1. Introduction
Bananas are the fourth most widely cultivated fruit in the world, with the majority of global production occurring in southern China. As indicated in the China Statistical Yearbook 2021, China produced 11.513 million tons of bananas in 2020 [
1], with banana peels accounting for 30%-40% of the total yield [
2]. The banana peel and its residue contain nutrients and phytochemicals [
3,
4]. The banana peel is a rich source of dietary fiber [
5] and pectin [
6]. These banana by-products have been developed into animal feed [
7]. Furthermore, the literature indicates that banana peel has been utilized in ruminant feeds [
8].
The microbial fermentation of banana peel can enhance its palatability and augment its nutritional value. In a related study, Caicedo [
9] investigated the addition of natural yogurt, whey, and molasses to banana silage fermentation. The physicochemical, biological, and sensory indexes of these fermented banana silages were determined, and the results demonstrated that these silages were suitable for pig breeding. The experimental group of Siamese catfish, which was fed a diet containing 20% fermented banana peel, exhibited comparable feed consumption, specific growth rate, feed efficiency, fat retention, and energy retention to the control group, which was fed a commercial diet [
10]. Nevertheless, there is a paucity of literature examining the impact of incorporating fermented banana peel and pulp residue into poultry diets, particularly with regard to the effects on feed quality and the flavor components of poultry meat.
A review of the literature reveals a paucity of studies on the application of fermented fruit pulp residues to poultry feeds. A review of the literature reveals no reports on the use of fermented banana pulp residues in poultry diets for the purpose of improving slaughter performance and meat quality. No comparison has been made between the nutritional parameters of meat from chickens fed fermented and unfermented fruit peels. Accordingly, the impact of incorporating fermented banana peels and pulp residues into poultry diets on slaughter performance, meat quality, and flavor components was assessed. The data may serve as a theoretical foundation for the utilization of banana by-products as a high-quality silage.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fermented Banana Peel and Banana Pulp Residue
The banana variety utilized in this experiment was Guijiao 6 (Musa AAA). It was the primary cultivar grown in the Guangxi region. The fruit was cultivated in a local plantation in the Guangxi region. The harvested, unripe bananas were stored at room temperature in the laboratory prior to undergoing further processing. The fruit was allowed to ripen before removing the peel. Subsequently, the pieces were reduced in size and inoculated with a fermentation agent. Following homogenization, the fruit peels were packed and sealed and then stored at a room temperature of 25 °C for 15 days. Following partial fermentation, 0.8% pectinase and 0.5% cellulase were added onto it, and left to stand for 2 h. The enzymatically hydrolyzed peel samples were filtered, and the filtrate was collected. In contrast, the pulp residues were inoculated with the fermentation agent, packed, and sealed prior to undergoing fermentation at room temperature for 15 days.
The ash content of the fermented banana samples was determined by ashing the oven-dried banana samples at 550 °C for 3 h. The dry matter content was determined by oven-drying the samples at 105 °C until a constant weight obtained was obtained [
11]. The carbohydrate content was estimated using the anthrone-sulfuric acid method [
12], and the crude protein content was determined using the Kjeldahl method [
13]. The pH values of the sample homogenates (1:9, w/v, diluted with normal saline) were determined using a pH meter, and the titratable acidity was calculated after titration with a calibrated sodium hydroxide solution. The amounts of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) in the sample homogenates were quantified according to the standard plate count method [
14]. The chemical constituents of these fermented samples are presented in
Table 1.
2.2. Poultry Feeding Experiment
The poultry experimentation was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards set forth by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Nanning, China (GXAAS/AEEIF/005). Prior to the commencement of the feeding experiment, 120 Guangxi Partridge chicken (Gallus gallus domesticus) were acclimated at the Tiandong poultry farm in Guangxi. The chicken (hens) were 12 weeks old, with an average body weight of 1.25±0.02 g. They were randomly assigned to five experimental groups (n=24), including a control group (CK) and four supplementation groups.
The chickens were provided with ad libitum access to the experimental feeds and tap water throughout the 140-day experimental period. The control group (CK) was fed a basal diet, while the other four supplementation groups were fed diets supplemented with 10% fermented banana peel (PE-10), 20% fermented banana peel (PE-20), 10% fermented banana pulp residue (PU-10), and 20% fermented banana pulp residue (PU-20), respectively. During the feeding period, all chicken had access to tap water ad libitum. The poultry house was cleaned on a weekly basis and ventilated with temperatures ranging from 27 °C to 33 °C.
The standard daily feed consisted of a corn and soybean mixed meal. The feed consisted of the following ingredients: 57.5% corn, 25% soybean meal, 5% wheat bran, 2.5% soy oil, and 10% premix. The sample contained 17% crude protein. The two essential amino acids were lysine (0.8%) and methionine (0.4%). The energy content was 2.75 megacalories per kilogram.
2.3. Preparation of Samples
At the conclusion of the feeding trial (32 weeks of age), all fasted chicken underwent a blood draw prior to slaughter. The poultries were fasted for a period of 12 h prior to being sacrificed in accordance with the procedures outlined in GB/T 19478-2018 procedure [
15]. Following exsanguination via the jugular vein, the carcass was blanched in boiling water, and the feathers were removed by pulling them off the body. The weights of all organs were recorded, and the pectoral and thigh muscles were collected for subsequent analysis. Additionally, the layers of abdominal fat surrounding the muscular stomach and abdomen were also separated and weighed. The pectoral muscles, situated along the sternum ridge were obtained with the chicken skin removed. The thigh muscles were collected after the skin, subcutaneous fat, and bones were removed. The slaughter performance of the chicken was presented in the form of carcass weights and percentages of pectoral and thigh muscles.
2.4. Nutritional Compositions and Color Values of Chicken Chest Meats
The pectoral muscle, commonly referred to as “chest meat”, was analyzed for its moisture content and fatty acid (FA) composition. These parameters were analyzed in accordance with the Chinese standard analytical methods. The standards in question were GB 5009.3—2016 [
16] and GB5009.168—2016 [
17], respectively. The L*, a*, and b* values were analyzed at the 45-min mark post-slaughter. The values were determined using a chromometer (CR400/410, Minolta, Japan) in triplicate, as previously described [
18].
2.5. Shear Force and Water Holding Capacity of Chicken Chest Meats
The shear force test and water loss analysis were conducted on the chest meat samples within 24 h of slaughter. The shear force value of the meat samples was determined in accordance with the methodology outlined in the referenced literature [
19]. The meat samples were initially subjected to a water bath maintained at a constant temperature of 80 °C. The meat samples were cut into cubes measuring 2.5 cm in length, 1.0 cm in width, and 0.25 cm in height. The RH-N50 Meat Tenderness Tester (Runhu Instrument Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China) was employed to ascertain the shear force value at three distinct points, with the resulting values averaged. The water-holding capacity of the meat samples was determined using an RH-1000 Water Holding Capacity Tester (Runhu Instrument Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China). In summary, the meat sample was subjected to a pressure of 35 kg for a period of 5 min, after which it was weighed.
