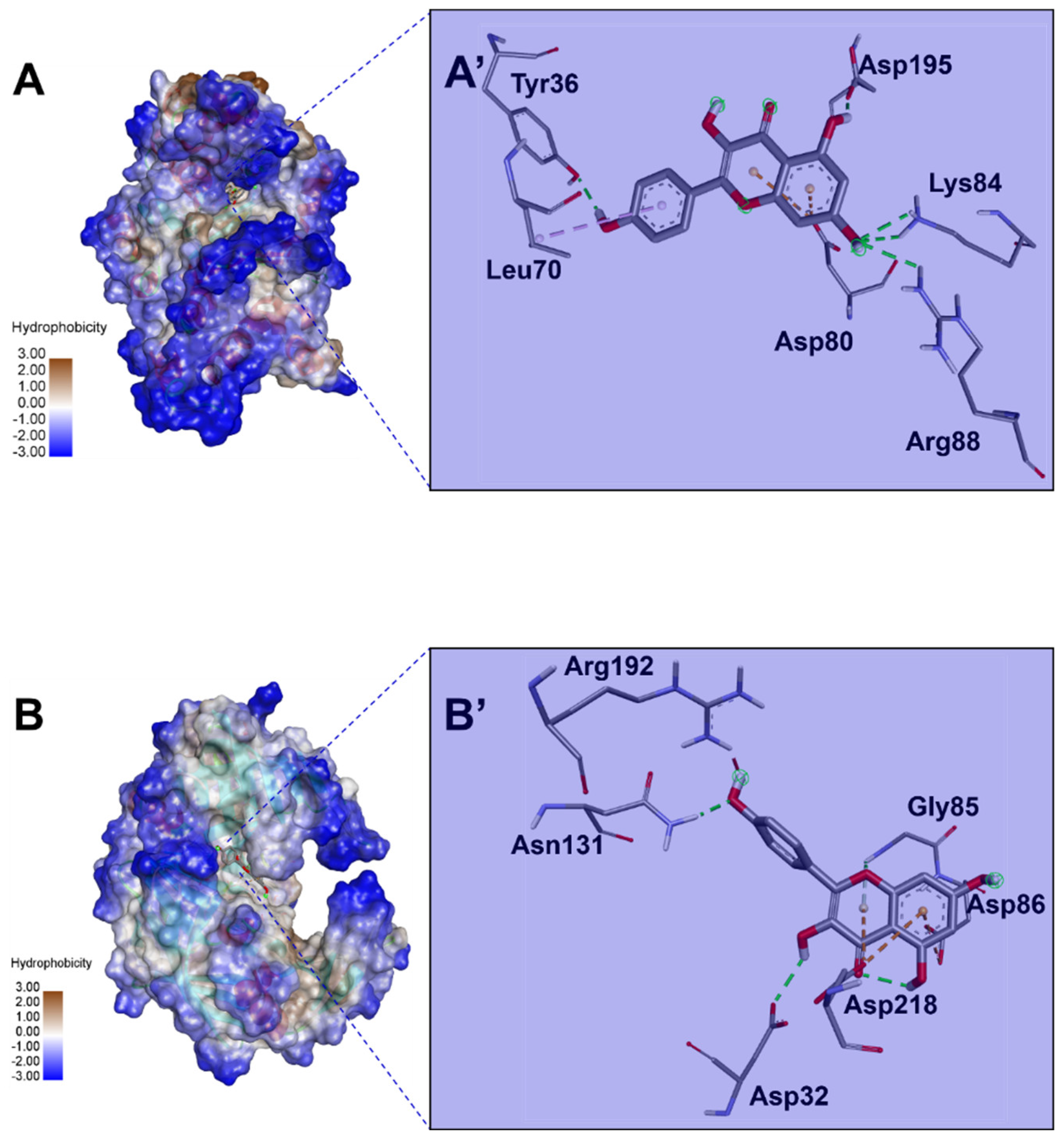
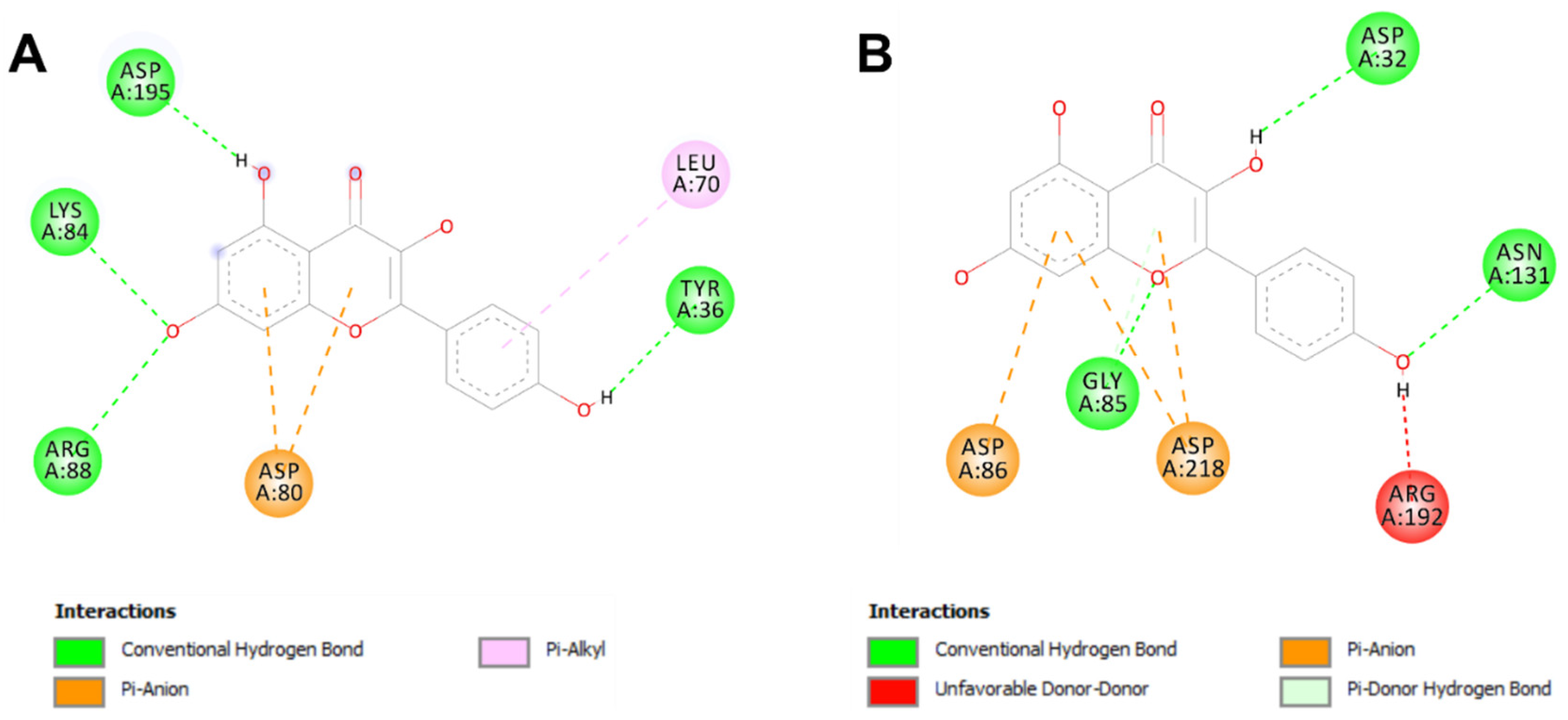
Table 6). All the 22 ginger-identified compounds had negative binding affinities that support their potential bioactivities. The compound no. 22 had negative affinities of −9.5 kcal/mol for 1JIJ and −7.5 kcal/mol. The compounds with the best scores (no. 22, 20, 16, and 9) were further analyzed for bond category, molecular interactions, and deep embedding, as shown in
Table 7 and
Figure 4. These compounds established good molecular interactions with 1JIJ and 2QZW (
Table 6,
Figure 5).
