1. Introduction
The hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell is increasingly important in various power generators and electrical-consuming devices, including dismounted soldier power supplies [
1], automobiles [
2], and autonomous undersea vehicles [
3]. It is valued for its zero-carbon emissions, quick refueling ability, low signal characteristics, and high energy conservation efficiency. However, the traditional hydrogen refueling routine relies on infrastructure construction, which has become the main obstacle to further fuel cell application. Therefore, the concept of “hydrogen production onboard” has gained extensive attention due to the simplification of hydrogen usage procedures. Several onboard hydrogen production methods such as metal hydrolysis [
4], metal hydride hydrolysis [
5] or pyrolysis [
6], methanol steam reforming [
7], and sodium borohydride hydrolysis [
8,
9], have been proposed to achieve this concept. Among these methods, Al hydrolysis has been considered as the most practical way to generate hydrogen on demand due to its affordable hydrogen production cost, high hydrogen storage density, and simplicity in usage.
Although the Al-water reaction is thermodynamically favorable, producing hydrogen at a sufficient rate for practical applications remains a challenge. The formation of a dense oxide passivation layer on the surface of Al prevents contact between Al and water and severely reduces the reaction’s activity [
10]. One effective way to improve the hydrolysis activity of Al is by adding alkaline [
11], which dissolves the oxide passivation layer and Al-containing reaction products. However, this method poses a risk of equipment corrosion and environmental pollution. To continuously produce hydrogen through the Al hydrolysis reaction in a neutral solution, various additives such as metals [
12,
13], salts [
14], oxides [
15], hydride [
16] and graphite [
17] have been introduced into Al via alloying, high-energy ball milling, or atomization methods, and these techniques show great potential in promoting the Al-water reaction.
Woodall [
18,
19] discovered that certain Al alloys with liquid phases, such as Al-Ga [
20] and Al–Ga–In–Sn [
21], can induce the Al-water reaction in a neutral solution at room temperature, resulting in a significant rate of hydrogen production. The liquid regions within the alloys act as channels for Al diffusion, enabling internal Al atoms to breach the passive oxide barrier and react with water [
22]. Following these findings, a number of studies have employed Al-Ga-based alloy hydrolysis reactions to generate hydrogen onboard. Wang et al. [
23] analyzed the hydrogen production performance of a range of multicomponent low-melting-point Al alloys containing Al, Ga, In, and Sn, and the results indicated that quaternary Al alloys outperformed binary and ternary Al alloys. Jin et al. [
24] investigated the effects of additive In and Sn on the hydrolysis performance of Al–Ga-based alloy. They discovered that In causes more severe cracks to form on the surface of the alloy, while Sn tends to collect more Ga to create a low-melting-point phase at the grain boundary. This implies that In yields better hydrogen production, while Sn yields a higher rate of hydrogen production. However, the low-melting-point alloying elements Ga and In are very expensive, making them unaffordable for practical applications.
Previous studies conducted by our research group have demonstrated a novel method for enhancing the hydrolysis activity of Al-Bi-Sn-based alloy powder, excluding Ga and In doping, through atomization [
25,
26]. Leveraging the liquid phase immiscibility effect, an incomplete shell composed of (Bi, Sn)-rich phases formed over the powder surface, disrupting the continuous passive oxide layer of Al and causing cracks [
27]. As a result, the Al-Bi-Sn-based alloy powder demonstrated excellent hydrogen production efficiency. Although the cost of producing hydrogen through Al-Bi-Sn-based alloy powder is significantly lower than that of Al-Ga-based alloy, the use of Sn remains cost-prohibitive for practical applications. To address this issue, our research group [
28,
29] explored the use of low-cost alloy elements, such as Cu and Fe, to reduce Sn content. A series of quaternary Al-Bi-Sn-X (Cu and Fe) alloy powders, with X element added in varying proportions ranging from 0 to 3 wt.%, were fabricated and tested. The results revealed that while Cu suppresses hydrolysis in Al-Bi-Sn-based powders, Fe enhances it, indicating that replacing Sn with a cheaper element can be an efficient way to lower the cost of hydrogen production.
Despite reducing Sn content in previous works, it remains a primary alloying element (up to 7 wt.%) to ensure adequate hydrolysis properties, limiting large-scale applicability. To overcome this challenge, this study employed phase diagram calculations to design a series of Sn-free, cost-effective Al-Bi-Fe alloy powders. These powders were produced via atomization and thoroughly characterized for their microstructure, hydrolysis performance, and reaction kinetics. The findings demonstrate that appropriate Fe additions significantly enhance hydrogen generation in Sn-free Al-Bi-based alloys.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
In this study, Al-10Bi-xFe (x = 3, 7, 10) wt.% alloy powders were prepared using the gas atomization method. The raw materials, comprising high-purity (99.9%) bulk metals of Al, Bi, and Fe, underwent controlled melting within a high-frequency induction melting furnace under argon protection. Subsequently, the molten alloy was atomized through a high-pressure argon flow ranging from 5 to 8 MPa. The atomized powders were efficiently collected and any abnormally coarse particles were filtered out by sieves in the argon environment. The resulting powder was stored in labeled glass bottles for subsequent experiments.
2.2. Hydrolysis Test
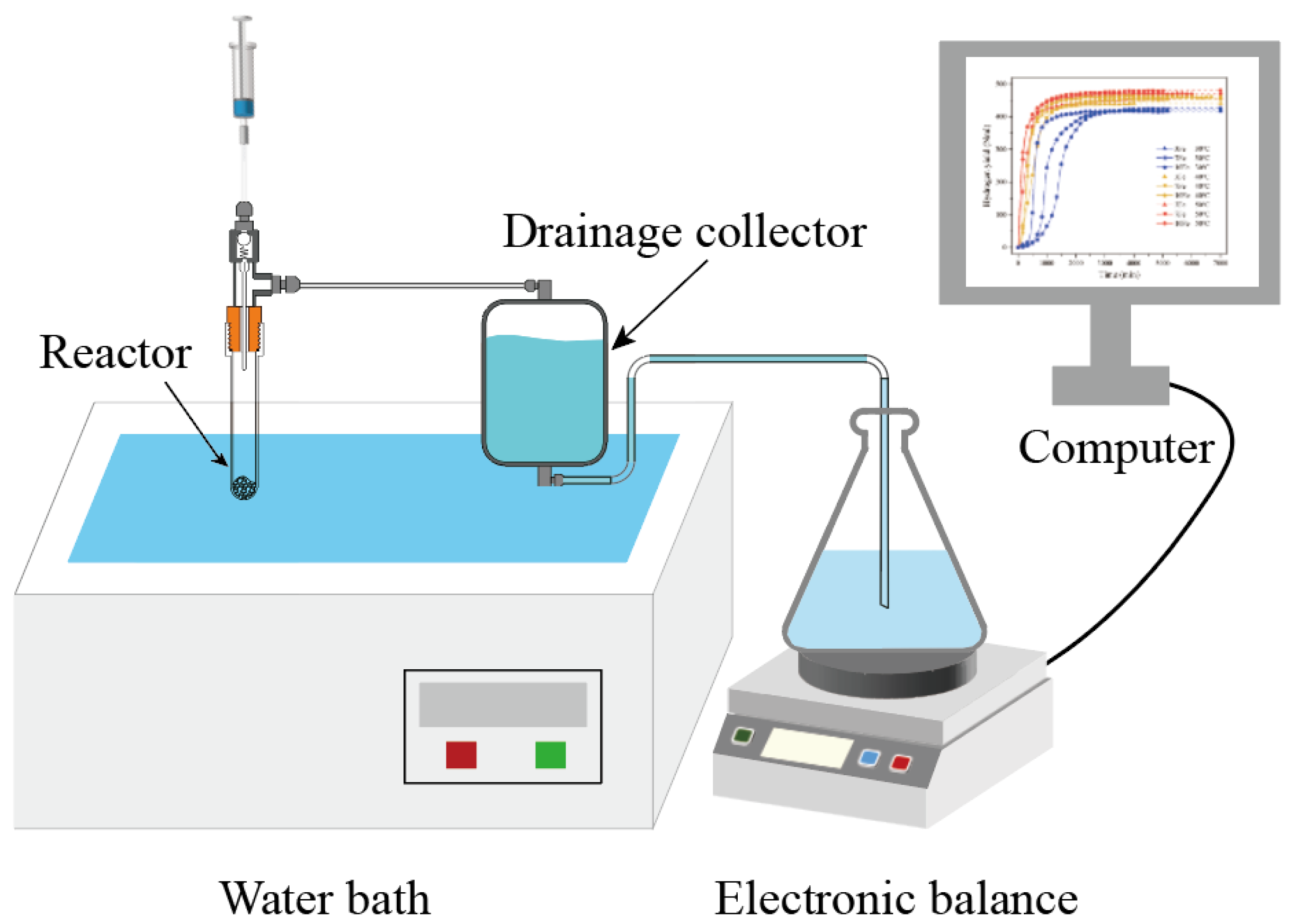
The hydrogen volume was measured using the drainage method, and the experimental setup for the hydrolysis test is illustrated in
Figure 1. Hydrolysis tests for Al-Bi-Fe variations were carried out at different reaction temperatures ranging from 30 to 50 °C, employing deionized water. Both the reactor and drainage collector were immersed in a water bath at the reaction temperature. Throughout the test, 10 mL of deionized water at the reaction temperature was injected into a meticulously designed reactor containing 0.5 g of Al-Bi-Fe alloy powders. A computer connected to the electronic balance recorded the weight change. To ensure comparability of recorded data between tests at different reaction temperatures, the volume of hydrogen yield was normalized under standard conditions (0 °C, 1 atm) with the unit of Nml.