2.6. Determination of Flavor Compounds in Chicken Chest Meats
The analysis was conducted using gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS). The GC analysis of flavor substances was conducted using a method described in the literature with some modifications [
20]. In summary, 2.0 g of chest meat samples were weighed and placed in a 20-mL headspace bottle, incubated at 90 °C for 15 min, and analyzed by a FlavourSpec
® GC-IMS flavor analyzer (Dortmund, Germany). The following are the analytical conditions for GC-IMS: The stationary phase was a FS-SE-54-CB-1 capillary column (15 m, ID: 0.53 mm), the column temperature was 60 °C, the IMS temperature was 45 °C, the injection volume was 500 μL, high-purity nitrogen was used as the carrier gas, and the total run time was 30 min. The gradient gas flow conditions as follows: 0-2 min, 2 mL/min; 2-10 min, 2-10 mL/min; 10-20 min, 10-100 mL/min; 20-30 min, 100-150 mL/min.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was conducted using the statistical software package SPSS (version 20.0, SPSS, Inc., Chicago, USA). The data were subjected to one-way ANOVA, and a P-value of less than 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. The qualitative, quantitative, and fingerprint characteristics of the flavor compounds present in the meat samples were determined using the VOCal, Reporter, Gallery Plot, and Dynamic PCA plug-ins. The SIMCA method was employed for the analysis of flavor compounds, utilizing the orthogonal partial least squares approach and cluster analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Slaughter Performance
The slaughter performance of poultry is an important quality indicator in the field of poultry farming. The provision of a standard daily feed to poultries can facilitate optimal growth, which is a crucial aspect of this industry. The addition of the fermented banana peels and pulp residues was observed to promote growth of the experimental chicken (
Table 2). The results demonstrated that the pectoral muscle percentages of the chicken in the supplementation groups were significantly higher than those of the CK group following the addition of varying proportions of fermented banana peels and residues to their daily feed, with the exception of the Pu-20 group (P < 0.05). The percentages of thigh muscle of chicken in the Pe groups were notably higher than in the control group. No significant differences were observed in the remaining tested parameters of the chicken in the supplementation groups when compared with the control group (P < 0.05), with the exception of the carcass weight and abdominal fat content of the chicken in the Pe-10 group and Pu-10 groups, respectively.
The existing literature indicates that the inclusion of fermented plant products, such as fermented leaves and fruit peels, in poultry feeds may enhance the slaughter performance of broiler chickens and the quality of their meat. The experimental broiler chickens that were fed with the fermented and unfermented grape skins exhibited superior slaughter performance compared to the control group. However, no significant differences were observed between the fermented and unfermented sample groups [
21]. The slaughter performance of the broiler chickens that were fed fermented mulberry leaf powder was observed to be superior to that of the control group, which was fed unfermented mulberry leaf powder [
22]. Additionally, the administration of moringa leaf extract has been demonstrated to enhance the growth performance of broilers [
23]. The aforementioned studies corroborate our findings that poultry fed with fermented plant products exhibit, to some extent, improved slaughter performance and meat quality.
3.2. Quality Parameters of Chicken Chest Meats
3.2.1. Meat Brightness and Colors
The primary quality characteristics of the chicken chest samples are presented in
Table 3. The color of the meat is one of the primary indicators of its quality. The parameters included brightness (L*), redness (a*), and yellowness (b*). The results demonstrated that there were significant differences in the L*, a*, and b* values among the various experimental groups. The meat samples of the chicken in the Pu-20 group exhibited the most notable increase in L* value (P < 0.05), while the L* values of the other experimental chicken meats did not demonstrate a significant elevation but also exhibited a notable decrease relative to the CK group. The meat sample from the Pu-10 group exhibited a darker hue than that of the control group. Additionally, the meat samples in the Pe-10 and Pu-10 groups exhibited the most significantly elevated a* and b* values, respectively. The meat samples in the Pu-20 group exhibited low a* and b* values despite having the highest L* value. Furthermore, the meat samples in the Pe-10 group exhibited the lowest b* value and the highest a* value.
The literature indicates that an elevated a* value is indicative of a heightened red hue, whereas a higher b* value is suggestive of an augmented yellow hue [
24]. The chest meat samples of the chicken in the Pe-10 group exhibited intense redness and minimal yellow hues with moderate brightness. This suggests that the meat sample from this group exhibited superior meat quality in comparison to the other groups. The low meat redness observed in the CK group indicates that the supplementation of fermentation banana samples effectively enhanced the quality of the meat. The reduction in meat redness may be attributed to the oxidation of myoglobin [
25]. Other factors, including temperature, oxygen partial pressure, pH value, light, osmotic pressure, and surface microbial activity, have the potential to alter the morphology of myoglobin, thereby influencing the observed color differences [
26].
The tenderness of the meat is indicative of its quality. This is typically expressed as a shear force value. A high shear force value indicates a reduction in the freshness of the meat sample, which in turn results in a reduction in its chewiness. Fresh meat is inherently tender. As illustrated in
Table 3, the shear forces of the meat samples from the chicken in the supplementation groups were markedly lower than those in the control group. The meat sample of the chicken in the Pe-10 group exhibited the most notable reduction in shear force (P < 0.05). The findings of this study indicate that the addition of 10% fermented banana samples to poultry feeds results in superior meat quality compared to the inclusion of 20% fermented banana samples. Additionally, the literature indicates that the inclusion of fermented soybean meal in poultry diets enhances the quality of the meat produced by broiler chicken [
27].
3.2.2. Moisture Content and Water-Holding Capacity
The findings indicated that the moisture content of the chest meat samples in the experimental and control groups exceeded 70%. The moisture content of the meat samples in the Pe groups was comparable to that of the CK group, whereas the meat samples in the Pu groups exhibited a significantly lower moisture content than that observed in the CK group (P < 0.05). The lowest moisture content was observed in the meat sample from the Pu-20 group. In addition to its low moisture content, the meat sample in the Pu-20 group demonstrated a reduced water-holding capacity in comparison to the other supplementation groups. The highest water-holding capacity was observed in the Pe-10 group.
The addition of varying quantities of fermented banana samples to poultry feeds did not significantly impact the meat quality, particularly in terms of color, tenderness, and water-holding capacity. The water-holding capacity of meat is defined as the ability of postmortem animal muscles to retain their original moisture under the influence of external forces, which impact the freshness and tenderness of the meat [
28]. The animal muscle with a high water-holding capacity was observed to exhibit greater tenderness and juiciness. In this study, the meat samples with a high water-holding capacity exhibited a high moisture content. Furthermore, the literature indicates that the administration of probiotics to poultry enhances the water-holding capacity of the meat [
29].
3.3. Fatty Acid Compositions of Chicken Chest Meats
The fatty acid (FA) compositions of the chest meat samples from the experimental groups are presented in
Table 4. The results demonstrated that 12, 19, 22, 13, and 15 FAs were identified in the meat samples of the CK, Pe-10, Pe-20, Pu-10, and Pu-20 groups, respectively. The identified fatty acids were classified as saturated fatty acids (SFAs), monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). The meat samples in the Pe groups exhibited the highest total fatty acid content, followed by the Pu and CK groups. The meat sample in the CK group exhibited the highest total SFA content, followed by the Pe and Pu groups. The total PUFA contentwas higher in the Pu groups than in the Pe groups, while the total MUFA content was lower in the Pu groups than in the Pe groups. The content of these FAs was not found to differ significantly between the experimental groups.