The molecular interactions included conventional H-bonds associated with a network of electrostatic and hydrophobic bonds. Taken together, the computational modeling analyses showed that the antimicrobial effects of ginger phytochemicals are thermodynamically possible. These antimicrobial effects had already been reported in the current study using in vitro analyses.
Discussion
The present study aims to comprehensively analyze ginger rhizome’s antibacterial, phytochemical, and GC-MS properties and explore its possible applications. This study provided a detailed insight into the various chemical constituents present in the ginger rhizome, their potential antibacterial effects, and possible therapeutic uses. The findings of this research will contribute to the global understanding of Ginger’s health benefits and support its widespread use in various medical and culinary applications.
3.1. Antibacterial Properties
The ginger extract exhibited varying levels of effectiveness against different bacteria, with M.I.C. values ranging from 6.25 to 50 µg/mL. The extract demonstrated bacteriostatic activity against S. aureus and P. aeruginosa while displaying bactericidal action against K. pneumoniae and E. coli. These findings indicate the potential of the ginger extract as a source of antibacterial agents, which can inhibit and kill certain pathogenic microorganisms. The M.B.C./M.I.C. ratio is greater than or equal to 4 for the latter two bacteria, further supporting the bactericidal nature of the extract’s action. This information contributes to the understanding of the potential antimicrobial properties of Ginger and its potential applications in developing new antibacterial agents.
In previous studies, Ginger has been shown to inhibit the growth of various bacteria, including
E. coli and
S. aureus, and
Salmonella enterica [
34]. The active compounds in Ginger, such as gingerol, shogaol, and paradol, are believed to be responsible for these antibacterial effects [
35,
36]. These compounds interact with bacterial cell membranes, disrupting their integrity and ultimately leading to bacterial death. Additionally, Ginger has been found to have a synergistic effect when combined with certain antibiotics, enhancing their efficacy against resistant strains of bacteria [
37].
Numerous researchers have reached the consensus that
Zingiber officinale exhibits exceptional antimicrobial properties. However, they attributed these properties to naphthalenamine, decanal, alpha-copaene, and numerous other chemical constituents [
38,
39,
40]. On the other hand, Shareef et al. [
41], utilized the diffusion method on agar to evaluate the in vitro antibacterial activity of a methanolic extract containing bioactive compounds from
Zingiber officinale against
Proteus mirabilis, E. coli, P. aerogenosa, Stap. aureus, and
K. pneumonia. Inhibitory zones were compared to those of various standard antibiotics. All regimens’ inhibition zone diameters varied between 4.93±0.290 and 0.89±0.210 mm.
Overall, the antibacterial study demonstrated that Ginger aqueous extract possesses significant in vitro antibacterial activity against the tested bacteria. As indicated in the tables, the results highlighted dose dependent inhibition zones. In fact, higher concentrations generally resulted in larger inhibition zones. Moreover, the specific impact of the ginger extract on S. aureus, the most highly inhibited bacteria, underscores its potential as an effective antibacterial agent. These findings contribute to understanding Ginger’s medicinal properties and its potential application in combating bacterial infections.
3.2. Phytochemical Properties
The phytochemical analysis showed that Ginge rhizome revealed the presence of various compounds in the ginger rhizome. Our findings were from other investigators who found that Ginger is also rich in phytochemicals, which are bioactive compounds in plants associated with numerous health benefits. The Sudanese rhizome contains many bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenolic acids. These phytochemicals have been shown to possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties, among others. In particular, ginger flavonoids, such as quercetin and kaempferol, have been extensively studied for their potential to combat various diseases [
42,
43]. Compared to other studies, Thakor
et al. [
44] found that the qualitative examination of phytochemicals revealed the presence of saponins, alkaloids, flavonoids, and steroids in ginger extracts. Ginger in acetone had the best antibacterial activity against
Escherichia coli MTCC 334 with 24 mm of clear zone, whereas ginger in methanol had the lowest activity against Bacillus subtilis MTCC 441 with 10 mm of clear zone.
The presence of phenols and tannins, alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenoids, sterols, cardiac glycosides, and saponins in the extracts has various implications across different fields. For example, phenols and tannins are known for their antioxidant properties and are often associated with potential health benefits. Alkaloids are present in many medicinal plants and have various pharmacological effects. They belong to a class of naturally occurring compounds with various pharmacological properties. Plant-based natural compounds, such as alkaloids, have shown promise as preventive measures against chronic inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases (N.D.D.s) (Aryal et al. 2022)[
43].
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory qualities are well-known for flavonoids [
9,
10]. Many health advantages are associated with flavonoids, such as their antiviral, anticancer, and antioxidant qualities. They also have cardio- and neuroprotective properties.
The potential of terpenoids as antibacterial and anticancer agents has been investigated. In the pharmaceutical business, steroids are crucial for the synthesis of medications like corticosteroids [
45]. For many years, cardiac glycosides have been prescribed as medications to treat arrhythmias and heart failure. The principal mechanism of action of these substances is their inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPase (NKA), which controls the intracellular concentration of calcium ions and sodium and potassium ions. These changes in the intracellular concentration of Ca2+ result in a positive inotropic effect on the heart muscle, for which they are used in the indications above [
46,
47].
Research has been done on saponins’ potential as antifungal and anticancer drugs. Consequently, the presence of these chemicals in the extract points to possible industrial, medical, and pharmacological uses. High structural diversity in saponins is associated with their anticancer properties. Numerous studies have demonstrated the role of saponins in cancer and their mechanism of action, including antioxidant activity, suppression of cellular invasion, cell-cycle arrest, induction of autophagy, and apoptosis. There are currently no known FDA-approved saponin-based anticancer medications despite the substantial anticancer properties of saponins and their vast research. Numerous restrictions, such as toxicities and drug-like qualities, can be blamed for this [
48]. The antibacterial properties of Sudanese ginger are linked to its phytochemical composition, which can be influenced by environmental factors like climate. Temperature, sunlight, and rainfall are crucial in this regard, with plants in warmer climates typically producing higher levels of secondary metabolites [
49].
