1. Introduction
Amebiasis, caused by the protozoan parasite
Entamoeba histolytica, is a significant parasitic infection. The World Health Organization estimates that each year, approximately 50 million people in regions such as India, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America contract amebic dysentery and amebiasis, leading to at least 100,000 deaths. Transmission typically occurs through the ingestion of contaminated food or water. Once ingested, the cysts excyst in the intestinal lumen, where the trophozoites then colonize the large intestine. The lifecycle continues as both trophozoites and cysts are excreted in stools. While most infected individuals (90%) remain asymptomatic, symptomatic cases can experience diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. Severe infections can lead to life-threatening abscesses in the liver or other organs [
1]. Treatment generally involves antibiotics, with metronidazole being the standard therapy for invasive amebiasis in both adults and children [
2]. However, metronidazole can have side effects such as nausea, headaches, metallic taste, and even neurotoxicity. Additionally, there are emerging concerns about
E. histolytica developing resistance to metronidazole, highlighting the need for alternative treatments [
3,
4].
The gut microbiota, consisting of numerous bacteria, coexists with
E. histolytica in the intestinal environment.
E. histolytica not only consumes these bacteria as a food source but also interacts intricately with them. One key interaction involves the salvage of queuine from gut bacteria by
E. histolytica. Queuine, the nucleobase of queuosine (Q), is highly conserved across bacteria, plants, fishes, insects, and mammals. While bacteria can synthesize queuine de novo, eukaryotes lack this capability and must acquire queuine either through diet or from their intestinal microbiota [
5,
6,
7]. Q is a modified nucleoside found in the first position of transfer RNA (tRNA) anticodons with G
34U
35N
36 such as Asp, Asn, His, and Tyr [
8]. The enzyme responsible for incorporating Q into tRNA instead of G34 is tRNA-guanine transglycosylase (TGT), which in
E. histolytica is a heterodimer composed of EhQTRT1 and EhQTRTD1 [
9]. Once incorporated into the corresponding tRNA, queuine regulates translational speed and fidelity in eukaryotes [
10,
11] and influence the expression of genes involved in oxidative stress responses and virulence in
E. histolytica [
9]. The two known transporter families that salvage Q precursors are QPTR/COG1738 [
12] and QrtT/QueT [
13] in
Escherichia coli. A recent study identified three new families that facilitate Q precursor (preQ0 and preQ1) transport: a ureide permease (PF07168) from
Acidobacteriota bacterium, a hemolysin III family protein (PF03006) from
Bifidobacterium breve, and a Major Facilitator Superfamily protein (PF07690) from
Bartonella henselae [
14]. EhDUF2419 (EHI_098190), a protein homologous to DNA glycosylase, catalyzes the formation of Q from queuine in
E. histolytica [
15]. Despite its known role in queuine salvage, the interaction network of EhDUF2419 in
E. histolytica remain poorly understood. In this study, we employed immunoprecipitation (IP) combined with mass spectrometry (MS) to investigate the EhDUF2419 interactome, uncovering its multifaceted role in the parasite’s cellular processes.
2. Materials and Methods
E. histolytica Culture
The HM-1:IMSS strain of
E. histolytica was kindly supplied by Prof. Samudrala Gourinath from Jawaharlal Nehru University in New Delhi, India. The amoebae were cultivated at 37°C in 13 × 100 mm screw-capped Pyrex glass tubes using Diamond’s TYI-S-33 medium until they reached the exponential growth phase. Trophozoites were then collected from the culture tubes by tapping them and subsequently centrifuging, following previously established protocols [
16].
Construction of the Myc-Tagged EhDUF2419 (MycEhDUF2419) or Truncated EhDUF2419 Vector (TrunEhDUF2419)
To construct the Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 expression vector, the EhDUF2419 gene was amplified from
E. histolytica cDNA using sense and antisense primers (
Table 1) incorporating SmaI and XhoI sites, respectively. The resulting PCR product was cloned into the pGEM-T Easy vector system (Promega, Beit Haemek, Israel), digested with SmaI and XhoI, and subsequently subcloned into the pKT-3M AGO2-2 expression vector (kindly supplied by Prof. Upinder Singh from Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, USA; [
17]) that included a Myc-tag and had been previously linearized with SmaI and XhoI. The plasmids were sequenced to verify the absence of unwanted mutations.
For the TrunEhDUF2419, we identified a putative active site based on the DUF2419 protein from
Sphaerobacter thermophilus (StDUF2419) as described in a referenced article [
18]. Sequence alignment showed that EhDUF2419 and StDUF2419 share 33% identity, with active site residues D298 and W302 in StDUF2419 corresponding to D280 and W284 in EhDUF2419. We truncated EhDUF2419 starting just before site D280, added a stop codon and restriction sites, and amplified this segment from
E. histolytica cDNA using specific primers (
Table 1). The remaining steps were identical to those used for constructing the Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 vector.
Transfection of E. histolytica Trophozoites
The transfection of
E. histolytica trophozoites was carried out following the method outlined by Olvera et al. [
19].
Quantitative-Real Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was isolated from either control or Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 trophozoites using TRI reagent (Merck, Rehovot, Israel), and its concentration was determined using a nanodrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific (Heysham), Lancashire, UK). Reverse transcription was carried out using the RevertAid First strand cDNA synthesis kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific (Heysham), Lancashire, UK) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The primers utilized for amplifying EhDUF2419 and rDNA are detailed in
Table 1. The qRT-PCR was conducted using the qPCR-Bio SyGreen Mix Hi-ROX (PCR Biosystems, London, UK) as per the manufacturer’s protocol and run on the Real-Time PCR QuantStudio3 (Thermo Fisher Scientific (Heysham), Lancashire, UK) with the following cycling conditions: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 2 min, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 5 s, and annealing/extension at 50 °C for 30 s. The melting curve analysis was performed under the following conditions: 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 1 min, and a final step at 95 °C for 15 s. The relative fold change was determined using the 2ˆ
(−∆∆Ct) method [
20]. qRT-PCR values were normalized to the expression level of rDNA gene. PCR amplification controls were included for each primer pair to confirm product formation.
Western Blot Analysis
Western blotting was conducted on total protein extracts from
E. histolytica trophozoites (50 μg) following a previously established protocol [
9]. For experiments involving Q (a gift from Prof. Peter C. Dedon, MIT, USA) treatment, trophozoites were incubated with 0.1 μM Q for 2 days prior to protein extraction. In experiments involving MG132 (Merck, Rehovot, Israel) treatment, trophozoites were exposed to 20 μM MG132 for 2 days. For combined treatment conditions, trophozoites were co-treated with 20 μM MG132 and 0.1 μM Q for 2 days. Proteins were separated on a 12% SDS gel and then transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Whatman, Protran BA83, Merck, Rehovot, Israel). The membranes were subsequently blocked with 5% skim milk and incubated with mouse anti-Myc antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA) (diluted 1:1000) overnight at 4°C. Following incubation, the blots were washed and probed with a secondary antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA, USA) at room temperature for 1 hour, followed by detection using an enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (WesternBright
TM ECL, Advansta, CA, USA). Then photographed with Fusion FX7 Edge Spectra.
Immunoprecipitation
We followed a protocol similar to that outlined in reference [
21], with slight adjustments. 5 × 10
6 cells were lysed in 3 ml of lysis buffer containing 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 1 mM MgCl
2, 10% (vol/vol) glycerol, 50 mM NaCl, 0.5% (vol/vol) Nonidet P-40 (NP-40), 1 mM NaF, 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), EDTA-free protease inhibitors (Thermo Fisher Scientific (Heysham), Lancashire, UK), and RNase inhibitor (1 unit/ml). Following a 15-minute incubation on ice, the cell lysate was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 20 minutes at 4°C. For each anti-Myc immunoprecipitation, 50 μl of packed Pierce anti-c-Myc agarose beads (Thermo Fisher Scientific (Heysham), Lancashire, UK) were prewashed and incubated with 1 ml of whole-cell lysate (1 to 2 mg/ml) for 2 hours with rotation at 4°C. Following six washes (each for 5 minutes) using a low-stringency buffer (containing 1 mM PMSF, 0.1% [vol/vol] Tween 20, and 0.1% [vol/vol] NP-40) at 4°C, the IP-bound proteins were released by adding 50 μl of protein loading buffer and heating at 95°C for 5 minutes.
In Gel Proteolysis and MS Analysis
Gel-based proteolysis was performed according to a previously described method [
22]. Initially, the proteins in the gel were reduced with 3 mM DTT at 60°C for 30 minutes, followed by alkylation with 10 mM iodoacetamide in 100 mM ammonium bicarbonate in a light-protected environment at room temperature for 30 minutes. The proteins were then digested enzymatically with modified trypsin (Promega, Beit Haemek, Israel) in a solution containing 10% acetonitrile and 10 mM ammonium bicarbonate at an enzyme-to-substrate ratio of 1:10, overnight at 37°C. A secondary digestion with trypsin was performed for an additional 4 hours at 37°C. The resultant tryptic peptides were desalted using homemade C18 stage tips, dried, and re-suspended in 0.1% formic acid. These peptides were further separated by reverse-phase chromatography on a 0.075 × 300 mm fused silica capillary column (J&W, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) packed with Reprosil reversed-phase material (Dr Maisch GmbH, Ammerbuch, Germany). Peptide elution was achieved using a linear gradient of 5% to 28% acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid in water over 60 minutes, followed by a 15-minute gradient of 28% to 95% acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid in water, and finally, 15 minutes at 95% acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid in water, at a flow rate of 0.15 μl/min. Mass spectrometry analysis was conducted using a QExactive Plus mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) operating in positive mode. The procedure involved repetitive full MS scans followed by High Collision Dissociation (HCD) of the 10 most abundant ions selected from the initial MS scan.
For data analysis, MaxQuant software version 2.1.1.0 [
23] was used, facilitating peak picking and identification through the Andromeda search engine. The search was conducted against the
E. histolytica section of the Uniprot database, with a mass tolerance of 4.5 ppm for precursor ions and 20 ppm for fragment ions. Accepted variable modifications included oxidation of methionine, protein N-terminus acetylation, and biotin on lysine, while carbamidomethylation of cysteine was considered static. Peptides with a minimum length of seven amino acids and up to two miscleavages were allowed. Label-free quantification was performed using the same software, with peptide- and protein-level false discovery rates (FDRs) filtered to 1% using the target-decoy strategy. Protein tables were filtered to remove identifications from the reverse database and common contaminants. Statistical analysis of identification and quantification results was performed using Perseus software (Perseus 1.6.7) from Mathias Mann’s group. Proteins were considered significantly altered if they exhibited at least a 2-fold change in abundance in the Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 strain compared to the control, with a
p-value < 0.05 and Razor + unique peptides > 1.
PANTHER Classification System
The PANTHER Classification System (Version 18.0) was employed for data analysis in this study, accessed via
http://pantherdb.org/ on October 20, 2023 [
24]. To categorize proteins, the “protein class” ontology setting was utilized. The statistical overrepresentation test was carried out using default settings, employing the annotation dataset corresponding to PANTHER protein class and opting for FDR correction for multiple testing.
