Submitted:
25 September 2024
Posted:
26 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
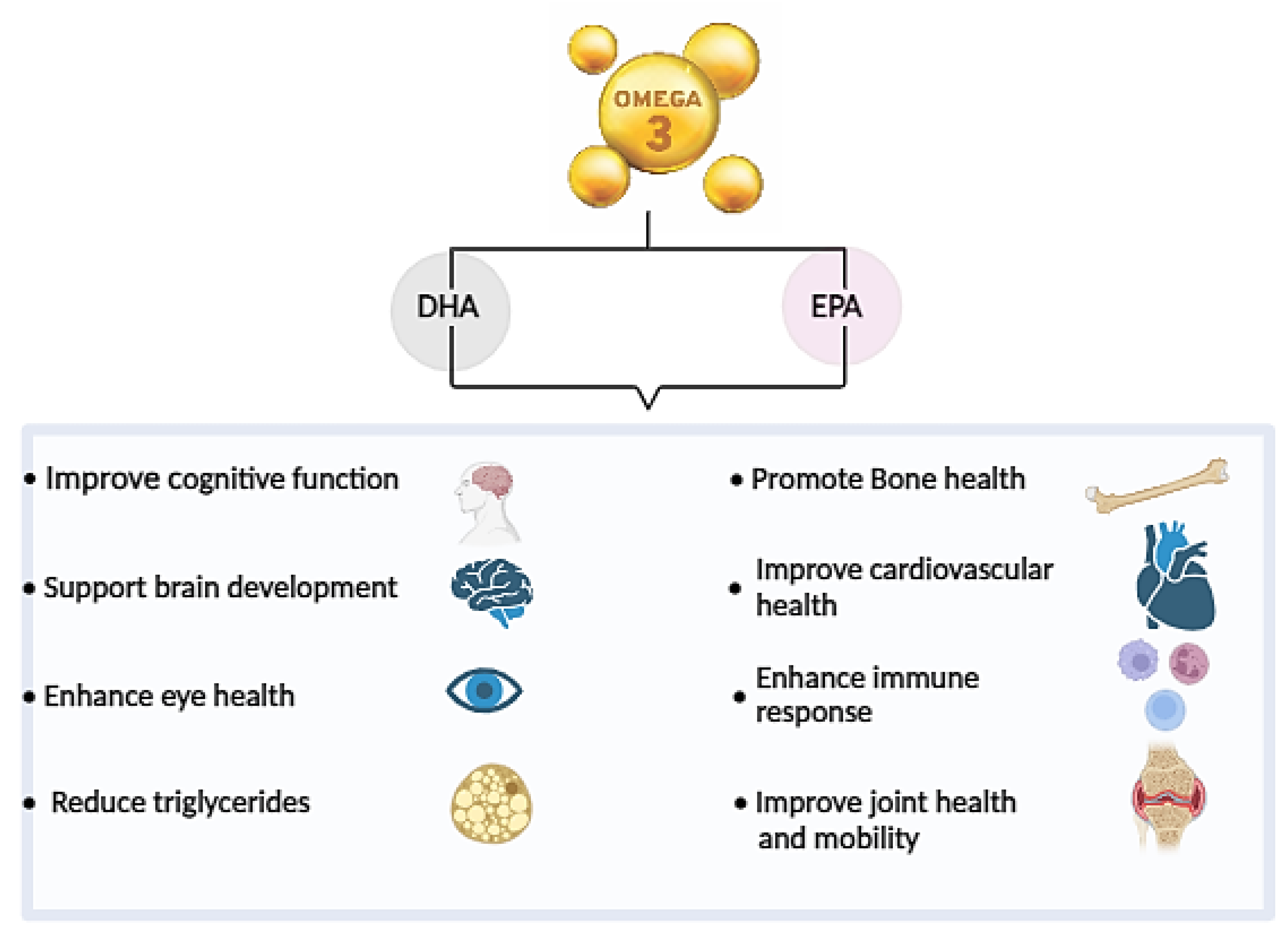
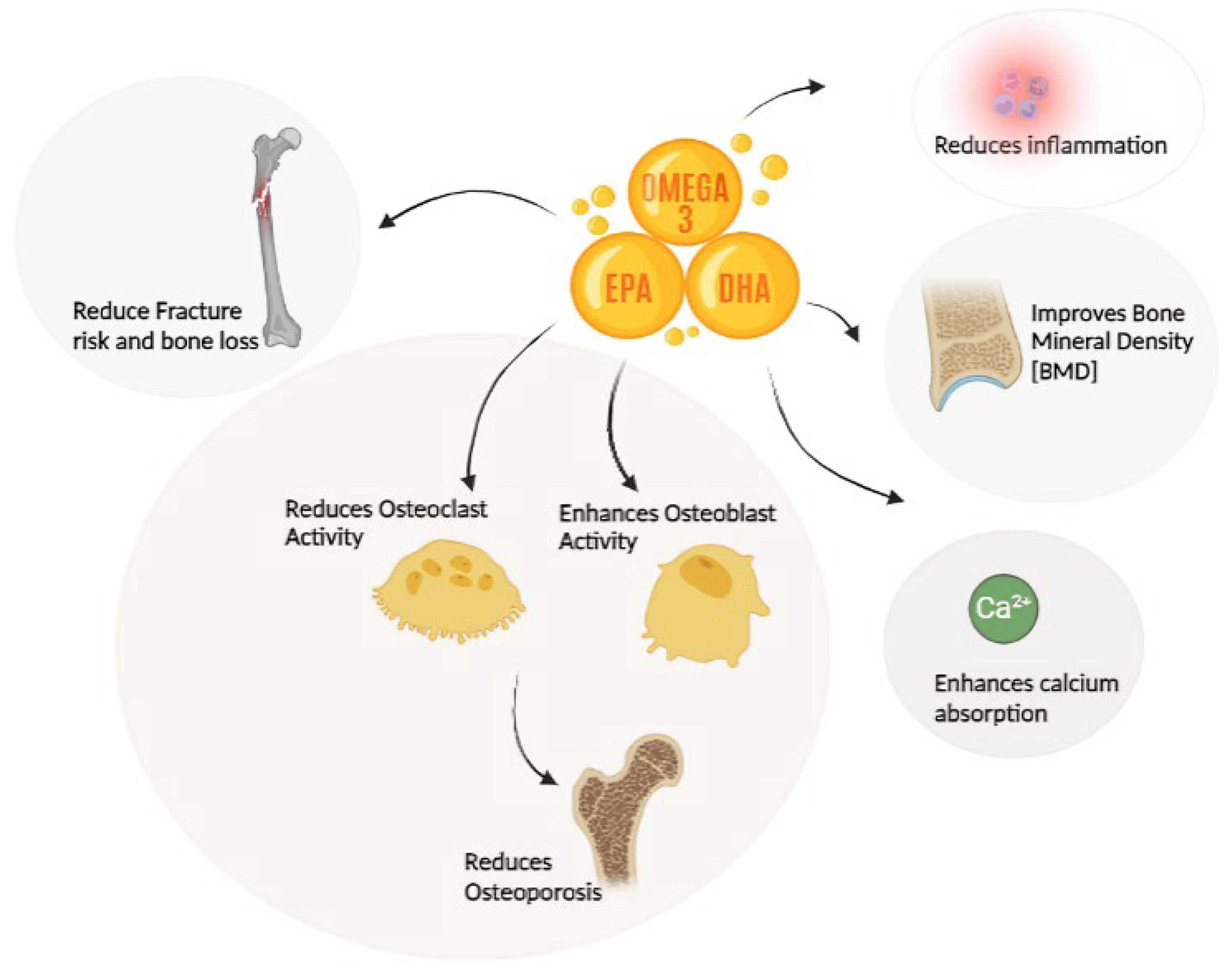
2. Omega -3 Fatty Acids and Bone Health
2.1. Preclinical Studies
2.2. Clinical Studies
2.2.1. Conflicting Evidences
2.2.2. Positive Results
2.3. Epidemiological Studies
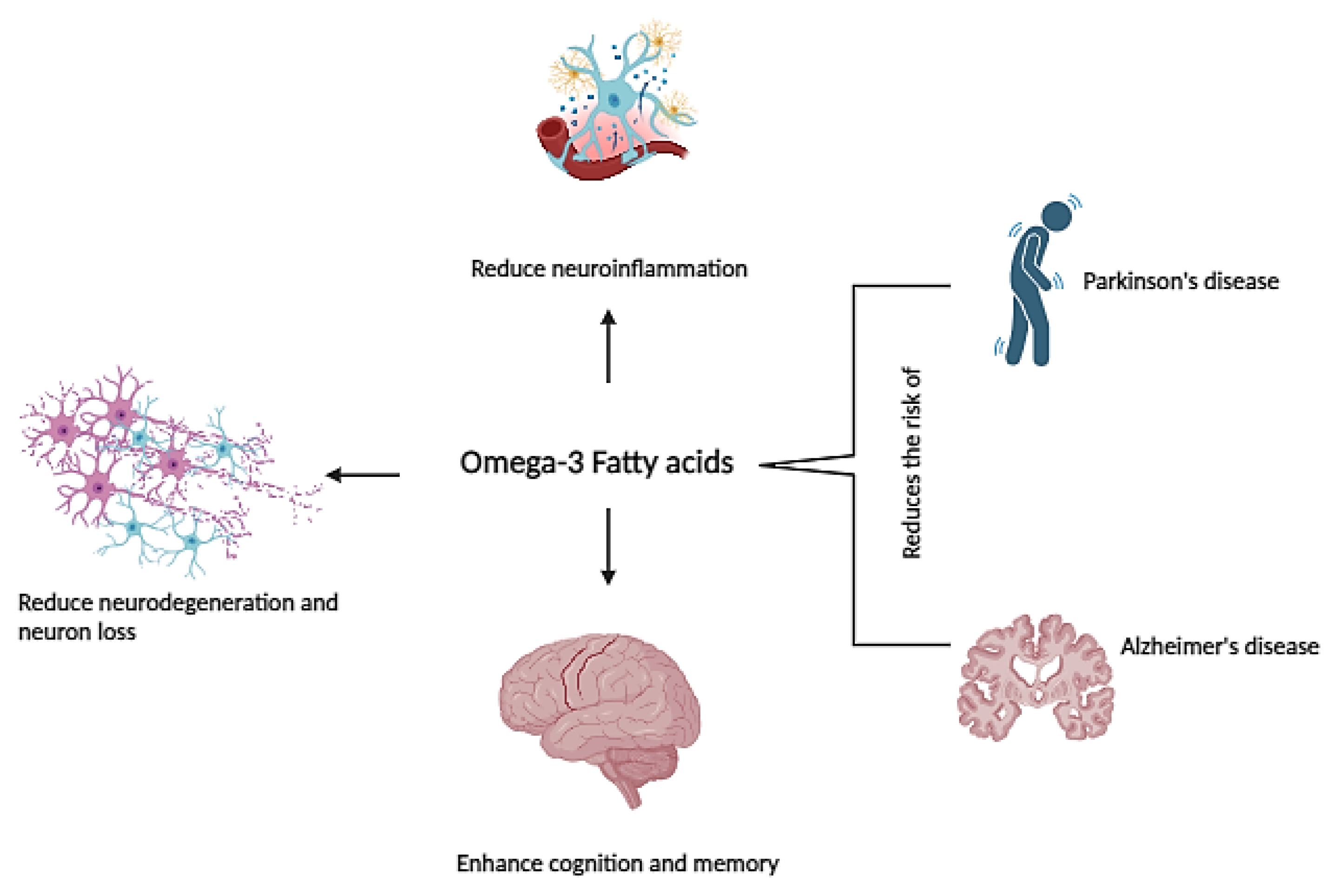
3. Omega -3 Fatty Acids and Aging
3.1. Preclinical Studies
3.2. Clinical Studies
3.3. Epidemiological Studies
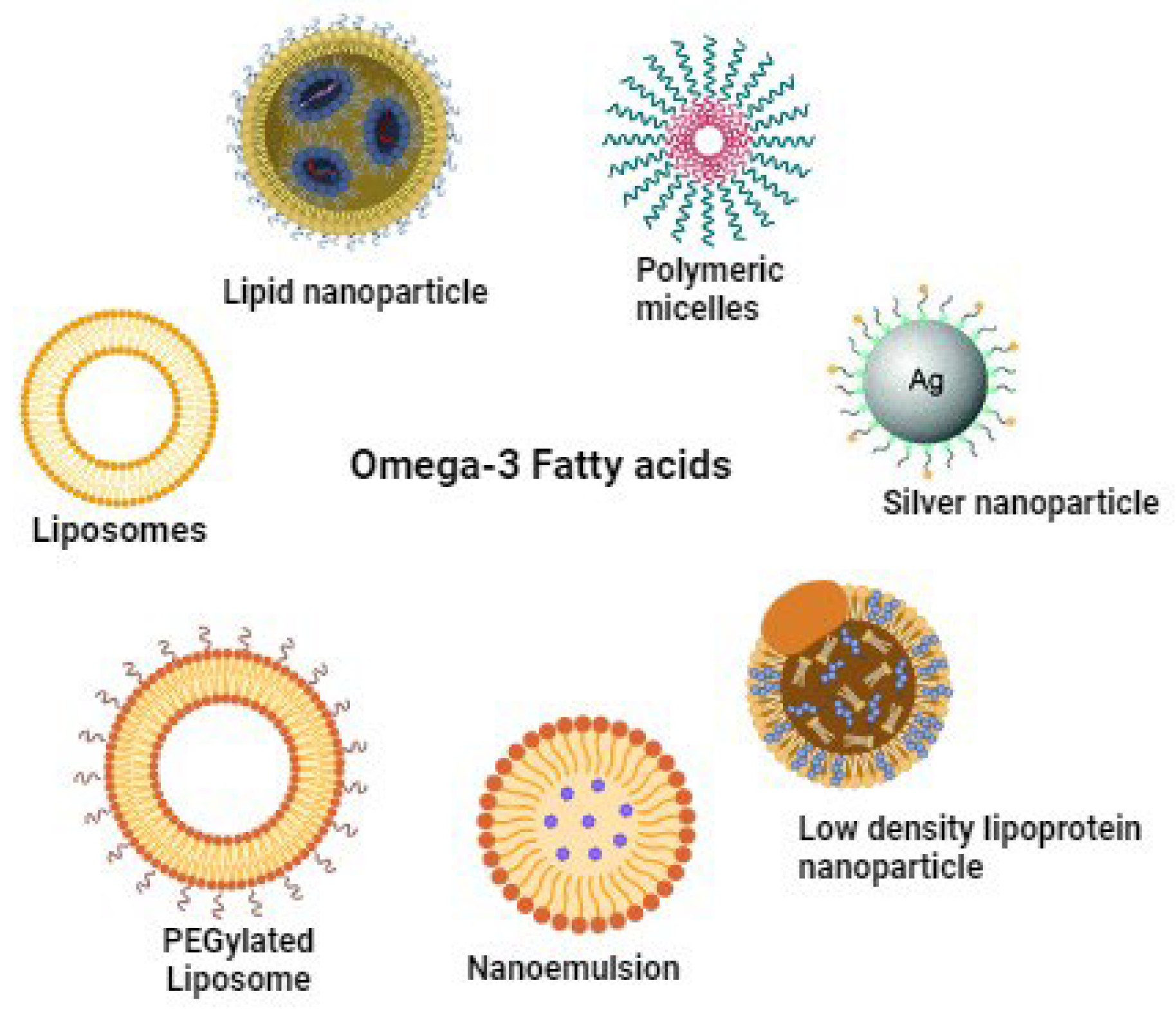
4. Challenges in Omega-3 Supplementation and Potential Solution
4.1. Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators
4.2. Enhanced Delivery of Omega-3 Fatty Acids through Nano Encapsulation
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gropper, S.S. The Role of Nutrition in Chronic Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gammone, M.A.; Riccioni, G.; Parrinello, G.; D’orazio, N. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Benefits and Endpoints in Sport. Nutrients 2018, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, M.; Arukha, A.P.; Bashir, T.; Yadav, D.; Prasad, G.B.K.S. All New Faces of Diatoms: Potential Source of Nanomaterials and Beyond. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.-B.; Wang, G.-X.; Cai, G.-Z.; Zhang, P.-X.; Liu, D.-L.; Chu, S.-F.; Li, H.-L.; Zhao, H.-X. Association between fatty acids intake and bone mineral density in adults aged 20–59: NHANES 2011–Front. Nutr. 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.; Afonso, C.; Bandarra, N.M. Dietary DHA and health: cognitive function ageing. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2016, 29, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyall, S.C.; Michael, G.J.; Michael-Titus, A.T. Omega-3 fatty acids reverse age-related decreases in nuclear receptors and increase neurogenesis in old rats. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freemantle, E.; Vandal, M.; Tremblay-Mercier, J.; Tremblay, S.; Blachère, J.-C.; Bégin, M.E.; Brenna, J.T.; Windust, A.; Cunnane, S.C. Omega-3 fatty acids, energy substrates, and brain function during aging. Prostaglandins, Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2006, 75, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlory, C.; Calder, P.C.; Nunes, E.A. The Influence of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Skeletal Muscle Protein Turnover in Health, Disuse, and Disease. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, C.I.; Zerbi, V.; Mutsaers, M.P.; de Jong, B.S.; Wiesmann, M.; Arnoldussen, I.A.; Geenen, B.; Heerschap, A.; Muskiet, F.A.; Jouni, Z.E.; et al. Impact of dietary n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on cognition, motor skills and hippocampal neurogenesis in developing C57BL/6J mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 26, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, E.J.; Gordon, W.C.; Jun, B.; Do, K.; Bazan, N.G. Retinal Pigment Epithelium and Photoreceptor Preconditioning Protection Requires Docosanoid Signaling. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 901–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzolino, D.; Bertoni, C.; De Cosmi, V.; Spolidoro, G.C.I.; Agostoni, C.; Lucchi, T.; Mazzocchi, A. Omega-3 polyunsatured fatty acids and physical performance across the lifespan: a narrative review. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1414132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Sun, D.; Rahman, M.; Fernandes, G. Different ratios of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic omega-3 fatty acids in commercial fish oils differentially alter pro-inflammatory cytokines in peritoneal macrophages from C57BL/6 female mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2006, 18, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Ambigaipalan, P. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Health Benefits. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 345–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adarme-Vega, T.C.; Lim, D.K.Y.; Timmins, M.; Vernen, F.; Li, Y.; Schenk, P.M. Microalgal biofactories: a promising approach towards sustainable omega-3 fatty acid production. Microb. Cell Factories 2012, 11, 96–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, A.H.; Crawford, M.A.; Reifen, R. Update on alpha-linolenic acid. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Kothapalli, K.S.; Brenna, J.T. Desaturase and elongase-limiting endogenous long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2016, 19, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Xie, F.; Huang, W.; Hu, M.; Yan, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, L. The review of alpha-linolenic acid: Sources, metabolism, and pharmacology. Phytotherapy Res. 2021, 36, 164–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, W.S. The omega-3 index: From biomarker to risk marker to risk factor. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2009, 11, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Products, N.A.A. (.E.P.O.D. Scientific Opinion on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and docosapentaenoic acid (DPA). EFSA J. [CrossRef]
- Longo, A.B.; E Ward, W. PUFAs, Bone Mineral Density, and Fragility Fracture: Findings from Human Studies. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2016, 7, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, B.Y.; Ward, W.E.; Kang, J.X.; Ma, D.W. Femur EPA and DHA are correlated with femur biomechanical strength in young fat-1 mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodin, S.; Lemay, A.; Jacques, H.; Légaré, F.; Forest, J.-C.; Masse, B. The Effects of Flaxseed Dietary Supplement on Lipid Profile, Bone Mineral Density, and Symptoms in Menopausal Women: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Wheat Germ Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, G.K.; Bu, S.Y. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation on Skeletal Muscle Mass and Strength in Adults: A Systematic Review. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2023, 12, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, T.B.; Song, X.; Reinders, I.; Lang, T.F.; E Garcia, M.; Siggeirsdottir, K.; Sigurdsson, S.; Gudnason, V.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Sigurdsson, G.; et al. Plasma phospholipid fatty acids and fish-oil consumption in relation to osteoporotic fracture risk in older adults: the Age, Gene/Environment Susceptibility Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.-J.; Kim, T.-H.; Byun, D.-W.; Park, Y. Positive Correlation between Erythrocyte Levels of n–3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Bone Mass in Postmenopausal Korean Women with Osteoporosis. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 60, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Högström, M.; Nordström, P.; Nordström, A. n−3 Fatty acids are positively associated with peak bone mineral density and bone accrual in healthy men: the NO2Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanis, J.A.; Norton, N.; Harvey, N.C.; Jacobson, T.; Johansson, H.; Lorentzon, M.; McCloskey, E.V.; Willers, C.; Borgström, F. SCOPE 2021: a new scorecard for osteoporosis in Europe. Arch. Osteoporos. 2021, 16, 1–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Rahman, M.; Banu, J.; Lawrence, R.A.; McGuff, H.S.; Garrett, I.; Fischbach, M.; Fernandes, G. Inhibition of Osteoporosis in Autoimmune Disease Prone MRL/Mpj-FaslprMice by N-3 Fatty Acids. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2005, 24, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhao, K.; Zha, X.; Du, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Opportunistic Screening Using Low-Dose CT and the Prevalence of Osteoporosis in China: A Nationwide, Multicenter Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2020, 36, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, A.; Frontera, G.; Cacheda, A.P.; Ros, I.; Narváez, J.; Marí, B.; Nolla, J.M. Epidemiology of osteoporosis and its determinants in physically active Majorcan elderly. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paunescu, A.-C.; Ayotte, P.; Dewailly. ; Dodin, S.; Pedersen, H.S.; Mulvad, G.; Côté, S. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and calcaneal ultrasound parameters among Inuit women from Nuuk (Greenland): a longitudinal study. Int. J. Circumpolar Heal. 2013, 72, 20988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-C.; Su, K.-P.; Cheng, T.-C.; Liu, H.-C.; Chang, C.-J.; Dewey, M.E.; Stewart, R.; Huang, S.-Y. The effects of omega-3 fatty acids monotherapy in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: A preliminary randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacology Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.-Y.; Cheng, C.; Satyanarayanan, S.K.; Chiu, L.-T.; Chien, Y.-C.; Chuu, C.-P.; Lan, T.-H.; Su, K.-P. Omega-3 fatty acids and blood-based biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Brain, Behav. Immun. 2022, 99, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2021 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures [J]. Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association. 2021, 17, 327–406. [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.Z.A.; Gleeson, P.A. The role of membrane trafficking in the processing of amyloid precursor protein and production of amyloid peptides in Alzheimer's disease. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 697–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, L.G.; James, M.J.; Proudman, S.M. Fish oil: what the prescriber needs to know. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, 202–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conquer, J.A.; Tierney, M.C.; Zecevic, J.; Bettger, W.J.; Fisher, R.H. Fatty acid analysis of blood plasma of patients with alzheimer's disease, other types of dementia, and cognitive impairment. Lipids 2000, 35, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Külzow, N.; Witte, A.V.; Kerti, L.; Grittner, U.; Schuchardt, J.P.; Hahn, A.; Flöel, A. Impact of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation on Memory Functions in Healthy Older Adults. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2016, 51, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.Z.; Ahmad, J.; Zafar, S.; Warsi, M.H.; A Abdel-Wahab, B.; Akhter, S.; Alam, A. Omega-3 fatty acids as adjunctive therapeutics: prospective of nanoparticles in its formulation development. Ther. Deliv. 