1. Introduction
CU is a persistent inflammatory skin condition characterized by erythematous, maculo-papular lesions, angioedema, or both, due to mast cell activation and degranulation resulting in histamine and other mediators release. While up to 20% of the global population may experience urticaria at some point in their lives, most instances are cases of acute urticaria (AU), which last up to six weeks and are often associated with infections, dietary factors, or medications [
1,
2]. In contrast, CU, whether spontaneous or inducible, persists for more than six weeks and typically lasts over a year. CU substantially impacts patients' quality of life and correlates with psychiatric comorbidities [
3] and high healthcare costs [
4,
5]. CSU differs from chronic inducible urticaria (CIndU) in that the latter presents specific, well-defined triggers that induce symptoms [
1,
2]. The pathogenesis of CSU involves a series of interconnected events, including autoantibodies, complement activation, and the coagulation cascade [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. Diagnosis is clinical, though various tests are conducted to exclude other diagnoses and identify underlying causes in CSU or triggering factors in CIndU [
1,
2]. Current treatment targets complete response, employing a stepwise approach with second-generation H1 antihistamines, omalizumab, and cyclosporine [
1]. Emerging therapeutic strategies focus on targeting mediators, signaling pathways, cytokines [
12,
13] and receptors of mast cells and other immune cells [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19]. Future research should aim to define disease endotypes and their biomarkers, identify new therapeutic targets, and develop improved therapies, as a significant proportion of patients remain symptomatic with severe and uncontrolled forms of the disease [
20,
21,
22].
IL-33, a member of the IL-1 cytokine family, has been consistently implicated in CSU in previous studies [
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28]. Originally discovered in human tissues in 2003 as a nuclear factor of high endothelial venules (NF-HEV), IL-33 has been found to have a three-dimensional folding similar to IL-1 and can induce a type 2 immune response through its receptor, ST2 [
29]. The confirmation of IL-33's identity with NF-HEV and its role as a chromatin-bound nuclear factor were further elucidated [
30]. Secreted by various cell types, including endothelial, epithelial, macrophages, fibroblasts, and dendritic cells, IL-33 is released during cellular injury, necrosis, necroptosis, stress, and viral infection, and activates various immune cell types [
31,
32,
33,
34]. Although known for its role in allergic reactions, asthma, and parasitic infections, IL-33 has also been suggested to play a role in chronic inflammation due to the complex role of high endothelial venules in lymphocyte activation and mobilization [
23].
Given the grounding of autoimmunity in the etiopathogenesis of CSU and its association with various autoimmune diseases as reported in the literature [
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40], our research investigated how IL-33, a molecule common to both CSU and autoimmune diseases, has been genetically approached in previous studies. Observing that a specific IL-33 polymorphism, SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) rs1929992, has been associated with susceptibility to various autoimmune diseases [
41], raises the critical question of whether this SNP also impacts susceptibility to CSU.
This study aims to evaluate the prevalence of the IL-33 SNP rs1929992 in patients with CU and determine the relationship between this IL-33 SNP and serum IL-33 levels, thus deepening our understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in this complex condition and identifying potential biomarkers for more accurate diagnostic and personalized therapeutic strategies. The main hypothesis is that IL-33 plays a significant role in the etiopathogenesis of CSU, functioning as an immunological mediator directly involved in inflammation and immune responses [
24,
25,
26,
41,
42,
43]. Through a detailed analysis of demographic and clinical data, allele and genotype frequencies, Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, and serum IL-33 levels, while also considering age and sex influences, our hypothesis was tested using robust statistical models, including binomial logistic regression and correction for multiple comparisons, employing the R statistical software. This approach has allowed us to elucidate the potential of the IL-33 genetic polymorphism (rs1929992) as a predictor of susceptibility to CSU and to deepen the understanding of the underlying etiopathogenic mechanisms. Our findings aim to strengthen both the theoretical framework in the field and the clinical applicability in improving diagnostic and treatment strategies for patients affected by CSU.
2. Results
2.1. Clinical and Paraclinical Data: Collection and Visualisation
In the present study, sex and age of the CU patients were not matched with non-CU group (
Table 1), therefore, when we tested the difference in genotype distributions between CU patients and non-CU group, age and sex were adjusted. As can be seen from
Table 1, baseline IgE level was in the interquartile range of 55.08 – 355.50 (median 132) in CU patients; CRP was in the interquartile range of 0.2–0.53 (median 0.30 mg/dl), and 12/48 CU patients had increased level of CRP.
