1. Introduction
Arboviruses, transmitted primarily by arthropods such as mosquitoes and ticks, represent a global public health concern, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions [1,2]. These viruses, including notable members like Dengue, Zika, and Chikungunya, have shown an alarming capacity for rapid spread and adaptation to new environments and hosts [3-5]. The resurgence of arbovirus outbreaks, coupled with the emergence of novel strains, poses a substantial challenge for public health systems, necessitating the development of effective therapeutic strategies and vaccines [6-8]. Recent advancements in pharmaceutical research have focused on identifying antiviral compounds, developing vaccine candidates, and exploring innovative delivery systems to enhance efficacy and stability [9-11]. Given the complexity of arbovirus transmission dynamics and the potential for co-infections, integrated approaches that combine vector control with pharmacological interventions are essential for mitigating the impact of these viruses on global health [12-15]. Among the most significant vectors is Aedes aegypti, the mosquito responsible for spreading these arboviruses across tropical and urbanized regions [16-17]. The species adaptability to human environments, daytime biting habits, and resistance to traditional insecticides, complicate control efforts. While traditional chemical insecticides have been widely used, their effectiveness is declining due to the growing resistance in mosquito populations [18-21]. This challenge has prompted a shift toward more sustainable and eco-friendly approaches, with an increasing focus on natural products as alternatives. Plant-based compounds, essential oils, and botanical extracts are being extensively researched for their potential to act as larvicides, repellents, and adulticides against Aedes aegypti [22-26]. For example, essential oils from plants like Cymbopogon citratus (D.C.) Stapf (lemongrass), Azadirachta indica A. Juss. (neem), and Eucalyptus globulus Labill. have shown promising results in disrupting the mosquito’s life cycle and reducing its ability to transmit diseases [27-34]. These natural products are not only environmentally benign but also less likely to contribute to resistance, making them an appealing strategy in integrated vector management. The continued exploration of these natural compounds, coupled with advancements in formulation and delivery methods, offers a promising avenue for sustainable mosquito control that could significantly reduce the incidence of arbovirus-related diseases. The integration of nanoformulations in mosquito control strategies presents a transformative approach to combating Aedes aegypti [35, 36]. Nanoformulations offer enhanced stability, targeted delivery, and controlled release of active agents, thereby increasing efficacy while minimizing environmental impact [37]. By encapsulating natural products within nanocarriers, these formulations can achieve prolonged activity and reduce the frequency of application. Moreover, the precision targeting of Aedes aegypti populations with these nano-based systems has the potential to disrupt the transmission cycle of arboviruses, leading to a substantial reduction in disease prevalence. This innovative approach underscores the synergy between nanotechnology and vector control, offering a promising avenue for the development of next-generation solutions in the fight against vector-borne diseases [38,39]. Nanogels and nanoemulsions have emerged as a versatile platform for the delivery of bioactive compounds in vector control. Their three-dimensional polymeric network allows for high loading capacity and controlled release of active ingredients, making them particularly suitable for sustained mosquito control interventions. When formulated with essential oils or other natural products, nanogels can provide a protective matrix that enhances the stability and bioavailability of these agents, while reducing their volatility and degradation. This ensures prolonged efficacy against Aedes aegypti and can help in overcoming challenges related to the rapid degradation of traditional insecticides. Moreover, the biocompatibility and tunable properties of nanogels and nanoemulsions allow for the design of targeted delivery systems that can minimize non-target effects and environmental impact [40-43]. Aiming to broaden the existing research on the use of nanoformulations containing natural products as an efficient alternative for combating arbovirus vectors, we present, for the first time, the development of a thermoresponsive nanogel using a low-energy and solvent-free method. This nanogel predominantly contains the copolymer F127, a material already approved by the FDA for various pharmacological uses, along with a smaller amount of the polymer 974p and a high concentration of EOPb. The Pectis genus, known for its high content in monoterpenes, holds significant potential as a source of natural larvicides. Monoterpenes such as neral, geranial, -pinene, and limonene, present in OEPb, exhibit strong larvicidal activity against mosquito species like Aedes aegypti [44-46]. These compounds disrupt essential physiological processes in larvae, leading to high mortality rates [47]. Leveraging the monoterpene-rich Pectis genus as a natural larvicide presents an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic chemicals, enhancing integrated vector management strategies to control disease-transmitting mosquitoes. However, the nanogel nGF2002Pb, presented here for the first time and loaded with a high concentration of EOPb, stands out as an efficient and eco-friendly alternative with proven larvicidal activity against Aedes aegypti, offering an innovative and sustainable approach to arbovirus vector control.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Pluronic F127 (poly (ethylene oxide)–poly (propylene oxide)–poly (ethylene oxide)) triblock copolymer (MW = 12600 g/mol; (EO99(PO)67(EO)99)), ultrapure water, anhydrous sodium sulfates, deuterated chloroform (CDCl3), and alkane standard mixture were commercially acquired from the Merck company (Rahway, NJ, USA). Carbopol® 974p NF polymer was kindly provided by IMCD Brasil (São Paulo, SP, Brazil). Aedes aegypti eggs were supplied by the Biofactory MOSCAMED (São Francisco Juazeiro, BA, Brasil) and temephos was provided by sanitary surveillance agents (São Luís, MA, Brasil).
2.2. Plant Material
The herbaceous plant P. brevipedunculata was collected from the campus of Universidade Federal do Maranhão (UFMA) in São Luís, MA, Brazil, at coordinates 2°33’20.5” S and 44°18’32.7” W.A voucher specimen (No. 5287) was deposited in the Herbarium Rosa Mochel (SLUI) at Universidade Estadual do Maranhão (UEMA), São Luís, MA, Brazil. The collection of the plant adhered to Brazilian biodiversity protection laws (SisGen registration AAFB38B).
2.3. Extraction Procedure
Hydrodistillation using a Clevenger-type apparatus was employed to extract the essential oil from P. brevipedunculata (EOPb). Plant material (300 g) was air-dried and cut into small pieces using pruning shears to facilitate the hydrodistillation extraction. Distilled water (500 mL) was added to the flask, and the hydrodistillation process was maintained for 2.5 h after the reflux began. Following the extraction period, the oil/water (O/W) phase mixture was centrifugated at 3500 rpm for 10 min at a controlled temperature of 25°C. Anhydrous sodium sulfate was used to eliminate any remaining traces of water, and the (EOPb) was yielded in 0.81% of the initial plant material weight.
2.4. CG-MS Analysis
Analyses were conducted utilizing a CG-2010 SE (Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan) equipped with a flame ionization detector (FID) and electronic integrator. Compound separation was achieved using an RXi-1MS fused capillary column (30m X 0.25mm X 0.25µm film thickness) coated with 5%-phenyl-arylene-95%-dimethylpolysiloxane. Helium served as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. The column temperature program followed a sequence of 40°C at 4 min, ramping at a rate of 4°C/min to 240°C, then at 10°C/min to 280°C, with a hold at 280°C for 2 min. Injector and detector temperatures were maintained at 250°C and 280°C, respectively. Samples (10 mg/mL in CH2Cl2) were injected with a 1:50 split ratio. Retention indices were established using a standard solution of n-alkanes (C10-C40), while peak areas and retention times were determined using an electronic integrator. The relative amounts of individual compounds were calculated from GC peak areas without FID response factor correction. GC–MS analyses were performed in a QP2010 SE CG-MS system (Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan) system equipped with an AOC-20i auto-injector. MS spectra were acquired at 70 eV with scan intervals of 0.5 s and fragments ranging from 40-550 Da. Experimental conditions mirrored those of the GC analysis. Identification of essential oil components was achieved by comparing GC peak retention times with standard compounds run under identical conditions, and by comparing retention indices and MS spectra with those reported in the literature and stored in the NIST and Wiley libraries.
