Submitted:
26 September 2024
Posted:
27 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Reagents
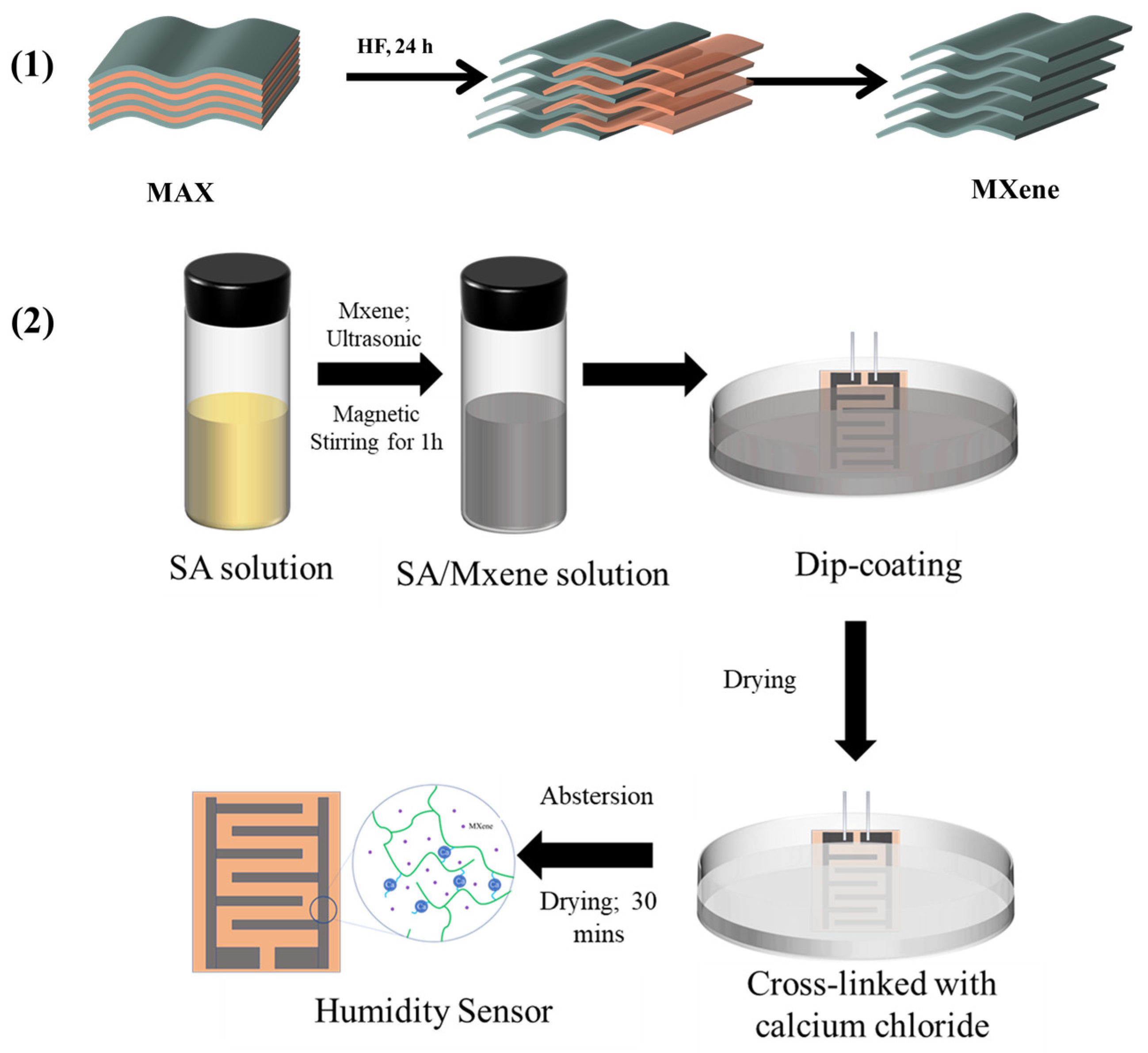
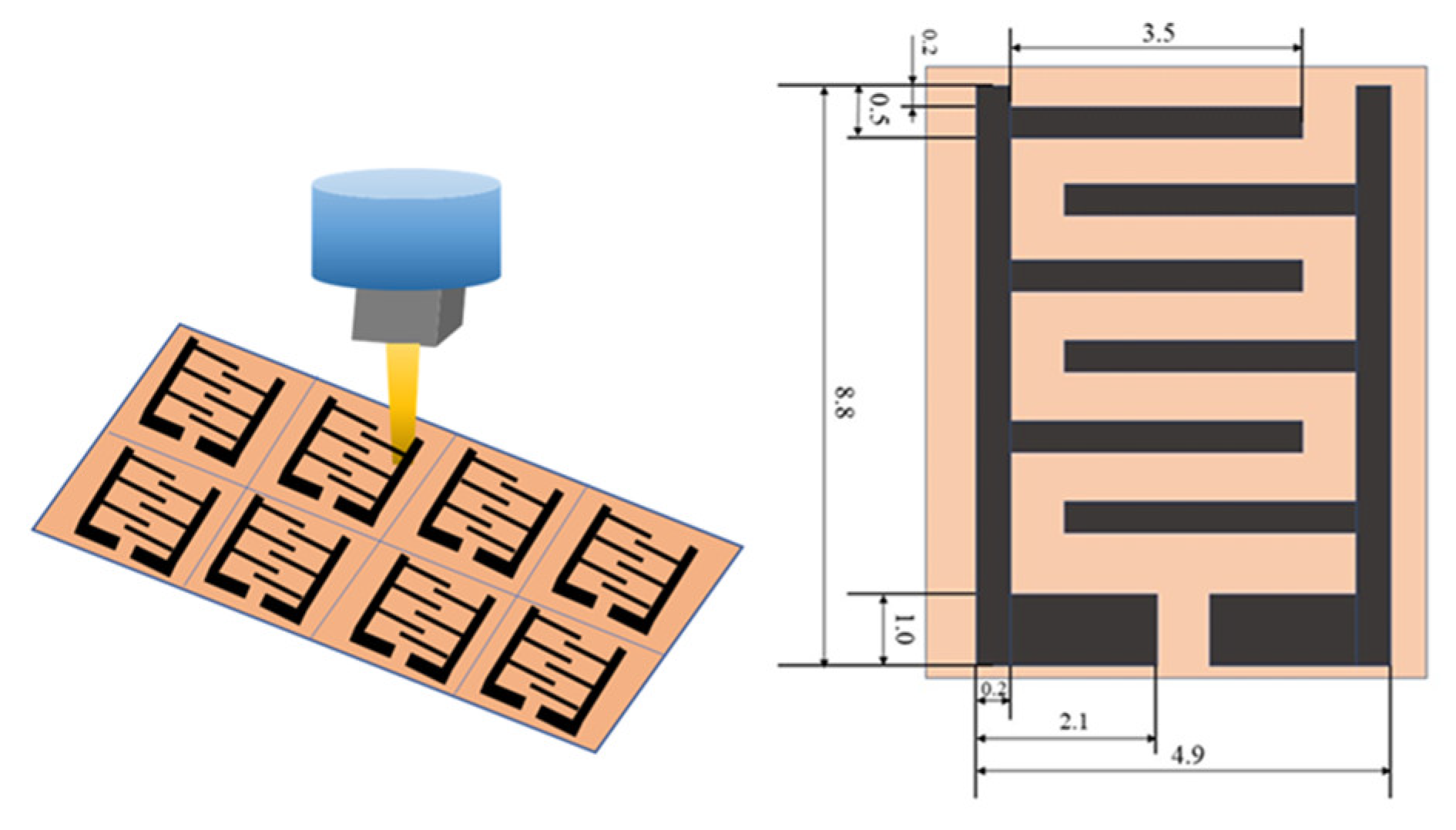
2.2. Preparation of Crosslinked SA (c-SA)/MXene FHS
2.3. Characterizations
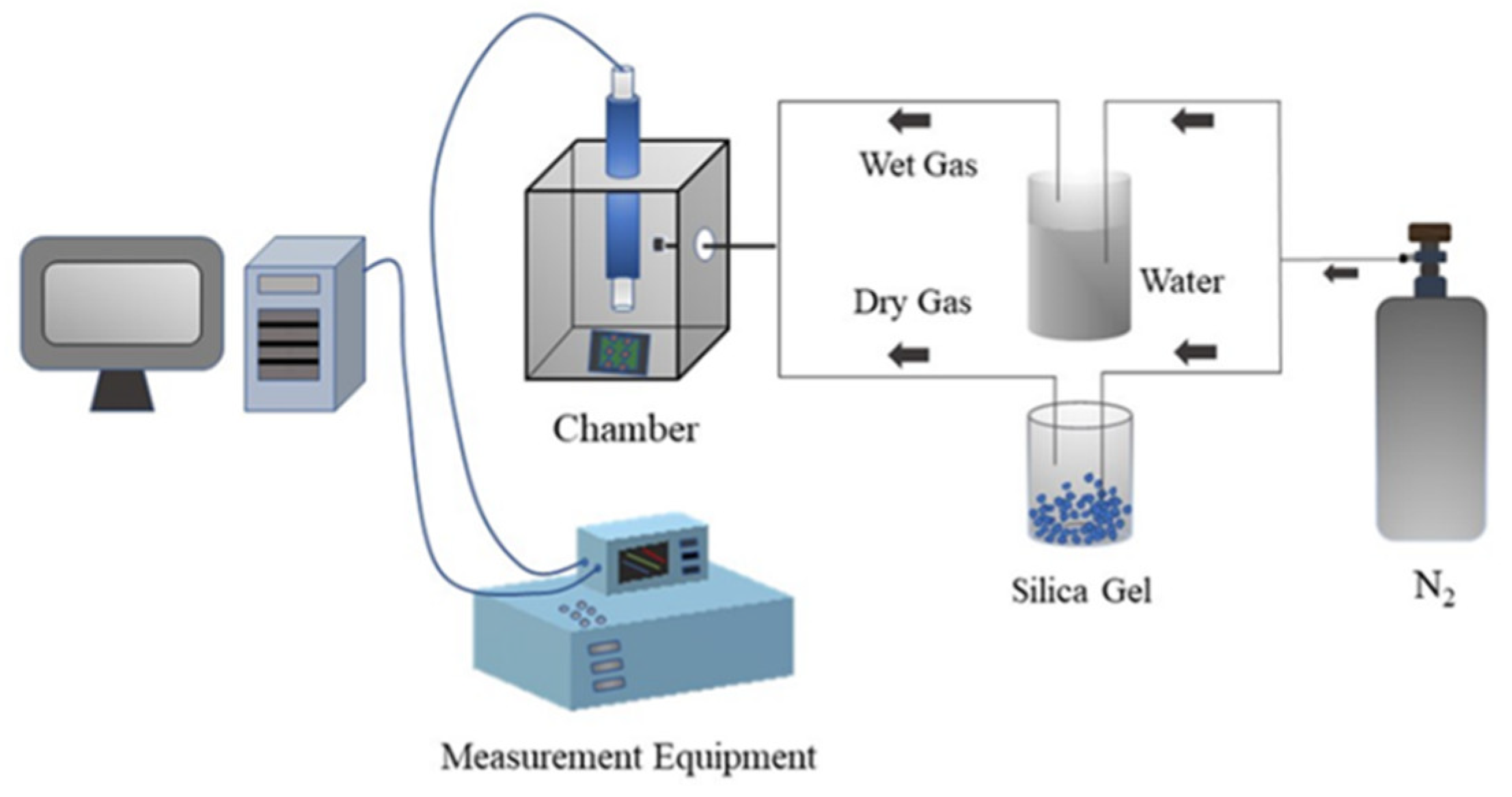
2.4. Measurements of Humidity Sensing Properties
2.5. Application of c-SA/MXene1-30 FHS
3. Results and Discussion
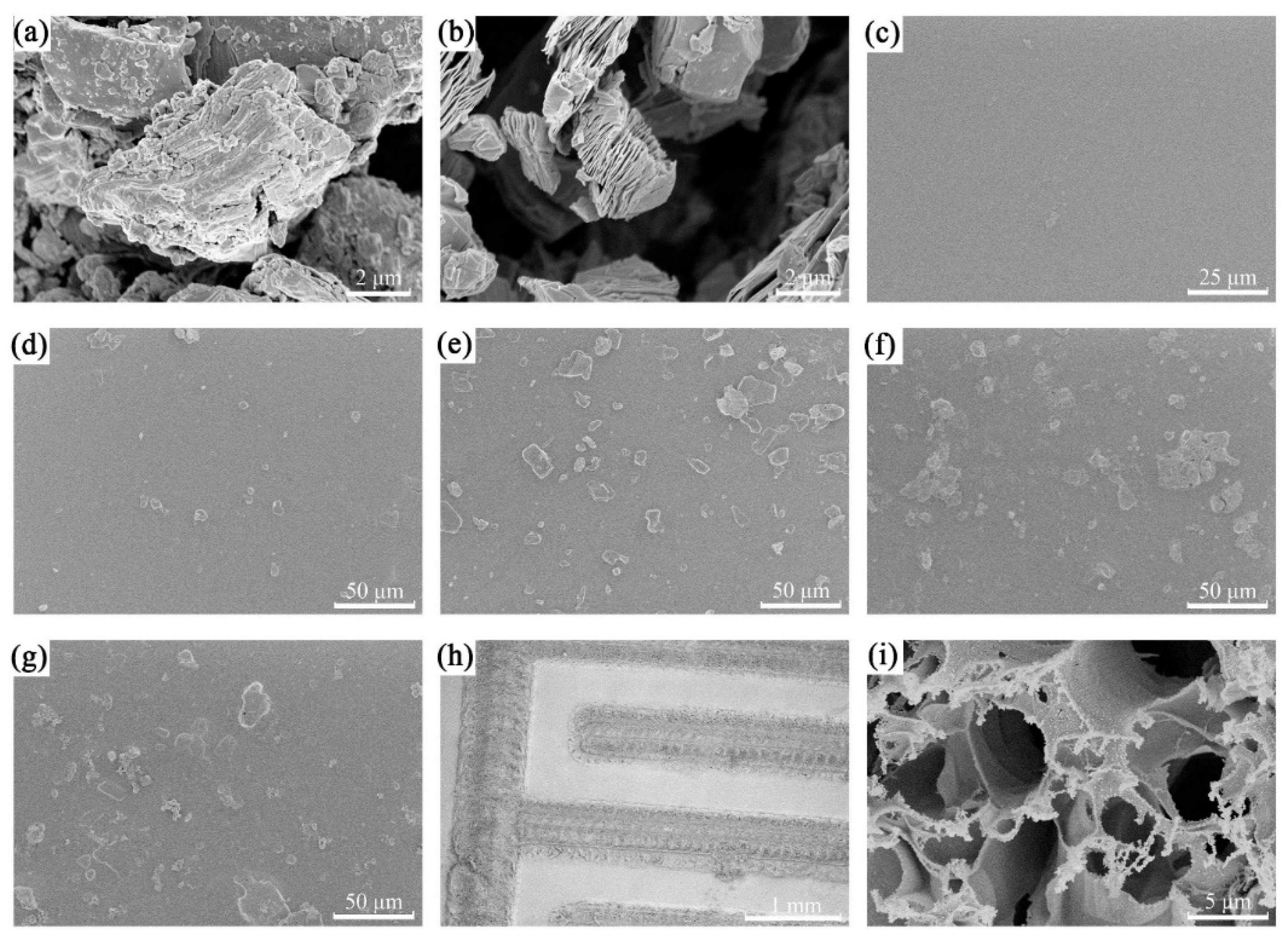
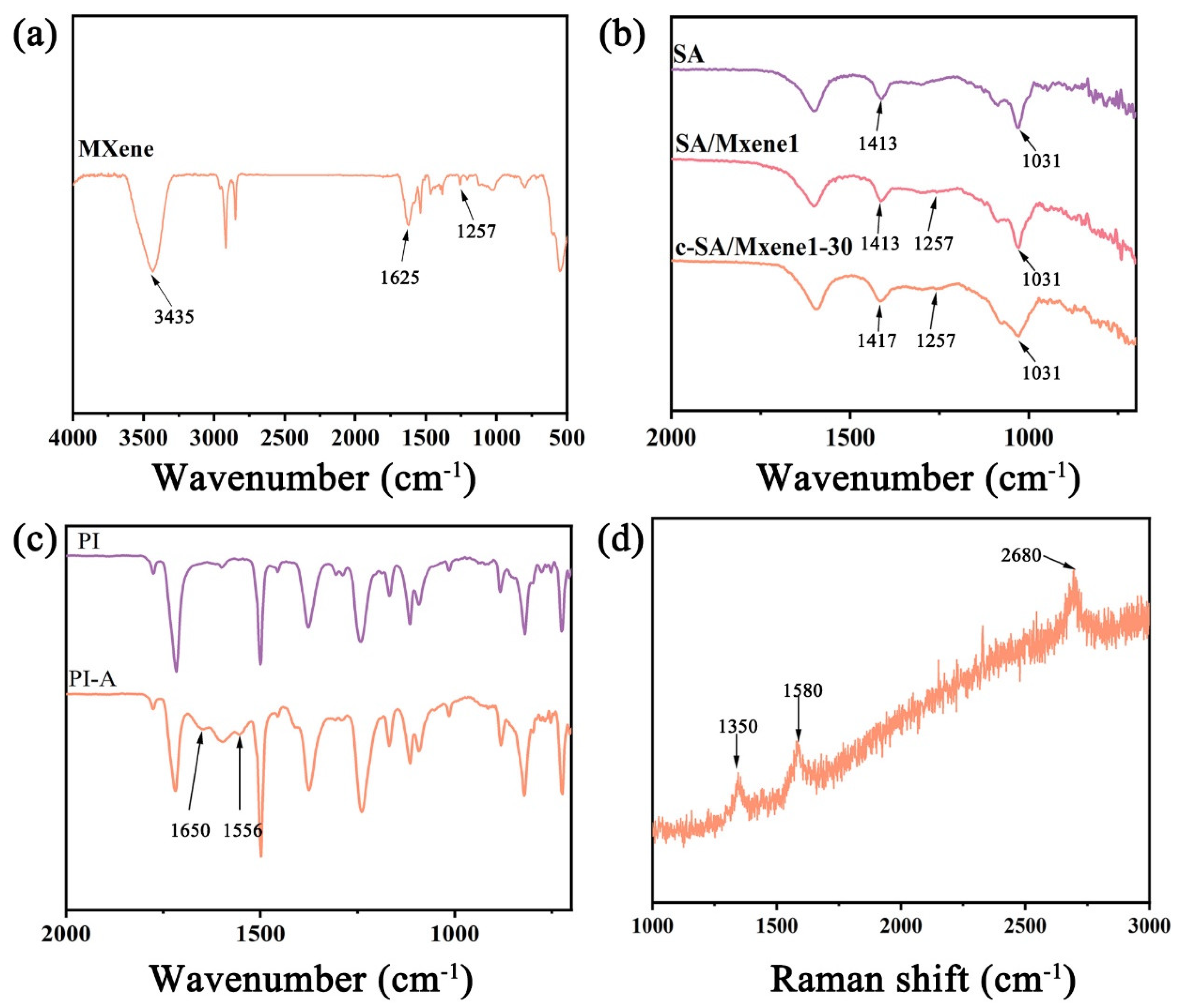
3.1. Characterization of FHS
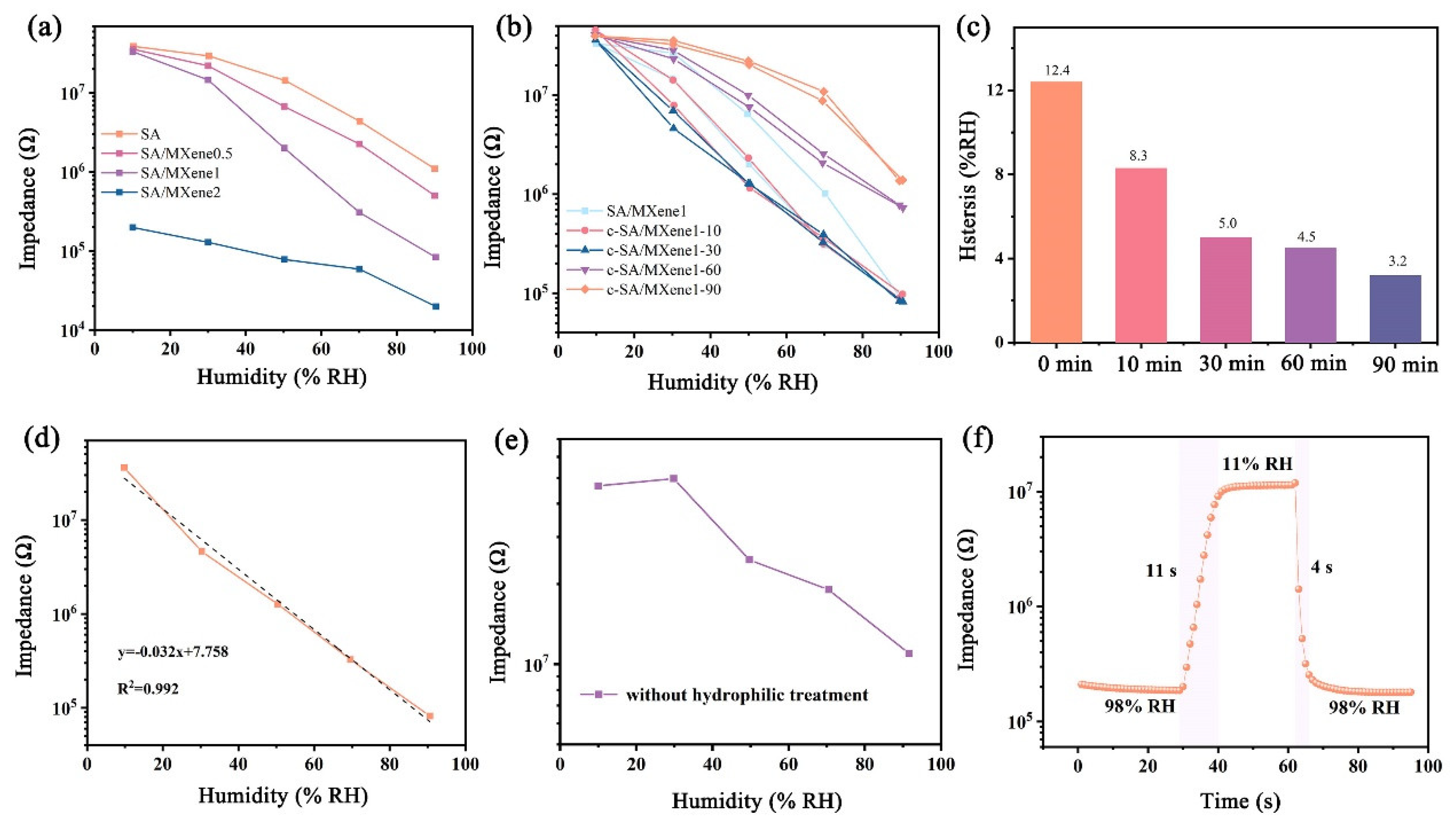
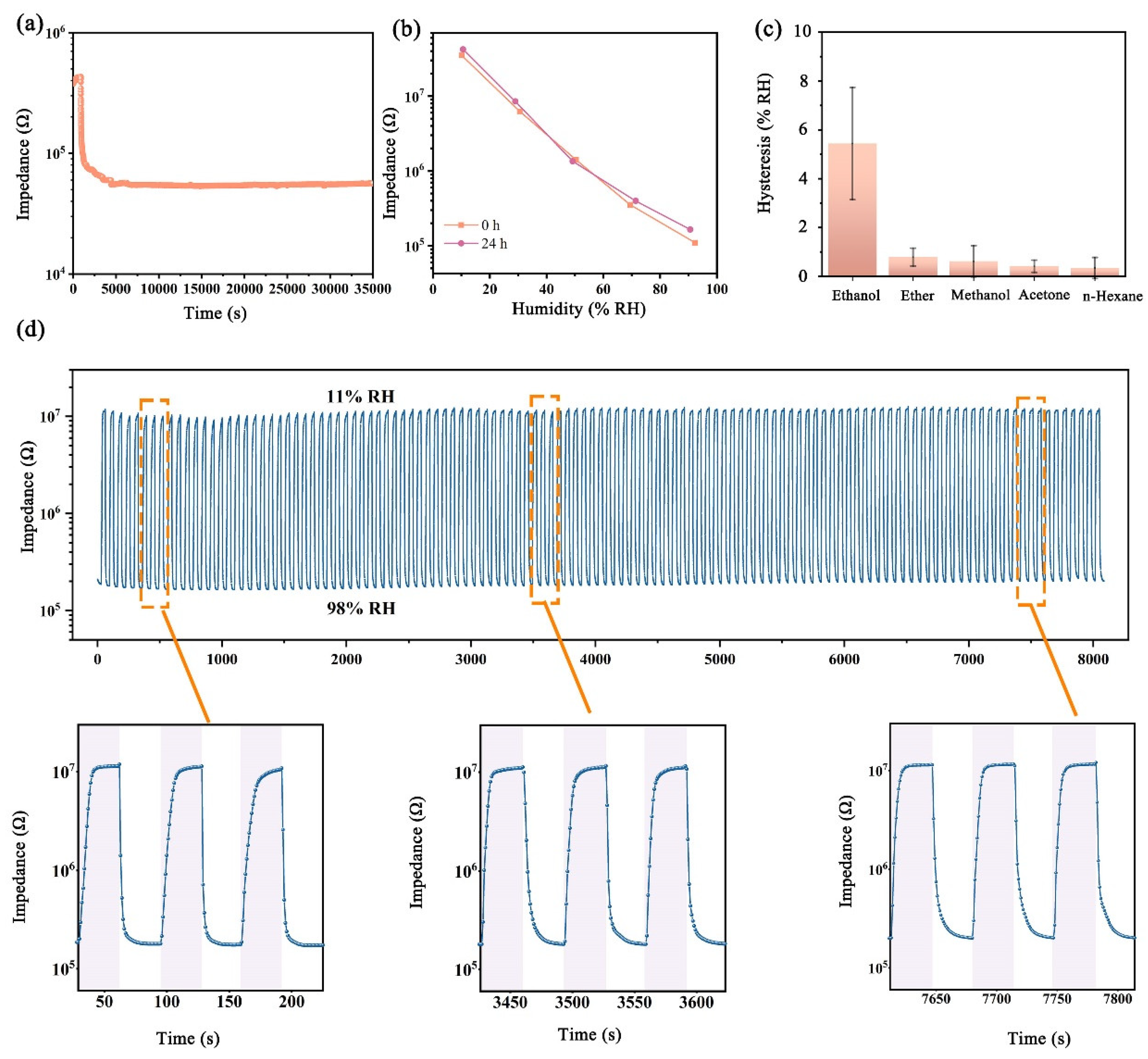
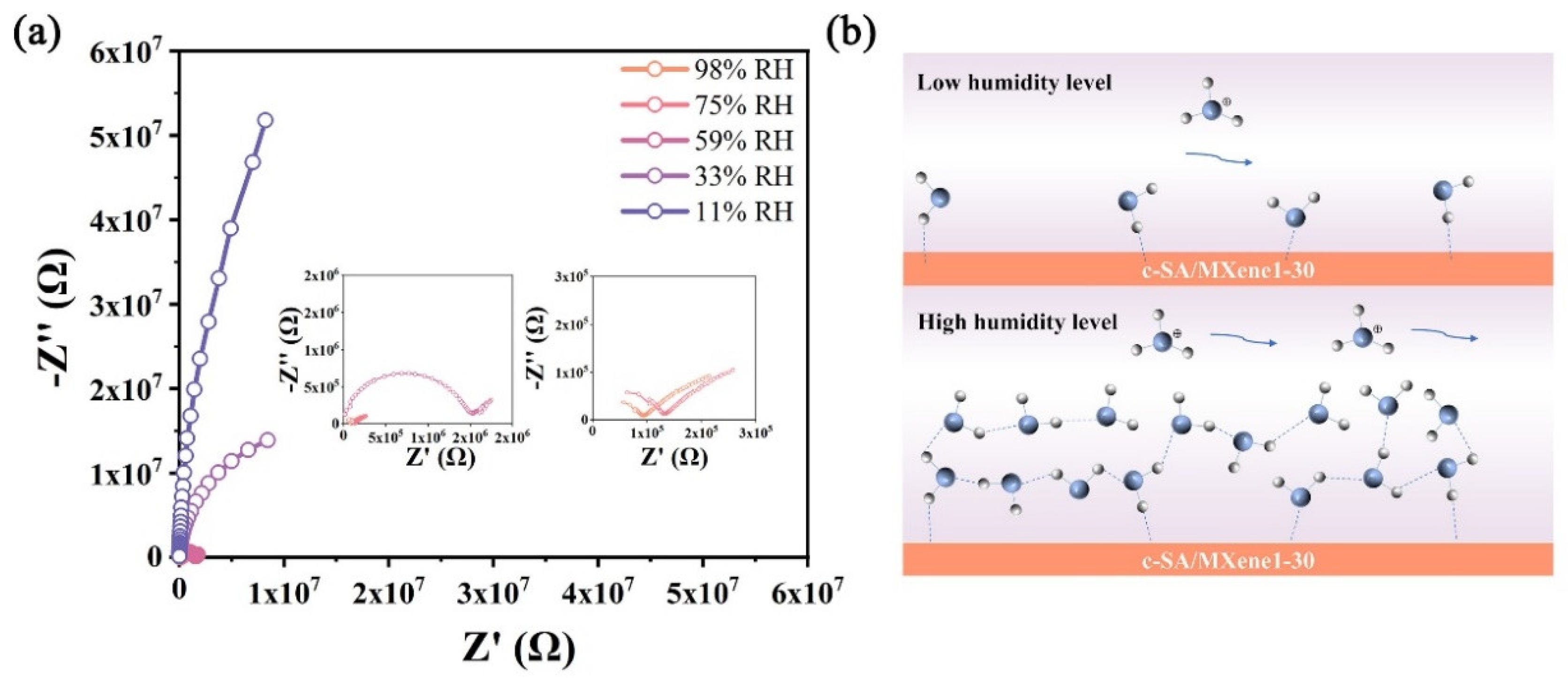
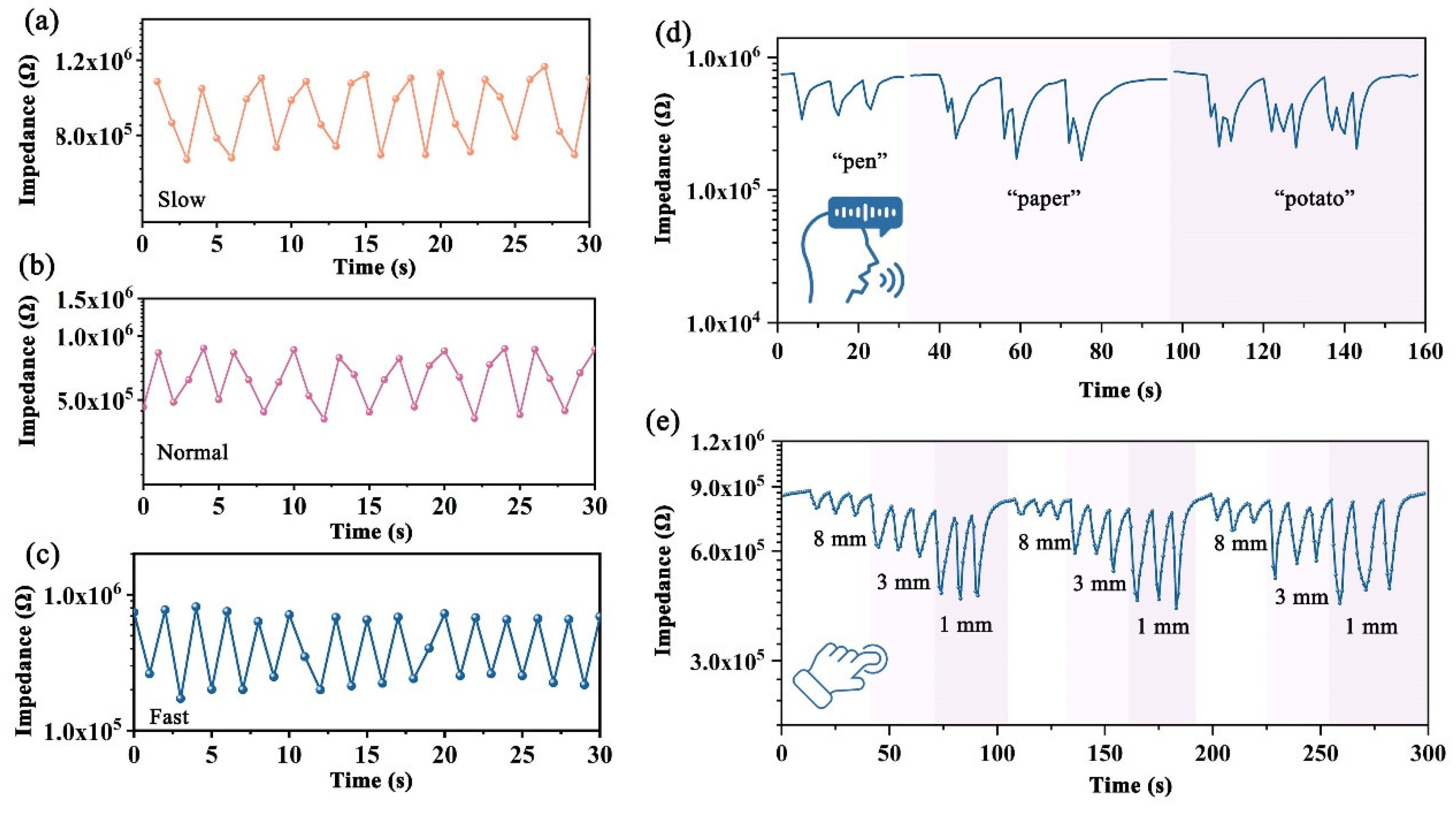
3.2. Humidity Sensing Properties of FHS
3.3. Applications of FHS
4. Conclusions
Author contributions:
Declaration of Competing Interest:
Acknowledgments
References
- Yan, S.Z.; Shen, D.D.; Xin, B.J.; Newton, M.A.A.; Wu, Y. Rhombus-patterned flexible self-supported PVDF-based humidity sensor for respiratory monitoring. Polymer. 2023, 282, 126139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.X.; Zhou, J.M.; Weng, S.C.; Wu, X.J. Flexible Chitosan-Based Capacitive Humidity Sensors for Respiratory Monitoring. Sensors. 