Submitted:
25 September 2024
Posted:
25 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. The Importance of Molecular Studies in Understanding Head and Neck Cancer
1.2. Introduction to miRNAs in Head and Neck Cancer
1.3. Introduction to miRNAs in Head and Neck Cancer
2. Signature Protein/Gene in Head and Neck Cancer
2.1. Literature-Driven Insights
2.2. Database-Driven Insights
3. Molecular Pathways Involved in Head and Neck Cancer
4. Role of Biomarkers in Head and Neck Cancer
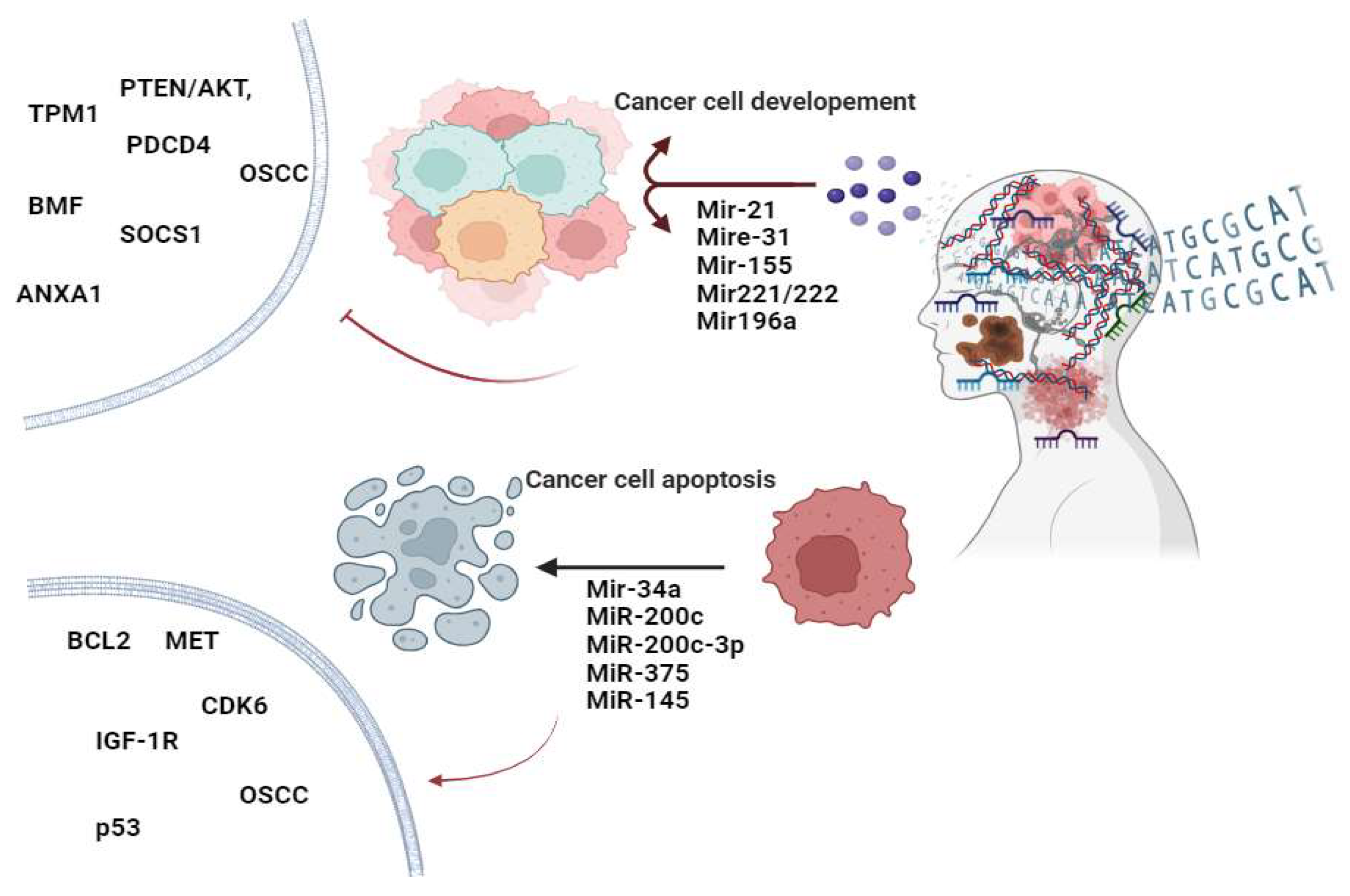
5. Functional Roles of miRNAs in Head and Neck Cancer
5.1. OncomiRs in Head and Neck Cancer
5.2. Tumor-Suppressive miRNAs in Head and Neck Cancer
5.3. In Silico Validation of miRNAs in Head and Neck Cancer
6. Recent Studies Profiling miRNA Expression in Head and Neck Cancer Using High-throughput Technologies
7. Future Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Authors contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Informed Consent Statement
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
References
- Mody, M.D.; Rocco, J.W.; Yom, S.S.; Haddad, R.I.; Saba, N.F. Head and neck cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J Oncol 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebello, R.J.; Oing, C.; Knudsen, K.E.; Loeb, S.; Johnson, D.C.; Reiter, R.E.; Gillessen, S.; Van der Kwast, T.; Bristow, R.G. Prostate cancer. Nature reviews. Disease primers 2021, 7, 9. [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Xiao, W.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, Y.; Chen, G. Epidemiological Trends of Head and Neck Cancer: A Population-Based Study. BioMed research international 2021, 2021, 1738932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.; Fedewa, S.; Chen, A.Y. Epidemiology and Demographics of the Head and Neck Cancer Population. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 2018, 30, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chulam, T.C.; Bertonha, F.B.; Villacis, R.A.R.; Filho, J.G.; Kowalski, L.P.; Rogatto, S.R. Epidemiological, Clinical, and Genomic Profile in Head and Neck Cancer Patients and Their Families. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, J.; Cescon, D.W.; Tse, D.; Bradbury, P.; Xu, W.; Ma, C.; Wheatley-Price, P.; Waldron, J.; Goldstein, D.; Meyer, F.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms and head and neck cancer outcomes: a review. Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention : a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive Oncology 2008, 17, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraguti, G.; Terracina, S.; Petrella, C.; Greco, A.; Minni, A.; Lucarelli, M.; Agostinelli, E.; Ralli, M.; de Vincentiis, M.; Raponi, G.; et al. Alcohol and Head and Neck Cancer: Updates on the Role of Oxidative Stress, Genetic, Epigenetics, Oral Microbiota, Antioxidants, and Alkylating Agents. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Pilleron, S.; Sarfati, D.; Janssen-Heijnen, M.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F.; Soerjomataram, I. Global cancer incidence in older adults, 2012 and 2035: A population-based study. International journal of cancer 2019, 144, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemans, C.R.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Brakenhoff, R.H. The molecular landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2018, 18, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.H.; Thomas, G.; Ottensmeier, C.H.; King, E.V. Importance of the immune system in head and neck cancer. Head & neck 2019, 41, 2789–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, J.D. Immunity in head and neck cancer. Cancer immunology research 2015, 3, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ye, J.; Dong, Z.; Hu, S.; Xiao, M. Novel genetic alterations and their impact on target therapy response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer management and research 2019, 11, 1321–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, K.; Barbieri, C.E. Molecular Subtypes of Prostate Cancer. Curr Oncol Rep 2018, 20, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, L.P.; Coletta, R.D.; Salo, T.; Maschietto, M.; Chojniak, R.; Lima, J.M.; Mlynarek, A.; Hier, M.P.