Submitted:
21 September 2024
Posted:
24 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Treatment and Purity Control
2.2. Combustion Calorimetry
2.3. High-Temperature Calvet Microcalorimetry
2.4. Computational Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Studies
3.1.1. Enthalpies of Combustion and Formation in the Liquid Phase
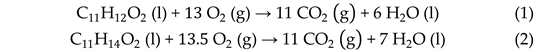
3.1.2. Enthalpy of Vaporization
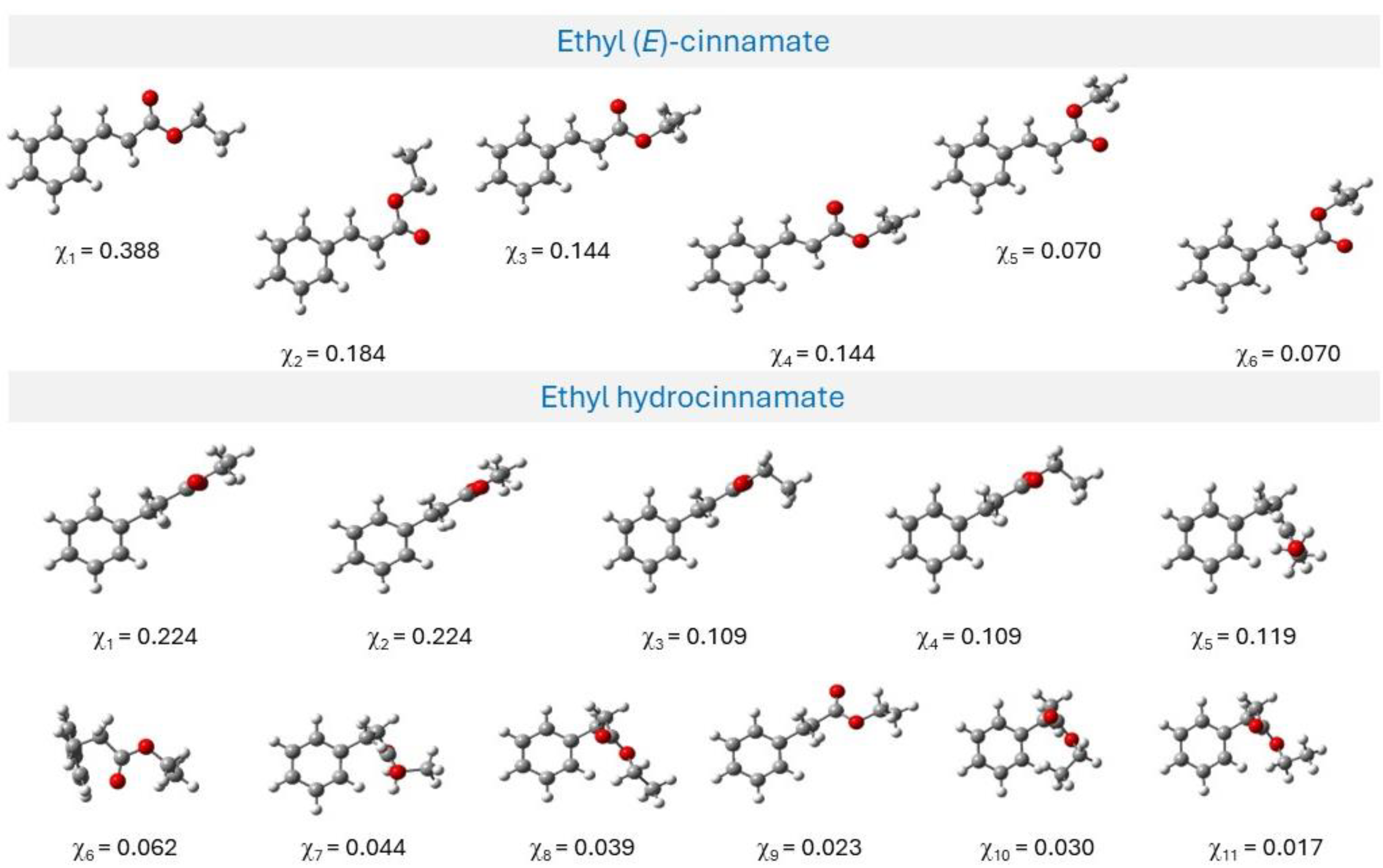
3.2. Computational Studies
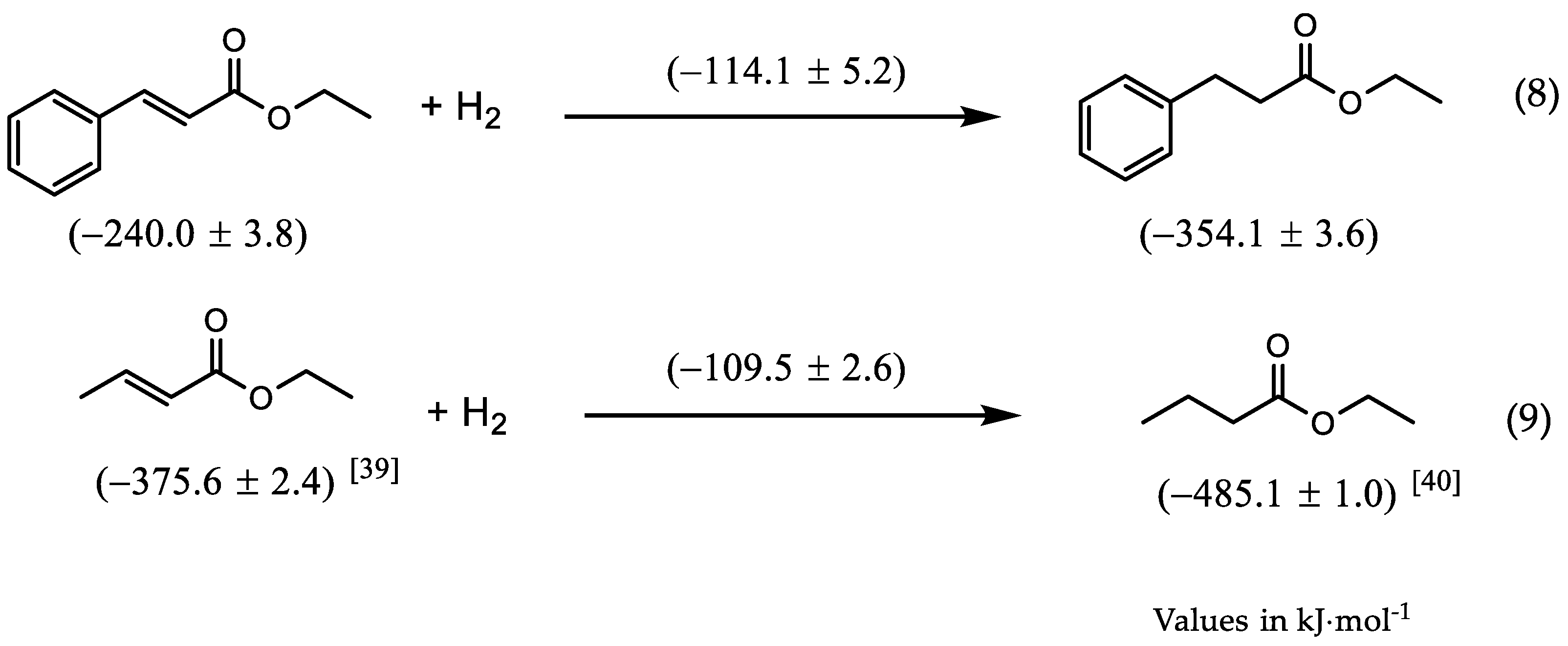
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoessel, F. Thermal Safety of Chemical Processes: Risk Assessment and Process Design, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, C.A.O.; Freitas, V.L.S.; Ribeiro da Silva, M.D.M.C. Determination and Analysis of Thermodynamic Properties of Methyl Methylanthranilate Isomers. Molecules 2023, 28, 6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledo, J.M.; Flores, H.; Freitas, V.L.S.; Solano-Altamirano, J.M.; Hernández-Pérez, J.M.; Ribeiro da Silva, M.D.M.C.; Camarillo, E.A. Thermal and structural properties of ethyl 2- and 3-aminobenzoates: Experimental and computational approaches. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 133, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ximello-Hernández, A.; Freitas, V.L.S.; Ribeiro da Silva, M.D.M.C. ; Assessment of thermochemical data of γ-butyrolactone from experimental and computational studies. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 1968–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlbusch, K.-G.; Hammerschmidt, F.-J.; Panten, J.; Pickenhagen, W.; Schatkowski, D.; Bauer, K.; Garbe, D.; Surburg, H. Flavors and Fragrances. In Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, Z.; et al. Characterization of the differences in the aroma of cherry wines from different price segments using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, odor activity values, sensory analysis, and aroma reconstitution. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Hao, J.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Z.; Qin, Q. Flavor Contribution of Esters in Lager Beers and an Analysis of Their Flavor Thresholds. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2017, 75, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.P.; Wellington, G.A.; Cocchiara, J.; Lalko, J.; Letizia, C.S.; Api, A.M. Fragrance material review on ethyl cinnamate. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, S90–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masselink, W.; Reumann, D.; Murawala, P.; Pasierbek, P.; Taniguchi, Y.; Bonnay, F.; Meixner, K.; Knoblich, J.A.; Tanaka, E.M. Broad applicability of a streamlined ethyl cinnamate-based clearing procedure. In Proceedings of the Development, 1 February 2019. 146 (3): dev166884., 1 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Barandiaran, A.; Gomez-Caturla, J.; Ivorra-Martinez, J.; Lascano, D.; Selles, M.A.; Moreno, V.; Fenollar, O. Esters of Cinnamic Acid as Green Plasticizers for Polylactide Formulations with Improved Ductility. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023, 308, 2300022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, M.C.; Oliveira Lima, E.; Perez-Castillo, Y.; Sousa, D.P. Synthetic Cinnamides and Cinnamates: Antimicrobial Activity, Mechanism of Action, and In Silico Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.O.; Pérez-Castillo, Y.; Oliveira, L.H.G.; Nunes, F.C.; de Sousa, D.P. Larvicidal Activity of Cinnamic Acid Derivatives: Investigating Alternative Products for Aedes aegypti L. Control. Molecules 2021, 26, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.G.; Martins, C.; Tavares, T.