Submitted:
22 September 2024
Posted:
24 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
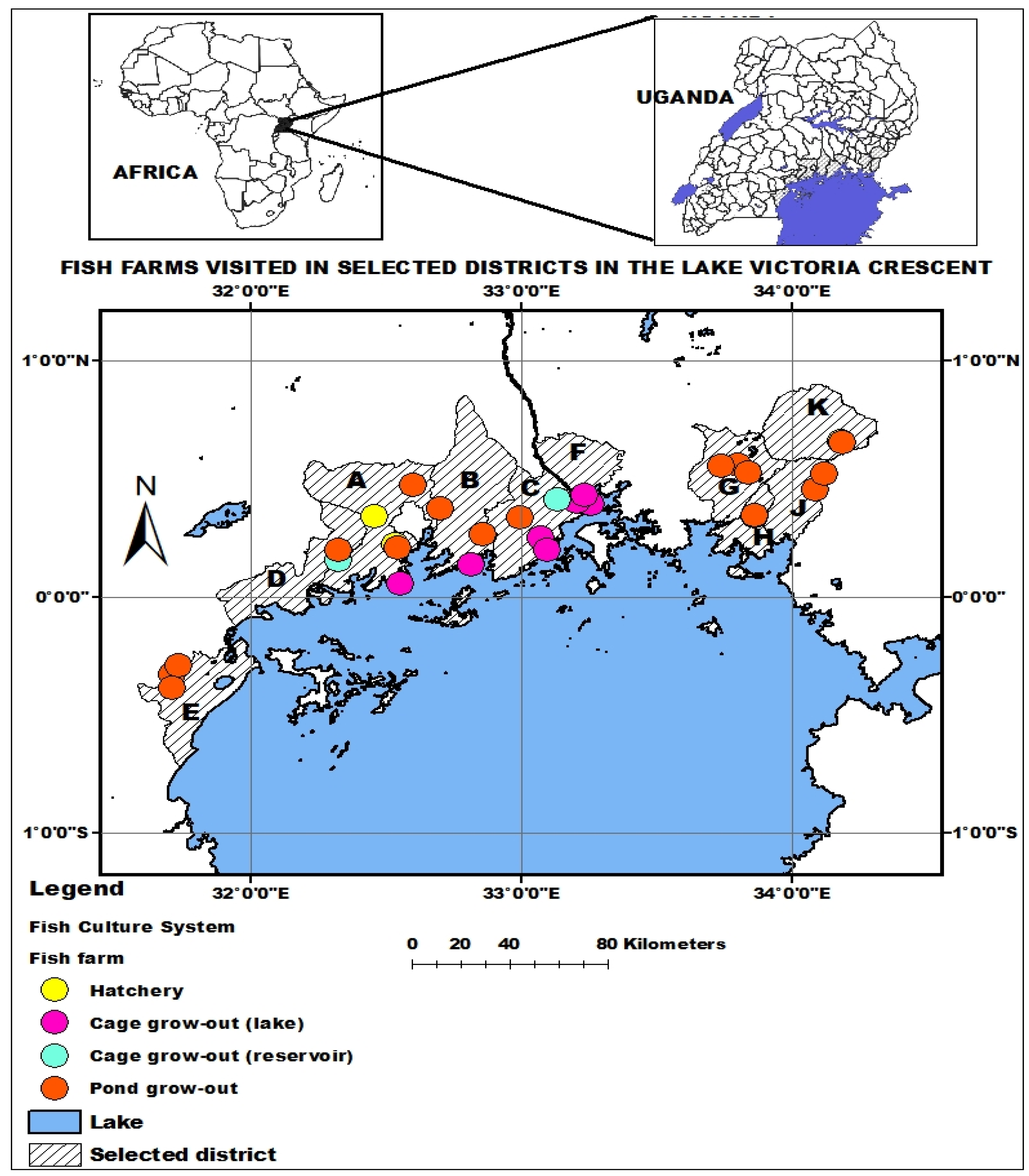
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
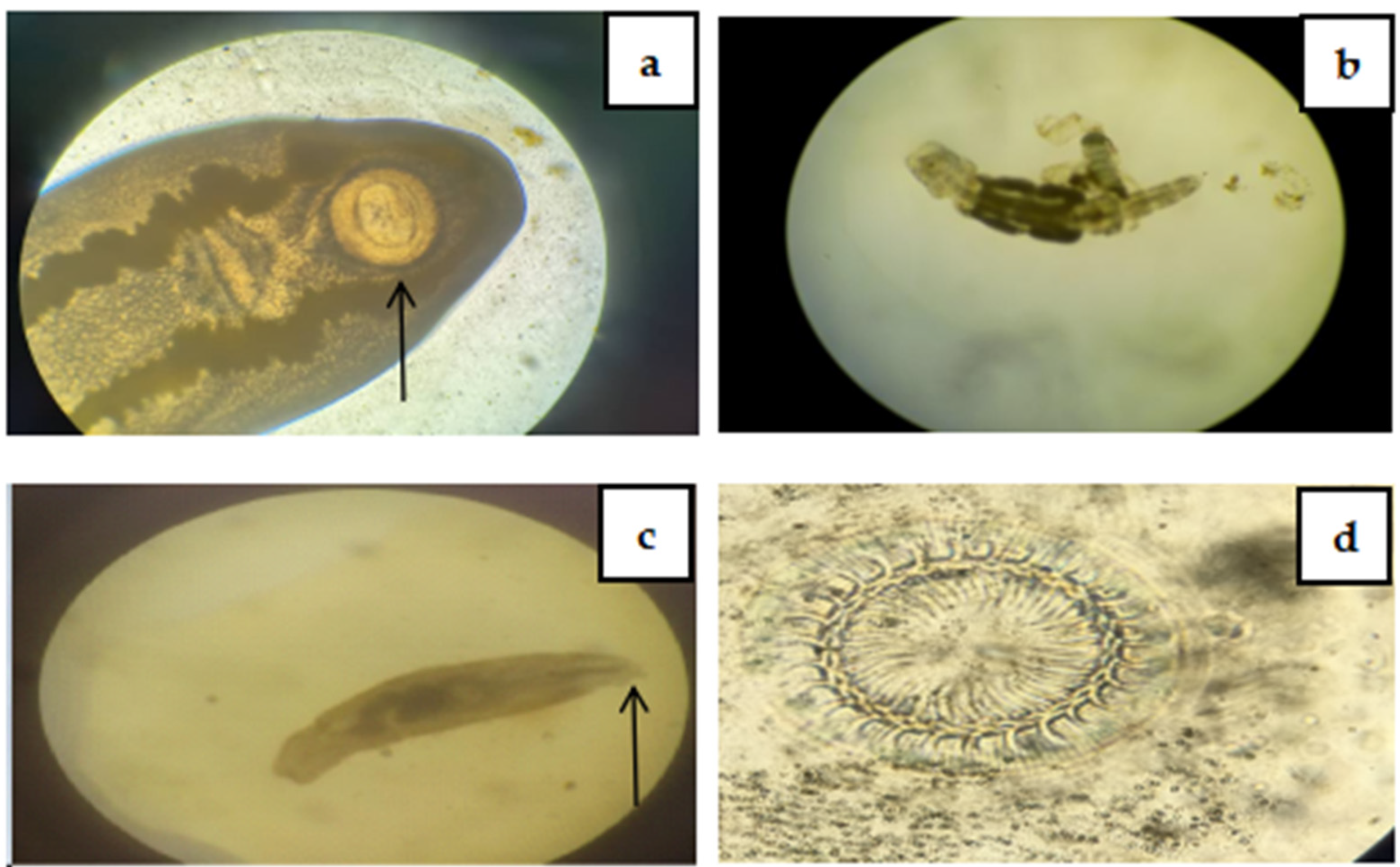
2.2. Examination of Fish for Different Parasites
2.2.1. Macroscopic Examination
2.2.2. Microscopic Examination
2.3. Collection of Water Quality, Farm Management Practices and Other External Factors (Intermediate Hosts and Wild Fish Entry)
2.3.1. Water Quality
2.3.2. Farm Management Practices Data and External Factors
2.4. Assessment of Geographical Areas for Potential Parasitic Proliferation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Parasite Diversity and Infestation Levels
2.5.2. Effect of Water Quality, Farm Management Practices and External Factors on Parasitic Proliferation
2.5.3. Assessment of Fish Farms in Lake Victoria Crescent for Potential Parasitic Infestation
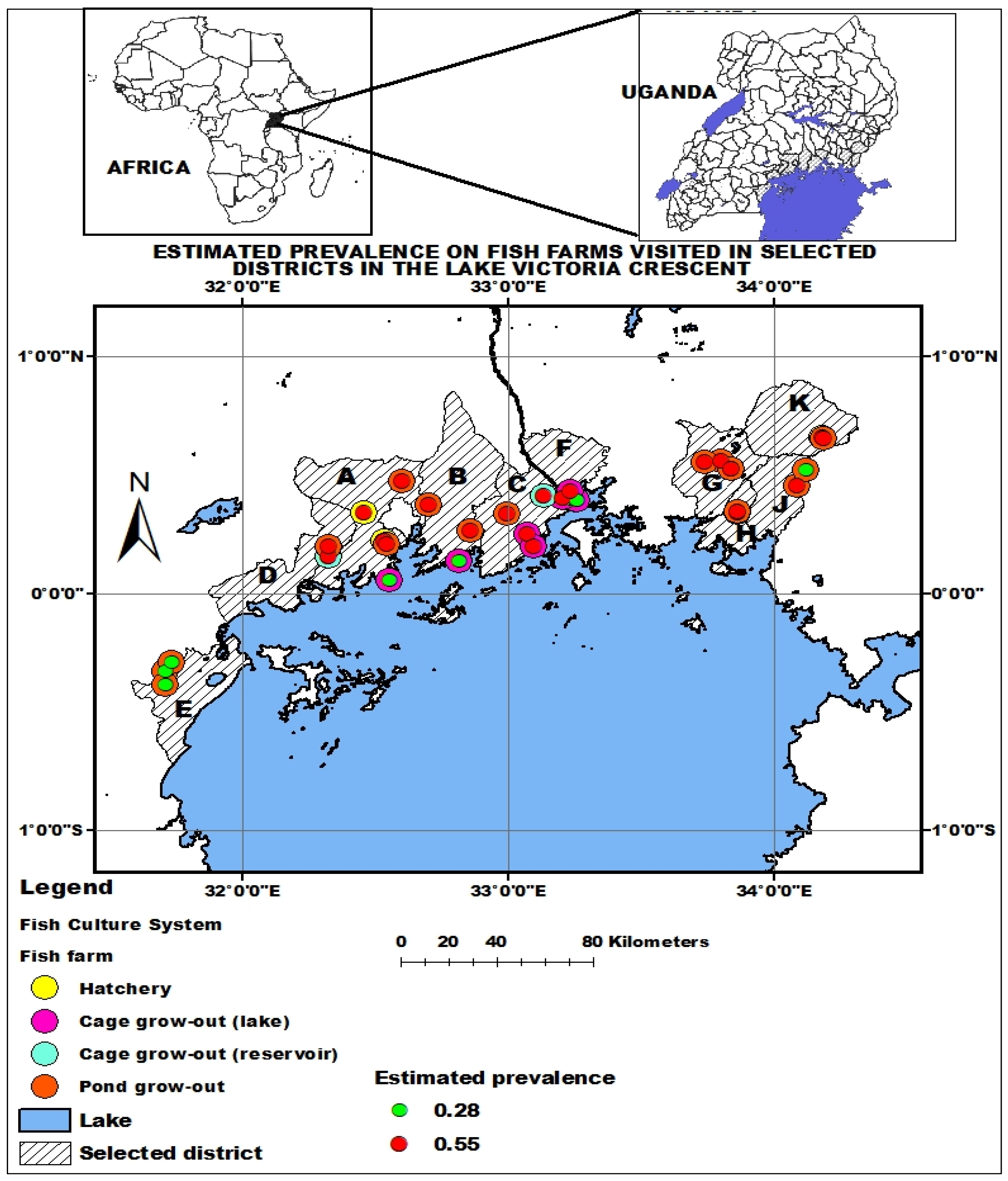
2.5.4. Mapping of the Estimated Parasitic Infestation on Fish Farms in the Lake Victoria Crescent
3. Results
3.1. Parasite Diversity and Infestation Levels
3.2. Water Quality, Farm Management Practices, External Factors and Parasitic Infestation
3.2.1. Water Quality, Farm Management Practices and External Factors in the Various Fish Farms
3.2.2. Effect of Water Quality, Farm Management Practices and External Factors on Parasitic Infestation
| No. | Model covariates | Estimate | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | intercept + dissolved oxygen | -0.0244 | 0.306 |
| 2. | intercept + temperature | -0.0610 | 0.093 |
| 3. | intercept + pH | -0.109 | 0.147 |
| 4. | intercept + salinity | -0.227 | 0.832 |
| 5. | intercept + total dissolved solids | 0.0149 | 0.985 |
| 6. | intercept + conductivity | -0.0000569 | 0.915 |
| 7. | intercept + ammonia | -0.0347 | 0.658 |
| 8. | intercept + hardness | 0.00236 | 0.264 |
| 9. | intercept + nitrite | -0.194 | 0.729 |
| 10. | intercept + chloride | 0.00630 | 0.130 |
| 11. | intercept + fish seed source | -0.116 | 0.228 |
| 12. | intercept + feeding and nutrition | 0.0958 | 0.402 |
| 13. | intercept + stocking density | 0.0000000152 | 0.339 |
| 14. | intercept + wild fish entry | 0.153 | 0.0931 |
| 15. | intercept + intermediate hosts | 0.267 | 0.00465* |
| 16. | intercept + disinfection | -0.0571 | 0.530 |
3.3. Estimation of Parasitic Infestation
4. Discussion
4.1. Parasite Diversity and Infestation Levels
4.2. Effect of Water Quality, Farm Management Practices and External Factors on Parasitic Infestation
4.2.1. Water Quality, Farm Management Practices and External Factors on Parasitic Infestation
4.2.2. Effect of Risk Factors on Parasitic Infestation at Various Farms across the Lake Victoria Crescent
4.3. Parasitic Infestation Estimation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024. Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy. 2024. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/items/ef79a6ba-d8df-41b9-9e87-2b6edd811511 (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Magunda, M. Situational analysis study of the agriculture sector in Uganda CCAFS Report, CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS).CCAFS: Wageningen,Netherlands. 2020. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10568/111685 (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- MAAIF. Annual performance report of financial year 2019/2020; Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry and Fisheries: Entebbe, Uganda, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The state of Food and Agriculture 2007. Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy. 2007. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/d0c64d8e-f537-40a7-970e-bb89733fc54d/content (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Adeleke, B.; Robertson-Andersson, D.; Moodley, G.; Taylor, S. Aquaculture in Africa: A comparative review of Egypt, Nigeria, and Uganda vis-a-vis South Africa. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2021, 29, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasozi, N.; Rutaisire, J.; Nandi, S.; Sundaray, J.K. A review of Uganda and India’s freshwater aquaculture: Key practices and experience from each country. J. Ecol. Nat. Environ. 2017, 9, 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Walakira, J.; et al. Common fish diseases and parasites affecting wild and farmed tilapia and catfish in central and western Uganda. Uganda J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Akoll, P.; Konecny, R.; Mwanja, W.; Nattabi, J.K.; Agoe, C.; Schiemer, F. Parasite fauna of farmed Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and African catfish (Clarias ariepinus) in Uganda. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 110, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.S.; Dhiman, M.; Swain, P.; Das, B.K. Fish diseases and health management issues in aquaculture ICAR-CIFA Training manual No.18; Central Institute of Freshwater Aquaculture: Bhubaneswar, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Modu, B.M.; Zaleha, K.; Shaharom-Harrison, F.M. Water quality assessment using monogenean gill parasites of fish in Kenyir Lake, Malaysia. Nig. J. Fish. Aquac. 2014, 2, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Delwar, M.; Kabil, M.; Habibur, M. Water quality parameters and incidence of fish diseases in some water bodies in Natore, Bangladesh. J. Earth Sci. 2011, 2, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Abowei, J.F.; Briyai, O.F.; Bassey, S.E. A Review of Some Basic Parasite Diseases in Culture Fisheries Flagellids, Dinoflagellides and Ichthyophthriasis, Ichtyobodiasis, Coccidiosis Trichodiniasis, Heminthiasis, Hirudinea Infestation, Crustacean Parsite and Ciliates. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- Md. Ali, R.F. Fish parasite: infectious diseases associated with fish parasite; Department of Aquaculture, Bangladesh Agricultural University: Mymensingh, Bangladesh, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shinn, A.P.; Pratoomyot, J.; Bron, J.; Brooker, A. Economic impacts of aquatic parasites on global Finfish production; Global Aquaculture Advocate: Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Akoll, P.; Mwanja, W.W. Fish health status, research and management in East Africa: past and present. Afr. J. Aquat. 2012, 37, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenyambuga, S.W.; Mwandya, A.; Lamtane, H.A.; Madalla, N.A. Productivity and marketing of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) cultured in ponds of small-scale farmers in Mvomero and Mbarali districts, Tanzania. Livest. Res. Rural Dev. 2014, 26, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ragasa, C.; Ulimwengu, J.; Randriamamonjy, J.; Badibanga, T. Factors affecting performance of agricultural extension: Evidence from Democratic Republic of Congo. J. Agric. Educ. Ext. 2016, 22, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulu, S.; Munganga, B.; Hasimuna, O.; Hambiya, L.; Seemani, B. A Review of the Science and Technology Developments in Zambia’s Aquaculture Industry. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Giana, B.G.; Kate, S.H.; Jose,, S.D.; Catherine, C.; Scott, H.; Terrence, L.M.; Dean, R.J. Predicting parasite outbreaks in fish farms through environmental DNA; Global Aquaculture Advocate: Queensland, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Juhásová, L.; Králová-Hromadová, I.; Zeleňáková, M.; Blišťan, P.; Bazsalovicsová, E. Transmission risk assessment of invasive fluke Fascioloides magna using GIS-modelling and multicriteria analysis methods. Helminthologia 2017, 54, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavornpanich, S.; Mathilde, P.; Viljugrein, H.; Abrial, D.; Jimenez, D.; Brun, E. Risk map and spatial determinants of pancreas disease in the marine phase of Norwegian Atlantic salmon farming sites. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, A.G. Using simple models to review the application and implications of different approaches used to simulate transmission of pathogens among aquatic animals. Prev. Vet. Med. 2009, 88, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinodhkumar, O.R.; Sinha, D.K.; Singh, B.R. Use of Geographical Information System (GIS) in veterinary science; Biotech Books: India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Peeler, E.J.; Taylor, N.G. The application of epidemiology in aquatic animal health - opportunities and challenges. Vet. Res. 2011, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.M.; Moore, J.H. A call for biological data mining approaches in epidemiology. BioData Min. 2016, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagum, N.; Monir, M.S.; Khan, M.H. Present status of fish diseases and economic losses due to incidence of disease in rural freshwater aquaculture of Bangladesh. J. Innov. Dev. Strategy 2013, 7, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zolovs, M.; Priekule, M.; Gasperovich, O.; Kolesnikova, J.; Osipovs, S.; Spuòìis, V. The spatial distribution of Perch (Perca fluviatilis) ectoparasites and the effect of chemical water quality parameters on ectoparasite spatial niche size. Proc. Latv. Acad. Sci. B: Nat. 2018, 72, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranaya, P.K.; Amiya, K.S.; Bima, P.M. GIS applications in fish disease mapping and forecasting. Adv.Fish. Res. 2019, 7, 355–369. [Google Scholar]
- Falconer, L.; Telfer, T.; Pham, K.L.; Ross, L. GIS technologies for sustainable aquaculture. In Comprehensive Geographic Information Systems, Huang, B.; Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences: Oxford, England, 2018; pp. 209–314. [Google Scholar]
- Longley, P.A.; Goodchild, M.F.; Maguire, D.J.; Rhind, D.W. Geographic Information Science and Systems, 4th ed.; John Wiley and Sons Inc: New Jersey, United States, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- UNMA. September to December 2019 seasonal rainfall outlook over. Uganda National Meteorological Authority: Kampala, Uganda. 2019. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/uganda/september-december-2019-seasonal-rainfall-outlook-over-uganda (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Pech, D.; Aguirre-Macedo, L.M.; Lewis, J.M.; Vidal-Martínez, M.V. Rainfall induces time-lagged changes in the proportion of tropical aquatic hosts infected with metazoan parasite. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, S.M.; Salem, A.M.; Mahdy, O.A.; Ibrahim, E.S. Prevalence of metacercarial infection in some marketed fish in Giza Governorate, Egypt. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2019, 49, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitiku, M.A.; Konecny, R.; Haile, A.L. Parasites of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) from selected fish farms and Lake Koftuin, Central Ethiopia. Ethiop. Vet. J. 2018, 22, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shahawy, I.; El-Seify, M.; Metwally, A.; Fwaz, M. Survey on endoparasitic fauna of some commercially important fishes of the River Nile, southern of Egypt (Egypt). Rev. De Med. Vet. 2017, 168, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Reavill, D.; Roberts, H. Diagnostic cytology of fish. Vet. Clin. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2007, 10, 207–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.S.; Procop, G.W. Diagnostic medical parasitology. Man. Commer. Methods Clin. Microbiol. Int. Ed. 2016, 284. [Google Scholar]
- Soulsby, E.J.L. Helminths, Arthropods and Protozoa of Domesticated Animals, 7th ed.; Bailliere Tindall: London, UK, 1982; pp. 42–50, 800–809. [Google Scholar]
- Fleck, S.L.; Moody, A.H. Diagnostic Techniques in Medical Parasitology ELBS; Butterworth-Heinemann: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.A.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.; Sakran, T.; Abdel-Baki, A.-A.; Abdel-Ghaffar, F.A. Some species of the genus Myxobolus (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) infecting freshwater fish of the River Nile, Egypt, and the impact on their hosts. Parasitol. Res. 2002, 88, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elseify, M.; El Shihawy, I.; Metwally, A.; Fawaz, M. Studies on nematode parasites infecting freshwater fish in Qena governorate, Kafrelsheikh. Vet. Med. J. 2015, 13, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Hoogendoorn, C.; Smit, N.J.; Kudlai, O. Resolution of the identity of three species of Diplostomum (Digenea: Diplostomidae) parasitising freshwater fishes in South Africa, combining molecular and morphological evidence. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 11, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, X.-H.; Ge, H.-L.; Xie, C.-Y.; Cai, R.-Y.; Hu, Z.-C.; Zhang, Y.-G.; Wang, Z.-J. The discovery of Clinostomum complanatum metacercariae in farmed Chinese sucker, Myxocyprinus asiaticus. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, R.M. First record of Euclinostomum heterostomum from the naturally-infected heron “Ardeola ralloides” in Egypt: A light and scanning electron microscopy study. Egypt. J. Zool. 2019, 72, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, R.; Baker, J.R. Advances in Parasitology; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, E.; Abdallah, H.; Mohamed, A. Acanthogyrus Tilapiae Infections in Wild and Cultured Nile Tilapia Oreochromis Niloticus. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2017, 63, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, W.-M. Fish-borne zoonotic trematode metacercariae in the Republic of Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2009, 47, S103–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waikagul, J.; Thaenkham, U. Approaches to research on the systematics of fish –borne trematodes. Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2014, pp. 49–60.