2020, 11, 851–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoud, S.; Bou-Maroun, E.; Dujourdy, L.; Waschatko, G.; Billecke, N.; Cayot, P. Fast and direct analysis of oxidation levels of oil-in-water emulsions using ATR-FTIR. Food Chem. 2019, 293, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Öztürk, B. Utilization of Nanotechnology to Improve the Handling, Storage and Biocompatibility of Bioactive Lipids in Food Applications. Foods 2021, 10, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, M.D.; Patel, J.; Staton, K.; Martindale, R.G.; Moore, F.A.; Upchurch, G.R. Can Specialized Pro-resolving Mediators Deliver Benefit Originally Expected from Fish Oil? Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2018, 20, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florencio-Silva, R.; da Silva Sasso, G.R.; Sasso-Cerri, E.; Simões, M.J.; Cerri, P.S. Biology of Bone Tissue: Structure, Function, and Factors That Influence Bone Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 421746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, T.A.; Aronow, M.; Shalhoub, V.; Barone, L.M.; Wilming, L.; Tassinari, M.S.; Kennedy, M.B.; Pockwinse, S.; Lian, J.B.; Stein, G.S. Progressive development of the rat osteoblast phenotype in vitro: Reciprocal relationships in expression of genes associated with osteoblast proliferation and differentiation during formation of the bone extracellular matrix. J. Cell. Physiol. 1990, 143, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, M.; Coetzee, M.; Haag, M.; Weiler, H. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids: Selected mechanisms of action on bone. Prog. Lipid Res. 2010, 49, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado-Díaz, A.; Ferreiro-Vera, C.; Priego-Capote, F.; Dorado, G.; Luque-De-Castro, M.D.; Quesada-Gómez, J.M. Effects of arachidonic acid on the concentration of hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids in culture media of mesenchymal stromal cells differentiating into adipocytes or osteoblasts. Genes Nutr. 2013, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbecki, J.; Bobiński, R.; Dutka, M.; Korbecki, J.; Bobiński, R.; Dutka, M.; Korbecki, J.; Bobiński, R.; Dutka, M. Self-regulation of the inflammatory response by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zha, Y.; Lei, H.; Xu, X. MRI Study on the Changes of Bone Marrow Microvascular Permeability and Fat Content after Total-Body X-Ray Irradiation. Radiat. Res. 2018, 189, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Jia, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z. Omega-3 fatty acids reduce post-operative risk of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism after surgery for elderly patients with proximal femoral fractures: a randomized placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 2089–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, A.B.; E Ward, W. PUFAs, Bone Mineral Density, and Fragility Fracture: Findings from Human Studies. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2016, 7, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawata, K.; Yamauchi, M.; Takaoka, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sugimoto, T. Association of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Intake with Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2013, 93, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yu, X.; Ma, D. Effect of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid on bone health: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 10, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Zheng, T.; Zhao, B. Cytokine-mediated immunomodulation of osteoclastogenesis. Bone 2022, 164, 116540–116540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.G.; Contaifer, D.; Madurantakam, P.; Carbone, S.; Price, E.T.; Van Tassell, B.; Brophy, D.F.; Wijesinghe, D.S. Dietary Bioactive Fatty Acids as Modulators of Immune Function: Implications on Human Health. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, B.A.; Li, Y.; Allen, K.G.D.; Hoffmann, W.E.; Seifert, M.F. Dietary Ratio of (n-6)/(n-3) Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Alters the Fatty Acid Composition of Bone Compartments and Biomarkers of Bone Formation in Rats. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pilbeam, C.; Pan, L.; Breyer, R.; Raisz, L. Effects of prostaglandin E2 on gene expression in primary osteoblastic cells from prostaglandin receptor knockout mice. Bone 2002, 30, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, B.; Budakovic, A.; Nassuato, M.A.; Vezzoli, G.; Manzato, E.; Luisetto, G.; Zaninotto, M. Plasma phospholipid arachidonic acid content and calcium metabolism in idiopathic calcium nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajarabille, N.; Díaz-Castro, J.; Hijano, S.; López-Frías, M.; López-Aliaga, I.; Ochoa, J.J. A New Insight to Bone Turnover: Role of ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 589641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, B.Y.; Cohen, D.J.; Ward, W.E.; Ma, D.W. Investigating the Role of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Bone Development Using Animal Models. Molecules 2013, 18, 14203–14227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Rahman, M.; Sun, D.; Fernandes, G. Effect of fish oil on bone mineral density in aging C57BL/6 female mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2006, 18, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Díaz, A.; Santiago-Mora, R.; Dorado, G.; Quesada-Gómez, J.M. The omega-6 arachidonic fatty acid, but not the omega-3 fatty acids, inhibits osteoblastogenesis and induces adipogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells: potential implication in osteoporosis. Osteoporos. Int. 2012, 24, 1647–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, S.R.; Pierson, D.; Mehta, S.; Gonda, S.; Smith, S.M. Capacity of omega-3 fatty acids or eicosapentaenoic acid to counteract weightlessness-induced bone loss by inhibiting NF-κB activation: From cells to bed rest to astronauts. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banu, J.; Bhattacharya, A.; Rahman, M.; Kang, J.X.; Fernandes, G. Endogenously produced n-3 fatty acids protect against ovariectomy induced bone loss in fat-1 transgenic mice. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2010, 28, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Krishnan, A.; Zaman, K.; Lawrence, R.; Bhattacharya, A.; Fernandes, G. Dietary n-3 Fatty Acids Decrease Osteoclastogenesis and Loss of Bone Mass in Ovariectomized Mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2003, 18, 1206–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, H.; Barrios, J.A.; Shea, J.E.; Miller, S.C. Dietary fish oil results in a greater bone mass and bone formation indices in aged ovariectomized rats. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2008, 26, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, R.C.; Moughan, P.J.; Kruger, M.C. Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Regulation of Bone Metabolism. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 232, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, B.A.; Li, Y.; Seifert, M.F. Dietary ratio of n-6/n-3 PUFAs and docosahexaenoic acid: actions on bone mineral and serum biomarkers in ovariectomized rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 17, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, E.B.; Alderghaffar, M.; Wauquier, F.; Coxam, V.; Demontiero, O.; Vogrin, S.; Wittrant, Y.; Duque, G. The effects of dietary fatty acids on bone, hematopoietic marrow and marrow adipose tissue in a murine model of senile osteoporosis. Aging 2019, 11, 7938–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Bhattacharya, A.; Fernandes, G. Docosahexaenoic acid is more potent inhibitor of osteoclast differentiation in RAW 264.7 cells than eicosapentaenoic acid. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 214, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, Y.H.; Chen, C.; Sweeney, K.M.; Kim, M.; Voy, B.H.; Wilson, J.L.; Kim, W.K. The effects of maternal fish oil supplementation rich in n-3 PUFA on offspring-broiler growth performance, body composition and bone microstructure. PLOS ONE 2022, 17, e0273025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Chandrasekar, B.; Rahman, M.; Banu, J.; Kang, J.X.; Fernandes, G. Inhibition of inflammatory response in transgenic fat-1 mice on a calorie-restricted diet. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, S.S. NF-κB as a therapeutic target in chronic inflammation: recent advances. Mol. Med. Today 2000, 6, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicero, A.F.; Colletti, A. Krill oil: evidence of a new source of polyunsaturated fatty acids with high bioavailability. Clin. Lipidol. 2015, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, D.; Park, S.-J.; Yun, J.M.; Oh, D.H.; Lee, J. Antarctic Krill Oil Ameliorates Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Irregularities in Articular Cartilage and Inflammatory Response in the Rat Models of Osteoarthritis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Han, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, C. Antarctic Krill Oil improves articular cartilage degeneration via activating chondrocyte autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis in osteoarthritis mice. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 46, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, S.-K.; Kim, J.-K.; Chun, Y.-S.; Song, C.-H. Anti-Osteoarthritic Effects of Antarctic Krill Oil in Primary Chondrocytes and a Surgical Rat Model of Knee Osteoarthritis. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Z.; Li, Z.; Fu, M.; Xue, C.; Wang, J. A low proportion n-6/n-3 PUFA diet supplemented with Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) oil protects against osteoarthritis by attenuating inflammation in ovariectomized mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 6766–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.Y.; Cesari, M.; Anton, S.; Marzetti, E.; Giovannini, S.; Seo, A.Y.; Carter, C.; Yu, B.P.; Leeuwenburgh, C. Molecular inflammation: Underpinnings of aging and age-related diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2008, 8, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.X.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Kang, Z.B. Fat-1 mice convert n-6 to n-3 fatty acids. Nature 2004, 427, 504–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.-J.; Wang, L.; Jin, D.-D.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Chen, T.-Y.; Jia, C.-H.; Wang, Y.; Zhen, X.-C.; Huang, B.; Yan, B.; et al. Enhancement of the synthesis of n-3 PUFAs infat-1transgenic mice inhibits mTORC1 signalling and delays surgically induced osteoarthritis in comparison with wild-type mice. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 73, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Bai, X.; Dai, Y.; Dong, P.; Wang, J. Different n-6/n-3 PUFA diets with fish oil attenuated osteoarthritis in ovariectomized mice via targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome. Food Biosci. 2022, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Bhattacharya, A.; Banu, J.; Kang, J.X.; Fernandes, G. Endogenous n-3 fatty acids protect ovariectomy induced bone loss by attenuating osteoclastogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 1833–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, S.; Mei, F.; Zhao, M.; Xia, G.; Shen, X. Tilapia nilotica Head Lipids Improved Bone Loss by Regulating Inflammation and Serum Metabolism Through Gut Microbiota in Ovariectomized Rats. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 792793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cifuentes-Mendiola, S.E.; Moreno-Fierros, L.; González-Alva, P.; García-Hernández, A.L. Docosahexaenoic acid improves altered mineralization proteins, the decreased quality of hydroxyapatite crystals and suppresses oxidative stress induced by high glucose. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugno, C.; Kizhakayil, D.; Calzone, R.; Rahman, S.M.; Halade, G.V.; Rahman, M. Omega-3 fatty acid-rich fish oil supplementation prevents rosiglitazone-induced osteopenia in aging C57BL/6 mice and in vitro studies. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, A.; Iitsuka, N.; Tsukamoto, I. Fish oil suppresses bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis through decreased expression of M-CSF, PU.1, MITF and RANK in ovariectomized rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Saleh, H.; Ouhtit, A.; Halade, G.V.; Rahman, M. Bone Benefits of Fish Oil Supplementation Depend on its EPA and DHA Content. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anez-Bustillos, L.; Cowan, E.; Cubria, M.B.; Villa-Camacho, J.C.; Mohamadi, A.; Dao, D.T.; Pan, A.; Fell, G.L.; Baker, M.A.; Nandivada, P.; et al. Effects of dietary omega-3 fatty acids on bones of healthy mice. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 38, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbahnasawy, A.S.; Valeeva, E.R.; El-Sayed, E.M.; Stepanova, N.V. Protective effect of dietary oils containing omega-3 fatty acids against glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. J. Nutr. Heal. 2019, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhong, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, P.; Shen, H. Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits bone remodeling and vessel formation in the osteochondral unit in a rat model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaengler, S.; Sadlon, A.; Molino, C.D.G.R.C.; Willett, W.C.; Manson, J.E.; Vellas, B.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Von Eckardstein, A.; Ruschitzka, F.; Rizzoli, R.; et al. Effects of vitamin D, omega-3 and a simple strength exercise programme in cardiovascular disease prevention: The DO-HEALTH randomized controlled trial. J. Nutr. Heal. Aging 2024, 28, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, H.S.; Eide, I.A.; Jenssen, T.; Åsberg, A.; Bollerslev, J.; Godang, K.; Hartmann, A.; Schmidt, E.B.; Svensson, M. Marine n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Bone Mineral Density in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggio, B.; Budakovic, A.; Ferraro, A.; Checchetto, S.; Priante, G.; Musacchio, E.; Manzato, E.; Zaninotto, M.; Maresca, M.-C. Relationship between Plasma Phospholipid Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Composition and Bone Disease in Renal Transplantation. Transplantation 2005, 80, 1349–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassey, E.J.; Littlewood, J.J.; Rothwell, M.C.; Pye, D.W. Lack of effect of supplementation with essential fatty acids on bone mineral density in healthy pre- and postmenopausal women:two randomized controlled trials of Efacal® v. calcium alone. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 83, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBoff, M.S.; Chou, S.H.; Murata, E.M.; Donlon, C.M.; Cook, N.R.; Mora, S.; Lee, I.-M.; Kotler, G.; Bubes, V.; E Buring, J.; et al. Effects of Supplemental Vitamin D on Bone Health Outcomes in Women and Men in the VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL). J. Bone Miner. Res. 2020, 35, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaram, S.; Yip, E.L.; Reghunathan, R.; Mohan, S.; Sabaté, J. Effect of Altering Dietary n-6:n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Ratio with Plant and Marine-Based Supplement on Biomarkers of Bone Turnover in Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Hill, C.L.; Lester, S.; Ruediger, C.D.; Battersby, R.; Jones, G.; Cleland, L.G.; March, L.M. Supplementation with omega-3 fish oil has no effect on bone mineral density in adults with knee osteoarthritis: a 2-year randomized controlled trial. Osteoporos. Int. 2015, 27, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, A.M.; Crotty, M.; Cleland, L.G.; James, M.J.; Fraser, R.J.; Cobiac, L.; Miller, M.D. Fish oil administration in older adults with cardiovascular disease or cardiovascular risk factors: Is there potential for adverse events? A systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 4371–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleton, K.M.; Fraser, W.D.; Rogers, P.J.; Ness, A.R.; Tobias, J.H. Supplementation with a low–moderate dose ofn-3 long-chain PUFA has no short-term effect on bone resorption in human adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 105, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebble, T.M.; Stroud, M.A.; Wootton, S.A.; Calder, P.C.; Fine, D.R.; Mullee, M.A.; Moniz, C.; Arden, N.K. High-dose fish oil and antioxidants in Crohn's disease and the response of bone turnover: a randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 94, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razny, U.; Goralska, J.; Calder, P.C.; Gruca, A.; Childs, C.E.; Kapusta, M.; Slowinska-Solnica, K.; Dembinska-Kiec, A.; Solnica, B.; Malczewska-Malec, M. The Effect of Caloric Restriction with and without n-3 PUFA Supplementation on Bone Turnover Markers in Blood of Subjects with Abdominal Obesity: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stammers, T.; Sibbald, B.; Freeling, P. FISH OIL IN OSTEOARTHRITIS. Lancet 1989, 334, 503–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, M.C.; Coetzer, H.; de Winter, R.; Gericke, G.; van Papendorp, D.H. Calcium, gamma-linolenic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid supplementation in senile osteoporosis. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 1998, 10, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchins-Wiese, H.L.; Picho, K.; Watkins, B.A.; Li, Y.; Tannenbaum, S.; Claffey, K.; Kenny, A.M. High-Dose Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid Supplementation Reduces Bone Resorption in Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Survivors on Aromatase Inhibitors: A Pilot Study. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 66, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Veigas, J.M.; Williams, P.J.; Fernandes, G. DHA is a more potent inhibitor of breast cancer metastasis to bone and related osteolysis than EPA. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 141, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papandreou, P.; Agakidis, C.; Scouroliakou, M.; Karagiozoglou-Lampoudi, T.; Kaliora, A.; Kalogeropoulos, N.; Siahanidou, T. Early Postnatal Changes of Bone Turnover Biomarkers in Very Low-Birth-Weight Neonates—The Effect of Two Parenteral Lipid Emulsions with Different Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Content: A Randomized Double-Blind Study. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 44, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichinose, T.; Matsuzaki, K.; Kato, M.; Tanabe, Y.; Tachibana, N.; Morikawa, M.; Kato, S.; Ohata, S.; Ohno, M.; Wakatsuki, H.; et al. Intake of Docosahexaenoic Acid-Enriched Milk Beverage Prevents Age-Related Cognitive Decline and Decreases Serum Bone Resorption Marker Levels. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 1829–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonolla-Joya, J.; Reyes-García, R.; García-Martín, A.; López-Huertas, E.; Muñoz-Torres, M. Daily Intake of Milk Enriched with n-3 Fatty Acids, Oleic Acid, and Calcium Improves Metabolic and Bone Biomarkers in Postmenopausal Women. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2016, 35, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Bautista, E.; Muñoz-Torres, M.; Fonolla, J.; Quesada, M.; Poyatos, A.; Lopez-Huertas, E. Improvement of bone formation biomarkers after 1-year consumption with milk fortified with eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, oleic acid, and selected vitamins. Nutr. Res. 2010, 30, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-J.; Yoo, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Kwak, M.K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Hamrick, M.W.; Isales, C.M.; Ahn, S.H.; Koh, J.-M. Association of blood n-3 fatty acid with bone mass and bone marrow TRAP-5b in the elderly with and without hip fracture. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchard, T.S.; Ing, S.W.; Lu, B.; A Belury, M.; Johnson, K.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Jackson, R.D. The association of red blood cell n-3 and n-6 fatty acids with bone mineral density and hip fracture risk in the women's health initiative. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 28, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartibian, B.; Maleki, B.H.; Kanaley, J.; Sadeghi, K. Long-term aerobic exercise and omega-3 supplementation modulate osteoporosis through inflammatory mechanisms in post-menopausal women: a randomized, repeated measures study. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 8, 71–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlint, S.J.; Ried, K. Efficacy and tolerability of calcium, vitamin D and a plant-based omega-3 oil for osteopenia: A pilot RCT. Maturitas 2011, 71, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabour, H.; Larijani, B.; Vafa, M.R.; Hadian, M.R.; Heshmat, R.; Meybodi, H.A.; Razavi, H.E.; Javidan, A.N.; Shidfar, F. The effects of n-3 fatty acids on inflammatory cytokines in osteoporotic spinal cord injured patients: A randomized clinical trial. 2012, 17, 322–327.