This brief passage highlights the importance of phytochemical screening in identifying the chemical composition of plant materials. Overall, ginger rhizomes exhibit a diverse array of bioactive compounds, which could have implications for their potential uses in various applications, such as traditional medicine or food science.
3.3. The GC-MS Constituents
The GC-MS analysis of Sudanese ginger rhizome identified 22 various compounds, including two terpenoids (Zingiberene and β-bisabolene), three N-containing compounds (Benzeneethanamine, 2,5-dimethoxy-, 2,4-bis (hydroxyamino)-5-nitropyrimidine, and 1-(5-bicyclo[
2,
2,
1]heptyl)ethylamine), one phenolic compound (Phenol, 2-methoxy-3-(2-propenyl)-), and two esters (Docosanoic acid, ethyl ester, and E-11-hexadecenoic acid, ethyl ester). The concentrations of the main constituents were as follows: gingerol at 41.30%, Zingiberene at 14.04%, β-D-glucopyranose, 4-O-beta-D-galactose at 7.96%, Cyclohexane, 3-(1,5-dimethyl-4-hexenyl)- at 6.69%, 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid at 4.65%, β-bisabolene at 3.44%, and Exo-2,7,7-trimethyl bicyclo [
2,
2,
1] heptane-2-ol at 2.39%.
The GC-MS analysis of ginger rhizome did not detect any Cl-containing compounds. The GC-MS analysis of ginger rhizome identified several key compounds, with gingerol being the most abundant. Various other compounds within the rhizome further enhance its potential for pharmaceutical and therapeutic applications. This comprehensive chemical profiling is essential for understanding Ginger’s biological activities and potential health benefits, paving the way for its utilization in various fields, including medicine, nutrition, and natural product development. Compared to earlier research, Ginger essential oil had 45 phytochemical components, with Geranial, 1,8-Cineole, Neral, Camphene, α-Zingiberene, and α-Farnesene being the most abundant [
50].
As a frequent condiment or essential spice in food and drink, Ginger is widely used. Zingerone, shogaols, gingerols, paradols, wikstromol, and carinol were found to be the main constituents of the pungent compounds, according to GC-MS analysis [
51,
52]. By steam distillation, the volatile chemicals that give Ginger its flavor have been removed. According to the data, more than 90 components were discovered and separated. The most prevalent chemical found was zinziberene. According to Jedli et al. [
53], chemical investigations on ginger-based dietary supplements showed the presence of gingerols, shogaols, parasols, and gingerdiones.
Dafaalla [
54] identified twenty-two distinct components from ginger rhizome’s hexane extraction, and the primary constituent was the alkaloid gingerol (18%).
Furthermore, the GC-MS analysis revealed a diverse array of chemical compounds present in the Argel leaves. The compounds identified belong to various chemical classes, including alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, furans, acids, esters, etc. Additionally, the area percentages of the identified compounds provide insights into their relative abundance within the sample. For instance, the relatively high area percentage of 3-Pentanol,2,2,4,4-tetramethyl- suggests its significant presence in the Argel leaves, while compounds with lower area percentages may be in smaller quantities. The comprehensive nature of the analysis and the diverse range of identified compounds underscore the complex chemical composition of Argel leaves, shedding light on their potential pharmacological and therapeutic properties.
3.4. Computational Modeling Results
Table 7 shows the lipophilicity, bioavailability, and pharmacokinetic properties of the identified compounds based on the absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) properties. Our findings showed acceptable ADMET properties for most of the ginger-identified compounds. Most of the latter did not inhibit the five assessed cytochrome P450 (C.Y.P.s) isoforms (1A2, 2C19, 2C9, 2D6, and 3A4) and possessed good oral bioavailability (
Table 7). These predictions have been confirmed by the mapped boiled egg model (
Figure 3) and supported the high gastrointestinal (G.I.) absorption and the blood-brain-barrier (B.B.B.) permeation. The skin absorption varied between 0 and 136, which means low to high permeation [
55,
56]. Furthermore, all the Ginger-identified compounds obeyed the Lipinski rule. They were predicted not to be P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrates, which means there will be no disruption of distribution and metabolism [
55,
56]. The synthetic accessibility varied between 1 and 4.81, which indicates that these compounds are easy to synthesize [
55,
56].
Ginger compounds bound TyrRS from
S. aureus (1JIJ) and aspartic proteinase from
C. albicans (2QZW) with acceptable affinities (from −4.5 to −9.5 kcal/mol) (
Table 5). Recently, it has been shown that binding affinities depend mainly on the ligands’ 3D chemical structure and structural geometry [
57,
58]. All the 22 ginger-identified compounds had negative binding affinities that support their potential bioactivities. The compound no. 22 had negative affinities of −9.5 kcal/mol for 1JIJ and −7.5 kcal/mol. The compounds with the best scores (no. 22, 20, 16, and 9) were further analyzed for bond category, molecular interactions, and deep embedding (see
Table 7). These compounds established good molecular interactions with 1JIJ and 2QZW (
Table 6).
The molecular interactions included conventional H-bonds associated with a network of electrostatic and hydrophobic bonds. As previously described, this network contributes to the stability of the ligand-receptor complex [
59,
60]. These interactions involved several key residues and deep embedding (<2.5 Å). Tight embedding is commonly associated with potential biological effects, including anti-inflammatory, antiproliferative, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects [
55,
56]. Previous studies outlined several benefits of ginger compounds. Nevertheless, our GC-MS phytochemical composition, as reported in
Table 4, is different and might have particular outcomes. In fact, such combination might resulted in particular antimicrobial findings. In this context, beneficial effects can be greater than the sum of the individual effect of each ginger identified compound [
35,
57]. Taken together, the computational modeling analyses showed that the antimicrobial effects of ginger phytochemicals are thermodynamically possible. These antimicrobial effects had already been reported in the current study using in vitro analyses. These results confirmed the health promotion and promising benefits of natural-derived compounds and their phytotherapeutic potential, especially the ginger rhizome.
Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
All the chemicals employed in the study were of analytical grade. These chemicals and indicators were utilized in their original state without any purification processes, and were procured from Merck (Merck®, USA).