Ribosome Purification
Ribosomes were pelleted according to the method described in [
25,
26] with some modifications. For experiments involving Q treatment, trophozoites were incubated with 0.1 μM Q for 2 days prior to collection. Briefly, 1 × 10
7 cells were treated with 0.1 mg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) for 5 minutes and then harvested. Following collection, cells were lysed on ice for 10 minutes using lysis buffer containing 20 mM Hepes (pH 7), 100 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl
2, 0.1% Triton, 2 mM DTT, proteinase inhibitor, and RNase inhibitor. DNase treatment was carried out at 25°C for 5 minutes. Nuclei were removed by centrifugation at maximum speed for 10 minutes at 4°C, and the resulting supernatant was collected. Ribosomes were then isolated by pelleting with a sucrose cushion (prepared with 10 ml lysis buffer and 12.5 ml of a solution containing 20 mM HEPES pH 7, 100 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl
2, and 0.5 M sucrose) through ultracentrifugation at 60,000 RPM for 1 hour and 50 minutes. The obtained ribosome pellets were subsequently resuspended in 20 μl of lysis buffer and boiled at 95°C for 5 minutes. Samples were loaded onto a 12% SDS-PAGE gel and subjected to immunoblotting using a mouse anti-Myc antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA) at a 1:1000 dilution and a homemade anti-SSM1 antibody targeting Ribosomal 60S subunit protein L1A (RPL1A) in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. RPL1A in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae exhibits a 53% sequence identity with 60S ribosomal protein L10a-2 (EHI_012480) in
E. histolytica HM-1:IMSS. In this study, EHI_012480 was significantly enriched in the pull-down proteins that interact with EhDUF2419.
Assessment of Protein Synthesis through Surface Sensing of Translation (SUnSET)
Protein synthesis in trophozoites was evaluated using the SUnSET method [
27,
28]. For experiments involving Q treatment, trophozoites were incubated with 0.1 μM Q for 2 days prior to collection. Briefly, trophozoites (2 × 10
6) were incubated with 10 μg/ml puromycin (Merck, Rehovot, Israel), a structural analog of tyrosyl-tRNA, for 20 minutes at 37°C. After incubation, the trophozoites were lysed using 1% Igepal (Merck, Rehovot, Israel) in PBS. Proteins were separated on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel in SDS-PAGE running buffer and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane in protein transfer buffer. To ensure equal loading, the membrane was stained with Ponceau-S (Merck, Rehovot, Israel) before immunostaining. Puromycin incorporation was detected by immunoblotting with a 1:1000 dilution of monoclonal puromycin antibody (12D10 clone, Merck Millipore, Rosh-Ha’ayin, Israel). After the primary antibody incubation, the blots were treated with a 1:5000 dilution of secondary antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA, USA) for 2 hours at room temperature. Enhanced chemiluminescence (WesternBright™ ECL, Advansta, CA, USA) was used for development, and the blots were photographed using a Fusion FX7 Edge Spectra. Protein synthesis quantification was performed by measuring the intensity of immunoreactive blots (densitometry) with Fiji software version 1.54f [
29].
N-Acryloyl-3-Aminophenylboronic Acid (APB) Northern Blotting for E. histolytica tRNAHisGUG
Gels containing acryloyl aminophenylboronic acid were prepared with slight modifications based on the method by Igloi and Kossel [
30]. For experiments involving Q treatment, trophozoites were incubated with 0.1 μM Q for 2 days prior to extraction. In brief, 15 μg of RNA was deacetylated in 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 9) for 30 minutes at 37°C. The RNA was then precipitated using ethanol and resuspended in 10 ml DEPC-treated water. The samples were denatured for 10 minutes at 70°C and subsequently run on Tris-acetate EDTA (TAE) buffer gels at 4°C. These gels contained 8 M urea, 15% acrylamide, and 5 mg/ml aminophenylboronic acid (Merck, Rehovot, Israel) and were run using a Bio-Rad mini gel system at 75 V for 7 hours until the bromophenol blue dye reached the gel’s bottom. Post-electrophoresis, the gels were stained with ethidium bromide in 1× TAE buffer for 20 minutes to verify equal sample loading, then destained with ultrapure water for another 20 minutes. Samples were transferred onto a Hydrobond-XL membrane (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA) via electrotransfer in 0.5 × TAE buffer for 45 minutes at 150 V. The membrane was UV cross-linked using a Stratagene UV linker set to 120 mJ, followed by two 15-minute hybridizations in 5 ml of hybridization buffer (20 mM sodium phosphate buffer [pH 7.3], 300 mM NaCl, 1% SDS). Next, 150 μg/ml heat-denatured salmon sperm DNA (ssDNA) was added to the buffer for blocking, performed at 60°C for 1 hour. The membrane was incubated with 15 pmol biotinylated tRNA probes targeting tRNA
HisGUG at 60°C for 16 hours, then washed for 10 minutes in wash buffer (20 mM sodium phosphate buffer [pH 7.3], 300 mM NaCl, 2 mM EDTA, 0.5% SDS) at 60°C. An additional 10-minute incubation in hybridization buffer at room temperature was followed by a 30-minute incubation with streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) conjugate in 5 ml hybridization buffer (diluted 1:5,000). Subsequent washes were performed twice for 10 minutes each in wash buffer. The membrane was then treated with enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (WesternBright
TM ECL, Advansta, CA, USA), and photographed with Fusion FX7 Edge Spectra.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis and graphical representations were performed using Prism 9 (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). The data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) from 2 to 4 biological replicates. Unless stated otherwise, significance was determined using one-way ANOVA for multiple comparisons and the unpaired t test for comparisons between two groups.
3. Results
3.1. Interactome of MycEhDUF2419 in E. histolytica Trophozoites
We have previously identified that EhDUF2419, a protein with homology to DNA glycosylase, acts as a queuine salvage enzyme in E. histolytica by catalyzing the conversion of Q into queuine [
15]. However, the interaction networks, or interactome, of EhDUF2419 within the parasite remain largely unexplored. To investigate the interactome of EhDUF2419, we transfected E. histolytica trophozoites with a plasmid encoding Myc-tagged EhDUF2419. We induced the overexpression of EhDUF2419 by increasing the plasmid copy number, which was achieved by elevating the concentration of the antibiotic G418. The plasmid copy number is directly proportional to the level of resistance of the cultures to G418, allowing us to control the level of EhDUF2419 expression [
31]. We quantified EhDUF2419 mRNA expression levels in trophozoites carrying the pKT-3M AGO2-2 vector (empty vector) and Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites using qPCR. Our results showed a significant increase in EhDUF2419 mRNA levels in trophozoites treated with 24 μg/ml G418 compared to both empty vector trophozoites and Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites cultivated with 12 μg/ml G418 (
Figure 1a). Western blot analysis revealed a distinct 39.5 kDa band corresponding to MycEhDUF2419 in Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites cultivated with 24 μg/ml G418 (
Figure 1b). In contrast, MycEhDUF2419 was expressed with less intensity in trophozoites cultivated with 12 μg/ml G418 (
Figure 1B), which aligns with the lower levels of Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 mRNA observed at this concentration (
Figure 1a). Additionally, the Myc antibody detected a 30 kDa band of unknown origin, which may result from non-specific binding or degradation of the Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 recombinant protein (
Figure 1b). Overall,Western blot analysis using a Myc antibody confirmed the overexpression of the EhDUF2419 protein in Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites.
Based on the optimal expression level of Myc-tagged EhDUF2419, we selected transfectants treated with 24 μg/ml G418 for the pulldown of EhDUF2419. This process involved using anti-c-Myc agarose beads for immunoprecipitation, followed by mass spectrometry-based proteomics analysis.
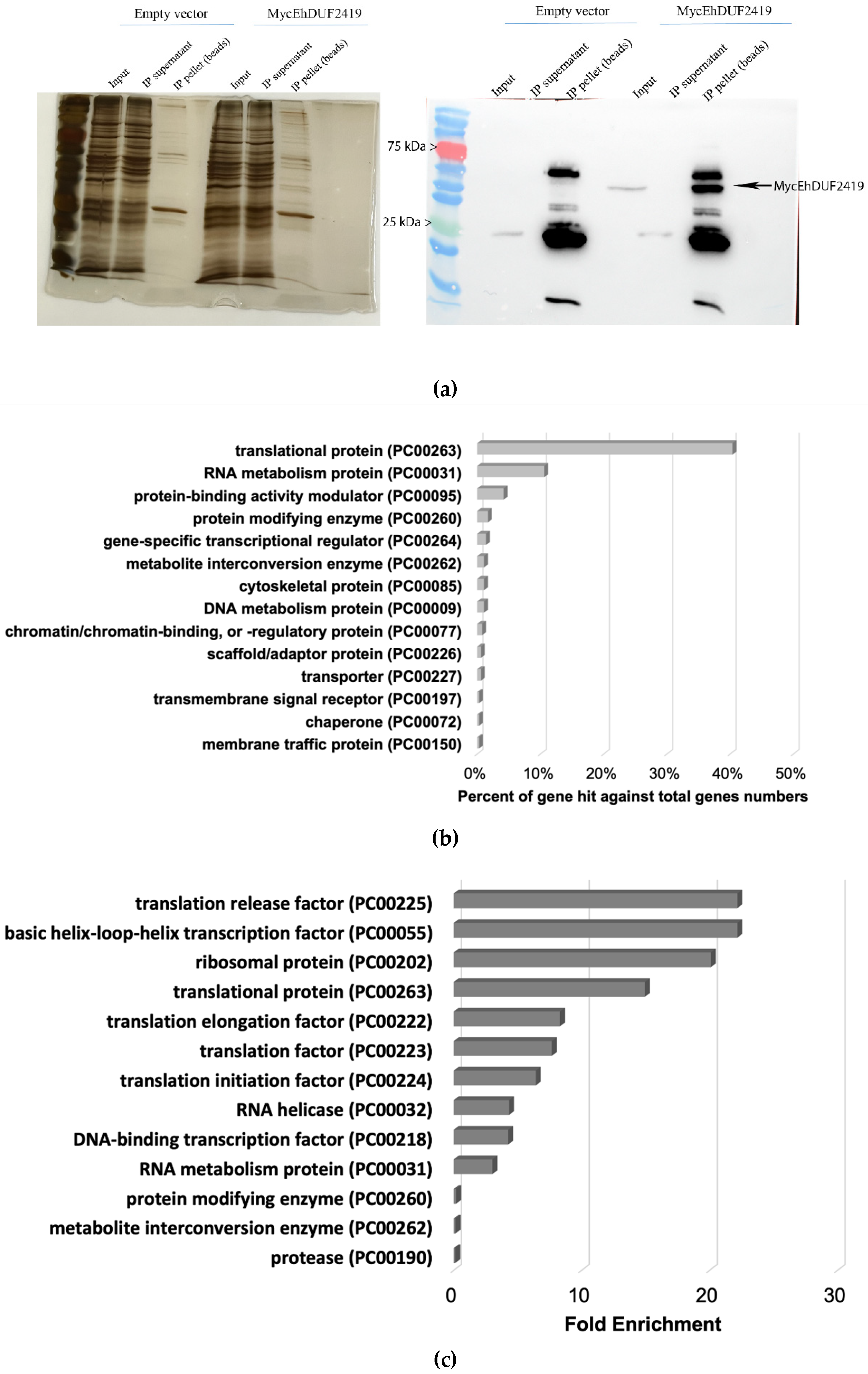
Protein enrichment post-immunoprecipitation was verified using Western blotting and silver staining. The successful pulldown of Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 protein in the IP sample confirmed that the tagged protein was successfully immunoprecipitated (
Figure 2a). In contrast, no Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 protein was detected in the IP product of empty vector trophozoites (
Figure 2a). Lysates prepared from three biological replicates of empty vector trophozoites and Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites were immunoprecipitated. Pulled-down proteins were eluted from the beads with SDS-PAGE sample loading buffer, separated by SDS-PAGE, and subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis following in-gel trypsin digestion. We identified 335 proteins that potentially interact with EhDUF2419 (
p-value < 0.05, fold change > 2) in the Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites (
Table S1). These 335 proteins were categorized using the PANTHER classification system [
24] (
Figure 2b). The six most prevalent protein families included translational protein (PC00263) (exemplified by 60S ribosomal protein L10 [EHI_044810]), RNA metabolism protein (PC00031) (exemplified by tRNA (Cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase, EhDNMT2 [EHI_103830]), protein-binding activity modulator (PC00095) (exemplified by Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor EHI_159500), protein modifying enzyme (PC00260) (exemplified by E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase listerin [EHI_190430]), gene-specific transcriptional regulator (PC00264) (exemplified by Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma [EHI_044930]) and metabolite interconversion enzyme (PC00262) (exemplified by Glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase [EHI_159730]. The PANTHER statistical overrepresentation test, which compares classifications of multiple clusters to a reference list, revealed significant enrichment (
p-value and q-value < 0.05) for proteins annotated as translation release factor (PC00225) (exemplified by Eukaryotic peptide chain release factor subunit 1 [EHI_152750]), basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor (PC00055) (exemplified by Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma [EHI_044930]), ribosomal protein (PC00202) (exemplified by 60S ribosomal protein L10 [EHI_044810]), translational protein (PC00263) (exemplified by Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 30 kDa subunit [EHI_178890]), translation elongation factor (PC00222) (exemplified by Elongation factor 2 [EHI_155660]), translation factor (PC00223) (exemplified by WD domain containing protein [EHI_118720]), translation initiation factor (PC00224) (exemplified by Eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF-5 [EHI_129770]), RNA helicase (PC00032) (exemplified by Helicase [EHI_053600]) and so on (
Figure 2c).
