1. Introduction
The aggregation and accumulation of beta-amyloid (Aβ) peptide plays an important role in the pathological sequence of events leading to Alzheimer's disease (AD) [
1]. The transmembrane protein, amyloid precursor protein (APP), is processed by sequential enzymatic cleavage of the beta [
2] and gamma secretase enzyme complexes [
3] to release Aβ species, terminating at amino acid residues 40 (Aβ
1-40) and 42 (Aβ
1-42). Although the Aβ
1-42 peptide is a minor component of both deposited and secreted Aβ species in AD brain, it has been found to accumulate in the senile plaques of all types [
4] and to be more amyloidogenic than the Aβ
1-40 peptide [
5] as the two additional hydrophobic residues at the C-terminus facilitate the rapid formation of more stable β-sheet structures by Aβ
1-42 [
6]. Because of the known association between the propensity to form higher order assemblies and neurotoxicity [
6], knowledge of structural toxicity of Aβ
1-42 peptides would greatly facilitate the knowledge of the causative role of the Aβ
1-42 peptide in AD and the development of therapeutic agents.
The amyloid cascade hypothesis initially proposed the link between cognitive deficits and amyloid plaques in AD. Subsequently, several lines of evidence have linked the earliest amyloid toxicities to soluble Aβ species, although the Aβ peptide can exist in multiple forms, including monomers, oligomers, protofibrils and fibrils [
7]. An increasing number of studies support the role of oligomeric Aβ as being the critical initiator of toxicity in the pathogenesis of AD [
1]. For example, cognitive impairment and synaptic dysfunction have been shown to precede the formation of amyloid plaques [
8,
9], and these phenomena correlated and coincided with increases in Aβ
1-42 oligomer levels [
10]. Aβ
1-42 oligomers have been isolated from parenchymal and vascular brain deposits as well as CSF of AD patients and discovered to be elevated in a region-specific manner [
11,
12,
13]. Furthermore, Aβ
1-42 oligomers appear sequentially in the brain regions associated with cognitive function, including the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus [
14]. Overall, these data highlight that Aβ
1-42 oligomers are the toxic culprit species that play a central role in the aetiology of AD [
15].
The hippocampus has the ability to form episodic memory related to past events or experiences through one-trial association of spatial, temporal and novel information [
16]. The CA1 subregion, an output structure of the hippocampus, is involved in the temporal processing of information to provide spatial or non-spatial context [
17] and is important for formation of spatial working memory [
18] and spatial memory [
19], as well as contextual memory [
20,
21], and recognition memory [
22]. Interestingly, CA1 was selectively affected in the early stage of AD which is characterized by degenerative anatomical and functional consequences with differential vulnerability along the radial, transverse, and longitudinal axes [
23]. Although physiological action potential trains are important for transmission and maintenance of signals as well as neuronal survival [
24], little effort has been made to investigate the effects of Aβ
1-42 oligomers on the intrinsic properties of CA1 pyramidal neurons. Here, we found training-dependent hyperexcitability of CA1 pyramidal neurons together with increased membrane resistance and decreased rheobase. Furthermore, we demonstrated a dose-dependent protective effect of riluzole (RLZ) against Aβ
1-42 oligomer-induced hyperexcitability.
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Aβ1-42 Oligomers on IA Learning
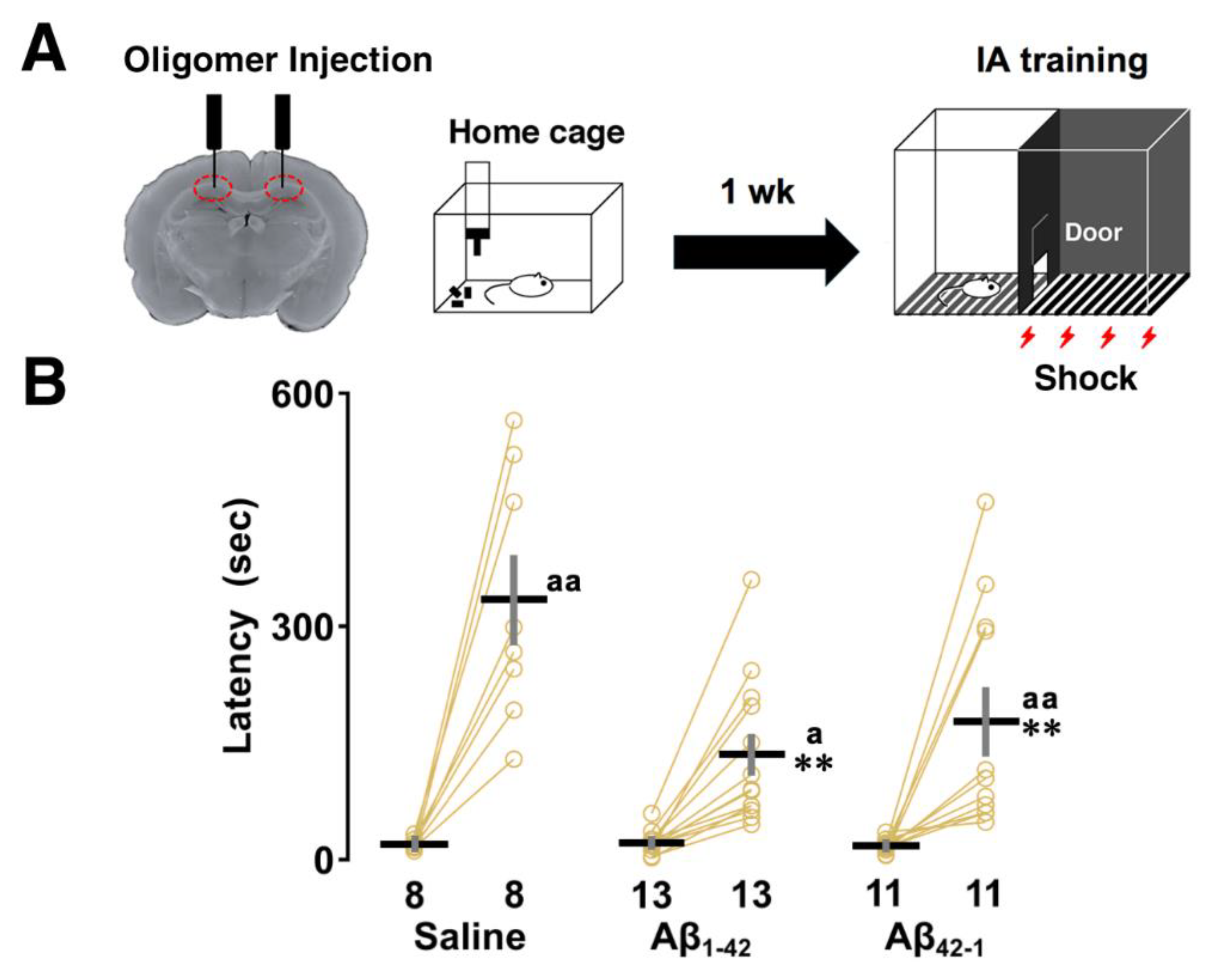
To investigate contextual learning performance, rats were subjected to the IA task 1 week after bilateral injections of Aβ
1-42 oligomers into dorsal CA1. In this learning paradigm, rats were allowed to cross from a light chamber to a dark chamber where an electric foot shock (1.6 mA, 2 s) was delivered. Half an hour after the IA task, the latency to enter the illuminated side after the shock was measured as an index of contextual learning (
Figure 1A). Two-way ANOVA revealed the main effects of training (
F1,58 = 67.916,
p < 0.0001) and oligomers (
F2,58 = 5.951,
p = 0.005) with a significant interaction between them (
F2,58 = 6.021,
p = 0.004). Post hoc analysis showed that the latency to enter the dark box was significantly prolonged after training in each group (saline;
p < 0.0001, Aβ
1-42;
p = 0.046, Aβ
42-1;
p = 0.0025 vs training;
Figure 1B), but was shorter in both the Aβ
1-42 (vs saline;
p = 0.0002) and Aβ
42-1 injected groups (vs saline;
p = 0.008) compared to the saline group. Therefore, despite their successful learning, the rats which received oligomers containing both Aβ
1-42 sequence and its reverse Aβ
42-1 sequence showed impaired performance during retrieval, highlighting the similar adverse effect of oligomers on contextual memory.