- Hamada, S.; Arafa, S.; El-Naggar, M. A new record of the cestode Monobothrioides chalmersius (Caryophyllidea, Lytocestidae) from the catfish Clarias gariepinus in Egypt, with a note on the cholinergic components of the nervous system. J. Egypt. Ger. Soc. Zool. 2004, 43, 159–176. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-ELrahman, S.M.; Gareh, A.; Mohamed, H.I.; Alrashdi, B.M.; Dyab, A.K.; El-Khadragy, M.F.; Khairy Elbarbary, N.; Fouad, A.M.; El-Gohary, F.A.; Elmahallawy, E.K.; et al. Prevalence and Morphological Investigation of Parasitic Infection in Freshwater Fish (Nile Tilapia) from Upper Egypt. Animals 2023, 13, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodore, M.; Tamara, B.; Collette, B.; Jayde, F.; Davis, S.; Norman, S. Diseases of Wild and Cultured Fishes in Alaska. Alaska Fish and Game: Alaska, United States. 2019. Available online: https://www.adfg.alaska.gov/static/species/disease/pdfs/fishdiseases/trichophry (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Ragasa, C.; Ulimwengu, J.; Randriamamonjy, J.; Badibanga, T. Factors affecting performance of agricultural extension: Evidence from Democratic Republic of Congo. J. Agric. Educ. Ext. 2016, 22, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.S.; Das, R.; Dhiman, M.; Choudhary, P.; Debbarma, J. Present status of fish disease management in freshwater aquaculture in India: State-of-the-art-review. Int. J. Fish. Aquac. 2017, 1, 003. [Google Scholar]
- Magguran, A.E. Measuring biodiversity; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, United Kingdom, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, A.O.; Lafferty, K.D.; Lotz, J.M.; Shostak, A.W. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 75–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D. CARBayes version 6.0: An R Package for Spatial Areal Unit Modelling with Conditional Autoregressive Priors. J. Stat. Softw. 2013, 55, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullan, R.L.; Kabatereine, N.B.; Bukirwa, H.; Staedke, S.G.; Brooker, S. Heterogeneities and consequences of plasmodium species and hookworm coinfection: a population based study in Uganda. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P. Notes on continuous stochastic phenomena. Biometrika 1950, 37, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NaFIRRI. Guidelines for Cage Fish Farming in Uganda. National Fisheries Resources Research Institute: Jinja, Uganda. 2018. Available online: https://www.firi.go.ug/PESCA/Outputs/Cage%20Fish%20farming%20Brochure%20July%202018.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Stone, N.M.; Thormforde, H.K. Understanding your fish pond water analysis report. University of Arkansas Co-operative Extension Printing services: Arkansas, USA, 2003.
- Davis, J. Survey of Aquaculture effluents permitting and 1993 standards in the South. Southern Regional Aquaculture Centre, SRAC publication no 465 USA, 4PP; Southern Regional Aquaculture Centre: Mississippi, United states, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, R.J. The parasitology of teleosts. In Fish pathology, 4th ed.; Roberts, R.J., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing Limited: Oxford, United Kingdom, 2012; pp. 292–338. [Google Scholar]
- Florio, D.; Gustinelli, A.; Caffara, M.; Turci, F.; Quaglio, F.; Konecny, R.; Fioravanti, M.L. Veterinary and public health aspects in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) aquaculture in Kenya, Uganda and Ethiopia. Ittiopatologia 2009, 6, 51–93. [Google Scholar]
- Owani, S.; Hishamunda, N.; Cai, J. Report of the capacity building workshop on conducting aquaculture as a business in Mukono, Uganda. In Commission, Report/Rapport: SF-FAO/2012/06. October/Octobre 2012: Ebene, Mauritius, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2012;pp. 10 – 25.