Moreover, STRING (a database of known and predicted protein-protein interactions (
https://string-db.org/)) predicts possible interactions between EhDUF2419 and EhTGT (EHI_035660), EhDUF2419 and a pseudouridine synthase and archaeosine transglycosylase domain RNA-binding motif containing protein (EHI_016460), EhDUF2419 and an endonuclease (EHI_134360) and so on (
Table S2). Notably, the pseudouridine synthase and archaeosine transglycosylase domain RNA-binding motif-containing protein (EHI_016460) is one of the proteins identified in the EhDUF2419 interactome (
Table S1).
3.2. EhDUF2419 Co-Purified with Ribosomal Proteins in the Ribosome Fraction
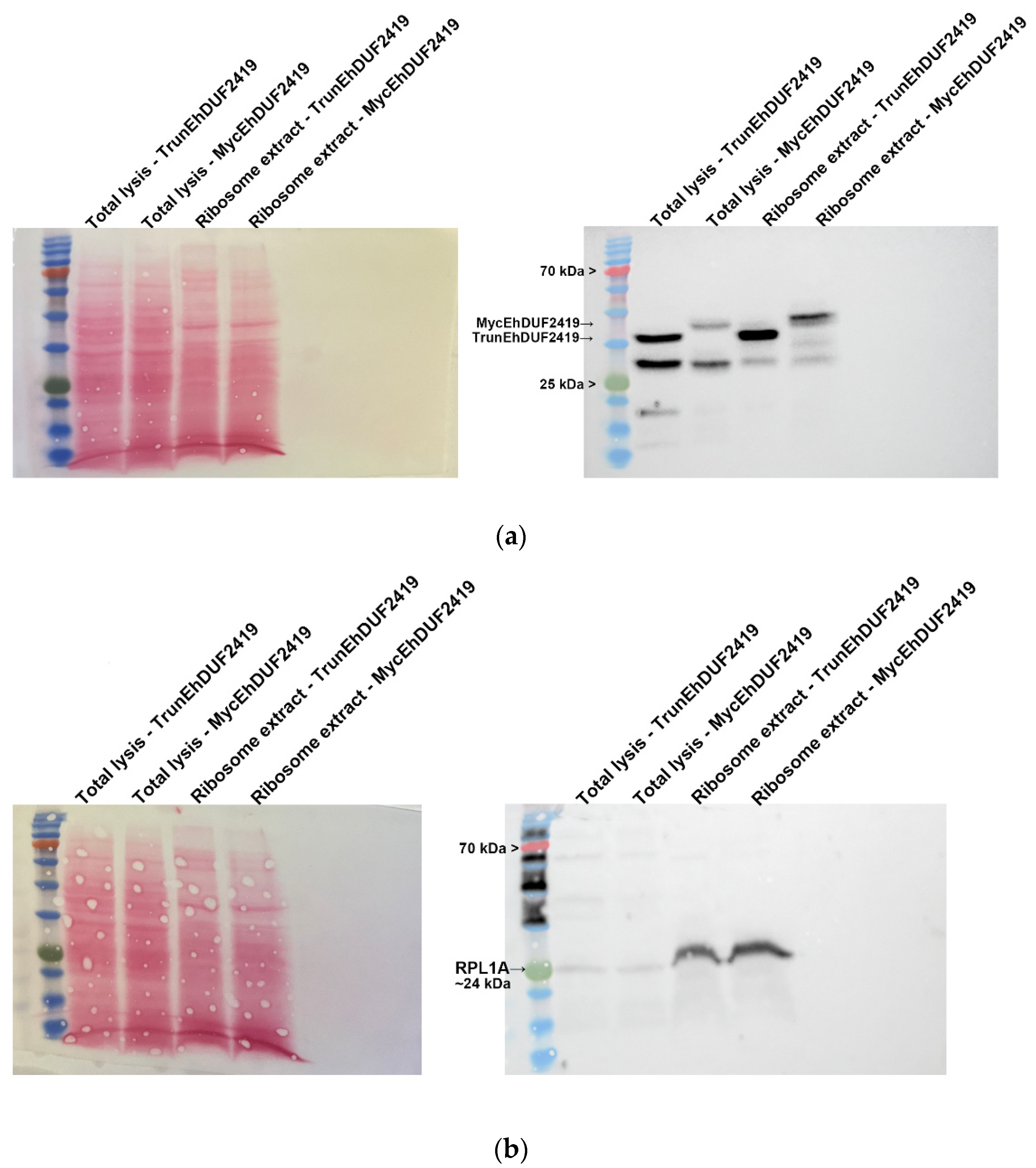
The identification of ribosomal and other translation-related proteins in the anti-c-Myc agarose bead immunoprecipitation (
Figure 2b,c), indicates that EhDUF2419 interacts with ribosomal proteins and may play a role in regulating translation in the parasite. To validate this hypothesis, we purified ribosomes and checked if EhDUF2419 co-purified with them. Our results showed that EhDUF2419 was significant enriched in the ribosome fraction (
Figure 3a). Additionally, we verified that one of the ribosomal proteins, RPL1A (corresponding to the 60S ribosomal protein L10a-2 in
E. histolytica, EHI_012480), identified among the proteins significantly enriched following the pulldown of Myc-EhDUF2419, was also present in the ribosome fraction (
Figure 3b). These results strongly suggest that EhDUF2419 interacts with ribosomal proteins.
3.3. EhDUF2419 Interacts with Ribosomal Protein Independent of Its Catalytic Domain
Given that some proteins, such as Shiga-like Toxin 1 [
32] or protein-arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) [
33], interact with ribosomal proteins through their catalytic sites, we decided to construct a catalytically inactive MycEhDUF2419 plasmid to investigate whether EhDUF2419 interacts with ribosomal proteins in a manner dependent on its catalytic domain. The active site of DUF2419 protein was deduced based on the StDUF2419 protein from
Sphaerobacter thermophilus [
18]. Sequence alignment showed that EhDUF2419 shares 33% identity with StDUF2419, with the active site residues D298 and W302 in StDUF2419 corresponding to D280 and W284 in EhDUF2419. We truncated EhDUF2419 between residue D280 and the stop codon, resulting in the deletion of 26 amino acids, including part of the active pocket. We then constructed a plasmid expressing this truncated version of EhDUF2419 with a Myc-tag and transfected it into
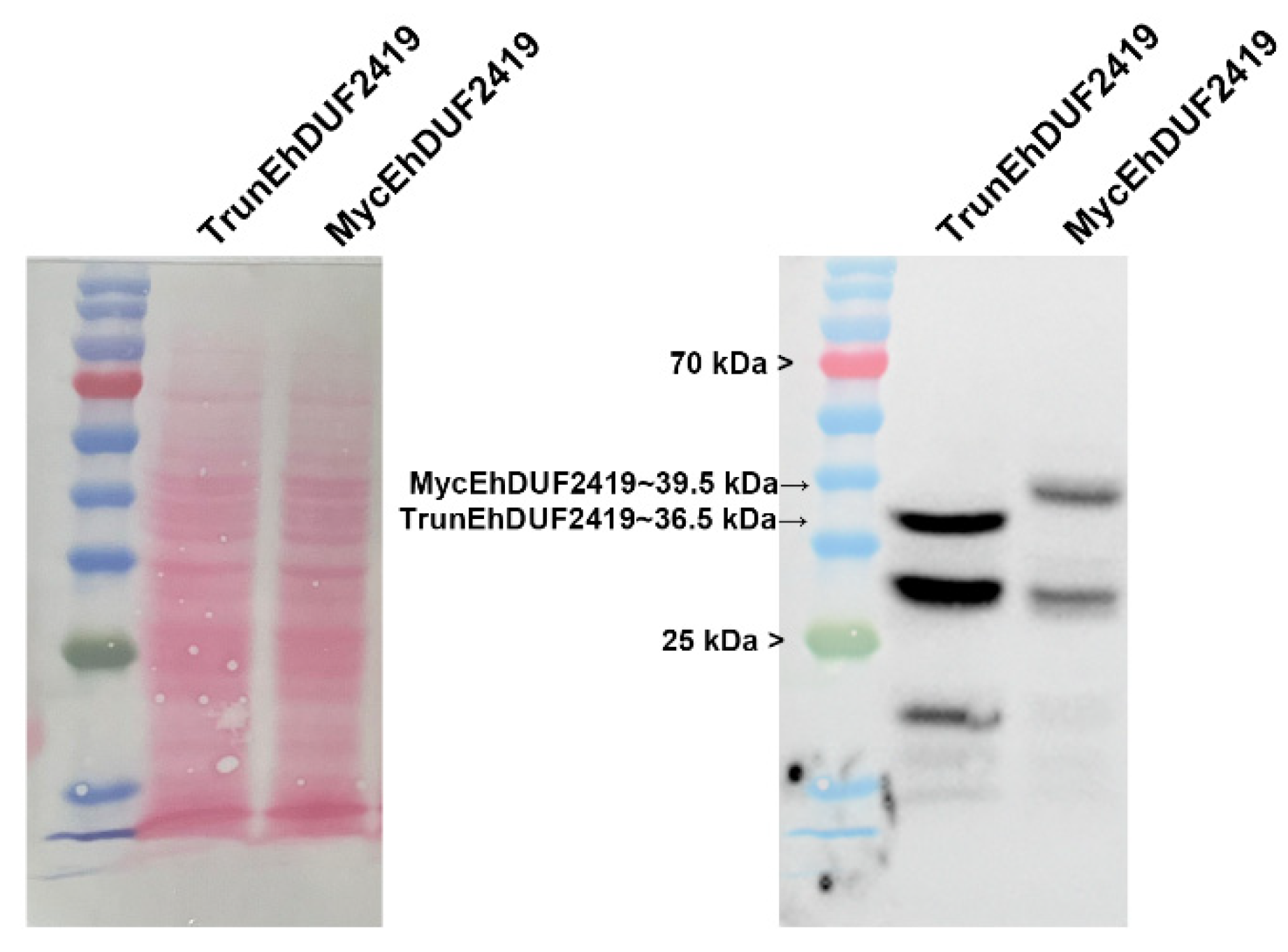
E. histolytica trophozoites. TrunEhDUF2419 transfectants were cultivated in presence of 24 μg/ml G418. Western blot analysis using a Myc antibody revealed a distinct 36.5 kDa band corresponding to the expected size of the TrunEhDUF2419 in TrunEhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites, different from the 39.5 kDa full length MycEhDUF2419 (
Figure 4).