2.2. Associations of Allele Frequencies of IL33 rs1929992 gene polymorphism with odds of Chronic Urticaria (CU)
The observed genotype distribution of IL33
rs1929992 gene polymorphism was consistent with the expected distribution of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in the non-CU group (p = 0.3197) but not in the CU group (p = 0.0016).
Table 2 highlighted the allele frequencies of IL33
rs1929992 gene polymorphism between the groups. We noticed that the frequency of subjects carrying the minor allele of IL33
rs1929992 gene polymorphism was significantly higher in CU group than in the non-CU group (31.25 % versus 17.35 %).
2.3. Association between genotypes frequencies of IL33 rs1929992 gene polymorphism and odds of CU
The frequencies of genotype distributions of the GG and GA genotypes in the two groups was statistically significant (
Table 3), individuals carrying the AG genotype had significantly higher odds of CU than patients carrying the GG genotype (OR = 3.1, 95% CI: [1.37, 7.19]). After adjusting for sex and age, association between the
IL33 rs1929992 gene polymorphism and odds of CU remained statistically significant, individuals carrying the heterozygous AG genotype were 2.208 times more likely to develop CU than individuals carrying the homozygous GG genotype (adjusted p ≤ 0, 001, adjusted OR = 2, 208, 95% CI: 1.548–3.149).
2.4. Association between IL33 rs1929992 gene polymorphism and IL-33 serum level stratified by CU patients and non-CU group
The distributions of IL-33 according to cytokine gene polymorphism in CU patients and the non-CU groups have been presented in
Table 4. The median of serum level of IL-33 in patients with GA genotype (17.55 pg/ml) was higher than median serum of GG (15.23 pg/ml) genotype, but the differences were not statistically significant (p = 0.5439). Significant differences in levels of IL-33 were observed between CU patients carrying GG genotype and GA genotype of rs1929992 and non-CU group (p = 0.0000001).
2.5. Association of IL33 rs1929992 gene polymorphism with UAS7 and DLQI scores in CU patients
Comparisons of the IL-33
rs1929992 genotypes among the CU patients were performed using clinical parameters such as UAS7 scores and DLQI scores (
Table 5). Although CU patients carrying the IL-33
rs1929992 GG genotype had lower values of baseline UAS7 and DLQI scores than patients carrying the AG genotype, no significant association between UAS7 or DLQI and IL-33 rs1929992 gene polymorphism was observed (p > 0.05).
When we classified disease activity status by the scores of UAS7 as mild or moderate and severe, no significant association was found between the disease activity status and IL-33 rs1929992 gene polymorphism (Fisher’s exact test, p = 0.5451), frequency distribution of variant GA genotype being similar in patients with severe form of pruritus (32, 65.6 %) or mild/moderate form of pruritus (16, 56.2%). Also, we found no significant association between IL-33 rs19299 gene polymorphism and patients’ quality of life defined using the dermatology life quality index DLQI as “moderate impact”, “very important impact” and “extremely important impact” of disease (Fisher’s exact test, p = 0.5451). The frequency distribution of variant GA genotype being similar in patients with moderate impact of disease on quality of life (6, 50 %), patients with very important impact of disease (21, 57.1 %) and patients with extremely important impact of disease (21, 71.4 %).
3. Discussion
This study focuses on the association between the IL33 rs1929992 gene polymorphism, serum IL-33 levels, and the risk and severity of CU, as well as its impact on patients' quality of life. The genetic polymorphism rs1929992 of IL-33 has been linked to various autoimmune conditions [
44,
45,
4647], reinforcing its role in the pathogenesis of CU. Xu et al. [
44] initially identified the association between the IL-33 rs1929992 polymorphism and lupus erythematosus (LES), which was confirmed by Bagheri-Hosseinabadi et al. [
45] in 2023. The comorbidity of CU with LES has been extensively documented, demonstrating a potential common pathogenic mechanism [
48,
49]. Our results, indicating an increased prevalence of the IL-33 polymorphism in CU patients compared to controls, align with existing literature, suggesting a strong autoimmune foundation for CU and underscoring the need to further explore the role of IL-33 polymorphism in this condition.