The SFAs are primarily composed of palmitic acid (C16:0) and stearic acid (C18:0). The predominant MUFA in the meat samples was oleic acid (C18:1n9c), while the principal PUFA was linoleic acid (C18:2n6c). The concentrations of palmitic, stearic, oleic, and linoleic acids in the meat samples from the Pe-10, Pe-20, Pe-20, and Pe-20 groups were found to be significantly higher (P < 0.05) in comparison to the other groups. The levels of these fatty acids in all supplementation groups were significantly higher than in the control group, with the exception of the Pu-10 group (P < 0.05). Additionally, the oleic acid content in the Pe groups was significantly higher than that in the Pu groups (P < 0.05). Conversely, the trans-oleic acid (C18:1n9t, elaidic acid) was identified in all meat samples, whereas only the meat sample in the CK group exhibited trans-linoleic acid (C18:2n6t, linolelaidic acid). The meat samples from chickens that had been fed the Pe samples exhibited a significantly higher trans-oleic acid content than those from chicken that had been fed the Pu samples. The meat sample from the Pu-10 group exhibited the lowest trans-oleic acid content.
Despite the meat sample in Pe-20 exhibiting the highest total FAs content, pentadecanoic acid (C15:0), docosanoic acid (C22:0, behenic acid), and cis-15-tetracosenoic acid (C24:1, nervonic acid) were not identified in this particular meat sample. Pentadecanoic acid is a FA that is typically found in egg, milk, poultry, and ruminant meats. In this study, pentadecanoic acid was identified exclusively in the meat sample of the Pe-10 group, while nervonic acid was detected in both Pe-10 and Pu-20. The undecanoic acid (C11:0), tridecanoic acid (C13:0), and icosanoic acid (C20:0) were exclusively identified in the meat samples of the Pe-20 group. Additionally, medium-chain fatty acids were undetected in the chicken fed with the fermented banana pulp residue (Pu-10 and Pu-20 groups) and the control groups. Among the long-chain FAs, C15:0 and C20:0 were not detected in the Pu-10, Pu-20, and CK groups.
It is plausible that the trans-FAs identified in the chest meat samples may have been introduced during the de-feathering process, which involved blanching in boiling water. The heating of unsaturated FA-containing chicken muscles resulted in the oxidation of FAs [
30]. The application of elevated temperatures may facilitate the release of these volatiles [
31]. Therefore, it can be concluded that the oxidation of FAs occurred in the meat samples, resulting in an increase in the levels of flavor substances. It is possible that this FA oxidation may result in alterations to the flavor of the meat [
32]. The elevated levels of trans-fat identified in the meat samples of the Pe groups may be attributed to the antioxidant content of banana peel being comparatively lower than that of banana pulp. The ingestion of antioxidant-rich feeds by the broiler chicken may also assist in maintaining oxidative stability in their muscles [
33]. Therefore, the reduction in oxidation of FAs in skeletal muscles is achieved. The findings of this study are corroborated by the literature, which indicates that rabbits fed an antioxidant-rich extract exhibited lower trans-FA levels than the control group [
34].
3.4. Flavor Compounds of Chicken Chest Meats
The identification and analysis of flavor compounds in the chest meat samples were conducted using HS-GC-IMS. The specific HS-GC-IMS analytical parameters are presented in
Table 5. A total of 60 distinct flavor compounds were identified in the meat samples. The identified compounds were cross-referenced with the GC-IMS library, which yielded 22 aldehydes, 14 alcohols, six ketones, two acids, one furan, and 15 compounds of an unidentified nature. The data are presented
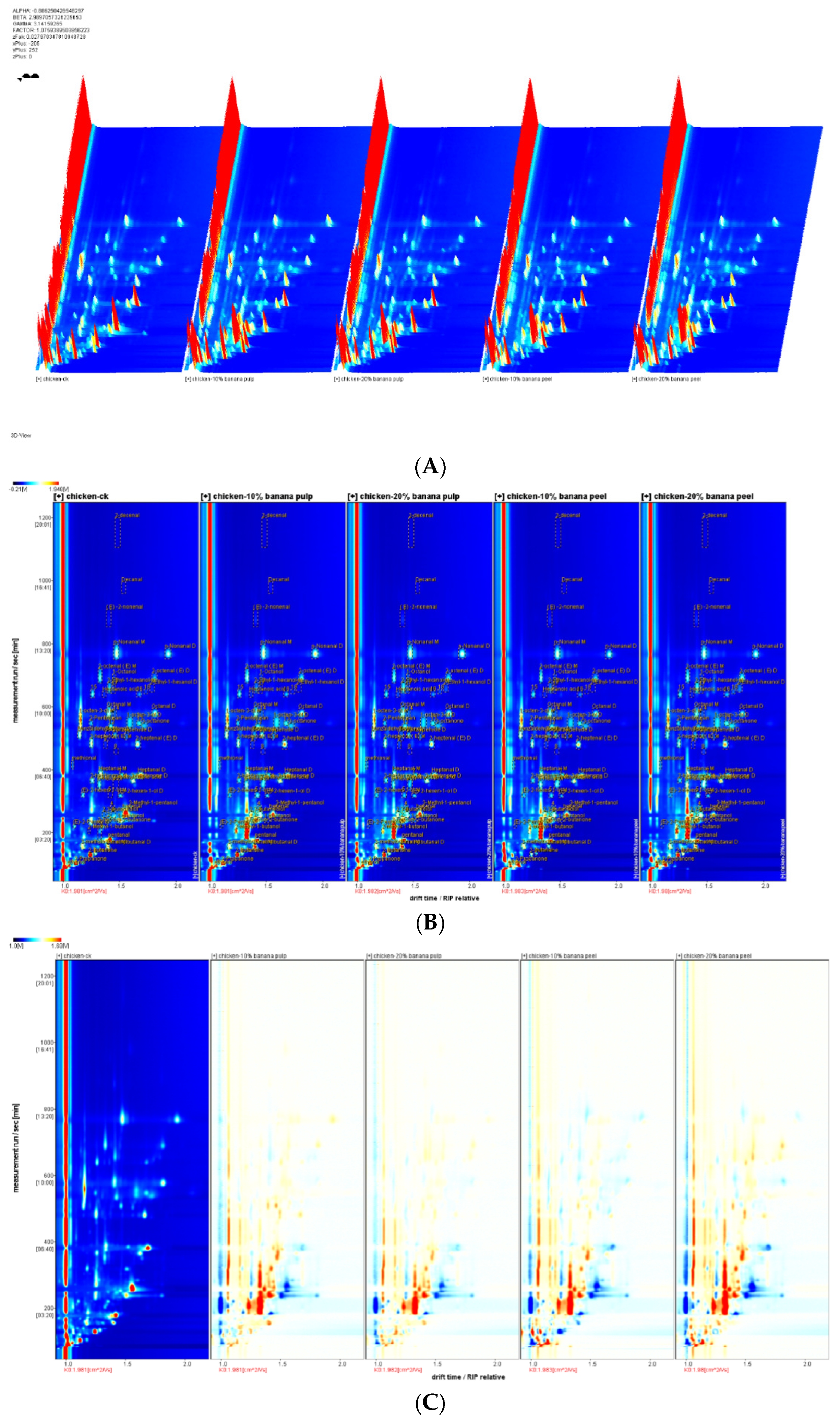
Figure 1 as the topographical plots. The x-axis represents the ion migration time, and the y-axis represents the GC retention time. The peak intensity is represented on the Z-axis. The three-dimensional (3D) spectra of gas-ion migration demonstrated the flavor composition of the meat samples (
Figure 1A). The flavor compositions exhibited comparable patterns. The results demonstrated that 3-hydroxy-2-butanone was exclusively identified in the meat samples of the supplemented chicken group, but not in those of the CK group.
