1. Introduction
Complexity of care, adequate staffing levels, and workflow are key factors affecting nurses’ workloads [
1]. In fact, a defined a priori nurse to patient ratio does not reflect the severity of the disease among admitted patients with different characteristics and needs [
2]. Clinical complexity classification and related staffing adjustment remain notable gaps in the current evidence limiting the capacity for optimal staffing practices [
3,
4]. Further research on this topic, including a standard and valid measure of nursing workload, is urgently needed [
5].
Nursing workload is defined as the ratio of demands or ‘task load’ to available resources [
6]. It encompasses physical, emotional, cognitive, and organisational aspects of work [
6,
7]. This has a significant impact on the quality of care, patient outcomes, and nurses’ well-being [
8,
9,
10]. In particular, in neonatal and paediatric settings, nursing overtime (which can be a consequence of an increase in workloads) is associated with higher health care–associated infections (HCAI), augmented unplanned extubation, and increased risk for bloodstream infections (BSI) in very low birth weight infants (VLBWI) [
11,
12,
13,
14]. Furthermore, strategies to reduce HCAIs are based on the management of risk factors (e.g. line management, hand hygiene, reduced use of antibiotics), and it has been described that daily nursing overtime periods should also be considered as an important risk factor [
11]. Evidence-based staffing strategies (monitoring nursing satisfaction, experience, and stress) can lead to improvements in patient safety and decreased rates of adverse outcomes [
5].
Nurses working in NICUs have experienced a higher level of workload than nurses in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) and Coronary Care Unit (CCU); therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the distribution of nurse staffing in these wards [
15].
In Italy, the number of admitted newborns, the size of the NICU and the volume of activities in these units are highly variable [
16]. Evidence also highlights an imbalance in terms of nurse-patient ratio (NPR) between units with low volumes of activities compared to those with high volumes; this finding implies higher nurse workloads in the largest NICUs [
16]. In this heterogeneous context, a tool that evaluates nursing workload based on the needs of newborns and their families is even more urgent.
The Winnipeg Surgical Complex Assessment of Neonatal Nursing Needs Tool (WANNNT-SC) was chosen because it is a modified version of the Winnipeg Assessment of Neonatal Nursing Needs Tool (WANNNT) [
17], which appears to be the most up-to-date instrument for all the technological and clinical changes that have occurred in the last two decades in neonatal intensive care. Furthermore, as described by Hart et al., the National Aeronautics and Space Administration Task Load Index (NASA TLX) [
18], which is a recent tool used to measure the workload of neonatal nurses, has few surgery-specific indicators, and this metric does not quantitatively determine the staff required [
19]. A previous study showed that a lower ratio of nursing care calculated using the WANNNT during the first seven days of admission was associated with an increased risk of mortality and morbidity in very preterm infants [
20]. The WANNNT-SC, adding corrected gestational age and assigning an acuity score of 1.0 to very preterm infants in the first week of life, should not have this weakness. Furthermore, the Clinical Risk Index for Babies score (CRIB-II) used to evaluate the criterion validity of the WANNNT-SC was significantly better in predicting mortality than gestational age or birth weight alone. The time-dependent performance of CRIB II was good up to the first 90 days [
21].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This was a validation study to evaluate the reliability and validity of the Italian version of the neonatal nursing workload WANNNT-SC [
19]. The study was conducted following The COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement INstruments (COSMIN) reccomandations [
22,
23] in four phases from May 2023 to February 2024.
2.2. Forward and Backward Translation And Cross-Cultural Adaptation
The authorisation to use the tool was obtained from the authors. All WANNNT-SC items were first translated into Italian by a NICU critical care nurse certified as competent in the English language and an Italian native speaker; then, a backward translation was performed by an expert NICU nurse who was a native English speaker and certified as competent in the Italian language [
24]. The original WANNNT-SC tool and the translation obtained were compared by two researchers who confirmed its consistency and homogeneity. Cultural adaptation was needed and performed according to the Italian context and with the WANNNT-SC authors’ permission.