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Alves, F.; Rocha, S.M. Volatile Composition of Fortification Grape Spirit and Port Wine: Where Do We Stand? Foods 2023, 12, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieniuk, B.; Fabiszewska, A.; Wołoszynowska, M.; Białecka-Florjańczyk, E. Synthesis of flavor compound ethyl hydrocinnamate by Yarrowia lipolytica lipases. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2021, 39, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Shi, X.; Qu, R.; Junge, K.; Junge, H.; Beller, M. Toward a Hydrogen Economy: Development of Heterogeneous Catalysts for Chemical Hydrogen Storage and Release Reactions. ACS Energy Lett. 2022, 7, 3734–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuster, P.; Papp, C.; Wasserscheid, P. Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers (LOHCs): Toward a Hydrogen-Free Hydrogen Economy. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlovskiy, M.; Gobble, C.; Chickos, J. Vapor pressures and vaporization enthalpies of a series of esters used in flavors by correlation gas chromatography. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2015, 86, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, V.L.S.; Oliveira, L.I.P.; Ribeiro da Silva, M.D.M.C. Standard molar enthalpies of formation of the acetylpyridine isomers. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2007, 39, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TCI Europe, N.V. "Ethyl (E)-Cinnamate" Safety Data Sheet, 2024. Available online: https://tcichemicals.com (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- TCI Europe, N.V. "Ethyl 3-Phenylpropionate" Safety Data Sheet, 2024. Available online: https://tcichemicals.com (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Certificate of Analysis, Standard Reference Material 39j, Benzoic Acid Calorimetric Standard, N. B. S., Washington, 1995.