Figure 1B,C illustrates the two-dimensional (2D) spectrum of gas-ion migration of the meat samples. The reactive ion peaks in the plots were normalized. The points to the right of the reactive ion peak represented a flavor compounds in the meat samples. The red points indicated a higher signal intensity, whereas the white spots exhibited a low signal intensity. The signal intensities thus correspond to the concentrations of the flavor compounds in question. The meat sample from the CK group was utilized as a reference point. The ratio of a flavor compound in the meat samples of the supplementary group was identical to the reference ratio, which was indicated by a white spot after the deduction. The red and blue points indicated ratios that exceeded the reference value. As illustrated in
Figure 1C, the majority of the signals were observed within the retention time range of 50 s to 800 s and the drift time range of 1.0 to 1.8. The flavor compounds, such as 2-ethylhexanol, exhibited notable differences between the various groups.
Table 5 presents the qualitative analytical results for flavor compounds in chest muscle samples. Aldehydes were identified as the most significant flavor compounds in chicken meat due to their low flavor threshold and capacity to influence the overall meat profile [
35]. Noleau and Toulemonde (1986) [
36] demonstrated that the removal of aldehydes resulted in the loss of the distinctive flavor profile of chicken meat, with an aroma that was more similar to beef. The aforementioned aldehydes, including hexanal, octanal, heptanal, nonanal, trans-2-pentenal, benzaldehyde, and trans-2-nonenal, have also been identified in chicken meat samples as documented in the literature [
37,
38]. The literature also indicates that the majority of aldehydes, including hexanal, octanal, octenal, nonanal, 2, 4-heptadienal, 2-heptenal, and heptanal, are derived from lipid oxidation reactions [
39,
40]. Hexanal is the most prevalent aldehyde compound in chicken. It is the primary product of the oxidation of linoleic acid [
37]. Additionally, it possesses a subtle aroma reminiscent of grass [
41].
In addition to aldehydes, alcohols and ketones are the other products of lipid metabolism. The flavor thresholds of alcohol are relatively high, and their contribution to the flavor of chicken meat is relatively low. The flavor thresholds of ketones are lower than those of aldehydes, and their contribution to the flavor of meat is also lower. Among the alcohols identified in the chicken meat, 1-octene-3-ol identified as the flavor compound that affected the meat flavor [
38]. It has been demonstrated in pertinent research that 1-octene-3-ol evinces a flavor profile analogous to that of mushrooms [
42]. It imparts a delightful soup-like quality to the flavor profile. Additionally, ketones are regarded as a significant flavor component in meat products [
43].
3.5. Characteristic Fingerprint of Flavor Compounds in Chicken Chest Meats
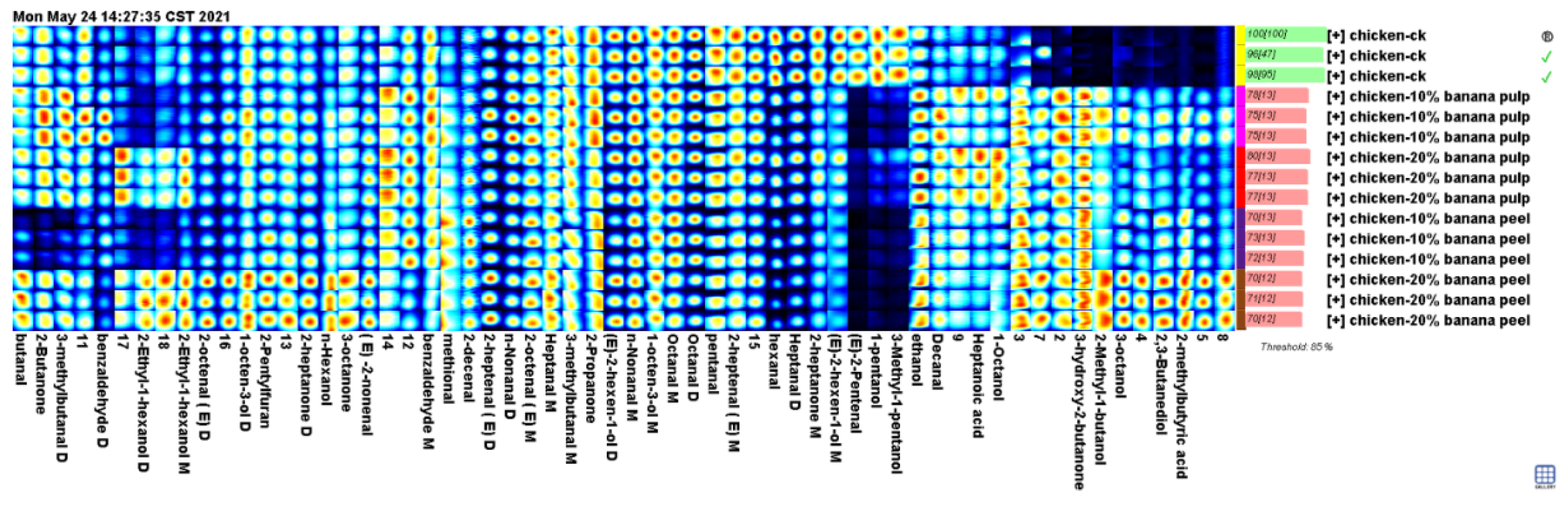
To comprehensively analyze the differences in flavor composition of the chest meat samples, all flavor compound peaks identified in the spectrograms of these samples were selected to form fingerprints (
Figure 2). The results demonstrated that the meat samples in the Pu-10, Pu-20, Pe-10, and Pe-20 groups exhibited the presence of specific flavor compounds that were not observed in other samples. These compounds include 3-hydroxy-2-butanone, 2-methylbutyric acid, 3-octanol, 2,3-butanediol, and 2-methyl-1-butanol. The meat samples in the Pe-20 group exhibited the highest levels of these flavor compounds. The levels of ethanol, 1-octanol, decanal, and heptanoic acid levels in the meat samples of the Pu-10, Pu-20, Pe-10, and Pe-20 groups were found to be higher than those in the control group. In contrast, the levels of pentanal, (E)-2-pentenal, hexanal, heptanal, octanal, 1-pentanol, 3-methyl-1-pentanol, and (E)-2-hexen-1-ol in the meat samples of the control group were higher than those observed in the supplementary groups. However, the levels of these flavor compounds in the meat samples of the supplementary groups exhibited variability.