2.3. Characterization
As-atomized powders were mounted, ground, and polished for preparing specimens of the cross-section of the powers. The microstructure was characterized by a Quanta 650 FEG scanning electron microscope (SEM) performed at 15 kV with an energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) to conduct a semi-qualitative analysis of elements. Rigaku Rapid IIR X-ray diffractometer (XRD) with Cu-Kɑ operated at a step rate of 2° per minute was used to analyze the crystal structure of the as-atomized powders.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Design of Powder Composition
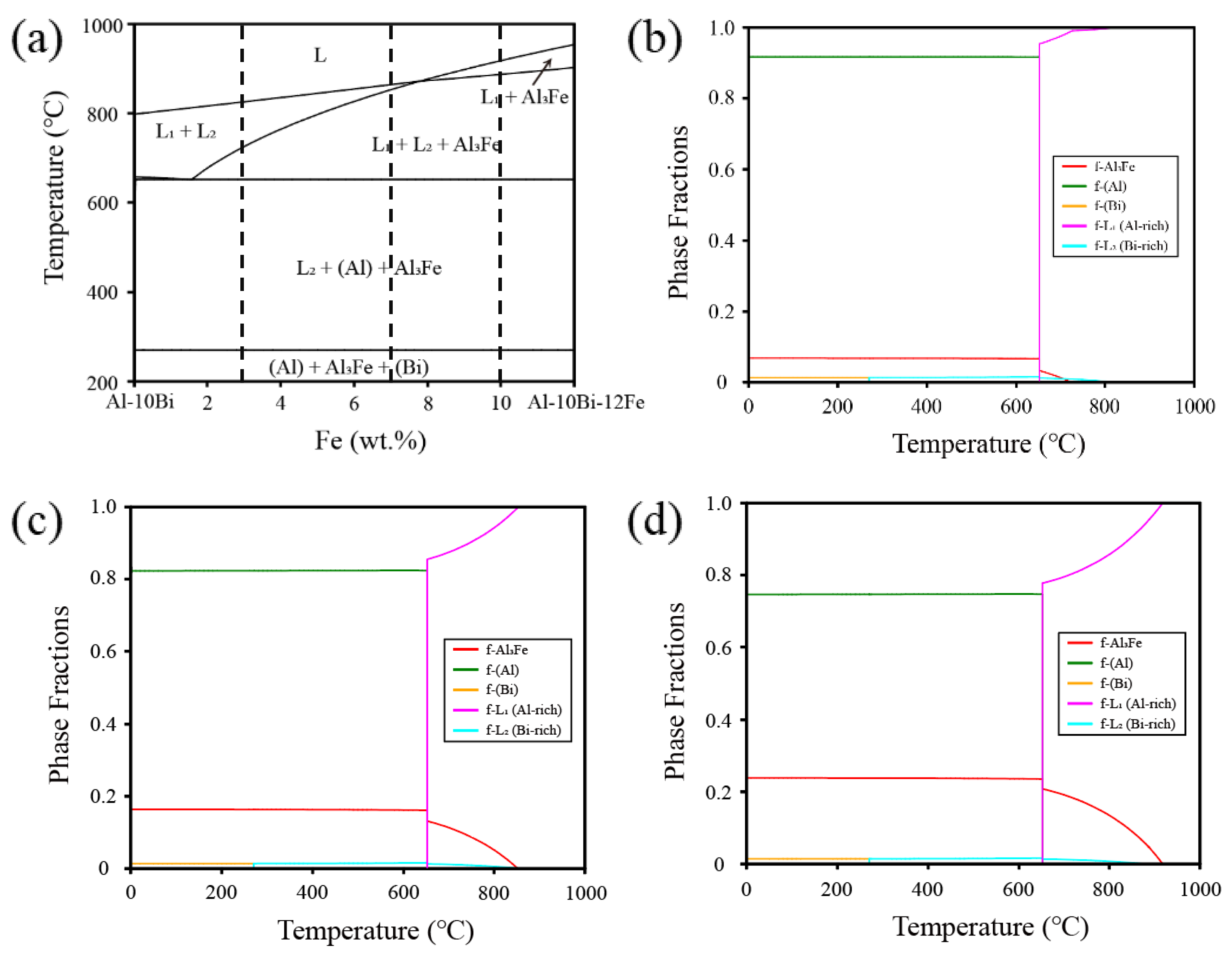
The phase diagram calculations of the ternary Al-Bi-Fe alloy were conducted using the Pandat software based on the Al alloy database, and the results are presented in
Figure 2. Notably,
Figure 2(a) shows a distinct liquid phase miscibility region labeled as (L1+L2) or (L1+L2+Al
3Fe). This suggests that the alloy has the potential to form an incomplete shell without the presence of Sn, leading to high activity in the Al-water reaction. Subsequently, a series of Al-Bi-Fe alloys with Fe additions varying from 3 to 10 wt.% was designed, and their calculated phase fraction diagrams are depicted in
Figure 2(b-d). As shown in the figures, the types of phases in the alloys remain relatively unchanged despite variations in Fe content. Detailed phase equilibrium calculations for Al-10Bi-3Fe, Al-10Bi-7Fe, and Al-10Bi-10Fe (wt.%) at 700 °C, within the range of liquid phase miscibility gap, were conducted, and the results are provided in
Table 1. The calculations suggest that the phase fraction of L2(Bi-rich) and Al
3Fe increase with the Fe content, while L1(Al-rich) decreases. To explore the influence of phase fraction variation on hydrolysis performance, these alloy powders were fabricated and tested.