- I Smith, G.; Julliand, S.; Reeds, D.N.; Sinacore, D.R.; Klein, S.; Mittendorfer, B. Fish oil–derived n−3 PUFA therapy increases muscle mass and function in healthy older adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Hossain, S.; Wakatsuki, H.; Tanabe, Y.; Ohno, M.; Kato, S.; Shido, O.; Hashimoto, M. Perilla seed oil improves bone health by inhibiting bone resorption in healthy Japanese adults: A 12-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Phytotherapy Res. 2023, 37, 2230–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaengler, S.; Sadlon, A.; Molino, C.D.G.R.C.; Willett, W.C.; Manson, J.E.; Vellas, B.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Von Eckardstein, A.; Ruschitzka, F.; Rizzoli, R.; et al. Effects of vitamin D, omega-3 and a simple strength exercise programme in cardiovascular disease prevention: The DO-HEALTH randomized controlled trial. J. Nutr. Heal. Aging 2024, 28, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Griel, A.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Hilpert, K.F.; Zhao, G.; West, S.G.; Corwin, R.L. An increase in dietary n-3 fatty acids decreases a marker of bone resorption in humans. Nutr. J. 2007, 6, 2–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.; Park, Y. The Association between the Consumption of Fish/Shellfish and the Risk of Osteoporosis in Men and Postmenopausal Women Aged 50 Years or Older. Nutrients 2016, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.; Woo, J.; Leung, J. Effects of food groups and dietary nutrients on bone loss in elderly Chinese population. J. Nutr. Heal. Aging 2011, 15, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalloua, P.A.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Terwedow, H.; Zang, T.; Wu, D.; Tang, G.; Li, Z.; Hong, X.; Azar, S.T.; Wang, B.; et al. Impact of seafood and fruit consumption on bone mineral density. Maturitas 2006, 56, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.; Kim, Y.; Kweon, S.; Kim, S.; Yun, S.; Park, S.; Lee, Y.-K.; Kim, Y.-T.; Park, O.; Jeong, E.K. Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 20th anniversary: accomplishments and future directions. Epidemiology Heal. 2021, 43, e2021025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahns, L.; Raatz, S.K.; Johnson, L.K.; Kranz, S.; Silverstein, J.T.; Picklo, M.J. Intake of Seafood in the US Varies by Age, Income, and Education Level but Not by Race-Ethnicity. Nutrients 2014, 6, 6060–6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, J.K.; Mozaffarian, D.; A Cauley, J.; Mukamal, K.J.; Robbins, J.; Siscovick, D.S. Fish consumption, bone mineral density, and risk of hip fracture among older adults: The cardiovascular health study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 1972–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Ho, S.C.; Lam, S.S. Higher sea fish intake is associated with greater bone mass and lower osteoporosis risk in postmenopausal Chinese women. Osteoporos. Int. 2009, 21, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Xue, W.-Q.; Wu, B.-H.; He, M.-G.; Xie, H.-L.; Ouyang, W.-F.; Tu, S.-L.; Chen, Y.-M. Higher Fish Intake Is Associated with a Lower Risk of Hip Fractures in Chinese Men and Women: A Matched Case-Control Study. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e56849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Brutto, O.H.; Mera, R.M.; Rumbea, D.A.; Arias, E.E.; Guzmán, E.J.; Sedler, M.J. On the association between dietary oily fish intake and bone mineral density in frequent fish consumers of Amerindian ancestry. The three villages study. Arch. Osteoporos. 2024, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benetou, V.; Orfanos, P.; Zylis, D.; Sieri, S.; Contiero, P.; Tumino, R.; Giurdanella, M.C.; Peeters, P.H.M.; Linseisen, J.; Nieters, A.; et al. Diet and hip fractures among elderly Europeans in the EPIC cohort. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 65, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavado-García, J.; Roncero-Martin, R.; Moran, J.M.; Pedrera-Canal, M.; Aliaga, I.; Leal-Hernandez, O.; Rico-Martin, S.; Canal-Macias, M.L. Long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid dietary intake is positively associated with bone mineral density in normal and osteopenic Spanish women. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0190539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, F.; Liu, M.; Huang, X.; Xue, S.; Zhang, X.; Hao, H.; Zhang, J. Association between omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and osteoarthritis: results from the NHANES 2003–2016 and Mendelian randomization study. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2024, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, T.; Ohta, H.; Onoe, Y.; Tsugawa, N.; Shiraki, M. Intake of omega-3 fatty acids contributes to bone mineral density at the hip in a younger Japanese female population. Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 2887–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feehan, O.; Magee, P.J.; Pourshahidi, L.K.; Armstrong, D.J.; Slevin, M.M.; Allsopp, P.J.; Conway, M.C.; Strain, J.J.; McSorley, E.M. Associations of long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids with bone mineral density and bone turnover in postmenopausal women. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 62, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, E.K.; Kiel, D.P.; Roubenoff, R.; Schaefer, E.J.; Cupples, L.A.; Tucker, K.L. Protective effects of fish intake and interactive effects of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid intakes on hip bone mineral density in older adults: the Framingham Osteoporosis Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, E.K.; Kiel, D.P.; Roubenoff, R.; Schaefer, E.J.; Cupples, L.A.; Tucker, K.L. Dietary Intakes of Arachidonic Acid and α-Linolenic Acid Are Associated with Reduced Risk of Hip Fracture in Older Adults. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järvinen, R.; Tuppurainen, M.; Erkkilä, A.T.; Penttinen, P.; Kärkkäinen, M.; Salovaara, K.; Jurvelin, J.S.; Kröger, H. Associations of dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids with bone mineral density in elderly women. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 66, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haveman-Nies, A.; de Groot, L.C.; van Staveren, W.A. Dietary quality, lifestyle factors and healthy ageing in Europe: the SENECA study. Age and Ageing 2003, 32, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Dan, X.; Babbar, M.; Wei, Y.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker-Drob, E.M. Cognitive Aging and Dementia: A Life-Span Perspective. Annu. Rev. Dev. Psychol. 2019, 1, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzorou, M.; Vadikolias, K.; Pavlidou, E.; Tryfonos, C.; Vasios, G.; Serdari, A.; Giaginis, C. Mediterranean diet adherence is associated with better cognitive status and less depressive symptoms in a Greek elderly population. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 33, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zussy, C.; John, R.; Urgin, T.; Otaegui, L.; Vigor, C.; Acar, N.; Canet, G.; Vitalis, M.; Morin, F.; Planel, E.; et al. Intranasal Administration of Nanovectorized Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Improves Cognitive Function in Two Complementary Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurko-Mauro, K.; Alexander, D.D.; Van Elswyk, M.E. Docosahexaenoic Acid and Adult Memory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0120391–e0120391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyall, S.C. Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and the brain: a review of the independent and shared effects of EPA, DPA and DHA. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 52–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troesch, B.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Laviano, A.; Rolland, Y.; Smith, A.D.; Warnke, I.; Weimann, A.; Calder, P.C. Expert Opinion on Benefits of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids (DHA and EPA) in Aging and Clinical Nutrition. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.-C.; Frangou, S.; Chang, C.-J.; Chiu, W.-C.; Liu, H.-C.; Sun, I.-W.; Liu, S.-I.; Lu, M.-L.; Chen, C.-H.; Huang, S.-Y.; et al. Associations between n−3 PUFA concentrations and cognitive function after recovery from late-life depression. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, I.; Arola, L.; Caimari, A.; Escoté, X.; Puiggròs, F. Structured Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Improvement of Cognitive Function during Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plourde, M.; Cunnane, S.C. Extremely limited synthesis of long chain polyunsaturates in adults: implications for their dietary essentiality and use as supplements. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 32, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Halade, G.V.; Bhattacharya, A.; Fernandes, G. The Fat-1 Transgene in Mice Increases Antioxidant Potential, Reduces Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Levels, and Enhances PPARγ and SIRT-1 Expression on a Calorie Restricted Diet. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2009, 2, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halade, G.V.; Rahman, M.; Bhattacharya, A.; Barnes, J.L.; Chandrasekar, B.; Fernandes, G. Docosahexaenoic Acid-Enriched Fish Oil Attenuates Kidney Disease and Prolongs Median and Maximal Life Span of Autoimmune Lupus-Prone Mice. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5280–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veigas, J.M.; Williams, P.J.; Halade, G.; Rahman, M.M.; Yoneda, T.; Fernandes, G. Fish oil concentrate delays sensitivity to thermal nociception in mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 63, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Gao, X.; Shi, B.; Chen, S.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Gan, Y.; Cui, L.; Kang, J.X.; Li, W.; et al. Enriched endogenous n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids alleviate cognitive and behavioral deficits in a mice model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 2016, 333, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, H.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Kok, A.; van Knegsel, A.; Zhang, S.; Pang, X.; Jiang, S.; Kemp, B.; et al. Effects of endogenous DHA milk and exogenous DHA milk on oxidative stress and cognition in SAMP8 mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 174, 116467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Yang, L.; Huang, C.; Deng, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Song, C. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Eicosapentaenoic Acid or Docosahexaenoic Acid Improved Ageing-Associated Cognitive Decline by Regulating Glial Polarization. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, P.D. Neural bases of visual deficits during aging. Vis. Res. 1993, 33, 2589–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopiou, E.; Kolovos, P.; Georgiou, C.; Kalogerou, M.; Potamiti, L.; Sokratous, K.; Kyriacou, K.; Georgiou, T. Omega-3 fatty acids supplementation protects the retina from age-associated degeneration in aged C57BL/6J mice. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2019, 4, e000326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela-Lopez, A.; Pérez-López, M.P.; Ramirez-Tortosa, C.L.; Battino, M.; Granados-Principal, S.; Ramirez-Tortosa, M.d.C.; Ochoa, J.J.; Vera-Ramirez, L.; Giampieri, F.; Quiles, J.L. Gene pathways associated with mitochondrial function, oxidative stress and telomere length are differentially expressed in the liver of rats fed lifelong on virgin olive, sunflower or fish oils. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 52, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wei, Y.; Chen, X.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, Y. Polyunsaturated fatty acids ameliorate aging via redox-telomere-antioncogene axis. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 7301–7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinn, N.; Milte, C.M.; Street, S.J.; Buckley, J.D.; Coates, A.M.; Petkov, J.; Howe, P.R.C. Effects of n-3 fatty acids, EPA v. DHA, on depressive symptoms, quality of life, memory and executive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a 6-month randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1682–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurko-Mauro, K.; McCarthy, D.; Rom, D.; Nelson, E.B.; Ryan, A.S.; Blackwell, A.; Salem, N., Jr.; Stedman, M. ; MIDAS Investigators Beneficial effects of docosahexaenoic acid on cognition in age-related cognitive decline. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2010, 6, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, R.; Nolan, J.M.; Prado-Cabrero, A.; Roche, W.; Coen, R.; Power, T.; Mulcahy, R. Omega-3 fatty acid, carotenoid and vitamin E supplementation improves working memory in older adults: A randomised clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 41, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellanes, I.C.; Choe, N.; Solomon, V.; He, X.; Kavin, B.; Martinez, A.E.; Kono, N.; Buennagel, D.P.; Hazra, N.; Kim, G.; et al. Brain delivery of supplemental docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. EBioMedicine 2020, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisés, F.P.P.; Torres-Mendoza, B.M.G.; Ortiz, G.G.; Sánchez-Romero, L.; Delgado-Lara, D.L.C.; Martínez, M.T.G.; Mireles-Ramírez, M.-A.; Serrano, J.A.C. Dietary fish oil increases catalase activity in patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease. 2022, 39, 1364–1368. [CrossRef]