From another perspective, CU can be seen as a TH2-type immunological condition, similar to asthma and other allergic diseases [
7,
9,
50]. IL-33, along with IL-25 and TSLP, plays a crucial role as an alarmin in triggering this type of immune response [
26]. This aligns with findings from Canoğlu et al. [
51] and Rabea et al. [
52], who reported the same polymorphism associated with asthma, suggesting its importance in inducing susceptibility to a TH2 immunological profile and in the association of allergic and inflammatory diseases.
The surprising discovery by Guo et al. [
53] of an association between stroke and the IL-33 gene polymorphism adds an intriguing element to our understanding. Given that the pathogenesis of CU partly involves the coagulation cascade [
8,
42,
54], though not fully understood, this association opens new avenues for research into the deeper mechanisms of the disease. Additionally, the same polymorphism was found in the study by Fang et al. [
47] in the context of Henoch-Schönlein Purpura (HSP), an autoimmune, autoinflammatory, and vasculitic condition, adding complexity to this genetic marker. These findings suggest that IL-33 may play a significant role in pathologies involving both inflammation and coagulation disorders and could serve as a starting point for future research in this area.
Our results indicated an increased incidence of the minor allele among CU patients, suggesting that genetic variations might influence susceptibility to this condition. The study was based on a robust set of clinical and demographic data and employed appropriate statistical methodologies to test the proposed hypothesis. Adjustments for age and sex were crucial given the initial imbalance between the CU and non-CU groups. These corrections ensured a more accurate assessment of the genetic polymorphism's influence on UC risk, moving beyond simple correlation to achieve clinically relevant association. Additionally, observations on serum IL-33 levels reinforce the potential of this parameter as a biomarker for assessing and monitoring CU, although differences between genotypes did not reach statistical significance in our study. This may provide clues on how variations in IL-33 contribute to the inflammatory response and symptomatology in CU.
However, the absence of statistical significance between the associations of IL-33 rs1929992 polymorphism and clinical scores UAS7 and DLQI is an intriguing component of our study. This might suggest that while genetic variants influence disease susceptibility, their impact on symptom severity or quality of life is less direct. This reflects the multifactorial nature of CU's clinical expression, where genetic mechanisms contribute to initial susceptibility, while environmental factors and other biomarkers may play decisive roles in disease progression and severity.
While extensive research exists, our study adds a valuable perspective by focusing on a specific population and employing cutting-edge molecular techniques to evaluate genetic polymorphisms. Deepening the understanding of the etiopathogenic mechanisms of CU through such studies will contribute to the development of targeted and personalized therapeutic strategies.
Nonetheless, we must acknowledge that our study has limitations. The sample size and the nature of the case-control study require caution in generalizing the results. Moreover, the complex nature of CU, involving numerous genetic and environmental factors, suggests that further studies are needed to validate and extend our findings. These observations underscore the ongoing need for research to elucidate the roles that genetic polymorphisms play in the complex pathology of CU. In particular, longitudinal studies and larger cohorts are needed to confirm the role of IL-33 polymorphisms in CU and to assess their potential as targets in developing new therapies. Advancing knowledge on cytokine involvement and associated signaling networks may lead to the optimization of therapeutic approaches and improve the prognosis for these patients.
Thus, this study represents an important step in mapping the genetic landscape in CU and opens promising avenues for targeted and personalized therapies. Continued research into this disease will continue to provide new insights and support the medical community in managing CU more effectively.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Selection and Study Design
This case-control study was conducted at the Department of Allergology within the Regional Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology in Cluj-Napoca, Romania. It involved 50 patients diagnosed with CSU according to the latest international guidelines. CSU is characterized by repeated occurrences of maculopapular rashes and possible angioedema, appearing at least twice weekly for a minimum of six weeks. For comparison, a control group of 50 institutional staff members without any history of urticaria or systemic diseases that could cause urticaria or pruritus was included. The exclusion criteria for CSU patients were closely linked to the diagnostic criteria and excluded any chronic systemic diseases that involve itching or urticaria, including renal, hepatic, psychiatric, or infectious diseases.
The study protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee of the "Iuliu Hatieganu" University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca (AVZ270/10.10.2022) and the Regional Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology (IRGH) (12637/11.10.2022). All participants gave written informed consent, and basic demographic data, including age and gender, were collected.