3.2. Microstructure Characterization of as-Atomized Powders
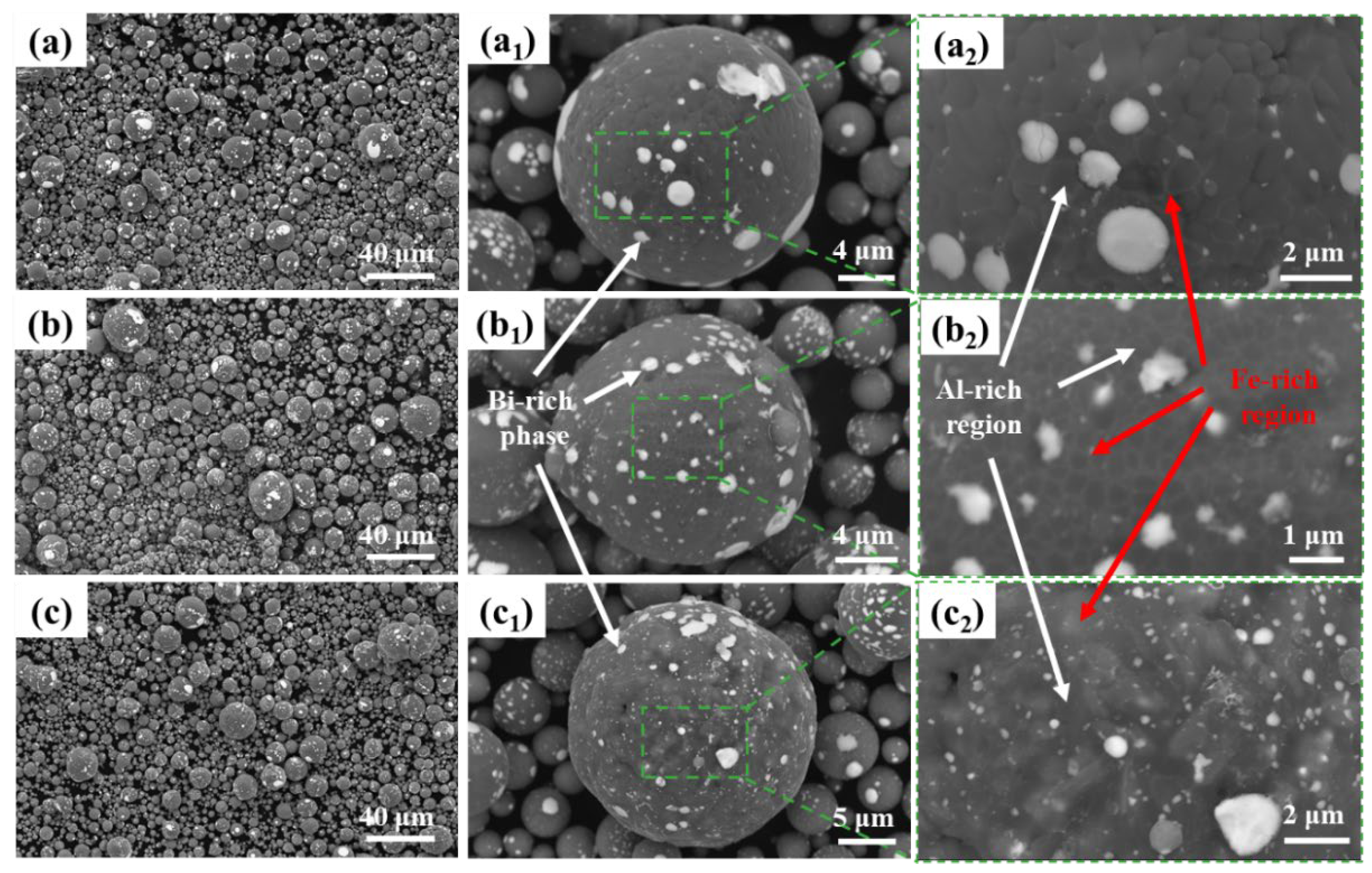
The as-atomized powder particles and surface morphology of Al-10Bi-3Fe, Al-10Bi-7Fe, and Al-10Bi-10Fe (wt.%) were characterized using SEM, as illustrated in
Figure 3. The particles exhibit good sphericity, with sizes primarily ranging from 1 to 50 μm. Due to the liquid-phase miscibility effect and the significant phase fraction difference between the Al-rich (L1) and Bi-rich (L2) phases, the white Bi-rich phase is dispersed across the powder surface, as shown in
Figure 3(a
1, b
1, c
1). The results suggest that an incomplete shell of the Bi-rich phase forms on the surface of these powders, potentially disrupting the continuous oxide layer and promoting favorable hydrolysis activity [
27].
Figure 3(a
2, b
2, c
2) presents magnified SEM images of the regions outlined by green dashed lines, revealing two distinct matrix regions with varying contrasts. The whiter matrix region increases with Fe content, indicating a tendency for Fe segregation. While few Fe-rich regions are observed at the grain boundaries of Al-10Bi-3Fe, a notable number are present in Al-10Bi-7Fe. As the Fe content increases to 10 wt.%, the Fe-rich regions expand, indicating a more inhomogeneous Fe distribution with higher Fe content.
Further characterization was conducted to unveil the phase distribution in powder variations.
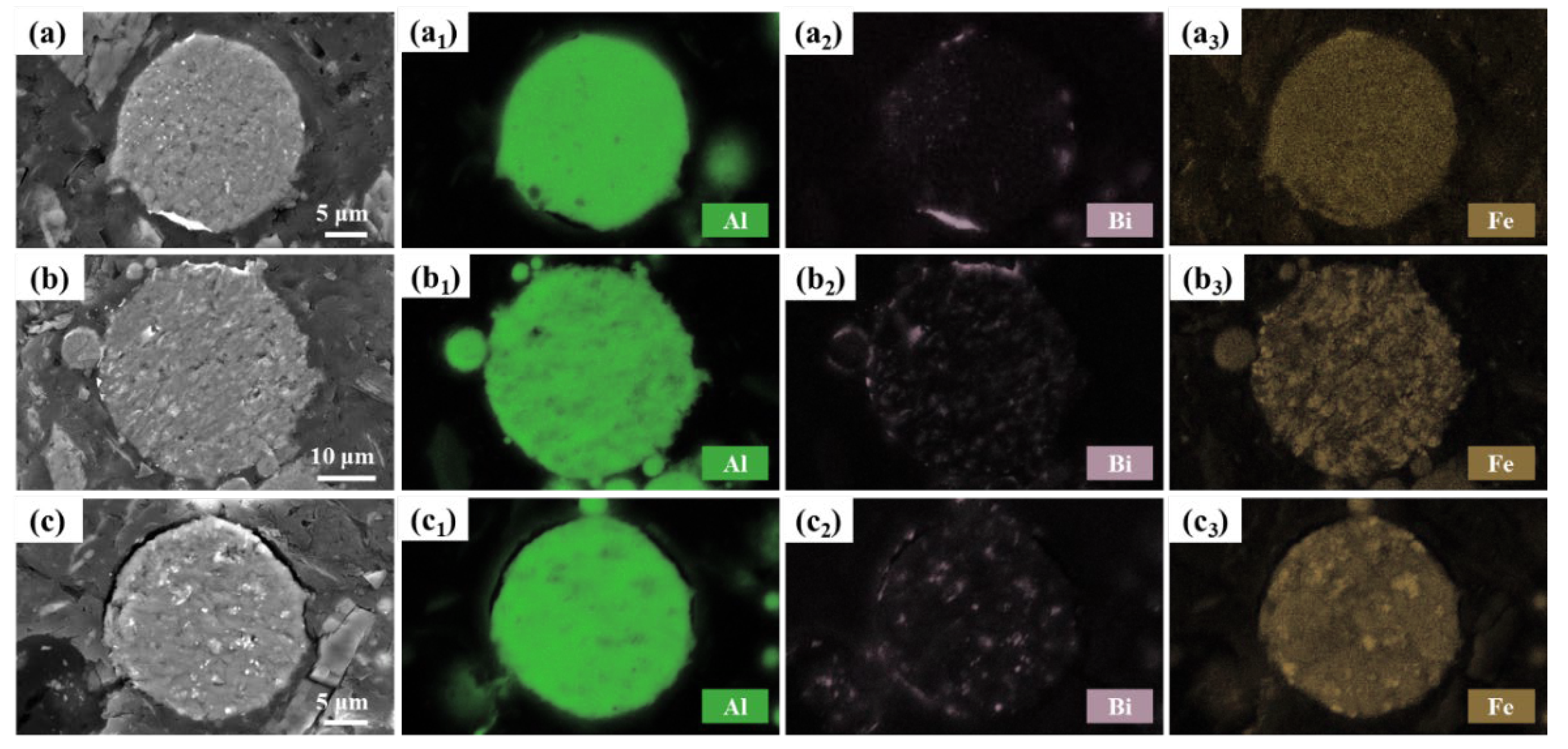
Figure 4 illustrates the cross-sectional morphology of Al-10Bi-3Fe, Al-10Bi-7Fe, and Al-10Bi-10Fe (wt.%), showcasing the element distribution in these plates. In
Figure 4(a
2, b
2, c
2), it is observed that the Bi-rich phase is primarily distributed on the surface of the powders, forming an incomplete shell that encloses the Al-rich phase within the powders. The remaining Bi-rich phase is dispersed throughout the matrix. Additionally, the amount of Bi-rich phase accumulated on the surface decreases with the increasing Fe content, indicating that the solidification of Fe atoms impedes the separation of L1 (Al-rich) and L2 (Bi-rich), resulting in a relatively homogeneous distribution of the Bi-rich phase.
