Submitted:
25 September 2024
Posted:
26 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
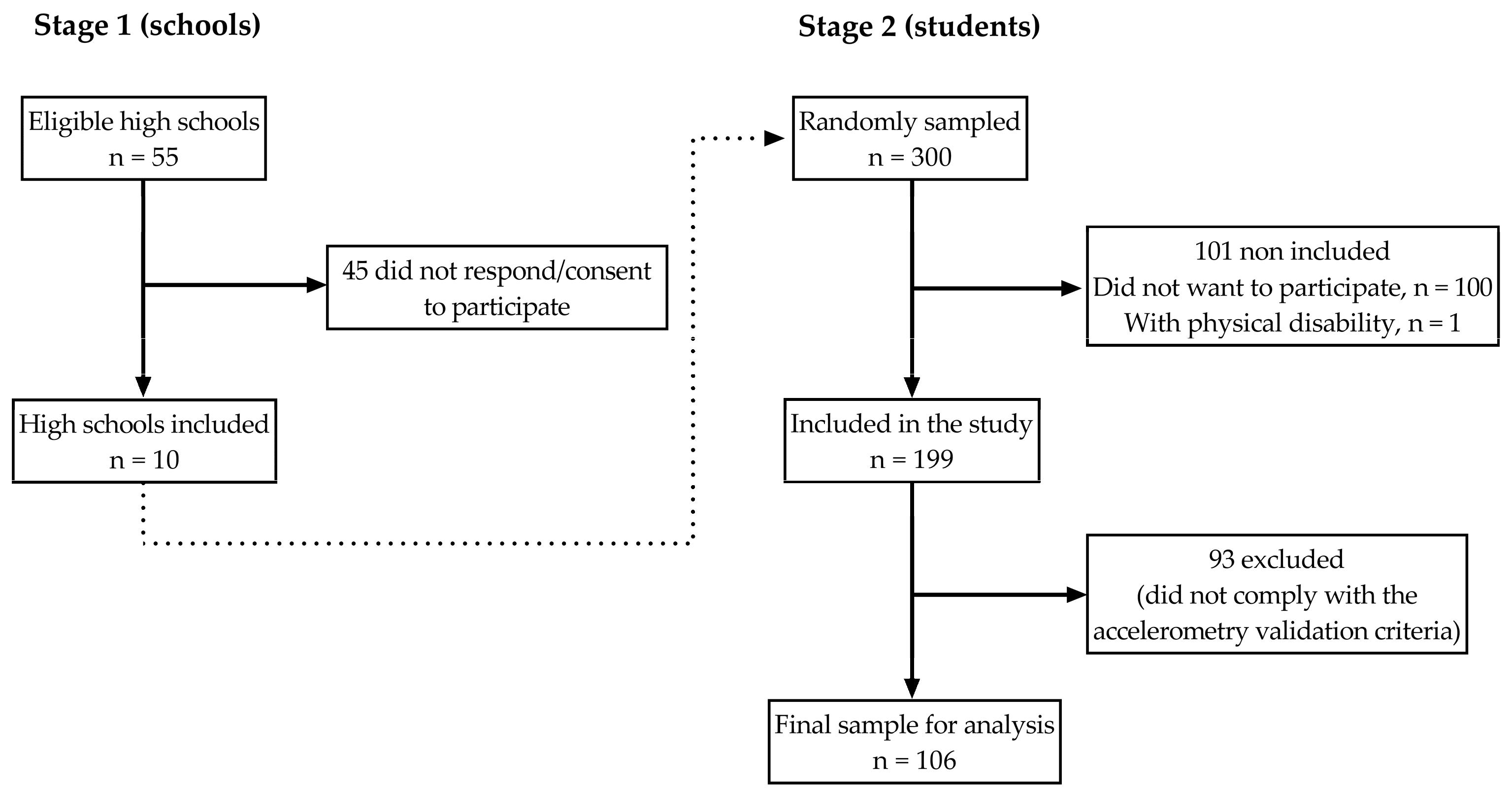
2.1. Study’s Design and Participants
2.2. Geographical Location
2.3. Anthropometric Measurements
2.4. Physical Activity
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
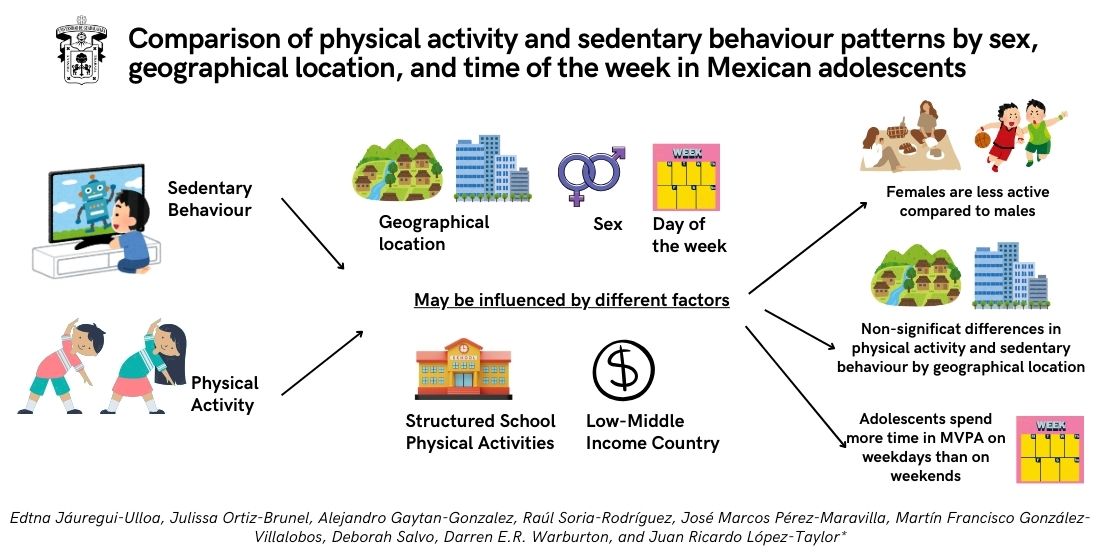
3.2. Physical Activity by Sex
3.3. Physical Activity by Geographical Location
3.4. Interaction between Sex and Geographical Location
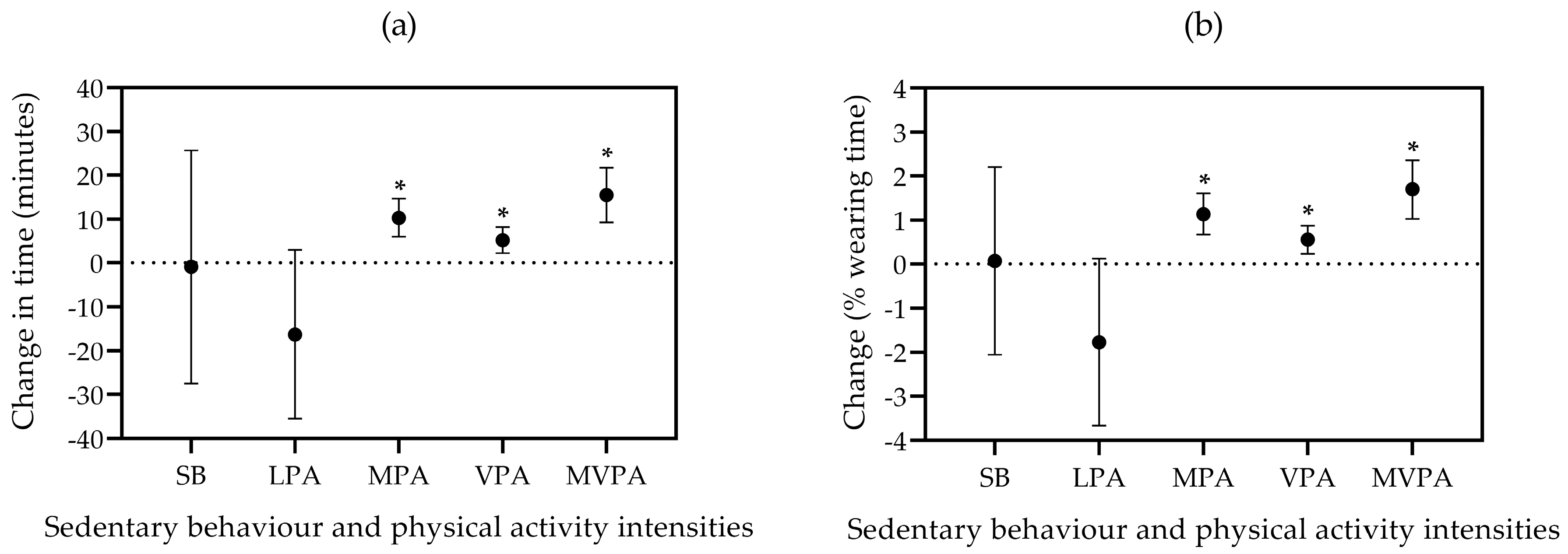
3.5. Physical Activity by Time of the Week
3.6. Compliance with Physical Activity Recommendations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bull, F. C.; Al-Ansari, S. S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M. P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J. P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour. Br J Sports Med 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, T.; Luo, J. Can Physical Activity Counteract the Negative Effects of Sedentary Behavior on the Physical and Mental Health of Children and Adolescents? A Narrative Review. Front Public Health 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hills, A. P.; Dengel, D. R.; Lubans, D. R. Supporting Public Health Priorities: Recommendations for Physical Education and Physical Activity Promotion in Schools. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2015, 57, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, R. G. de; Guedes, D. P. Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Metabolic Syndrome in Adolescents: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Evidence. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0168503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthold, R.; Stevens, G. A.; Riley, L. M.; Bull, F. C. Global Trends in Insufficient Physical Activity among Adolescents: A Pooled Analysis of 298 Population-Based Surveys with 1·6 Million Participants. Lancet Child Adolesc Health 2020, 4, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, C.; Jáuregui, A.; Campos-Nonato, I.; Barquera, S. Prevalencia y Tendencias de Actividad Física En Niños y Adolescentes: Resultados de Ensanut 2012 y Ensanut MC 2016. Salud Publica Mex 2018, 60, may–jun). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, C.; Jáuregui, A.; Hernández, C.; González, C.; Olvera, A. G.; Blas, N.; Campos, I.; Barquera, S. Prevalence of Movement Behaviors in Mexico. Salud Publica Mex 2023, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euler, R.; Jimenez, E. Y.; Sanders, S.; Kuhlemeier, A.; Van Horn, M. L.; Cohen, D.; Gonzales-Pacheco, D.; Kong, A. S. Rural–Urban Differences in Baseline Dietary Intake and Physical Activity Levels of Adolescents. Prev Chronic Dis 2019, 16, 180200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Fu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, R. Associations between Psychosocial Variables, Availability of Physical Activity Resources in Neighborhood Environment, and Out-of-School Physical Activity among Chinese Adolescents. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18, 6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromel, K.; Kudlacek, M.; Groffik, D.; Svozil, Z.; Simunek, A.; Garbaciak, W. Promoting Healthy Lifestyle and Well-Being in Adolescents through Outdoor Physical Activity. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2017, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Zhou, X. Correlates of Physical Activity Habits in Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Front Physiol 2023, 14, 1131195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazo-Sayavera, J.; Aubert, S.; Barnes, J. D.; González, S. A.; Tremblay, M. S. Gender Differences in Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior: Results from over 200,000 Latin-American Children and Adolescents. PLoS One 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, C. S. Sex-Dependent Differences in Voluntary Physical Activity. J Neurosci Res 2017, 95, (1–2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comte, M.; Hobin, E.; Majumdar, S. R.; Plotnikoff, R. C.; Ball, G. D. C.; McGavock, J. Patterns of Weekday and Weekend Physical Activity in Youth in 2 Canadian Provinces. Applied Physiology, Nutrition and Metabolism 2013, 38, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corder, K.; Schiff, A.; Kesten, J. M.; Van Sluijs, E. M. F. Development of a Universal Approach to Increase Physical Activity among Adolescents: The GoActive Intervention. BMJ Open 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco Arevalo D, Feu S, de la C. S. E. Diferencias Entre El Medio Rural y Urbano En El Nivel de Actividad Física En La Transición de La Educación Primaria a La Educación Secundaria. Rev Esp Salud Publica 2020, 29, e202005026. [Google Scholar]
- White, B.; García Bengoechea, E.; Spence, J. C.; Coppell, K. J.; Mandic, S. Comparison of Physical Activity Patterns across Large, Medium and Small Urban Areas and Rural Settings in the Otago Region, New Zealand. 2021, 134, 1534.