The CSU diagnosis was confirmed through patient history and clinical examination, excluding individuals under 18 years or those with other chronic diseases. Blood samples of 10 milliliters were collected from all subjects and divided into four vacutainers: the first two for complete blood count and routine analyses, the third for IL-33 determination via Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) using a commercial kit, and the fourth collected in EDTA for whole blood DNA extraction and molecular study of SNP IL-33 rs1929992 using Polymerase Chain Reaction - Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (PCR-RFLP).
4.2. DNA Isolation
Peripheral blood was collected in EDTA tubes. DNA was isolated from leukocytes using the Zymo Research Quick-DNA Miniprep Kit and stored at -20°C.
4.3. PCR and RFLP Analysis
In order to identify the IL-33 A/G transversion (rs1929992), we used the method described by Bassagh (2019) [
55] and optimized in our laboratory. PCR amplification was performed using an iCycler BioRad (Bio-Rad Life Science, Hercules, CA, USA). The reaction mixture contained 5 µl DNA, 0.2 µM forward and reverse primers, 2.0 mM MgCl2, 10X Taq polymerase buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 mM DTT, 0.1 mM EDTA, 100 mM KCl, 0.5% (v/v) Nonidet P-40, 0.5% (v/v) Tween 20, and 50% (v/v) glycerol), 200 µM each dNTP (dATP, dGTP, dCTP, dTTP), and 0.625 U Taq polymerase enzyme. The sequences of the primers were: forward primer: 5’-GTCATCATCAACTTGGAACCTT-3’ and reverse primer: 5’-CTGTGGAGTGCTTTGCCTTT-3’.
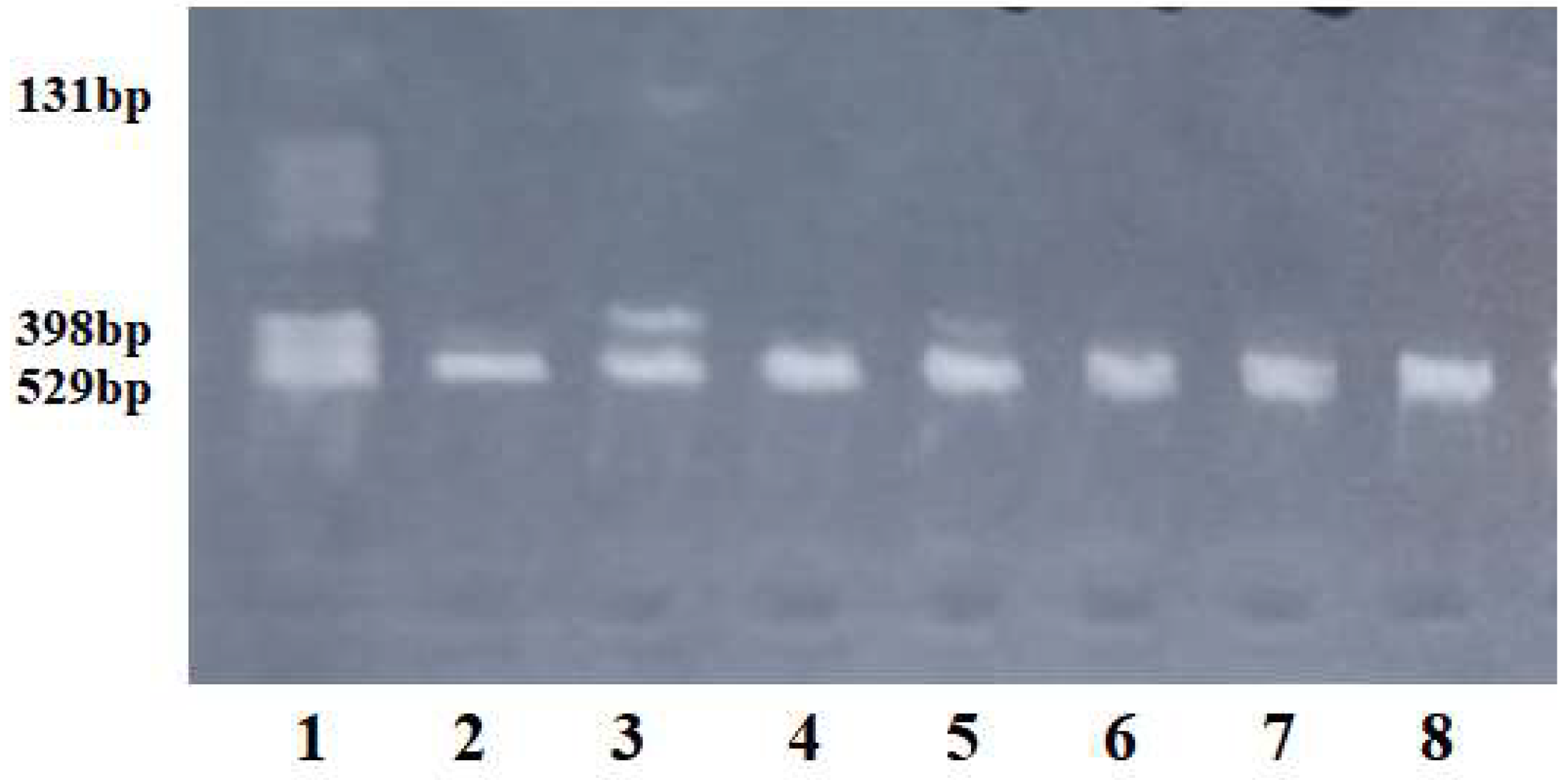
The PCR amplification program was as follows: denaturation for 0.6 sec at 95ºC, followed by 34 cycles of amplification with denaturation for 0.1 sec at 95ºC, annealing of primers for 0.2 sec at 57.6ºC, extension of primers for 27 sec at 72ºC, and a final extension for 0.3 sec at 72ºC. The length of the PCR product was 529 bp. After PCR amplification, enzymatic digestion was performed. A 6 µl PCR product was incubated for 3 hours at 37ºC with 5 U SspI restriction enzyme. After enzymatic digestion, the wild-type G allele produced an undigested fragment of 529 bp, while the mutated A allele produced two fragments of 398 bp and 131 bp.
The specificity of amplification and enzymatic digestion was checked using agarose gel electrophoresis, and the fragments were visualized under UV light (
Figure 1). The primers were obtained from Kaneka Eurogentec S.A. Biologics Division, Liège, Belgium, and the restriction enzyme was from New England Biolabs.
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Continuous demographic and clinical variables were summarized using measures of central tendency and dispersion. For normally distributed data, the arithmetic mean and standard deviation were used, while the median and interquartile range (IQR) were applied for non-normally distributed data. Univariate normality was assessed through a combination of descriptive and inferential statistical methods, including descriptive statistics, Q-Q plots, and the Shapiro-Wilk test with Holm correction for multiple comparisons. Qualitative variables were described using frequencies and percentages.