Fe is homogeneously distributed throughout the cross-section without obvious preferential segregation in Al-10Bi-3Fe powder (
Figure 4(a
3)). However, Fe demonstrates segregation tendencies in high Fe-containing powders, forming several Fe-rich regions in the matrix, consistent with observations in
Figure 3(a
2, b
2, c
2). Notably, the formation of the secondary Al
3Fe phase appears minimal in the powder variations, contradicting the calculated phase diagrams. This discrepancy can be attributed to the high solubility of Fe in Al and the rapid cooling rates achieved during atomization, which significantly inhibit the formation of the Al
3Fe phase.
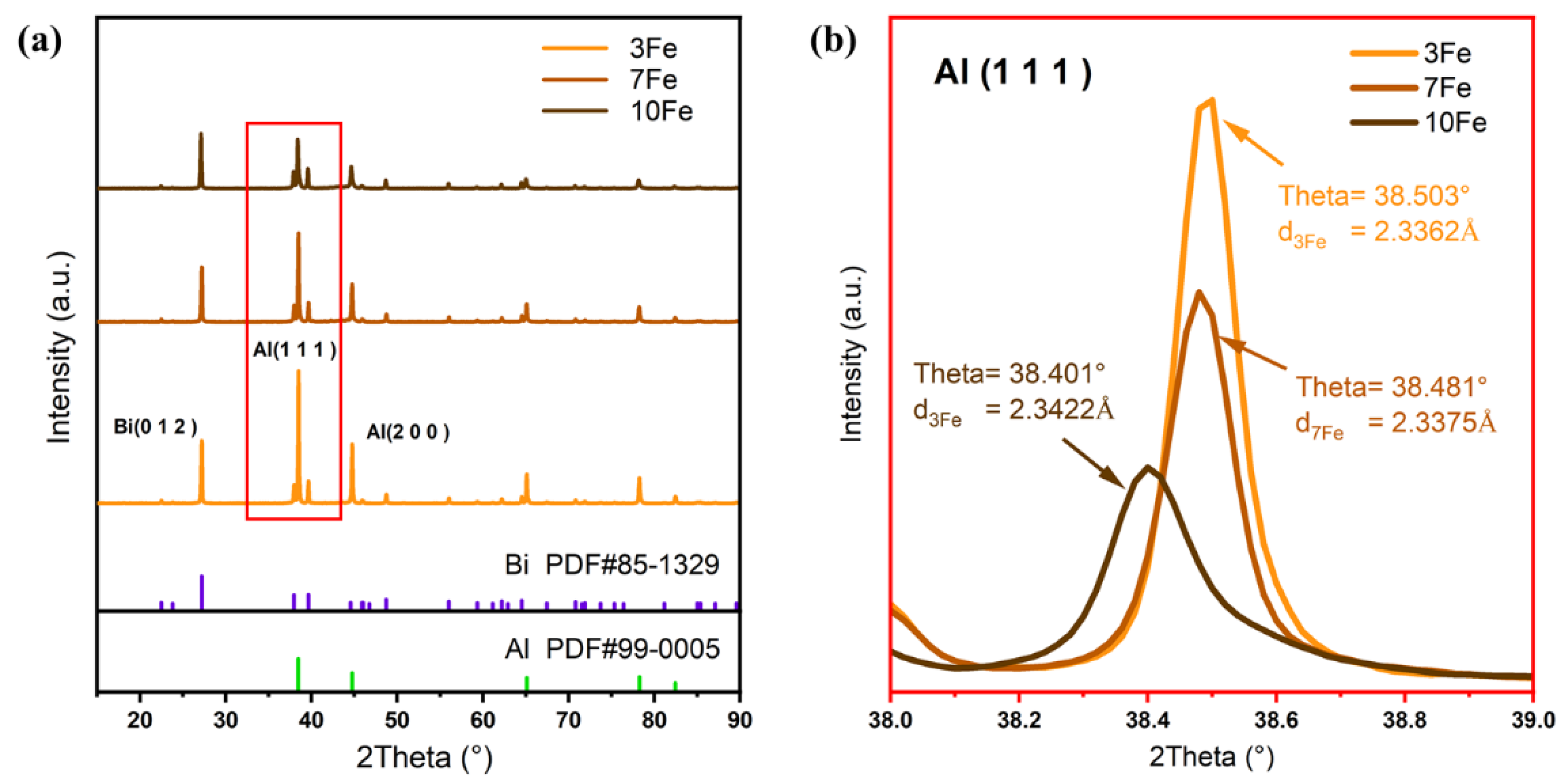
Figure 5 depicts the XRD patterns of the as-atomized Al-Bi-Fe alloy powders. In addition to the discernible Al and Bi diffraction peaks, Al
3Fe peaks are scarcely detected, indicating significant Fe solid solution and the absence of the Al
3Fe phase. This observation is consistent with EDS analysis, which revealed minimal secondary phases other than the Bi-rich phase within the powder cross-sections. Thus, the regions where Fe segregates are coherent with the Al matrix, indicating two distinct Fe solidification regions (Al-rich and Fe-rich) within the matrix, as shown in
Figure 4(b
3, c
3).
As Fe content increases, the Bi diffraction peaks remain unchanged, while the Al diffraction peaks decrease, suggesting that Fe doping mitigates the surface segregation tendency of Bi, aligning with the EDS observations (
Figure 4(a
2, b
2, c
2)). Additionally, the lattice parameters for Al-10Bi-3Fe, Al-10Bi-7Fe, and Al-10Bi-10Fe were calculated from the XRD patterns for the Al (111) peak using Jade software, yielding values of 2.3362 Å, 2.3375 Å, and 2.3422 Å, respectively, as shown in
Figure 5(b). These results further demonstrate that increasing Fe content leads to more pronounced Fe solid solution, as Fe atoms have larger atomic radii than Al atoms.
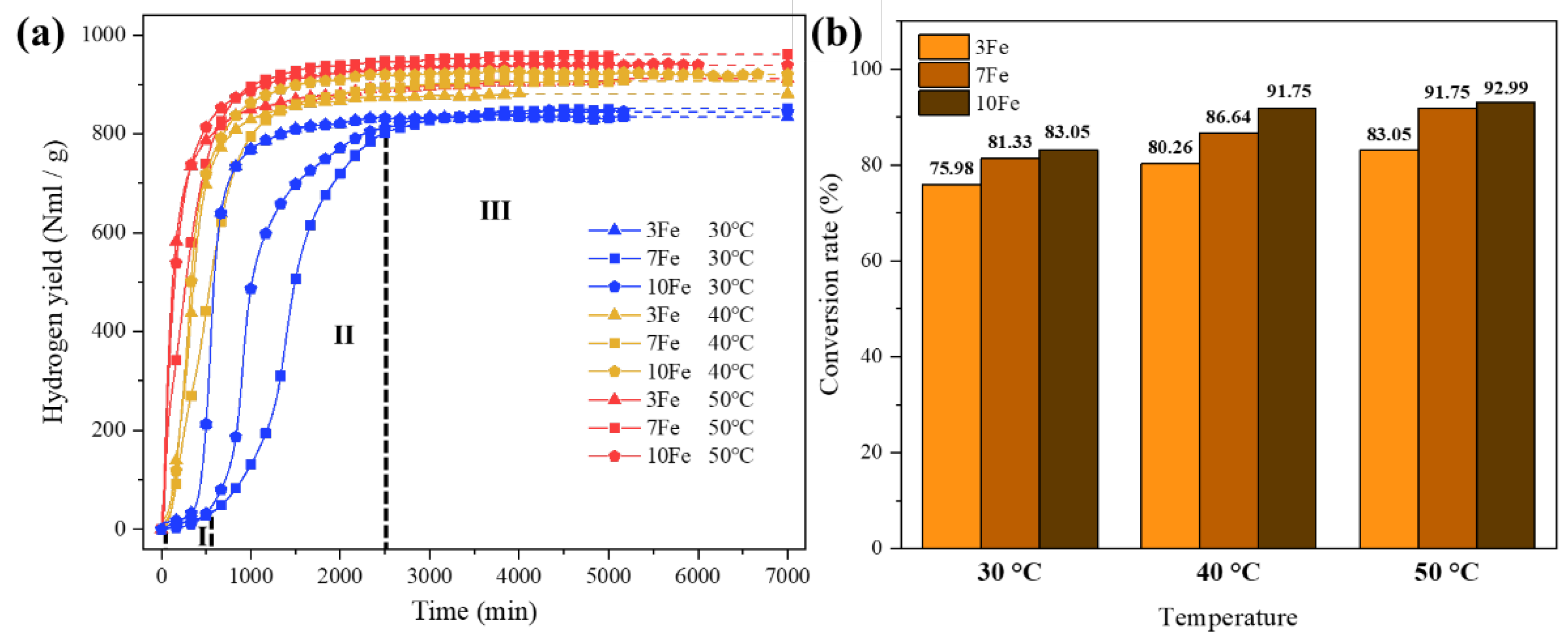
3.3. Hydrolysis Performance
Figure 6 illustrates the hydrogen yield versus time curves and conversion rates for the hydrolysis of Al-Bi-Fe variations in deionized water at reaction temperatures ranging from 30 to 50 °C. The hydrolysis process of as-atomized Al-based alloy powders generally consist of three distinct periods: the incubation period (Period I), the rapid reaction period (Period II), and the faded reaction period (Period III), as noted in previous studies [
26,
28,
29]. These three stages are evident for Al-10Bi-7Fe in
Figure 6(a). Initially, during the incubation period, the hydrogen generation rate is negligible. This is followed by an acceleration in hydrogen generation during the rapid reaction period, which leads to substantial hydrogen accumulation. Finally, the hydrogen generation rate slows down and approaches zero in the faded reaction period.