2.3. Face Validity
The face validity phase involved expert nurses expressing their opinions on the face validity of the instrument regarding its clarity and adequacy in measuring nursing neonatal workload of nursing. From the 1st to 30th of June 2023, each expert received a questionnaire to fill out with the possibility of making suggestions if needed [
23]. The experts took part in an educational training course based on the tool. The precision and completeness of this phase were ensured by maintaining anonymity in the process and involving experts from different nursing contexts and clinical settings (NICU head nurses, NICU nurses, cardiac ICU nurses).
2.4. Internal Validity
Inter-rater reliability was performed from the 1st to 31 of July 2023 using a double-bind process to evaluate the constancy of the measure from different users over time [
23]. After an educational course focused on the tool and its use, two nurses performed their evaluations at the same time. The test-retest reliability phase was performed from the 1st to the 31st of August 2023. The time interval was defined a priori using the duration of the entire shift (approximately 8 h). Evaluations were performed at the start of the shift and by another nurse at the end. In light of the objective set, only the clinical variations in the newborns evaluated at the beginning of the shift were considered. To avoid selection bias, all emergency activities (NETS, call from delivery room, call from surgery room) and new admissions were included.
2.5. External Validity
From 15 November 2023 to 15 February 2024, criterion validity was performed to evaluate the degree of agreement between the tools and a gold standard [
23]. The gold standard measure chosen was the risk of mortality, calculated using the CRIB-II to highlight the correlation between care complexity and risk of mortality [
25]. A recent study found the CRIB-II score to have good predictive performance for overall mortality in VLBWI, and it was highlighted as a proper risk adjustment tool for quality improvement initiatives to reduce mortality [
21].
2.6. Tools
The WANNNT-SC is a nursing workload tool used in surgical and complex medical needs NICUs [
19]. It is a modified version of the WANNNT [
17]. The WANNNT was developed using an acuity-quality approach. A group of newborn nursing experts identified several specific indicators to classify lower- to higher-level nursing workloads. Fractions were used rather than nurse/patient ratios to create more manageable combinations of nursing assignments. For example, “1.0” value means that one nurse was required to care the newborn for the entire shift [
17]. The WANNNT-SC includes several modifications. The authors added the corrected gestational age, divided the tool into systems, and included indicators related to neurocritical and surgical care [
19]. Neurodevelopmental care, such as transfers for skin-to-skin care, and certain subjective aspects of workload, such as interacting with parents, were not explicitly addressed but, as an inherent patient care activity, were expected to be captured by corrected gestational age scoring. Indicators, including preoperative and postoperative care and transfers out of the unit or to other sites, were added. The WANNNT-SC considered only direct bedside care, excluding admitting nursing staff and charge nurses. WANNNT-SC is clinically valid and reliable. This tool accurately captures and standardizes perceived work intensity from both charge nurses and senior nursing staff, indicating inter-rater reliability. Indeed, the inter-rater Kappa was 0.73 (CI 0.60–0.87). No significance was found when comparing the mean difference between charge nurse and senior nurse use of the WANNNT-SC (p = 0.94, SD 0.32, CI -0.077 - 0.083) [
19].
Clinical Risk Index for Babies: The CRIB score is a risk-adjustment instrument widely used in neonatal intensive care to assess mortality risk in newborns [
26]. Parry et al. developed the CRIB II for infants up to 1 h after admission to neonatal intensive care. Authors used the Akaike information criteria to identify the best model, which included birthweight, gestational age, gender, body temperature at admission, and base excess. An increased CRIB II score is related to an increased mortality risk. The possible CRIB II scores range from 0 to 27 [
25].
2.7. Sample and Setting
This study enrolled neonatal patients admitted to the NICU with diagnoses related to medical, surgical, neurological, and cardiovascular diseases. Upon admission to the NICU, each newborn was evaluated using the Italian Winnipeg Surgical Complex Assessment of Neonatal Nursing Needs Tool (I-WANNNT-SC) and CRIB-II. A reliable and suitable sample size of 82 evaluations was determined using an a priori power analysis for the criterion validity analysis, as shown in
Figure 1.
