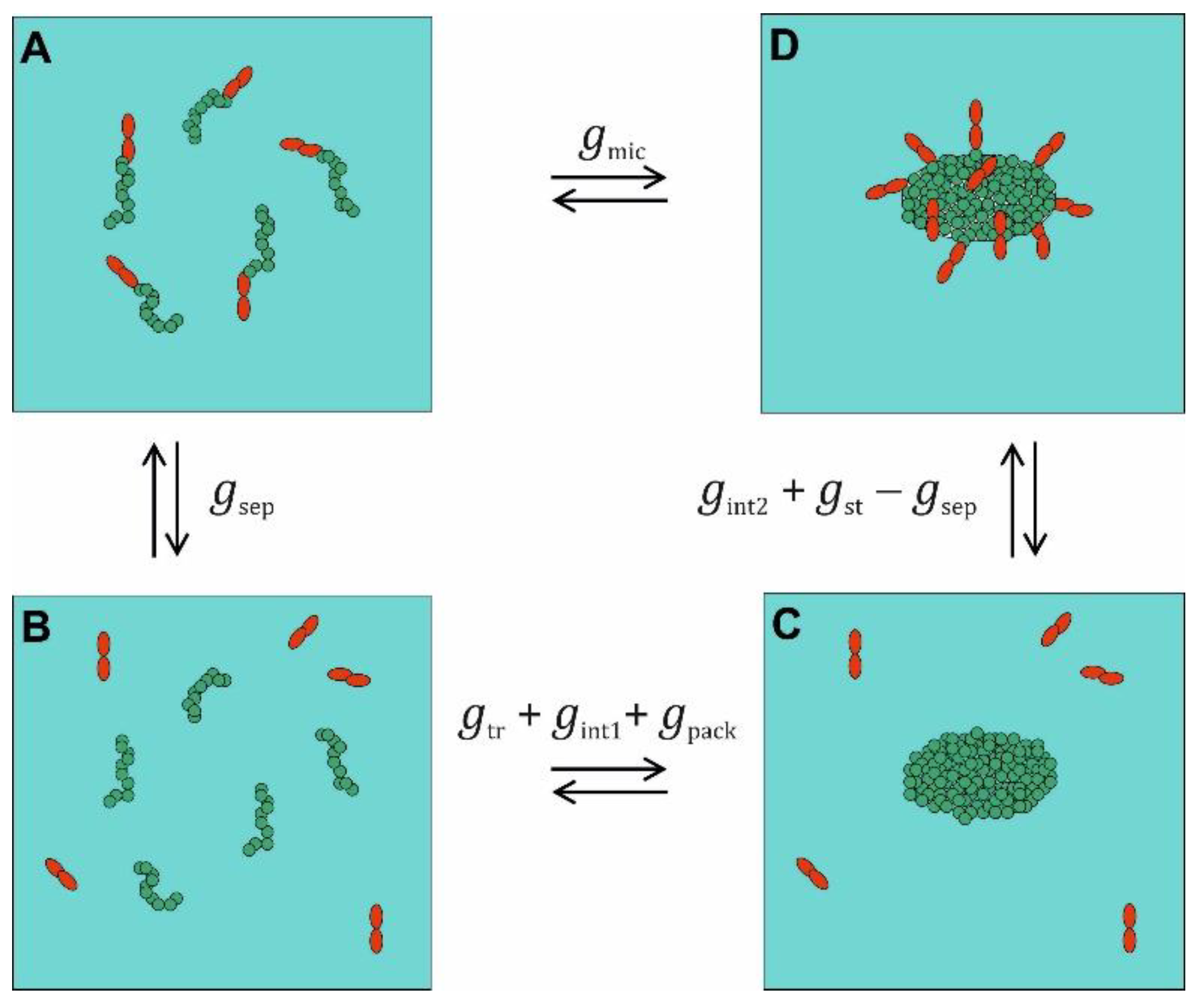
1. Introduction
The self-assembly in water of amphiphilic molecules (detergents, surfactants) – in particular those with a head-tail architecture like
n-alkyl-ß-D-maltosides, where the maltose head (a sugar moiety) is hydrophilic and the alkyl tail is hydrophobic – is a vital process whose understanding bears implications for many research fields such as detergency [
1], biochemistry [
2,
3,
4,
5], and biophysics [
6,
7,
8,
9]. In their seminal paper on the theory of self-assembly of hydrocarbon amphiphiles, Israelachvili et al. [
10] quoted the opening paragraph of a review by Parsegian [
11]: “Despite enormous progress in understanding the genetics and biochemistry of molecular synthesis we still have only primitive ideas of how linearly synthesized molecules form the multimolecular aggregates that are cellular structures. We assume that the physical forces acting between aggregates of molecules and between individual molecules should explain many of their associative properties; but available physical methods have been inadequate for measuring or computing these forces in solids and liquids.” Israelachvili et al. [
10] continue by discussing the burden of linking physical concepts like force and free energy to observable properties of condensed matter and conclude their own opening paragraph by stating: “To be convincing, and to have any hope whatever of reducing to some semblance of order the vast complexity of those intricate multimolecular structures that are the subject of biology, any successful theories of self-assembly must have as a minimal requirement
extreme simplicity to make them accessible to the biologist who has enough concerns of his own not to be dragged into the
subtleties of modern physics” (italics by the present author). Some 50 years later, we face similar problems. It seems even that in the area of life science, the ratio of scientific studies requiring simplicity as regards self-assembly to those dwelling on the subtleties of modern physics (e. g., statistical physics [
12]) has increased.