2.2. Effects of Aβ1-42 Oligomers on the Intrinsic Properties after IA Learning
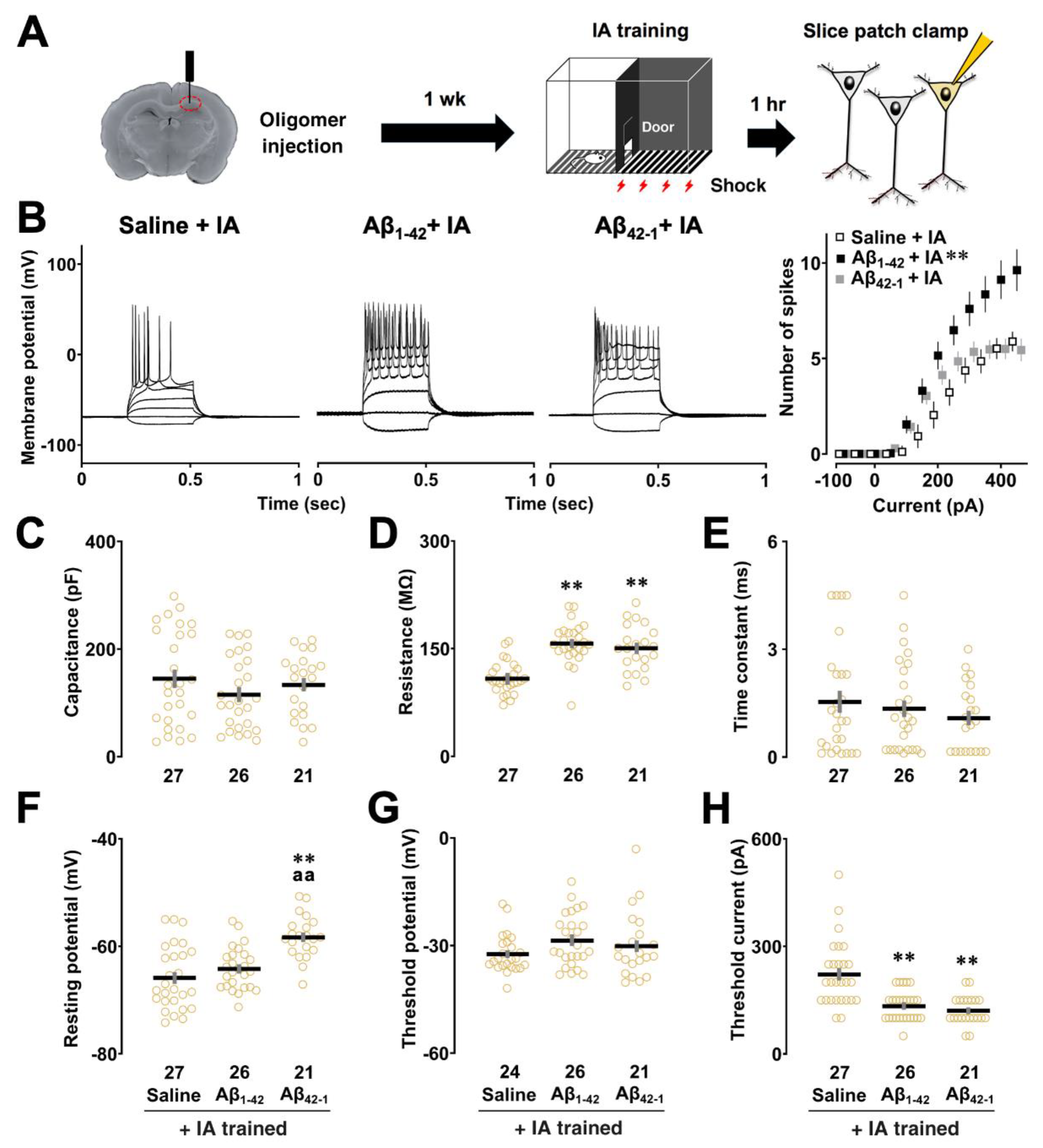
To assess the intrinsic properties of CA1 pyramidal neurons after contextual learning, we performed a slice patch clamp experiment using a 300 ms square current injection 1 week after unilateral injection which did not affect learning performance (
Figure 2A).
Figure 2B (right panel) shows the relationship between the number of spikes and current intensity in the saline, Aβ
1-42, and Aβ
42-1 injected groups after the IA task. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA showed the main effects of oligomers (
F2,781 = 52.224,
p < 0.0001) and current (
F10,781 = 32.036,
p < 0.0001) with a significant interaction between them (
F20,781 = 2.586,
p = 0.0002). Post hoc analysis showed that the number of evoked spikes was increased in the Aβ
1-42 group (vs saline + IA;
p < 0.0001), suggesting that cells in the Aβ
1-42 group were more excitable after contextual learning. We also confirmed that there was no significant difference in spike counts between the saline and Aβ
1-42 groups without the IA task (Aβ
1-42 vs saline;
p = 0.678,
Supplementary Figure S1), highlighting the role of training-dependent changes in CA1 neuronal excitability.