The incorporation of varying quantities of the fermented banana samples into the poultry feeds resulted in notable alterations in the levels of flavor compounds present in the meat samples. Therefore, the presence of butanal, 3-methyl-butanal, (E)-2-heptenal, (E)-2-octenal, (E)-2-nonenal, N-nonanal, n-hexanol, 2-methyl-1-butanol, 2-ethyl-1-hexanol, 1-octen-3-ol, 3-octanol, 2,3-butanediol, 2-butanone, 2-heptanone, 3-octanone, 2-methylbutyric acid, and 2-pentylfuran was confirmed. The proportion of fermented banana peel added to the poultry feed was found to have a significant impact on the levels of certain flavor compounds present in the meat samples. However, the levels of certain other flavor compounds in the meat samples of the chickens fed with 20% fermented banana samples were found to be lower than in the chickens given 10% fermented banana samples.
3.6. Multivariate Analysis of Flavor Compounds in Chicken Chest Meats
Principal component analysis (PCA) represents one of the most commonly employed methods for reducing the dimensionality of data sets. The method was employed for the purpose of analyzing the principal chemical components present in the samples of chest meat. PCA reduces the number of multivariate data indicators to a smaller number, thereby facilitating comprehensive simplification of the multivariate statistical analysis [
46]. As illustrated in
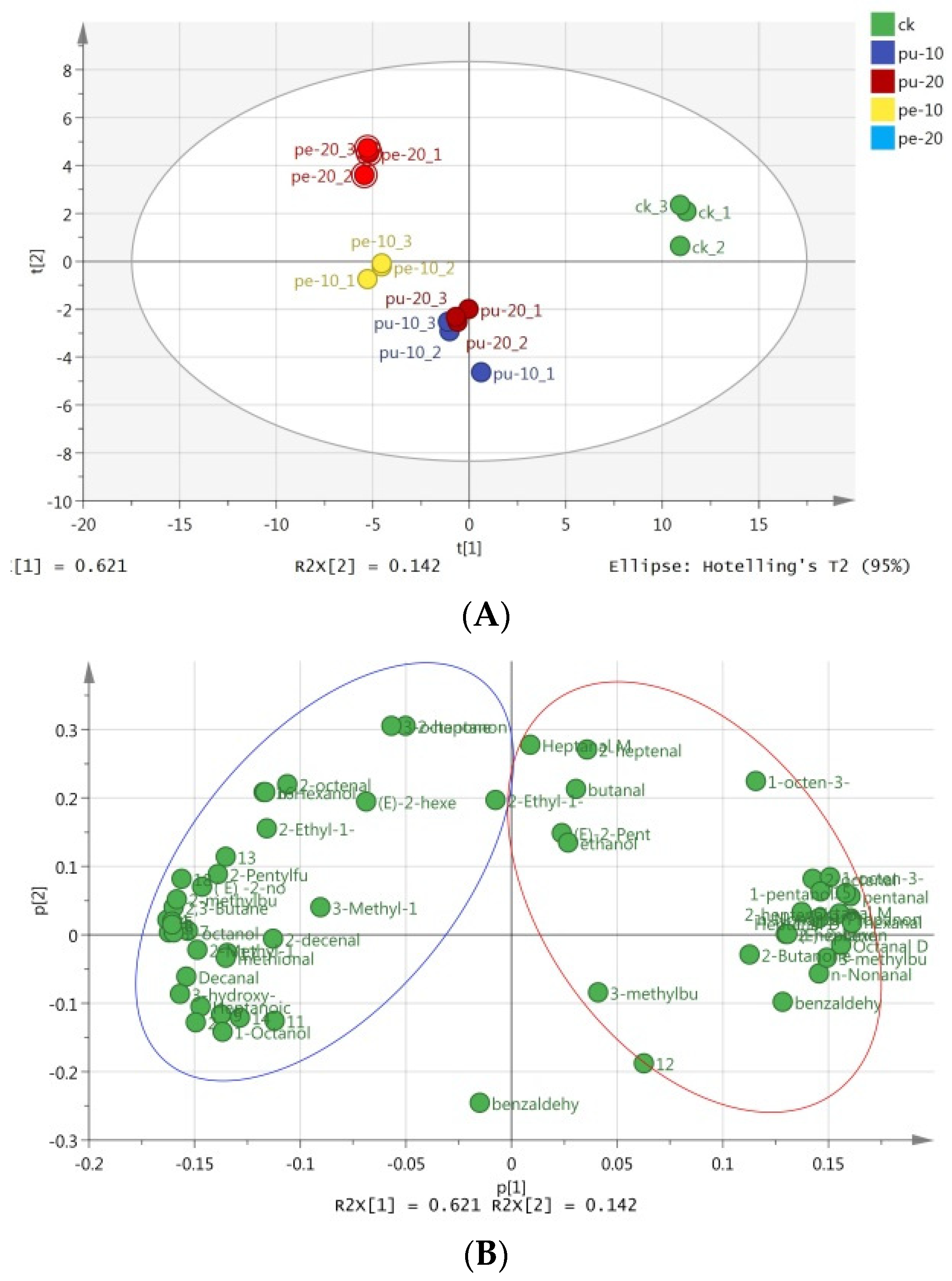
Figure 3A, PC1 and PC2 collectively accounted for 62.1% and 14.2% of the total variance, respectively. The cumulative variance contribution rate of the two principal components is 75.3%. This result demonstrates that the two principal components collectively account for 75.3% of the total variance. The majority of the original information present in the two PCs was retained. Moreover, the analytical efficacy of the principal components was satisfactory.
The flavor profiles of the meat samples in the supplementary groups exhibited notable differences from those of the control group. Additionally, the flavor composition and levels of the meat samples in the Pu groups were found to be similar. As illustrated in
Figure 3B, the aromatic substances displayed on the right side of the PCA loading plot exhibited a positive correlation with PC1. A positive PC1 score was observed for these compounds in the CK group. In contrast, the aromatic substances displayed on the left side of the PCA loading plot exhibited a negative correlation with PC1. This is evidenced by the negative PC1 scores observed for these flavor compounds in the Pe groups
An OPLS-DA model was employed to facilitate a more comprehensive understanding of the distribution patterns of these flavor compounds in the meat samples of the various experimental groups [
47]. As a supervised multivariate statistical analysis method, OPLS-DA was characterized by removal of the data variation in the independent variable X, which was not related to the categorical variable Y. The information was also analyzed as one principal component. Consequently, the model is straightforward and readily comprehensible. It is established that the discriminant effect and the visualization effect of the principal component score plot are known. In this study, the OPLS-DA model employed to identify the most statistically significant variables based on the data matrix regression modelling of the flavor compound peaks detected in the chest meat samples. This was followed by the specific marker compounds that caused the difference in flavor being identified.