A noteworthy observation is the non-monotonic hydrolysis behavior of the Al-Bi-Fe variations with increasing Fe content, particularly with Al-10Bi-7Fe, which exhibits the longest incubation period and the slowest hydrogen generation rate during the rapid reaction period. This can be attributed to structural changes in the Al-Bi-Fe alloy powders. As discussed, increased Fe content enhances Fe solidification and leads to a more homogenous distribution of the Bi-rich phase. The former strengthens the matrix, while the latter reduces the effectiveness of the Bi-rich phase in disrupting the oxide layer, making the alloy powder more resistant to rupture. This extends the incubation period and reduces the hydrogen generation rate during the rapid reaction period.
Conversely, higher Fe content increases the number of Fe-rich regions, forming micro-galvanic couples with Al-rich regions, which accelerate the hydrolysis process, shortening the incubation period and increasing the hydrogen generation rate during the rapid reaction period. This interplay results in the observed non-linear relationship between Fe content and hydrolysis behavior in Al-Bi-Fe variations.
As reaction temperature increases, the hydrolysis kinetics are enhanced across all Al-Bi-Fe variations, improving overall performance. At 50 °C, Al-10Bi-7Fe produces the highest hydrogen yield (961.0 Nml/g), while Al-10Bi-3Fe and Al-10Bi-10Fe generate 911.8 Nml/g and 938.8 Nml/g, respectively.
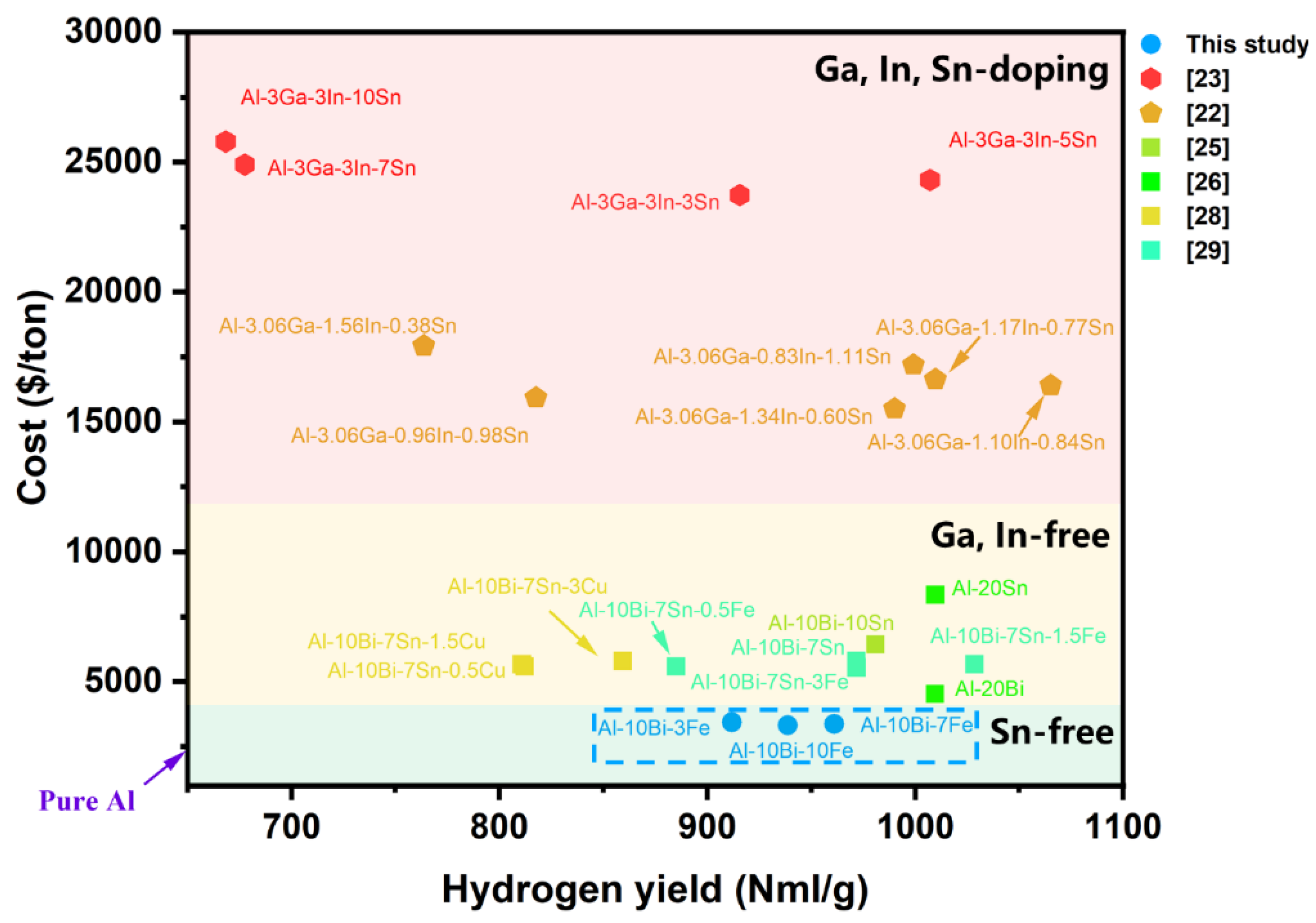
Figure 6(b) shows the conversion rates for each variation, indicating that both higher reaction temperatures and increased Fe content boost the conversion rates. Al-10Bi-10Fe, with the highest Fe content, achieves a remarkable conversion rate of 92.99%, surpassing Al-10Bi-3Fe and Al-10Bi-7Fe, which reach 83.05% and 91.75%, respectively, at 50 °C. Despite Al-10Bi-10Fe’s higher conversion rate, its hydrogen yield is lower than that of Al-10Bi-7Fe due to a smaller amount of hydrolyzable Al. Figure7 presents a comparison of the cost and hydrolysis performance of various active Al alloys at temperatures near 50°C, with detailed data provided in
Table S1
The extent of Fe doping plays a critical role in enhancing the conversion rate, as it alters the Bi-phase distribution. With higher Fe doping, more Bi-phase is distributed within the matrix rather than on the surface, creating favorable conditions for powder rupture, as highlighted in previous studies [
27,
30]. This leads to more thorough hydrolysis, improving the conversion rate for Al-Bi-Fe variations with elevated Fe content.