2.8. Ethical Considerations
The study protocol was approved by the Local Ethics Committee “Palermo 1” (Protocol CI-NICU-00). The nurses and infants who participated in this study did not receive any intervention. This research was carried out according to the principles of the original Declaration of Helsinki and its subsequent amendments. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. Participation was voluntary and anonymous. The data were stored and managed according to the current Italian personal data protection code (Legislative Decree no. 196 of 30 June 2003). Data were collected and analysed anonymously.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
The dataset was stored in the ZENODO consultable using the identifier 10.5281/zenodo.13823401. Descriptive statistics were reported as appropriate after testing continuous variables for normality using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Frequency and percentage were reported for nominal variables, whereas median and interquartile range [IQR], or mean and standard deviation (SD) were calculated for continuous variables with normal distributions. The Pearson coefficient was used to evaluate correlations between the inter-rater and test-retest phases, and between scores obtained by the tools during the external validity phase. Finally, a variance analysis was performed to estimate the size of the association between the predicted mortality risk and the Italian WANNNT-SC score. Statistical significance was set at a P value of less than 0.05. Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 22.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp., whereas statistical power analysis was performed using G * Power 3.1.
3. Results
3.1. Cross-Cultural Adaptation Phase
To adapt the WANNNT-SC tool to the Italian context, several items were modified (Beaton et al. 2000).
“THAM infusion” item was replaced by “Sodium Bicarbonate infusion”. As described previously, sodium bicarbonate and Tris-hydroxymethyl-aminomethane (THAM) have both been used to correct metabolic acidosis in neonates [
28]. Sodium bicarbonate is commonly used in Italy.
“Transfer out of town” and "transfer to another inner-city hospital" items were replaced by “Neonatal Emergency Transport Service (NETS)” and “Back transport”, respectively. In Canada, the health system is managed at a provincial level; therefore, less acute infants are frequently transferred from high-risk centres (classified as Level III) to low-risk regional hospitals (classified as Level II) to create space for more acute patients. However, in Italy, regional governments have autonomy to legislate issues related to healthcare, resulting in regional organizational variations in resources and models [
29]. Approximately 30% of low-level delivery hospitals that handle fewer than 500 births/year are still active and there are more II-level NICU beds than are actually needed, while level III–IV beds are inadequate, forcing back transport as soon as the clinical conditions of the newborn allow it [
30]. Therefore, the authors decided to modify the items based on the type of transport.
3.2. Face Validity
An expert panel of 9 members with high clinical experience in the NICU was questioned. There were 3 (33.33%) head NICU nurses, 4 NICU (44.44%) nurses, and 2 (22.22%) cardiac NICU nurses. The median experience in NICU or cardiac NICU was 12 [9 – 15] years. The panellists came from children’s and general hospitals in northern, central, and southern Italy. The overall agreement regarding face validity was 92.3%, as detailed in
Table 1.
3.3. Inter-Rater Reliability
The ratings were given by 30 nurses, of which 18 (60%) were female. The median experience of the evaluators in the NICU was 5 [4 – 10] years. A total of 239 pairs of double-blind evaluations were performed. To evaluate the reliability of the tool among different professionals, a correlation test was performed using Pearson’s correlation, which resulted in a strong correlation (r = 0.967, p = 0.01).
3.4. Test-Retest Reliability
In this phase, 286 pairs of evaluations were performed by the same nurse; there was a significant correlation (r = 0.910 and p = 0.01).