- Zenic, N.; Taiar, R.; Gilic, B.; Blazevic, M.; Maric, D.; Pojskic, H.; Sekulic, D. Levels and Changes of Physical Activity in Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Contextualizing Urban vs. Rural Living Environment. Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibar, A.; Bois, J. E.; Zaragoza Casterad, J.; Generelo, E.; Paillard, T.; Fairclough, S. Weekday and Weekend Physical Activity Patterns of French and Spanish Adolescents. Eur J Sport Sci 2014, 14, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lätt, E.; Mäestu, J.; Jürimäe, J. Associations of Accumulated Time in Bouts of Sedentary Behavior and Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity With Cardiometabolic Health in 10- to 13-Year-Old Boys. J Phys Act Health 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treuth, M. S.; Catellier, D. J.; Schmitz, K. H.; Pate, R. R.; Elder, J. P.; McMurray, R. G.; Blew, R. M.; Yang, S.; Webber, L. Weekend and Weekday Patterns of Physical Activity in Overweight and Normal-Weight Adolescent Girls. Obesity 2007, 15, 1782–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C. H.; Wang, S.; Wang, W. L.; Belcher, B. R.; Dunton, G. F. Day-Level Associations of Physical Activity and Sedentary Time in Mother–Child Dyads across Three Years: A Multi-Wave Longitudinal Study Using Accelerometers. J Behav Med 2022, 45, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Ochoa, M.; Brazo-Sayavera, J.; Vizmanos-Lamotte, B.; Mañas, A.; Ricardo López-Taylor, J.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Guadalupe-Grau, A. Health-Related Factors in Rural and Urban Mexican Adolescents: The HELENA-MEX Study. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Shamah-Levy, T. T.; Cuevas-Nasu, L.; Gaona-Pineda, E. B.; Gómez-Acosta, L. M.; Morales-Ruán, M. del C.; Hernández-ávila, M.; Rivera-Dommarco, J. Á. Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents, 2016 Halfway National Health and Nutrition Survey Update. Salud Publica Mex 2018, 60, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, C.; Jáuregui, A. Prevalencia y Tendencias de Actividad Física En Niños y Adolescentes : Resultados de Ensanut 2012 y Ensanut MC 2016. 2018, 60, 263–271.
- Shamah-Levy, T.; Cuevas-Nasu, L.; Rivera-Dommarco, J.; Hernández-Ávila, M. Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición de Medio Camino 2016.; 2016.