The focus of our own research in this context [
13,
14,
15,
16] is on understanding the self-assembly of mild, nonionic detergents such as alkyl maltosides in the context of isolating membrane protein complexes from the native membrane [
17], keeping them in aqueous solution as detergent-protein complex (PDC) [
8,
18,
19], and ultimately crystallizing them for structural characterization [
6,
17,
19,
20]. Building on the traditional molecular thermodynamic modeling (TMT) approach [
10,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26], we searched for a formula that links the critical micelle concentration (CMC) – a characteristic measurable quantity indicating the minimal detergent concentration required for the formation of globular detergent aggregates, termed micelles [
27] – to a sum of contributions to the free energy change associated with this self-assembly. In the spirit of the simplicity alluded to above, the TMT approach seeks to explain each part of the sum in terms of molecular properties and comprehensible physical models. Our hope is that such a model, which in the first instance describes only the detergent, can ultimately be incorporated into a model for a more complex system containing, e. g., membrane proteins, vesicles etc. and serve as a prototype for modeling the formation of other types of aggregates such as the detergent belt surrounding a membrane protein in a PDC in aqueous solution [
8,
13].
A problem is here that in a biochemical context, the self-assembly of the detergent takes place in an aqueous medium that is not pure water, but contains a number of ingredients such as buffer and salt. Since the majority of models build within the TMT approach refers to pure water, the question arises of how to incorporate the “salt effects” in a sufficiently simple way into the model. An example of an answer to this question is the work by Carale et al. [
26]. As shown below in
Section 2.2., there are two contributions to the micellization free energy, termed
and
, that are related to the contact of hydrophobic molecular surfaces with water. One term,
, refers to the transfer of the alkyl tail of the detergent monomer into the micelle interior and is modeled on the basis of transfer free energies of alkanes into water. According to Carale et al. [
26], salt effects may be modeled by using instead transfer free energies of alkanes into aqueous salt solutions. The second term,
, referring to the formation of an interface between the hydrophobic interior of the micelle and the surrounding water (partially shielded by the detergent head groups), is modeled by considering the interfacial area of the micellar core and an interfacial tension believed to be identical with the measurable interfacial tension of a macroscopic alkane-water interface [
21]. The solution to the problem of salt effects by Carale et al. [
26] in this context is to use measured interfacial tensions of alkane-aqueous electrolyte interfaces [
28].
Motivated by the idea that cosolute effects on micelle formation might be incorporated into the theory by simply changing the surface tension, we recast
in terms of the molecular surface of the alkyl tail and proposed to lump it together with
[
14]. Since data on the interfacial tension of alkanes and buffer solutions are generally not available, Bothe et al. [
15] devised a fitting procedure, in which experimental CMC data of a series of detergents with the same head group but alkyl tails of different length were combined with molecular properties of the detergents to yield the remaining contributions to the micellization free energy. The surface tension
describing the change in interaction between hydrophobic molecular surfaces of the detergent and the aqueous phase upon micelle formation could then be obtained from the slope value of a linear regression. The resulting value of
30 mN/m [
15] was significantly smaller than the macroscopic value of
50 mN/m [
14,
21,
28]. This discrepancy cannot be traced back to the buffer ingredients. Rather, it is related to an old problem that surface tensions associated with molecular surfaces (“microscopic” surface tensions) are found to be smaller than their measurable “macroscopic” counterparts [
29,
30].