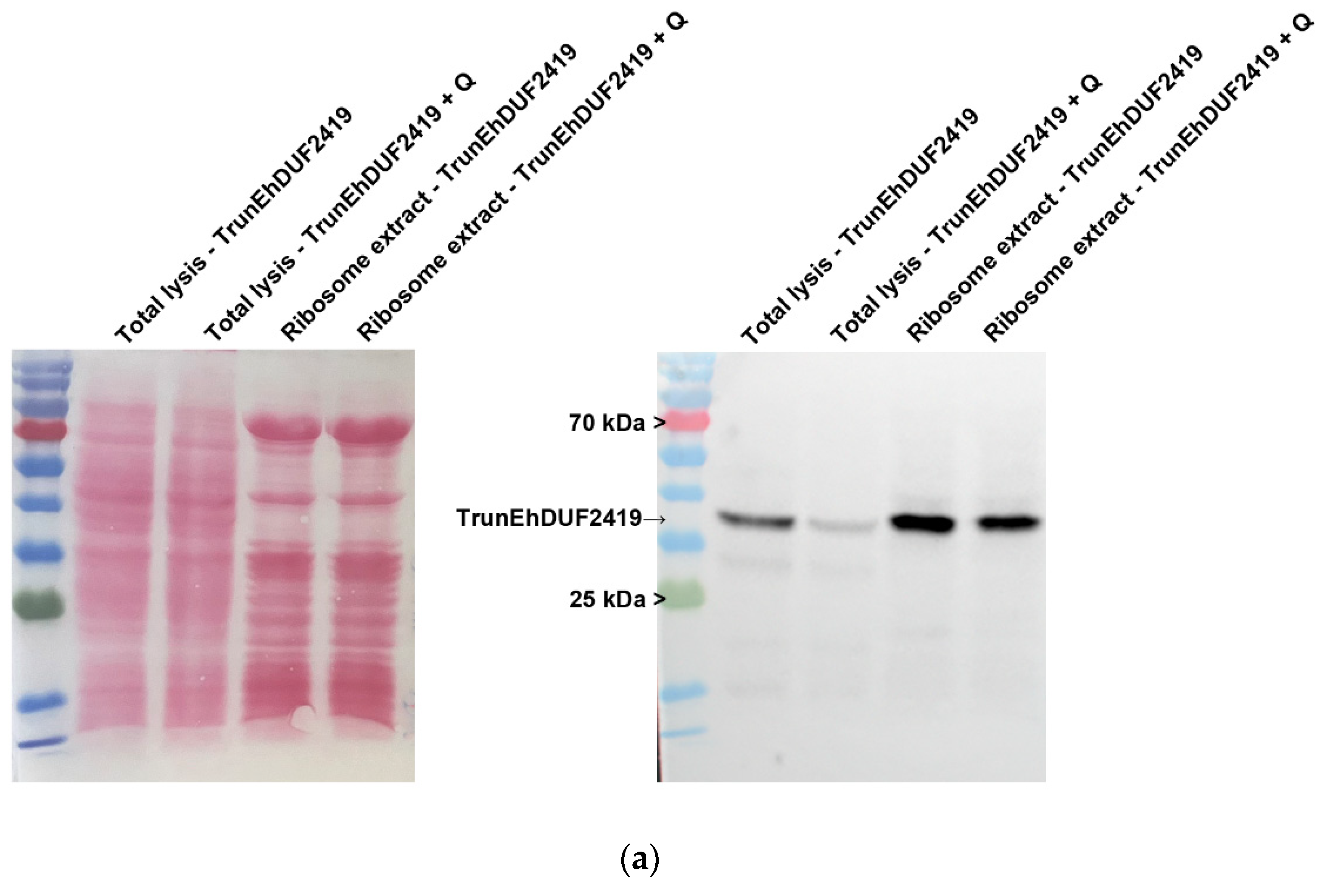
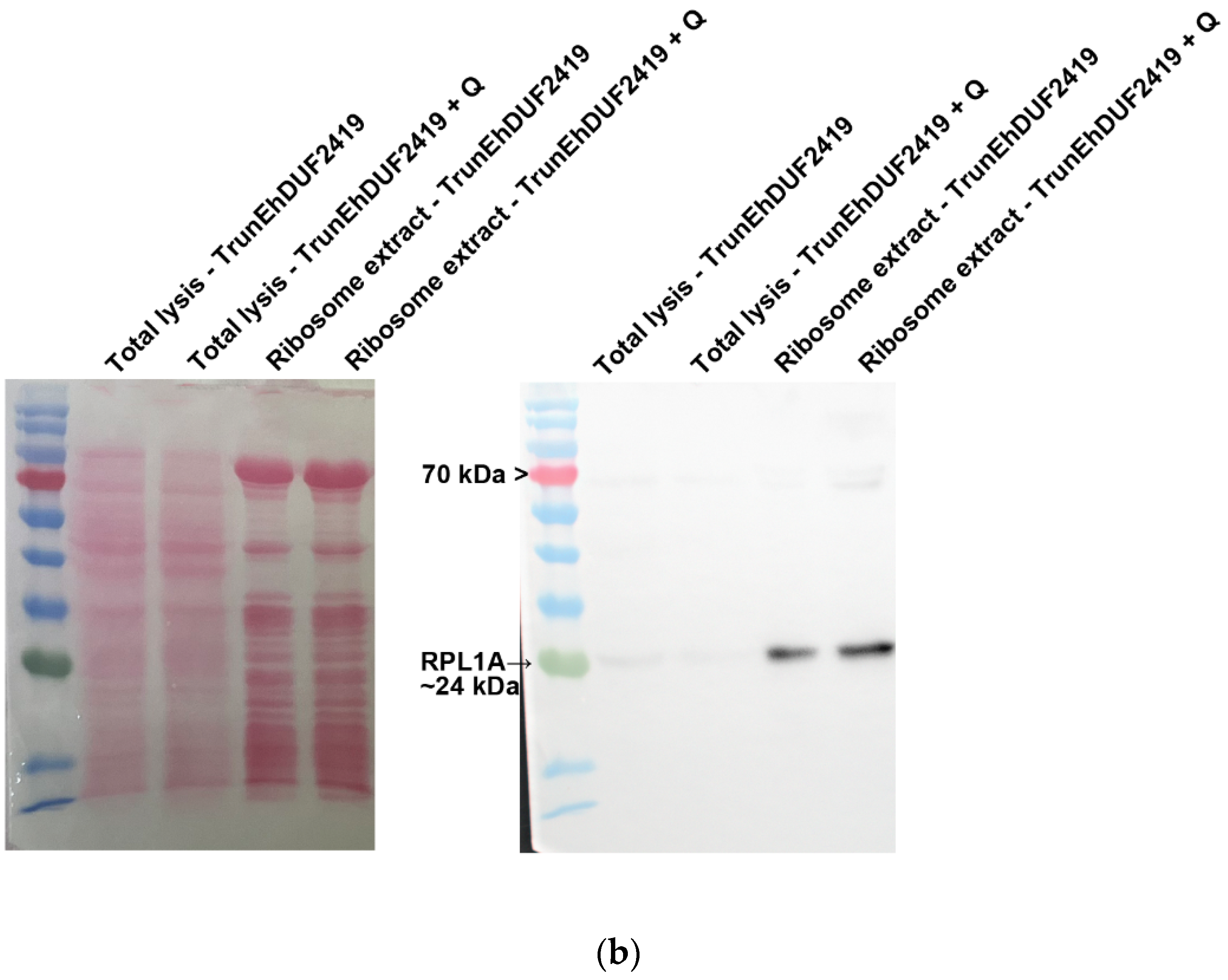
To investigate whether the interaction between EhDUF2419 and ribosomal proteins depends on its active site, we purified ribosomes and examined whether the TrunEhDUF2419 co-purified with them. The co-detection of the TrunEhDUF2419 (
Figure 5a) and the ribosomal protein RPL1A (
Figure 5b) in the ribosome enriched fraction strongly suggests that the EhDUF2419 catalytic domain is not necessary for its interaction with ribosomal proteins.
3.4. EhDUF2419 Overexpression Reduces Q-tRNA Formation in Presence of Q.
EhDUF2419 plays a crucial role in salvaging queuine from Q, which is subsequently incorporated into tRNA by EhTGT to form Q-tRNA [
9,
15]. Since Q is limited in the
E. histolytica culture medium (
Figure 6 and [
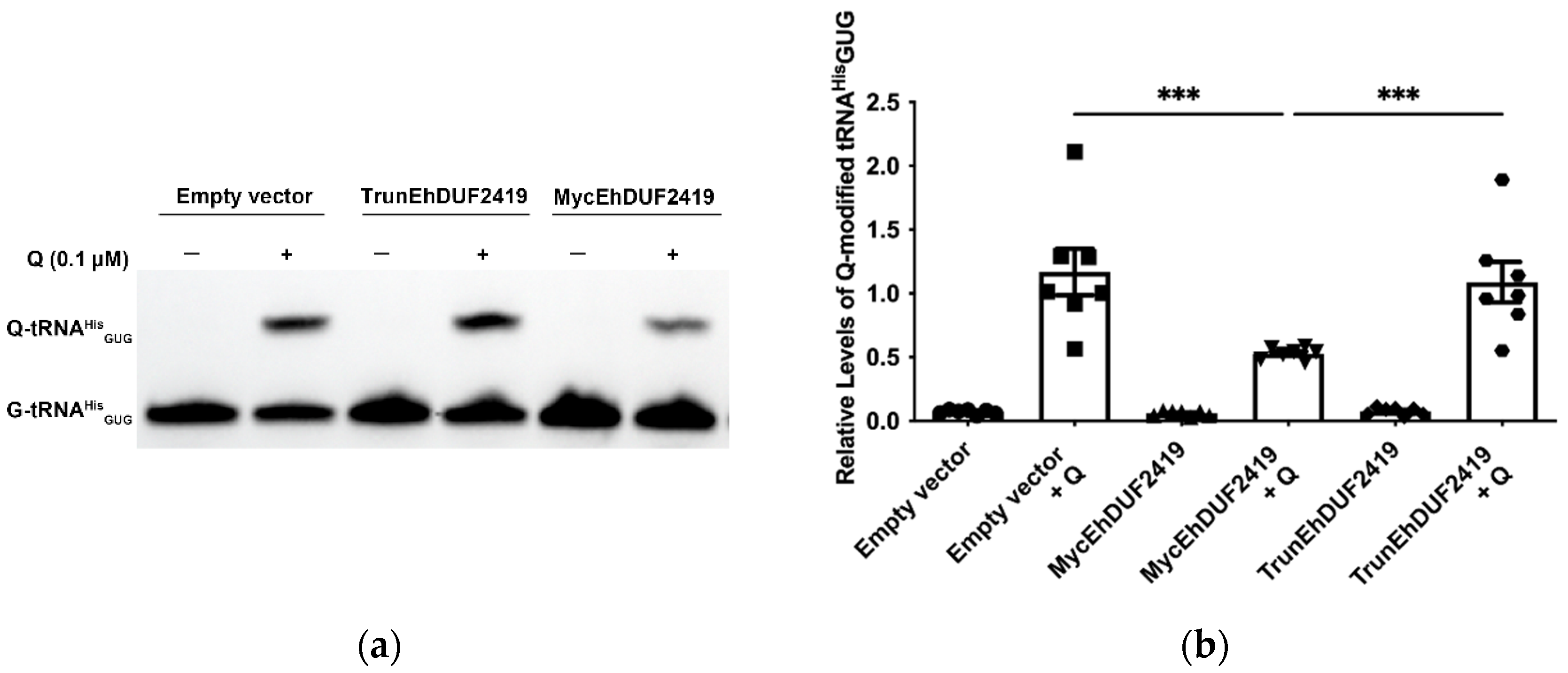
15]), we hypothesized that overexpression of EhDUF2419 without additional Q in the culture media of the parasite would not affect Q-tRNA levels. However, in presence of supplemental Q, we expected that overexpression of EhDUF2419 would increase queuine availability, leading to higher Q-tRNA formation. To assess this, we examined the effect of EhDUF2419 overexpression on Q-tRNA
HisGUG levels using APB polyacrylamide gel analysis in TrunEhDUF2419, MycEhDUF2419 transfectants, as well as in controls with or without additional Q. The APB gel method detects Q-tRNA using Northern blots by exploiting the cis-diol group on the Q-modification, which slows the migration of Q-modified tRNA compared to unmodified tRNA in the presence of APB [
34]. The results showed that prior to the addition of Q to the culture medium, Q-tRNA
HisGUG levels in
E. histolytica trophozoites were nearly undetectable across all experimental conditions. However, upon supplementation with Q, Q-tRNA
HisGUG levels in trophozoites overexpressing MycEhDUF2419 were significantly lower compared to controls and TrunEhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites. However, no significant difference was observed between controls and trophozoites overexpressing TrunEhDUF2419 (
Figure 6).