- Prohaska, T.; Irrgeher, J.; Benefield, J.; Böhlke, J.; Chesson, L.; Coplen, T.; Ding, T.; Dunn, P.; Gröning, M.; Holden, N.; Meijer, H.; Moossen, H.; Possolo, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Vogl, J.; Walczyk, T.; Wang, J.; Wieser, M.; Yoneda, S.; Zhu, X.; Meija, J. Standard atomic weights of the elements 2021 (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2022, 94, 573–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro da Silva, M.A.V.; Ribeiro da Silva, M.D.M.C.; Pilcher, G. The construction, calibration and use of a new high-precision static bomb calorimeter. Rev. Port. Quim. 1984, 26, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, H.A.; Snelson, A. The heats of combustion of the four isomeric butyl alcohols. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1960, 56, 1776–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.M.N.B.F.; Silva, M.T.; Schröder, B.; Gomes, L. ; LABTERMO: Methodologies for the calculation of the corrected temperature rise in isoperibol calorimetry. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2007, 89, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, F.A.; Brown, D.L.S.; Connor, J.A.; Leung, W.L.; Paz-Andrade, I.M.; Skinner, H.A. Thermochemistry of arene chromium tricarbonyls and the strengths of arene-chromium bonds. J. Organomet. Chem. 1975, 97, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro da Silva, M.A.V.; Matos, M.A.R.; Amaral, L.M.P.F. Thermochemical study of 2-, 4-, 6-, and 8-methylquinoline. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 1995, 27, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.M.N.B.F.; Schröder, B.; Fernandes, O.O.P.; Ribeiro da Silva, M.A.V. Measurement of enthalpies of sublimation by drop method in a Calvet type calorimeter: design and test of a new system. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 415, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, R.; Xu-Wu, A.; Chickos, J.S.; Planas Leitão, M.L.; Roux, M.V.; Torres, L.A. Reference materials for calorimetry and differential thermal analysis. Thermochim. Acta. 1999, 331, 93–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Li, X.; Caricato, M.; Marenich, A.; Bloino, J.; Janesko, B.G.; Gomperts, R.; Mennucci, B.; Hratchian, H.P.; Ortiz, J.V.; Izmaylov, A.F.; Sonnenberg, J.L.; Williams-Young, D.; Ding, F.; Lipparini, F.; Egidi, F.; Goings, J.; Peng, B.; Petrone, A.; Henderson, T.; Ranasinghe, D.; Zakrzewski, V.G.; Gao, J.; Rega, N.; Zheng, G.; Liang, W.; Hada, M.; Ehara, M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Nakajima, T.; Honda, Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Vreven, T.; Throssell, K.; Montgomery, J.A., Jr.; Peralta, J.E.; Ogliaro, F.; Bearpark, M.; Heyd, J.J.; Brothers, E.; Kudin, K.N.; Staroverov, V.N.; Keith, T.; Kobayashi, R.; Normand, J.; Raghavachari, K.; Rendell, A.; Burant, J.C.; Iyengar, S.S.; Tomasi, J.; Cossi, M.; Millam, J.M.; Klene, M.; Adamo, C.; Cammi, R.; Ochterski, J.W.; Martin, R.L.; Morokuma, K.; Farkas, O.; Foresman, J.B.; Fox, D.J. Gaussian 09, Revision A.02; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford CT, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss, L.A.; Raghavachari, K.; Redfern, P.C.; Rassolov, V.; Pople, J.A. Gaussian-3 (G3) theory for molecules containing first and second-row atoms. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 109, 7764–7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baboul, A.G.; Curtiss, L.A.; Redfern, P.C.; Raghavachari, K. ; Gaussian-3 theory using density functional geometries and zero-point energies. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 7650–7657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, V.L.S.; Lima, A.C.M.O.; Sapei, E.; Ribeiro da Silva, M.D.M.C. Comprehensive thermophysical and thermochemical studies of vanillyl alcohol. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2016, 102, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, W.N.; Scott, D.W. Standard states and corrections for combustions in a bomb at constant volume. In Experimental Thermochemistry; Rossini, F.D., Ed.; Interscience, New York, 1956; Volume 1.
- Cox, J.D.; Wagman, D.D.; Medvedev, V.A. CODATA Key values for Thermodynamics; Hemisphere, New York, 1989.
- Taylor, B.N.; Kuyatt, C.E. Guidelines for evaluating and expressing the uncertainty of NIST measurement results. NIST Technical Note 1297, 1994 Edition.