- Barker, A. R.; Gracia-Marco, L.; Ruiz, J. R.; Castillo, M. J.; Aparicio-Ugarriza, R.; González-Gross, M.; Kafatos, A.; Androutsos, O.; Polito, A.; Molnar, D.; et al. Physical Activity, Sedentary Time, TV Viewing, Physical Fitness and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Adolescents: The HELENA Study. Int J Cardiol 2018, 254, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekelund, U.; Luan, J.; Sherar, L. B.; Esliger, D. W.; Griew, P.; Cooper, A. Moderate to Vigorous Physical Activity and Sedentary Time and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents. JAMA - Journal of the American Medical Association 2012, 307, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon-larsen, P.; Nelson, M. C.; Popkin, B. M. Longitudinal Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior Trends Adolescence to Adulthood. Am J Prev Med 2004, 27, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontostoli, E.; Jones, A. P.; Pearson, N.; Foley, L.; Biddle, S. J. H.; Atkin, A. J. The Association of Contemporary Screen Behaviours with Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviour and Sleep in Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Millennium Cohort Study. Int J Behav Med 2023, 30, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sluijs, E. M. F.; Ekelund, U.; Crochemore-Silva, I.; Guthold, R.; Ha, A.; Lubans, D.; Oyeyemi, A. L.; Ding, D.; Katzmarzyk, P. T. Physical Activity Behaviours in Adolescence: Current Evidence and Opportunities for Intervention. Lancet 2021, 398, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sluijs, E. M. F.; Ekelund, U.; Crochemore-Silva, I.; Guthold, R.; Ha, A.; Lubans, D.; Oyeyemi, A. L.; Ding, D.; Katzmarzyk, P. T. Physical Activity Behaviours in Adolescence: Current Evidence and Opportunities for Intervention. The Lancet 2021, 398, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, K.; Olds, T.; Mazza, J. C. Antropométrica : Un Libro de Referencia Sobre Mediciones Corporales Humanas Para La Educación En Deportes y Salud, 2nd ed.; Biosystem, 2000.
- World Health Organization. In WHO Anthro Survey Analyser, 1st ed.; World Health Organization, 2019.
- World Health Organization. WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weight-for-Height and Body Mass Index-for-Age: Methods and Development, 2006.
- Volker, M. A. Reporting Effect Size Estimates in School Psychology Research. Psychol Sch 2006, 43, 653–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corder, K.; Craggs, C.; Jones, A. P.; Ekelund, U.; Griffin, S. J.; van Sluijs, E. M. Predictors of Change Differ for Moderate and Vigorous Intensity Physical Activity and for Weekdays and Weekends: A Longitudinal Analysis. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2013, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, S.; Barnes, J. D.; Tremblay, M. S. Evaluation of the Process and Outcomes of the Global Matrix 3.0 of Physical Activity Grades for Children and Youth. J Exerc Sci Fit 2020, 18, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfledderer, C. D.; Burns, R. D.; Byun, W.; Carson, R. L.; Welk, G. J.; Brusseau, T. A. School-based Physical Activity Interventions in Rural and Urban/Suburban Communities: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Obesity Reviews 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvo, D.; Torres, C.; Villa, U.; Rivera, J. A.; Sarmiento, O. L.; Reis, R. S.; Pratt, M. Accelerometer-Based Physical Activity Levels among Mexican Adults and Their Relation with Sociodemographic Characteristics and BMI: A Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2015, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazendale, K.; Beets, M. W.; Armstrong, B.; Weaver, R. G.; Hunt, E. T.; Pate, R. R.; Brusseau, T. A.; Bohnert, A. M.; Olds, T.; Tassitano, R. M.; et al. Children’s Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity on Weekdays versus Weekend Days: A Multi-Country Analysis. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2021, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J. M.; Sirard, J. R.; Deutsch, N. L.; Weltman, A. The Influence of Friends and Psychosocial Factors on Physical Activity and Screen Time Behavior in Adolescents: A Mixed-Methods Analysis. J Behav Med 2016, 39, 610–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, J.; Hakonen, H.; Syväoja, H.; Kulmala, J.; Kankaanpää, A.; Ekelund, U.; Tammelin, T. Changes in Physical Activity and Sedentary Time during Adolescence: Gender Differences during Weekdays and Weekend Days. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2020, 30, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlakha, D.; Salvo, D.; Hipp, A.; Brownson, R. C.; Pratt, M. Is Physical Activity in Middle-Income Countries Driven by Necessity or Choice? Exploring the Roles of Motor-Vehicle Ownership and Socioeconomic Status on Transport-Based Physical Activity in Cuernavaca, Mexico and Chennai, India. J Phys Act Health 2018, 15, S113–S113. [Google Scholar]
- Sallis, J.; Cerin, E.; Kerr, J.; Adams, M.; Sugiyama, T.; Christiansen, L.; Schipperijn, J.; Davey, R.; Salvo, D.; Frank, L.; et al. Built Environment, Physical Activity, and Obesity: Findings from the International Physical Activity and Environment Network (IPEN) Adult Study. Annu Rev Public Health 2020, 41, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Varela, A.; Salvo, D.; Pratt, M.; Milton, K.; Siefken, K.; Bauman, A.; Kohl, H. W.; Lee, I. M.; Heath, G.; Foster, C.; et al. Worldwide Use of the First Set of Physical Activity Country Cards: The Global Observatory for Physical Activity - GoPA! International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2018, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groffik, D.; Fromel, K.; Badura, P. Composition of Weekly Physical Activity in Adolescents by Level of Physical Activity. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, A.-M.; Okely, A. D.; Salmon, J.; Trost, S.; Hammersley, M.; Murdoch, A. Making ‘Being Less Sedentary Feel Normal’ –Investigating Ways to Reduce Adolescent Sedentary Behaviour at School: A Qualitative Study. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2023, 20, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburton, D. E. R.; Bredin, S. S. D. Health Benefits of Physical Activity: A Systematic Review of Current Systematic Reviews. Curr Opin Cardiol 2017, 32, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galaviz, K. I.; Argumedo García, G.; Gaytán González, A.; González-Casanova, I.; Francisco González Villalobos, M.; Jáuregui, A.; Jáuregui Ulloa, E.; Medina, C.; Selene Pacheco Miranda, Y.; Pérez Rodríguez, M.; et al. · 2 ·.