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.A.; Silva, S.D. Head and neck cancer: Emerging concepts in biomarker discovery and opportunities for clinical translation. Clin Transl Med 2020, 10, e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Rai, A.K.; Das, D.; Das, R.; Kumar, R.S.; Sarma, A.; Sharma, S.; Kataki, A.C.; Ramteke, A. Alcohol and Tobacco Increases Risk of High Risk HPV Infection in Head and Neck Cancer Patients: Study from North-East Region of India. PloS one 2015, 10, e0140700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhania, N.; Mishra, A. Alcohol Consumption, Tobacco Use, and Viral Infections: A Multifactorial Approach to Understanding Head and Neck Cancer Risk. International Journal of Applied Health Care Analytics 2024, 9, 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.M.; Rubenstein, L.M.; Haugen, T.H.; Hamsikova, E.; Turek, L.P. Tobacco and alcohol use increases the risk of both HPV-associated and HPV-independent head and neck cancers. Cancer Causes Control 2010, 21, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Molecular Taxonomy of Primary Prostate Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 1011–1025. [CrossRef]
- Soares, P.C.; Abdelhay, E.S.; Thuler, L.C.S.; Soares, B.M.; Demachki, S.; Ferro, G.V.R.; Assumpção, P.P.; Lamarão, L.M.; Ribeiro Pinto, L.F.; Burbano, R.M.R. HPV positive, wild type TP53, and p16 overexpression correlate with the absence of residual tumors after chemoradiotherapy in anal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol 2018, 18, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levva, S.; Kotoula, V.; Kostopoulos, I.; Manousou, K.; Papadimitriou, C.; Papadopoulou, K.; Lakis, S.; Koukoulias, K.; Karavasilis, V.; Pentheroudakis, G.; et al. Prognostic Evaluation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Genotype and Phenotype Parameters in Triple-negative Breast Cancers. Cancer genomics & proteomics 2017, 14, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, C.L.T.; Forsare, C.; Bendahl, P.O.; Falck, A.K.; Fernö, M.; Lövgren, K.; Aaltonen, K.; Rydén, L. Expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related markers and phenotypes during breast cancer progression. Breast cancer research and treatment 2020, 181, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Zhong, R.; Spiotto, M.T. Notch Signaling and Human Papillomavirus-Associated Oral Tumorigenesis. Advances in experimental medicine and biology 2021, 1287, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalto, F.I.; De Amicis, F. Cyclin D1 in Cancer: A Molecular Connection for Cell Cycle Control, Adhesion and Invasion in Tumor and Stroma. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Long, S.; Shi, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wu, W.; Han, L.; Wang, S. The role of PD-1/PD-L1 and application of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in human cancers. Frontiers in Immunology 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanji, M.A.; Rotimi, D.; Adeyemi, O.S. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors as an Alternative Source of Treatment Strategy for Cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 2019, 8547846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.S.; Manda, G. Metabolic Pathways of the Warburg Effect in Health and Disease: Perspectives of Choice, Chain or Chance. International journal of molecular sciences 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groblewska, M.; Siewko, M.; Mroczko, B.; Szmitkowski, M. The role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors (TIMPs) in the development of esophageal cancer. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 2012, 50, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Méndez-Huergo, S.P.; Blidner, A.G.; Rabinovich, G.A. Galectins: emerging regulatory checkpoints linking tumor immunity and angiogenesis. Curr Opin Immunol 2017, 45, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Guan, C.; Li, K.; Zheng, G.; Wang, T.; Zhang, S.; Liao, G. MMP25 Regulates Immune Infiltration Level and Survival Outcome in Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Frontiers in oncology 2020, 10, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.H.; Du, W.D.; Li, Y.F.; Al-Aroomi, M.A.; Yan, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Liu, F.Y.; Sun, C.F. The Overexpression of Fibronectin 1 Promotes Cancer Progression and Associated with M2 Macrophages Polarization in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Int J Gen Med 2022, 15, 5027–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinucci, B.; Cucielo, M.S.; Minatel, B.C.; Cury, S.S.; Caxali, G.H.; Aal, M.C.E.; Felisbino, S.L.; Pinhal, D.; Carvalho, R.F.; Delella, F.K. Fibronectin Modulates the Expression of miRNAs in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Front Vet Sci 2022, 9, 879997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosper, P.F.; Bradley, S.; Luo, L.; Kimple, R.J. Biology of HPV Mediated Carcinogenesis and Tumor Progression. Semin Radiat Oncol 2021, 31, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, H.K.; Ku, M.; Yang, J. Beyond EGFR inhibition: multilateral combat strategies to stop the progression of head and neck cancer. Exp Mol Med 2019, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Su, W.; Dou, Z.; Zhao, D.; Jin, X.; Lei, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Cheng, B.; et al. Mutant p53 in cancer: from molecular mechanism to therapeutic modulation. Cell death & disease 2022, 13, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zou, Q.; Yu, F.