2.5. FTIR and UV-Vis Analysis
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analyses in reflectance mode were carried out using an FTIR Tracer-100 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu). Samples of the materials nGF2002 and nGF2002Pb were lyophilized and pelletized with KBr, while a small amount of pure OEPb material was analyzed in Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) mode. For the ATR-FTIR analysis, the spectrometer was equipped with a horizontal ATR accessory, and a ZnSe crystal window (PIKE Technologies) was used. Spectra were collected over the range of 400 to 4000 with a resolution of 8 and 50 scans. The sample spectra were obtained by first spreading the sample evenly on the ATR crystal surface, acquiring the spectrum, and then cleaning the crystal window with hexane and acetone before collecting subsequent spectra. Electronic absorption spectra of nanogels at a concentration of 5.0 x 10−3 g/mL in water were recorded at room temperature using a UV–Vis 1800 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu).
2.6. NMR Analysis
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra of the sample, both one-dimensional (1H and 13C NMR) and two-dimensional (COSY, HSQC, and HMBC), were acquired on a BRUKER AVANCE III HD spectrometer, operating at 11.75 Tesla (500.13 MHz for 1H NMR and 125.76 MHz for 13C NMR). The sample was dissolved in deuterated chloroform (CDCl3) and chemical shifts were expressed in parts per million (ppm) relative to tetramethylsilane (TMS), used as an internal reference standard with 0.00 (0.00 ppm).
2.7. Particle Size and Potential
Average hydrodynamic diameters (DH) and potential analyses were determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS) in water at 25°C and 40 mW semiconductor laser of 658 nm with a Litesizer 500 (Anton Paar GmbH) instrument (Module BM 10). The DH measurement was performed using a quartz cuvette of 3.0 mL. The potential was performed using a low-volume cuvette (Univette). All the measurements were performed in triplicate (mean ± SD).
2.8. Preparation of Nanogel Formulations
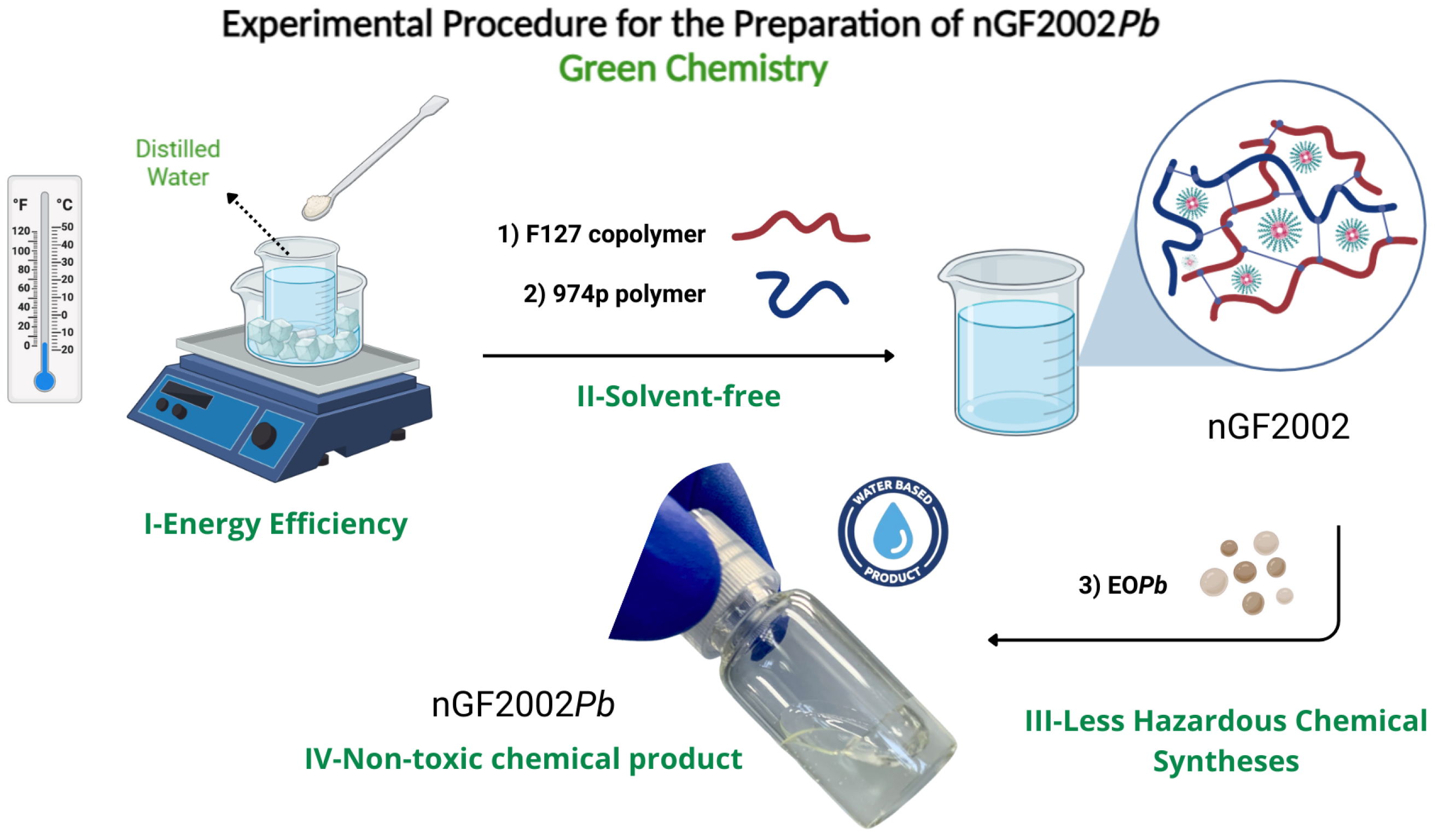
The nanogel formulations were prepared following the experimental procedure described by Schmolka using the cold technique [48]. A weight of F127 copolymer was slowly added to cold distilled water kept in an ice bath (5 - 10°C) and the mixture was kept under gentle stirring to allow each flake of the copolymer to hydrate on solution. After this period, 974p is gradually added, and the solution is gently stirred at 5 - 10°C until complete dissolution is achieved. EO
Pb is then added to the solution drop by drop, keeping the solution under continuous stirring for 30 min. To ensure complete solubility of the ingredients, the solution is kept quiescent in the refrigerator at 5°C overnight (
Figure 1).
2.9. Stability Assay of Nanogel Formulations
To investigate the influence of temperature on the physical and chemical stability properties of nanogel formulations, accelerated stability tests were performed following the ANVISA Cosmetics Stability Guide and the US Pharmacopeia [49]. One milliliter of the formulation was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 30 min at 25 ± 1°C. The formulation was stored throughout the study both at room temperature (25 ± 3°C) and under controlled refrigeration (5 ± 3°C) (temperature was monitored daily). Therefore, the formulations were subjected to 7 cycles of 24 h at 5°C and 24 h at 25°C. Thus, physical stability was determined by observing parameters such as homogeneity, phase separation, and organoleptic characteristics (appearance, color, and odor). The chemical stability of the nanogels was evaluated by GC–MS analysis comparing the concentration of EOPb in the formulations immediately after nanogel preparation (day 0) and subsequently at intervals of 7 days, totaling 7 analysis points.