- Feng J; Huang WY; Zheng C; Jiao J; Khan A; Nisar M; Wong SH. The Overflow Effects of Movement Behaviour Change Interventions for Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Sports Med, 2024.
- Makinen, T.; Kestila, L.; Borodulin, K.; Martelin, T.; Rahkonen, O.; Prattala, R. Effects of Childhood Socio-Economic Conditions on Educational Differences in Leisure-Time Physical Activity. The European Journal of Public Health 2010, 20, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, P. J.; Carraça, E. V; Markland, D.; Silva, M. N.; Ryan, R. M. Exercise, Physical Activity, and Self-Determination Theory: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2012, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidar, A.; Ranjit, N.; Archer, N.; Hoelscher, D. M. Parental and Peer Social Support Is Associated with Healthier Physical Activity Behaviors in Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Texas School Physical Activity and Nutrition (TX SPAN) Data. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sex | |||||
| Males (n = 51) | Females (n = 55) | p-value e | |||
| Age, y a | 15.7 ± 0.8 | 15.6 ± 0.7 | 0.403 f | ||
| Geographical location b MA NMA |
33 (64.7) 18 (35.3) |
32 (58.2) 23 (41.8) |
0.552 g |
||
| Height, cm | 172.9 ± 5.8 | 160.2 ± 6.2 | < 0.001 | ||
| Weight, kg | 70.6 ± 14.0 | 56.7 ± 12.9 | < 0.001 f | ||
| BMI, kg/cm2 | 23.5 ± 4.3 | 22.0 ± 4.5 | 0.031 f | ||
| BMI categories Thinness Normal Overweight Obese |
3 (5.9) 25 (49.0) 12 (23.5) 11 (21.6) |
1 (1.8) 43 (78.2) * 5 (9.1) * 6 (10.9) |
0.019 g |
||
| Sum of five skinfolds, mm c | 71.6 ± 31.8 | 91.1 ± 32.3 | 0.002 f | ||
| Waist circumference, cm | 79.5 ± 9.6 | 70.6 ± 9.4 | < 0.001 | ||
| Hip circumference, cm | 96.2 ± 8.0 | 94.3 ± 9.1 | 0.093 f | ||
| Waist-to-hip ratio | 0.82 ± 0.05 | 0.75 ± 0.04 | < 0.001 | ||
| Geographical location | |||||
| MA (n = 65) | NMA (n = 41) | p-value | |||
| Age, y | 15.3 ± 0.7 | 15.6 ± 0.7 | 0.827 f | ||
| Sex Male Female |
33 (50.8) 32 (49.2) |
18 (43.9) 23 (56.1) |
0.552 g |
||
| Height, cm | 166.6 ± 8.4 | 165.9 ± 9.3 | 0.719 | ||
| Weight, kg | 63.6 ± 14.2 | 63.1 ± 16.6 | 0.878 | ||
| BMI, kg/cm2 | 22.8 ± 4.0 | 22.8 ± 5.1 | 0.982 | ||
| BMI categories Thinness Normal Overweight Obese |
1 (1.5) 43 (66.2) 12 (18.5) 9 (13.8) |
3 (7.3) 25 (61.0) 5 (12.2) 8 (19.5) |
0.327 g |
||
| Sum of five skinfolds, mm d | 80.0 ± 29.8 | 84.2 ± 38.4 | 0.538 | ||
| Waist circumference, cm | 75.3 ± 10.0 | 74.3 ± 11.3 | 0.648 | ||
| Hip circumference, cm | 95.2 ± 8.2 | 95.2 ± 9.3 | 0.977 | ||
| Waist-to-hip ratio | 0.79 ± 0.06 | 0.78 ± 0.6 | 0.367 | ||
| a Reported as mean ± standard deviation. b Reported as frequency count (percentage). c Males n = 49, Females n = 52. d MA n = 61, NMA n = 40. e Calculated from independent samples t-test unless otherwise stated. f Calculated from Mann-Whitney U-test. g Calculated from chi-squared test of independence. * Denotes statistically significant differences by sex within the specified category (p < 0.05). BMI: Body mass index; MA: Metropolitan area; NMA: Non-metropolitan area. | |||||
| Males (n = 51) | Females (n = 55) | Difference d | p-value | Effect size g | |
| Whole week | |||||
| Wearing time, min a | 4610 ± 53 | 4616 ± 50 | -6 ± 73 | 0.933 e | 0.000 |
| SB, min | 2745 ± 58 | 2884 ± 54 | -140 ± 79 | 0.080 | 0.002 |
| LPA, min | 1600 ± 43 | 1554 ± 40 | 46 ± 58 | 0.433 | 0.000 |
| MPA, min | 174 ± 9 | 145 ± 9 | 28 ± 13 | 0.027 | 0.037 |
| VPA, min | 91 ± 9 | 32 ± 8 | 59 ± 12 | < 0.001 | 0.181 |
| MVPA, min | 265 ± 14 | 177 ± 13 | 88 ± 20 | < 0.001 | 0.153 |
| Weekdays b | |||||
| Wearing time, min | 922 ± 11 | 922 ± 10 | 0 ± 15 | 0.988 f | 0.000 |
| SB, min | 548 ± 12 | 577 ± 11 | -29 ± 16 | 0.070 | 0.022 |
| LPA, min | 318 ± 8 | 307 ± 8 | 11 ± 11 | 0.322 | 0.000 |