Some 30 years ago, in their 1991 paper in Science, Sharp et al. [
31] suggested that the discrepancy between “microscopic” and “macroscopic” surface tensions is due to the neglect of molecular volume differences between solute and solvent. It is at this stage, where the entropy of mixing comes into play. In the ideal-mixing models usually employed, the entropy of mixing for a simple solution consisting of the solvent (1) and one solute (2) has the form
, where
and
are, respectively, the particle number and mole fraction of species
(
). The simplest way to take into account volume differences between molecular species is to use the theory developed by Flory and Huggins for polymer solutions based on lattice models [
12,
32,
33,
34]. According to this theory, one has to replace the mole fractions
in the above equation for the entropy of mixing by volume fractions
(see below, Eq. (10)). As we shall discuss in detail in the present paper (and as is actually known since 1947 [
35]), the same result can be obtained under appropriate approximations without invoking lattice models. Accordingly, Bothe et al. [
15] speculated that their finding of a small surface tension value could be an artifact of the used ideal-mixing model.
The goal of the present paper is to clarify this issue by developing a Flory-Huggins type of theory for describing the CMC in combination with the TMT approach and - related to the latter – reanalyzing the solubility of alkanes in water in terms of surface tensions. As it turns out, the “microscopic” surface tensions are correct, which bears implications not only for modeling micellization, but also for understanding hydrophobic solvation in aqueous media of complex composition in general. A key aspect is that Sharp et al. [
31] used a modified version of Flory-Huggins theory that was debated [
36]. Here, we attempt an interpretation of this theory and try to explain, why it does not work in modeling micelle formation. In this respect, it was helpful to connect the theory to the concept of the pseudo-chemical potential (PCP) introduced by Ben-Naim [
37,
38]. This connection revealed a deeper problem in the modeling of micellization that is related to the treatment of kinetic energy in statistical mechanics.
The present paper necessarily deals with some of the subtleties of physics. To make these easier accessible, the paper contains a lot of explanations of theoretical concepts and partly has the character of a review. We hope that this is to the benefit of the reader who wants to understand the theory.
4. Discussion
In the present work, we sought to solve a problem in the modeling of the self-assembly of amphiphiles into micelles that is related to the change of the contact free energy of hydrophobic molecular surfaces in contact with the aqueous phase. Following traditional approaches, we modeled the contact free energy in terms of molecular surfaces and an associated surface tension. In agreement with earlier findings [
29,
30,
36,
52], we found the appropriate surface tension value (
= 27-30 mN/m,
Table 3 and
Table 4) to be significantly smaller than the value typically associated with macroscopic alkane-water interfaces (50-53 mN/m [
14,
21,
28]), which cannot be explained with the effects of cosolutes [
28]. Apart from the problem of using different surface definitions (SASA vs. SESA), there has been the proposal in the literature that the discrepancy in surface tension values is due to the neglect of molecular volume differences between solvent and solute [
31]. Since a proposed solution to this issue [
31] is based on a variant of Flory-Huggins theory, we approached the subject by deriving a Flory-Huggins type of theory for the micellization problem. It should be noted that the use of such a theory in the context of micellar solutions is not new. In a study of entropy models related to micelle formation and phase separation in surfactant solutions – which to our knowledge is the only one of this sort available in the literature – Nagarajan [
23] also tested a Flory-Huggins model. In fact, his Eq. (25) for the micellar size distribution is essentially the same as our Eq. (29). However, Nagarajan did not say anything about the derivation of this equation. So we had to start from scratch. The advantage of this line of action was that we learned about the implications of Flory-Huggins theory. In particular, we did not derive it from a lattice model, but based on approximations suggested earlier by Hildebrand [
35].