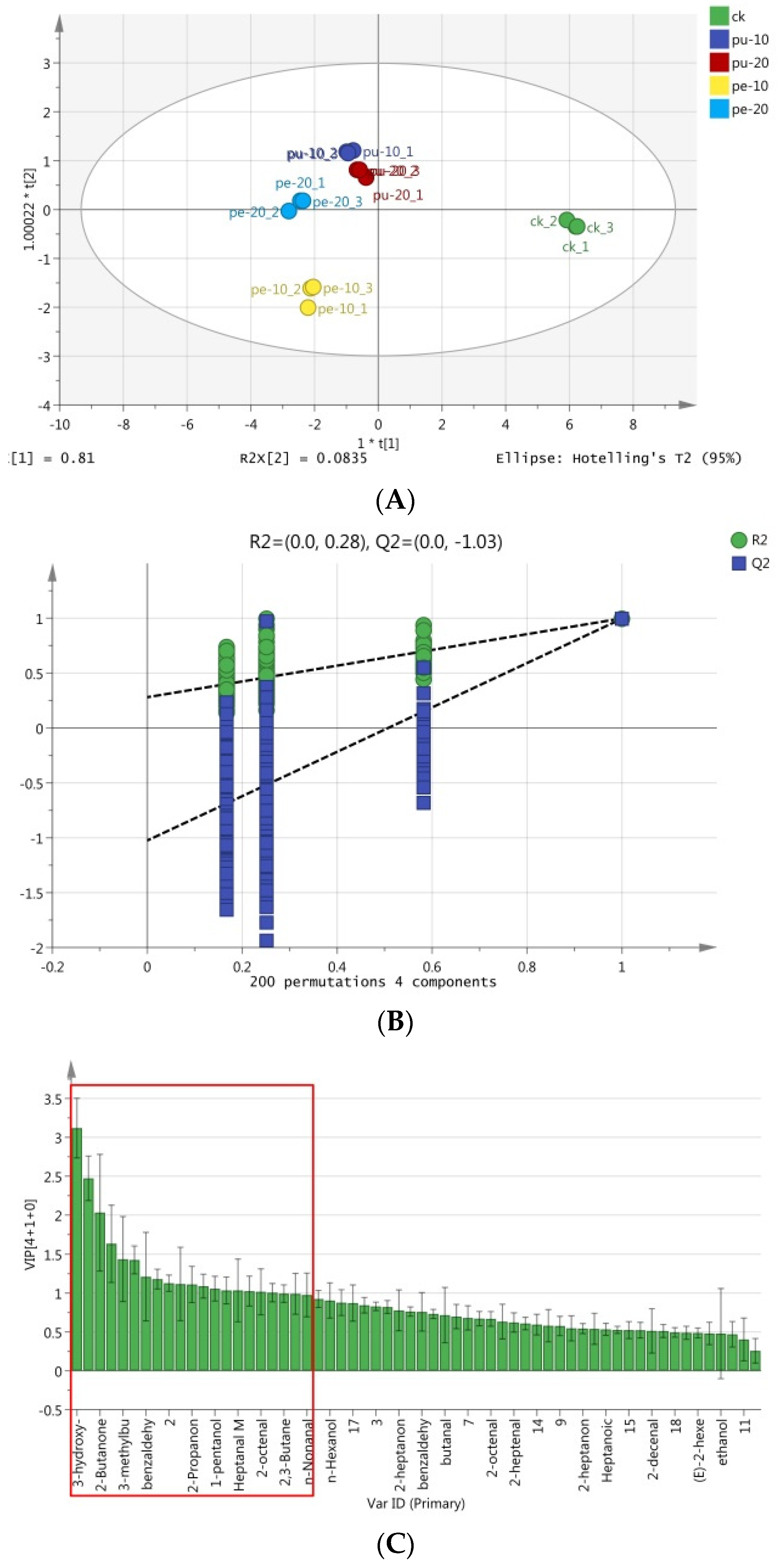
The peak information of flavor compounds in chest meat samples was initially standardized to remove the unit limitation of the data and then converted into a pure value without dimension. This approach allows the lower peak index to be achieved without compromising the flavor value or undermining the reliability of the result. The results of the OPLS-DA analysis of these substances in the meat samples are presented in
Figure 4. The total variance was 89.35%, the R2Y value was 99.1%, and the Q2 value was 94.2%. The flavor compounds in the meat samples were distributed across three of out the four quadrants, with the Pu-10, Pu-20, and Pe-20 groups situated in the second quadrant (with the exception of Pe-20-2), the Pe-10 group in the first quadrant, and the CK group in the fourth quadrant (
Figure 4A). A permutation test was conducted as part of the analysis. Subsequently, the experimental data was randomly rearranged by modifying the sorting order of the categorical variable (Y), and Q2Y was randomly assigned up to 200 times to validate the model.
Figure 4B illustrates the outcomes of the permutation test, wherein the regression line at the Q2 point is observed to intersect the vertical axis below zero, thereby indicating that the discriminant model did not exhibit signs of overfitting the data [
48]. It can thus be concluded that the initial model was superior to the random arrangement model. The 18 characteristic flavor compounds in different groups were also selected according to the variable projection importance index (VIP) exceeding 1 (
Figure 4C). The identified substances were 3-hydroxy-2-butanone, hexanal, 2-butanone, 2-ethyl-1-hexanol M, 3-methylbutanal D, heptanal D, benzaldehyde D, and 2-methylbutyric acid. The remaining compounds were identified as (E)-2,2-heptenal D, 2-propanone, pentanal, 1-pentanol, 1-octen-3-ol M, heptanal M, 2-methyl-1-butanol, (E)-2-octenal D, 2,3-butanediol, and n-nonanal M.