2024, 24, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Y.; Mei, S.X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, X.M.; Cui, Z.; Fu, P.; Pang, X.C.; Liu, M.; Ye, Y. Thermoplastic polyamide elastomer based flexible humidity sensor for breath monitoring. Mater. Des. 2023, 235, 112438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.K.; Hu, C.; Li, Z.X.; Zhao, Q.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Zheng, D.Z.; Yang, G.Y.; Liu, B. A fast response humidity sensor based on MXene-SWCNTs for the monitoring of respiration. Sens. Actuators, B. 2024, 410, 135655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Xu, X.; Huang, M.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Xu, Z.Q.; Feng, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.g.; Wang, Y. Interlayer cross-linked MXene enables ultra-stable printed paper-based flexible sensor for real-time humidity monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.L.; Wang, H.X.; Dou, Y.H.; Lai, P.G. Meshed, Flexible, and Self-Supported Humidity Sensors by Direct-Writing with Multifunctional Applications. ACS Omega. 2024, 9, 33261–33269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.C.; Li, Z.J.; Zheng, H.X.; Jiang, X.H.; Wu, H.W.; Zhou, H.W.; Liu, H.B. Disposable, strain-insensitive, and room-temperature-operated flexible humidity and VOC sensor with enhanced sensitivity and selectivity through interface control. Sens. Actuators, B. 2024, 399, 