The starting point of Hildebrand´s approach is Eq. (7), which formulates the entropy of mixing in terms of changes of the free volume for each molecular species including solute and solvent. In the derivation of this equation from classical statistical mechanics, we had to assume that the integration over the spatial coordinates in the partition function yields the free volume (
Appendix A). This is actually wrong given our definition of the free volume (see below). To obtain Eq. (A3) from Eq. (A2), we have to integrate over the empty space not occupied by molecules. However, the integration variables
and
are the COM positions of the molecules, which can sample the empty space only, if we neglect their volumes
. So, there is a contradiction. We encounter here an old problem in condensed matter physics. As discussed by Barrat and Hansen [
55] for the case of spherical molecules, it is “important to realize that, while the excluded volume associated with each individual sphere is
, the total volume
from which the centre of a test sphere is excluded is less then
, since the exclusion spheres of neighbouring particles can overlap” (English spelling from the original). This problem makes the determination of the volume accessible to the COM of a molecule practically impossible, if not determined numerically. In fact, one may use Monte-Carlo (MC) or molecular dynamics (MD) techniques to gain insight into the accessible volume. In contrast, the free volume in Hildebrand´s theory – as it is perceived by Flory – “is considered to represent the difference between the actual volume of the liquid (or the amorphous polymer) and the minimum volume which it would occupy if its molecules were packed firmly in contact with each other. Incompressible molecules with rigid dimensions are implied in this definition of a free volume. The unrealistic nature of this implication undermines precise determination, or even an exact definition, of the free volume.
The concept has proved useful nevertheless“ (see footnote on p. 506 of [
34]; italics by the present author). In view of these difficulties, we rigorously defined the free volume by the space not occupied by molecules. Then, in order to base Eq. (7) on statistical mechanics, which mainly serves to underscore that
is a free energy
difference, we have to temporarily reinterpret the integration variables in Eq. (A2) in order to get the right results. This bold step might be justified by the fact that subsequent approximations necessary to arrive at Flory-Huggins theory mitigate the inconsistency. The definition of the free volume by
is necessary to have the actual volume
of a molecule as reference for the subsequent approximations.
As pointed out by Barrat and Hansen [
55], each particle in a condensed liquid is trapped on average in a cage of neighboring molecules. Leaving large-sale diffusion aside, it is then useful to ask for the volume that the COM of a molecule can sample while it rattles in its solvent cage. In a hard-core description, where we neglect the subtleties of intermolecular interactions, the SES of each molecule and its neighbors define the ultimate limits of the molecular motion in the cage. The volume of the cage – on average – is in fact
, which is related to the molar volume by
and can in principle, at least for pure substances, be determined experimentally (cf. the molar volumes of alkanes in
Table 2). If we imagine the molecule moving in its cage, it is reasonable to assume that the volume sampled by the COM of the molecule is at least approximately determined by the difference between the volume of the cage and the volume of the molecule itself. This is the basic idea of introducing the free volume as
. Whatever the quality of this approximation is, it allows for a consistent treatment in statistical mechanics, since now it is the integration over the COM coordinate of each molecule that determines
. Therefore, the partition function given for the pure substance in Eq. (A4) is consistent. Introducing the concept of an additive solution then allows carrying over this consistency to the mixture, so that Eq. (8) for the entropy of mixing, albeit approximate and unable to account for excess volumes, is more firmly rooted in statistical mechanics than Eq. (7).
The next bold step in Hildebrand´s approach is to assume that is proportional to with the same proportionality constant for all molecule types. This assumption entails a corresponding proportionality between and . Only with this trick are we able to convert the ratio of free volumes between the pure substances and the mixture into the volume fraction according to Eq. (9). After all, it is not surprising that restrictive conditions are required to formulate a theory that has been derived before on the basis of a lattice model. Nonetheless, Hildebrand´s approach is instructive, since it allows us to learn more about the implications of Flory-Huggins theory. In the context of micelle formation, we learn from Eq. (17) that we cannot model the volume difference between a micelle with aggregation number and detergent monomers in water.