Comparison of demographic and clinical characteristics between CU and non-CU groups was performed using Chi squared test, Fisher’s exact test, Welch t-test or Mann-Whitney test for independent samples.
Differences in allele and genotype frequencies of IL-33 gene polymorphism (rs1929992) between CU and non-CU groups were compared using the Chi-square test. The departure from Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE) was tested using the exact Chi-square test from "SNPassoc" R package [
56].
The association between IL-33 gene polymorphism (rs1929992) and odds of CU was evaluated by unconditional binomial logistic regression. The effect size of association was described using the unadjusted odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) and adjusted odds ratio (OR) with adjustment for age and sex.
All statistical analysis was performed in R software, version 4.3.2 [
57]. The level of statistical significance for all two-sided tests was set at 5 %.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study highlights the importance of the IL-33 gene polymorphism (rs1929992) as a potential susceptibility factor in chronic urticaria (CU) and opens new avenues for future research. Such findings are crucial for advancing the comprehensive understanding of CU and for the ongoing improvement of clinical management and patient outcomes. This underscores the significance of an integrated approach that combines genetic, clinical, and immunological aspects in the evaluation and treatment of CU.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța and Gabriela Adriana Filip; Data curation, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța, Diana Mihaela Deleanu and Ioana Adriana Muntean; Formal analysis, Mihaela Iancu; Investigation, Lucia Maria Procopciuc, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța, Irena Nedelea and Radu-Gheorghe Bălan; Methodology, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța, Mihaela Iancu and Gabriela Adriana Filip; Resources, Diana Mihaela Deleanu; Software, Mihaela Iancu and Ioana Adriana Muntean; Supervision, Gabriela Adriana Filip; Validation, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța and Gabriela Adriana Filip; Writing – original draft, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța and Mihaela Iancu; Writing – review & editing, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța, Irena Nedelea and Gabriela Adriana Filip. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the UMF "Iuliu Hatieganu" [AVZ270/10.10.2022] and by the ”Octavian Fodor” Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology [12637/11.10.2022].