- NIST Computational Chemistry Comparison and Benchmark Database, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 101, Release 16a, August 2013, Editor: Russell D. Johnson III. https://cccbdb.nist.gov/vibscalex.asp. Accessed 5 july 2023. 20 August.
- Freitas, V.L.S.; Ribeiro da Silva, M.D.M.C.; Gomes, J.R.B. A computational study on the thermochemistry of methylbenzo- and methyldibenzothiophenes. J. Mol. Struct.: THEOCHEM 2010, 946, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedley, J.B. Thermochemical Data and Structures of Organic Compounds Thermodynamics, Research Center, College Station, Texas, 1994.
- Wiberg, K.B.; Waldron, R.F. Lactones. 2. Enthalpies of hydrolysis, reduction, and formation of the C4-C13 monocyclic lactones. strain energies and conformations, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1991, 113, 7697–7705. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.B. Heats of Catalytic Hydrogenation in Solution. I. Apparatus, Technique, and the Heats of Hydrogenation of Certain Pairs of Stereoisomers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1942, 64, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.W. Heats of hydrogenation: experimental and computational hydrogen thermo-chemistry of organic compounds. World Scientific, 2006. Available online: https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ (accessed on 4 August 2024).
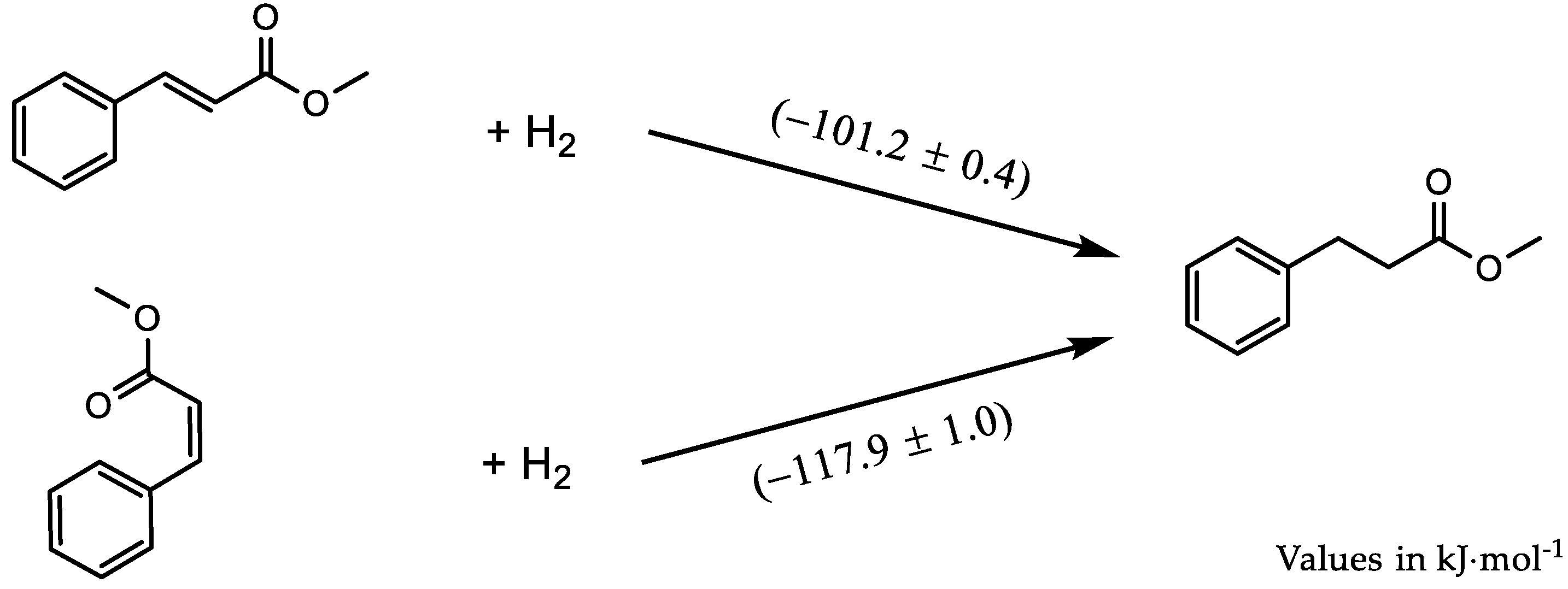