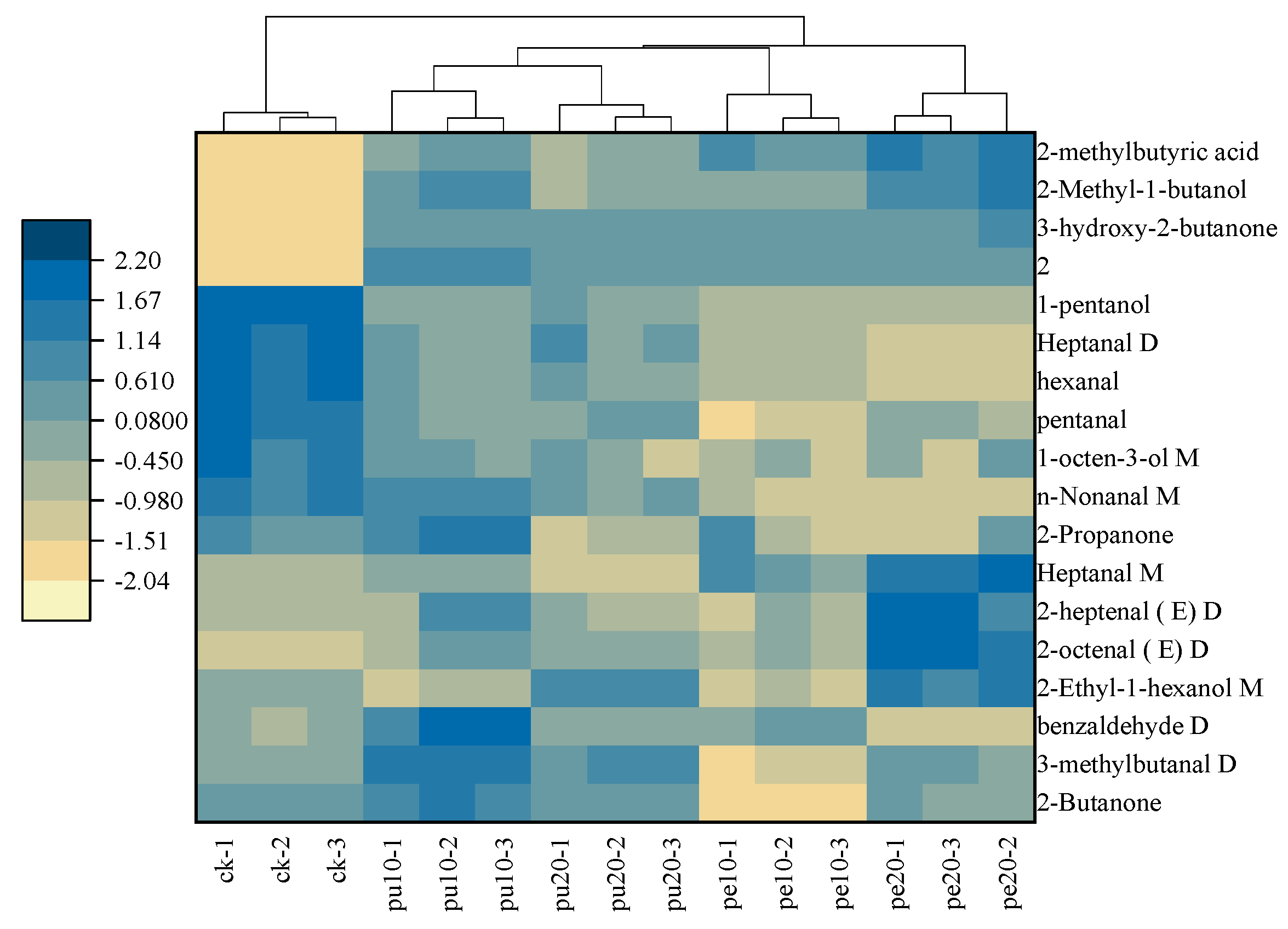
3.7. Cluster Heat Map of Flavor Compounds in Chicken Chest Meats
The OPLS-DA model was employed for the purpose of analyzing the characteristic flavor compounds present in the chest meat samples. The hierarchical cluster analysis was conducted on the 18 characteristic flavor compounds with a VIP score greater than 1. The heat map of these flavor substances was presented to illustrate the clustering of the flavor compounds (
Figure 5). The light to dark-colored squares of the heat map were used to indicate the relative levels of characteristic flavor compounds, with low levels represented by light squares and high levels represented by dark squares. The hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) yielded two categories, the first of which included the control group (CK) and the second of which included the supplementary groups (Pu-10, Pu-20, Pe-10, and Pe-20).
The results demonstrated that the relative content of 2-methylbutyric acid, 2-methyl-1-butanol, 3-hydroxy-2-butanone, and compound 2 in the initial category was less than that observed in the subsequent category. However, the relative content of 1-pentanol, heptanal D, hexanal, pentanal, 1-octen-3-ol M, and N-nonanal M in the first category was higher than in the second category. Among these compounds, hexanal and 1-octen-3-ol were identified as the key flavor compounds in the chest meat samples [
38]. The observed differences in aroma among the meat samples were attributed to variations in flavor content.
4. Conclusions
The findings of this study indicate that the incorporation of varying proportions of fermented banana peel and pulp residue into the daily diet resulted in increased carcass weights and percentages of chicken pectoral and thigh muscles. Additionally, the moisture content, FAs, and flavor components of the chest meat samples demonstrated improvement. Furthermore, the addition of varying proportions of fermented banana peel and banana pulp residue to the daily diet influenced the profile and concentration of flavor compounds in the chicken samples. In conclusion, the incorporation of varying proportions of fermented banana peel and banana pulp residue into the daily diet has the potential to enhance the quality of chicken and influence its flavor profile.
Author Contributions
Zhichun Li: Investigation, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing—original draft. Xuemei He: Methodology, Resources, Project administration. Yayuan Tang: Methodology, Investigation. Ping Yi: Methodology, Investigation. Ying Yang: Formal analysis, Investigation. Jiemin Li: Methodology, Investigation. Dongning Ling: Methodology, Investigation. Bo Jie Chen: Software, Resources. Hock Eng Khoo: Methodology, Writing—review & editing. Jian Sun: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision.
Funding
This study received financial support from the National Modern Agricultural Technology System Construction Special Fund of China (CARS-31).
Institutional Review Board Statement
In accordance with the ethical standards set forth by the relevant institutional review board, the necessity for ethical review and approval was waived for this study. This decision was made due to the fact that the animal subjects involved in the study were domesticated broiler chicken that were subsequently subjected to the commercial slaughtering procedure.
Data Availability Statement
All data are presented in this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the contributions of the research assistants and technical staffs at the laboratories of the Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Guangxi State Farm Jinguang Dairy Co., Ltd., Nanning, China.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Peking, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Oberoi, H.S.; Sandhu, S.K.; Vadlani, P.V. Statistical optimization of hydrolysis process for banana peels using cellulolytic and pectinolytic enzymes. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2012, 90(2), 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Irfan, S.; Nadeem, M.; Mahmood, S. A comprehensive review on nutritional value, medicinal uses, and processing of banana. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38(2), 199–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, G.; Jeevitha, P.; Shadeesh, L. Nutritional analysis of Musa acuminata. Res. Rev. J. Food Dairy Technol. 2017, 5(4), 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wachirasiri, P.; Julakarangka, S.; Wanlapa, S. The effects of banana peel preparations on the properties of banana peel dietary fibre concentrate. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2009, 31(6), 605–611. [Google Scholar]
- Khamsucharit, P.; Laohaphatanalert, K.; Gavinlertvatana, P.; Sriroth, K.; Sangseethong, K. Characterization of pectin extracted from banana peels of different varieties. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, S.; Méndez, P.; Martínez-Fernández, A. Fermentative and nutritive quality of banana by-product silage for goats. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2015, 43(4), 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigueira, J.P.S.; de Jesus, N.G.; Júnior, V.R.R.; Monção, F.P.; Costa, N.M.; David, G.S.S.; e Silva, F.V.; da Cunha Siqueira Carvalho, C. Effects of different banana crop wastes on nutrient intake and digestibility, microbial protein synthesis, feeding behavior, and animal performance of ¾ Holstein× Zebu heifers in a semiarid rangeland. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo, W.; Vargas, J.C.; Uvidia, H.; Samaniego, E.; Valle, S.; Flores, L.; Moyano, J.; Aguiar, S. Physicochemical, biological and organoleptic indicators in banana silage (Musa sapientum) for pig feeding. Cuba J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 51(1). [Google Scholar]
- Aisyah, A.; Gustiningrum, A.S.; Al-Arif, M.A. Substitution of commercial feed with fermented banana peel flour (Musaceaea sp.) and fish meal to feed consumption level, specific growth rate, feed efficiency, fat retention, and energy retention in siam catfish (Pangasius hypophthalmus). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nie, L.; Sun, J.; Hong, Y.; Yan, H.; Li, M.; You, X.; Zhu, L.; Fang, F. Impacts of environmental factors on pasting properties of cassava flour mediated by its macronutrients. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 598960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Sheng, J.; He, X.; Sun, J.; Wei, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Lin, B. , Li, L. Novel antioxidant and hypoglycemic water-soluble polysaccharides from jasmine tea. Foods 2021, 10(10), 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Tang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Deng, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; He, X.; Sun, J. Study on quality change and processing suitability evaluation of the low-temperature vacuum frying of bananas. Foods 2023, 12(9), 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Lin, S.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Sun, J.; Luo, D.; Zeng, S.; Yang, B. Analysis of Chinese olive cultivars difference by the structural characteristics of oligosaccharides. Food Anal. Methods 2013, 6, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Liu, R.; Li, C.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Meat quality and flavor compounds of soft-boiled chickens: effect of Chinese yellow-feathered chicken breed and slaughter age. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101(12), 102168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Xiao, J.