- Isyag, N.; Atukunda, G.; Aliguma, L.; Ssebisubi, M.; Walakira, J.; Kubiriza, G.; Mbulameri, E. Assessment of national aquaculture policies and programmes in Uganda; SARNISSA: Kampala, Uganda, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Paladini, G.; Longshaw, M.; Gustinelli, A.; Shinn, A.P. Parasitic diseases in aquaculture: their biology, diagnosis and control. In Diagnosis and control of diseases of fish and shellfish, 1st ed.; Austin, B.A., Newaj-Fyzul, A., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons Limited: New Jersey, USA, 2017; pp. 37–107. [Google Scholar]
- Molnár, K.; Székely, C.; Láng, M. Field guide to the control of warmwater fish diseases in Central and Eastern Europe, the Caucasus and Central Asia. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular No.1182. Ankara; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2019; p. 124. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes-trujillo, A.; Velázquez-abunader, I.; Torres-irineo, E.; Romero, D.; Vidal-martínez, V.M. Geographical distribution of protozoan and metazoan parasites of farmed Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) (Perciformes : Cichlidae) in Yucatán, México. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.E.; Mona, S.Z.; Abdel, R.Y.; Hossam, H.A.; Osman, K.A.; Attia, A.A. Seasonal variations and prevalence of some external parasites affecting freshwater fishes reared at upper Egypt. Life Sci. 2011, 8, 397–400. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsi, S.; Day, S.; Zhu, X.; McLellan, M.; Barton, D.P.; Dang, M.; Nowak, B.F. Wild fish as reservoirs of parasites on Australian Murray cod farms. Aquaculture 2021, 539, 736584. [Google Scholar]
- Yanong, R.P. Nematode (Roundworm) infections in fish. University of Florida: Gainesville, United States, 2017. 2017. Available online: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/FA091 (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Uglem, I.; Karlsen, Ø.; Sanchez-Jerez, P.; Sæther, B. Impacts of wild fishes attracted to open-cage salmonid farms in Norway. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2014, 6, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oidtmann, B.C.; Crane, C.N.; Thrush, M.A.; Hill, B.J.; Peeler, E.J. Ranking freshwater fish farms for the risk of pathogen introduction and spread. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011, 102, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.C.; et al. Copaifera duckei oleoresin as a novel alternative for treatment of monogenean infections in pacu Piaractus mesopotamicus. Aquaculture 2017, 471, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, P.; Francis-foyd, R.; Klinger, R. Monogenean parasites of fish; University of Florida: Floria, United States, 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Nehemia, A.; Maganira, J.D.; Rumisha, C. Length-Weight relationship and condition factor of tilapia species grown in marine and fresh water ponds. Agric. Biol. J. North Am. 2012, 3, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otachi, E.O. Studies on occurrence of protozoan and helminth parasite in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus, L.) from Central and Eastern provinces. MSc. Thesis, Egerton University, Njoro, Kenya, July, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- NEA. Aquaculture Road Map Uganda Opportunities in the aquaculture value chain. Netherlands Enterprise Agency: Prinses Beatrixlaan, Netherlands. 2022. Available online: https://www.rvo.nl/sites/default/files/2022-05/Aquaculture-Road-Map-Uganda-Opportunities-in-the-aquaculture-value-chain.pdf (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Halwart, M.; Soto, D.; Arthur, J.R. (eds). Cage Aquaculture: Regional Reviews and Global Overview. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper No. 498; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2007; p. 241. [Google Scholar]
- Moura, R.S.T.; Valenti, W.; Henry-Silva, G.G. Sustainability of Nile tilapia net-cage culture in a reservoir in a semi-arid region. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onada, O.A. Study of interrelationship among water quality parameters in earthen pond and concrete tank. MSc. Thesis, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria, February, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tarrant, A.M.; et al. Molecular physiology of copepods - from biomarkers to transcriptomes and back again. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 30, 230–247. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafizur, M.R. Factors influencing the vertical distribution of copepods in a tropical oligotrophic estuary, South China sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 250, 107165. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Okanurak, K.; Lv, Z. Liver fluke infection and cholangiocarcinoma: a review. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mereta, S.T.; Boets, P.; Bayih, A.A.; Malu, A.; Ephrem, Z.; Sisay, A.; Endale, H.; Yitbarek, M.; Jemal, A.; De Meester, L.; et al. Analysis of environmental factors determining the abundance and diversity of macroinvertebrate taxa in natural wetlands of Southwest Ethiopia. Ecol. Inform. 2012, 7, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koprivnikar, J.; Leung, T.L.F. Flying with diverse passengers: greater richness of parasitic nematodes in migratory birds. Oikos 2015, 124, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MWE. Sector performance report of financial year 2017/2018. Ministry of Water and Environment: Kampala, Uganda. 2018. Available online: https://www.mwe.go.ug/library/sector-performance-report-2018 (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- MDLG. Geographical features. Masaka District Local Government: Masaka, Uganda. 