Several changes in intrinsic membrane properties were observed in CA1 pyramidal neurons after the IA task. First, one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc comparison revealed that membrane capacitance was not altered (
F2,71 = 1.082,
p = 0.345; Aβ
1-42 + IA vs saline + IA,
p = 0.275;
Figure 2C). A significant effect of oligomers was observed in R
m (One-way ANOVA:
F2,71 = 25.058,
p < 0.0001), where neurons in both Aβ
1-42 (vs saline + IA;
p < 0.0001;
Figure 2D) and Aβ
42-1 (vs saline + IA;
p < 0.0001) groups had higher membrane resistance after IA learning. There was no significant difference in membrane time constant (
F2,71 = 0.741,
p = 0.481; Aβ
1-42 + IA vs saline + IA,
p = 0.8411;
Figure 2E). With respect to RMP, a significant effect of oligomers was found (One-way ANOVA:
F2,71 = 15.949,
p < 0.0001;
Figure 2F) with the Aβ
42-1 group having a more depolarized RMP compared to both saline (vs saline + IA;
p < 0.0001) and Aβ
1-42 groups (vs Aβ
1-42 + IA;
p = 0.0002) whereas RMP was not affected in the Aβ
1-42 group (saline + IA vs Aβ
1-42 + IA;
p = 0.492). No significant difference was found in the threshold potential subtracted from the dV/dt of the first spike elicited at 300 pA (One-way ANOVA:
F2,68 = 1.032,
p = 0.362; Aβ
1-42 + IA vs saline + IA,
p = 0.963;
Figure 2G). However, one-way ANOVA showed a significant main effect associated with rheobase (
F2,71 = 18.077,
p < 0.0001), as CA1 pyramidal neurons in both Aβ
1-42 (vs saline + IA;
p < 0.0001;
Figure 2H) and Aβ
42-1 groups (vs saline + IA;
p < 0.0001) requ
ired less current injection to evoke one AP. We found that R
m of the Aβ
1-42-injected group was elevated without the IA task, although other intrinsic properties of CA1 pyramidal neurons were not altered by Aβ
1-42 oligomers (
Supplementary Table S1), suggesting that learning-dependent changes in the intrinsic properties account for the electrophysiological features of Aβ
1-42 oligomer-induced neuronal hyperexcitability after the IA task
.
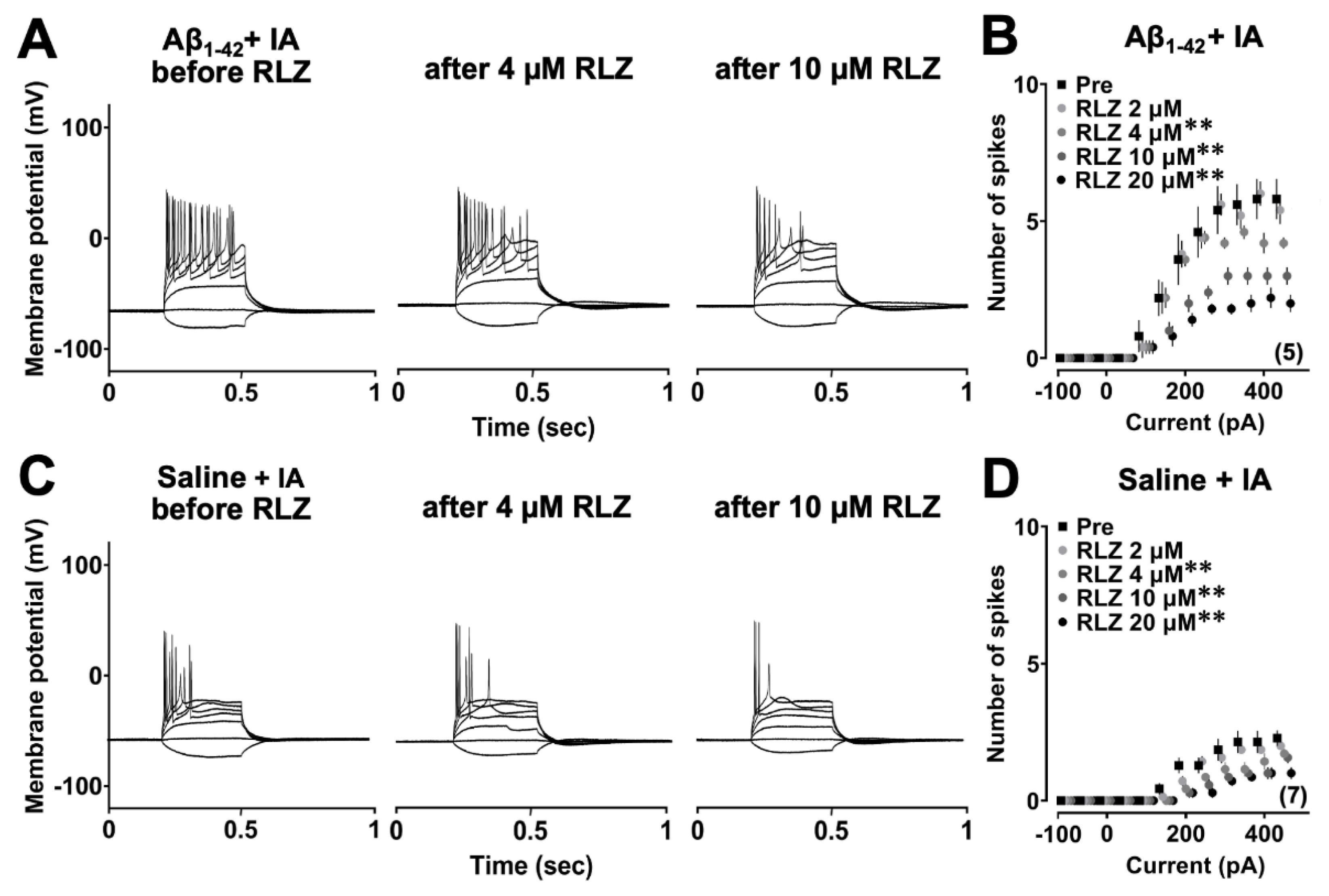
To determine whether persistent sodium current (
INaP) contributes to Aβ
1-42 oligomer-induced hyperexcitability, RLZ was bath applied to aCSF at increasing concentrations (2, 4, 10 and 20 µM) (
Figure 3A, C). Two-way repeated measures ANOVA revealed the main effects of RLZ (
F4,280 = 73.301;
p < 0.0001) and current (
F13,280 = 114.494;
p < 0.0001) with a significant interaction between them (
F52,280 = 3.691;
p < 0.0001) in the Aβ
1-42 group after the IA task. Post hoc analysis showed that spikes were less evoked after the addition of 4, 10 and 20 µM RLZ to CA1 pyramidal neurons (
Figure 3B), and this inhibitory effect was enhanced with increasing concentrations (2 µM vs 4 µM;
p = 0.0009, 4 µM vs 10 µM;
p = 0.0001, 10 µM vs 20 µM;
p = 0.0039). A similar finding was also observed in the saline group in the IA task. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA showed the main effects of RLZ (
F4,420 = 35.010,
p < 0.0001) and current (
F13,420 = 93.635,
p < 0.0001) with a significant interaction between the two factors (
F52,420 = 1.994,
p = 0.0001) and the effect was significant after application of 4, 10 and 20 µM RLZ (
Figure 3D). Taken together, these results indicate that RLZ can inhibit Aβ
1-42 oligomer-induced CA1 neuronal hyperexcitability in a concentration-dependent manner.