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, L. A rapid and multi-element method for the determination of As, Cd, Ni, Pb, Sn, and Zn in scallops using high definition X-ray fluorescence (HDXRF) spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15(10), 2712–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Wei, J.; Khoo, H.E.; Wei, Z.; Mo, R. Growth performance and beef quality of Xinjiang brown cattle fed with different dosages of selenized yeast. SciAsia 2021, 47(6). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Pang, Q.; Yang, H.; Diao, X.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Effects of dietary resveratrol supplementation on the chemical composition, oxidative stability and meat quality of ducks (Anas platyrhynchos). Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, J.; Shao, Y.; Yao, W.; Xia, J.; He, Q.; Huang, F. The effect of dietary garcinol supplementation on oxidative stability, muscle postmortem glycolysis and meat quality in pigs. Meat Sci. 2020, 161, 107998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Jiao, X.; Liu, J.; Jia, M.; Blanchard, C.; Zhou, Z. Characterizing the volatile compounds of different sorghum cultivars by both GC-MS and HS-GC-IMS. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardoia, M.; Romero, C.; Brenes, A.; Arija, I.; Viveros, A.; Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Chamorro, S. Addition of fermented and unfermented grape skin in broilers’ diets: Effect on digestion, growth performance, intestinal microbiota and oxidative stability of meat. Animal 2020, 14(7), 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yao, X.; Zhang, H.; Song, Z.; He, X.; Cao, R. Effects of feeding fermented mulberry leaf powder on growth performance, slaughter performance, and meat quality in chicken broilers. Animals 2021, 11(11), 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teteh, A.; Lawson, E.; Tona, K.; Decuypere, E.; Gbeassor, M. Moringa oleifera leave: hydro-alcoholic extract and effects on growth performance of broilers. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2013, 12(7), 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Qiao, P.; Pan, J.; Qin, Z.; Li, X.; Khoo, H. E.; Dong, X. CaCl2 treatment effectively delays postharvest senescence of passion fruit. Food Chem. 2023, 417, 135786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatkitanan, T.; Harnkarnsujarit, N. Development of nitrite compounded starch-based films to improve color and quality of vacuum-packaged pork. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 25, 100521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, R.A.; Hunt, M. Current research in meat color. Meat Sci. 2005, 71(1), 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Xv, J.; Hou, Y.; Wu, X.; Du, E.; Ding, B. Partial substitution of fermented soybean meal for soybean meal influences the carcass traits and meat quality of broiler chickens. Animals 2020, 10(2), 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.M.; Oiseth, S.K.; Purslow, P.P.; Warner, R.D. A structural approach to understanding the interactions between colour, water-holding capacity and tenderness. Meat Sci. 2014, 98(3), 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, T. Effect of probiotics in poultry for improving meat quality. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 14, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimah, R.; Azrina, A.; Khoo, H.E. Stability of blended palm oils during potato frying. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24(4). [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, S.; Krings, U.; Berger, R.G.; Orlien, V. Aroma development in high pressure treated beef and chicken meat compared to raw and heat treated. Meat Sci. 2010, 86(2), 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, A.C.; Silletti, E.; Mattioli, S.; Dal Bosco, A.; Sebastiani, B.; Menchetti, L.; Koot, A.; Ruth, S.V.; Castellini, C. Fatty acid profile, oxidative status, and content of volatile organic compounds in raw and cooked meat of different chicken strains. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100(2), 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziza, A.E.; Quezada, N.; Cherian, G. Antioxidative effect of dietary Camelina meal in fresh, stored, or cooked broiler chicken meat. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89(12), 2711–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.R.; Gokulakrishnan, P.; Giriprasad, R.; Yatoo, M.A. Fruit-based natural antioxidants in meat and meat products: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55(11), 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Tang, J.; Huang, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J. Influence of partial replacement of NaCl with KCl on formation of volatile compounds in Jinhua ham during processing. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noleau, I.; Toulemonde, B. Quantitative study of roasted chicken flavour. LWT 1986, 19(2), 122–125. [Google Scholar]
- Shahidi, F.; Hossain, A. Role of lipids in food flavor generation. Molecules 2022, 27(15), 5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H.; Wang, G.Y.; Xun, W.; Yu, Y.R.; Ge, C.R.; Liao, G.Z. Characterisation of volatile flavour compounds in Chinese Chahua chicken meat using a spectroscopy-based non-targeted metabolomics approach. Int. Food Res. J. 2021, 28(4), 763–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansorena, D.; Gimeno, O.; Astiasaran, I.; Bello, J. Analysis of volatile compounds by GC–MS of a dry fermented sausage: Chorizo de Pamplona. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34(1), 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, A.; Navarro, J.L.; Flores, M. The influence of nitrite and nitrate on microbial, chemical and sensory parameters of slow dry fermented sausage. Meat Sci. 2006, 73(4), 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ao, Z.; Chui, W.; Shen, C.; Tao, W.; Zhang, S. Characterization of the aroma-active compounds in Daqu: a tradition Chinese liquor starter. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 234, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Liu, H.; Wu, Q.; Hao, L.; Pan, D.; Dang, Y. The flavor quality of dried Lentinus edodes with different species and drying methods (charcoal roasting and naturally drying). J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purrinos, L.; Bermúdez, R.; Franco, D.; Carballo, J.; Lorenzo, J.M. Development of volatile compounds during the manufacture of dry-cured “Lacón,” a Spanish traditional meat product. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76(1), C89–C97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; You, L.; Ji, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Geng, D.; Gao, S.; Bi, Y.; Luo, R. Formation of volatile flavor compounds, maillard reaction products and potentially hazard substance in China stir-frying beef sao zi. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Chen, J.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, G. Effect of star anise (Illicium verum) on the volatile compounds of Stewed chicken. J. Food Process Eng. 2014, 37(2), 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Mitchell, J.P. A comparison of soil quality indexing methods for vegetable production systems in Northern California. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 90(1), 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, C.; He, J.; Dai, Q.; Fang, R. Comparison of the meat metabolite composition of Linwu and Pekin ducks using 600 MHz 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96(1), 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Duan, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Huang, M.; Sun, B. Different distillation stages Baijiu classification by temperature-programmed headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry and gas chromatography-olfactometry-mass spectrometry combined with chemometric strategies. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).