4.1. Samples Collection and Preparation
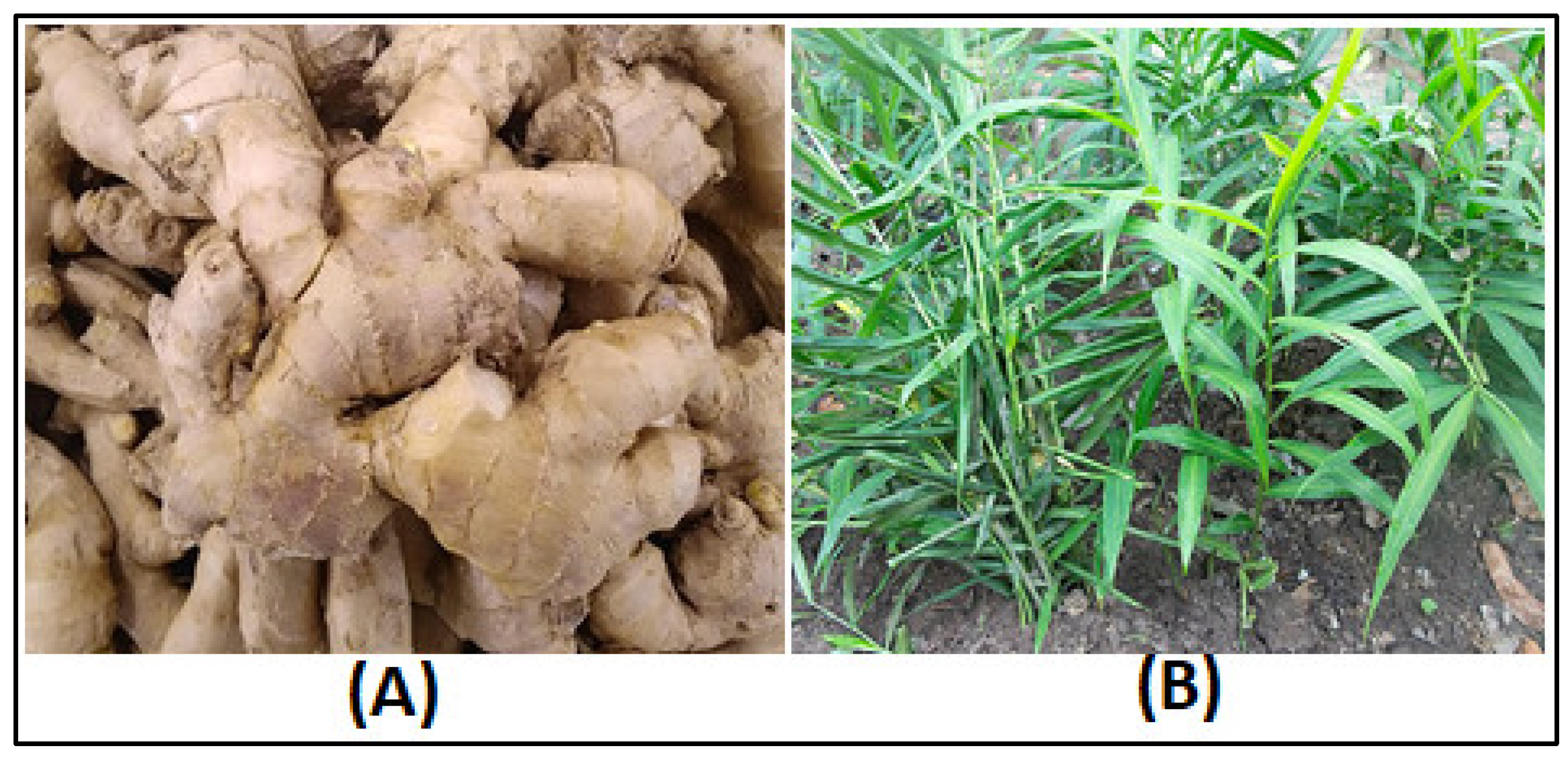
The ginger rhizomes of (Zingiber officinale) as shown in figure (1) used in this investigation were obtained from the local markets of Wad-Medani town (located in Central Sudan) on 15 April 2022 at the geographical coordinates Latitude: 14.39795320, Longitude: 33.52513160, and Elevation: 411.46 m. Afterwards, the specimens were sent to the Central Laboratories of the University of Gezira. The identification technique followed a rigorous and systematic approach, which included conducting morphological analysis utilizing identification keys and referring to herbarium records from the Gezira University Herbarium. Dr. Mutaman Ali Abdelgadir Kehail from the College of Sciences recognized the rhizomes and given them a voucher number, Keh-15APR2022-GeziraUniv-Sudan. The rhizomes were washed with flowing distilled water, left to air-dry at room temperature for 48, and then crushed into fine powder using a blender. To perform the ethanolic extraction, 100 grams of finely powdered ginger rhizomes were placed in an orbital shaker incubator at room temperature. They were shaken regularly in 1000 mL of 80% ethanol for several days. The ethanolic extract was concentrated using a rotary evaporator (8 kW, 50 L, Henan Lanphan Industry Co., Ltd, Zhengzhou, China). The obtained solution was then filtered through filter paper, and the extract was dried on a glass Petri dish at room temperature. The powdered ginger extract was used for phytochemical screening and GC/MS analysis.
4.2. Phytochemical Screening
A conventional analytical method suggested by Banso and Adeyemo in [
61] were used for qualitative phytochemical analysis to determine for the presence of phenols and tannins, alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenoids, sterols, cardiac glycosides, and saponins in ethanol and aqueous ginger rhizomes extracts. These methods are established protocols for chemical analysis and are widely recognized in the scientific community for their reliability and accuracy in identifying the presence of specific compounds in extracts. By following these methods, researchers can ensure the credibility and reproducibility of their findings, as well as gain valuable insights into the potential uses and properties of the analyzed compounds. The compounds analyzed include a wide range of chemical classes, each with its own significance in various fields such as pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and environmental studies. This comprehensive approach to chemical analysis aims to identify the presence of key compounds in the extracts, providing valuable insights into their potential uses and properties [
59,
60]. For qualitative phytochemical analysis, 0.5 g of ginger rhizomes extracts was diluted in 100 mL each of ethanol and water to provide a stock solution concentration of 5 mg/ mL.
4.3. GC-MS Analysis
0.1 g of the extract was dissolved in 10 mL of analytical-grade ethanol. The solution was then passed through a 0.45 mm syringe filter and into a 1.5 mL vial, where it was prepared for injection into GC-MS. The samples were analyzed using GC-MS at the Central Laboratories of the University of Gezira. The GC-MS analysis identified various chemical constituents present in the extract, providing detailed information such as their retention time, base peak, molecular weight, molecular formula, and compound names. The NIST 14S library was utilized to identify the compounds detected in the samples.
The conditions of analysis are as follows:
This analytical approach allowed for the comprehensive characterization of the chemical composition of the ginger rhizome extract. The study’s findings offer valuable information regarding the chemical profile of the ginger rhizome extract, laying the groundwork for potential applications in various fields such as pharmacology, food science, and natural product research.
Figure 1.
Ginger rhizome cultivated in Sudan. (A: the underground stem (rhizome), B: The areal parts of the plant (Zingiber officinale).