3.5. Criterion Validity
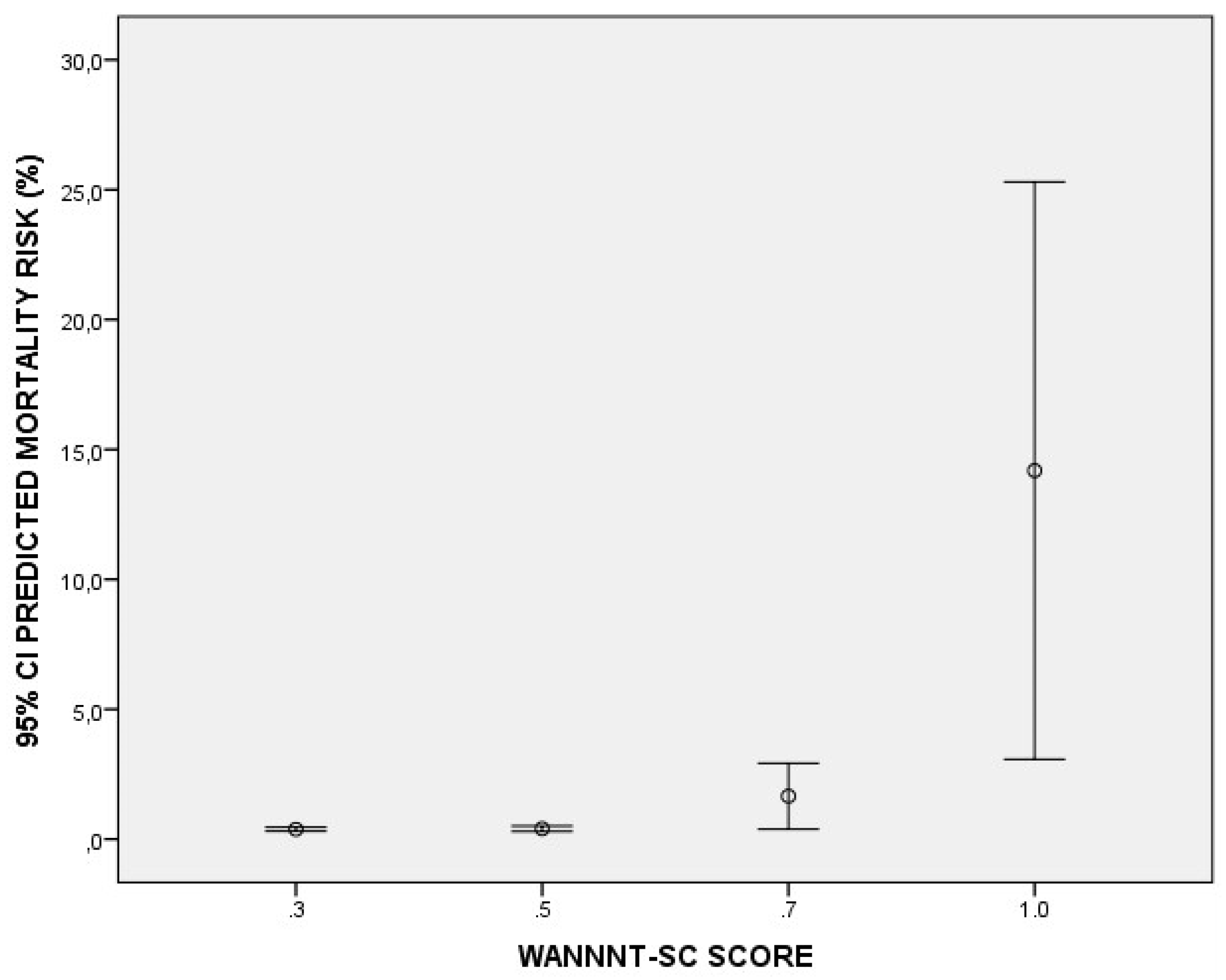
A total of 100 newborns were included in this study. The median weight and gestational age were 2540 [1950 – 2850] grams and 37 [34 – 38] weeks, respectively. A large number of newborns reported low/medium care complexity: 34% (n=34) and 32% (n = 32) reported a score of 0.3 and 0.5, respectively. Nineteen percent of newborns (n = 19) needed intensive care with a score of 0.7, and only 15% (n = 15) needed a one-to-one nurse-to-patient ratio with a score of 1. Lastly, using an analysis of variance, we found that the higher the I-WANNNT-SC score, the higher the predicted death rate (F = 13.05 and p < 0.001). In fact, the groups ‘0.3’, ‘0.6’, ‘0.7’ and ‘1’ reported an average mortality risk of 0.37% (95% IC: 0.30 – 0.45), 0.40% (95% IC: 0.29 – 0.50), 1.65% (95% IC: 0.38 – 2.91) and 14.18 (95% IC: 3.07 – 25.29), respectively (
Figure 2).