Since the addition of Q altered the Q-tRNA levels in MycEhDUF2419 transfectants (
Figure 6), we wanted to determine whether the interaction between EhDUF2419 and ribosomal proteins is influenced by Q treatment. We purified ribosomes and assessed the co-purification of Myc-EhDUF2419 and TrunEhDUF2419 with ribosomal proteins under both Q-treated and untreated conditions. The presence of Myc-EhDUF2419 and TrunEhDUF2419 in ribosome-enriched fractions of trophozoites, regardless of Q treatment (
Figure 7a and
Figure 8a), along with the co-detection of ribosomal protein RPL1A (
Figure 7b and
Figure 8b), strongly suggests that the interaction between EhDUF2419 and ribosomal proteins is independent of Q treatment.
EhDUF2419 is involved in the production of Q-tRNA, which subsequently regulates translational speed and fidelity in eukaryotes [
10,
11] and influences translation of stress related proteins in
E. histolytica [
9]. This suggests that EhDUF2419 indirectly influences translation through Q-tRNA modification. However, our results strongly suggest that EhDUF2419 interacts with ribosomal proteins, indicating a more direct role for EhDUF2419 in regulating translation. To investigate this, we employed the SUnSET method [
35] to monitor changes in protein synthesis in control trophozoites, MycEhDUF2419 and TrunEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites, both with or without Q treatment. Our results revealed no significant differences in protein synthesis between the control, Myc-EhDUF2419, and Trun-EhDUF2419 overexpressing strains, regardless of Q treatment (
Figure S1).
3.5. EhDUF2419 Is Regulated by Proteasome-Mediated Degradation Pathways
We initially expected that the addition of Q to the culture medium would result in elevated Q-tRNA
HisGUG levels in trophozoites overexpressing MycEhDUF2419. However, contrary to our expectations, we observed a reduction in Q-tRNA
HisGUG levels following Q supplementation (
Figure 6). This decrease, along with the identification of proteins associated with proteasome-mediated degradation pathways—such as RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase (EHI_020100), E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase listerin (EHI_190430), and ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase family protein (EHI_035180)—among those pulled down by anti-c-Myc agarose bead immunoprecipitation suggests that the proteasome-mediated degradation machinery might regulate the levels of EhDUF2419 in the cell, subsequently affecting Q-tRNA
HisGUG levels. To validate this, we performed Western blot analysis with a Myc antibody on MycEhDUF2419 and TrunEhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites, treated with or without Q or the proteasome inhibitor MG132 [
36]. The results showed that, in the absence of MG132 treatment, there was a significant reduction in MycEhDUF2419 levels following Q treatment, while the reduction in TrunEhDUF2419 levels with Q treatment was not significant (
Figure 9). Following MG132 treatment, MycEhDUF2419 levels significantly increased regardless of Q treatment, indicating that MycEhDUF2419 degradation is mediated by the proteasome (
Figure 9a,b). This result explains that the significant reduction in Q-modified tRNA
HisGUG levels for MycEhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites after Q treatment compared to the control (
Figure 6) is due to the decrease in protein levels regulated by the proteasome. Although TrunEhDUF2419 levels also showed an increasing trend with MG132 treatment (regardless of Q treatment), the change was not significant (
Figure 9c,d).
4. Discussion
It has been recently established that DUF2419 salvages Q in many prokaryotes and eukaryotes [
37], including
E. histolytica, where direct salvage of Q from phagocytosed bacteria by the parasite has been demonstrated [
15]. Structural analysis of
Sphaerobacter thermophilus Qng1 (formerly DUF2419) has provided insights into the interaction of this enzyme with queuosine-5′-monophosphate, its primary substrate [
37]. Despite this progress in understanding DUF2419 biology, our knowledge about the proteins that interact with DUF2419 remains limited. STRING predicts possible interaction between EhDUF2419 and another 9 proteins (
Table S2). While these predictions offer valuable starting points for defining DUF2419 interactome, they require experimental validation to confirm their relevance. In this study, we explore the interactome of EhDUF2419 to uncover additional functions of this protein. We identified 335 proteins that potentially interact directly or indirectly with EhDUF2419, including over 100 ribosomal proteins from both the 40S and 60S subunits, as well as numerous translation initiation factors, elongation factors, and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. The presence of EhDUF2419 in cellular fractions enriched with ribosomal proteins confirms the interactome data and strongly suggests that EhDUF2419 is involved in translation through mechanisms that extend beyond its established role in salvaging Q, which is itself integral to the formation of Q-tRNAs involved in translation [
9,
10]. However, overexpressing EhDUF2419 as a Myc-tagged protein does not affect global protein synthesis, which may seem contradictory to this observation. Interestingly, it is well known that Q-modification of tRNAs regulates specific processes, such as the translation of stress-related proteins or biofilm formation in bacteria, by influencing the translation of NAU codon-enriched genes [
38]. Therefore, specific alterations in protein synthesis may have occurred, but they could not be detected using the SunSet method.
The overexpression of EhDUF2419 in the parasite decreases the level of Q-tRNAHis in the presence of Q—a response not observed when a catalytically truncated version of EhDUF2419 is overexpressed. The mechanism behind this reduction in Q-tRNAHis levels is unclear, but several scenarios are possible. The most likely explanation is that overexpression leads to improperly folded or non-functional enzyme forms acting as dominant negatives, or to the formation of non-functional aggregates that sequester the endogenous enzyme. This sequestration could reduce queuine processing, leading to decreased Q-tRNAHis formation. The validity of this scenario is supported by the observation that the proteasome inhibitor MG132 prevents the degradation of Myc-tagged EhDUF2419 in the presence of Q, suggesting that misfolded or aggregated proteins are targeted for degradation. It is important to emphasize that the interactome analysis of EhDUF2419 was performed in the absence of added Q in the media, which reduces the likelihood that the observed interactions reflect a non-specific response to unfolded proteins.
Among the proteins predicted by STRING to interact with EhDUF2419, only one, the PUA domain-containing protein (EHI_016460), has been identified in the EhDUF2419 interactome. PUA domain-containing proteins are involved in RNA modification and serve as translation factors [
39]. This finding supports the notion that EhDUF2419 may interact with factors related to RNA processing and translation. However, further investigations are necessary to elucidate the precise nature of this interaction and its functional implications within the cellular context.
The possible interaction between EhDUF2419 and EhDNMT2 (Dnmt2) (EHI_103830) in
E. histolytica revealed by the present interactome analysis could have significant implications for translation regulation. DNMT2, known for its role in 5-cytosine methylation (m5C) of tRNA, particularly near the wobble base, is crucial for the precise control of translation efficiency [
40,
41,
42]. This modification, which has been shown to enhance translation efficiency in other organisms [
42], might also affect the processing and function of tRNAs in
E. histolytica. Previous studies indicate that Q modification of tRNA enhances the activity of DNMT2 homologs, such as Pmt1 from
Schizosaccharomyces pombe, DnmA from
Dictyostelium discoideum and EhDnmt2 in
E. histolytica [
9,
11,
43]. The dual modification of tRNAs by Q and m5C not only protects against endonucleolytic cleavage but also influences aminoacylation and codon-anticodon interactions [
44]. Therefore, the interaction between EhDUF2419 and EhDNMT2 might modulate these processes through direct or indirect interaction, potentially impacting the translation of specific proteins and overall cellular function. Further investigation is needed to elucidate the exact mechanisms and consequences of this interaction within the parasite. It is also remarkable that other RNA modification enzymes were identified in the EhDUF2419 interactome, including RNA cytidine acetyltransferase (N-acetyltransferase 10, NAT10, EHI_033750), rRNA adenine N(6)-methyltransferase (EHI_013870), and RNA 3′-terminal phosphate cyclase (EHI_115370). These enzymes are involved in various aspects of RNA modification and processing, which could further elucidate the role of EhDUF2419 in regulating translation and RNA metabolism in
E. histolytica.
Furthermore, the identification of interactions between various helicases and EhDUF2419 suggests a potential role for EhDUF2419 in regulating RNA metabolism. Helicases are essential for unwinding nucleic acids and are involved in multiple aspects of RNA metabolism. DEAD box helicases, in particular, play crucial roles in processes such as nuclear transcription, pre-mRNA splicing, ribosome biogenesis, nucleocytoplasmic transport, translation, RNA decay, and organellar gene expression [
45,
46]. Given that EhDUF2419 is a queuine salvage protein, its interactions with these helicases and other RNA-related proteins suggest an integrated role in modulating RNA metabolism and tRNA function. Queuine modification typically occurs within tRNA molecules, and helicases are known to interact with tRNAs, especially those with endonuclease-mediated ‘nicks’ in their anticodon loops [
47]. Additionally, RNA helicases can operate within acetyltransferase complexes that modify specific tRNA anticodons [
48]. Therefore, the interaction between EhDUF2419 and helicases may influence the structure or folding of tRNA, potentially affecting its functionality and the associated translation processes. These findings suggest that EhDUF2419 may have a role in RNA metabolism beyond its involvement in queuine salvage, warranting further investigation to fully understand the implications of these interactions.
5. Conclusions
This study provides a comprehensive analysis of the interactome of EhDUF2419, highlighting its complex role in translation and RNA metabolism. Our findings reveal that EhDUF2419, a key player in queuine salvage, interacts with a diverse set of proteins involved in various aspects of translation and RNA processing. This includes interactions with ribosomal proteins, translation factors, helicases, and RNA modification enzymes. The evidence suggests that EhDUF2419’s function extends beyond queuine salvage, potentially influencing tRNA function and translation efficiency. The observed impact on Q-tRNAHis levels further underscores its multifaceted role in the parasite’s cellular processes. These insights into the protein-protein interactions of EhDUF2419 pave the way for further research into its broader biological functions and regulatory mechanisms, offering new avenues for understanding its role in E. histolytica.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1: Protein synthesis level of control, MycEhDUF2419 and TrunEhDUF2419 overexpressed trophozoites with or without Q treatment using the SUnSET method. Table S1: List of all proteins interacted with EhDUF2419 that were enriched by IP in three independent experiments. Table S2: STRING analysis of EhDUF2419 interaction. Table S3: Description of the parameters that are given in Table S1.