| MPA, min | 37 ± 2 | 31 ± 2 | 6 ± 3 | 0.050 | 0.027 |
| VPA, min | 19 ± 2 | 7 ± 2 | 12 ± 3 | < 0.001 | 0.146 |
| MVPA, min | 56 ± 3 | 38 ± 3 | 18 ± 4 | < 0.001 | 0.123 |
| Weekend days c | |||||
| Wearing time, min | 921 ± 20 | 926 ± 18 | -5 ± 27 | 0.848 f | 0.000 |
| SB, min | 553 ± 21 | 575 ± 19 | -22 ± 28 | 0.432 | 0.000 |
| LPA, min | 328 ± 16 | 328 ± 15 | 0 ± 22 | 0.979 | 0.000 |
| MPA, min | 27 ± 3 | 21 ± 3 | 6 ± 4 | 0.146 | 0.011 |
| VPA, min | 14 ± 2 | 3 ± 2 | 11 ± 2 | < 0.001 | 0.165 |
| MVPA, min | 40 ± 4 | 24 ± 4 | 17 ± 5 | 0.002 | 0.078 |
| a Reported as least squares mean ± standard error of the mean; b Time spent in one average weekday; c Time spent in one weekend day; d Some discrepancies are expected because of rounding. e Calculated from a two-way ANOVA for the effect of sex adjusted for geographical location for the whole week variables; f Calculated from a three-way ANOVA for the effect of sex adjusted for geographical location and moment of the week for the weekday and weekernd day variables; g Calculated as omega squared. LPA: Low-intensity physical activity; MPA: Moderate-intensity physical activity; MVPA: Moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity; SB; Sedentary behaviour; VPA: Vigorous-intensity physical activity. | |||||
| Males (n = 51) | Females (n = 55) | Difference d | p-value | Effect size g | |
| Whole week | |||||
| SB, % a | 59.4 ± 1.0 | 62.5 ± 1.0 | -3.1 ± 1.4 | 0.030 e | 0.036 |
| LPA, % | 34.8 ± 0.9 | 33.6 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 1.2 | 0.337 | 0.000 |
| MPA, % | 3.8 ± 0.2 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 0.023 | 0.040 |
| VPA, % | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | < 0.001 | 0.187 |
| MVPA, % | 5.8 ± 0.3 | 3.8 ± 0.3 | 1.9 ± 0.4 | < 0.001 | 0.159 |
| Weekdays b | |||||
| SB, % | 59.3 ± 1.0 | 62.6 ± 1.0 | -3.2 ± 1.4 | 0.022 f | 0.041 |
| LPA, % | 34.6 ± 0.9 | 33.3 ± 0.8 | 1.3 ± 1.2 | 0.276 | 0.002 |
| MPA, % | 4.0 ± 0.2 | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 0.043 | 0.030 |
| VPA, % | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | < 0.001 | 0.150 |
| MVPA, % | 6.1 ± 0.4 | 4.2 ± 0.3 | 1.9 ± 0.5 | < 0.001 | 0.126 |
| Weekend days c | |||||
| SB, % | 59.7 ± 1.8 | 62.2 ± 1.7 | -2.5 ± 2.4 | 0.302 f | 0.001 |
| LPA, % | 35.9 ± 1.6 | 35.3 ± 1.5 | 0.6 ± 2.2 | 0.777 | 0.000 |
| MPA, % | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 0.114 | 0.015 |
| VPA, % | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | < 0.001 | 0.180 |
| MVPA, % | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 2.5 ± 0.4 | 1.9 ± 0.6 | < 0.001 | 0.090 |
| a Reported as least squares mean ± standard error of the mean; b Percentage of time spent in one average weekday; c Percentage of time spent in one weekend day; d Some discrepancies are expected because of rounding; e Calculated from a two-way ANOVA for the effect of sex adjusted for geographical location for the whole week variables; f Calculated from a three-way ANOVA for the effect of sex adjusted for geographical location and moment of the week for the weekday and weekend day variables; g Calculated as omega squared. LPA: Low-intensity physical activity; MPA: Moderate-intensity physical activity; MVPA: Moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity; SB; Sedentary behaviour; VPA: Vigorous-intensity physical activity. | |||||
| MA (n = 65) | NMA (n = 41) | Difference d | p-value | Effect size g | |
| Whole week | |||||
| Wearing time, min a | 4655 ± 45 | 4571 ± 57 | 84 ± 73 | 0.250 e | 0.003 |
| SB, min | 2856 ± 49 | 2773 ± 62 | 83 ± 79 | 0.297 | 0.001 |
| LPA, min | 1560 ± 36 | 1595 ± 46 | -35 ± 58 | 0.550 | 0.000 |
| MPA, min | 171 ± 8 | 148 ± 10 | 23 ± 13 | 0.070 | 0.022 |