2.3. Effects of Aβ1-42 Oligomers on Sensory/Motor Functions, Pain Sensitivity and Emotional State
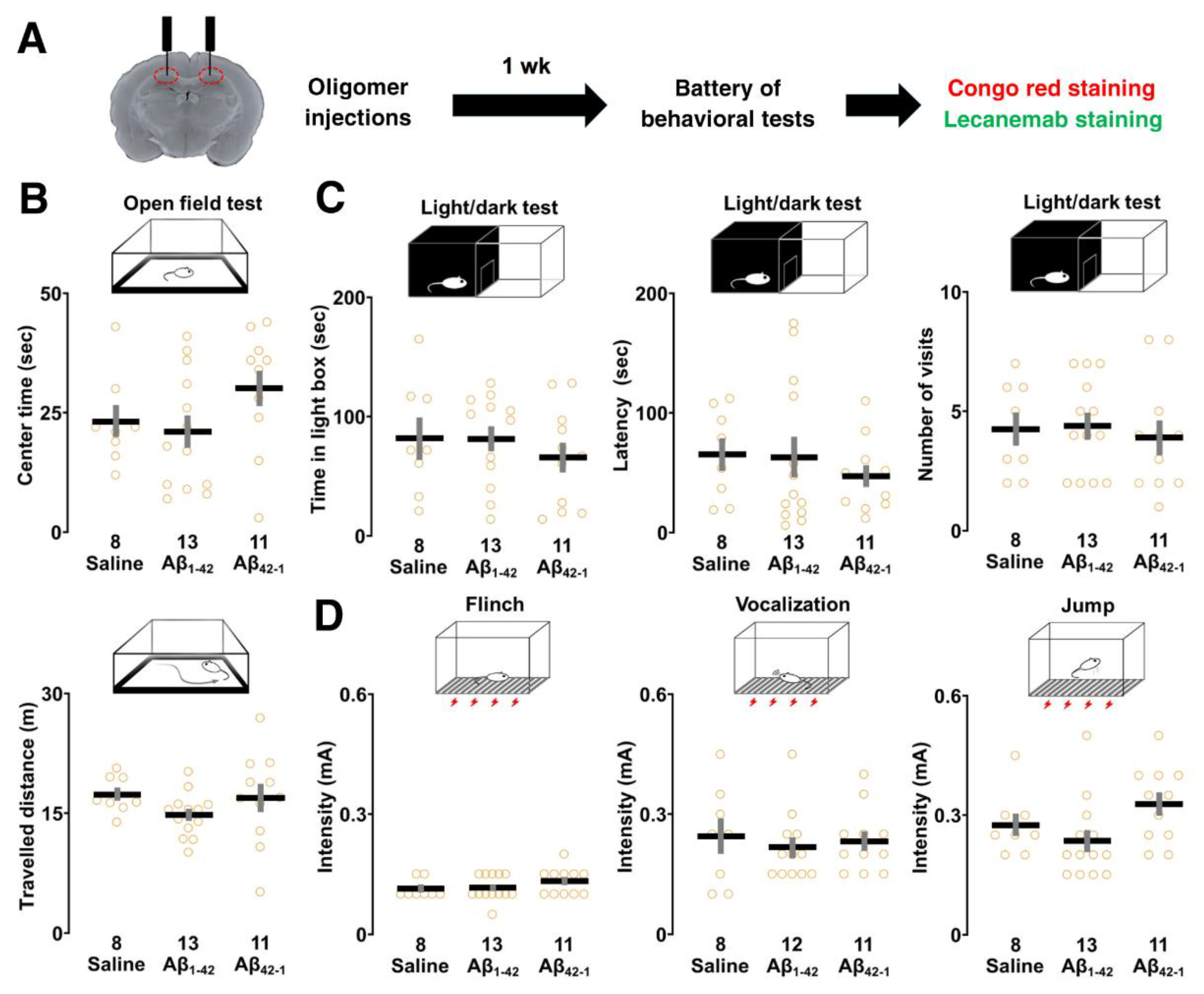
Because oligomers could affect basic physiological functions which may influence contextual learning performance, the open field, light/dark box, and flinch-jump tests were performed after 1 week of bilateral injections to rule out these possibilities (
Figure 4A).
The open field test was used to determine whether the oligomers would affect the exploratory behavior of the animals. One-way ANOVA showed no significant main effect of oligomers on center time (
F2,29 = 1.891,
p = 0.169) and distance travelled (
F2,29 = 1.297,
p = 0.289), suggesting that the motor performance and emotional state of the animals did not differ (
Figure 4B). In the light/dark test, one-way ANOVA revealed that the main effect of oligomers was not significant for the following parameters: time spent in the light box (
F2,29 = 0.522,
p = 0.599), latency (
F2,29 = 0.470,
p = 0.630), and number of visits (
F2,29 = 0.156,
p = 0.857) to the light box, highlighting no detectable change in anxiety levels (
Figure 4C). Next, one-way ANOVA showed that there was no significant main effect associated with the current thresholds of flinch (
F2,29 = 1.212,
p = 0.312), vocalization (
F2,28 = 0.197,
p = 0.823), and jump (
F2,29 = 2.868,
p = 0.073) in the flinch-jump test, suggesting the rats had similar pain sensitivity (
Figure 4D). Overall, Aβ
1-42 oligomers did not affect sensory/motor functions, pain sensitivity, and emotional state.
2.4. Effects of Aβ1-42 Oligomers on Other Hippocampus-Dependent Tasks
We also examined the effects of oligomers on other hippocampus-dependent tasks. First, although two-way ANOVA failed to show a significant effect of oligomers (
F2,58 = 3.156,
p = 0.050), the main effect of training (
F1,58 = 126.132,
p < 0.0001) was observed with a significant interaction between training and oligomers (
F2,58 = 3.271,
p = 0.045) in the fear conditioning test. In addition, post hoc analysis showed that freezing time was prolonged in all groups after training when re-exposed to the same context (saline;
p < 0.0001, Aβ
1-42;
p < 0.0001, Aβ
42-1;
p < 0.0001 vs training;
Figure 5A), but the Aβ
1-42 injected rats showed less freezing compared to the control (vs saline;
p = 0.037).