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L. Comprehensive Analysis Revealed that CDKN2A is a Biomarker for Immune Infiltrates in Multiple Cancers. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology 2021, 9, 808208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirico, M.; D'Angelo, A.; Gianni, C.; Casadei, C.; Merloni, F.; De Giorgi, U. Current State and Future Challenges for PI3K Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Castruita-De la Rosa, C.; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Human Diseases. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhad, M.; Rolig, A.S.; Redmond, W.L. The role of Galectin-3 in modulating tumor growth and immunosuppression within the tumor microenvironment. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1434467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Avila, G.; Sommer, B.; Mendoza-Posada, D.A.; Ramos, C.; Garcia-Hernandez, A.A.; Falfan-Valencia, R. Matrix metalloproteinases participation in the metastatic process and their diagnostic and therapeutic applications in cancer. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology 2019, 137, 57–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-L.; Xu, C.-F.; Yang, X.-H.; Wang, M.-S. Fibronectin promotes tumor progression through integrin αvβ3/PI3K/AKT/SOX2 signaling in non-small cell lung cancer. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zheng, W.; Peng, F.; Xu, Y. Predicting AURKA as a novel therapeutic target for NPC: A comprehensive analysis based on bioinformatics and validation. Frontiers in genetics 2022, 13, 926546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.H.; Idris, A.; Johnson, N.W.; Fallaha, S.; Clarke, D.T.W.; Martin, D.; Morgan, I.M.; Gabrielli, B.; McMillan, N.A.J. Aurora kinases are a novel therapeutic target for HPV-positive head and neck cancers. Oral oncology 2018, 86, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Song, L.J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Lin, K.; He, H. Identification of Prognostic Markers for Head and NeckSquamous Cell Carcinoma Based on Glycolysis-Related Genes. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022, 2022, 2762595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binabaj, M.M.; Soleimani, A.; Rahmani, F.; Avan, A.; Khazaei, M.; Fiuji, H.; Soleimanpour, S.; Ryzhikov, M.; Ferns, G.A.; Bahrami, A.; et al. Prognostic value of high mobility group protein A2 (HMGA2) over-expression in cancer progression. Gene 2019, 706, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, L.M.; Fonseca, L.; Erthal, I.D.; Malta, T.M. Epigenomic integrative analysis pinpoint master regulator transcription factors associated with tumorigenesis in squamous cell carcinoma of oral tongue. Genet Mol Biol 2023, 46, e20220358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajez, N.M.; Shi, W.; Wong, D.; Lenarduzzi, M.; Waldron, J.; Weinreb, I.; Liu, F.F. Lin28b promotes head and neck cancer progression via modulation of the insulin-like growth factor survival pathway. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 1641–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, S.T.; Antunes, A.A.; Pontes-Junior, J.; Sousa-Canavez, J.M.; Dall'Oglio, M.F.; Piantino, C.B.; Cruz, J.A.; Morais, D.R.; Srougi, M.; Leite, K.R. Underexpression of MMP-2 and its regulators, TIMP2, MT1-MMP and IL-8, is associated with prostate cancer. Int Braz J Urol 2012, 38, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Mao, Y.Y.; Han, N.N.; Wu, H.; Zhang, S. PLAU1 Facilitated Proliferation, Invasion, and Metastasis via Interaction With MMP1 in Head and Neck Squamous Carcinoma. Frontiers in oncology 2021, 11, 574260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Bai, Y.; Bai, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, X. PLAU promotes cell proliferation and migration of head and neck cancer via STAT3 signaling pathway. Experimental cell research 2024, 438, 114056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, S.; Laureano, N.K.; Hadiwikarta, W.W.; Visioli, F.; Bonrouhi, M.; Pajdzik, K.; Conde-Lopez, C.; Herold-Mende, C.; Eidt, G.; Langie, R.; et al. The Role of SOX2 and SOX9 in Radioresistance and Tumor Recurrence. Cancers 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doescher, J.; von Witzleben, A.; Boukas, K.; Weissinger, S.E.; Thomas, G.J.; Laban, S.; Thomas, J.