Figure 1.
Ginger rhizome cultivated in Sudan. (A: the underground stem (rhizome), B: The areal parts of the plant (Zingiber officinale).
4.4. Bacterial Strains
A range of five pathogenic bacteria including one Gram-positive (Staph. aureus) and four Gram-negative (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Salmonella typhi) were generously provided by the Department of Microbiology of the University of Gezira. The source of bacterial is clinical isolates previously identified and sent from Wad Madani Hospital, Sudan. These strains were chosen for their clinical significance as common pathogens, making them ideal for evaluating the antibacterial efficacy of ginger. The pure bacterial samples were subculture for further research by growing the bacteria on a Brain Heart Infusion Agar (B.H.I. agar) for overnight incubation at 35-37 oC. Before the experiment, a loop-full of the bacterial specimen was adjusted to McFarland using sterile normal saline (0.9%), to make the working bacterial solution which equals approximately 106 CFU/ml.
4.5. Preparation of the Plant Extract
In aqueous extraction, 20 grams of air-dried powder was added to 150 milliliters of distilled water and gently boiled for 2 hours. The fluid was filtered through eight layers of muslin fabric and centrifuged at 5000 times gravity for 10 minutes. The liquid supernatant was carefully collected. Two times, the technique was repeated. After 6 hours, the supernatant was collected at 2-hour intervals, consolidated, and concentrated to one-fourth of the starting volume. This systematic approach ensures the extraction process is conducted with accuracy and attention to detail. This process is essential for achieving a thorough extraction of the desired compounds from the powder. Additionally, the gentle boiling helps to ensure that the extraction is conducted at an optimal temperature without causing degradation of the extracted compounds.
4.6. Antibacterial Activity Test
In the present study, the standard disc-diffusion test was utilized, following the methodology described by Tambe et al. [
63] with some modifications. Briefly, B.H.I. agar plates were prepared for bacterial strains, and bacteria were inoculated using the spread plate technique in a sterile environment. The inoculation was conducted using a working solution adjusted to the McFarland standard of 10
6 CFU/ml. Discs of filter paper, with a diameter of 6 mm and made from Whatman’s No. 1 filter paper, were created and sterilized. The ginger aqueous extracts under investigation were prepared at different concentrations of 1, 2, and 3 mg/mL. Each disc absorbed precisely 10 µl of the solution, resulting in loaded discs containing 10, 20, and 30 µg of the plant extract, respectively. The filled discs were allowed to settle for a maximum of 10 minutes before being carefully placed on the agar surface using sterilized forceps. Subsequently, all plates were placed in an incubator and maintained at a temperature range of 35-37 °C for a duration of 24 hours. After the incubation period, the diameter of the inhibition zones was measured, and the meaning of three replicates was computed.
4.7. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration Test
The M.I.C. was determined using the micro-dilution method in Mueller Hinton (MH) broth as previously recommended [
24,
64] with minor modifications. Serial two-fold dilutions of the aqueous ginger rhizome extract (ranging from 100 to 3.125 µg/ml) were prepared in duplicate wells of a 96-well plate. Control wells containing only MH broth and others with bacteria, but no extract was also included. A 75 μl bacterial suspension in MH broth, adjusted to 10
6 CFU/ml, was added to the designated wells. Subsequently, 75 μl of each serially diluted extract was added vertically into each well starting from the first row. To ensure reproducibility, the entire procedure was repeated on another 96-well plate. The plates were then incubated at 35-37°C for 24 hours. After incubation, a 0.01% solution of 2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (T.T.C.) was added to the wells. Following an additional hour of incubation, the color change of the tetrazolium salt was observed. A lack of color change indicates growth inhibition by the biologically active extract, with the minimum inhibitory concentration (M.I.C.) resulting in complete growth suppression and no discernible color change.
4.8. Minimum Bactericidal Concentration Test
The minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of the aqueous extract derived from the rhizome of Sudanese ginger was determined against the selected bacterial strains in the following method: 100 µL from each MIC tube with no apparent growth was subcultured onto Mueller-Hinton agar plates and incubated at 35-37°C for 24 hours. Subsequently, the plates underwent examination to identify any bacterial colonies. The minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) was determined as the concentration at which no bacterial colonies were detected [
25,
65].
4.9. Phytochemical Analysis
The methods suggested by Banso and Adeyemo [
61] were used to analyze the extracts ginger rhizome for the presence of phenols and tannins, alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenoids, sterols, cardiac glycosides, and saponins. These methods are established protocols for chemical analysis and are widely recognized in the scientific community for their reliability and accuracy in identifying the presence of specific compounds in extracts. By following these methods, researchers can ensure the credibility and reproducibility of their findings, as well as gain valuable insights into the potential uses and properties of the analyzed compounds.
The compounds analyzed include a wide range of chemical classes, each with its own significance in various fields such as pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and environmental studies. This comprehensive approach to chemical analysis aims to identify the presence of key compounds in the extracts, providing valuable insights into their potential uses and properties [
44,
45].
4.10. GC-MS Analysis
In this study, the ethanol extract of the ginger rhizome was subjected to analysis using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) at the Central Laboratories of the University of Gezira. The GC-MS analysis identified various chemical constituents present in the extract, providing detailed information such as their retention time, base peak, molecular weight, molecular formula, and compound names. The NIST 14S library was utilized to identify the compounds detected in the analysis.
The conditions of analysis are as follows:
The split ratio of 1 L injected sample was 10:1. Set the oven temperature program to 280 °C for 25 minutes at 80 °C/minute from 60 °C. The show was 53.5 minutes. Conditions for G.C.–M.S. leaf oil analysis: As noted, G MS detected FAME molecules.
The helium flow was 0.7 mL/min. The ion source, transfer, and injector were heated to 250, 250, and 220 °C. After 1 minute at 50 °C, the oven was heated to 250 °C at 40 °C each minute. From 35 to 500 amu, full-scan mass spectra were acquired for all data. Spectra were compared to mass spectral databases to identify substances. We set system calibration and minimal detection limits using manufacturing circumstances. Other sources provide the equation [
31].
This analytical approach allowed for the comprehensive characterization of the chemical composition of the ginger rhizome extract. The study’s findings offer valuable information regarding the chemical profile of the ginger rhizome extract, laying the groundwork for potential applications in various fields such as pharmacology, food science, and natural product research.
4.11. Computational Study
The pharmacokinetic properties of the ginger identified compounds have been explored as previously reported [
9,
54]. The assessment of these parameters was based on the ADMET (for absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity) properties [
54,
55].