2.10. In vitro Assays Against Aedes aegypti Larvae
The larvicidal profile of the nanogel nGF2002Pb was evaluated against Aedes aegypti larvae, following a protocol adapted from the WHO guidelines [50]. The hatching and larval-rearing procedures followed a methodology adapted from Amaral et al. and Carvalho et al [51, 52]. For the assays, 10 third-instar larvae were immersed in 20 mL of the nGF2002Pb formulation and in three control groups, all placed in polystyrene cups with a final volume of 50 mL. Five concentrations in EOPb were applied: 5, 50, 100, 250, and 500 g/mL, with 10 repetitions for each concentration, totaling 50 experiments and a sample size of 500 larvae. Additionally, 10 repetitions were conducted for the control group using mineral water for the hatching and larval growth stage and for the negative control with nGF2002, totaling 20 experiments and a sample size of 200 larvae. For the positive control, the commercial larvicide, temephos fersol was used. Ten replicates were conducted, totaling 10 experiments and a sample size of 100 larvae. The assays were monitored over a 24 and 48 h period to determine the percentage of live and dead larvae, with the mortality rate calculated as the % mean and standard deviation.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis and determination of the lethal concentrations 50 and 90 (LC50 and LC90), as well as the adjusted coefficient of determination (R Adj), were performed using Origin Pro software (version 8.5) with a confidence interval set at 95% (p < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of EOPb by GC-MS and NMR
In this study, the chemical composition of the volatile fraction of EOPb was analyzed using the GC-MS technique (
Table 1). A total of thirteen components were identified, accounting for 91.17% of the oil’s composition. The major component was citral comprising 64.58% of the oil, represented by two isomeric oxygenated monoterpenes: geranial (36.06%) and neral (28.52%). Other significant constituents included
-pinene (15.73%) and D-limonene (8.28%). This chemical profile is consistent with previous studies of
Pectis species collected from different regions of Brazil where citral content was reported to range from 81.6% to 86.5%, with
-pinene and D-limonene as secondary components (53).
To confirm the structure of the main compounds, EO
Pb was analyzed by
1H, and
13C, and NMR spectroscopy (
Table 2 and
Table 3). The
1H NMR spectrum of EO
Pb (Figures S1 and S2) displayed resonances indicative of a mixture of two isomers, as shown by the variations in the single hydrogen peaks (H-9). Aldehyde protons were identified by two doublets at
9.99 and 9.89. The integration of these signals yielded a neral-to-geranial ratio of 0.87:1.0. The proton signals resonating at
5.18 and 5.20 correspond to the methine protons of cycloalkenes (H-3 and H-2), confirming the presence of
-pinene and D-limonene on EO
Pb. In the
13C NMR spectra (Figures S3 and S4) the carbonyl signals (C-1) are observed at
191.2 and 191.5 respectively to neral and geranial isomers. The signals at
144.5 (C-2) and 116.0 (C-3) are related to the
sp2 carbons of
-pinene, while the signals at
133.6 (C-1), 120.6 (C-2), 163.8 (C-8), and 108.4 (C-9) correspond to the
sp2 carbons of D-limonene. The
1H and
13C NMR data align with the findings of Glamočlija et al. [54] and Farias et al. [55].
3.2. Development of the Empty Nanogels
To achieve the thermoresponsive behavior of the nanogels, some combinations ranging from 5-20:0.1-0.3% (w/w) F127:974p were considered. Combinations of 5-10:0.1-0.3 resulted in liquid formulations at 5 and 30°C, exhibiting no thermoresponsive behavior. Conversely, formulations comprising 20:0.1-0.3 remained liquid at 5°C and transitioned to semi-solid at 30°C, with a transition time of approximately 10 min from sol-gel. Notably, the combination of 20:0.1 yielded a low-viscosity formulation, whereas the combination of 20-0.3 resulted in high-viscosity formulations upon sensory evaluations. The optimized combination was determined to be 20:0.2 serving as the basis for incorporating the active ingredient EO
Pb at various mass percentages, designated as nGF2002 with a rapid sol-to-gel transition
Figure 2D.
3.3. Development of EOPb-Loaded Nanogels
Table 4 shows the combination of nGF2002 with different % (w/w) EO
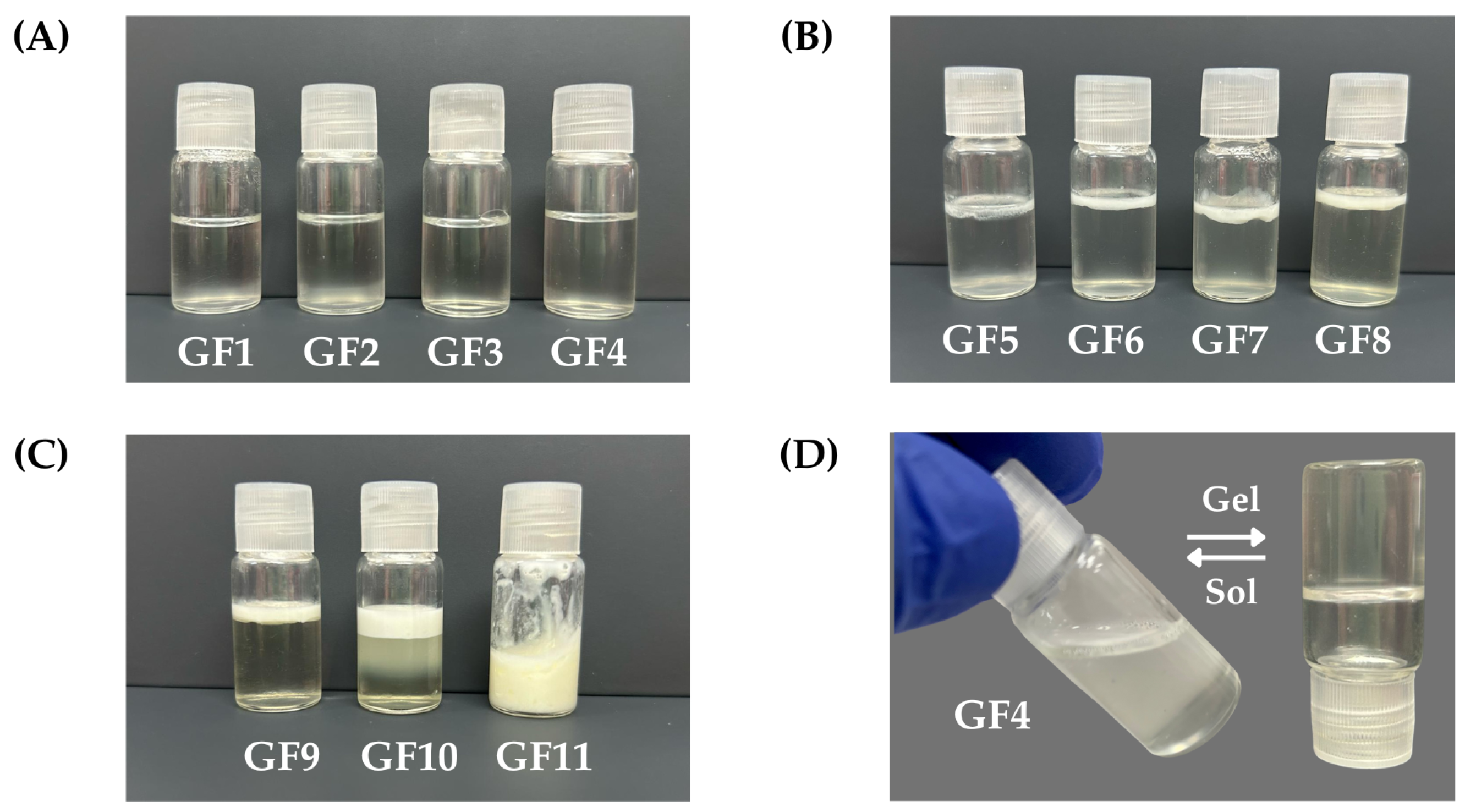
Pb. The preliminary stability evaluation of formulations GF1-GF11 provided valuable insights into their physical characteristics and potential suitability for nanogel development. Formulations GF1-GF4 presented as homogeneous, transparent solutions immediately after preparation, maintaining their integrity with no observable changes in physical appearance after 24 h of storage (
Figure 2A). These formulations are promising candidates for further optimization and potential use in nanogel development, as their stability under refrigerated conditions indicates their suitability for practical applications. In contrast, formulations GF5-GF10 exhibited signs of instability, including slight turbidity upon preparation and phase separation after 24 h of storage, characterized by the appearance of an oily layer on the formulation’s surface (
Figure 2B and
Figure 2C). The thickness of this oily layer increased from GF5 to GF9, indicating a decline in stability over time, and formulation adjustments to enhance stability and improve their potential for nanogel development. Formulation GF10 displayed poor stability, characterized by turbidity immediately post-preparation and triphasic separation after 24 h of storage. These observations suggest that GF10 may require significant modifications to address stability issues and render it suitable for further development. However, the formulation GF11 showed promising stability characteristics, maintaining an emulsion-like appearance after 24 h of storage (
Figure 2C). This indicates its potential suitability for continued investigation and development of emulsion formulation. However, given that the study aimed to formulate nanogels (O/W), GF1-GF4 took precedence for subsequent accelerated stability investigations. This decision was made to streamline resources and focus on formulations demonstrating initial stability, potentially expediting the development process.