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Ottensmeier, C.H. Changes in Gene Expression Patterns in the Tumor Microenvironment of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Under Chemoradiotherapy Depend on Response. Frontiers in oncology 2022, 12, 862694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Sun, Z.; Chen, H.; Ling, J.; Zhao, H.; Chang, A.; Zhuo, X. SERPINE1 as an Independent Prognostic Marker and Therapeutic Target for Nicotine-Related Oral Carcinoma. Clinical and experimental otorhinolaryngology 2023, 16, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, A.; Hess, J. Epidemiology and Molecular Biology of Head and Neck Cancer. Oncol Res Treat 2017, 40, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Pharmacological research 2014, 79, 34–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gamal, M.I.; Mewafi, N.H.; Abdelmotteleb, N.E.; Emara, M.A.; Tarazi, H.; Sbenati, R.M.; Madkour, M.M.; Zaraei, S.O.; Shahin, A.I.; Anbar, H.S. A Review of HER4 (ErbB4) Kinase, Its Impact on Cancer, and Its Inhibitors. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Saba, N.F.; Chen, G.Z.; Shin, D.M. Targeting HER (ERBB) signaling in head and neck cancer: An essential update. Mol Aspects Med 2015, 45, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne, M.C.; Pivot, X.; Formento, J.L.; Bensadoun, R.J.; Formento, P.; Dassonville, O.; Francoual, M.; Poissonnet, G.; Fontana, X.; Schneider, M.; et al. A multifactorial approach including tumoural epidermal growth factor receptor, p53, thymidylate synthase and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase to predict treatment outcome in head and neck cancer patients receiving 5-fluorouracil. British journal of cancer 1999, 79, 1864–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, N.I.; Grandis, J.R. HER2 as a therapeutic target in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2015, 21, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Serebriiskii, I.G.; Dunbrack, R.L., Jr.; Robinson, M.K.; Burtness, B.; Golemis, E.A. Protein-intrinsic and signaling network-based sources of resistance to EGFR- and ErbB family-targeted therapies in head and neck cancer. Drug Resist Updat 2011, 14, 260–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.L.; Veras, S.S.; Silveira, E.J.; Seabra, F.R.; Pinto, L.P.; Souza, L.B.; Freitas, R.A. The role of matrix extracellular proteins and metalloproteinases in head and neck carcinomas: an updated review. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 2005, 71, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.U.; Arakeri, G.; Subash, A.; Bagadia, R.K.; Thakur, S.; Kudpaje, A.S.; Nayar, R.; Patil, S.; Paiva Fonseca, F.; Gomez, R.S.; et al. Circulating tumour cells in head and neck cancers: Biological insights. Journal of oral pathology & medicine : official publication of the International Association of Oral Pathologists and the American Academy of Oral Pathology 2020, 49, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, F.; Lauffenburger, D.; Friedl, P. Towards targeting of shared mechanisms of cancer metastasis and therapy resistance. Nature reviews. Cancer 2022, 22, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, L.; Barras, D.; Medová, M.; Aebersold, D.M.; Medo, M.; Poliaková, M.; Koch, J.; Bojaxhiu, B.; Eliçin, O.; Dettmer, M.S.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Profiling of Patient-matched Head and Neck Cancer Cells: A Preclinical Pipeline for Metastatic and Recurrent Disease. Molecular cancer research : MCR 2018, 16, 1912–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R.; Castro, E.; Aragón, I.M.; Cendón, Y.; Cattrini, C.; López-Casas, P.P.; Olmos, D. Genetic aberrations in DNA repair pathways: a cornerstone of precision oncology in prostate cancer. British journal of cancer 2021, 124, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konings, H.; Stappers, S.; Geens, M.; De Winter, B.Y.; Lamote, K.; van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Specenier, P.; Vanderveken, O.M.; Ledeganck, K.J. A Literature Review of the Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Head and Neck Neoplasms. Frontiers in oncology 2020, 10, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Singh, A.; Chen, X.; Rosenberg, A.J.; Pearson, A.T.; Zhavoronkov, A.; Savage, P.A.; Lingen, M.W.; Agrawal, N.; Izumchenko, E. Application of liquid biopsy as multi-functional biomarkers in head and neck cancer. British journal of cancer 2022, 126, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapado-González, Ó.; Martínez-Reglero, C.; Salgado-Barreira, Á.