| VPA, min | 68 ± 8 | 55 ± 10 | 13 ± 12 | 0.285 | 0.001 |
| MVPA, min | 239 ± 12 | 203 ± 15 | 36 ± 20 | 0.070 | 0.022 |
| Weekdays b | |||||
| Wearing time, min | 928 ± 9 | 917 ± 12 | 11 ± 15 | 0.460 f | 0.000 |
| SB, min | 568 ± 10 | 557 ± 13 | 11 ± 16 | 0.487 | 0.000 |
| LPA, min | 308 ± 7 | 317 ± 9 | -8 ± 11 | 0.460 | 0.000 |
| MPA, min | 37 ± 2 | 31 ± 2 | 5 ± 3 | 0.065 | 0.023 |
| VPA, min | 15 ± 2 | 12 ± 2 | 3 ± 3 | 0.278 | 0.002 |
| MVPA, min | 51 ± 3 | 43 ± 4 | 8 ± 4 | 0.067 | 0.023 |
| Weekend days c | |||||
| Wearing time, min | 944 ± 17 | 904 ± 21 | 40 ± 27 | 0.142 f | 0.011 |
| SB, min | 583 ± 18 | 545 ± 22 | 38 ± 28 | 0.183 | 0.008 |
| LPA, min | 327 ± 13 | 328 ± 17 | -1 ± 22 | 0.960 | 0.000 |
| MPA, min | 25 ± 2 | 23 ± 3 | 2 ± 4 | 0.619 | 0.000 |
| VPA, min | 9 ± 1 | 8 ± 2 | 1 ± 2 | 0.715 | 0.000 |
| MVPA, min | 33 ± 3 | 30 ± 4 | 3 ± 5 | 0.595 | 0.000 |
| a Reported as least squares mean ± standard error of the mean; b Time spent in one average weekday; c Time spent in one weekend day; d Some discrepancies are expected because of rounding. e Calculated from a two-way ANOVA for the effect of geographical location adjusted for sex for the whole week variables; f Calculated from a three-way ANOVA for the effect of geographical location adjusted for sex and moment of the week for the weekday and weekend day variables; g Calculated as omega squared. LPA: Low-intensity physical activity; MA: Metropolitan area; MPA: Moderate-intensity physical activity; MVPA: Moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity; NMA: Non-metropolitan area; SB; Sedentary behaviour; VPA: Vigorous-intensity physical activity. | |||||
| MA (n = 51) | NMA (n = 55) | Difference d | p-value | Effect size f | |
| Whole week | |||||
| SB, % a | 61.3 ± 0.9 | 60.6 ± 1.1 | 0.7 ± 1.4 | 0.637 e | 0.000 |
| LPA, % | 33.6 ± 0.8 | 34.9 ± 1.0 | -1.3 ± 1.2 | 0.279 | 0.002 |
| MPA, % | 3.7 ± 0.2 | 3.2 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 0.117 | 0.014 |
| VPA, % | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.3 | 0.389 | 0.000 |
| MVPA, % | 5.1 ± 0.3 | 4.5 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 0.125 | 0.013 |
| Weekdays b | |||||
| SB, % | 61.2 ± 0.9 | 60.8 ± 1.1 | 0.4 ± 1.4 | 0.766 f | 0.000 |
| LPA, % | 33.3 ± 0.7 | 34.5 ± 0.9 | -1.2 ± 1.2 | 0.302 | 0.001 |
| MPA, % | 3.9 ± 0.2 | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 0.095 | 0.017 |
| VPA, % | 1.6 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.3 | 0.338 | 0.000 |
| MVPA, % | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 4.7 ± 0.4 | 0.9 ± 0.5 | 0.099 | 0.017 |
| Weekend days c | |||||
| SB, % | 61.7 ± 1.5 | 60.2 ± 1.9 | 1.5 ± 2.4 | 0.526 f | 0.000 |
| LPA, % | 34.7 ± 1.3 | 36.4 ± 1.7 | -1.7 ± 2.2 | 0.442 | 0.000 |
| MPA, % | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 2.5 ± 0.3 | 0.1 ± 0.4 | 0.750 | 0.000 |
| VPA, % | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.0 ± 0.3 | 0.974 | 0.000 |
| MVPA, % | 3.5 ± 0.3 | 3.4 ± 0.4 | 0.1 ± 0.6 | 0.802 | 0.000 |
| a Reported as least squares mean ± standard error of the mean; b Percentage of time spent in one average weekday; c Percentage of time spent in one weekend day; d Some discrepancies are expected because of rounding. e Calculated from a two-way ANOVA for the effect of geographical location adjusted for sex for the whole week variables; f Calculated from a three-way ANOVA for the effect of geographical location adjusted for sex and moment of the week for the weekday and weekend day variables; g Calculated as omega squared. LPA: Low-intensity physical activity; MA: Metropolitan area; MPA: Moderate-intensity physical activity; MVPA: Moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity; NMA: Non-metropolitan area; SB; Sedentary behaviour; VPA: Vigorous-intensity physical activity. | |||||