Table 4.
Different compositions % (w/w) of EOPb and water, were combined to F127:974p (20:02%, w/w) to achieve GF1-GF11.
Table 4.
Different compositions % (w/w) of EOPb and water, were combined to F127:974p (20:02%, w/w) to achieve GF1-GF11.
| |
Components |
|
| Code |
Water |
F127 |
974p |
EOPb |
Stability |
| GF1 |
79.7 |
20 |
0.2 |
0.125 |
Sa
|
| GF2 |
79.6 |
20 |
0.2 |
0.25 |
Sa
|
| GF3 |
79.3 |
20 |
0.2 |
0.5 |
Sa
|
| GF4 |
78.8 |
20 |
0.2 |
1 |
Sa
|
| GF5 |
78.6 |
20 |
0.2 |
1.25 |
PS |
| GF6 |
78.3 |
20 |
0.2 |
1.5 |
PS |
| GF7 |
77.8 |
20 |
0.2 |
2 |
PS |
| GF8 |
77.3 |
20 |
0.2 |
2.5 |
PS |
| GF9 |
74.8 |
20 |
0.2 |
5 |
PS |
| GF10 |
69.8 |
20 |
0.2 |
10 |
PS |
| GF11 |
59.8 |
20 |
0.2 |
20 |
Sb
|
Table 5.
Different compositions % (w/w) of EOPb and water, were combined to F127:974p (20:02%, w/w) to achieve GF1-GF11.
Table 5.
Different compositions % (w/w) of EOPb and water, were combined to F127:974p (20:02%, w/w) to achieve GF1-GF11.
| Entry |
Treatment g/mL |
Mortality % ± SD |
| |
nGF2002Pba
|
24 h |
48 h |
| 1 |
5 |
1.0 ± 3.2 |
1.0 ± 3.2 |
| 2 |
50 |
1.0 ± 3.2 |
2.0 ± 4.2 |
| 3 |
100 |
11.0 ± 12.9 |
16.0 ± 13.5 |
| 4 |
250 |
67.0 ± 9.5 |
89.0 ± 3.2 |
| 5 |
500 |
96.0 ± 7.0 |
100.0 ± 0.0 |
| 6 |
Water |
0.0 ± 0.0 |
0.0 ± 0.0 |
| 7 |
nGF2002b |
0.0 ± 0.0 |
0.0 ± 0.0 |
| 8 |
Temephosc |
100.0 ± 0.0 |
100.0 ± 0.0 |
3.4. Physical Stability Assay of GF1-GF4
The results of the accelerated stability testing conducted on formulations GF1-GF4 provide valuable insights into the physical stability profiles of these semi-solid dosage forms. Adhering to the guidelines outlined by the US Pharmacopoeia (USP), our study scrutinized both the chemical integrity of the active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) and the physical characteristics of the formulations over a rigorous evaluation period [49]. Following USP standards, the chemical stability of compounded preparations is gauged by the maintenance of API concentration within 90-110% of the initial value recorded on day 0. Our findings reveal that formulations GF1-GF4 remained within this specified range throughout the 7-cycle evaluation period, indicating robust physical stability under the simulated storage conditions of alternating temperatures (5 and 32°C). Furthermore, the absence of any visible alterations such as particle sedimentation or phase separation, as well as the preservation of organoleptic properties (odor and color), underscores the physical stability of the formulations. These observations were held irrespective of the storage conditions, signifying the formulations’ resilience to temperature fluctuations and light exposure over the 14-day accelerated stability testing period. The shelf-life assay was performed for 180 days under refrigerated conditions (5°C) reaffirming the formulations’ sustained physical integrity and organoleptic characteristics. This prolonged stability underscores the suitability of the formulations for extended storage periods, particularly in environments where temperature control is a critical factor. The comprehensive evaluation of formulations GF1-GF4 demonstrates their robust physical and chemical stability profiles, positioning them as promising candidates for pharmaceutical applications. These findings contribute to the body of knowledge regarding the stability of semi-solid dosage forms and pave the way for their potential utilization in various therapeutic contexts. However, further studies incorporating additional parameters and longer-term evaluations are warranted to bolster our understanding and confidence in the stability and efficacy of these formulations. Considering the stable performance of nanogel formulations GF1-GF4 in stability assays, formulation GF4 was selected for further studies due to its higher content of EO
Pb. This formulation has been designated as nGF2002
Pb throughout this study (
Figure 2D).
3.5. Characterization of nGF2002Pb by CG, FTIR, and UV-Vis
The CG analysis of nGF2002
Pb was performed after the stability assay to investigate their chemical stability. A comparison of the chromatograms for EO
Pb and nGF2002
Pb reveals a high similarity of chromatograph profile, with the same elution order
-pinene, D-limonene, geranial, and neral. Interestingly, the chromatogram of nGF2002
Pb shows a higher intensity of signals corresponding to the geranial and neral isomers related to the
-pinene and D-limonene compounds (Figure S7). Our interpretation is that being less hydrophobic, the isomers are accommodated in regions near the PEO chains of F127, making them more accessible. On the other hand, the greater interaction of
-pinene and D-limonene with the hydrophobic PPO chains allows for their preferential accommodation in the core of the F127 micelles, keeping them more protected from the external environment. The FTIR analysis of nGF2002 also supports these interpretations. FTIR analysis is a highly effective tool often used to investigate the encapsulation process of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) within polymeric nanoplatforms for drug delivery applications. By examining shifts or changes in band intensities and broadening of vibrations in the FTIR spectra, one can gain insights into properties such as miscibility and interactions between macromolecule-API chains. In the FTIR spectrum of EO
Pb (
Figure 3A), the medium-intensity absorption band between 2954–2870 cm
−1 is associated with the symmetric and asymmetric stretching of C-H bonds. The sharp bands at 1442 and 1377 cm
−1 are also associated with C-H bond vibrations, corresponding, respectively to the scissor and rocking vibrational modes The sharp, high-intensity band at 1674 cm
−1 and the low-intensity band between 887–789 cm
−1 are related, respectively, to the stretching and bending of C=C bonds in trisubstituted alkenes, supporting the presence of
-pinene and D-limonene in the chemical composition of EO
Pb. The small shoulder observed at 1712
, characteristic of the carbonyl stretch of conjugated aldehydes, confirms the presence of the isomers neral and geranial in the composition of EO
Pb.