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; Muinelo-Lorenzo, J.; López-López, R.; Díaz-Lagares, Á.; Suárez-Cunqueiro, M.M. Salivary DNA Methylation as an Epigenetic Biomarker for Head and Neck Cancer. Part I: A Diagnostic Accuracy Meta-Analysis. Journal of personalized medicine 2021, 11. [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Patel, S.; Patel, P.; Tanavde, V. Saliva Based Liquid Biopsies in Head and Neck Cancer: How Far Are We From the Clinic? Frontiers in oncology 2022, 12, 828434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattuso, G.; Crimi, S.; Lavoro, A.; Rizzo, R.; Musumarra, G.; Gallo, S.; Facciponte, F.; Paratore, S.; Russo, A.; Bordonaro, R.; et al. Liquid Biopsy and Circulating Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Precancerous and Cancerous Oral Lesions. Noncoding RNA 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, D.M.; Broseghini, E.; Carosi, F.; Molin, D.D.; Riefolo, M.; Fabbri, L.; Abeshi, A.; Fernandez, I.J.; Ferracin, M. A Systematic Review of Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Head and Neck Cancer of Unknown Primary: An Unmet Clinical Need. Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Lechner, M.; Liu, J.; Masterson, L.; Fenton, T.R. HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer: epidemiology, molecular biology and clinical management. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2022, 19, 306–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.; Basu, S.; Lall, S.P.; Ganti, A.K.; Batra, S.K.; Seshacharyulu, P. Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway in cancer therapy: What's new in 2023? Expert Opin Ther Targets 2023, 27, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krsek, A.; Baticic, L.; Sotosek, V.; Braut, T. The Role of Biomarkers in HPV-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Towards Precision Medicine. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaidou, A.C.; Batsaki, P.; Adamaki, M.; Goulielmaki, M.; Baxevanis, C.N.; Zoumpourlis, V.; Fortis, S.P. Promising Biomarkers in Head and Neck Cancer: The Most Clinically Important miRNAs. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.S.; Jiang, W.W.; Smith, I.; Poeta, L.M.; Begum, S.; Glazer, C.; Shan, S.; Westra, W.; Sidransky, D.; Califano, J.A. MicroRNA alterations in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2008, 123, 2791–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.; Su, W.; Mao, D.; Li, C.; Hu, X.; Deng, W.; Yao, Y.; Ji, Y. MicroRNA-21 induces cisplatin resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0267017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, H.; Li, Y.; Kang, M. Activation of miR-21 by STAT3 induces proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting PTEN gene. PLoS One 2014, 9, e109929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimie-Aghiorghiesei, A.I.; Pop-Bica, C.; Pintea, S.; Braicu, C.; Cojocneanu, R.; Zimța, A.A.; Gulei, D.; Slabý, O.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Prognostic Value of MiR-21: An Updated Meta-Analysis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). J Clin Med 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahabi, M.; Blandino, G.; Di Agostino, S. MicroRNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a possible challenge as biomarkers, determinants for the choice of therapy and targets for personalized molecular therapies. Transl Cancer Res 2021, 10, 3090–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobah, M.L.; Liongue, C.; Ward, A.C. SOCS Proteins in Immunity, Inflammatory Diseases, and Immune-Related Cancer. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021, 8, 727987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Gay, H.A.; Chernock, R.D.; Zhang, T.R.; Luo, J.; Thorstad, W.L.; Lewis, J.S., Jr.; Wang, X. A microRNA expression signature for the prognosis of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 2013, 119, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiyama, T.; Serada, S.; Fujimoto, M.; Ohkawara, T.; Komori, M.; Hyodo, M.; Naka, T. SOCS1 Gene Therapy for Head and Neck Cancers: An Experimental Study. Anticancer Res 2022, 42, 3361–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Tao, X.; Huang, F.; Wu, T.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Kuang, Z.; Cheng, B. Overexpression of miR-155 promotes the proliferation and invasion of oral squamous carcinoma cells by regulating BCL6/cyclin D2. Int J Mol Med 2016, 37, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, M.; Jayachandran, D.; Aishwarya, S.Y.; Md. Younus, P.; Venugopal, A.; Suresh Babu, H.W.; Ajay, E.; Sanjana, M.; Arul, N.; Balachandar, V. A new insight into the diverse facets of microRNA-31 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics 2022, 23, 149. [CrossRef]