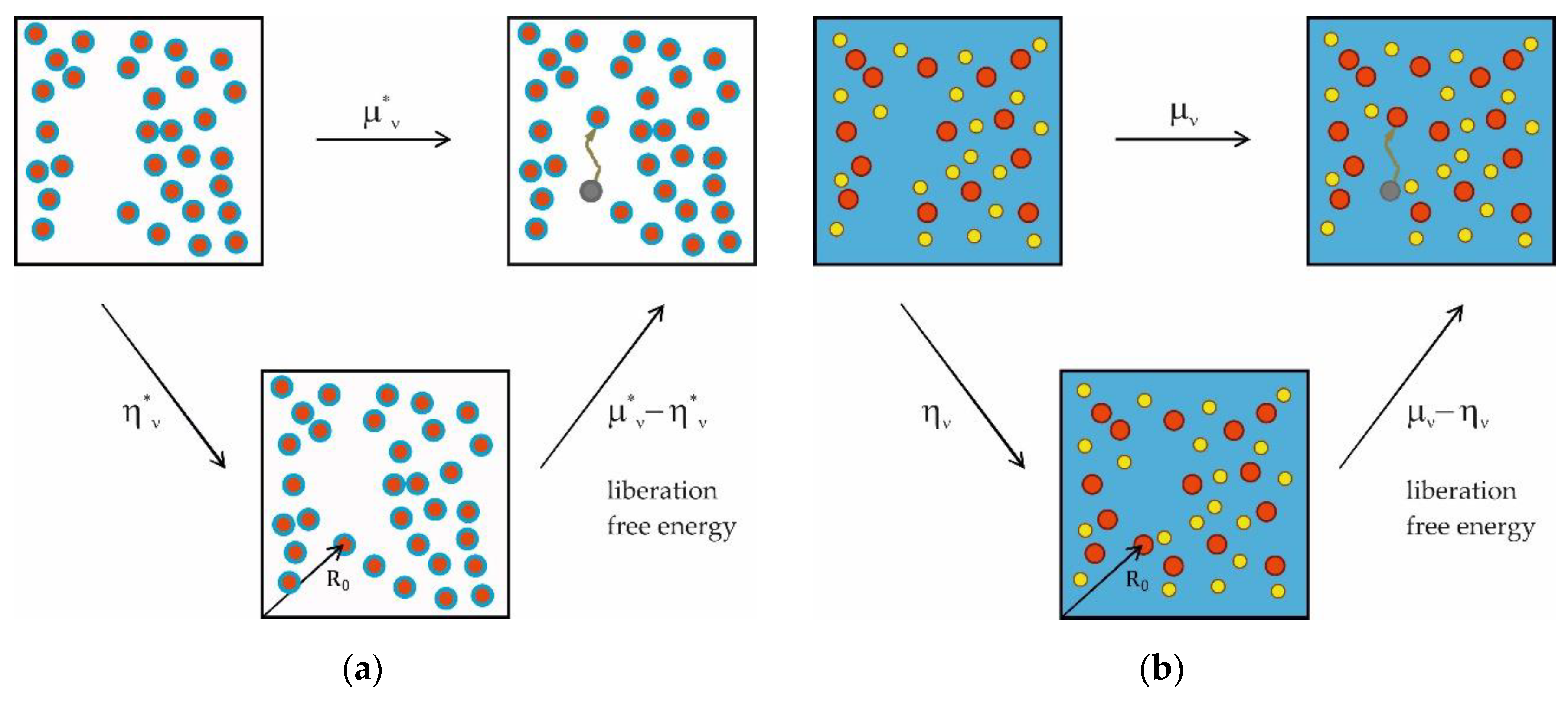
The further consequences of Flory-Huggins theory become more transparent, when we consider the concept of the PCP [
37,
38]. We see that the micellization free energy modeled in the TMT approach is actually a PCP difference, which is, however, not sufficient to model micelle formation. In contrast to the alkane partitioning problem, where according to
Section 2.3.1., the kinetic energy contribution cancels out, so that the PCP difference is related to the volume fraction in a simple way within Flory-Huggins theory (see Eq. (57)), there is a contribution from kinetic energy and free volume changes in a self-assembly problem. Curiously, this contribution is found to be largely canceled by the terms necessary to convert mole fractions into volume fractions. This seems to indicate that the parameters of the TMT model taken over from ideal-mixing approaches work well only because of error compensation. On the other hand, assuming that these parameters are actually good enough and the cancelation is not merely due to error compensation, we estimated the ratio
of the free volume of the detergent monomer to its thermal deBroglie wavelength to the power of 3. The result is that the characteristic length scale for the rattling of the COM position of a detergent monomer in its solvent cage is between 3 to 4 times the thermal deBroglie wavelength. Given that the latter is on the order of 0.046 Å for the detergents studied here, this would imply a COM motion amplitude on the order of 0.14 to 0.18 Å. At present, we cannot say, whether this is a realistic value. Future research should reevaluate the parameters from TMT modeling, before any conclusions about the free volume can be drawn.