134831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.H.; Jiang, Y.D.; Huang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Pan, H.; Zhao, Q.N.; Xie, G.Z.; Du, X.S.; Tai, H.L. Paper and carbon ink enabled low-cost, eco-friendly, flexible, multifunctional pressure and humidity sensors. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 30, 055012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.J.; Jiang, C.P.; Hu, G.S.; Liu, J.Q.; Yang, B. Flexible Noncontact Sensing for Human–Machine Interaction. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Chen, G.D.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, N.; Wen, J.; Zhou, N.; Li, S.J.; Mao, H.Y.; Huang, C.J. Wafer-Level, High-Performance, Flexible Sensors Based on Organic Nanoforests for Human–Machine Interactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2023, 15, 30793–30803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.M.; Bu, M.M.; Ma, Z.T.; Sun, J.Y.; Yan, Y.H.; Xiu, K.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Hu, N.; Li, Y.F. Flexible, non-contact and multifunctional humidity sensors based on two-dimensional phytic acid doped co-metal organic frameworks nanosheets. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 2010–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.L.; Feng, W.Q.; Yu, D.; Wang, W. High sensitive humidity sensor based on PEDOT:PSS/CMC-Na coated polyester fabric with directional moisture transport performance. Colloids Surf., A. 2024, 682, 132880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.K.; Zhao, T.T.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, L.; Cheng, C.C.; Dai, J.S.; Xue, L.W.; Zhou, J.X.; Liu, H.; Yin, L.Q.; et al. A skin-conformal and breathable humidity sensor for emotional mode recognition and non-contact human-machine interface. npj Flexible Electron. 2024, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.L.; Qiao, J.Y.; Zhang, L.X.; Yue, Y.W.; Qiu, Q.D.; Hou, Z.J.; Yin, J.; Bie, L.J. High-Performance Flexible Humidity Sensors Based on MCl (M = Li, Na, K) Doped PVP/PVDF Self-Supporting Films for Boosted Real-Time Noncontact Moisture Monitoring. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 7458–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Shi, R.L.; Lou, Z.; Chai, R.Q.; Jiang, K.; Shen, G.Z. Flexible Smart Noncontact Control Systems with Ultrasensitive Humidity Sensors. Small. 2019, 15, 1902801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Tai, H.L.; Su, Y.J.; Xie, G.Z.; Du, X.S.; Jiang, Y.D. Self-assembled graphene oxide/polyethyleneimine films as high-performance quartz crystal microbalance humidity sensors. Rare Met. 2021, 40, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Guan, X.; Hou, Z.N.; Liu, L.C.; Zhao, H.R.; Liu, S.; Fei, T.; Zhang, T. Humidity sensors based on metal organic frameworks derived polyelectrolyte films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 602, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.Y.; Ma, Z.H.; Duan, Q. Preparation of stable crosslinked polyelectrolyte and the application for humidity sensing. Sens. Actuators, B. 2018, 272, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.X.; Zhao, H.R.; Lin, X.Z.; Liu, S.; Fei, T.; Zhang, T. Humidity Sensors Based on 3D Porous Polyelectrolytes via Breath Figure Method. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 1900846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Kurtoglu, M.; Presser, V.; Lu, J.; Niu, J.; Heon, M.; Hultman, L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Two-Dimensional Nanocrystals Produced by Exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4248–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Guo, S.J.; Chen, K.L.; Zhao, M.; Wu, W.X.; Xia, X.J.; Zhao, J. CuO nanoparticles embedded in laser-induced graphene for flexible planar micro-supercapacitors. Surf. Interfaces. 2024, 52, 104968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.; Rasheed, A.; Ayman, I.; Rasheed, T.; Munir, S.; Ajmal, S.; Agboola, P.O.; Warsi, M.F.; Shahid, M. Synthesis of Ultrathin MnO2 Nanowire-Intercalated 2D-MXenes for High-Performance Hybrid Supercapacitors. Energy & Fuels. 2021, 35, 3469–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Y.; Zhao, X.; Illeperuma, W.R.K.; Chaudhuri, O.; Oh, K.H.; Mooney, D.J.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z. Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels. Nature. 2012, 489, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.R.; Hu, X.M.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Wu, M.Y.; Feng, Y.; He, Z.L.; Qi, G.S.; Ren, W.X.; Liang, Y.T.; Wang, W.; et al. Research and development of a sodium alginate/calcium ion gel based on in situ cross-linked double-network for controlling spontaneous combustion of coal. Fuel. 2022, 322, 124260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Fan, W.; Huang, Y.P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, T. Graphene/carbon aerogels derived from graphene crosslinked polyimide as electrode materials for supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houeix, Y.; Gerardo, D.; Romero, F.J.; Toral, V.; Hernandez, L.; Rivadeneyra, A.; Castillo, E.; Morales, D.P.; Rodriguez, N. Dry Laser-Induced Graphene Fractal-like ECG Electrodes. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2024, 10, 2300767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.R.; Jia, B.H.; Chen, X.; Gu, M. In Situ Third-Order Non-linear Responses During Laser Reduction of Graphene Oxide Thin Films Towards On-Chip Non-linear Photonic Devices. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2699–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.T.; Wu, Z.J.; Jiang, D.W.; Guo, N.; Wang, Y.; Ding, T.; Weng, L. A highly stretchable, sensing durability, transparent, and environmentally stable ion conducting hydrogel strain sensor built by interpenetrating Ca2+-SA and glycerol-PVA double physically cross-linked networks. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 1712–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.C.; Yuan, Q.; Jiang, X.M.; Tu, J.C.; Duan, L.B.; Gu, J.W.; Zhang, Q.Y. Humidity sensing mechanism of mesoporous MgO/KCl–SiO2 composites analyzed by complex impedance spectra and bode diagrams. Sens. Actuators, B. 2012, 174, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, X.S.; Tang, N.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, H.N.; Duan, X.X. Rapid response flexible humidity sensor for respiration monitoring using nano-confined strategy. Nanotechnology. 2020, 31, 125302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.J.; Chen, F.Y.; Lai, H.L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.P. Wearable breath monitoring based on a flexible fiber-optic humidity sensor. Sens. Actuators, B. 2021, 349, 130794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.F.; Zha, L.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, X.J. Fully integrated wearable humidity sensor for respiration monitoring. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1070855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.J.; Chen, H.Z.; Yang, M.J.; Li, Y. Facile fabrication of poly (diallyldimethyl ammonium chloride)/Ti3C2Tx/poly (vinylidene fluoride) 3D hollow fiber membrane flexible humidity sensor and its application in the monitoring of health-related physiological activity. Sens. Actuators, B. 2023, 374, 132773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.K.; Zhao, T.T.; Tian, X.M.; Yuan, L.; Xue, X.Y.; Wang, Z.G.; Yin, L.Q.; Zhang, J.H. A high-performance humidity sensor based on alkalized MXenes and poly(dopamine) for touchless sensing and respiration monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2022, 10, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Lou, J.; Ding, Q.J.; Jiang, Y.F.; Li, X.; Han, W.J. Bacterial cellulose/MWCNT coatings for highly sensitive and flexible paper-based humidity sensors. Cellulose. 2023, 30, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