Author Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual contributions must be provided. The following statements should be used “Conceptualization, JY. and SA.; methodology, JY, MTG, SA..; validation, JY; formal analysis, JY and SA.; investigation, JY and SA.; resources, SA.; data curation, JY and SA.; writing—original draft preparation, JY and SA.; writing—review and editing, MTG, SA.; visualization, JY.; supervision, SA.; project administration, SA.; funding acquisition, SA. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Israel (1020546).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We extend our special thanks to Prof. Reut Shalgi and her team from the Department of Biochemistry, Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel, for their support with ribosome purification experiment. Additionally, we acknowledge the technical support provided by the staff of the Smoler Proteomics Center at the Technion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Haque, R.; Huston, C.D.; Hughes, M.; Houpt, E.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Amebiasis. N Engl J Med 2003, 348, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Maitra, S.C.; Arya, A.; Sagar, P. Action of metronidazole on Entamoeba histolytica: An ultrastructural study. J Commun Dis 1990, 22, 47–54, Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2230021. [Google Scholar]
- Samarawickrema, N.A.; Brown, D.M.; Upcroft, J.A.; Thammapalerd, N.; Upcroft, P. Involvement of superoxide dismutase and pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase in mechanisms of metronidazole resistance in Entamoeba histolytica. J Antimicrob Chemother 1997, 40, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, D.; Sehgal, R.; Chawla, Y.; Mahajan, R.C.; Malla, N. In vitro activity of antiamoebic drugs against clinical isolates of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 2004, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katze, J.R.; Basile, B.; McCloskey, J.A. Queuine, a modified base incorporated posttranscriptionally into eukaryotic transfer RNA: Wide distribution in nature. Science 1982, 216, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, G.; Kersten, H.; Nishimura, S. Dictyostelium discoideum: A useful model system to evaluate the function of queuine and of the Q-family of tRNAs. FEBS Lett 1982, 146, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, W.R. Effect of diet on the queuosine family of tRNAs of germ-free mice. J Biol Chem 1980, 255, 6832–6835, Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6771278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergus, C.; Barnes, D.; Alqasem, M.A.; Kelly, V.P. The queuine micronutrient: Charting a course from microbe to man. Nutrients 2015, 7, 2897–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, S.; et al. . Queuine Is a Nutritional Regulator of Entamoeba histolytica Response to Oxidative Stress and a Virulence Attenuator. mBio 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.; et al. . Queuine links translational control in eukaryotes to a micronutrient from bacteria. Nucleic acids research 2019, 47, 3711–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuorto, F.; et al. . Queuosine-modified tRNAs confer nutritional control of protein translation. The EMBO journal 2018, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zallot, R.; Yuan, Y.; de Crecy-Lagard, V. The Escherichia coli COG1738 Member YhhQ Is Involved in 7-Cyanodeazaguanine (preQ(0)) Transport. Biomolecules 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; et al. . Discovery of novel bacterial queuine salvage enzymes and pathways in human pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116, 19126–19135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaiyum, S.; Yuan, Y.; Kuipers, P.J.; Martinelli, M.; Jaroch, M.; de Crecy-Lagard, V. Deciphering the Diversity in Bacterial Transporters That Salvage Queuosine Precursors. Epigenomes 2024, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarid, L.; et al. . Queuine Salvaging in the Human Parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, L.S.; Harlow, D.R.; Cunnick, C.C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1978, 72, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Veira, J.; Bauer, S.T.; Yip, C.; Singh, U. RISC in Entamoeba histolytica: Identification of a Protein-Protein Interaction Network for the RNA Interference Pathway in a Deep-Branching Eukaryote. mBio 2021, 12, e0154021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zallot, R.; et al. . Plant, animal, and fungal micronutrient queuosine is salvaged by members of the DUF2419 protein family. ACS chemical biology 2014, 9, 1812–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera, A.; et al. . Stable transfection of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites by lipofection. Arch Med Res 1997, 28, 49–51, Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9033009. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.R.; Collins, K. Physical and functional coupling of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and Dicer in the biogenesis of endogenous siRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2007, 14, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarid, L.; Zanditenas, E.; Ye, J.; Trebicz-Geffen, M.; Ankri, S. Insights into the Mechanisms of Lactobacillus acidophilus Activity against Entamoeba histolytica by Using Thiol Redox Proteomics. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat Biotechnol 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; et al. . PANTHER version 16: A revised family classification, tree-based classification tool, enhancer regions and extensive API. Nucleic acids research 2021, 49, D394–D403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalgi, R.; Hurt, J.A.; Krykbaeva, I.; Taipale, M.; Lindquist, S.; Burge, C.B. Widespread regulation of translation by elongation pausing in heat shock. Mol Cell 2013, 49, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Rios, R.; Arias-Romero, L.E.; Mde, J.A.-B.; Hernandez-Rivas, R.; Guillen, N.; Vargas, M. L10 ribosomal protein from Entamoeba histolytica share structural and functional homologies with QM/Jif-1: Proteins with extraribosomal functions. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2003, 127, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, R.; et al. . The Entamoeba histolytica Dnmt2 homolog (Ehmeth) confers resistance to nitrosative stress. Eukaryot Cell 2014, 13, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebicz-Geffen, M.; et al. . Identification of S-Nitrosylated (SNO) Proteins in Entamoeba histolytica Adapted to Nitrosative Stress: Insights into the Role of SNO Actin and In vitro Virulence. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2017, 7, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; et al. . Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igloi, G.L.; Kossel, H. Affinity electrophoresis for monitoring terminal phosphorylation and the presence of queuosine in RNA. Application of polyacrylamide containing a covalently bound boronic acid. Nucleic Acids Res 1985, 13, 6881–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, L.; Nickel, R.; Tannich, E. Transfection and continuous expression of heterologous genes in the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. (in eng), Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1995, 92, 8975–8979, Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7568055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCluskey, A.J.; et al. . The catalytic subunit of shiga-like toxin 1 interacts with ribosomal stalk proteins and is inhibited by their conserved C-terminal domain. J Mol Biol 2008, 378, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, S.; Xu, Z. Methylation of ribosomal protein S10 by protein-arginine methyltransferase 5 regulates ribosome biogenesis. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 12695–12705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirzi, C.; Tuorto, F. Analysis of Queuosine tRNA Modification Using APB Northern Blot Assay. Methods Mol Biol 2021, 2298, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.K.; Clavarino, G.; Ceppi, M.; Pierre, P. SUnSET, a nonradioactive method to monitor protein synthesis. (in eng), Nature methods 2009, 6, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makioka, A.; Kumagai, M.; Ohtomo, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Takeuchi, T. Effect of proteasome inhibitors on the growth, encystation, and excystation of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba invadens. Parasitol Res 2002, 88, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.H.; et al. . Structural basis of Qng1-mediated salvage of the micronutrient queuine from queuosine-5′-monophosphate as the biological substrate. Nucleic acids research 2023, 51, 935–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Rullo, J.; Gonzalez-Pastor, J.E. tRNA queuosine modification is involved in biofilm formation and virulence in bacteria. Nucleic acids research 2023, 51, 9821–9837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Arellano, I.; Gallego, J.; Cervera, J. The PUA domain - a structural and functional overview. The FEBS journal 2007, 274, 4972–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Yacoubi, B.; Bailly, M.; de Crecy-Lagard, V. Biosynthesis and function of posttranscriptional modifications of transfer RNAs. Annu Rev Genet 2012, 46, 69–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agris, P.F.; Vendeix, F.A.; Graham, W.D. tRNA’s wobble decoding of the genome: 40 years of modification. J Mol Biol 2007, 366, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeltsch, A.; et al. . Mechanism and biological role of Dnmt2 in Nucleic Acid Methylation. RNA Biol 2017, 14, 1108–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, M.; et al. . Dynamic modulation of Dnmt2-dependent tRNA methylation by the micronutrient queuine. Nucleic Acids Res 2015, 43, 10952–10962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrenhofer-Murray, A.E. Cross-Talk between Dnmt2-Dependent tRNA Methylation and Queuosine Modification. Biomolecules 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller-Pace, F.V. DExD/H box RNA helicases: Multifunctional proteins with important roles in transcriptional regulation. Nucleic Acids Res 2006, 34, 4206–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, P.; et al. . Comparative structural analysis of human DEAD-box RNA helicases. PLoS ONE 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drino, A.; et al. . Identification of RNA helicases with unwinding activity on angiogenin-processed tRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, 1326–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimnaronk, S.; et al. . RNA helicase module in an acetyltransferase that modifies a specific tRNA anticodon. EMBO J 2009, 28, 1362–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Overexpression of MycEhDUF2419 in E. histolytica trophozoites. (a) Quantification of EhDUF2419 mRNA expression levels in empty vector and MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (MycEhDUF2419 12 μg/ml, MycEhDUF2419 24 μg/ml) was performed by qPCR. The relative fold change was calculated using the 2ˆ(−∆∆Ct) method. The data represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments, each with one to two technical replicates. Statistical significance is denoted by asterisks (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). (b) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Western blotting was performed on total protein extracts prepared from empty vector and MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (MycEhDUF2419 12 μg/ml, MycEhDUF2419 24 μg/ml). The proteins were separated on 12% SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by Western blotting using a Myc antibody (1:1,000). The trophozoites were grown with 12 μg/ml or with 24 μg/ml G418. The experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results.
Figure 1.
Overexpression of MycEhDUF2419 in E. histolytica trophozoites. (a) Quantification of EhDUF2419 mRNA expression levels in empty vector and MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (MycEhDUF2419 12 μg/ml, MycEhDUF2419 24 μg/ml) was performed by qPCR. The relative fold change was calculated using the 2ˆ(−∆∆Ct) method. The data represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments, each with one to two technical replicates. Statistical significance is denoted by asterisks (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). (b) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Western blotting was performed on total protein extracts prepared from empty vector and MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (MycEhDUF2419 12 μg/ml, MycEhDUF2419 24 μg/ml). The proteins were separated on 12% SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by Western blotting using a Myc antibody (1:1,000). The trophozoites were grown with 12 μg/ml or with 24 μg/ml G418. The experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results.
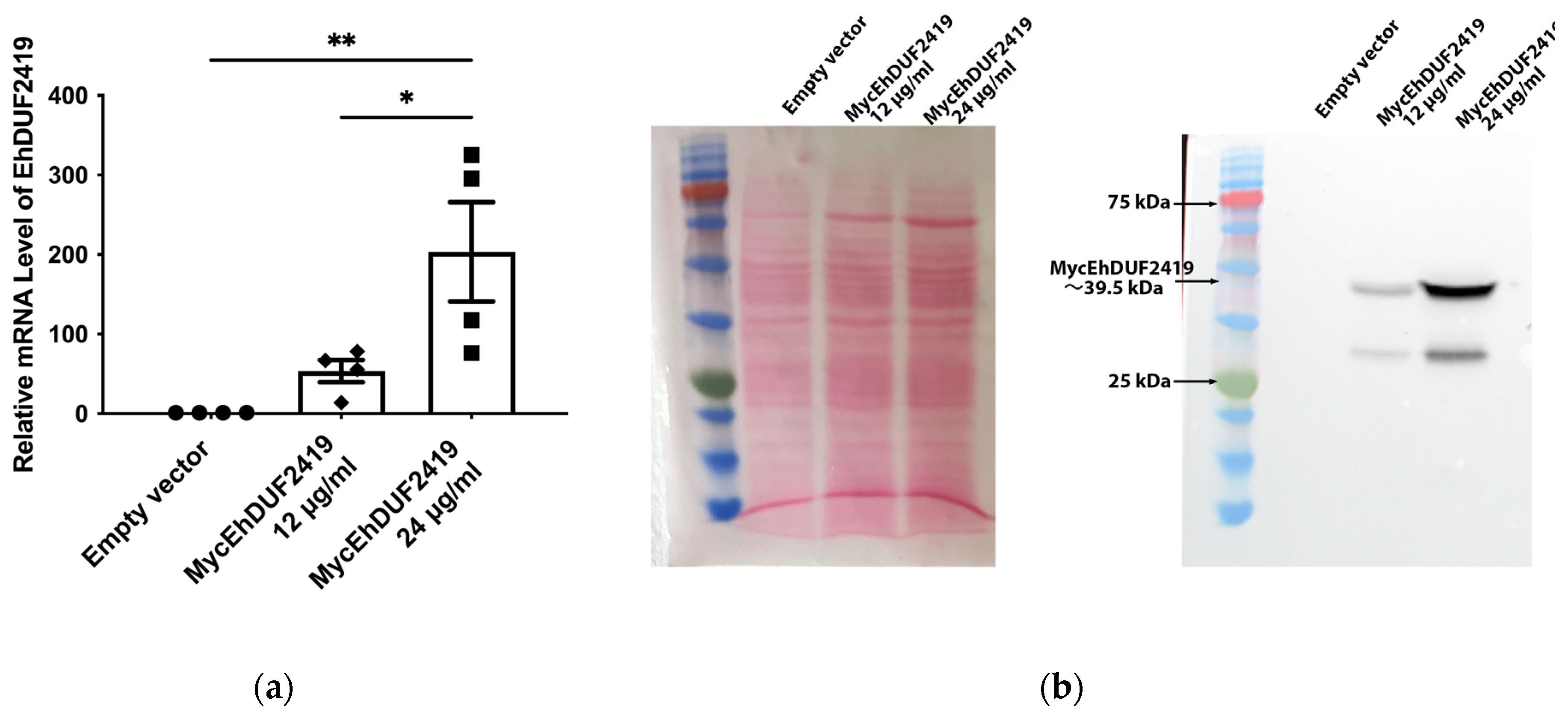
Figure 2.