3.4. Chemical Kinetics of Hydrolysis Reaction
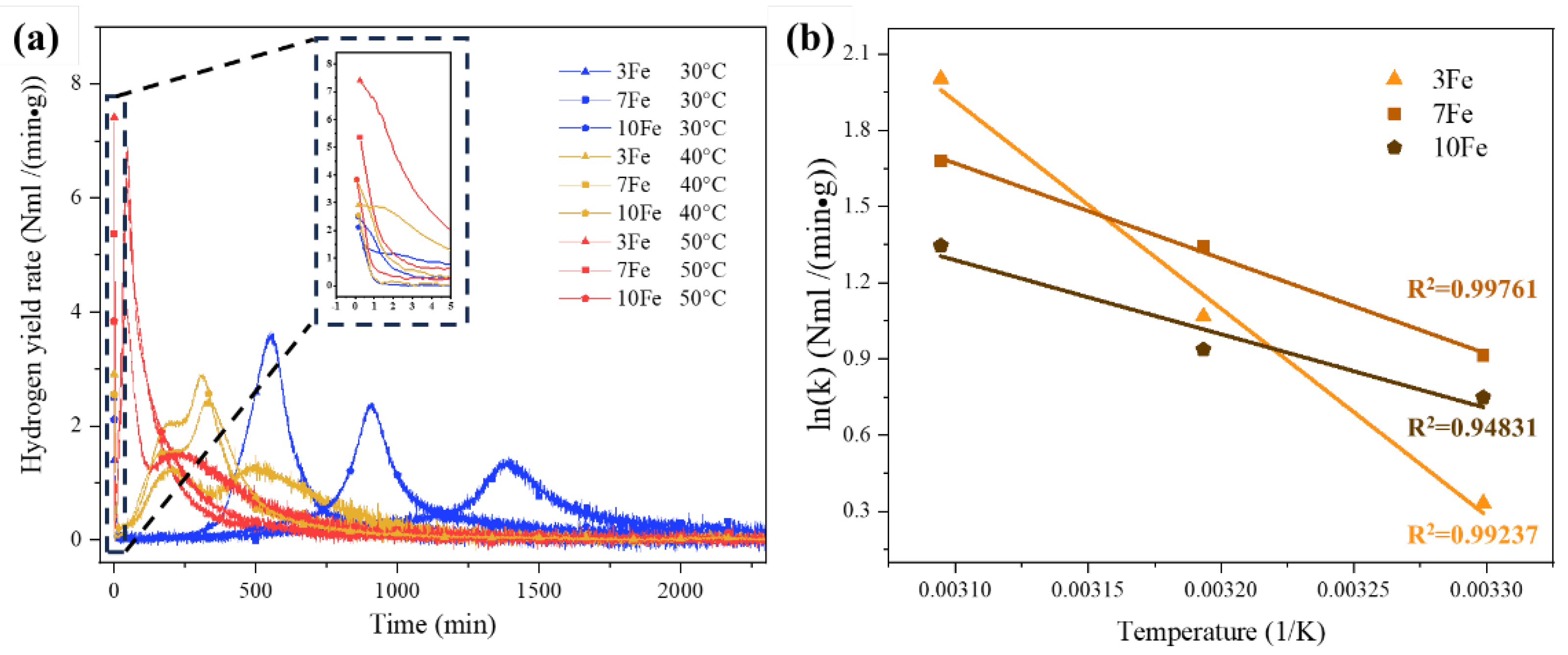
Figure 8(a) illustrates the hydrogen yield rates (k) vs. time curves of the hydrolysis reaction of Al-Bi-Fe variations. These curves are derived by taking the derivative of the curves presented in
Figure 6(a) and applying smoothing using the Savitzky-Golay method with a window size of 12 (interval between data points is 5 seconds) and a polynomial order of 1. The initial hydrogen yield rates of Al-Bi-Fe variations are observed even at a reaction temperature of 30 °C due to the immediate reaction of the as-atomized powders with sufficiently small sizes when exposed to deionized water [
31]. This occurrence takes place despite the existence of the incubation period. As shown in the inset of
Figure 8(a), the initial hydrogen yield rates of Al-Bi-Fe variations are strongly relevant to the reaction temperature, and the Arrhenius equation is used to model the initial hydrogen yield rates of hydrolysis reaction and for calculating the activation energy of Al-Bi-Fe variations, the formula is expressed as [
32,
33]:
Here, k is the hydrogen yield rate of Al-Bi-Fe variations (Nml/(min*g)), Ea is the activation energy for hydrolysis reaction (J/mol), R is the universal gas constant (8.314 J/(mol*K)), T is the absolute temperature (K), A is the Arrhenius factor.
Figure 8(b) depicts the Arrhenius plots of Al-Bi-Fe variations in deionized water. The plots demonstrate a significant linear correlation between ln(k) and 1/T across all Al-Bi-Fe variations, and the calculated activation energy values are listed in
Table 2. As indicated in the table, the activation energy of the as-atomized Al-10Bi-3Fe, Al-10Bi-7Fe, and Al-10Bi-10Fe powders are 67.888, 31.178, and 24.224 kJ/mol, respectively. This suggests a reduction in activation energy achieved by doping Fe in the Al-Bi-based alloy.
3.5. Hydrolysis Process
SEM images of the hydrolysis products from Al-Bi-Fe variations exposed to deionized water at reaction temperatures ranging from 30 to 50 °C are shown in
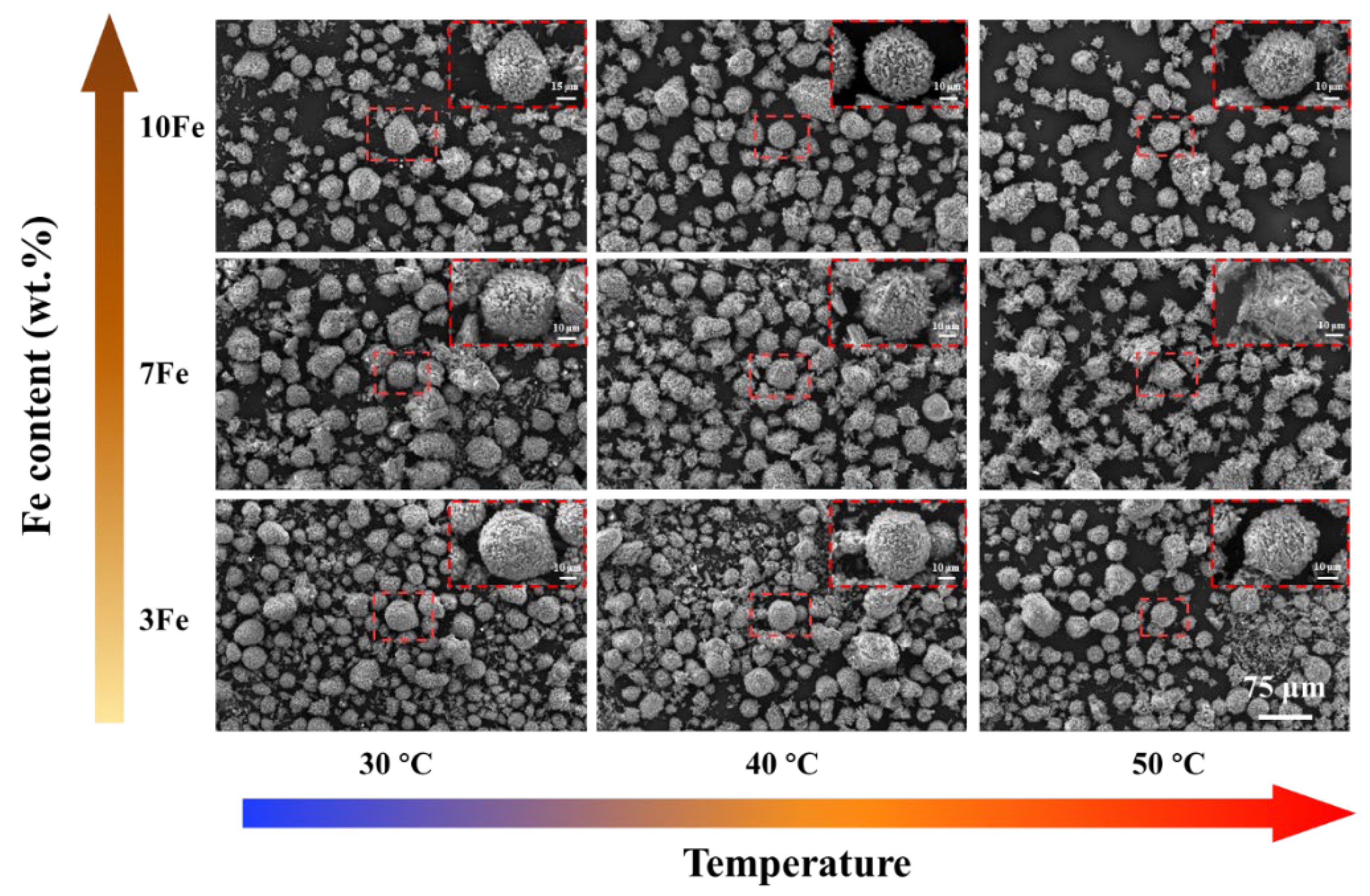
Figure 9. As observed in the figure, powders with minimal sizes nearly undergo complete dissolution, whereas larger particles undergo extensive hydrolysis, as depicted in the inset with the red dashed line. This observation underscores the remarkable hydrolysis efficacy of Al-Bi-Fe alloy powders at moderate temperatures, revealing the promising potential for hydrogen production from Sn-free Al-Bi-based alloys.