Next, to assess recognition memory, object recognition and social recognition tasks were administered in our test battery. In the object recognition task, the percentage of time spent on the novel object was increased in both the saline (
t = 4.404,
p = 0.003, paired t-test;
Figure 5B) and Aβ
42-1 groups (
t = 5.291,
p = 0.0004, paired t-test), but not in the Aβ
1-42 group (
t = 1.108,
p = 0.290, paired t-test) during the test phase. In addition, one-way ANOVA showed a significant effect of oligomers (
F2,29 = 4.714,
p = 0.017), and touch time to a novel object was significantly reduced in the Aβ
1-42 injected group (vs saline;
p = 0.044) in post hoc analyses. This difference was not due to preference, as all groups showed no left/right preference in the sampling phase (
Supplementary Table S2) and similar levels of exploration in the test phase (
Supplementary Table S3). In the social recognition task, the percentage of social interaction time with the novel target was increased in both the saline (
t = 4.746,
p = 0.002, paired t-test;
Figure 5C) and Aβ
42-1 groups (
t = 4.310,
p = 0.002, paired t-test), but not in the Aβ
1-42 group (
t = 0.811,
p = 0.434, paired t-test) during the test phase. One-way ANOVA revealed no main effect of oligomers on social interaction time (%) with the novel target (
F2,29 = 2.680,
p = 0.086), although the Aβ
1-42-injected group showed a reduced tendency to spend time with the novel target that was not statistically significant (vs saline;
p = 0.192). Total exploration time of both social targets in the test phase was comparable in all groups (
Supplementary Table S4). Spatial working memory was assessed by using Y-maze task. One-way ANOVA suggested no significant main effect of oligomers on alternation rate (
F2,29 = 1.123,
p = 0.339;
Figure 5D) and number of arm entries (
F2,29 = 3.079,
p = 0.061;
Figure 5E), although both parameters tended to decrease in the Aβ
1-42 group.
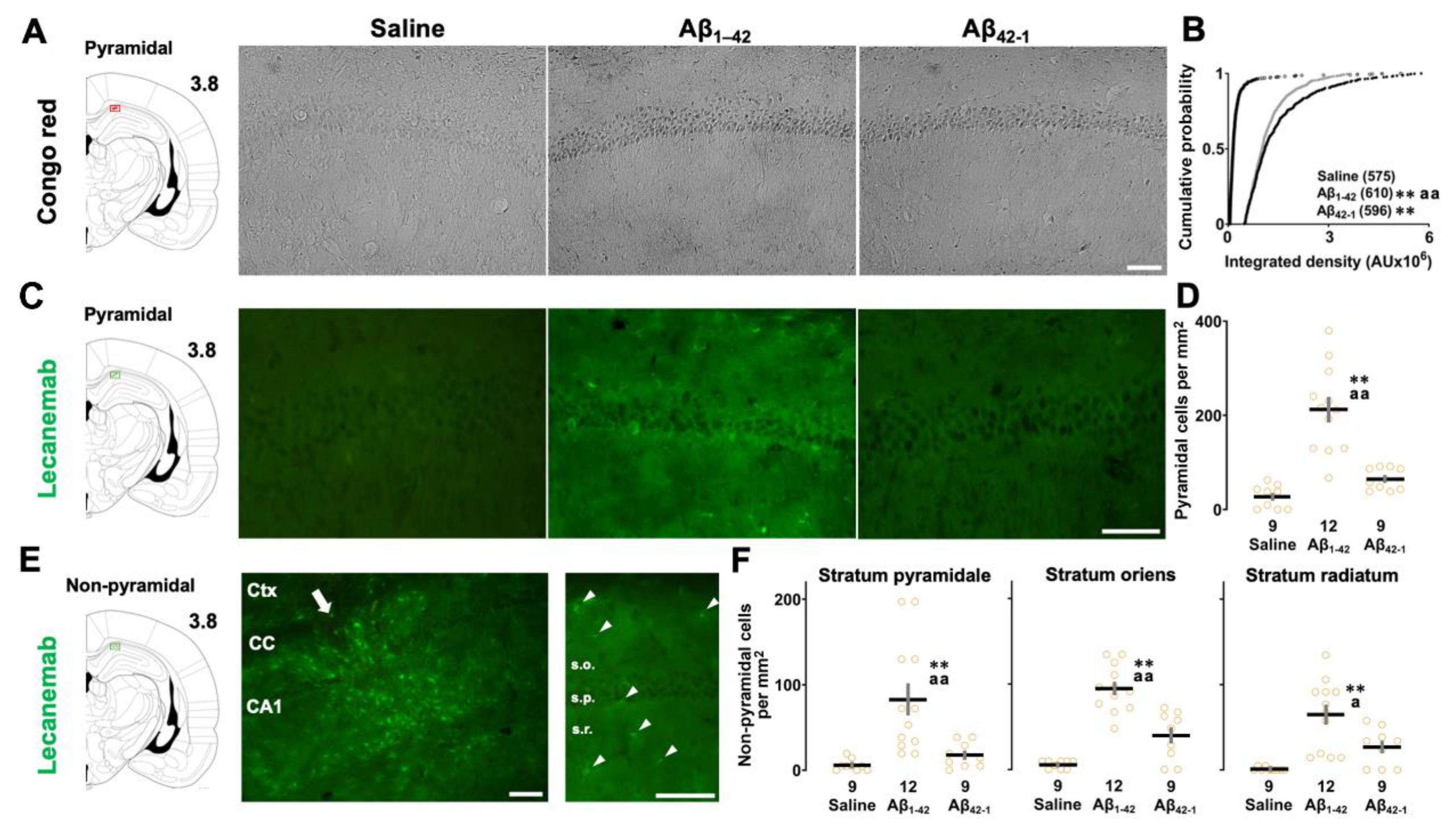
2.5. Aβ Deposition in the CA1 Region
Congo red staining was used to determine whether injection of Aβ
1-42 oligomers would lead to Aβ deposition (
Figure 6A). A previous study suggested that a conformational change to the β-sheet structure is the first step in the aggregation process, and the Aβ
1-42 peptide contains amino acid residues 16-20 (KLVFF) that constrain the monomer into the compact amyloid fold [
25]. Congo red staining is known to detect compacted β-sheet amyloid and to label both parenchymal and vascular amyloid deposits in the AD brain [
26]. One-way ANOVA showed a significant effect of oligomers on Congo red staining (
F2,1778 = 402.214,
p < 0.0001) and post hoc comparisons revealed that the integrated density of CA1 pyramidal neurons was higher in both the Aβ
1–42 (vs saline;
p < 0.0001;
Figure 6B) and Aβ
42-1 (vs saline;
p < 0.0001) groups. In addition, the staining intensity of Aβ
1-42 group was also more intense than that of Aβ
42-1 group (Aβ
1-42 vs Aβ
42-1;
p < 0.0001).