- Hammouz, R.Y.; Kołat, D.; Kałuzińska, Ż.; Płuciennik, E.; Bednarek, A.K. MicroRNAs: Their Role in Metastasis, Angiogenesis, and the Potential for Biomarker Utility in Bladder Carcinomas. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Gholipour, M.; Taheri, M.; Shirvani Farsani, Z. MicroRNA profile in the squamous cell carcinoma: prognostic and diagnostic roles. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Che, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Fan, C.; Yuan, W. Potential Value of miR-221/222 as Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Biomarkers for Diseases. Front Immunol 2017, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.Q.; Ahmed, E.I.; Elareer, N.R.; Junejo, K.; Steinhoff, M.; Uddin, S. Role of miRNA-Regulated Cancer Stem Cells in the Pathogenesis of Human Malignancies. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raulf, N.; Lucarelli, P.; Thavaraj, S.; Brown, S.; Vicencio, J.M.; Sauter, T.; Tavassoli, M. Annexin A1 regulates EGFR activity and alters EGFR-containing tumour-derived exosomes in head and neck cancers. Eur J Cancer 2018, 102, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.C.; Gupta, A. MicroRNAs: potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of different cancers. Transl Cancer Res 2020, 9, 5798–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumbres, M. miRNAs and cancer: an epigenetics view. Mol Aspects Med 2013, 34, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sinha, T.; Panda, A.C. Regulation of microRNA by circular RNA. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: RNA 2024, 15, e1820. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Tie, Y.; Alu, A.; Ma, X.; Shi, H. Targeted therapy for head and neck cancer: signaling pathways and clinical studies. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2023, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, N.; Cao, L.; Xiao, D.; Ye, X.; Luo, E.; Zhang, Z. Down-regulation of miR-200c associates with poor prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol 2020, 25, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdigão-Henriques, R.; Petrocca, F.; Altschuler, G.; Thomas, M.P.; Le, M.T.; Tan, S.M.; Hide, W.; Lieberman, J. miR-200 promotes the mesenchymal to epithelial transition by suppressing multiple members of the Zeb2 and Snail1 transcriptional repressor complexes. Oncogene 2016, 35, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanli, F.; Tatar, A.; Gundogdu, B.; Karatas, O.F. IP3R1 dysregulation via mir-200c-3p/SSFA2 axis contributes to taxol resistance in head and neck cancer. Eur J Pharmacol 2024, 973, 176592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Hou, D.; Shi, Q.; Yang, S.; Li, Q. MicroRNA-375 Inhibits Growth and Enhances Radiosensitivity in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Targeting Insulin Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor. Cell Physiol Biochem 2017, 42, 2105–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozłowska-Masłoń, J.; Guglas, K.; Kolenda, T.; Lamperska, K.; Makałowska, I. miRNA in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: promising but still distant future of personalized oncology. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 2023, 28, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.A.; Moeng, S.; Sim, S.; Kuh, H.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, J.K. MicroRNA-Based Combinatorial Cancer Therapy: Effects of MicroRNAs on the Efficacy of Anti-Cancer Therapies. Cells 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganci, F.; Sacconi, A.; Manciocco, V.; Covello, R.; Benevolo, M.; Rollo, F.; Strano, S.; Valsoni, S.; Bicciato, S.; Spriano, G.; et al. Altered peritumoral microRNA expression predicts head and neck cancer patients with a high risk of recurrence. Mod Pathol 2017, 30, 1387–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Shi, Z.; Liu, H.; Ye, J. Identification of candidate plasma miRNA biomarkers for the diagnosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Future Sci OA 2024, 10, Fso928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laprovitera, N.; Riefolo, M.; Porcellini, E.; Durante, G.; Garajova, I.; Vasuri, F.; Aigelsreiter, A.; Dandachi, N.; Benvenuto, G.; Agostinis, F.