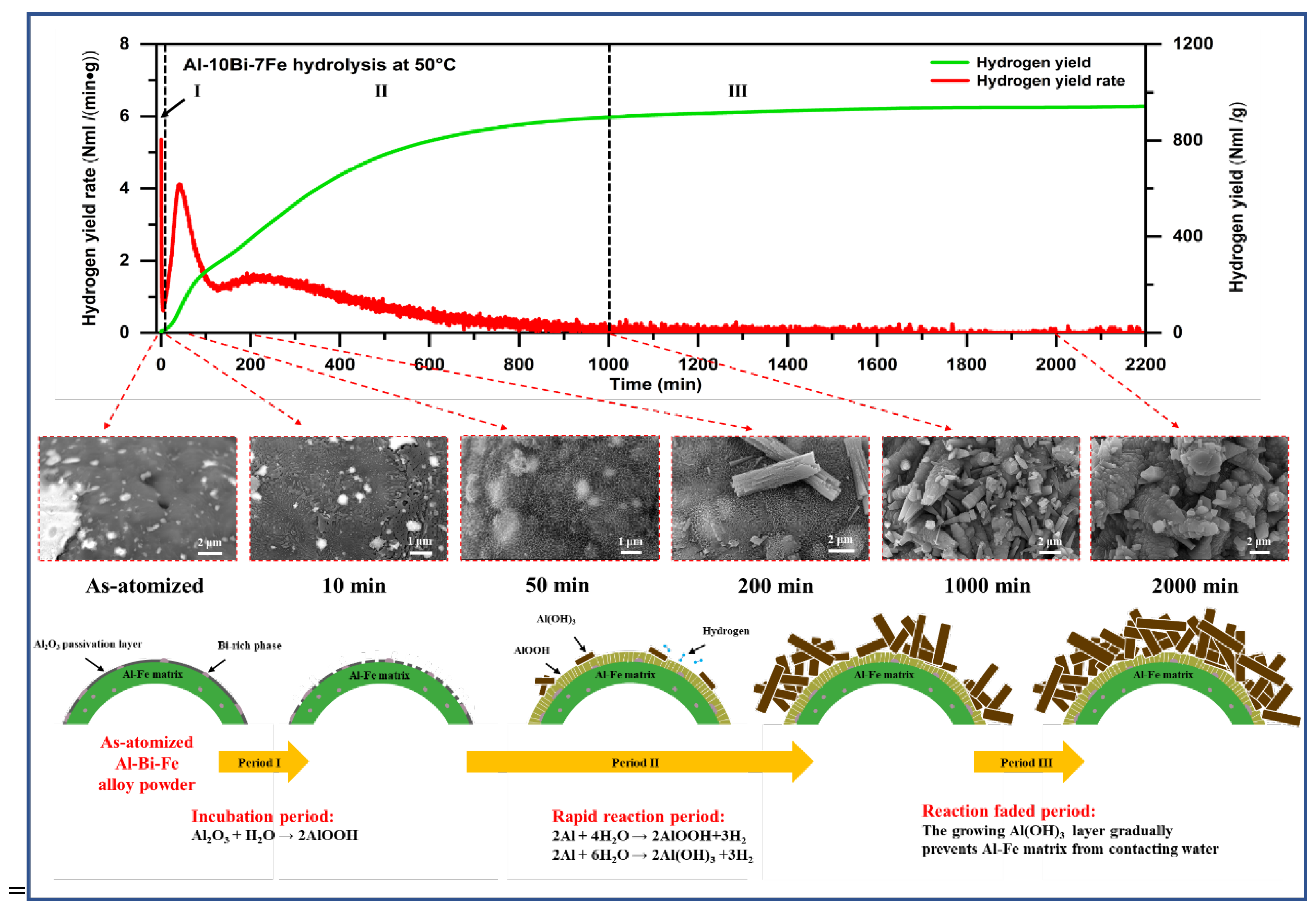
To investigate the hydrolysis behavior of Al-Bi-Fe alloy powders during each reaction period, a series of Al-10Bi-7Fe powders were subjected to hydrolysis in deionized water for varying reaction times, and the resulting hydrolysis products were characterized using SEM.
Figure 10 shows the morphological changes on the surface of these products at different stages of the hydrolysis process.
During the incubation period, the Al
2O
3 passive layer is hydrated without hydrogen generation, resulting in pitting on the powder surface [
34], as shown in the SEM image for a reaction time of 10 minutes, according to Equation (2):
Once the Al
2O
3 passive layer breaks down, water begins to react with the Al-Fe matrix, marking the onset of the rapid reaction period. During this phase, water reacts with the Al-Fe matrix according to Equation (3), until the powder surface is covered by stacked AlOOH platelets [
35,
36], as seen in the SEM image for a reaction time of 50 minutes. The hydrolysis then follows Equation (4), resulting in the formation of columnar Al(OH)
3 [
37], as shown in the SEM image for a reaction time of 200 minutes.
Both hydrolysis processes generate a significant amount of hydrogen. The columnar Al(OH)
3 layer grows rapidly during the rapid reaction period and eventually almost completely inhibits the contact between the Al-Fe matrix and water, as seen in the SEM image for a reaction time of 1000 minutes. Consequently, the hydrolysis process enters the faded reaction period, during which the hydrogen yield rate gradually declines to zero as the coarsening columnar Al(OH)
3 on the powder surface prevents further contact between the Al-Fe matrix and water, as seen in the SEM image for a reaction time of 2000 minutes. The complete hydrolysis process of the Al-Bi-Fe alloy powders is detailed in
Figure S1 and schematically represented in
Figure 10.
5. Conclusions
In summary, a series of Al-Bi-Fe alloy powders were meticulously designed and prepared using the gas atomization method. Microstructural characterizations unveiled the successful fabrication of an incomplete shell comprised of the Bi-rich phase on the powder surfaces, achieved without Sn doping. Increased Fe content enhances the solidification strengthening effect, alters the distribution of the Bi-rich phase, and promotes the formation of micro-galvanic couples. The intricate interplay of these factors results in significant hydration during hydrolysis and contributes to the excellent hydrolysis performance of these alloy powders. Specifically, Al-10Bi-7Fe exhibited the highest hydrogen yield, reaching 961.0 Nml/g, while Al-10Bi-10Fe demonstrated the peak conversion rate at 92.99%. The reduction in activation energy achieved through Fe doping, along with the observed microstructural changes, substantiates the valuable potential of these alloys for efficient and cost-effective hydrogen generation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1: Morphological changes on the surface of Al-Bi-Fe alloy powders at different reaction time of the hydrolysis process; Table S1: Cost and hydrolysis performance data for various active Al alloys.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Xingjun Liu and Cuiping Wang; Funding acquisition, Xingjun Liu; Investigation, Rui Deng, Hao Zhang, Kai Zhen and Yifei Liu; Methodology, Xingjun Liu and Cuiping Wang; Writing—original draft, Rui Deng and Mingshuai Wang; Writing—review & editing, Ruijun Yao and Xingjun Liu.