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Acknowledgments
This research is part of the PhD thesis entitled "Immunological Signature and the Role of Mast Cells in Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria", authored by Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța, the first author of this article, and defended at the "Iuliu Hațieganu" University of Medicine and Pharmacy in July 2024.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zuberbier T, Abdul Latiff AH, Abuzakouk M, et al. The international EAACI/GA²LEN/EuroGuiDerm/APAAACI guideline for the definition, classification, diagnosis, and management of urticaria. Allergy 2022, 77, 734–766.
- Burks AW, Holgate S, O'Hehir R, Bacharier L, Broide D, Hershey G, Peebles RS. Middleton’s Allergy: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. eBook ISBN: 9780323546980, Hardcover ISBN: 9780323544245.
- Ozkan M, Oflaz SB, Kocaman N, et al. Psychiatric morbidity and quality of life in patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2007, 99, 29–33. [CrossRef]
- Katelaris CH, Lima H, Marsland A, Weller K, Shah A, Waserman S. How to measure disease activity, impact, and control in patients with recurrent wheals, angioedema, or both. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2021, 9, 2151–2157. [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell BF, Lawlor F, Simpson J, Morgan M, Greaves MW. The impact of chronic urticaria on the quality of life. Br J Dermatol 1997, 136, 197–201.
- Saini, SS. Chronic spontaneous urticaria: etiology and pathogenesis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 2014, 34, 33–52 24262688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalom G, Magen E, Dreiher J, et al. Chronic urticaria and atopic disorders: a cross-sectional study of 11,271 patients. Br J Dermatol 2017, 177, e96–7 28129676. [CrossRef]
- Davis MDP, van der Hilst JCH. Mimickers of urticaria: urticarial vasculitis and autoinflammatory diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2018, 6, 1162–1170 29871797.
- Ying S, Kikuchi Y, Meng Q, et al. TH1/TH2 cytokines and inflammatory cells in skin biopsy specimens from patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria: comparison with the allergen-induced late-phase cutaneous reaction. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002, 109, 694–700 11941321.
- Dobrican CT, Muntean IA, Pintea I, Petricău C, Deleanu DM, Filip GA. Immunological signature of chronic spontaneous urticaria (Review). Exp. Ther. Med 2022, 23, 381. [CrossRef]
- Kolkhir P, Church MK, Weller K, et al. Autoimmune chronic spontaneous urticaria: what we know and what we do not know. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2017, 139, 1772–1781 e1 27777182. [CrossRef]
- Kasutani K, Fujii E, Ohyama S, Adachi H, Hasegawa M, Kitamura H, Yamashita N. Anti-IL-31 receptor antibody is shown to be a potential therapeutic option for treating itch and dermatitis in mice. Br J Pharmacol 2014, 171, 5049–5058. [CrossRef]
- Dobrican-Băruța CT, Deleanu DM, Muntean IA, Pintea I, Florea CM, Filip GA. IL-31—Pruritus Interleukin: Serum Values and Clinical Impact in Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria—A Romanian Retrospective Study. J Clin Med 2023, 12, 5957. [CrossRef]
- Kubo N, Senda M, Ohsumi Y, et al. Brain histamine H1 receptor occupancy of loratadine measured by positron emission topography: comparison of H1 receptor occupancy and proportional impairment ratio. Hum Psychopharmacol 2011;26, 133-139. [CrossRef]
- Guillen-Aguinaga S, Jauregui Presa I, Aguinaga-Ontoso E, Guillen-Grima F, Ferrer M. Updosing nonsedating antihistamines in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol 2016;175, 1153-1165. [CrossRef]
- Saini S, Rosen KE, Hsieh HJ, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study of single-dose omalizumab in patients with H-1-antihistamine-refractory chronic idiopathic urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;128, 567-U195.