4. Discussion
This study aimed to adapt and validate the WANNNT-SC tool in the Italian context. We found strong inter-rater reliability and good stability over time. Furthermore, the I-WANNNT-SC highlighted a strong correlation with CRIB II, where mortality risk increased as the acuity score increased. This is important because, before the I-WANNNT-SC, no ad-hoc tools had been thought of or validated from other contexts for the assessment of care complexity in the neonatal setting in Italy; this has made a correlation between nursing workload and nursing-sensitive outcomes impossible. The daily use of the I-WANNNT-SC could lead hospital managers to adjust nursing staffing based on neonatal intensive care activities and could help optimize nurses according to patient needs. NICUs can have tremendous variability in patient acuity and a wide range of possible admission diagnoses, requiring many different types of nursing skills [
16], and a defined nurse/patient ratio does not reflect the severity of the disease among admitted patients [
2]. Furthermore, the Italian organizational standards for perinatal care [
31] defines a nurse per patient ratio of 1:2 in NICUs without a specific description of the clinical care needs, thus increasing risk of over-or underestimation of the necessary nurses. Another important aspect that the I-WANNNT-SC considers is the relational and educational activities focused on the parents and families of the newborn - activities that are often not considered in the evaluation of Italian nurses’ workload in the NICU. However, this study had some limitations. During criterion validity, only mortality risk was assessed, but future studies will be necessary to relate the I-WANNNT-SC to other nursing-sensitive outcomes (pressure injuries, HCAI, and drug administration errors). Furthermore, this study focused only on patient acuity. Other factors affect the nursing workload, such as environmental aspects (the layout of the NICU), organizational aspects, and the nursing skill mix. Unfortunately, as described, in Italy, there is high variability in organizational characteristics and work environments among NICUs and an uneven distribution of human resources in relation to the volume of activity [
16], with a critical shortage of nurses in pediatric settings [
32]. However, precisely defining the patient's needs using I-WANNNT-SC could be a good starting point.
5. Conclusions
The Italian Winnipeg Surgical Complex Assessment of Neonatal Nursing Needs Tool represents the first tool available for the Italian context that aims to measure the nursing workload in neonatal intensive care. It showed strong validity, reliability, and good correlation with CRIB II. The I-WANNNT-SC could allow adjustments in nursing staffing based on NICU activities and patient needs. Future studies are necessary to allow for a description of the Italian context, to compare NICUs of different levels, and to objectively relate and stratify nursing outcomes with their workload.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.B., F.P., S.B..; methodology, D.A..; validation, A.L.C., and The Italian Neonatal Nursing Workload Study Group; formal analysis, E.B..; investigation, V.P.; data curation, A.L.C.; writing—original draft preparation, E.B., F.P., and L.R..; writing—review and editing, K.H., A.M., J.L.W., A.H..; visualization, S.B.; supervision, L.R.; project administration, E.B.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Local Ethics Committee of “Palermo 1” (Protocol CI-NICU-00).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset used in the current study is available in ZENODO and consultable using the identifier 10.5281/zenodo.13823401.
Public Involvement Statement
No public involvement in any aspect of this research.
Guidelines and Standards Statement
This manuscript was drafted against The COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement INstruments (COSMIN). A complete list of reporting guidelines can be accessed via the equator network:
https://www.equator-network.org/.