The potential antimicrobial effect was also assessed by computational modelling and interactions assay. TyrRS from
S. aureus (1JIJ) and the aspartic proteinase from
C. albicans (2QZW were retrieved from RCSB data bank. Their active sites have been targeted to assess the antimicrobial effects. ChemDraw was used to draw the structure of the identified chemicals, which did not exist on the PubChem website. The CHARMm force field was applied between ligands and receptors as previously reported [
56,
63] after removal of water molecules and addition of Kollman charges and polar hydrogens... The bond types and binding scores were analyzed as previously reported [
52,
59]. The major reason behind targeting 1JIJ and 2QZW is the implication in the pathogenesis of infectious diseases [
38].
4.12. Statistical Analysis
The obtained data were subjected to simple descriptive analysis. The significant cases were determined through the least significant difference (L.S.D.) analysis, which was reflected by letters for each case (the different letters reflected different significant levels).
5. Conclusions
This comprehensive study focuses on the Zingiber officinale rhizome grown in the central part of Sudan (Gezira), an area that has received less attention regarding its tropical climate. The aqueous extract exhibits moderate antibacterial properties against a range of pathogens. Further investigation is recommended to focus on non-polar or semi-polar phytochemicals using different extraction methods. This suggestion is based on the results of the phytochemical screening, which identified approximately 22 bioactive chemical compounds belonging to various phytochemical classes, such as saponins, flavonoids, glycosides, alkaloids, steroids, and terpenoids. Furthermore, computational investigations have shown ginger compounds have binding solid affinities to proteins 1JIJ and 2QZW, with values as low as -9.5 kcal/mol, further confirming their potential as therapeutic agents. This work increases the current understanding of the antibacterial and phytochemical features of ginger rhizome from Sudan and establishes a solid basis for future research. It is recommended that additional research pathways be explored in the future. It is advisable to carry out in vivo research to confirm the antibacterial activity.
Author Contributions
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, A.M.E.S. and E.M.A.; methodology, S.M.I., R.B. and M.A. validation,F.A. ; investigation, N.A.A. and A.M.E.S., resources, H.I.; data curation, H.I., A.S., and N.A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, S.M.I., A.J. and H.I.; writing—review and editing, R.B., and E.M.A.; supervision, A.M.E.S, R.B. and E.M.A.; project administration, M.A., N.A.A., and A.S.; funding acquisition, F.A. and S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by of the University of Hail; grant number RG 23 0-35 And The APC was funded by the University of Hail.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research of the University of Hail for funding this research (RG 23 0-35).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yudaev: P.; Mezhuev, Y.; Chistyakov, E.; Nanoparticle-containing wound dressing: Antimicrobial and healing effects. Gel. 2022, 24;8(6):329. [CrossRef]
- Yudaev, P. A., Chistyakov, E. M. Progress in dental materials: Application of natural ingredients. Uspekhi Khimii. 2024, 93 (3), 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Tao, X.Y.; Dang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liu, G.; Tian, Y.; Tian, L.J. Near-Native Imaging of Label-Free Silver Nanoparticles-Triggered 3D Subcellular Ultrastructural Reorganization in Microalgae. ACS nano. 2024, 10;18(3):2030-46. [CrossRef]
- Sulieman, A.M.; Abdallah, E.M.; Alanazi, N.A.; Ed-Dra. A.; Jamal, A.; Idriss, H.; Alshammari, A.S; Shommo, S.A. Spices as sustainable food preservatives: a comprehensive review of their antimicrobial potential. Pharmaceut. 2023, 12;16(10):1451. [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, W.E.; Abdallah, E.M. Antibacterial activity of ginger (Zingiber Officinale Rosc.) Rhizome: a mini review. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Chin. Med. 2018, 2(4):000142.
- Indrawati, I.D.; Miranti, M.I.; Isyaini, R.M. Antibacterial activity of ethanolic extracts of rhizome from three ginger varieties against acne isolated bacteria. Nusant. Biosc. 2017, 20;9(1):92-6. [CrossRef]
- Olaleye, O.N.; Momoh, J.O. Evaluation of secondary metabolites profiling of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) rhizome using GC-MS and Its antibacterial potential on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Microbiology. Res. Jour. Inter. 2022, Oct 7;32(7):7-31. [CrossRef]
- Noman, Z,A.; Anika, T.T.; Sachi, S.; Ferdous, J.; Sarker, Y.A.; Sabur, M.A.; Rahman, M.T.; Sikder, M.H. Evaluation of antibacterial efficacy of garlic (Allium sativum) and ginger (Zingiber officinale) crude extract against multidrug-resistant (MDR) poultry pathogen. J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2023, 30;10(2):151-156.
- Zammel, N.; Jedli, O.; Rebai, T.; Hamadou, W.S.; Elkahoui, S.; Jamal, A.; Alam, J.M.; Adnan, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Alreshidi, M.M.; Naïli, H. Kidney injury and oxidative damage alleviation by Zingiber officinale: pharmacokinetics and protective approach in a combined murine model of osteoporosis. 3 Biotech. 2022, May;12(5):112. [CrossRef]
- ALFahdawi, S. M.; Joudah, M. T. Study On Antibacterial And Antifungal Activity Of Ginger (Zingiber officinale) On Selected Pathogenic Microorganism. Biochemical and Cellular Archives, 2020, 20(2): 4629-4633.
- Nishidono, Y.; Saifudin, A.; Deevanhxay, P.; Tanaka, K. Metabolite profiling of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) using GC-MS and multivariate statistical analysis. Journal of the Asia-Japan Research Institute of Ritsumeikan University, 2020,2: 1-14.
- Akhlaghi, N.; Najafpour-Darzi, G. Potential Applications of Ginger Rhizomes as a Green Biomaterial: A Review. Inter. Jour. of Eng. 2023, 1;36(2):372-83. [CrossRef]
- Islam, M. M., F.; Khatun, M. I.; Faruk, M. M.; Rahman, M. A.; Hossain M.A.. “An integrated approach to manage the rhizome rot disease of ginger. 2022, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.H.; Aly, S.M. Active ingredients of ginger as potential candidates in the prevention and treatment of diseases via modulation of biological activities. Inter. Jour. of phys. Path.and pharm. 2014, 6(2):125.
- Malu SP, Obochi GO, Tawo EN, Nyong BE. Antibacterial activity and medicinal properties of ginger (Zingiber officinale). Glob. Jour. of pur and appl. Scien. 2009,15(3-4). [CrossRef]
- Jedli O, Ben-Nasr H, Zammel N, Rebai T, Saoudi M, Elkahoui S, Jamal A, Siddiqui AJ, Sulieman AE, Alreshidi MM, Naïli H. Attenuation of ovalbumin-induced inflammation and lung oxidative injury in asthmatic rats by Zingiber officinale extract: Combined in silico and in vivo study on antioxidant potential, STAT6 and TNF-α pathways. 3 Biotech. 2022, 12 (9):191. [CrossRef]
- Mošovská, S., Nováková, D., & Kaliňák, M. (2015). Antioxidant activity of ginger extract and identification of its active components. Acta Chimica Slovaca, 8(2), 115-119. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Saxena, K.; Singh, U.N.; Saxena, R. Anti-inflammatory action of ginger: A critical review in anemia of inflammation and its future aspects. Int J Herb Med. 2013;1(4):16-20.