2024. Available online: https://masaka.go.ug/content/geographical-features (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Hossain, M.D.; Hossain, M.K.; Rahman, M.H. Water quality parameters and incidence of fish diseases in some water bodies in Natore, Bangladesh. J. Life Earth Sci. 2007, 2, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassali, J.; Yongji, Z.; Fangninou, F. A systematic review of threats to the sustainable utilization of transboundary fresh water lakes: a case study of Lake Victoria. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publications 2020, 10, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olokotum, M.; Mitroi, V.; Troussellier, M.; Semyalo, R.; Bernard, C.; Montuelle, B.; Okello, W.; Quiblier, C.; Humbert, J.-F. A review of the socioecological causes and consequences of cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Victoria. Harmful Algae 2020, 96, 101829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egessa, R.; Pabire, G.W.; Ocaya, H. Benthic macroinvertebrate community structure in Napoleon Gulf, Lake Victoria: effects of cage aquaculture in eutrophic lake. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ssebugere, P.; Sillanpää, M.; Kiremire, B.T.; Kasozi, G.N.; Wang, P.; Sojinu, S.O.; Otieno, P.O.; Zhu, N.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, H.; Shang, H.; Ren, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, G. Polychlorinated biphenyls and hexachlorocyclohexanes in sediments and fish species from the Napoleon Gulf of Lake Victoria, Uganda. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPIC. Establishment of Vetiver Grass Nursery and Hedgerows for control of Eutrophication in Lake Victoria. Environmental Protection Information Centre: Kampala, Uganda. 2018. Available online: https://sdm.satoyama-initiative.org/projects/2018_uganda/ (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Turinayo, Y.K. Impact of Wastewater Effluents from a Sugar Industry and a Molasses Based Distillery on Water Quality of River Musamya in Lugazi, Uganda. MSc. Thesis, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda, May, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Birk, S.; Chapman, D.; Carvalho, L.; et al. Impacts of multiple stressors on freshwater biota across spatial scales and ecosystems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Diversity parameter | Oreochromis niloticus (n = 640) |
|---|---|
| Total number of genera | 16 |
| Shannon index (H′) | 0.961 |
| Evenness (E) | 0.347 |
| Berger–Parker Dominance index (d) | 0.79 |
| Diversity estimators | |
| Chao | 16.125 |
| Jackknife | 16.998 |
| No. | Genus | Prevalence (%) | Mean intensity | Mean abundance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Trichodina | 23.4 | 41.21 | 9.66 | |
| 2. | Dactylogyrus | 14.2 | 4.16 | 0.59 | |
| 3. | Neascus | 5.6 | 4.9 | 0.28 | |
| 4. | Clinostomum | 3.6 | 3.22 | 0.12 | |
| 5. | Ergasilus | 5.9 | 4.61 | 0.27 | |
| 6. | Myxobolus | 4.4 | 13.64 | 0.60 | |
| 7. | Amirthalingamia | 0.6 | 2.25 | 0.014 | |
| 8. | Acanthocephalus | 1.4 | 1.56 | 0.022 | |
| 9. | Monobothroides | 0.2 | 25 | 0.039 | |
| 10. | Contracaecum | 0.3 | 3 | 0.0094 | |
| 11. | Eimeria | 0.2 | 35 | 0.055 | |
| 12. | Gyrodactylus | 0.6 | 4.5 | 0.028 | |
| 13. | Chilodonella | 0.3 | 17.5 | 0.055 | |
| 14. | Ichthyobodo | 1.9 | 6 | 0.11 | |
| 15. | Ambiphrya | 0.3 | 12 | 0.038 | |
| 16. | Diphyllobothrium | 3 | 11.47 | 0.34 | |
| Fish farming system | Genera present (Number of farms infested (n)) | Mean number of genera on farms (range) | Mean parasite frequencies on farms (range) | Mean prevalence on farms (range) |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Pond grow-out (N = 18) |
Trichodina (n = 16) Dactylogyrus (n =12) Neascus (n = 3) Clinostomum (n = 4) Ergasilus (n = 3) Myxobolus (n = 3) Amirthalingamia (n =1) Contracaecum (n = 1) Gyrodactylus (n =2) Chilodonella (n = 1) Ichthyobodo (n = 4) Ambiphrya (n = 1) Diphyllobothrium (n = 1) |
3(1 -7) | 118 (12 - 447) | 0.49 (0.15 - 0.8) | |||||||
| Cage grow-out (lake)(N= 9) | Trichodina (n = 5 ) Dactylogyrus (n = 5) Neascus (n = 1) Diphyllobothrium (n = 1) |
1(0 - 3) | 30(18 - 87) | 0.29 (0 -0.65) | |||||||
|
Cage grow-out (reservoir) (N = 2) |
Trichodina (n = 2) Dactylogyrus (n =2) Myxobolus (n = 1) |
3(2-3) | 2555(1021- 4089) | 0.73(0.55-0.9) | |||||||
|
Hatchery (N =3) |
Trichodina (n = 2) Dactylogyrus (n =2) Neascus (n = 3) Clinostomum (n = 3) Ergasilus (n = 1) Myxobolus (n = 2) Amirthalingamia (n =1) Acanthocephalus (n = 2) Monobothro (n = 1) Eimeria (n = 1) |
6(4-8) | 108(57-193) | 0.78(0.65-1) |
| Pond grow -out farms (N = 18) |
Parameter | Mean values (range) values of pond water |
Recommended limits* | Percentage (%) above or below recommended limits (N = 18) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water quality | DO (mg/l) | 5.1 (2.1- 9.7a ) | 5.5 – 10 | 38.9% (n = 7) |
| T(°C) | 24.9 (21.9 - 26.9a) | 26 – 32 | 72.2% (n = 13) | |
| pH | 7.6 (6.7 - 8.1) | 6.5–8.5 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Salinity (PSU) | 0.06 (0 - 0.2) | 0 -20 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Total dissolved solids (mgl-1) | 0.08 (0 - 0.27b) | < 0.13 | 22.2% (n = 4) | |
| Conductivity (µS/cm) | 121 (5 - 408a) | 100 -2000 | 44.4% (n = 8) | |
| Ammonia free nitrogen (mg/l) | 1.2 (0.05 - 2b) | 0 – 0.2 | 94.4% (n = 17) | |
| Hardness (ppm as CaCO3) | 36 (8 - 88b) | < 50 | 27.8% (n = 5) | |
| Nitrite (mgl-1) | 0.05 (0.005 - 0.5b) | 0 – 0.2 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Chloride (ppm) | 17 (4 - 40) | <230 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Farm management practices | Fish seed source (1-Certified hatchery, 2- Other: wild catch or from fellow farmers) | 2 (1 - 2b) | Certified hatchery-1 | 83.3% (n = 15) |
| Feeding and nutrition status n status (Rank 1 to 5 according to feed type, ration and intervals) | 3(2 - 5a) | Rank 4, 5 | 77.8% (n = 14) | |