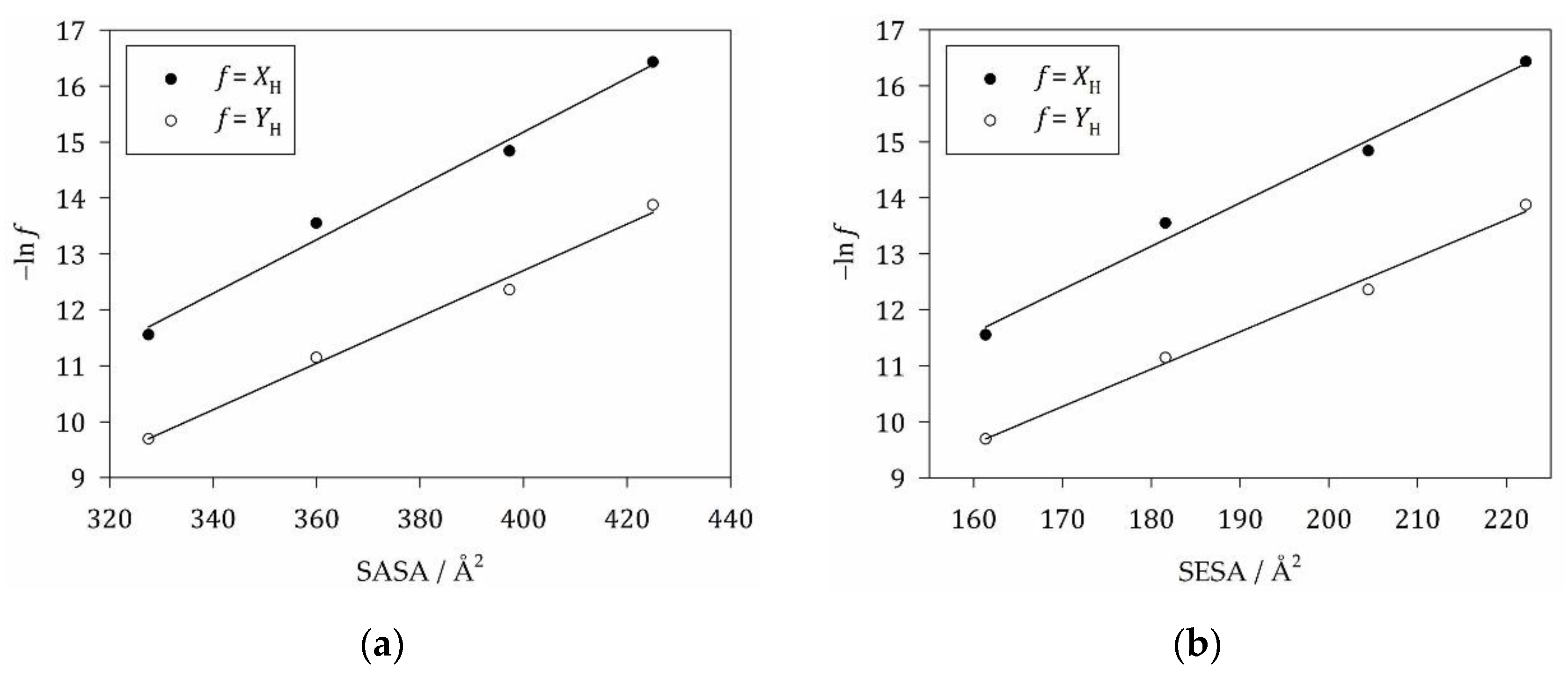
The correlation plots in
Figure 5 indicate that those parts of the micellization free energy that depend on the contact of hydrophobic molecular surfaces with the aqueous environment can well be modeled with a surface tension that is similar to that obtained from the analysis of alkane solubility in water. The crucial point is here that the transfer free energy involves the full PCP including the part due to the free volume
. This makes sense, because besides the hydrocarbon-water interaction, the change of the free volume in the aqueous phase, matters in both the transfer of the alkane from water into the pure alkane phase (or vice versa) and the transfer of the detergent´s alkyl tail from water into the micelle interior. Accordingly, the same surface tension has to be used in both cases, if the transfer free energy is related to the SESA of the respective hydrocarbon. And the corresponding surface tension value is the one referred to as “microscopic”.