- Kumar, D., & Kumar, A. (2023). Cellular attributes of Candida albicans biofilm-associated in resistance against multidrug and host immune system. Microbial Drug Resistance. 2024: 29(9), 423-437. [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, E.M.; Alhatlani, B.Y.; de Paula Menezes, R.; Martins, C.H.; Back to Nature: Medicinal plants as promising sources for antibacterial drugs in the post-antibiotic era. Plant. 2023, 28;12(17):3077. [CrossRef]
- Roque-Borda, C.A; da Silva, P.B.; Rodrigues, M.C.; Azevedo, R.B.; Di Filippo, L.; Duarte, J.L.; Chorilli, M.; Festozo Vicente, E.; Pavan, F.R. Challenge in the discovery of new drugs: antimicrobial peptides against WHO-list of critical and high-priority bacteria. Pharmac. 2021, 21;13(6):773. [CrossRef]
- Havenga; B.; Ndlovu, T.; Clements, T.; Reyneke, B.; Waso, M.; Khan, W. Exploring the antimicrobial resistance profiles of WHO critical priority list bacterial strains. BMC microb. 2019,19:1-6. [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, W.E.; Abdallah, E.M. Promising Sudanese medicinal plants with antibacterial activity. InBiol. Forum 2016 (Vol. 8, No. 1, pp. 299-323).
- Kabtni S.; Sdouga, D; Bettaib Rebey, I.; Save, M.; Trifi-Farah, N.; Fauconnier, M.L.; Marghali, S. Influence of climate variation on phenolic composition and antioxidant capacity of Medicago minima populations. Scien. Repor. 2020, 19;10(1):8293. [CrossRef]
- Alrajhi, M.; Al-Rasheedi, M.; Eltom, S.E.; Alhazmi, Y.; Mustafa, M.M.; Ali, A.M. Antibacterial activity of date palm cake extracts (Phoenix dactylifera). Cog. Foo & Agric.. 2019, 1;5(1):1625479. [CrossRef]
- Pasquina-Lemonche, L.; Burns, J.; Turner, R.D.; Kumar, S.; Tank, R.; Mullin, N.; Wilson, J.S.; Chakrabarti, B.; Bullough, P.A,; Foster, S.J.; Hobbs, J.K. The architecture of the Gram-positive bacterial cell wall. Natur. 2020, Jun 11;582(7811):294-7. [CrossRef]
- Nourbakhsh, F.; Lotfalizadeh, M.; Badpeyma, M.; Shakeri, A.; Soheili, V. From plants to antimicrobials: Natural products against bacterial membranes. Phyto. Res. 2022 Jan;36(1):33-52. [CrossRef]
- Jain, P., Bansal, D., Bhasin, P. A., & Anjali, A. (2010). Antimicrobial activity and phytochemical screening of five wild plants against Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus. J Pharm Res. 2010; 3(6), 1260-1262.
- Islam, K.; Rowsni, A.A.; Khan, M.M.; Kabir, M.fS. Antimicrobial activity of ginger (Zingiber officinale) extracts against food-borne pathogenic bacteria. International Journal of Science, Environ. and Technol. 2014, 3(3):867-71.
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Thakur, K.; Han, J.; Zhang, J.G.; Hu, F.; Wei, ZJ. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of ginger essential oil against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Molecu. 2020, 30;25(17):3955. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Thakur, K.l.; Han, J.; Zhang, J.G.; Hu, F.; Wei, Z.J. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of ginger essential oil against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Molecu. 2020, 30;25(17):3955. [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, R.; Shakya, R.; Baral, P.; Chapagain, P. Molecular modeling and simulation of the peptidoglycan layer of Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. Jour. of Chem. Inform. and Model. 2022, 18;62(20):4955-62. [CrossRef]
- Mogana, R.; Adhikari, A.; Tzar, M.N.; Ramliza, R.; Wiart, C.J. Antibacterial activities of the extracts, fractions and isolated compounds from Canarium patentinervium Miq. against bacterial clinical isolates. BMC complemen med and thera. 2020, 20:1-1. [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, M.; Vasić, S.; Đurđević, J.; Stefanović, O.; Čomić, L. Antibacterial and anti-biofilm activity of ginger (Zingiber officinale (Roscoe)) ethanolic extract. Kraguj Jour. of Scien. 2014, 36:129-36. [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghi, N.; Najafpour-Darzi, G. Potential Applications of Ginger Rhizomes as a Green Biomaterial: A Review. Inter. Jour. of Eng. 2023, 1;36(2):372-83. [CrossRef]
- Islam, M. M., F.; Khatun, M. I.; Faruk, M. M.; Rahman, M. A.; Hossain M.A.. “An integrated approach to manage the rhizome rot disease of ginger. 2022, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Malu SP, Obochi GO, Tawo EN, Nyong BE. Antibacterial activity and medicinal properties of ginger (Zingiber officinale). Glob. Jour. of pur and appl. Scien. 2009,15(3-4). [CrossRef]
- Kela, E.; Sogbesan, A.O.; Wakil, U.B. Evaluation of Phytochemical Composition of Ginger Extracts. Fish. and Aquacul. Jour. 2021, 30;12(7):1e-.
- Rahmani, A.H.; Aly, S.M. Active ingredients of ginger as potential candidates in the prevention and treatment of diseases via modulation of biological activities. Intern. jour. of physiol, pathophys.and pharm. 2014, 6(2):125.
- Sulieman, A.E.; Medani, W.; Kamal, L.B.; Ali, A.O. Chemical composition of ginger (Zingiber officinale) rose and the evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of its oil. Gez Jour. of Agric. Scien. 2007;5(1).
- Shareef, H. K., Muhammed, H. J., Hussein, H. M., & Hameed, I. H. (2016). Antibacterial effect of ginger (Zingiber officinale) roscoe and bioactive chemical analysis using gas chromatography mass spectrum. Oriental Journal of Chemistry, 32(2), 20-40. [CrossRef]
- Vasanthakumar, K.; Dineshkumar, G.; Jayaseelan, K. Phytochemical screening, GC-MS analysis and antibacterial evaluation of ethanolic leaves extract of Avicennia marina. Jour.of Dru. Del and Ther. 2019, 7;9(4-A):145-50. [CrossRef]
- Aryal, B.; Raut, B.K.; Bhattarai, S.; Bhandari, S.; Tandan, P.; Gyawali, K.; Sharma, K.; Ranabhat, D.; Thapa, R.; Aryal, D.; Ojha, A. Potential therapeutic applications of plant-derived alkaloids against inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. Evid.-Base. Compl. and Alter. Med. eCAM. 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Thakor, H. J., Rathi, Y. S., & Nayak, N. S. (2023). Phytochemical screening of ginger (Zingiber officinale), a medicinal plant. Sch Int J Tradit Complement Med, 6(4), 58-62. [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Tian, W.; Cui, X.; Tu, P.;, Li, J.; Shi, S.; Liu, X. Biosynthesis investigations of terpenoid, alkaloid, and flavonoid antimicrobial agents derived from medicinal plants. Antibiotics. 2022 Oct 9;11(10):1380. [CrossRef]
- Reuter, H.; Henderson, S.A.; Han, T.; Ross, R.S.; Goldhaber, J.I.; Philipson. K.D. The Na+-Ca2+ exchanger is essential for the action of cardiac glycosides. Circul. Res. 2002, 22;90(3):305-8.