Next, to validate the location and extent of distribution of Aβ
1–42 oligomers in the CA1 region (
Figure 6C), immunohistochemistry was performed using the anti-Aβ antibody lecanemab. Based on recent reports, lecanemab, which binds to amino acid residues (1-16) of the Aβ peptide [
27], was found to be specific for soluble Aβ
1-42 oligomers [
28]. In our experiments, the main effect of oligomers was significant (One-way ANOVA:
F2,27 = 27.351,
p < 0.0001), and the cell density of positive CA1 pyramidal cells was higher in the Aβ
1–42 group than in the saline (vs saline;
p < 0.0001;
Figure 6D) and Aβ
42-1 groups (vs Aβ
42-1;
p < 0.0001), whereas immunolabeling was insignificant in the latter groups (saline vs Aβ
42-1;
p = 0.617). We also observed immunoreactivity along the injection track (
Figure 6E, left panel) and abundant positive non-pyramidal cells (
Figure 6E, right panel) along the radial axis of the CA1 region. One-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis revealed that the Aβ
1-42 group had more lecanemab-positive non-pyramidal cells in the stratum pyramidale (vs saline;
p < 0.0001;
Figure 6F), stratum oriens (vs saline;
p < 0.0001) and stratum radiatum (vs saline;
p < 0.0001) of the CA1 region, whereas this increase in cell density was significant only in the stratum oriens of the Aβ
42-1 group (vs saline;
p = 0.0176). Thus, Congo red staining and lecanemab immunolabeling confirmed Aβ amyloid deposition along with oligomer-positive non-pyramidal cells in the CA1 region of the Aβ
1-42 injected group.
3. Discussion
3.1. Aβ1-42 Oligomers Impaired CA1-Dependent IA Learning
Hippocampus has provoked a particular interest in the injection model of AD [
14] and its subregion CA1 is initially affected in Alzheimer's disease [
23]. CA1, a primary output to extrahippocampal circuits, integrates contextual [
20] and spatial information [
22], leading to formation of episodic memory. In our study, Aβ
1-42 oligomers impaired contextual learning 1 week after injection into CA. As contextual memory formation is dependent on the integrity of hippocampus [
20], our data suggests that Aβ
1-42 oligomers triggered specific impairment of contextual memory related to CA1 region.
Unexpectedly, this deficit was observed along with increased membrane resistance and amyloid deposition as evidenced by Congo red staining in both Aβ
1-42 and Aβ
42-1-injected rats. These findings have highlighted the possibility that amino acids in different sequences may fold into a structure that may share convergent mechanisms, and the affinity for Congo red further indicates the propensity of the reverse sequence Aβ
42-1 to form aggregates [
15].
The deleterious effects of Aβ peptides have been shown to be specifically related to their amyloidogenicity, which in turn depends on the amino acid sequence [
29]. This could be partly explained by using WALTZ algorithm (Waltz (switchlab.org)) in which we identified that the two regions of the Aβ
1-42 peptide between residues 15-22 and 36-42 are amyloidogenic whereas one region of the Aβ
42-1 peptide between residues 8 and 13 has similar amyloidogenic potential (
Supplementary Figure S2). Moreover, consistent with our interest, the Aβ
1-42 peptide appears to interact directly [
30] or indirectly [
31] with the bilayer membrane, thereby disrupting mechanical and biophysical functions which underlie the physiological properties of the neurons. Thus, the Aβ
1-42-induced deficit may be triggered by a direct effect of oligomers on the cell membrane of CA1 pyramidal neurons.
3.2. Aβ1-42 Oligomers Induced Neuronal Hyperexcitability after IA Learning
Several preclinical and clinical studies have suggested that neuronal hyperexcitability are strongly associated with cognitive impairment, probably via adversely affecting the intrinsic properties [
32,
33]. To address this issue, we performed an IA task followed by an
in vitro slice patch clamp 1 week after unilateral injection which did not affect learning performance (data not shown). Membrane resistance was higher in both groups, whereas rheobase was specifically lower in the Aβ
1-42-injected group with concomitant increased spike numbers, highlighting specific Aβ
1-42 oligomer-induced neuronal hyperexcitability after contextual learning.
Consistent with our data, several studies reported that membrane resistance was increased after exposure to Aβ
1−42 oligomers [
34,
35]. This enhanced R
m, derived from differences in voltage response, could probably result from either TASK current mediated by TASK1 and TASK3, subtypes of leak K
+ channels [
36] and/or subthreshold
IM and
INaP currents [
37]. Alternatively, because membrane resistance is strongly associated with neuronal morphology [
38], it is also possible that the Aβ peptides also affected the biophysical properties of the membrane by altering membrane stiffness [
39] and perturbing membrane permeability via both ion channel-dependent [
31] and -independent mechanisms [
40].
In addition, previous reports showing that Aβ
1-42 oligomers induced hyperexcitability [
34,
41] and minimized rheobase to elicit AP [
35] were consistent with our present data. Furthermore, our findings that Aβ
1-42 oligomers did not affect other subthreshold membrane properties such as C
m, Tau and RMP were supported by other studies [
35,
42,
43].
Interestingly, neuronal hyperexcitability was not observed without the IA task, and Aβ
1-42-induced hyperexcitability was specifically training-dependent. Contextual learning is accompanied by of membrane proteins, including receptors [
44,
45] and regulatory sites for voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels are located intracellularly [
46,
47]. These facts suggest that learning increases intracellular levels of Aβ
1-42 [
47,
48], and that intracellular Aβ
1-42 affects the channel dynamics and single-channel current of
INaP [
49], which may have decreased rheobase and increased excitability [
50]. Since Since Nav1.6 channels were particularly expressed in CA1 pyramidal cells [
47], it is possible that Nav1.6 is a target molecule of Aβ
1-42.
To test our hypothesis, we bath applied RLZ, an antagonist of
INaP, to aCSF and found that Aβ
1-42 oligomer-induced hyperexcitability was reduced by RLZ in a dose-dependent manner. In support of our data, another study showed that Aβ
1-42-induced
INaP enhancement, which mediates neuronal hyperexcitability, was reversed by RLZ [
51]. Finally, our preliminary
in vivo study showed that daily injection of RLZ into CA1 for 1 week ameliorated Aβ
1-42 oligomer-related impairment in contextual learning (data not shown). Taken together, these results suggest that Aβ
1-42 oligomer-induced neuronal hyperexcitability with reduced rheobase may be mediated via
INaP, and RLZ may have a protective effect against Aβ
1-42-induced neuronal hyperexcitability.
3.3. Aβ1-42 Oligomers Selectively Impaired Other Hippocampus-Dependent Tasks
Since changes in sensory/motor or emotional functions may affect learning, basic physiological functions were assessed by using behavioral test battery. We also confirmed that impaired contextual learning was not confounded by sensory/motor functions, pain sensitivity and emotional state. Consistent with our data, no detectable change in exploratory behavior and anxiety level was reported in another studies [
52,
53].