In contrast, Sharp et al. [
31] for the SASA and Tuñón et al. [
53] for the SESA found higher surface tension values from a correlation of the quantity
in Eq. (D2), which we confirmed (
Figure S2,
Table S1). Our analysis reveals that the “microscopic” and “macroscopic” surface tensions differ, because the latter does not take into account the free volume contribution
. This could make sense either, because the free volume change due to incorporation of an alkane molecule into the aqueous phase is not of relevance for the interfacial energy of a macroscopic alkane surface in contact with water. In other words: The molecular volume ratio of alkane and water is relevant for the solvation of the alkane in water, but not for the alkane molecules at the macroscopic interface.
This seems to be bad news for our attempts to model cosolute effects in a simple way. If the “microscopic” surface tension is relevant for the micellization free energy, what is then the relevance of measured macroscopic alkane-aqueous electrolyte interfacial tensions? First of all, we have to note that we cannot yet draw any conclusions about cosolute effects due to the error margins in the present analysis of experiments. Irrespectively, the connection between and via in Eq. (D2) could be a means to derive reasonable values of the “microscopic” surface tension for electrolyte solutions or buffer solutions from experiment.
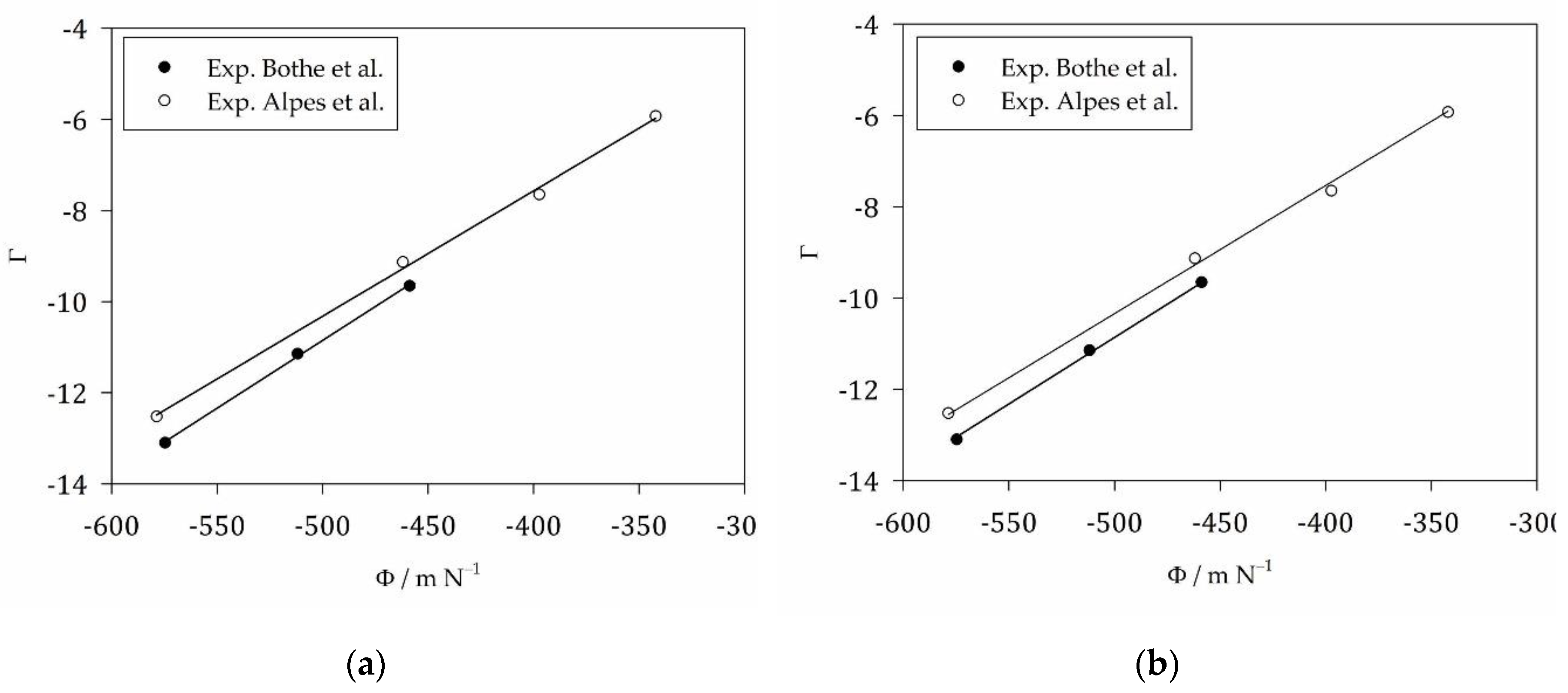
Finally, we have to discuss an error source that could cause different slopes in the alkane partitioning plots in
Figure 4 compared to the micellization plots in
Figure 5. In the latter, the surface tension is not related to a pure SESA, but to
, which results from lumping together
and
(see Eq. (47) in
Section 2.2.3.). The effective area
contains the surface area
of the micellar core per detergent molecule, so that the actual surface area of the core is
mA. The surface of the core is defined as the smooth surface of an oblate spheroid [
14]. Yet, the problem is not necessarily the surface itself, but the meaning of the free energy contribution. Since the free-volume effect of partitioning of the alky tail into water is already accounted for in
, it is possibly not relevant for
. Therefore, it might be necessary to use the “macroscopic” surface tension in
. So, was the merging of
and
premature? This is one of the many questions that will have to be answered in future work.