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiling with a droplet digital PCR assay enables molecular diagnosis and prognosis of cancers of unknown primary. Mol Oncol 2021, 15, 2732–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarasamy, C.; Madhav, M.R.; Sabarimurugan, S.; Krishnan, S.; Baxi, S.; Gupta, A.; Gothandam, K.M.; Jayaraj, R. Prognostic Value of miRNAs in Head and Neck Cancers: A Comprehensive Systematic and Meta-Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerukala Sathipati, S.; Ho, S.Y. Survival associated miRNA signature in patients with head and neck carcinomas. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabzinski, J.; Maczynska, M.; Majsterek, I. MicroRNA as a Novel Biomarker in the Diagnosis of Head and Neck Cancer. Biomolecules 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, B.; Syeda, A.F.; Rynjah, D.; Hussain, S.M.; Chandra Bora, S.; Pegu, P.; Sahu, R.K.; Khan, J. Pharmacological impact of microRNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Prevailing insights on molecular pathways, diagnosis, and nanomedicine treatment. Front Pharmacol 2023, 14, 1174330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, S.M. Personalized medicine: a new horizon for medical therapy. Precis Clin Med 2018, 1, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.H.; Szczepski, K.; Al-Younis, I.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Jaremko, M. Fluxomics - New Metabolomics Approaches to Monitor Metabolic Pathways. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 805782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtivelman, E.; Beer, T.M.; Evans, C.P. Molecular pathways and targets in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 7217–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, X.; Fernández-Galan, E.; Fernández Bonifacio, R.; Foj, L. Emerging biomarkers in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Pharmgenomics Pers Med 2018, 11, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.; Young, R.J.; Rischin, D. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Genomics and emerging biomarkers for immunomodulatory cancer treatments. Semin Cancer Biol 2018, 52, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Molecular Subtype | Characteristic Features | Clinical Implications | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| HPV-positive |
Presence of HPV DNA, overexpression of p16, and absence of TP53 mutations. | Better response to treatment and prognosis compared to HPV-negative tumours. | [20] |
| Basal |
High expression of basal cell markers, EGFR amplification, and TP53 mutations. | Poor differentiation and worse prognosis. | [21] |
| Mesenchymal |
Features of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, expression of mesenchymal markers. | Resistance to chemotherapy and radiation therapy. | [22] |
| Atypical |
Mutations in NOTCH1, low HPV, and p16 expression. | Diverse prognosis, potential sensitivity to NOTCH inhibitors. | [23] |
| Classical |
High expression of genes involved in cell cycle regulation, notably cyclin D1 and CDK6. | Aggressive behaviour, potential targets for cell cycle inhibitors. | [24] |
| Immune-Related |
High infiltration of immune cells and expression of immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-L1. | Potential responsiveness to immunotherapy, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors. | [25] |
| Hypoxic |
Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), adaptation to low oxygen environments. | Poor prognosis, potential targets for therapies aimed at hypoxic conditions. | [26] |
| Metabolic |
Alterations in metabolic pathways, increased glycolysis (Warburg effect), overexpression of GLUT1. | Potential for targeting metabolic pathways, implications for metabolic inhibitors. | [27] |
| Key Protein/Gene | Role in Cancer | Clinical Relevance | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| HPV E6/E7 |
Oncogenic viral proteins that inactivate p53 and Rb, promoting cell cycle progression. | HPV status is a critical prognostic marker and determines treatment strategies. | [33] |
| EGFR |
Overexpressed in many HNCs, leading to increased cell proliferation. | Targeted by EGFR inhibitors like cetuximab, it predicts responsiveness to therapy. | [34] |
| TP53 |
Mutations lead to loss of tumour suppressor function, contributing to carcinogenesis. | Associated with poor prognosis and aggressive disease; potential target for therapy. | [35] |