- Tamtaji, O.R.; Taghizadeh, M.; Aghadavod, E.; Mafi, A.; Dadgostar, E.; Kakhaki, R.D.; Abolhassani, J.; Asemi, Z. The effects of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E co-supplementation on gene expression related to inflammation, insulin and lipid in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 176, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, M.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Dadgostar, E.; Kakhaki, R.D.; Bahmani, F.; Abolhassani, J.; Aarabi, M.H.; Kouchaki, E.; Memarzadeh, M.R.; Asemi, Z. The effects of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E co-supplementation on clinical and metabolic status in patients with Parkinson's disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 108, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantzaris, M.; Loukaides, G.; Paraskevis, D.; Kostaki, E.-G.; Patrikios, I. Neuroaspis PLP10™, a nutritional formula rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids with antioxidant vitamins including gamma-tocopherol in early Parkinson’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 210, 106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Brutto, O.H.; Mera, R.M.; Del Brutto, V.J.; Recalde, B.Y.; A Rumbea, D.; Sedler, M.J. Dietary oily fish intake and progression of diffuse subcortical damage of vascular origin: A longitudinal prospective study in community-dwelling older adults. Eur. Stroke J. 2022, 7, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksdotter, M.; Vedin, I.; Falahati, F.; Freund-Levi, Y.; Hjorth, E.; Faxen-Irving, G.; Wahlund, L.-O.; Schultzberg, M.; Basun, H.; Cederholm, T.; et al. Plasma Fatty Acid Profiles in Relation to Cognition and Gender in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients During Oral Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation: The OmegAD Study. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2015, 48, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xu, L.; He, R.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Li, T.; Rong, S. Association of aquatic food consumption, long-chain polyunsaturated n-3 fatty acid intake, and blood mercury levels with cognitive function in middle-aged and older adults. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammann, E.M.; Pottala, J.V.; Harris, W.S.; Espeland, M.A.; Wallace, R.; Denburg, N.L.; Carnahan, R.M.; Robinson, J.G. Omega-3 fatty acids and domain-specific cognitive aging. Neurology 2013, 81, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, S.; Sawada, N.; Matsuoka, Y.J.; Shikimoto, R.; Mimura, M.; Tsugane, S. Association Between Dietary Fish and PUFA Intake in Midlife and Dementia in Later Life: The JPHC Saku Mental Health Study. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2021, 79, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Devore, E.; Grodstein, F.; van Rooij, F.J.; Hofman, A.; Rosner, B.; Stampfer, M.J.; Witteman, J.C.; Breteler, M.M. Dietary intake of fish and omega-3 fatty acids in relation to long-term dementia risk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, D.R.; Bäckman, K.; Scarmeas, N.; Stern, Y.; Manly, J.; Mayeux, R.; Gu, Y. Dietary fatty acids and risk of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias: Observations from the Washington Heights-Hamilton Heights-Inwood Columbia Aging Project (WHICAP). Alzheimer's Dement. 2020, 16, 1638–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.-Z.; Li, L.; Dong, C.-W.; Tan, C.-C.; Xu, W. The Relationship of Omega-3 Fatty Acids with Dementia and Cognitive Decline: Evidence from Prospective Cohort Studies of Supplementation, Dietary Intake, and Blood Markers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117, 1096–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Morales, A.; Hatley, O.J.D.; Turner, D.; Galetin, A.; Aarons, L.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. The Use of ROC Analysis for the Qualitative Prediction of Human Oral Bioavailability from Animal Data. Pharm. Res. 2013, 31, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.N.; Amidon, G.L. A Mechanistic Approach to Understanding the Factors Affecting Drug Absorption: A Review of Fundamentals. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 42, 620–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, J.; Gardner, I.; Swales, N. An Introduction to Drug Disposition: The Basic Principles of Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion. Toxicol. Pathol. 1995, 23, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doogue, M.P.; Polasek, T.M. The ABCD of clinical pharmacokinetics. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2013, 4, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, P.; Jayasooriya, A.P.; Cheemaψ, S.K. Diets Enriched in Fish-Oil or Seal-Oil have Distinct Effects on Lipid Levels and Peroxidation in BioF1B Hamsters. Nutr. Metab. Insights 2011, 4, NMI.S6728–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Kumamaru, J.; Mawatari, M.; Ikeda, I.; Imaizumi, K.; Tsuji, H.; Seto, A. Lymphatic Absorption of Seal and Fish Oils and Their Effect on Lipid Metabolism and Eicosanoid Production in Rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.S.; Høy, C. Effects of dietary triacylglycerol structure on triacylglycerols of resultant chylomicrons from fish oil- and seal oil-fed rats. Lipids 1996, 31, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchardt, J.P.; Hahn, A. Bioavailability of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids. Prostaglandins, Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2013, 89, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, R.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Development of food-grade nanoemulsions and emulsions for delivery of omega-3 fatty acids: opportunities and obstacles in the food industry. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heileson, J.L.; Funderburk, L.K. The effect of fish oil supplementation on the promotion and preservation of lean body mass, strength, and recovery from physiological stress in young, healthy adults: a systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremmell, K.E.; Briskey, D.; Meola, T.R.; Mallard, A.; Prestidge, C.A.; Rao, A. A self-emulsifying Omega-3 ethyl ester formulation (AquaCelle) significantly improves eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acid bioavailability in healthy adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2729–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnoudi-Nia, S.; Forghani, Z.; Jafari, S.M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of fish oil encapsulation within different micro/nanocarriers. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 62, 2061–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-H.; Inoue, Y.; Miyazawa, T. Oxidative Stability of Docosahexaenoic Acid-containing Oils in the Form of Phospholipids, Triacylglycerols, and Ethyl Esters. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1997, 61, 2085–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab-Tehrany, E.; Jacquot, M.; Gaiani, C.; Imran, M.; Desobry, S.; Linder, M. Beneficial effects and oxidative stability of omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 25, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Let, M.B.; Jacobsen, C.; Meyer, A.S. Sensory stability and oxidation of fish oil enriched milk is affected by milk storage temperature and oil quality. Int. Dairy J. 2005, 15, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Kampa, A.-P. M. Kampa, A.-P. Nifli, G. Notas, and E. Castanas, “Polyphenols and cancer cell growth.,” Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol., vol. 159, pp. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grootveld, M.; Percival, B.C.; Leenders, J.; Wilson, P.B. Potential Adverse Public Health Effects Afforded by the Ingestion of Dietary Lipid Oxidation Product Toxins: Significance of Fried Food Sources. Nutrients 2020, 12, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasquel-Oliveira, F.S.; da Silva, M.D.V.; Martelossi-Cebinelli, G.; Fattori, V.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A. Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators: Endogenous Roles and Pharmacological Activities in Infections. Molecules 2023, 28, 5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N. Pro-resolving lipid mediators are leads for resolution physiology. Nature 2014, 510, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliha, M. Tahsin, T. Z. Fabia, S. M. Rahman, and M. M. Rahman, “Pro-resolving metabolites: Future of the fish oil supplements,” J. Funct. Foods, vol. 121, p. 106439, Oct. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norling, L.V.; Headland, S.E.; Dalli, J.; Arnardottir, H.H.; Haworth, O.; Jones, H.R.; Irimia, D.; Serhan, C.N.; Perretti, M. Proresolving and cartilage-protective actions of resolvin D1 in inflammatory arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 1, e85922–e85922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, C.I.; Zattoni, M.; Serhan, C.N. Lipoxins and aspirin-triggered lipoxin inhibit inflammatory pain processing. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.; Yoo, S.; Oh, U.; Hwang, S.W. Endogenous lipid-derived ligands for sensory TRP ion channels and their pain modulation. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2010, 33, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrando, N.; Yang, T.; Carlström, M.; Gustavsson, D.; Harding, R.E.; Lindskog, M.; Eriksson, L.I.; Gómez-Galán, M. Aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 prevents surgery-induced cognitive decline. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 3564–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Pedersen, T. .; Mustafa, K.; Xue, Y.; Mustafa, M.; et al. The effect of resolvin D1 on bone regeneration in a rat calvarial defect model. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2022, 16, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, D.P.; Costa, M.; Neves, N.; Teixeira, J.H.; Santos, S.G.; Águas, A.P.; Barbosa, M.A.; Barbosa, J.N. Chitosan porous 3D scaffolds embedded with resolvin D1 to improve in vivo bone healing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariminezhad, Z.; Rahimi, M.; Fernandes, J.; Maltais, R.; Sancéau, J.-Y.; Poirier, D.; Fahmi, H.; Benderdour, M. Development of New Resolvin D1 Analogues for Osteoarthritis Therapy: Acellular and Computational Approaches to Study Their Antioxidant Activities. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrumaih, S.; Alshibani, N.; Alssum, L.; Alshehri, F.A.; AlMayrifi, M.A.; Alrahlah, A.; Bautista, L.S.J. The impact of Resolvin E1 on bone regeneration in critical-sized calvarial defects of rat model—A gene expression and micro-CT analysis. J. Periodontal Res. 2023, 59, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Han, B.; Xu, F.; Mao, M.; Guo, X.; Wang, J. Dexmedetomidine attenuates repeated propofol exposure-induced hippocampal apoptosis, PI3K/Akt/Gsk-3β signaling disruption, and juvenile cognitive deficits in neonatal rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Wei, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhu, M. Maresin 1 Improves Cognitive Decline and Ameliorates Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, C.; Arroyo-García, L.E.; Do, K.V.; Jun, B.; Ohshima, M.; Alcalde, S.G.; Cothern, M.L.; Maioli, S.; Nilsson, P.; Hjorth, E.; et al. Intranasal delivery of pro-resolving lipid mediators rescues memory and gamma oscillation impairment in AppNL-G-F/NL-G-F mice. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funaki, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Okazaki, R.; Yamasaki, A.; Sueda, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Yanai, M.; Fukushima, T.; Harada, T.; Makino, H.; et al. Resolvin E1 Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis and Bone Resorption by Suppressing IL-17-induced RANKL Expression in Osteoblasts and RANKL-induced Osteoclast Differentiation. Yonago Acta Medica 2018, 61, 008–018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlZahrani, S.; Shinwari, Z.; Alaiya, A.; Al-Kahtani, A. Impact of Resolvin-E1 and Maresin-1 on Bone Marrow Stem Cell Osteogenesis under Inflammatory Stress. Cells 2024, 13, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E. Interfacial Antioxidants: A Review of Natural and Synthetic Emulsifiers and Coemulsifiers That Can Inhibit Lipid Oxidation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 66, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J.; Jafari, S.M. Improving emulsion formation, stability and performance using mixed emulsifiers: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 251, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.; Al-Badr, M.; Alghouti, M.; Mohamed, N.A.; Abou-Saleh, H.; Rahman, M. Revolutionizing Cardiovascular Health with Nano Encapsulated Omega-3 Fatty Acids: A Nano-Solution Approach. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altemimi, A.B.; Farag, H.A.M.; Salih, T.H.; Awlqadr, F.H.; Al-Manhel, A.J.A.; Vieira, I.R.S.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Application of Nanoparticles in Human Nutrition: A Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, R.; Alam, M.; Sarkar, A.; Haque, I.; Hasan, M.; Hoque, M. Application of nanotechnology in food: processing, preservation, packaging and safety assessment. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopalan, V.K.; Gopakumar, L.R.; Kumaran, A.K.; Chatterjee, N.S.; Soman, V.; Peeralil, S.; Mathew, S.; McClements, D.J.; Nagarajarao, R.C. Encapsulation and Protection of Omega-3-Rich Fish Oils Using Food-Grade Delivery Systems. Foods 2021, 10, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. Davidov-Pardo, I. J. G. Davidov-Pardo, I. J. Joye, and D. J. McClements, “Food-grade protein-based nanoparticles and microparticles for bioactive delivery: fabrication, characterization, and utilization.,” Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol., vol. 98, pp. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Ramezanzade, L.; McClements, D.J. Recent advances in nanoencapsulation of hydrophobic marine bioactives: Bioavailability, safety, and sensory attributes of nano-fortified functional foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 322–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinčić, D.D.; Salević-Jelić, A.S.; Kostić, A. .; Stanojević, S.P.; Nedović, V.; Pešić, M.B. Food nanoemulsions: how simulated gastrointestinal digestion models, nanoemulsion, and food matrix properties affect bioaccessibility of encapsulated bioactive compounds. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 64, 8091–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Caster, J.M.; Eblan, M.J.; Wang, A.Z. Clinical Translation of Nanomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11147–11190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.K.; Koshy, P.; Yang, J.; Sorrell, C.C. Preclinical Cancer Theranostics—From Nanomaterials to Clinic: The Missing Link. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaarg, A.; Jordan, N.Y.; Verhoef, J.J.; Metselaar, J.M.; Storm, G.; Kok, R.J. Docosahexaenoic acid liposomes for targeting chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer: an in vitro assessment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, ume 11, 5027–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, D.; Negri, V.; Ballesteros, P.; Cerdán, S. Magnetoliposomes Loaded with Poly-Unsaturated Fatty Acids as Novel Theranostic Anti-Inflammatory Formulations. Theranostics 2015, 5, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J.; Rao, J. Food-Grade Nanoemulsions: Formulation, Fabrication, Properties, Performance, Biological Fate, and Potential Toxicity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 285–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, R.; Pereira, B.D.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Silva, P.; Pastrana, L.M.; Vicente, A.A.; Martins, J.T.; Bourbon, A.I. Lactoferrin-based nanoemulsions to improve the physical and chemical stability of omega-3 fatty acids. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1966–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesmes, U.; Sandra, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Impact of surface deposition of lactoferrin on physical and chemical stability of omega-3 rich lipid droplets stabilised by caseinate. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Zhao, S.; Li, X.; Meng, X.; Liu, B. Preparation, characterization of PLGA/chitosan nanoparticles as a delivery system for controlled release of DHA. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Hu, S.; Fleming, E.; Lee, J.-Y.; Luo, Y. Chitosan-caseinate-dextran ternary complex nanoparticles for potential oral delivery of astaxanthin with significantly improved bioactivity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wusiman, A.; Jiang, W.; Yu, L.; Zhu, T.; He, J.; Liu, Z.; Bo, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, D. Cationic polymer-modified Alhagi honey polysaccharide PLGA nanoparticles as an adjuvant to induce strong and long-lasting immune responses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulik, R.S.; Bing, C.; Ladouceur-Wodzak, M.; Munaweera, I.; Chopra, R.; Corbin, I.R. Localized delivery of low-density lipoprotein docosahexaenoic acid nanoparticles to the rat brain using focused ultrasound. Biomaterials 2016, 83, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovic, M.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Aponick, A.; Zimmermann, E.M.; Dahan, A. Lipids and Lipid-Processing Pathways in Drug Delivery and Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.-M.; Jeon, S.-W.; De, A.; Hong, T.-S.; Park, Y.-J. A Randomized, Open-Label, Single-Dose, Crossover Study of the Comparative Bioavailability of EPA and DHA in a Novel Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticle-Based Formulation of ω-3 Acid Ethyl Ester Versus Omacor® Soft Capsule among Healthy Adults. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serini, S.; Cassano, R.; Facchinetti, E.; Amendola, G.; Trombino, S.; Calviello, G. Anti-Irritant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of DHA Encapsulated in Resveratrol-Based Solid Lipid Nanoparticles in Human Keratinocytes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New approaches in protecting against atherosclerosis in experimental model of postmenopause. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, T.I.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Hussein, J.S.; El-Bana, M.; Emara, E.; El-Khayat, Z.; Fouda, M.M.; Ebaid, H.; Hebeish, A. Antidiabetic assessment; in vivo study of gold and core-shell silver-gold nanoparticles on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, J.; El-Banna, M.; Razik, T.A.; El-Naggar, M.E. Biocompatible zinc oxide nanocrystals stabilized via hydroxyethyl cellulose for mitigation of diabetic complications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ansari, D.E.; Mohamed, N.A.; Marei, I.; Zekri, A.; Kameno, Y.; Davies, R.P.; Lickiss, P.D.; Rahman, M.; Abou-Saleh, H. Internalization of Metal–Organic Framework Nanoparticles in Human Vascular Cells: Implications for Cardiovascular Disease Therapy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, J.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Latif, Y.A.; Medhat, D.; El Bana, M.; Refaat, E.; Morsy, S. Solvent-free and one-pot synthesis of silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles: Activity toward cell membrane component and insulin signaling pathway in experimental diabetes. Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, J.; Rasheed, W.; Ramzy, T.; Nabeeh, M.; Harvy, M.; El-Toukhy, S.; Ali, O.; Raafat, J.; El-Naggar, M. Synthesis of docosahexaenoic acid–loaded silver nanoparticles for improving endothelial dysfunctions in experimental diabetes. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Reference | Model type Invitro/in vivo | Treatment (consisting of ɷ-3 FA) |
Duration | Results | Overall Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Casado-Díaz, A et al., 2013 [61] |
Human MSC |
-Control= ethanol -Omega 6 fatty acids= 20 μM and 40 μM of AA -Omega 3 fatty acids = 20 μM and 40 μM of DHA ,EPA |
21 days | - ω-3 FAs reduced bone loss by increasing the OPG/RANKL ratio in osteoblasts and decreasing adipogenesis in MSCs. DHA and EPA (20 μM) enhanced bone health by increasing osteogenic markers (Runx2, OSX, ALP) and not affecting adipogenesis marker PPARγ2, supporting osteoblastogenesis without promoting fat cell development. | Positive | |
| Nakanishi A et al., 2013 [86] |
Ovariectomized or sham-operated (sham) Female Wistar/ST rats (9 weeks old) | -Control=Corn oil -Fish oil (FO)= DHA -9.2 g/100g, EPA -12.8 g/100g |
2 weeks | - ω-3 FAs treatment decreased mRNA levels of M-CSF, PU.1, MITF, RANK, RANKL, and serum TNFα, IL-6, and PGE2, promoting bone health by reducing ovariectomy-stimulated osteoclastogenesis. | Positive | |
| Abou-Saleh et al., 2019 [87] |
11-months-old C57BL/6 female mice | -4% SFO safflower oil (70%–80% ω-6 fatty acids, mainly LA) -1% CFO concentrated Fish oil [46.5% EPA and 37.5% DHA] -4% CFO -4% regular-fish oil FO -Untreated control group with standard lab chow diet |
12 months | 4% CFO Group - The treatment exhibited the highest BMD across all bone regions compared to other groups. It prevented aging-associated bone loss by modulating osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption, resulting in reduced levels of bone resorption markers RANKL and TRAP5b. 1% CFO Group -The treatment increased lumbar, tibial, and femoral BMD while decreasing the NF-κB, JNK, and p38 MAPK signaling pathways, which are associated with bone resorption. 4% Regular Fish Oil Group - The treatment moderately increased BMD in various bone regions compared to the 4% SFO group, enhancing reducing bone resorption, indicated by lower serum RANKL and TRAP5b levels. |
Positive | |
| Anez-Bustillos et al., 2019 [88] |
3-weeks-old male and female C57BL/6J mice | - SOY diet -DHA/ ARA diet in 20:1 ratio -DHA diet |
9 weeks | - DHA increased total area (TA) and bone area (BA) compared to SOY and DHA/ARA, but had no major effect on cortical or trabecular bone, showing no significant impact on bone metabolism. | Neutral | |
| Reference | Model type Invitro/in vivo | Treatment (consisting of ɷ-3 FA) |
Duration | Results | Overall Outcome | |
| Bani Hassan E et al., 2019 [68] |
1-month-old female senescence accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8) mice | -Sunflower oil based Diet (Total ω-3 PUFA =2.29%) -Borage oil enriched Diet (Total ω-3 PUFA =2.35%) -FO enriched diet(Total ω-3 PUFA=11.60%) |
10 months | - The FO group increased bone volume fraction and decreased MAT%, which positively associated with bone health by reducing age-related bone loss and hematopoietic bone marrow loss (HBM) through limited MAT expansion. | Positive | |
| Elbahnasawy AS et al., 2019 [89] |
12-week-old male Sprague Dawley rats | -Control = sunflower oil -Prednisolone control (10 mg/kg prednisolone per daily) - Prednisolone+ Soybean oil diet (7% SBO) -Prednisolone + Flaxseed oil diet (7%) -Prednisolone + Fish oil diet (7% FO with EPA =19.12% and DHA = 21.08%) |
3 weeks | - Fish oil increased plasma calcium levels and reduced oxidative stress and inflammatory markers. It suppressed bone resorption, as indicated by decreased CTX levels, increased BMD, and normal histological results compared to controls, effectively mitigating GC-induced osteoporosis. | Positive | |
| Xie Y et al., 2019 [90] |
12-week-old male Sprague Dawley rats | Anterior cruciate ligament transection ACLT-operated and treated with 1 mg/kg DHA per day | 2 month | - DHA-treated rats experienced less bone mass loss, with reduced TRAP, RANKL, CD31, and endomucin levels in the osteochondral unit, indicating decreased bone resorption. DHA also restrains bone remodeling and vessel formation, potentially protecting cartilage. | Positive | |
| Xie Y et al., 2019 [90] |
Monocyte-derived cell line RAW264.7 | 3 groups: sham, vehicle-treated (RANKL), and DHA treated (RANKL + DHA). | 2 months | - In DHA-treated cells, TRAP-stained cells, bone resorption pits, and mRNA levels of TRAP, CTSK, MITF, and NFATC1 were lower, indicating DHA inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. DHA-treated RAW264.7 cells exhibited fewer resorption pits than RANKL-only exposed cells, and DHA also attenuated cartilage degeneration. | Positive | |
| Dai Y et al., 2021 [77] |
8-week-old female C57BL/6J healthy and osteoarthritis mice |
- ω-6 FA with 1.57 % AKO [Antarctic krill oil] - ω-3 FAs with 39.66% AKO Containing DHA + EPA = 37.81% -n-6/n-3 ratio checked = 20 : 1, 6 : 1, 1 : 1 |
10 week | - Low n-6/n-3 PUFA ratios (1:1 to 6:1) improved cartilage structure, reduced polysaccharide loss, and decreased NF-κB signaling via GPR120 activation, thereby reducing inflammation and supporting bone health. These diets, including AKO rich in DHA and EPA, reduced cartilage degeneration, which can enhance bone formation and decrease resorption . | Positive | |
| Zhang T et al., 2021 [81] |
8 week old female C57BL/6 OVX mice [OP+OA Mice Model ] |
n-6/n-3 PUFAs -20:1 non- FO -20:1 FO (700mg FO /kg) -20:1 FO-High (1400mg FO /kg) - 6:1 non-FO - 6:1 FO-Low(700mg FO /kg) - 6:1 FO-High (700mg FO /kg) |
12 weeks. | - High dose FO improved bone and cartilage health in the osteoporotic OA model, even in a high n-6/n-3 PUFA diet. 20:1 FO-H improved bone microarchitecture, GPR120 expression, and BMD while enhancing osteogenesis. It decreased bone resorption by lowering TNF-α, PGE2, IL-1β, NFκB, and NLRP3 expression in cartilage. 6:1 FO-H diet performed best for bone improvement, reducing cartilage degradation and restoring cartilage area and thickness. | Positive | |
| Reference | Model type Invitro/in vivo | Treatment (consisting of ɷ-3 FA) |
Duration | Results | Overall Outcome | |
| Cifuentes-Mendiola S. E et al., 2022 [84] |
Human osteoblast cell line hFOB 1.19 | DHA (10 and 20 µM) | 21 days | -DHA enhanced bone mineral matrix quality and reduced oxidative stress induced by 24 mM glucose (HG). Osteoblasts cultured in HG and treated with DHA exhibited increased collagen type 1 (Col1) scaffolds, elevated OCN and BSP-II expression, increased NRF2 mRNA, and reduced ROS production, promoting bone health. | Positive | |
| Tompkins YH et al., 2022 [70] |
Ross 708 Broiler breederhen | -Control = 2.3% of soybean oil (SO) Intervention group(IG) = 2.3% FO [18% EPA and 12% DHA] | 28 days | - Maternal fish oil (FO) diet rich in ω-3 PUFAs positively impacted fat mass and skeletal integrity in broiler offspring. It increased bone mineral content (BMC), total volume, and bone surface (BS) in the tibia of 18-day-old embryos, indicating enhanced bone formation. Additionally, it reduced pore volume and levels of adipogenic transcription factors PPARγ, FABP4, and C/EBPβ, suggesting a reduction in adipogenesis. | Positive | |
| Zhu, Y et al., 2022 [83] |
3-month-old female pure Wistar rats | - OVX -E2 (OVX + high-dose estrogen) -nH (OVX + high-dose THLs) -nL (OVX + low-dose THLs) -Tilapia nilotica fish head lipids THLs containing neutral lipids (NL, 77.84%), phospholipids (PL, 11.86%), and glycolipids (GL, 6.47%) |
1 week | - Both high and low-dose THL groups improved trabecular microstructure by enhancing bone formation (increased BV/TV ,cortical density and Tb.N) and reducing bone resorption (decreased Tb.Sp and SMI), supporting bone health. - Treatment with THLs restored the OPG/RANKL ratio and reduced bone resorption markers CTX-1, Cath-K, and MMP-9, thus improving bone health through decreased bone resorption. |
Positive | |
| Ku SK et al., 2023 [76] |
Rat model of knee OsteoArthritis.OA | Orally administered KO at 200, 100, and 50 mg/kg (KO200, KO100, and KO50 |
8 weeks | - Both KO200 and KO100 groups exhibited increased BMD, reduced joint capsule thickness, and enhanced strength of femoral and tibial articular cartilage compared to the OA control. Additionally, oral KO doses promoted chondrogenic gene expression(type 2 collagen, aggrecan, Sox9), while decreasing inflammation markers (5-lipoxygenase, PGE2) and ECM-degrading enzymes (MMP-2, MMP-9) in cartilage and synovium, indicating improved joint health and cartilage preservation. | Positive | |
| Reference | Sample size (n) and population | Age / mean ± SD age | Treatment | Duration | Results | Overall Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trebble, T. M et al., 2005 [100] |
61 Crohn’s patients | Mean age = 45·4 | Fish oil supplement = 2·7 g/d EPA and DHA, (n=31) Placebo = olive oil, containing the MUFA oleic acid (n=30) |
24 weeks | - High intakes of EPA and DHA from fish oil do not appear to impact bone health in individuals with Crohn’s disease, as they do not influence bone turnover indices, evidenced by no differences in bone resorption marker Deoxypyridinoline (DPD), bone formation marker Osteocalcin levels, or the DPD/Osteocalcin ratio. | Neutral |
| Reference | Sample size (n) and population | Age / mean ± SD age | Treatment | Duration | Results | Overall Outcome |
| Martin-Bautista E et al., 2010 [109] |
72 Hyperlipidaemia patients | 35-65 years | Control [group C]=2.05 g oleic acid per 500 mL semi skimmed milk , (n=33) Group E -fortified supplement group= 5.17 g oleic acid, 0.14 g DHA, and 0.20 g EPA per 500 mL, (n=39) |
12-month | - Fortified milk increased bone markers, including plasma OPG, OPG/RANKL ratio, and osteocalcin, thus improving bone health in hyperlipidaemic adults, while showing no change in intact parathormone (Ipth) and type I collagen carboxyl-terminal telopeptide (CTX) levels. | Positive |
| AppletonK. M et al., 2011 [99] |
113 Mild–moderately depressed individuals |
18–67 years | Intervention group = 1·48 g ω-3 PUFAs (0·63 g EPA + 0·85 g DHA)/d Placebo =olive oil |
12 weeks | - Supplementation with ω-3 PUFAs did not prevent bone loss or reduce bone resorption, nor did it effect b-CTX levels (a marker of bone resorption) or overall bone resorption. | Neutral |
| TartibianB et al., 2011 [112] |
79 healthy sedentary post-menopausal women | 58-78 years | - (C) control (n=18) -(E+S) exercise +supplement (n = 21) - (E) exercise only (n=20) - (S) supplement only (n=20) Supplement is 1000 mg of ω-3 PUFAs containing 180 mg EPA, 120 mg DHA. |
24 weeks | - ω-3 FA improved bone health in post-menopausal osteoporosis by increasing BMD at the L2-L4 and femoral neck. It decreased inflammatory markers (TNF-α, PGE2, IL-6, and CTX) linked to bone resorption while increasing estrogen, calcitonin, and vitamin D and promoted overall skeletal integrity. |
Positive |
| Vanlint, S. J et al., 2011 [113] |
40 individuals with osteopenia (36 females, 4 males) |
Mean age = 59.2 years | - Intervention group = 0.2 g DHA from algal oil in sunflower oil (2 capsules/day) -Placebo = corn oil |
12 month | - The addition of DHA (0.4 g/day) did not affect calcium and vitamin D levels in osteopenic individuals. Although CTX levels decreased by 10.5%, there was no improvement in bone health, as mean BMD values remained unchanged at the lumbar spine, total proximal femur, and neck of femur. | Neutral |
| Sabour, H et al., 2012 [114] |