5. Conclusions
In an attempt to achieve the “extreme simplicity” in the modeling of micelle formation claimed by Israelachvili et al. [
10], we devised a theory, in which all contacts between hydrophobic molecule parts and water are modeled by the SESA and an appropriate surface tension [
14,
15]. This surface tension turns out to be smaller by a factor of about 3/5 than the interfacial tension of a macroscopic alkane-water interface. It has been suggested that this discrepancy is due to the neglect of volume differences between solute and solvent in the theory [
31]. Therefore, we re-derived a formalism that combines Flory-Huggins theory [
32,
33,
34] – the simplest way to incorporate molecular volume differences – with the TMT approach [
21,
24]. This theory practically replaces the description of the solution in terms of mole fractions (ideal mixing) by one in terms of volume fractions, which can be seen in particular from the expression for the entropy of mixing in Eq. (10). The derivation was based on ideas published some time ago by Hildebrand [
35], which shed light on the implications of Flory-Huggins theory beyond lattice models. Further insight was gained by considering the concept of the PCP introduced by Ben-Naim [
37,
38]. It turned out that the traditionally modeled micellization free energy corresponds to a PCP difference between micelles and monomers and has to be complemented by a term describing the liberation free energy difference. The neglect of the latter in earlier treatments might be the reason for the observed failure of Flory-Huggins theory in predicting CMCs [
23]. It remains to be clarified, to what extent earlier models based on mole fractions depend on error compensation.
The difference between “microscopic” and “macroscopic” surface tension is not due to the neglect of molecular volume ratios. In fact, incorporating molecular volume effects via Flory-Huggins theory slightly decreases the value of the surface tension. The reason for the high surface tension found by Sharp et al. [
31] for the SASA and by Tuñón et al. [
53] for the SESA is the separation of the term
(cf.
Figure S1). Here,
is the molecular volume ratio of hydrocarbon and water. This term is part of the PCP difference
in the transfer problem, which is the same for the transfer of the detergent´s alkyl tail into the micelle as for the transfer of an alkane molecule from water into a pure liquid alkane phase. It describes the free energy change due incorporation of a voluminous alkane molecule into the aqueous phase (change of the free volume) and consequently depends on the ratio
. In contrast, the quantity relevant to describe the contact free energy at a macroscopic alkane-water interface is
(cf. Eq. (S43)), which (approximately) does not contain contributions from the incorporation of alkane into the aqueous phase. Curiously, the ratio of surface tensions obtained from analyzing
compared to
is 44.8/27.4 ≈ 1.6, which is accidentally the same as the SASA/SESA ratio. This together with the fact the conversion factor from mN/m to cal/(mole Å
2) is similar (~1.4) led to some confusion in the past [
15].
Since cosolutes (salts, buffer) influence the solubility of hydrophobic substances in water, the idea was put forward that modified surface tension values could be used to model the influence of cosolutes on micelle formation [
15,
26]. The problem is here that the “microscopic” surface tension has to be used, which is not generally available for buffered solutions, if not based on fits to solubility data that are likewise not generally available. There is hope, however, that one could use measured macroscopic surface tension data corrected by the term
(or simply a factor 3/5) for this purpose. In this way, we could – after some struggle with the subtleties of condensed matter physics – get back to simplicity.