Funding
This research was funded by Shenzhen Science and Technology Program, grant number JCYJ20220531095212027.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Thampan T, Atwater T, Cook C, Novoa J, Sutorik AC: Hydrogen generation from aluminum hydride for wearable polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41:9402-9409.
- Luo Y, Wu Y, Li B, Mo T, Li Y, Feng S-P, Qu J, Chu PK: Development and application of fuel cells in the automobile industry. Journal of Energy Storage 2021, 42:103124.
- Pulsone NB, Hart DP, Siegel AM, Edwards JR, Railey KE: Aluminum-Water Energy System for Autonomous Undersea Vehicles. Lincoln Laboratory Journal 2017, 22.
- Wang S, Sun L-X, Xu F, Jiao C-L, Zhang J, Zhou H-Y, Huang F-L: Hydrolysis reaction of ball-milled Mg-metal chlorides composite for hydrogen generation for fuel cells. international journal of hydrogen energy 2012, 37:6771-6775.
- Qin H, Li H, Fu Q, Yu R, Zhao Y, Kang Z, Chen X, Wang M: Process optimisation of controlled and continuous MgH2 hydrolysis to produce hydrogen. Sustainable Materials and Technologies 2022, 33:e00505.
- Jiang W, Wang H, Zhu M: AlH 3 as a hydrogen storage material: Recent advances, prospects and challenges. Rare Metals 2021, 40:3337-3356.
- Yu KMK, Tong W, West A, Cheung K, Li T, Smith G, Guo Y, Tsang SCE: Non-syngas direct steam reforming of methanol to hydrogen and carbon dioxide at low temperature. Nature communications 2012, 3:1-7.
- Netskina O, Tayban E, Rogov V, Ozerova A, Mukha S, Simagina V, Komova O: Solid-state NaBH4 composites for hydrogen generation: Catalytic activity of nickel and cobalt catalysts. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46:5459-5471.
- Fan M-q, Liu S, Sun L-X, Xu F, Wang S, Zhang J, Mei D-s, Huang F-l, Zhang Q-m: Synergistic hydrogen generation from AlLi alloy and solid-state NaBH4 activated by CoCl2 in water for portable fuel cell. International journal of hydrogen energy 2012, 37:4571-4579.
- Wang H, Leung DY, Leung M, Ni M: A review on hydrogen production using aluminum and aluminum alloys. Renewable and sustainable energy reviews 2009, 13:845-853.
- Yang B, Chai Y, Yang F, Zhang Q, Liu H, Wang N: Hydrogen generation by aluminum-water reaction in acidic and alkaline media and its reaction dynamics. International Journal of Energy Research 2018, 42:1594-1602.
- He T, Wang W, Chen D, Yang K: Effect of Ti on the microstructure and Al–water reactivity of Al-rich alloy. International journal of hydrogen energy 2014, 39:684-691.
- Xu S, Zhao X, Liu J: Liquid metal activated aluminum-water reaction for direct hydrogen generation at room temperature. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2018, 92:17-37.
- Razavi-Tousi S, Szpunar J: Effect of addition of water-soluble salts on the hydrogen generation of aluminum in reaction with hot water. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2016, 679:364-374.
- Dupiano P, Stamatis D, Dreizin EL: Hydrogen production by reacting water with mechanically milled composite aluminum-metal oxide powders. International journal of hydrogen energy 2011, 36:4781-4791.
- Su M, Wang H, Xu H, Chen F, Hu H, Gan J: Enhanced hydrogen production properties of a novel aluminum-based composite for instant on-site hydrogen supply at low temperature. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47:9969-9985.
- Huang X-N, Lv C-J, Wang Y, Shen H-Y, Chen D, Huang Y-X: Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of aluminum/graphite composites with a core–shell structure. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37:7457-7463.
- Woodall J, Ziebarth JT, Allen CR, Sherman DM, Jeon J, Choi G: Recent results on splitting water with aluminum alloys. Materials Innovations in an Emerging Hydrogen Economy 2008, 1:119-127.
- Cuomo J, Woodall J: Solid state renewable energy supply. In No US 4358291, vol. 43582911982.
- Choi G, Ziebarth JT, Woodall JM, Kramer R, Sherman D, Allen CR: Mechanism of hydrogen generation via water reaction with aluminum alloys. In 2010 18th Biennial University/Government/Industry Micro/Nano SymposiumIEEE; 2010: 1-4.
- Ziebarth JT, Woodall JM, Kramer RA, Choi G: Liquid phase-enabled reaction of Al–Ga and Al–Ga–In–Sn alloys with water. international journal of hydrogen energy 2011, 36:5271-5279.
- An Q, Jin Z, Li N, Wang H, Schmierer J, Wei C, Hu H, Gao Q, Woodall JM: Study on the liquid phase-derived activation mechanism in Al-rich alloy hydrolysis reaction for hydrogen production. Energy 2022, 247:123489.
- Wang H, Chang Y, Dong S, Lei Z, Zhu Q, Luo P, Xie Z: Investigation on hydrogen production using multicomponent aluminum alloys at mild conditions and its mechanism. International journal of hydrogen energy 2013, 38:1236-1243.
- Jin Z, Wang H, Shi J, Wang H, Gao X, Gao Q, Sun X: Unveiling the role of indium and tin in Al–Ga based alloys for on-demand hydrogen supply from simulation to validation. Journal of Power Sources 2023, 554:232268.
- Wang C, Liu Y, Liu H, Yang T, Chen X, Yang S, Liu X: A novel self-assembling Al-based composite powder with high hydrogen generation efficiency. Scientific reports 2015, 5:17428.
- Liu Y, Liu X, Chen X, Yang S, Wang C: Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of activated Al-Bi, Al-Sn powders prepared by gas atomization method. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42:10943-10951.
- Chen X, Wang C, Liu Y, Shen Y, Zheng Q, Yang S, Lu H, Zou H, Lin K, Liu H: Popcorn-like aluminum-based powders for instant low-temperature water vapor hydrogen generation. Materials Today Energy 2020:100602.
- Wang C, Lin K, Liu Y, Chen X, Zou H, Qiu C, Yang S, Liu X: Design and fabrication of high activity retention Al-based composite powders for mild hydrogen generation. Materials 2019, 12:3328.
- Wang C, Yin B, Lin K, Wang M, Deng R, Guo Y, Zhang J, Yang S, Liu X: Effect of Fe on the Hydrogen Production Properties of Al-Bi-Sn Composite Powders. Materials 2022, 15:6702.
- Xiao F, Guo Y, Li J, Yang R: Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of activated aluminum composites in tap water. Energy 2018, 157:608-614.
- Gai W-Z, Liu W-H, Deng Z-Y, Zhou J-G: Reaction of Al powder with water for hydrogen generation under ambient condition. International journal of hydrogen energy 2012, 37:13132-13140.
- Kahveci O, Kaya MF: Hydrogen production from Al–Cu alloy using electric vehicle’s waste DC motor coils. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47:12179-12188.
- Kaya MF, Kahveci O, Erol H, Akkaya A: Effect of low B addition on Al-Zn alloy’s hydrogen production performance. international journal of hydrogen energy 2021, 46:15192-15202.
- Wang X, Li G, Eckhoff RK: Kinetics study of hydration reaction between aluminum powder and water based on an improved multi-stage shrinking core model. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46:33635-33655.
- Bunker BC, Nelson GC, Zavadil K, Barbour J, Wall F, Sullivan J, Windisch CF, Engelhardt M, Baer DR: Hydration of passive oxide films on aluminum. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2002, 106:4705-4713.
- Rider A, Arnott D: Boiling water and silane pre-treatment of aluminium alloys for durable adhesive bonding. International journal of adhesion and adhesives 2000, 20:209-220.
- Wang C, Huang Y, Wei H, Yu F, Wang M, Guo Y, Zhang J, Deng R, Yang S, Liu X: A brief strategy for designing self-encapsulated Al-Si base phase change materials with high thermal energy storage performance. Journal of Energy Storage 2023, 62:106957.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).