Pulldown of EhDUF2419 by anti-Myc IP and proteomics analysis. (
a) Silver staining (left) and western blotting (right) were used to assess anti-Myc IP samples prior to mass spectrometry analyses. The anti-Myc Western blot shows a Myc signal in the IP elution lanes for MycEhDUF2419 24 μg/ml trophozoites but not in the empty vector trophozoites, indicating specific pulldown of Myc-tagged protein. The arrow indicates the detected protein band for EhDUF2419 in the IP elution samples. (
b) Triplicate IP samples were subjected to in-gel trypsin digestion for LC-MS/MS-based proteomics analysis. The PANTHER classification (
http://pantherdb.org) of the 335 proteins identified in pulldown of MycEhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites compared to the empty vector trophozoites is shown. (
c) PANTHER fold enrichment analysis was performed on the 335 proteins identified in MycEhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites compared to empty vector trophozoites.
Figure 2.
Pulldown of EhDUF2419 by anti-Myc IP and proteomics analysis. (
a) Silver staining (left) and western blotting (right) were used to assess anti-Myc IP samples prior to mass spectrometry analyses. The anti-Myc Western blot shows a Myc signal in the IP elution lanes for MycEhDUF2419 24 μg/ml trophozoites but not in the empty vector trophozoites, indicating specific pulldown of Myc-tagged protein. The arrow indicates the detected protein band for EhDUF2419 in the IP elution samples. (
b) Triplicate IP samples were subjected to in-gel trypsin digestion for LC-MS/MS-based proteomics analysis. The PANTHER classification (
http://pantherdb.org) of the 335 proteins identified in pulldown of MycEhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites compared to the empty vector trophozoites is shown. (
c) PANTHER fold enrichment analysis was performed on the 335 proteins identified in MycEhDUF2419 overexpressing trophozoites compared to empty vector trophozoites.
Figure 3.
Co-purification of MycEhDUF2419 with ribosomal proteins. (a, b) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Total lysates prepared from control E. histolytica trophozoites (empty vector, 24 μg/ml) and MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) were subjected to ultracentrifugation through a sucrose cushion to pellet the ribosomes. The resulting pellets were resuspended, boiled, and loaded onto a 12% SDS-PAGE gel for immunoblotting with a Myc antibody (a) or RPL1A antibody (b). The experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results.
Figure 3.
Co-purification of MycEhDUF2419 with ribosomal proteins. (a, b) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Total lysates prepared from control E. histolytica trophozoites (empty vector, 24 μg/ml) and MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) were subjected to ultracentrifugation through a sucrose cushion to pellet the ribosomes. The resulting pellets were resuspended, boiled, and loaded onto a 12% SDS-PAGE gel for immunoblotting with a Myc antibody (a) or RPL1A antibody (b). The experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results.
Figure 4.
Overexpression and the catalytic function of full-length and truncated EhDUF2419 in E. histolytica trophozoites. Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Western blotting was performed on total protein extracts prepared from truncated EhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (TrunEhDUF2419, 24 μg/ml) and MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml). The proteins were separated on 12% SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by Western blotting using a Myc antibody (1:1,000).
Figure 4.
Overexpression and the catalytic function of full-length and truncated EhDUF2419 in E. histolytica trophozoites. Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Western blotting was performed on total protein extracts prepared from truncated EhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (TrunEhDUF2419, 24 μg/ml) and MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml). The proteins were separated on 12% SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by Western blotting using a Myc antibody (1:1,000).
Figure 5.
Co-purification of TrunEhDUF2419 with ribosomal proteins. (a, b) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Total lysates prepared from TrunEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) and MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) were subjected to ultracentrifugation through a sucrose cushion to pellet the ribosomes. The resulting pellets were resuspended, boiled, and loaded onto a 12% SDS-PAGE gel for immunoblotting with a Myc antibody (a) or RPL1A antibody (b). The experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results.
Figure 5.
Co-purification of TrunEhDUF2419 with ribosomal proteins. (a, b) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Total lysates prepared from TrunEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) and MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) were subjected to ultracentrifugation through a sucrose cushion to pellet the ribosomes. The resulting pellets were resuspended, boiled, and loaded onto a 12% SDS-PAGE gel for immunoblotting with a Myc antibody (a) or RPL1A antibody (b). The experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results.
Figure 6.
Overexpression and the catalytic function of full-length and truncated EhDUF2419 in E. histolytica trophozoites. (a) APB Northern blot analysis of tRNAHisGUG in control, MycEhDUF2419 and TrunEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites following cultivation with Q. Trophozoites were cultivated in the presence of 0.1 μM Q for 2 days. (b) Quantitative of relative levels of Q-modified tRNAHisGUG. The data represent means ± SEM of four independent experiments, each with one to two technical replicates. Statistical significance is denoted by asterisks (***p < 0.001).
Figure 6.
Overexpression and the catalytic function of full-length and truncated EhDUF2419 in E. histolytica trophozoites. (a) APB Northern blot analysis of tRNAHisGUG in control, MycEhDUF2419 and TrunEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites following cultivation with Q. Trophozoites were cultivated in the presence of 0.1 μM Q for 2 days. (b) Quantitative of relative levels of Q-modified tRNAHisGUG. The data represent means ± SEM of four independent experiments, each with one to two technical replicates. Statistical significance is denoted by asterisks (***p < 0.001).
Figure 7.
Co-purification of MycEhDUF2419 with ribosomal proteins, with or without Q treatment. (a, b) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Total lysates were prepared from MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) treated with or without Q. The lysates were subjected to ultracentrifugation through a sucrose cushion to pellet the ribosomes. The resulting pellets were resuspended, boiled, and loaded onto a 12% SDS-PAGE gel for immunoblotting with either a Myc antibody (a) or an RPL1A antibody (b). The experiment was repeated independently twice with similar results.Figure 8. Co-purification of TrunEhDUF2419 with ribosomal proteins, with or without Q treatment. (a, b) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Total lysates were prepared from TrunEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) treated with or without Q. The lysates were subjected to ultracentrifugation through a sucrose cushion to pellet the ribosomes. The resulting pellets were resuspended, boiled, and loaded onto a 12% SDS-PAGE gel for immunoblotting with either a Myc antibody (a) or an RPL1A antibody (b). The experiment was repeated independently twice with similar results.
Figure 7.
Co-purification of MycEhDUF2419 with ribosomal proteins, with or without Q treatment. (a, b) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Total lysates were prepared from MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) treated with or without Q. The lysates were subjected to ultracentrifugation through a sucrose cushion to pellet the ribosomes. The resulting pellets were resuspended, boiled, and loaded onto a 12% SDS-PAGE gel for immunoblotting with either a Myc antibody (a) or an RPL1A antibody (b). The experiment was repeated independently twice with similar results.Figure 8. Co-purification of TrunEhDUF2419 with ribosomal proteins, with or without Q treatment. (a, b) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Total lysates were prepared from TrunEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) treated with or without Q. The lysates were subjected to ultracentrifugation through a sucrose cushion to pellet the ribosomes. The resulting pellets were resuspended, boiled, and loaded onto a 12% SDS-PAGE gel for immunoblotting with either a Myc antibody (a) or an RPL1A antibody (b). The experiment was repeated independently twice with similar results.