| Disinfection (Present-1 , Absent-0) | 0 (0 -1a) | Present-1 | 77.8% (n = 14) | |
| Stocking density (1-overstocked, 2-recommended (4 to 8 fish/m2) or under-stocked) | 2 (1 - 2a) | Recommended or under-stocked -2 | 55.6% (n = 10) | |
| External factors | Intermediate hosts (Present-1 , Absent-0) | 1 (0 - 1b) | Absent-0 | 77.8 % (n = 14) |
| Wild fish entry (Entry-1 , No entry-0) | 1 (0 - 1b) | No entry -0 | 55.6% (n = 10) |
| Cage grow-out farms (lake) (N= 9) |
Parameter | Mean values (range) values of lake water |
Recommended limits* | Percentage (%) above or below recommended limits (N = 9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water quality | DO (mg/l) | 5.7 (4.3 - 6.9a) | 5.5 – 10 | 44.4% (n = 4) |
| T(°C) | 26.2 (25.2 - 27.7a) | 26 – 32 | 44.4% (n = 4) | |
| pH | 8.6 (8.0 - 9.5b) | 6.5–8.5 | 66.7% (n = 6) | |
| Salinity (PSU) | 0.04 (0.02 - 0.05) | 0 -20 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Total dissolved solids (mgl-1) | 0.05 (0.02 - 0.07) | < 0.13 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Conductivity (µS/cm) | 78 (38 - 109a) | 100 -2000 | 66.7% (n = 6) | |
| Ammonia free nitrogen (mg/l) | 1.5 (0.5 - 2b) | 0 – 0.2 | 100% (n = 9) | |
| Hardness (ppm as CaCO3) | 22 (6 - 48) | < 50 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Nitrite (mgl-1) | 0.05 (0 - 0.05) | 0 – 0.2 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Chloride (ppm) | 13 (5 - 38) | <230 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Farm management practices | Fish seed source (1-Certified hatchery, 2- Other: wild catch or from fellow farmers) | 2 ( 1 - 2b) | Certified hatchery-1 | 55.6% (n = 5) |
| Feeding and nutrition status n status (Rank 1 to 5 according to feed type, ration and intervals) | 4 (3 - 4a) | Rank 4, 5 | 11.1% (n = 1) | |
| Disinfection (Present-1 , Absent-0) | 1 (0 -1a) | Present-1 | 22.2% (n = 2) | |
| Stocking density (1-overstocked, 2-recommended (60 to 80 fish/m3) or under-stocked) | 1 (1 - 2a) | Recommended or under-stocked -2 | 77.8% (n = 7) | |
| External factors | Intermediate hosts (Present-1 , Absent-0) | 0 (0 -1b) | Absent-0 | 44.4% (n = 4) |
| Wild fish entry (Entry-1 , No entry-0) | 0(0 -0) | No entry -0 | 0% (n = 0) |
| cage grow -out farms (reservoir) (N = 2) |
Parameter | Mean values (range) values of reservoir water |
Recommended limits* | Percentage (%) above or below recommended limits (N = 2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water quality | DO (mg/l) | 3.8 (2.9 - 4.7a,b) | 5.5 – 10 | 100% (n = 2) |
| T(°C) | 24.1 (24 - 24.2a,b) | 26 – 32 | 100% (n = 2) | |
| pH | 7.7 (7.3 - 8) | 6.5–8.5 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Salinity (PSU) | 0.03 (0.02 - 0.03) | 0 -20 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Total dissolved solids (mgl-1) | 0.05 (0.04 - 0.05) | < 0.13 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Conductivity (µS/cm) | 62 (54 - 70a,b) | 100 -2000 | 100% (n = 2) | |
| Ammonia free nitrogen (mg/l) | 2 (2 - 2b) | 0 – 0.2 | 100% (n = 2) | |
| Hardness (ppm as CaCO3) | 26 (20 -32) | < 50 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Nitrite (mgl-1) | 0.005 (0.005 - 0.005) | 0 – 0.2 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Chloride (ppm) | 32 (25 - 38) | <230 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Farm management practices | Fish seed source (1-Certified hatchery, 2- Other: wild catch or from fellow farmers) | 2 (2 - 2) | Certified hatchery-1 | 100% (n = 2) |
| Feeding and nutrition status n status (Rank 1 to 5 according to feed type, ration and intervals) | 3 (3 - 3) | Rank 4, 5 | 100% (n = 2) | |
| Disinfection (Present-1 , Absent-0) | 0 (0 -0) | Present-1 | 100% (n = 2) | |
| Stocking density (1-overstocked, 2-recommended (60 to 80 fish/m3) or under-stocked) | 2 (2 -2) | Recommended or under-stocked -2 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| External factors | Intermediate hosts (Present-1 , Absent-0) | 1 (1 - 1) | Absent-0 | 0% (n = 0) |
| Wild fish entry (Entry-1 , No entry-0) | 1 (0 -1) | No entry -0 | 50% (n = 1) |
| Hatcheries (N = 3) |
Parameter | Mean values (range) values of hatchery pond water |
Recommended limits* | Percentage (%) above or below recommended limits (N = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water quality | DO (mg/l) | 5.7 (4.3 - 6.5a) | 5.5 – 10 | 33.3% (n = 1) |
| T(°C) | 24.7 (24.2 - 25.1a,b) | 26 – 32 | 100% (n = 3) | |
| pH | 7.8 (7.5 - 8.1) | 6.5–8.5 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Salinity (PSU) | 0.06 (0.03 - 0.09) | 0 -20 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Total dissolved solids (mgl-1) | 0.09 (0.05 - 0.13b) | < 0.13 | 33.3% (n = 1) | |
| Conductivity (µS/cm) | 118 (74 - 192a) | 100 -2000 | 66.7% (n = 2) | |
| Ammonia free nitrogen (mg/l) | 1.2 (1 - 1.5a,b) | 0 – 0.2 | 100% (n = 3) | |
| Hardness (ppm as CaCO3) | 32 (14 - 61b) | < 50 | 33.3% (n = 1) | |
| Nitrite (mgl-1) | 0.05 (0 - 0.05) | 0 – 0.2 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Chloride (ppm) | 12 (6 - 13) | <230 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Farm management practices | Fish seed source (1-Certified hatchery, 2- Other: wild catch or from fellow farmers) | 1 (1 -1) | Certified hatchery-1 | 0% (n = 0) |
| Feeding and nutrition status n status (Rank 1 to 5 according to feed type, ration and intervals) | 4 (3 - 5a) | Rank 4, 5 | 33.3% (n = 1) | |
| Disinfection (Present-1 , Absent-0) | 1 (1 - 1) | Present-1 | 0% (n = 0) | |
| Stocking density (1-overstocked, 2-recommended (4 to 8 fish/m2) or under-stocked) | 1 (1 - 2a) | Recommended or under-stocked -2 | 66.7% (n = 2) | |
| External factors | Intermediate hosts (Present-1 , Absent-0) | 1 (1 -1b) | Absent-0 | 100% (n = 3) |
| Wild fish entry (Entry-1 , No entry-0) | 0 (0 - 1a) | No entry -0 | 33.3% (n = 1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