Figure 3B shows the FTIR spectrum for the nanogel nGF2002
Pb.
The addition of 1% of the EO
Pb in the nGF2002 matrix significantly alters the absorption band values related to the F127/974p blend. The strong and sharp absorption band at 3676 cm
−1 results from a pronounced red shift with
= 112 cm
−1 from the band at 3564 cm
−1 observed in the nGF2002 spectrum (Figure S8). This finding indicates that a decrease in energy is required for stretching O-H bonds, likely because EO
Pb molecules can disrupt some of the F127/974p interactions to fit into the nGF2002
Pb matrix. The band at 3384
in nGF2002 is now shifted to 3340 cm
−1 (44 cm
−1 blue shift), likely due to the formation of new intermolecular hydrogen bonds between the blend F127/974p with the majority constituents of EO
Pb leading to the interpretation that the more hydrophobic EO
Pb molecules are preferentially accommodated in the PPO chains of F127. Part of this interpretation is based on the increased energy required for the anti-symmetric stretching of C-H bonds, as indicated by the increased intensity and blue shift (
= 19 cm
−1 ) of the band from 2904 cm
−1 (nGF2002) to 2885 cm
−1 in the nGF2002
Pb spectrum (
Figure 3B), indicating a significant increase in the hydrophobic interactions of the system. UV-Vis analyses performed on formulations GF1-GF4 at 5.0 x 10
−3 g/mL in water support the encapsulation of EO
Pb on the nGF2002 matrix (Figure S9). The absorption band observed at 240 nm corresponds to the presence of EO
Pb. It is observed that, at the same concentration, an increase in the percentage of EO
Pb in formulations GF1-GF4 results in a proportional increase in absorption at 240 nm, ensuring that EO
Pbmolecules remain solubilized and well-stabilized within the polymeric matrix of the nanogels.
3.6. Particle Size and Potential
The particle size and
potential of nGF2002
Pb were quantitatively measured using the DLS technique. DLS has emerged as a pivotal tool for determining nanoparticle size distribution in a solution. By analyzing the fluctuations in scattered light intensity caused by Brownian motion, DLS provides valuable insights into the hydrodynamic diameter (D
H) and polydispersity of nanogels assessing the homogeneity and stability of nanogel formulations. Complementary to DLS,
potential analysis offers a deeper understanding of nanogel behavior by evaluating their surface charge characteristics. The DLS analysis on the nGF2002
Pb was conducted under two concentrations, maximum and minimum dilution in distilled water to ensure that equipment could accurately measure the particle size and
potential properties in solution. The results of the DLS measurements revealed notable differences. Under maximum dilution, the D
H of the particles showed an average value of 30.44 nm and PDI of 0.54, indicating a greater dispersion of particles in the solution (
Figure 3C). Typically, nanoparticles intended for drug delivery fall within the size range of 10 to 200 nm. Therefore, selecting the appropriate nanoparticle size is crucial for optimizing the effectiveness of drug delivery systems. It is well-documented that F127 has a higher propensity to self-organize in dilute solutions, typically forming spherical aggregates. This range is chosen because nanoparticles within this size range exhibit favorable characteristics such as enhanced cellular uptake, prolonged circulation time in the bloodstream, and improved biodistribution.
significantly increased to 429.3 nm, and PDI of 0.27 under minimum dilution (Figure S10). At higher concentrations, F127 can self-assemble into a morphological complex. Larger aggregates may be interconnected by branched architecture, named worm-like micelles, leading to stable aggregates with even larger sizes, as evidenced in previous studies [56]. Additionally, at higher concentrations, the nanogels can remain intact for extended periods in applications requiring controlled release of active pharmaceutical ingredients. This behavior is attributed to the robust structure formed by worm-like micelles, which facilitates sustained and controlled release of the active substances. Studies show that due to their branched architecture and ability to organize in three-dimensional network forms, nanogels can maintain the stability of the pharmaceutical for a long time, releasing the active ingredient gradually and over a prolonged period. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for treatments requiring extended release, enhancing therapeutic efficacy, and reducing the need for frequent administration. The measurements of
potential did not show significant changes in values across these concentrations. Interestingly, both dilution conditions exhibited
potential values close to zero (
Figure 3D). Despite the proximity of the
potential to zero, indicating a lack of strong electrostatic repulsion between particles, the system’s stability was not noticeably affected.
3.7. In Vitro Assays against Aedes aegypti Larvae
The results presented in Table 5 underscore the potent larvicidal efficacy of the nGF2002Pb nanogel against Aedes aegypti larvae at varying concentrations in EOPb-loaded nGF2002, ranging from 5 to 500 g/mL, across 24 h and 48 h treatment intervals. The mortality rates, expressed as percentages with accompanying standard deviations, were evaluated for a sample size of 10 larvae per concentration, providing robust insights into the concentration-dependent effects of the nanogel formulation. The larvicidal activity observed at the lowest concentrations was minimal, with mortality rates of 1.0% ± 3.2 after 24 h and 1.0-2.0% ± 3.2-4.2 after 48h (Entries 1 and 2). These findings suggest that the nanogel at such low dosages is insufficient to disrupt critical biological functions in the larvae, highlighting the importance of optimizing the concentration for effective vector control. The application of nGF2002Pb at 100 g/mL resulted in a moderate increase in mortality, reaching 11.0% ± 12.9 at 24 h and 16.0% ± 13.5 at 48 h (Entry 3). Although a temporal increase in efficacy was noted, the overall larvicidal activity remained suboptimal. This observation underscores the need for a threshold concentration that can trigger significant physiological disturbances in the larvae, leading to mortality. A marked improvement in larvicidal efficacy was achieved at higher concentrations, with the 250 g/mL of nGF2002Pb causing 67.0% ± 9.5 mortality at 24 h and 89.0% ± 3.2 at 48 h (Entrie 4). At 500 g/mL, the efficacy was even more pronounced, with mortality rates of 96.0% ± 7.0 after 24 h and 100.0% ± 0.0 after 48 h (Entrie 5). These results indicate that the nGF2002Pb demonstrates a pronounced concentration-dependent larvicidal effect. This is likely attributed to the enhanced bioavailability and sustained release of EOPb, which disrupts the physiological processes of the larvae. The absence of larval mortality in the negative controls, which included water and nGF2002 without EOPb, confirmed that the observed mortality in the experimental groups is attributable solely to the bioactive effects of the EOPb(Entry 6). This highlights the specificity of the nanogel formulation and its potential as an effective larvicidal agent. The positive control group treated with temephos (Entry 7), a widely recognized larvicide, achieved 100% mortality at both time points, validating the experimental conditions and providing a benchmark for assessing the efficacy of the nGF2002Pb nanogel. The comparable performance of the highest concentration of nGF2002Pb with that of temephos underscores the promising potential of nanogel as an alternative larvicidal intervention. The findings from this study suggest that the nGF2002Pb nanogel represents a viable and eco-friendly alternative for controlling Aedes aegyptilarvae, particularly at higher concentrations. The concentration-dependent efficacy observed indicates that formulation optimization could enhance its practical applicability in vector control programs.