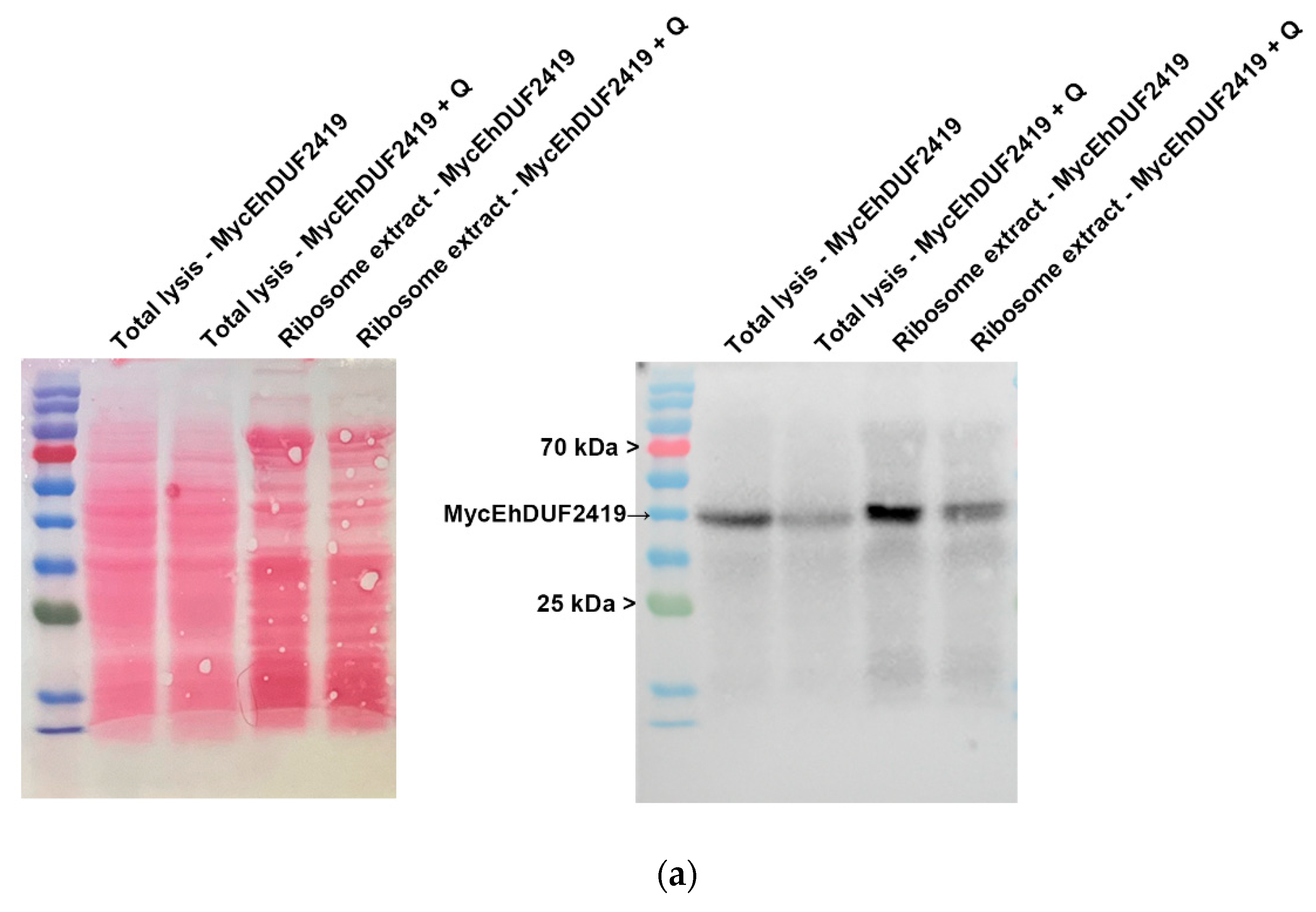
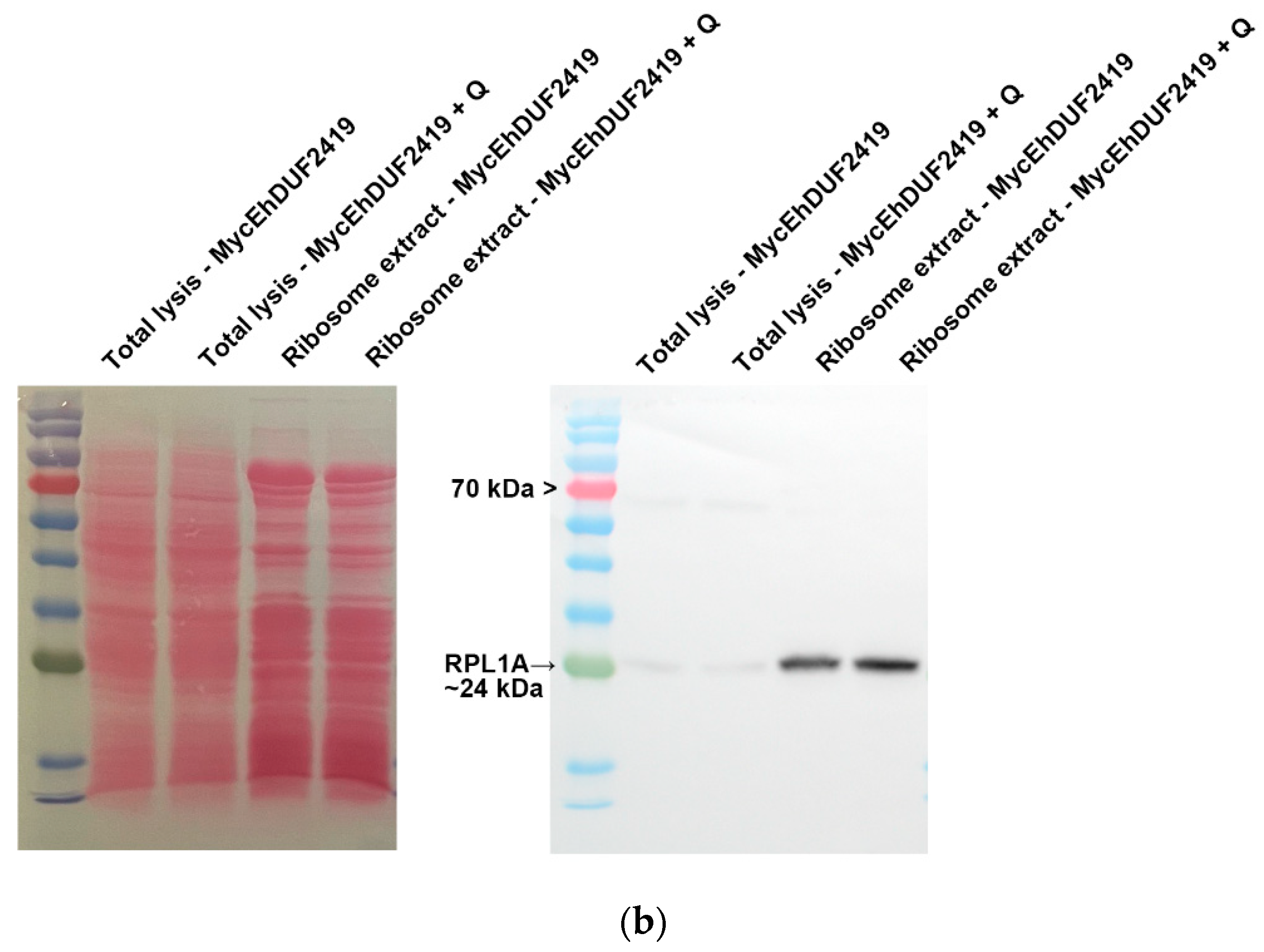
Figure 8.
Co-purification of TrunEhDUF2419 with ribosomal proteins, with or without Q treatment. (a, b) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Total lysates were prepared from TrunEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) treated with or without Q. The lysates were subjected to ultracentrifugation through a sucrose cushion to pellet the ribosomes. The resulting pellets were resuspended, boiled, and loaded onto a 12% SDS-PAGE gel for immunoblotting with either a Myc antibody (a) or an RPL1A antibody (b). The experiment was repeated independently twice with similar results.
Figure 8.
Co-purification of TrunEhDUF2419 with ribosomal proteins, with or without Q treatment. (a, b) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Total lysates were prepared from TrunEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) treated with or without Q. The lysates were subjected to ultracentrifugation through a sucrose cushion to pellet the ribosomes. The resulting pellets were resuspended, boiled, and loaded onto a 12% SDS-PAGE gel for immunoblotting with either a Myc antibody (a) or an RPL1A antibody (b). The experiment was repeated independently twice with similar results.
Figure 9.
Regulation of MycEhDUF2419 levels by proteasome-mediated degradation. (a) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Western blotting was performed on total protein extracts prepared from MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) treated with or without Q or MG132. The proteins were separated on 12% SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by Western blotting using a Myc antibody (1:1,000). (b) Quantification of relative levels of MycEhDUF2419 levels. The data represent means ± SEM of two independent experiments, each with two technical replicates. Statistical significance is denoted by asterisks (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). (c) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Western blotting was performed on total protein extracts prepared from TrunEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) treated with or without Q or MG132. The proteins were separated on 12% SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by Western blotting using a Myc antibody (1:1,000). (d) Quantification of relative levels of TrunEhDUF2419 levels. The data represent means ± SEM of two independent experiments, each with two technical replicates.
Figure 9.
Regulation of MycEhDUF2419 levels by proteasome-mediated degradation. (a) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Western blotting was performed on total protein extracts prepared from MycEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) treated with or without Q or MG132. The proteins were separated on 12% SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by Western blotting using a Myc antibody (1:1,000). (b) Quantification of relative levels of MycEhDUF2419 levels. The data represent means ± SEM of two independent experiments, each with two technical replicates. Statistical significance is denoted by asterisks (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). (c) Left: ponceau S stain showing total protein labeling. Right: Western blotting was performed on total protein extracts prepared from TrunEhDUF2419 overexpression trophozoites (24 μg/ml) treated with or without Q or MG132. The proteins were separated on 12% SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by Western blotting using a Myc antibody (1:1,000). (d) Quantification of relative levels of TrunEhDUF2419 levels. The data represent means ± SEM of two independent experiments, each with two technical replicates.
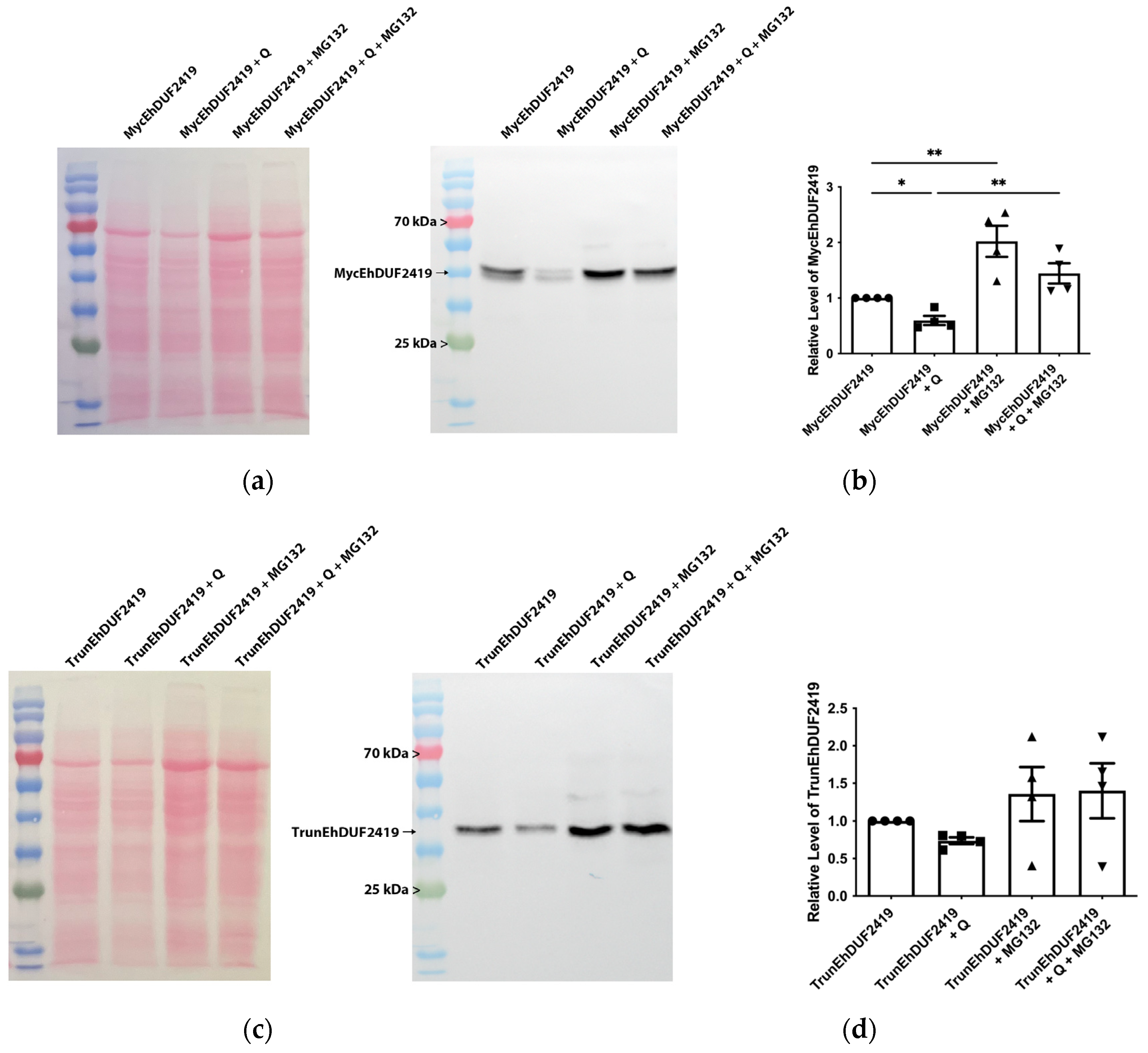
Table 1.
A list of primers used for construction of plasmids or qPCR.
Table 1.
A list of primers used for construction of plasmids or qPCR.
| Protein |
Forward Primer (5′ to 3′) |
Reverse Primer (5′ to 3′) |
Enzyme Site |
Notes |
| EhDUF2419 |
CCCCCGGGATGTGTGAATATGTTCG |
CCCTCGAGTCAATAAAAAATGGTTTGTGTTCG |
SmaI, XhoI |
|
| TrunEhDUF2419 |
CCCCCGGGATGTGTGAATATGTTCG |
CCCTCGAGTCAGCGATATCCTTCAATAAAT |
SmaI, XhoI |
|
| EhDUF2419 |
TCCATCTGGGTCTGAAGAAG |
GTTTGTGTTCGGTGGTGTGG |
|
qPCR |
| rDNA |
TCAAAAAGCAACGTCGCTA |
AGCCCGTAAGGTGATTTCT |
|
qPCR |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).