Next, we observed that other hippocampus-dependent tasks were also selectively affected by Aβ
1-42 oligomers, suggesting a specific impairment of hippocampal functions of dorsal CA1. The impairment of contextual freezing [
54] and object recognition [
52,
53] was consistent with our present findings. With respect to social recognition memory, we observed that rats injected with Aβ
1-42 oligomers were unable to discriminate between the novel and familiar social targets. Another study reported a delayed and persistent social memory deficit, although the social recognition memory impairment was not detected at day 7 post-injection [
55].
Surprisingly, the intact working memory in our experiment was supported by another report showing that spontaneous alternation was not altered by Aβ
1-42 oligomers [
52], whereas many studies have shown that Aβ
1-42 oligomers impaired spontaneous alternation in the Y-maze task probably due to variation in the target area and experimental paradigm [
53,
56,
57]. Therefore, selective impairment of hippocampal dependent tasks may be explained by a differential vulnerability of neural circuits as well as specific contribution of Aβ
1-42 oligomer-related pathology in the CA1 region.
3.4. Amyloid Deposition in the Target Area
Congo red staining, which detects amyloid aggregates in a compact rather than diffuse state, clearly showed amyloid deposition in CA1 pyramidal cells [
26]. This was consistent with other reports showing Aβ deposition in CA1 pyramidal and DG granule neurons after injection of oligomeric Aβ
1−42 [
56,
58]. Interestingly, we also found membrane labelling of CA1 pyramidal neurons using lecanemab, an anti-amyloid antibody specific for soluble Aβ
1−42 species [
28]. It is plausible that Aβ
1−42 oligomers may have direct interactions with the cell membrane due to their sticky properties to facilitate adhesion [
30], resulting in increased membrane resistance and immunoreactivity along the membrane. Two different techniques may suggest the presence of both β-pleated aggregates and soluble assemblies in the target area. It is likely that Aβ oligomers become insoluble after binding to the cell surface and may also undergo a transition between fibrils and lower order species by polymerization or depolymerization [
15].
Furthermore, lecanemab-positive non-pyramidal cells, exhibited unique cell bodies with ramified branches, suggesting astrocytes and microglia [
59,
60] along the radial axis in the target area. Although we did not use glial cell-specific molecular markers, our current results were consistent with previous studies showing activated astrocytes and microglial cells surrounding and infiltrating amyloid deposits in the hippocampus [
53,
61]. Taken together, our membrane labelling pattern suggests that the interaction between the oligomers and the cell membrane of CA1 pyramidal neurons may be responsible for the deleterious effects of Aβ
1−42 on contextual learning and neuronal excitability.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
Male Sprague–Dawley rats, aged 28-30 days (Chiyoda Kaihatsu Co., Tokyo, Japan) were housed individually in opaque plastic cages (length:25 cm; width: 40 cm; height: 25 cm) lined with woodchip. They were provided ad libitum access to food (MF, Oriental Yeast Co. Ltd, Tokyo Japan) and tap water and maintained at a constant temperature of 23 ± 1°C under a 12-hr light/dark cycle (lights on: 08.00 am to 8:00 pm).
4.2. Preparation of Aβ1-42 Oligomers
Synthetic Aβ1-42 and Aβ42-1 oligomers were kindly provided by Dr. Kimura. Briefly, Aβ1-42 peptide (1 mg) was dissolved in 221.5 ml of 100 % HFIP (1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol). The peptide solution was vortexed and subsequently dried under vacuum until complete elimination of HFIP. After this, the dried peptide was re-suspended in 40 µl of 20% DMSO and gently agitated every few minutes. Then, 160 µl of PBS was further added to the preparation to make a final concentration of 1 mM and stored at 4 ˚C for 24 hr followed by -40 ˚C until further use. The stock solution was further diluting in 0.9% NaCl to achieve the desired concentration in our study. The final concentration of DMSO was 0.4%.
4.3. Stereotaxic Surgery and Microinjection of Oligomers
The rats were anesthetized with a mixture of intraperitoneal ketamine (100 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg) injection and placed on the stereotaxic frame. The head was then immobilized with non-rupture ear bars. After a midline incision, the scalp was opened, and bilateral craniotomies were performed using a microdrill. The stainless-steel injector connected to a 10 µl Hamilton syringe was placed above the dorsal CA1. The stereotaxic coordinates were as follows: AP: -2.9 mm posterior to bregma, ML: ± 2.2 mm from midline, DV: -3.2 mm from the skull surface. The rats received bilateral injection of equal volume of either 500 µM Aβ1–42 oligomers or saline into the target region. The total volume of 2.4 µl (1.2 µl/side) was injected at a rate of 1 µl/ 5 min. After injection, the injector was left in place for the next 5 min to allow diffusion and prevent reflux of the solution and slowly withdrawn. The scalp incision was sutured, and the animals were kept warm until full recovery. The accuracy of stereotaxic injection to the target region was checked by examination of the needle tract within the brain slices.
4.4. Behavioral Test Battery
We designed the behavioral test battery for a comprehensive analysis of sensory/motor functions, anxiety, pain sensitivity as well as learning and memory. The sequence of the tests was optimized by choosing the least to the most stressful conditions for the rats, minimizing the interference among the tests and circumventing the influence of previous experience. The rats were subjected to the test battery 1 week after injection in the following order: open field test, object recognition task, Y-maze task, light/dark test, social recognition task, inhibitory avoidance task, fear conditioning test, and flinch-jump test. The animals were habituated to the dimly lit room illuminated by a single light bulb positioned overhead prior to the experiments and their performance was recorded with a video camera (IXY3, Canon Inc, Tokyo, Japan). The apparatus was cleaned with 70% ethanol and air-dried between the test, and the interval between each test was 30 min [
62].
4.4.1. Open Field Test
To assess locomotor activity, the open field test was performed in a novel empty field arena under low-light condition. The rats were placed in the center of an open field box (length 45 cm; width 45 cm; height 45 cm) with opaque walls and allowed to move freely for 5 min. Parameters of exploratory behavior: center time and total travelled distance were measured.
4.4.2. Object Recognition Task
We used the open field test to habituate the rats. In the sampling phase, two identical objects were placed symmetrically at the corner of the box and spaced 10 cm from the wall. The rats were put into the box without facing the objects and allowed to explore the objects for 5 min. After 30 min, one of the objects was randomly replaced with a novel object which was similar in size but different in texture, shape and color. The interaction of the rats with the two objects in the test phase was monitored for 5 min. The objects as well as their location were counterbalanced between the animals to avoid any potential bias due to their preference. To assess object recognition memory, we measured the touching time of each object over the first 3 min of test phase. The ratio of exploration time of the novel object to total exploration time was expressed as a percentage. Touching behavior was assumed to be pointing their nose toward the object less than 2 cm or touching the object with their forelimbs for at least 1 s while sitting on or leaning against the object was not considered [
62].