- Maurer M, Altrichter S, Bieber T, et al. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in patients with chronic urticaria who exhibit IgE against thyroperoxidase. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;128, 202-209. [CrossRef]
- Saini SS, Bindslev-Jensen C, Maurer M, et al. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in patients with chronic idiopathic/spontaneous urticaria who remain symptomatic on H1 antihistamines: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Invest Dermatol 2015;135, 67-75. [CrossRef]
- Maurer M, Rosen K, Hsieh HJ, et al. Omalizumab for the treatment of chronic idiopathic or spontaneous urticaria. N Engl J Med 2013;368, 924-935. [CrossRef]
- Metz M, Maurer M. Use of Biologics in Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria—Beyond Omalizumab Therapy? Allergol Select 2021, 5, 89–95.
- Metz M, Kolkhir P, Altrichter S, Siebenhaar F, Levi-Schaffer F, Youngblood BA, Church MK, Maurer M. Mast cell silencing: A novel therapeutic approach for urticaria and other mast cell-mediated diseases. Allergy 2023, 79, 37–51. [CrossRef]
- Manti S, Giallongo A, Papale M, Parisi GF, Leonardi S. Monoclonal antibodies in treating chronic spontaneous urticaria: New drugs for an old disease. J Clin Med 2022, 11, 4453. [CrossRef]
- Moussion C, Ortega N, Girard JP. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: A novel ‘alarmin’? PLoS One 2008, 3, e3331.
- Hsu CL, Neilsen CV, Bryce PJ. IL-33 is produced by mast cells and regulates IgE-dependent inflammation. PLoS One 2010, 5, e11944. [CrossRef]
- Saluja R, Khan M, Church MK, Maurer M. The role of IL-33 and mast cells in allergy and inflammation. Clin Transl Allergy 2015, 5, 33. [CrossRef]
- Dobrican-Băruța, C.-T.; Deleanu, D.M.; Muntean, I.A.; Nedelea, I.; Bălan, R.-G.; Filip, G.A.; Procopciuc, L.M. The Alarmin Triad—IL-25, IL-33, and TSLP—Serum Levels and Their Clinical Implications in Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2024, 25, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church MK, Kolkhir P, Metz M, Maurer M. The role and relevance of mast cells in urticaria. Immunol. Rev 2018, 282, 232–247. [CrossRef]
- Cayrol C, Girard JP. Interleukin-33 (IL-33): A critical review of its biology and the mechanisms involved in its release as a potent extracellular cytokine. Cytokine 2022, 156, 155891. [CrossRef]
- Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [CrossRef]
- Carriere V, Roussel L, Ortega N, Lacorre DA, Americh L, Aguilar L, et al. IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007, 104, 282–7.
- Liew FY, Girard JP, Turnquist HR. Interleukin-33 in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2016, 16, 676–689. [CrossRef]
- Bertheloot D, Latz E. HMGB1, IL-1alpha, IL-33 and S100 proteins: dual-function alarmins. Cell Mol Immunol 2017, 14, 43–64.
- Cayrol C, Girard JP. Interleukin-33 (IL-33): a nuclear cytokine from the IL-1 family. Immunol Rev 2018, 281, 154–68.
- Molofsky AB, Savage AK, Locksley RM. Interleukin-33 in tissue homeostasis, injury, and inflammation. Immunity 2015, 42, 1005–19. [CrossRef]
- Konstantinou GN, Asero R, Ferrer M, et al. EAACI taskforce position paper: evidence for autoimmune urticaria and proposal for defining diagnostic criteria. Allergy 2013, 68, 27–36. [CrossRef]
- Hoffman HM, Broderick L. The role of the inflammasome in patients with autoinflammatory diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2016, 138, 3–14 27373321. [CrossRef]
- Hashkes PJ, Toker O. Autoinflammatory syndromes. Pediatr Clin North Am 2012, 59, 447–470 22560579.
- Fiebiger E, Hammerschmid F, Stingl G, Maurer D. Anti-FcepsilonRIalpha autoantibodies in autoimmune-mediated disorders. Identification of a structure-function relationship. J Clin Invest 1998, 101, 243–51.
- Kolkhir P, Borzova E, Grattan C, Asero R, Pogorelov D, Maurer M. Autoimmune comorbidity in chronic spontaneous urticaria: a systematic review. Autoimmun Rev 2017, 16, 1196–1208. [CrossRef]
- Bonnekoh H, Maurer M, Krause K. Interleukin-1-related cytokines as potential biomarkers in autoinflammatory skin diseases. Pediatr Rheumatol 2015, 13(Suppl 1):P197. [CrossRef]
- Xu W, Liu Y, Ye D. Association between IL-33 Gene Polymorphisms (rs1929992, rs7044343) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a Chinese Han Population. Immunol Investig 2016, 45(7):575-583.