82 Osteoporotic patients with spinal cord injury (SCI), 1-year post injury. | ≥18 years | MorDHA capsules = 2 capsules (435 g of DHA and 0.065 g of EPA per day) Control: Placebo Gelatin 1g one capsule |
4 months | - No significant changes were observed in bone resorption markers, bone formation markers, or pro-inflammatory cytokines in osteoporotic patients. |
Neutral |
| Reference | Sample size (n) and population | Age / mean ± SD age | Treatment | Duration | Results | Overall Outcome |
| Hutchins-Wiese HL et al., 2014 [104] |
38 Postmenopausal women on AI for ≥6 months for estrogen-positive breast cancer, continuing treatment for ≥1 year. | 48–84 years Mean age= 62 years |
Fish oil -7 capsules/day containing 4 g EPA + DHA (2.52g EPA, 1.68mg DHA) (n=20) Placebo-7 capsules/day containing safflower oil (9% linoleic acid, 83% oleic acid) (n=18) |
3 months | - In the fish oil group, bone resorption markers DPD and SCTX decreased, confirming a reduction in bone resorption, with a significant decrease observed in DPD levels. | Positive |
| Chen et al., 2015 [97] |
202 Patients with knee osteoarthritis (49 % female) |
≥40 years Mean age =61.0±10.0 years |
- High dose = 4.5 g EPA and DHA - Low dose = 0.45 g/day |
2 years | - High-dose omega-3 fish oil did not alter bone loss in men and women with knee osteoarthritis, as indicated by no significant changes in BMD | Neutral |
| Smith, G. I et al., 2015 [115] |
60 healthy adults | 60–85-years | - Four 1-gram capsules per day of omega-3 acid ethyl esters = 1.86 g EPA and 1.50 g DHA /day, equivalent to the ω-3 PUFAs content of 200–400 g freshwater fatty fish | 6 months | - ω-3 PUFAs therapy enhanced thigh muscle volume, improved handgrip strength, increased one-repetition maximum (1-RM) muscle strength, and elevated average isokinetic power. | Positive |
| Fonolla-Joya J et al., 2016 [108] |
117 healthy postmenopausal women | 50 -70 years Mean age= 45 ± 7.7 year |
Intervention group [IG] =0.5 L/day of skimmed milk with hydrolysed lactose, enriched with 40 mg/100 mL EPA+DHA, 0.54 g/100 mL oleic acid, 0.5 g/100 mL soluble fiber, minerals, and vitamins (n = 63) Control group [CG]= 0.5 L/day of semi skimmed milk enriched with vitamins A and D ,n = 54 |
12-month | - EPA and DHA improved bone health by reducing i-PTH levels, which led to decreased RANKL and hs-CRP, lowering bone resorption and reducing inflammation. There were no changes in bone turnover markers or serum OPG in the intervention group; however, a higher omega-3 to omega-6 ratio was associated with protection against bone mass loss. | Positive |
| Rajaram S et al., 2017 [96] |
24 Healthy adults (15 females and 9 males) |
20 - 70 years Mean age = 42 ± 3 years |
- Control diet = 10:1, without supplement - EPA/DHA diet= 10:1, 1.40/5.04g from microalgae oil/week - ALA diet = 2:1, 42-49 g flaxseed oil/week + 10 g walnuts, 3 times/week - Combination diet = ALA + EPA/DHA |
8 weeks | - Adjusting the n-6:n-3 PUFA ratio or or adding EPA/DHA supplements did not impact short-term bone turnover in healthy adults, with no differences observed in bone formation, resorption markers, or PPAR-γ gene expression. | Neutral |
| Reference | Sample size (n) and population | Age / mean ± SD age | Treatment | Duration | Results | Overall Outcome |
| LeBoff, M. S et al., 2020 [95] |
771 (7.9% had fracture history, 80 had osteoporosis, 402 had osteopenia) |
Men ≥50 years and women ≥55 years Mean age 63.8 ± 6.1 |
Vitamin D + ω-3 PUFAs 1 g/d) | 2-year | - No benefit was observed in participants with osteoporosis, as there were no changes in bone strength indices (polar stress strength index, bone strength index) or bone structure (total, cortical, and trabecular vBMD, cortical thickness) between the supplement and placebo groups. Furthermore, ω-3 fatty acid supplementation had no effect on aBMD at the spine, femoral neck, total hip, or whole body. | Neutral |
| Papandreou P et al., 2020 [106] |
66 very low-birth-weight (VLBW) preterm neonates | Gestational age < 32 weeks admitted within 12 hours after birth | Soybean oil–based parenteral lipid emulsions [PLE]=Intralipid containing soybean oil (20 g%), egg yolk phospholipids (1.2 g%), glycerin (2.25 g%), and α-tocopherol (38 mg/L) (n=35) n-3/MCT-enriched PLE = Smoflipid containing fish oil (3 g%), soybean oil (6 g%),olive oil (5 g%), MCTs (6 g%), egg yolk phospholipids (1.2 g%), glycerin (2.5 g%), and α-tocopherol (200 mg/L) |
20 days | - ω-3 PUFAs enriched PLEs reduced early bone loss in VLBW neonates by maintaining higher OPG/sRANKL levels during the early postnatal period. | Positive |
| Ichinose T et al., 2021 [107] |
87 healthy Japanese elderly people |
69.1±5.3 years | Placebo group = 200 mL of milk (n=41) DHA group= 200 mL of milk beverage containing 0.297 g DHA and 0.137g EPA (n=46) |
12-month | - Even low-dose, long-term daily intake of DHA benefited bone health by reducing serum bone resorption markers. Bone resorption decreased, as indicated by a significant reduction in TRACP-5b. | Positive |
| Jorgensen et al., 2021 [92] |
132 Adult kidney transplant recipients |
>75 years | Intervention group = 2.6 ω-3 PUFAs supplements (0.460 g EPA + 0.380 g DHA) Placebo = olive oil |
44 weeks | - No changes were observed in BMD at the whole body, lumbar spine, proximal femur, or forearm between the intervention and control groups. Additionally, there were no changes in plasma levels of marine ω-3 PUFAs, TBS, or biochemical parameters of mineral metabolism. | Neutral |
| Reference | Sample size (n) and population | Age / mean ± SD age | Treatment | Duration | Results | Overall Outcome |
| Razny U et al., 2021 [101] |
64 Middle aged individuals with abdominal obesity |
25−65 years | Placebo (corn oil) 0.004g of vitamin E per capsule ω-3 PUFAs capsules =1.8 g DHA + EPA in a ratio of 5:1 Low-calorie diet = 1200 kcal/day for women and 1500 kcal/day for men + ω-3 PUFAs capsules |
3 month | - ω-3 PUFAs supplementation had no effect on bone resorption marker CTX-I, vitamin D levels, osteopontin, FGF-21, or bone formation markers (PINP, Gla-OC, Glu-OC). Even with calorie restriction, ω-3 PUFAs did not mitigate bone resorption, suggesting limited impact on bone turnover. | Neutral |
| Matsuzaki K et al., 2023 [116] |
52 Healthy Japanese adults | Mean age = 54.2 ± 6.4 years | Placebo group = 7.0 ml of olive oil daily (n=25) Intervention group = Perilla frutescens seed oil (PO)= 7.0 ml daily (n=27) |
12 months | - Long-term PO intake improved age-related BMD decline by reducing bone resorption, as evidenced by decreased TRACP-5b levels in the PO group. Additionally, %YAM levels increased compared to placebo, indicating improved bone density. However, there was no change in bone formation biomarker BALP levels in the PO group. | Positive |
| S. Gaengler et al., 2024 [117] |
1,493 older adults (12% osteoporosis, 55% osteopenia, 30% healthy bone density) |
≥70 years Mean age= 75 years |
1g EPA+DHA (1:2 ratio, 2 capsules/day) | 3-year | - EPA and DHA supplementation showed no significant effect on lumbar spine BMD, femoral neck BMD, or total hip BMD in healthy, vitamin D-replete, active adults. However, when combined with a simple home-based exercise program (SHEP), omega-3 supplementation slightly improved lumbar spine TBS. | Neutral |
| Reference |
Sample size (n) and population | Age / mean ± SD age | Treatment (consisting of ɷ-3 FA) |
Duration | Results | Overall Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen YM et al., 2010 [125] |
685 postmenopausal Chinese women. | 48 - 63 years | Mean sea fish intake in quantile categories Q1 = 0.6 g/day(n=129) Q2–Q4 = 16.8g/day (n=420) Q5 = 64.7g/day(n=136) |
12 years | - Higher sea fish consumption significantly increased mean BMDs. Women in the highest quintile (Q5) of sea fish intake had 4.0% greater whole body BMD, 4.1% higher lumbar spine BMD, and 6.2% to 8.4% higher BMD at hip sites compared to those in the lowest quintile (Q1). | Positive |
| Reference |
Sample size (n) and population | Age / mean ± SD age | Treatment (consisting of ɷ-3 FA) |
Duration | Results | Overall Outcome |
| Farina E. K et al., 2011 [133] |
623 women |
Mean age= 78.1± 6.88 y | Quartiles of fatty acid intakes for categorical analyses Q1, Q2,Q3,Q4 Low: <1 serving/wk Moderate: 1-3 servings/wk High: ≥3 servings/wk |
4 year | - Women with elevated EPA+DHA intakes showed increased FN-BMD in the highest intake group(Q4) compared to the lowest (Q1). Conversely, men with lower EPA+DHA intake had decreased FN-BMD. | Positive |
| Farina E. K et al., 2011 [134] |
904 (552 women and 352 men) | Mean age 75 years | Quartiles of fatty acid intakes for categorical analyses - Low (<1 serving/wk) - Moderate (At least 1 serving per week but less than 3 servings per week) - High (≥3 servings/wk) 1 serving of fish equivalent to 85–142 g (3–5 oz). |
17-years (1988-2005) |
- No effect in hip fracture risk was observed with EPA, DHA, EPA+DHA, or fish intake. | Neutral |
| Järvinen R et al., 2012 [135] |
554 postmenopausal women | Mean age 68 years | EPA and DHA = 0.41±0.47g/day PUFA = 8.8±3.4g/day MUFA=17.0±6.3g/day |
3-year | - PUFA intake increased BMD at the lumbar spine and total body, but not at the femoral neck. Higher total PUFA intake increased vitamin D levels, leading to higher lumbar spine and total body BMD. This association is observed in non-Hormone Therapy (HT) users, while no significant link is found for current HT users. | Positive |
| Harris T. B et al., 2015 [24] |
1438 older men and women (540-with fracture, 898- without fracture) |
66–96 years | - Never consumed fish oil (referent group) - Less than daily (1 time/mo, 1–3 times/mo, 1–2 times/ mo, or 5–6 times/wk) - Daily consumption of fish oil |
Median follow-up 7.0 y (4.1–7.6 y) |
- High ω-3 reduced fracture risk by 34% in men, while daily fish oil intake in midlife reduced fracture risk in women. - High EPA levels reduced fracture risk by 41% in men. |
Positive |
| Choi, E & Park Y et al., 2016 [119] |
- 7154 KNHANES:Korean participants - 2658, NHANES: American participants |
≥50 years | Quintiles of Consumption of Fish and Shellfish Q1-Q5 |
KNHANES -2008 to 2011 NHANES - 2007 to 2010 |
Fish consumption increased BMD in the total femur, femoral neck, and lumbar spine in Korean men and postmenopausal women, while no effects on BMD were observed in American men or postmenopausal women. | Positive |
| Kuroda T et al., 2017 [131] |
275 healthy Japanese female with peak bone mass (PBM) | 19 - 25 years Mean age =20.6 ± 1.4 years |
- n-3 fatty acid intake 1.3g/day - Median value of n-3 fatty acid intake=2.12 g/day (EPA = 0.15 g/day, DHA = 0.25 g/day). |
NA | - ω-3 fatty acids increased peak bone mass (PBM) at the total hip BMD. Body mass index (BMI) and serum bone alkaline phosphatase levels were significant contributors to lumbar BMD according to multiple regression analysis. | Positive |
| Reference |
Sample size (n) and population | Age / mean ± SD age | Treatment (consisting of ɷ-3 FA) |
Duration | Results | Overall Outcome |
| Lavado-García et al., 2018 [129] |
Total 1865 -women with osteoporosis (n=194) -with osteopenia (n=707) -healthy females- (n=964) |
20–79 years | Omega-3 acids - - Linoleic acid = 1.79 g/day - EPA = 0.22 g/day - DHA = 0.30 g/day - ALA = 0.79±0.5g/day |
NA | - DHA intake increased lumbar spine and hip BMD in healthy women, whereas no differences in lumbar spine and hip BMD observed with ω-3 PUFAs in osteoporotic women. | Positive |
| Fang Z. B et al., 2023 [4] |
8,942 | 20–59 years | Fatty acid intake divided by quartile- Q1-Q4 -Total SFAs intake = 0.6000–190.0570 g/d -Total MUFAs intake =0.6745–149.8885 g/d -Total PUFAs intake =0.2825–143.5885 g/d |
NA | -PUFAs intake is positively linked to BMD in the third and fourth quartiles, which represent the highest intake levels. | Positive |
| Feehan O et al., 2023 [132] |
300 Postmenopausal women. | 45 - 75 years Mean age 65 years |
High n−6: n−3 ratio= ≥6.5 Medium n−6: n−3 ratio =between 4.9 and 6.5 Low n−6: n−3 ratio = ≤4.9 |
NA | - ω-3 PUFAs, EPA, DPA, and DHA have no effect on bone turnover markers, femur and lumbar spine BMD, or T-score, including total ω-3 PUFAs. | Neutral |
| Del Brutto OH et al., 2024 [127] |
399 older adults 37% (n=149) with osteopenia 39% (n=56) with osteoporosis 24% (n=94) with normal BMD |
≥60 years Mean age 68.8±6.8 years |
- High consumption ≥5.2 servings/week [728 g] - Low consumption ≤5.2 servings/week -Mean dietary intake of oily fish = 8.8 ± 4.8 servings per week |
NA | - High fish consumption (≥5.2 servings/week) decreased the risk of lower BMD by over two times. - Consuming ≥ 5 servings/week of wild-caught oily fish reduced frequency of osteopenia and osteoporosis in older women - In women, significant association observed between high oily fish intake and BMD, not in men |
Positive |
| Liu Y et al., 2024 [130] |
22,834 13% (n=2831) patients with OA 87% (n=20,003) with non OA |
≥20 years | ω-3 PUFAs included: DHA, DPA, EPA, SDA, and ALA Omega-3 Intake Quartiles for Total Omega-3 (g/day): Q1-Reference Q2- 0.94g/day Q3-0.82g/day Q4 – 0.79 g/day |
NA | - Higher intake of ω-3 PUFAs is associated with reduced OA prevalence, particularly in adults aged 40–59. | Positive |
| Reference | Sample size (n) and population | Treatment | Duration | Results | Overall Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wu, K et al.,2016 [150] |
C57BL/6 fat-1/APP transgenic mice | Feeding a high n-6 PUFAs diet to transgenic mice with the fat-1 gene, which converts n-6 PUFAs to ω-3 PUFAs. | 12 months | -High PUFA ratios and endogenous ω-3 PUFAs improved AD symptoms by reducing sensorimotor dysfunction and cognitive deficits in mouse models. - n-3 PUFAs decreased amyloid beta aggregation, inflammatory activation, nuclear factor-kappa B activation and neuronal death in APP/fat-1 mice, which also showed lower anxiety levels in behavioral tests. |
Positive |
| Chen, J et al., 2017 [156] |
8-week-old male mice | Groups FO1= 400, 200, and 100 mg of fish oil per kg of body weight per day Group DHA = 120, 60, and 30 mg of DHA per kg of body weight per day |
2 months |
- ω-3 PUFAs enhanced aging resilience by improving redox homeostasis, increasing antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase and catalase), and lowering oxidative stress markers (monoamine oxidase and F2-isoprostanes). - ω-3 PUFAs protected against DNA damage and telomere shortening, with DHA inhibiting cellular senescence, promoting healthier aging. |
Positive |
| Prokopiou E et al., 2019 [154] |
24-month-old aged wild-type C57BL/6J mice | 3 groups (n=15/group): -Young untreated - Aged untreated -Aged treated with ω-3 PUFAs (571 mg/mL EPA and 114 mg/mL DHA fish formulation) |
2 months |
- ω-3 supplementation reduced age-related retinal degeneration in mice by decreasing lipofuscin granule formation and protecting the photoreceptor layer, effectively slowing normal aging processes. | Positive |
| Varela-Lopez et al., 2022 [155] |
72 male Wistar rats weighing 80–90 g | n-3 fatty acid profile of experimental dietary fats -olive oil =0.4g/100g -Sunflower oil =0.4g/100g - Fish oil = 31.3 g/100 g |