| CDKN2A (p16) |
Tumour suppressor gene, loss contributes to cell cycle deregulation. | Frequently mutated or deleted in HNC, indicative of poor prognosis. | [36] |
| PIK3CA | Mutation activates the PI3K/AKT pathway, promoting tumorigenesis. | Target for PI3K inhibitors associated with therapeutic resistance. | [37] |
| TIMPs (Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases) | Regulate ECM remodelling and metastasis by inhibiting MMPs, potentially suppressing tumour progression. | Targets for therapy and markers for disease progression and response to treatment. | [38] |
| Gal-3 (Galectin-3) |
Involved in cell adhesion, migration, and tumour progression. | Potential marker for prognosis and therapeutic targeting. | [39] |
| MMPs (Matrix Metalloproteinases) | Facilitate tumour invasion and metastasis through ECM degradation. | Biomarkers for invasive potential and therapeutic targets. | [40] |
| Fibronectin |
Contributes to cell adhesion and migration, influencing tumour growth and metastasis. | Insights into tumour progression and potential therapeutic implications. | [41] |
| Gene | Role in Cancer Identified in Previous Studies | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| AURKA |
High expression is associated with cancer progression, dysregulated proliferation, and inhibition of apoptosis. It is a good predictor of OS, with overexpression representing a poor prognosis. | [42,43,44] |
| HMGA2 |
Overexpression increases tumour cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and metastasis. A good predictor of OS, with high levels indicating poor prognosis. | [45,46,47] |
| MMP1 |
Upregulation is associated with ECM degradation and consequent cancer-promoting invasiveness. Its expression correlates with T stage (TNM classification) and cancer progression. | [48,49] |
| PLAU |
Overexpression is associated with ECM degradation, an increased risk of developing HNC, and an upregulation of MMP1. Knockdown inhibits proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. | [49,50] |
| SERPINE1 |
Overexpression is associated with N stage (TNM classification), poor DFS, and the promotion of radiotherapy resistance. Inhibition leads to decreased cell proliferation and invasion. | [4,51,52] |
| Biomarker | Diagnostic Use | Prognostic Use | Potential Effectiveness |
Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPV DNA |
Identifies HPV-associated HNC | Indicates better prognosis and response to treatment in HPV-positive cases | Highly effective for subclassification and prognosis | [72] |
| EGFR |
Used for identifying tumours with EGFR overexpression | Associated with poor response to radiation and certain chemotherapies | Effective in selecting candidates for EGFR-targeted therapies | [73] |
| p16 |
Surrogate marker for HPV oncogenic activity | Suggests improved outcomes in HPV-positive HNC | Widely used, offers good prognostic value | [74] |
| miRNA name | P-value T-Test | FDR T-Test | Upregulated in | Tumor Log2 Mean Expression | Normal Log2Mean Expression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-21-5p | 8.64E-15 | 6.65E-13 | Tumour | 0 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-31-5p | 1.12E-07 | 8.23E-07 | Tumour | 0 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-221-3p | 1.14E-03 | 3.09E-03 | Tumour | 0 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-222-3p | 2.07E-06 | 1.02E-05 | Tumour | 0 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-196a-5p | 2.44E-17 | 8.45E-15 | Tumour | 0 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-200c-3p | 1.44E-02 | 3.12E-02 | Tumour | 0 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-375 | 1.77E-11 | 3.60E-10 | Normal | 0 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-145-5p | 2.44E-04 | 7.54E-04 | Normal | 0 | 0 |
| miRNA name | Log Rank P-value |
Log Rank FDR |
Z-score | Upregulated in | Deceased Log2 Mean Expression |
Living Log2 Mean Expression |
T-Test P-value |
T-Test FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-155-3p | 3.46E-02 | 3.77E-01 | 1.985 | Living | 0.52 | 0.65 | 3.33E-01 | 5.94E-01 |
| Gene | Gene Description | Correlation | Correlation P-value | Correlation FDR | miRDB Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAI14 | Retinoic acid-induced 14 | -0.106 | 1.73E-02 | 5.67E-01 | 82 |
| S1PR5 | Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 5 | -0.0983 | 2.73E-02 | 5.67E-01 | 76 |
| OSBPL10 | Oxysterol binding protein-like 10 | -0.0961 | 3.09E-02 | 5.67E-01 | 90 |
| METTL6 | Methyltransferase like 6 | -0.0876 | 4.93E-02 | 5.79E-01 | 63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