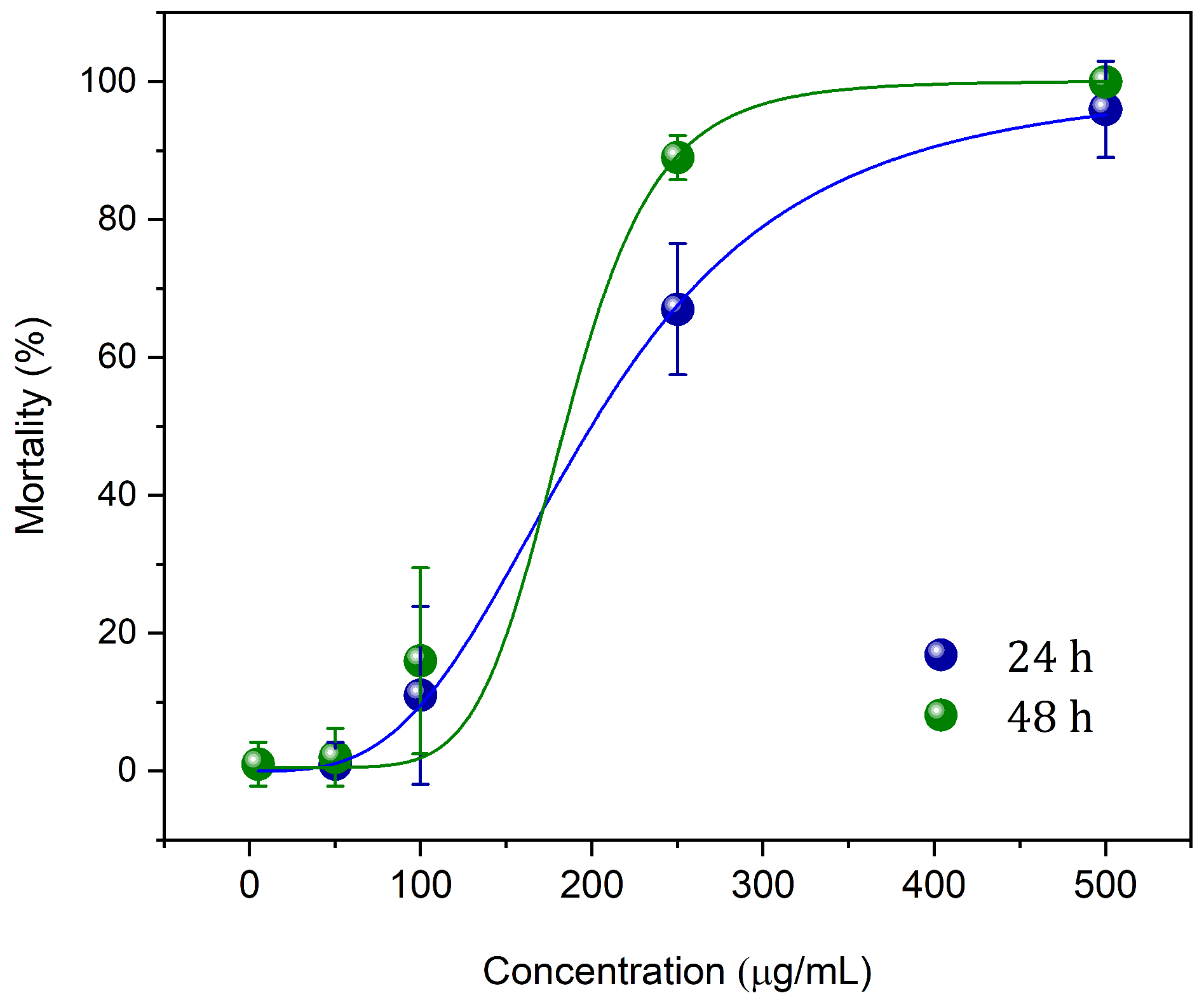
Figure 4 shows the results of lethal doses (LC
50 and LC
90) after 24 and 48 h of treatment with nGF2002
Pb. The results indicate that the nGF2002
Pb nanogel is highly effective in controlling
Aedes aegypti larvae, with a significant reduction in lethal concentrations over the exposure time. After 24 h, LC
50 was 199.5
g/mL, and LC
90 was 392.0
g/mL, while after 48 h, these values decreased to 184.5
g/mL and 253.4
g/mL, respectively. The decrease in lethal concentrations over time suggests increasing larval sensitivity to the nanogel, possibly due to higher absorption or a cumulative effect of the treatment. The R
2 values, very close to 1, indicate high precision in the dose-response models, reinforcing the reliability of the obtained data. These results highlight the potential of the nGF2002
Pb nanogel as a promising tool in the fight against the mosquito vector of diseases. Future studies should focus on the mechanical aspects of larval mortality induced by the nanogel, as well as field trials to validate its effectiveness in real-world settings. This is crucial to better understand the cytotoxic processes of the nanogel against Aedes aegypti larvae, with results to be published in forthcoming research. Integrating these nanotechnological approaches has the potential to significantly enhance mosquito control strategies, making them more sustainable and targeted, and effectively mitigating the spread of arboviral diseases.
4. Conclusions
The findings from this study suggest that the nGF2002Pb nanogel represents a viable and eco-friendly alternative for the control of Aedes aegypti larvae, particularly at higher concentrations. The concentration-dependent efficacy observed indicates that formulation optimization could enhance its practical applicability in vector control programs. Future studies should focus on the mechanical aspects of larval mortality induced by the nanogel, as well as on-field trials to validate its effectiveness in real-world settings. The integration of such nanotechnological approaches could significantly contribute to sustainable and targeted mosquito control strategies, thereby mitigating the spread of arboviral diseases.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1-S6: 1H and 13 NMR spectra of EOPb. Figure S7: FTIR spectra of empty nanogel nGF2002. Figure S9: UV-Vis spectrum of empty nanogel nGF2002. Figure S10: DLS analysis of the nGF2002Pb.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, data curation, methodology, investigation, writing-original draft, writing-review & editing, E.M.M and L.R.L.; Conceptualization, data curation, methodology, formal analysis, C.M.B., J.K.A.M.X., M.B.P.C., C.J.S.M., R.B.L., M.P.S., E.V.C.; Conceptualization, data curation, methodology, investigation, writing-original draft, writing-review & editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, R.S.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
http://img.mdpi.org/data/contributor-role-instruction.pdf
Funding
This research was funded by the Postgraduate Program in Chemistry (PPGQuim), Federal University of Maranhão (UFMA), São Luís, MA, Brazil. The authors thank the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) and the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) for their financial support through the Master’s scholarships provided to the students of the PPGQuim (Grant: PVCET3179-2022). They also thank the Foundation for the Support of Research and Scientific and Technological Development of Maranhão (FAPEMA) for funding the research initiation grant for the Institutional Scientific Initiation Scholarship Program (PIBIC/AGEUFMA Grant: PVCET3179-2022). The author E.V.C. also thanks the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and the National Institutes of Science and Technology (INCT/CNPq Grant: 465357/2014-8) for their financial support.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express our special thanks to IMCD Brasil (São Paulo, SP, Brazil) for generously providing the 974p NF polymer used in this study. The author E.V.C is also grateful to Central Analítica—Centro de Apoio Multidisciplinar—Universidade Federal do Amazonas (CA/CAM/UFAM) for the NMR analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The data presented in this study are available in this article.Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Soni, S.; Gill, V.J.S.; Anusheel; Singh, J.; Chhabra, J.; Gill, G.J.S.; Bakshi, R. Dengue, Chikungunya, and Zika: The Causes and Threats of Emerging and Re-emerging Arboviral Diseases. Cureus 2023, 15(7).