| Compound | / kJ⋅mol-1 | / kJ⋅mol-1 | / kJ⋅mol-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| EEC | −5726.2 ± 2.4 1 | −5731.2 ± 2.4 1 | −312.4 ± 2.8 2 |
| EHC | −5901.2± 2.8 1 | −5907.4 ± 2.8 1 | −422.0 ± 3.2 2 |
| Compound | T /K | /kJ·mol-1 | /kJ⋅mol-1 | / kJ·mol-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EEC (l) | 345.6 | 82.8 ± 0.81 | 10.4 ± 0.22 | 72.4 ± 2.53 |
| EHC (l) | 376.1 | 86.4 ± 0.31 | 18.6 ± 0.42 | 67.9 ± 1.74 |
 |
 |
| / kJ⋅mol-1 | / kJ⋅mol-1 | / kJ⋅mol-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| experimental | computational | |||
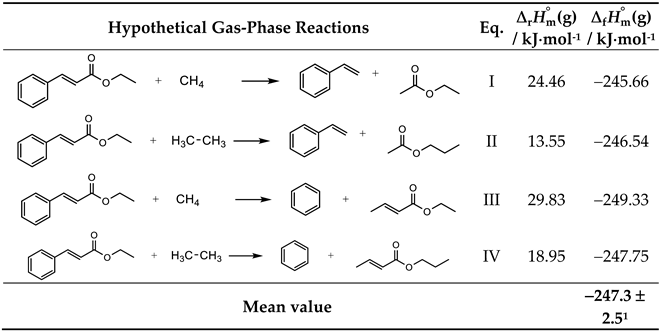
| EEC | 72.4 ± 2.51 | −312.4 ± 2.81 | −240.0 ± 3.82 | −247.3 ± 2.51 |
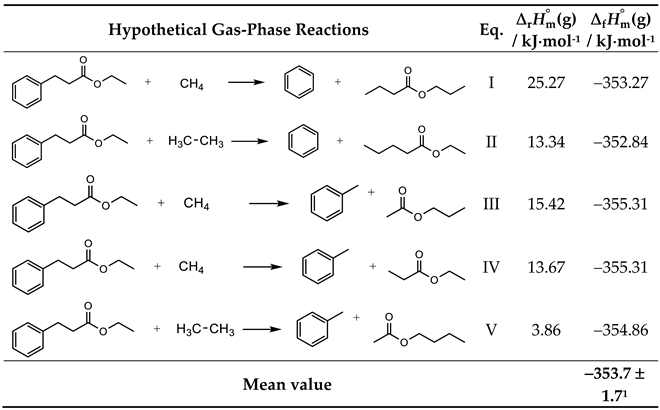
| EHC | 67.9 ± 1.71 | −422.0 ± 3.21 | −354.1 ± 3.62 | −353.7 ± 1.71 |
| Reactions | / kJ⋅mol-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Isomer E | Isomer Z | ||
| But-2-ene + H2 → Butane | −114.5 ± 0.4 | −118.5 ± 0.4 | |
| Pent-2-ene + H2 → Pentane | −114.6 ± 0.4 | −118.5 ± 0.4 | |
| Hex-2-ene + H2 → Hexane | −113.8 ± 1.3 | −115.8 ± 0.8 | |
| Hex-3-ene + H2 → Hexane | −112.3 ± 1.7 | −122.6 ± 1.3 | |
| Hept-2-ene + H2 → Heptane | −114.1 ± 0.5 | −117.9 ± 0.4 | |
| Hept-3-ene + H2 → Heptane | −114.7 ± 0.3 | −120.0 ± 2.9 | |
| Oct-2-ene + H2 → Octane | −115.5 ± 0.7 | −119.4 ± 1.1 | |
| Oct-3-ene + H2 → Octane | −115.8 ± 0.4 | −117.8 ± 0.4 | |
| Oct-4-ene + H2 → Octane | −115.0 ± 0.7 | −114.6 ± 0.4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