Acknowledgments
The Italian Neonatal Nursing Workload Study Group members are: Ilaria Ester Midea (IRCCS Meyer Children’s Hospital, Florence); Adelaide D’Errico (AORN Santobono-Pausillipon Children’s Hospital, Naples); Biagio Nicolosi (IRCCS Meyer Children’s Hospital, Florence); Paola Coscia (ASST Grande Ospedale Metropolitano Niguarda, Milan); Simona Serveli (IRCCS Gaslini Children’s Hospital, Genoa); Denise Ruaro (IRCCS Gaslini Children’s Hospital, Genoa); Carolina Cocca (Local Health Authority 3 of Pescara)
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ivziku, D.; Ferramosca, F.M.P.; Filomeno, L.; Gualandi, R.; De Maria, M.; Tartaglini, D. Defining Nursing Workload Predictors: A Pilot Study. J Nursing Management 2022, 30, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, A. Nurse Staffing Levels in Critical Care: The Impact of Patient Characteristics. Nursing in Critical Care 2023, 28, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogowski, J.A.; Staiger, D.O.; Patrick, T.E.; Horbar, J.D.; Kenny, M.J.; Lake, E.T. Nurse Staffing in Neonatal Intensive Care Units in the United States: NICU NURSE STAFFING. Res Nurs Health 2015, 38, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; Saville, C.; Ball, J.; Jones, J.; Pattison, N.; Monks, T. Nursing Workload, Nurse Staffing Methodologies and Tools: A Systematic Scoping Review and Discussion. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2020, 103, 103487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherenian, M.; Profit, J.; Schmidt, B.; Suh, S.; Xiao, R.; Zupancic, J.A.F.; DeMauro, S.B. Nurse-to-Patient Ratios and Neonatal Outcomes: A Brief Systematic Review. Neonatology 2013, 104, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, M.G. Nursing Workload: A Concept Analysis. J Nurs Manag 2016, 24, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.; Anderson, J.E.; Maben, J. What Is Nursing Work? A Meta-Narrative Review and Integrated Framework. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2021, 122, 103944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.D.; Aiken, L.H.; Sloane, D.M.; Windsor, C.; Douglas, C.; Yates, P. Effects of Nurse-to-Patient Ratio Legislation on Nurse Staffing and Patient Mortality, Readmissions, and Length of Stay: A Prospective Study in a Panel of Hospitals. The Lancet 2021, 397, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafferty, A.M.; Clarke, S.P.; Coles, J.; Ball, J.; James, P.; McKee, M.; Aiken, L.H. Outcomes of Variation in Hospital Nurse Staffing in English Hospitals: Cross-Sectional Analysis of Survey Data and Discharge Records. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2007, 44, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubbs-Cooley, H.L.; Mara, C.A.; Carle, A.C.; Mark, B.A.; Pickler, R.H. Association of Nurse Workload With Missed Nursing Care in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. JAMA Pediatr 2019, 173, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltempo, M.; Blais, R.; Lacroix, G.; Cabot, M.; Piedboeuf, B. Association of Nursing Overtime, Nurse Staffing, and Unit Occupancy with Health Care–Associated Infections in the NICU. Amer J Perinatol 2017, 34, 0996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küng, E.; Waldhör, T.; Rittenschober-Böhm, J.; Berger, A.; Wisgrill, L. Increased Nurse Workload Is Associated with Bloodstream Infections in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ream, R.S.; Mackey, K.; Leet, T.; Green, M.C.; Andreone, T.L.; Loftis, L.L.; Lynch, R.E. Association of Nursing Workload and Unplanned Extubations in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit*: Pediatric Critical Care Medicine 2007, PAP. [CrossRef]