| Variable | Subgroups a | Comparison within subgroups b | Mean 1 e | Mean 2 | Difference g | P-value |
| Whole week c | ||||||
| MPA, min | MA | Males vs Females | 199 ± 11 f | 144 ± 11 | 55 ± 16 | < 0.001 |
| NMA | Males vs Females | 149 ± 15 | 147 ± 13 | 1 ± 20 | 0.947 | |
| MVPA, min | MA | Males vs Females | 303 ± 17 | 175 ± 17 | 128 ± 24 | < 0.001 |
| NMA | Males vs Females | 226 ± 23 | 179 ± 20 | 47 ± 31 | 0.133 | |
| MPA, min | Males | MA vs NMA | 199 ± 11 | 149 ± 15 | 50 ± 18 | 0.008 |
| Females | MA vs NMA | 144 ± 11 | 147 ± 13 | -4 ± 17 | 0.824 | |
| MVPA, min | Males | MA vs NMA | 303 ± 17 | 226 ± 23 | 77 ± 29 | 0.009 |
| Females | MA vs NMA | 175 ± 17 | 179 ± 20 | -5 ± 27 | 0.864 | |
| Time of the week d | ||||||
| MPA, min | MA | Males vs Females | 36 ± 2 | 25 ± 2 | 11 ± 3 | 0.001 |
| NMA | Males vs Females | 27 ± 3 | 27 ± 3 | 1 ± 4 | 0.878 | |
| MVPA, min | MA | Males vs Females | 55 ± 3 | 30 ± 3 | 24 ± 5 | < 0.001 |
| NMA | Males vs Females | 42 ± 4 | 32 ± 4 | 10 ± 6 | 0.096 | |
| MPA, min | Males | MA vs NMA | 36 ± 2 | 27 ± 3 | 9 ± 4 | 0.025 |
| Females | MA vs NMA | 25 ± 2 | 27 ± 3 | -1 ± 4 | 0.688 | |
| MVPA, min | Males | MA vs NMA | 55 ± 3 | 42 ± 4 | 13 ± 6 | 0.023 |
| Females | MA vs NMA | 30 ± 3 | 32 ± 4 | -2 ± 5 | 0.751 | |
| a Refers to the categories of Sex or Geographical location. b Refers to the categories being compared within each subgroup of Sex or Geographical location. c Corresponds to the aggregated time from the five assessed days (i.e., minutes per week). d Corresponds to the average assessed day from the average weekday and weekend day (i.e., minutes per day). e The mean 1 and mean 2 belong to the first and second categories, which are compared in the third column. f Data reported as least squares means ± SEM. g Some discrepancies are expected due to rounding. MA: Metropolitan area; MPA: Moderate-intensity physical activity; MVPA: Moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity; NMA: Non-metropolitan area. | ||||||
| All | Sex | Geographical location | |||||
| Males | Females | p-value f | MA | NMA | p-value f | ||
| n | 106 | 51 | 55 | 65 | 41 | ||
| Days of compliance a Zero One Two or more |
43 (40.6) e 27 (25.5) 36 (34.0) |
13 (25.5) 10 (19.6) 28 (54.9) |
30 (54.5)* 17 (30.9) 8 (14.5)* |
< 0.001 |
25 (38.5) 15 (23.1) 25 (38.5) |
18 (43.9) 12 (29.3) 11 (26.8) |
0.458 |
| Weekly compliance b < 300 minutes ≥ 300 minutes |
85 (80.2) 21 (19.8) |
33 (64.7) 18 (35.3) |
52 (94.5) 3 (5.5) |
< 0.001 |
49 (75.4) 16 (24.6) |
36 (87.8) 5 (12.2) |
0.140 |
| Weekdays compliance c < 60 minutes ≥ 60 minutes |
80 (75.5) 26 (24.5) |
31 (60.8) 20 (39.2) |
49 (89.1) 6 (10.9) |
0.001 |
46 (70.8) 19 (29.2) |
34 (82.9) 7 (17.1) |
0.173 |
| Weekends compliance d < 60 minutes ≥ 60 minutes |
93 (87.7) 13 (12.3) |
41 (80.4) 10 (19.6) |
52 (94.5) 3 (5.5) |
0.037 |
55 (84.6) 10 (15.4) |
38 (92.7) 3 (7.3) |
0.362 |
| a Represents the number of days the participant met the physical activity recommendations of at least 60 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity per day. b Represents whether the participant met the recommendation by accumulating the minutes for the whole week (i.e., 5 days x 60 minutes a day). c Represents whether the participant met the recommendation on an average weekday. d Represents whether the participant met the recommendation on the weekend day. e Data expressed as frequency (percentage). f Calculated from a chi-squared test of independence for the comparison by sex and geographical location. * Denotes statistically significant differences by sex within the specified category (p < 0.05). MA: Metropolitan area; NMA: Non-metropolitan area. | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