24 months | - Fish oil did not show a major effect on preserving the liver during aging, it intensified age-related oxidation, reduced electron transport chain activity, and enhanced relative telomere length. | Neutral |
| Reference | Sample size (n) and population | Treatment | Duration | Results | Overall Outcome |
| Xia, J et al., 2023 [152] |
3 month old adult male and 24 month old male ageing Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats |
3 groups: - Ageing (saline) - Ageing + EPA = 500 mg/kg/day EPA - Ageing + DHA = 500 mg/kg/day DHA |
8 weeks | - DHA outperformed EPA in mitigating age-related neuroimmunological changes and enhancing memory. ω-3 PUFAs, especially DHA, corrected microglial M1/M2 polarization in the hippocampus, improving spatial memory in aging rats. DHA significantly lowered TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 levels, while EPA primarily suppressed IL-6, emphasizing DHA’s neuroprotective benefits. | Positive |
| Wang, X. et al., 2024 [151] |
Male Senescence Accelerated Mouse-Prone 8 (SAMP8) mice (3–5-month-old | endogenous and exogenous DHA milk powder containing 0.33% DHA. | 42 days | -0.33% DHA reduced oxidative stress in the brains and serum of SAMP8 mice, evidenced by increased SOD activity. Endogenous DHA milk outperformed exogenous DHA milk in improving liver SOD activity, oxidative stress levels, and cognitive abilities, as shown by improved performance in the water maze test. | Positive |
| Reference | Sample size (n) and population | Age / mean ± SD age | Treatment | Duration | Results | Overall outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yurko-Mauro, K.et al., 2010 [158] |
485 healthy Adults with ARCD | ≥55 years | 0.9g/d of DHA | 24 weeks | - 0.9 g/d DHA enhanced learning and memory function, reduced errors in the PAL test and improved immediate and delayed VRM scores, leading to a two-fold decrease in visuospatial learning and episodic memory errors. | Positive |
| Sinn et al., 2012 [157] |
50 Patients with MCI | >65 years | - Control (safflower oil) = 2·2 g LA/d -EPA-rich fish oil=1·67 g EPA + 0·16 g DHA/d -DHA-rich fish oil=1·55 g DHA + 0·40 g EPA/d |
6 months | - DHA and EPA improved mental health in older adults with MCI, enhancing verbal fluency and self-reported physical health. - DHA and EPA intake improved GDS scores, but no effects were observed on other cognitive or quality of life measures. |
Positive |
| Eriksdotter M et al., 2015 [166] |
174 AD patients | 74 ± 9 years | 2.3 g ω-3 PUFAs | 6 months | - Higher plasma levels of ω-3 FAs reduced cognitive deterioration in AD patients. | Positive |
| Taghizadeh, M. et al., 2017 [163] |
60 patients with PD | 50-80 years | 1g ω-3 PUFAs from flaxseed oil plus 400 IU vitamin E supplements | 3 months | - ω-3 FAs and vitamin E co-supplementation improved UPDRS scores in PD patients but had no effect on inflammation, oxidative stress biomarkers, or lipid profiles, and resulted in decreased insulin levels. | Positive |
| Tamtaji, O. R et al.,2019 [162] |
40 adults with PD | 50–80 years | 1g daily of ω-3 PUFAs from flaxseed oil + 400 IU/day of vitamin E | 12 weeks | - ω-3 FAs and vitamin E co-supplementation improved the gene expression of TNF-α, PPAR-γ, and LDLR, indicating beneficial anti-inflammatory and metabolic effects that positively manage PD. - Significantly improved UPDRS-part I |
Positive |
| Arellanes, I. C. et al., 2020 [160] |
33 with a first-degree family history of dementia | ≥55 years | -Placebo (n = 15, APOE4=7, non-APOE4=8) - Intervention group IG= 2.152 g/ day of TG-based DHA supplementation (n = 18, APOE4=8, non-APOE4=10) |
6 months | - Doses of 1 g/day or less of ω-3 FAs showed limited effects on brain health in dementia prevention trials. DHA treatment increased CSF DHA levels by 28% and EPA levels by 43%. | Positive |
| Reference | Sample size (n) and population | Age / mean ± SD age | Treatment | Duration | Results | Overall outcome |
| Pantzaris, M et al., 2021 [164] |
40 mild to moderate severity PD patients | 40–75 years old |
-Placebo=pure virgin olive oil 20 ml -Neuroaspis PLP10®= a mixture of omega-3 [0.810 g EPA and 4.14 g DHA) and omega-6 fatty acids (1.8 g GLA and 3.15 g LA) (1:1 w/w) |
30 months | - Neuroaspis PLP10™ supplementation in PD patients significantly delayed disease progression, as evidenced by an increase in UPDRS III scores. These positive effects persisted throughout the study, lasting until the end of the 30-month period . | Positive |
| Power, R. et al., 2021 [159] |
60 Cognitively healthy adults | ≥65 years | - Control group, Placebo = sunflower oil - Intervention group (IG)= 1 g fish oil (430 mg DHA, 90 mg EPA),22 mg carotenoids (10 mg lutein, 10 mg mesozeaxanthin, 2 mg zeaxanthin and 15 mg vitamin E) |
24 months | -DHA and EPA improved working memory, resulting in significantly fewer errors in tasks compared to placebo. -DHA and EPA showed improvements in attention, language, and global cognition following the intervention. |
Positive |
| Del Brutto, O. H.et al., 2022 [165] |
263 Individuals of Amerindian ancestry | ≥60 years |
Mean oily fish intake was 8.3±4 servings per week | 6.5 years | - High fish oil intake benefitted brain health and reduced neurodegeneration by providing a protective effect against the progression of WMH. | Positive |
| Lin, P. Y et al., 2022 [33] |
163 MCI or AD patients | 77.8(treatment) vs 78.1 (placebo) |
Placebo = soybean oil (n = 40) DHA = 0.7 g/day (n= 41) EPA= 1.6 g/day, (n = 40) EPA (0.8 g/day) + DHA (0.35 g/day) (n = 42) |
24 months | - ω-3 FAs supplements did not reduce cognitive, functional, or depressive symptoms, but they did improve spoken language - EPA intervention improved spoken language ability and constructional praxis, reducing TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-1β levels. |
Positive |
| Torres-Mendoza, B. M. G.et al., 2022 [161] |
87 AD patients | NA | Fish oil = .45g of EPA and 1g of DHA |
12 months | - ω-3 FAs intake reduced oxidative stress markers (protein, lipid oxidation) in AD patients, ω-3 FAs enhanced the antioxidant defense system in AD patients, as evidenced by the significant increase in catalase activity after 6 and 12 months of fish oil treatment. |
Positive |
| Reference | Sample size (n) and population | Age / mean ± SD age | Treatment | Duration | Results | Overall Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammann, E. M et al., 2013 [168] |
2157 dementia-free women with normal cognition | 65 - 80 years | RBC DHA + EPA content (%): High (n = 719) = 6.44% Middle (n = 719) =4.90% Low (n = 719)=3.83 % |
7.9 years | -DHA + EPA had no effect on age-related cognitive decline in older, dementia-free women, though those in the highest DHA + EPA tertile exhibited improved verbal knowledge, fine motor speed, and verbal fluency. | Neutral |
| Gustafson, D. R.et al., 2020 [171] |
2612 adults without dementia | 76 years | Tertiles of fatty acid intake T1,T2,T3 -Long-chain saturated fatty acids -Polyunsaturated fatty acids (DHA EPA) -Monounsaturated fatty acids |
4.9 years | - DHA and EPA reduced Alzheimer’s disease risk by 27% and 26%, respectively. - Participants experienced longer periods without AD (P < 0.05). |
Positive |
| Reference | Sample size (n) and population | Age / mean ± SD age | Treatment | Duration | Results | Overall Outcome |
| Nozaki, Shoko et al., 2021 [169] |
1,127 Japanese individuals 468 men, 659 women |
73 years | - Quartiles of fish consumption ω-3 PUFAs, EPA, DHA, EPA+DHA, DPA, ALA, n-6 PUFAs, LA, ARA | 15y | - Higher quartiles of fish, EPA, DHA, and DPA intake showed significantly reduced dementia risks. | Positive |
| Wei, B. Z et al., 2023 [172] |
ADNI study n=1,135 - 828 Participants free of AD - 307 Participants who developed AD, |
55 - 90 y Mean age- 73.36 ± 7.22 y) |
Omega-3 supplementation - Exposure (yes or no) Medium term exposure (1~9 y) - long-term exposure (10 y) |
6 years mean follow-up time of 2.81 ± 1.60 y |
- Long-term use of ω-3 PUFA supplements reduced the risk of Alzheimer’s disease by 64%. | Positive |
| Li, Benchao et al., 2024 [167] |
2621 older Chinese adults with MCI |
≥45 years |
Aquatic food consumption Quartile 1: 0 -12.38g/d Quartile 2: 12.39 -28.33 g/d Quartile 3: 28.34 - 56.20 g/d Quartile 4 : 56.20 g/d |
4.5 - 6.3 years | - Consumption of aquatic foods and higher intake of ω-3 PUFA reduced the risk of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and improved cognitive function. | Positive |
| Reference | Sample size (n) and population | Treatment | Duration | Results | Overall Outcome | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Norling, L. V et al., (2016) [193] |
Male 12-week-old, C57Bl/6 mice (30g) with induced Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) | Stable epimer 17R-RvD1 (100 ng/day) | 32 days | -17-RvD1 reduced joint inflammation and destruction, enhanced chondroprotection through increased expression of cartilage matrix synthesis genes in RA patients. - 17R-RvD1 significantly reduced arthritis severity, cachexia, hind-paw edema, and leukocyte infiltration, shortened the remission interval, and increased levels of SPMs. |
Positive | ||
| Funaki, Y et al., 2018 [204] |
RAW264.7 cells and Mouse calvarial cells (MC3T3-E1) |
100 nM RvE1 | 7 days | -RvE1 suppressed osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by inhibiting RANKL-induced NFATc1 and c-fos in osteoclasts and IL-17-induced RANKL in osteoblasts. -Co-treatment with 100 nM RvE1 reduced resorption pit area, evidenced by decreased TRAP-positive cells, increased OPG expression, and a favorable RANKL/OPG ratio, enhancing bone formation. |
Positive | ||
| Vasconcelos, D. P et al., 2018 [198] |
3-month-old male Wistar rats with femoral defect | - Ch + RvD1 scaffolds with 30 μL of RvD1 solution - Chitosan scaffolds without RvD1 (control) |
2 months | - RvD1 enhanced bone tissue repair, shown by increased collagen type I fibers, a higher Coll I/Coll III ratio, greater trabecular thickness, and a higher bone volume in the Ch+RvD1 group compared to the Ch group. | Positive | ||
| Yin P et al., 2019 [202] |
C57BL/6 mice (male, 3–4 months old, weight 26–31 g) | 0.01 µg/µl MaR1 | 7 days | - MaR1 improved cognitive decline by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, MCP-1) and increasing anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-2, IL-10) levels. |
Positive | ||
| Emre C et al., 2022 [203] |
C57BL/6 J wild-type (WT) mice | 40 ng per LM of RvE1, RvD1, RvD2, MaR1 and NPD1 |
9 weeks | - SPMs improved brain health and cognitive performance by reducing microglial activation, which in turn led to enhanced memory function and the restoration of normal brain wave patterns (gamma oscillation) in the brain. | Positive | ||
| Reference | Sample size (n) and population | Treatment | Duration | Results | Overall Outcome | ||
| Jiang, X.et al., 2022 [197] |
Female Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (180–200 g) with induced calvarial defects |
Implanted collagen 3D nanopore scaffold (COL) and Pluronic F127 hydrogel (F127) with or without RvD1 - RvD1-COL-F127 group (Added 5 ng/μL RvD1 to F127 solution) - COL-F127 group (control) - Subcutaneous RvD1: 100 ng every 7 days post-implantation. |
8 weeks | -RvD1 enhanced bone formation and vascularization while reducing bone resorption in rat calvarial defects. -It decreased TRAP-positive cells and inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and TNF-α), lowered RANKL expression, and increased osteoid-like tissue, blood vessel count, ALP, and VEGF in the RvD1-COL-F127 group. |
Positive | ||
| Sara Alrumaih et al., 2023 [200] |
Healthy female Wistar rats 250 -300g with induced critical-size calvarial defect |
-negative control with no treatment - positive control with bovine xenograft - RvE1 alone 100 ng -RvE1 100 ng + bovine xenograft |
12 weeks | -RvE1 improved bone mineral density and formation in the RvE1 + bovine xenograft group, which showed the highest ALP and OPN gene expression, as well as the highest mean NFB. | Positive | ||
| Al Zahrani, S et al., 2024 [205] |
Humanbone marrow MSCs | 100 nM concentration of RvE1 and MaR1 | 14 days | - Both RvE1 and MaR1 promoted osteogenic differentiation of hBMMSCs, enhancing bone formation by increasing calcified deposits and ALP activity. | Positiv | ||
| Reference | Nanoparticle Type | Loaded drug/ compound/ molecule |
Nanoparticles characteristics | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calle, D.et al.,2015 [218] |
liposomes containing the superparamagnetic nanoparticle Nanotex | ω-3 PUFA ethyl esther | Particle size :200 nm | Demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory effects against colonic inflammation and important anti-tumoral effects against glioma |
| Reference | Nanoparticle Type | Loaded drug/ compound/ molecule |
Nanoparticles characteristics | Findings |
| Alaarg, A.et al., 2016 [217] |
polyethylene glycol(PEG) liposomes | DHA | Particle size: 99 ± 16 nm encapsulation efficiency= 81.35±3.24% |
ω-liposomes represent a promising Nano nutraceutical formulation with potential benefits for treating inflammatory disorders. |
| Mulik, R. S et al., 2016 [225] |
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) nanoparticles | DHA | Particle size=22.4 ± 0.71 nm | LDL DHA administration doubled DHA and Resolvin D1 levels in targeted brain areas, enabling localized delivery for treating acute brain injuries. |
| Hussein, J. S.et al., 2019 [234] |
Silver nanoparticles | DHA | Particle size:24nm encapsulation efficiency= 97.67 % |
DHA combined with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) shows significant potential in alleviating diabetic complications and improving endothelial dysfunction in experimental diabetes. |
| Serini, S.et al., 2019 [228] |
Encapsulated in Resveratrol-Based Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (RV-SLNs) |
DHA | Particle size: 139.27nm | By encapsulating DHA in solid lipid nanoparticles, the DHA-RV-SLNs could enhance the protective effects of DHA against cytotoxic actions of surfactants in human keratinocytes . |
| Nunes R et al., 2020 [220] |
Nano emulsions utilizing Lactoferrin (Lf) as an emulsifier |
DHA and EPA | Particle size <200 nm Encapsulation efficiency = >99% |
Resulted in improved stability, controlled release profiles at different pH levels, antioxidant properties, and non-cytotoxicity to Caco-2 cells |
| Liu, E et al., 2021 [222] |
nanoparticle with PLGA and chitosan (PCSDNP) | DHA | Particle size= 256 nm encapsulation efficiency= 87% |
PCSNP enhances the stability of DHA and protects it from oxidation or degradation in the gastrointestinal tract, also provide a slow-release effect, improving the digestion and absorption of DHA. |
| Kang, K.-M.et al., 2023 [227] |
liquid crystalline nanoparticle-based formulation called IMD-Omega soft capsule | DHA and EPA | Particle size: < 154 ± 61 nm | The IMD-Omega soft capsule showed a substantial 110% increase in EPA bioavailability and an impressive 134% increase in DHA bioavailability over 72 hours. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