- Ushijima, Y.; Abe, H.; Nguema Ondo, G.; Bikangui, R.; Massinga Loembé, M.; Zadeh, V.R.; Essimengane, J.G.E.; Mbouna, A.V.N.; Bache, E.B.; Agnandji, S.T.; Lell, B.; Yasuda, J. Surveillance of the Major Pathogenic Arboviruses of Public Health Concern in Gabon, Central Africa: Increased Risk of West Nile Virus and Dengue Virus Infections. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, J.; Sammon, M.; Garg, M. Dengue, Zika and Chikungunya: Emerging Arboviruses in the New World. West J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 17, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côrtes, N.; Lira, A.; Prates-Syed, W.; Dinis Silva, J.; Vuitika, L.; Cabral-Miranda, W.; Durães-Carvalho, R.; Balan, A.; Cabral-Marques, O.; Cabral-Miranda, G. Integrated Control Strategies for Dengue, Zika, and Chikungunya Virus Infections. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1281667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, M.U.G.; Sinka, M.E.; Duda, K.A.; Mylne, A.Q.; Shearer, F.M.; Barker, C.M.; Moore, C.G.; Carvalho, R.G.; Coelho, G.E.; Van Bortel, W.; Hendrickx, G.; Schaffner, F.; Elyazar, I.R.F.; Teng, H.J.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Pigott, D.M.; Scott, T.W.; Smith, D.L.; Wint, G.R.W.; Golding, N.; Hay, S.I. The Global Distribution of the Arbovirus Vectors Aedes aegypti and Ae. albopictus. Elife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder-Smith, A.; Gubler, D.J.; Weaver, S.C.; Monath, T.P.; Heymann, D.L.; Scott, T.W. Epidemic Arboviral Diseases: Priorities for Research and Public Health. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, A. Emerging Infectious Encephalitides. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2021, 34, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Dimopoulos, G. Aedes aegypti Argonaute 2 Controls Arbovirus Infection and Host Mortality. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norshidah, H.; Vignesh, R.; Lai, N.S. Updates on Dengue Vaccine and Antiviral: Where Are We Heading? Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preciado, M.V.; Valva, P.; Escobar-Gutierrez, A.; Rahal, P.; Ruiz-Tovar, K.; Yamasaki, L.; Vazquez-Chacon, C.; Martinez-Guarneros, A.; Carpio-Pedroza, J.C.; Fonseca-Coronado, S.; Cruz-Rivera, M. Hepatitis C Virus Molecular Evolution: Transmission, Disease Progression and Antiviral Therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15992–16013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwaliko, C.; Nyaruaba, R.; Zhao, L.; Atoni, E.; Karungu, S.; Mwau, M.; Lavillette, D.; Xia, H.; Yuan, Z. Zika Virus Pathogenesis and Current Therapeutic Advances. Pathog. Glob. Health 2021, 115, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R. T.; Ant, T. H.; Cameron, M. M.; Logan, J. G. Novel Control Strategies for Mosquito-Borne Diseases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchinelli, L.; Badolo, A.; McCall, P. J. Biology and Behaviour of Aedes aegypti in the Human Environment: Opportunities for Vector Control of Arbovirus Transmission. Viruses 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y. S.; Higgs, S.; Vanlandingham, D. L. Emergence and Re-Emergence of Mosquito-Borne Arboviruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, P.; Yssel, H.; Missé, D. Zika Virus Infection: An Update. Microbes Infect. 2019, 21, 21(8–9). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Neto, J. A.; Powell, J. R.; Bonizzoni, M. Aedes aegypti Vector Competence Studies: A Review. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 67, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahebwa, A.; Hii, J.; Neoh, K. B.; Chareonviriyaphap, T. Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) Ecology, Biology, Behaviour, and Implications on Arbovirus Transmission in Thailand: Review. One Health 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Brown, D. J.; An, M.; Xue, R. D.; Liu, N. Insecticide Resistance: Status and Potential Mechanisms in Aedes aegypti. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 195, 105577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, S.; Maquart, P. O.; Chhuoy, K.; Suor, K.; Chhum, M.; Heng, K.; Leng, S.; Fontenille, D.; Marcombe, S. Monitoring Insecticide Resistance of Adult and Larval Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, R. R.; Sikder, J. R.; Vivero, R. J.; Matute, D. R.; Schrider, D. R. Strong Positive Selection in Aedes aegypti and the Rapid Evolution of Insecticide Resistance. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivabalakrishnan, K.; Thanihaichelvan, M.; Tharsan, A.; Eswaramohan, T.; Ravirajan, P.; Hemphill, A.; Ramasamy, R.; Surendran, S. N. Resistance to the Larvicide Temephos and Altered Egg and Larval Surfaces Characterize Salinity-Tolerant Aedes aegypti. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Barbosa Bitencourt, R.; de Souza Faria, F.; Marchesini, P.; Reis Dos Santos-Mallet, J.; Guedes Camargo, M.; Rita Elias Pinheiro Bittencourt, V.; Guedes Pontes, E.; Baptista Pereira, D.; Siqueira de Almeida Chaves, D.; da Costa Angelo, I. Entomopathogenic Fungi and Schinus Molle Essential Oil: The Combination of Two Eco-Friendly Agents against Aedes aegypti Larvae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2022, 194, 107827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, H. L.; Barreto Sousa, J. P.; Sousa-Moura, D.; Grisolia, C. K.; Espindola, L. S. Degradation Evaluation and Toxicity Profile of Bilobol, a Promising Eco-Friendly Larvicide. Chemosphere 2021, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishwarya, R.; Vaseeharan, B.; Anuradha, R.; Rekha, R.; Govindarajan, M.; Alharbi, N. S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J. M.; Benelli, G. Eco-Friendly Fabrication of Ag Nanostructures Using the Seed Extract of Pedalium murex, an Ancient Indian Medicinal Plant: Histopathological Effects on the Zika Virus Vector Aedes aegypti and Inhibition of Biofilm-Forming Pathogenic Bacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 174, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanigaivel, A.; Vasantha-Srinivasan, P.; Edwin, E. S.; Ponsankar, A.; Selin-Rani, S.; Chellappandian, M.; Kalaivani, K.; Senthil-Nathan, S.; Benelli, G. Development of an Eco-Friendly Mosquitocidal Agent from Alangium salvifolium against the Dengue Vector Aedes aegypti and Its Biosafety on the Aquatic Predator. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 10340–10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V. S. V.; Pereira, B. B. Low Toxicity and High Efficacy in Use of Novel Approaches to Control Aedes aegypti. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2020, 23, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R. M.; Stashenko, E.; Duque, J. E. Insecticidal and Repellent Activity of Several Plant-Derived Essential Oils Against Aedes aegypti. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2017, 33, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soonwera, M.; Sittichok, S. Adulticidal Activities of Cymbopogon citratus (Stapf.) and Eucalyptus globulus (Labill.) Essential Oils and Their Synergistic Combinations Against Aedes aegypti (L.), Aedes albopictus (Skuse), and Musca domestica (L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 20201–20214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manh, H. D.; Hue, D. T.; Hieu, N. T. T.; Tuyen, D. T. T.; Tuyet, O. T. The Mosquito Larvicidal Activity of Essential Oils from Cymbopogon and Eucalyptus Species in Vietnam. Insects 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, T. R. S. A.; de Mesquita, L. S. S.; Amaral, F. M. M. D.; Coutinho, D. F. Essential Oils and Their Chemical Constituents against Aedes aegypti L. (Diptera: Culicidae) Larvae. Acta Trop. 2020, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, K.; Jové, V.; Duvall, L. B. Methods to Assess Blood and Nectar Meals in Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cansian, R. L.; Staudt, A.; Bernardi, J. L.; Puton, B. M. S.; Oliveira, D.; de Oliveira, J. V.; Gomes, A. C. C.; Andrade, B. C. O. P.; Leal, I. C. R.; Simas, N. K.; Zeni, J.; Jungues, A.; Dallago, R. M.; Backes, G. T.; Paroul, N. Toxicity and Larvicidal Activity on Aedes aegypti of Citronella Essential Oil Submitted to Enzymatic Esterification. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiman, I.; Ishak, H.; Stang, I. E.; Daud, A.; Amiruddin, R. Essential Oil as a New Tool for Larvicidal Aedes aegypti: A Systematic Review. Gac. Sanit. 2021, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, L. P.; Amaral, A. C. F.; Ramos, A. S.; Ferreira, J. L. P.; Maria, A. C. B.; Oliveira, K. M. T.; Araujo, E. S., Jr.; Branches, A. D. S.; Silva, J. N.; Silva, N. G.; Barros, G. A.; Chaves, F. C. M.; Tadei, W. P.; Silva, J. R. A. Piper capitarianum Essential Oil: A Promising Insecticidal Agent for the Management of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 9760–9776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohra, T.; Khalil, A. T.; Saeed, F.; Latif, B.; Salman, M.; Ikram, A.; Ayaz, M.; Murthy, H. C. A. Green Nano-Biotechnology: A New Sustainable Paradigm to Control Dengue Infection. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2022, 2022, 399–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, E. V. R.; de Oliveira, J. L.; Abrantes, D. C.; Rogério, C. B.; Bueno, C.; Miranda, V. R.; Monteiro, R. A.; Fraceto, L. F. Recent Developments in Nanotechnology for Detection and Control of Aedes aegypti-Borne Diseases. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Dos Santos, D.; Lopes Chaves, L.; Couto Pires, V.; Soares Rodrigues, J.; Alves Siqueira de Assunção, M.; Bezerra Faierstein, G.; Gomes Barbosa Neto, A.; de Souza Rebouças, J.; Christine de Magalhães Cabral Albuquerque, E.; Alexandre Beisl Vieira de Melo, S.; Costa Gaspar, M.; Maria Rodrigues Barbosa, R.; Elga Medeiros Braga, M.; Cipriano de Sousa, H.; Rocha Formiga, F. New Weapons Against the Disease Vector Aedes aegypti: From Natural Products to Nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 643, 123221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuchuchua, O.; Sakulku, U.; Uawongyart, N.; Puttipipatkhachorn, S.; Soottitantawat, A.; Ruktanonchai, U. In Vitro Characterization and Mosquito (Aedes aegypti) Repellent Activity of Essential-Oils-Loaded Nanoemulsions. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, B.; Ogélio, H.; Brant, F.; Pereira-Pinto, C. J.; Workman, M. J.; Costa, M.; Lima, J. B. P.; Martins, A. J.; Ramalho-Ortigao, M.; Durvasula, R.; Hurwitz, I.; David, M. R.; Genta, F. A. High Larvicidal Efficacy of Yeast-Encapsulated Orange Oil Against Aedes aegypti Strains from Brazil. Parasit. Vectors 2021, 14, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subaharan, K.; Senthamarai Selvan, P.; Subramanya, T. M.; Senthoorraja, R.; Manjunath, S.; Das, T.; Pragadheesh, V. S.; Bakthavatsalam, N.; Mohan, M. G.; Senthil-Nathan, S.; Uragayala, S.; Samuel, P. P.; Govindarajan, R.; Eswaramoorthy, M. Ultrasound-Assisted Nanoemulsion of Trachyspermum ammi Essential Oil and Its Constituent Thymol on Toxicity and Biochemical Aspect of Aedes aegypti. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 71326–71337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustino, C. G.; de Medeiros, F. A.; Ribeiro Galardo, A. K.; Lobato Rodrigues, A. B.; Lopes Martins, R.; de Medeiros Souza Lima, Y.; Fechine Tavares, J.; Alves de Medeiros, M. A.; Dos Santos Cruz, J.; Almeida, S. S. M. D. S. Larvicide Activity on Aedes aegypti of Essential Oil Nanoemulsion from the Protium heptaphyllum Resin. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A. R.; Morais, W. A.; Oliveira, N. D.; Silva, W. C. G.; Gomes, A. P. B.; Espindola, L. S.; Araujo, M. O.; Araujo, R. M.; Albernaz, L. C.; De Sousa, D. P.; Aragão, C. F. S.; Ferreira, L. S. Nanoemulsions and Solid Microparticles Containing Pentyl Cinnamate to Control Aedes aegypti. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, J. L.; Maciel de Faria Motta Oliveira, A. E.; Pinto, M. C.; Chorilli, M. Botanical Insecticide-Based Nanosystems for the Control of Aedes (Stegomyia) aegypti Larvae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 28737–28748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S. K.; Tandon, S.; Ahmad, A.; Singh, A. K.; Tripathi, A. K. Structure-Activity Relationships of Monoterpenes and Acetyl Derivatives against Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) Larvae. Pest Manage. Sci. 2013, 69, 1235–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, P.; Xie, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z. Biological Activity and Safety Profile of Monoterpenes against Plutella xylostella L. (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 24889–24901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S. R.; Melo, M. A.; Cardoso, A. V.; Santos, R. L.; de Sousa, D. P.; Cavalcanti, S. C. Structure-Activity Relationships of Larvicidal Monoterpenes and Derivatives against Aedes aegypti Linn. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimane, B. B.; Ezzine, O.; Dhahri, S.; Ben Jamaa, M. L. Essential Oils from Two Eucalyptus from Tunisia and Their Insecticidal Action on Orgyia trigotephras (Lepidoptera, Lymantriidae). Biol. Res. 2014, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmolka, I. R. Artificial Skin. I. Preparation and Properties of Pluronic F-127 Gels for Treatment of Burns. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1972, 6, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary (USP 41-NF 36); United States Pharmacopeial Convention: 2016. Accessed November 01,2023.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Laboratory and Field Testing of Mosquito Larvicides; WHO: Geneva, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral, M. C. P. C.; Garziera, L.; Pinto, A. T. M.; Gomez, M. Manual de Procedimentos Criação em Massa de Aedes aegypti – Linhagem (MBR-001-); Biofábrica MOSCAMED BRASIL: Juazeiro-BA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, D. O.; Nimmo, D.; Naish, N.; McKemey, A. R.; Gray, P.; Wilke, A. B.; Marrelli, M. T.; Virginio, J. F.; Alphey, L.; Capurro, M. L. Mass Production of Genetically Modified Aedes aegypti for Field Releases in Brazil. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, S. L.; Marques, A. M.; Sudo, R. T.; Kaplan, M. A.; Zapata-Sudo, G. Vasodilator Activity of the Essential Oil from Aerial Parts of Pectis brevipedunculata and Its Main Constituent Citral in Rat Aorta. Molecules 2013, 18, 3072–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glamočlija, J.; Soković, M.; Tešević, V.; Linde, G. A.; Colauto, N. B. Chemical Characterization of Lippia alba Essential Oil: An Alternative to Control Green Molds. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42(4), 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira Farias, A. L.; Lobato Rodrigues, A. B.; Lopes Martins, R.; de Menezes Rabelo, É.; Ferreira Farias, C. W.; Moreira da Silva de Almeida, S.S. Chemical Characterization, Antioxidant, Cytotoxic and Microbiological Activities of the Essential Oil of Leaf of Tithonia diversifolia (Hemsl) A. Gray (Asteraceae). Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, C. S.; Marques, E. M.; do Nascimento, J. R.; Lima, V. A. S.; Santos-Oliveira, R.; Figueredo, A. S.; de Jesus, C. M.; de Souza Nunes, G. C.; Brandão, C. M.; de Jesus, E. T.; Sa, M. C.; Tanaka, A. A.; Braga, G.; Santos, A. C. F.; de Lima, R. B.; Silva, L. A.; Alencar, L. M. R.; da Rocha, C. Q.; Gonçalves, R. S. Design of Liquid Formulation Based on F127-Loaded Natural Dimeric Flavonoids as a New Perspective Treatment for Leishmaniasis. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).