- Rogowski, J.A.; Staiger, D.; Patrick, T.; Horbar, J.; Kenny, M.; Lake, E.T. Nurse Staffing and NICU Infection Rates. JAMA Pediatr 2013, 167, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, M.; Azimian, J.; Mafi, M.; Rashvand, F. Evaluation of Nurses’ Workload in the Intensive Care Unit, Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and Coronary Care Unit: An Analytical Study. JCDR 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corchia, C.; Fanelli, S.; Gagliardi, L.; Bellù, R.; Zangrandi, A.; Persico, A.; Zanini, R. Work Environment, Volume of Activity and Staffing in Neonatal Intensive Care Units in Italy: Results of the SONAR-Nurse Study. Ital J Pediatr 2016, 42, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatzky-Dickson, D.; Bodnaryk, K. Validation of a Tool to Measure Neonatal Nursing Workload. Journal of Nursing Management 2009, 17, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubbs-Cooley, H.L.; Mara, C.A.; Carle, A.C.; Gurses, A.P. The NASA Task Load Index as a Measure of Overall Workload among Neonatal, Paediatric and Adult Intensive Care Nurses. Intensive and Critical Care Nursing 2018, 46, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, K.; Marchuk, A.; Walsh, J.-L.; Howlett, A. Validation of a Surgical Neonatal Nursing Workload Tool. Journal of Neonatal Nursing 2019, 25, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux-Bourque, C.; Piedboeuf, B.; Gignac, S.; Taylor-Ducharme, S.; Julien, A.-S.; Beltempo, M. Comparison of Three Nursing Workload Assessment Tools in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and Their Association with Outcomes of Very Preterm Infants. Am J Perinatol 2020, s-0040-1718571. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Lee, M.H.; Chang, Y.S. ; and the Korean Neonatal Network The Clinical Risk Index for Babies II for Prediction of Time-Dependent Mortality and Short-Term Morbidities in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Neonatology 2019, 116, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokkink, L.B.; Prinsen, C.A.C.; Bouter, L.M.; Vet, H.C.W.D.; Terwee, C.B. The COnsensus-Based Standards for the Selection of Health Measurement INstruments (COSMIN) and How to Select an Outcome Measurement Instrument. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2016, 20, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnier, J.J.; Lai, J.; Mokkink, L.B.; Terwee, C.B. COSMIN Reporting Guideline for Studies on Measurement Properties of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures. Qual Life Res 2021, 30, 2197–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneesriwongul, W. Instrument Translation Process: A Methods Review. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2004. [CrossRef]
- Parry, G.; Tucker, J.; Tarnow-Mordi, W. CRIB II: An Update of the Clinical Risk Index for Babies Score. The Lancet 2003, 361, 1789–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Neonatal Network The CRIB (Clinical Risk Index for Babies) Score: A Tool for Assessing Initial Neonatal Risk and Comparing Performance of Neonatal Intensive Care Units. The Lancet 1993, 342, 193–198. [CrossRef]
- Beaton, D.E.; Bombardier, C.; Guillemin, F.; Ferraz, M.B. Guidelines for the Process of Cross-Cultural Adaptation of Self-Report Measures. Spine 2000, 25, 3186–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, C.J.; Wilkinson, A.R. Sodium Bicarbonate Infusion during Resuscitation of Infants at Birth. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gente, M.; Aufieri, R.; Agostino, R.; Fedeli, T.; Calevo, M.G.; Massirio, P.; Bellini, C. Nationwide Survey of Neonatal Transportation Practices in Italy. Ital J Pediatr 2019, 45, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, C.; Risso, F.M.; Ramenghi, L.A. The Impact of Italian Regionalisation on Transporting Neonatal Patients Back from the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit to the Referring Level Two Unit. Acta Paediatrica 2017, 106, 1358–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard organizzativi per l’assistenza perinatale; Zanini, R., Mosca, F., Eds.; IdeaCpa: Roma, 2021; ISBN 978-88-946318-9-0.
- Buccione, E.; Stellabotte, M. Don’t Forget the Pediatric Intensive Care Units: The Nurses’ Point of View. ij 2024, 3, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).