- Kay AB, Ying S, Ardelean E, et al. Elevations in vascular markers and eosinophils in chronic spontaneous urticarial weals with low-level persistence in uninvolved skin. Br J Dermatol 2014, 171, 505–511 24665899. [CrossRef]
- Kay AB, Clark P, Maurer M, et al. Elevations in T-helper-2-initiating cytokines (interleukin-33, interleukin-25 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin) in lesional skin from chronic spontaneous (‘idiopathic’) urticaria. Br J Dermatol 2015, 172, 1294–1302 25523947.
- Xu W, Liu Y, Ye D. Association between IL-33 Gene Polymorphisms (rs1929992, rs7044343) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a Chinese Han Population. Immunol Investig 2016, 45(7):575-583.
- Bagheri-Hosseinabadi Z, Mirzaei MR, Aliakbari M, et al. Association of interleukin 33 gene polymorphisms with susceptibility and regulation of inflammatory mediators in Systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clin Rheumatol 2023, 42, 2187–2197. [CrossRef]
- Jamali M, Rostami Rad M, Anani Sarab G, Mahdavi R. IL-33 polymorphism rs1929992 and its association with susceptibility to different pattern of multiple sclerosis. Tehran Univ Med J 2018, 76(7):446–451.
- Fang Y, Li W, Xu H, Mao J, Shang S. Association Between Interleukin-33 Polymorphism and Henoch-Schönlein Purpura in Chinese Children. Iran J Pediatr. 2019 Feb;29(1):e63038. [CrossRef]
- Kolkhir P, Borzova E, Grattan C, Asero R, Pogorelov D, Maurer M. Autoimmune comorbidity in chronic spontaneous urticaria: a systematic review. Autoimmun Rev 2017, 16, 1196–1208. [CrossRef]
- Kolkhir P, Pogorelov D, Olisova O, Maurer M. Comorbidity and pathogenic links of chronic spontaneous urticaria and systemic lupus erythematosus—a systematic review. Clin Exp Allergy 2016, 46, 275–287. [CrossRef]
- Kay AB, Clark P, Maurer M, et al. Elevations in T-helper-2-initiating cytokines (interleukin-33, interleukin-25 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin) in lesional skin from chronic spontaneous (‘idiopathic’) urticaria. Br J Dermatol 2015, 172, 1294–1302 25523947.
- Canoğlu K, Okutan O, Taş D, Yılmaz İ, Yeşilbaş S, Çalışkan T, Arpaçağ Koşar AF, Kartaloğlu Z, Ayten Ö, Uyar Y. Evaluation of serum interleukin-33 and gene polymorphisms in patients with bronchial asthma. Gulhane Medical Journal 2021, 63, 104–9. [CrossRef]
- Rabea RA, El-Gamal R, Fahmy EM, Taha HKE, Bakr AO, Zaki ME, Elabbasy LM. Serum interleukin 33 levels and single nucleotide polymorphism rs1929992 in Egyptian patients with chronic asthma. Egyptian Journal of Immunology 2021, 28(4):264–271. [CrossRef]
- Guo L, Zhou X, Guo X, et al. Association of interleukin-33 gene single nucleotide polymorphisms with ischemic stroke in north Chinese population. BMC Med Genet 2013, 14, 109. [CrossRef]
- Nebiolo F, Bergia R, Bommarito L, et al. Effect of arterial hypertension on chronic urticaria duration. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2009, 103, 407–410 19927539. [CrossRef]
- Bassagh A, Jafarzadeh A, Kazemipour N, Nemati M, Aminizadeh N, Larussa T, Ghazizadeh M, Abasi MH, Mirkamandar E. Decreased circulating interleukin-33 concentration in Helicobacter pylori-infected patients with peptic ulcer: Evaluation of its association with a cytokine gene polymorphism, gender of patients and bacterial virulence factor CagA. Microb Pathog. 2019 Nov;136, 103708. [CrossRef]
- Moreno V, Gonzalez J, Pelegri D (2022). _SNPassoc: SNPs-Based Whole Genome Association Studies_. R package version 2.1-0, .
- R Core Team (2023). _R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing_. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).