- Škubník, J.; Bejček, J.; Pavlíčková, V.S.; Rimpelová, S. Repurposing cardiac glycosides: Drugs for heart failure surmounting viruses. Molecul. 2021, 16;26(18):5627. [CrossRef]
- Elekofehinti, O.O.; Iwaloye, O.; Olawale, F.; Ariyo, E.O. Saponins in cancer treatment: Current progress and future prospects. Pathophys. 2021, 5;28(2):250-72. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S., Yadav, A., Yadav, M., & Yadav, J. P. (2017). Effect of climate change on phytochemical diversity, total phenolic content and in vitro antioxidant activity of Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f. BMC research notes, 10, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Gunasena, M. T., Rafi, A., Mohd Zobir, S. A., Hussein, M. Z., Ali, A., Kutawa, A. B., ... & Ahmad, K. Phytochemicals profiling, antimicrobial activity and mechanism of action of essential oil extracted from ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe cv. Bentong) against Burkholderia glumae causative agent of bacterial panicle blight disease of rice. Plants. 2022; 11(11), 1466.
- Hayati, R.F.; Better, C.D.; Denis, D.; Komarudin, A.G.; Bowolaksono, A.; Yohan, B.; Sasmono, R.T. [6]-Gingerol Inhibits Chikungunya Virus Infection by Suppressing Viral Replication. BioM. Res. Intern. 2021, 2021(1):6623400. [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.I.; Li, W.; Liang, W.; Van Breemen, R.B. Identification and quantification of gingerols and related compounds in ginger dietary supplements using high-performance liquid chromatography− tandem mass spectrometry. Jour. of agricul. and food chem. 2009,11;57(21):10014-21. [CrossRef]
- Jedli, O.; Ben-Nasr, H.; Zammel, N.; Rebai, T.; Saoudi, M.; Elkahoui, S.; Jamal, A.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Sulieman A.E.; Alreshidi, M.M.; Naïli, H. Attenuation of ovalbumin-induced inflammation and lung oxidative injury in asthmatic rats by Zingiber officinale extract: Combined in silico and in vivo study on antioxidant potential, STAT6 and TNF-α pathways. 3 Biotech. 2022,12(9):191. [CrossRef]
- Dafaalla, D.M. Phytochemistry and GC-MS Analysis of some Plant Products and Evaluation of their Biological Effects Using Mosquitoes Larvae as Bioindicators (Doctoral dissertation, University of Gezira) (2022).
- Bédoui, I.; Nasr, H.B.; Ksouda, K.; Ayadi, W.; Louati, N.; Chamkha, M.; Choura, S.; Gargouri, J.; Hammami, S.; Affes, H.; Hamadou, W.S. Phytochemical Composition, Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics of Scorzonera undulata Methanolic Extracts: Antioxidant, Anticancer, and Apoptotic Effects on MCF7 Cells. Pharma. Magaz. 2024, 20(1):218-29.
- Lakhrem, M., Eleroui, M., Boujhoud, Z.; Feki, A.; Dghim, A.; Essayagh, S.; Hilali, S.; Bouhamed, M.; Kallel, C.; Deschamps, N; Toffol, B.D. Anti-Vasculogenic, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Sulfated Polysaccharide Derived from Codium tomentosum: Pharmacokinetic Assay. Pharmaceut. 2024. 17(6):672.
- Zammel, N.; Saeed, M.; Bouali, N.; Elkahoui, S.; Alam, J.M,; Rebai, T.; Kausar, M.A.; Adnan, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Badraoui, R. Antioxidant and anti-Inflammatory effects of Zingiber officinale roscoe and Allium subhirsutum: In silico, biochemical and histological Study. Food. 2021,15;10(6):1383.
- Aldarhami, A.; Bazaid, A.S.; Alhamed, A.S.; Alghaith, A.F.; Ahamad, S.R.; Alassmrry, Y.A.; Alharazi, T.; Snoussi, M.; Qanash, H.; Alamri, A.; Badraoui, R. Antimicrobial Potential of Pithecellobium dulce Seed Extract against Pathogenic Bacteria: In Silico and In Vitro Evaluation. BioM. Res. Inter. 2023, 2023(1):2848198. [CrossRef]
- Akacha, A.; Badraoui, R.; Rebai, T.; Zourgui, L. Effect of Opuntia ficus indica extract on methotrexate-induced testicular injury: A biochemical, docking and histological study. Jour. of Biomol. Struct. and Dynam. 2022, 21;40(10):4341-51.
- Badraoui, R.; Allouche, M.; El Ouaer, D.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Ishak, S.; Hedfi, A.; Beyrem, H.; Pacioglu, O.; Rudayni. H.A.; Boufahja, F. Ecotoxicity of chrysene and phenanthrene on meiobenthic nematodes with a case study of Terschellingia longicaudata: Taxonomics, toxicokinetics, and molecular interactions modelling. Environ. Poll. 2023, 1;316:120459. [CrossRef]
- Banso, A.; Adeyemo, S.; Phytochemical screening and antimicrobial assessment of Abutilon mauritianum, Bacopa monnifera and Datura stramonium. Biokemisi. 2006;18(1).
- Al-Huqail, A.A.; Elgaaly, G.A/; Ibrahim, M.M. Identification of bioactive phytochemical from two Punica species using GC–MS and estimation of antioxidant activity of seed extracts. Saud Jour. of Biol. Scien. 2018. 1;25(7):1420-8. [CrossRef]
- Tambe, B.D.; Pedhekar, P.; Harshali, P.; Phytochemical screening and antibacterial activity of Syzygium cumini (L.)(Myrtaceae) leaves extracts. Asia Journ. of Pharm. Res. and Develop. 2021, 15;9(5):50-4.
- Dhiman, A.; Nanda, A.; Ahmad, S.; Narasimhan, B. In vitro antimicrobial activity of methanolic leaf extract of Psidium guajava L. Jour. of Pharm. and Bioal. Scien. 2011, 1;3(2):226-9. [CrossRef]
- Abdi, R.D.; Dego, O.K. Antimicrobial activity of Persicaria pensylvanica extract against Staphylococcus aureus. Europ. Journ.of Integ. Med. 2019 Aug 1;29:100921. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).