4.4.3. Y-Maze Task
Working memory was assessed by recording spontaneous alternation behavior which requires the rats to remember their previous choice to select the correct arm on the next choice [
63]. The Y-maze apparatus consisted of three grey, plastic arms converged in an equilateral triangular central area (MY-10, Shin factory, Japan). The wall of the arms had an outside slope of 76° (height 12 cm), allowing the rats to see distal landmarks with no inter-maze cues inside. Firstly, the animals were put at the end of one arm and allowed to move freely for 5 min. After 24 hr, they were placed in one arm again and their spontaneous behavior was recorded for 5 min. Arm entry was considered to be completed when the hind paws of the rats completely crossed the arm and alternation was defined as consecutive entries into the three arms without overlapping. By analyzing the number and sequence of arm entries, alternation percentage was calculated as the ratio of actual to possible alternations (defined as the total number of arm entries - 2) × 100 [
62,
64].
4.4.4. Light-Dark Box Test
The box (length 48 cm; width 20 cm; height 23 cm) which consisted of light and dark compartments separated by a sliding door (width 7 cm; height 8 cm) was used in our study. The rats were placed in the dark side and allowed to explore for 5 min. Then, the sliding door was opened, and the animals were freely accessible to both compartments for 5 min. Time spent in the light side as well as latency to enter and number of entries to the light side were evaluated to assess anxiety-like behavior [
65].
4.4.5. Social Recognition Task
The U-field two-choice box was created by partitioning the open field box with a wall (length 20 cm; height 45 cm) to test social recognition. Firstly, the rats were habituated to the box containing two empty cages (8 cm in diameter) for 5 min. In the sampling phase, they were allowed to explore a cage containing a social target (female; same strain and age) and an empty cage for 5 min. In the test phase, the rats were placed again to freely interact with both familiar and novel social targets for 5 min. To assess social recognition memory, we measured the time spent touching the social targets and calculated the ratio of exploration time of the novel social target to that of both targets. Touching behavior was assumed to be directing their nose toward the cage or touching the cage with their forelimbs [
66].
4.4.6. Inhibitory Avoidance (IA) Task
The IA task was performed according to our previous publications [
21,
62]. The IA apparatus was a two-chambered box consisting of an illuminated safe compartment and a dark shock compartment (length 33 cm; width 58 cm; height 33 cm) divided by a trap door. During training, the rats were placed in the lit compartment with their head facing opposite the door. After a few seconds, the door was gradually opened to allow the animals to access the dark side at their own will. The latency to enter the novel dark compartment before shock was measured (i.e., latency before IA learning). When the rats entered the dark side, the door was closed, and an electrical foot shock (1.6 mA, 2 s) was delivered via steel rods in the grid floor of the chamber. After 10 s, the animals were returned to their home cage. After 30 min, they were put back in the illuminated compartment and retrieval was performed with a criterion of 600 s. The latency to enter the previously experienced dark compartment after shock (i.e., latency after IA learning) was measured as an index of contextual learning.
4.4.7. Fear Conditioning Test
The fear conditioning paradigm was described previously [
62,
67]. The conditioning chamber (length 25 cm; width 31 cm; height 42 cm) consisted of Plexiglass on the top, front, and back, with 18 stainless steel bars (φ 4 mm; 15 mm spacing) on the bottom into which the coded shocks were delivered via a stimulator (LE100-26 Shocker, Panlab, Cornellà, Spain). During training, the rats were allowed to explore the chamber for 3 min and received an electrical foot shock as an unconditioned stimulus (0.8 mA, 2 s duration) three times with an interval of 30 s. They were allowed to recover in the chamber for 30 s and returned to their home cage. After 24 hr, the rats were again placed in the conditioning chamber, and freezing was monitored every 30 s for 5 min. Freezing was defined as the cessation of all behaviors except respiration for at least 1 s [
54,
68].
4.4.8. Flinch-Jump Test
To assess pain sensitivity, the flinch-jump test was performed as reported previously [
62,
69].
. The rats were placed individually in the conditioning chamber mentioned above and habituated for 30 s. Then, foot shocks were applied in a stepwise manner (0.05 mA increments; range 0.05 - 0.6 mA) with an interval of 30 s and each animal was tested only once at each intensity. The “flinch” and “jump” thresholds were defined as the lowest shock intensities that elicited a detectable response and simultaneous removal of at least three paws (including both hind paws) from the grid, respectively. The “vocalization” threshold was defined as the minimum shock intensity at which the rats produced a detectable vocalization in response to the shock.
4.5. Electrophysiology
For electrophysiological recording, the rats received a unilateral injection of 100 µM Aβ
1-42 oligomers into the right dorsal CA1 region (AP: -2.9 mm posterior to bregma, ML: ± 2.2 mm from midline, DV: -2.5 mm below the dura surface). After 1 week, lA task was performed, and the rats were sacrificed 60 min after the foot-shock. After confirming there was no tail reflex, acute brain slices were prepared as described previously [
21,
70]. The brain was quickly perfused with ice-cold dissection buffer containing 25.0 mM NaHCO
3, 1.25 mM NaH
2PO
4, 2.5 mM KCl, 0.5 mM CaCl
2,7.0 mM MgCl
2, 25.0 mM glucose, 110.0 mM choline chloride, 3.10 mM pyruvic acid, 11.6 mM ascorbic acid and rapidly transferred to the chamber containing ice-cold dissection buffer which was continuously gassed with 5%CO
2/95%O
2. After removal of the cerebellum and frontal parts, coronal brain slices (350 μm) were cut with a Leica vibratome (VT-1200; Leica Biosystems, Nussloch, Germany) submerged in the dissection buffer. The slices were then transferred and incubated in the storage chamber containing artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) solution (118 mM NaCl, 2.5 mM KCl, 26 mM NaHCO
3, 1 mM NaH
2PO
4, 10 mM glucose, 4 mM MgCl
2 and 4 mM CaCl
2, pH 7.4) at 22-25°C equilibrated with 5% CO
2/95% O
2 for 1 hr before recording. We kept 3-4 slices from each brain and then selected 1-2 slices for patch clamp based on the brain atlas by Paxinos and Watson [
71].
4.6. Current Clamp Recordings
The slices were placed into the recording chamber which was continuously perfused with aCSF solution bubbled with carbogen at 22-25°C. The dorsal CA1 pyramidal neurons were visually identified using infra-red (IR) differential interference contrast optics. The pipettes (7-9 MΩ) were made from borosilicate glass by using a horizontal puller (Model P97; Sutter Instrument, Novato, CA, USA) and filled with an internal solution containing 30 mM K-Gluconate, 5 mM KCl, 10 mM HEPES, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 4mM Na2ATP, 0.4 mM Na3GTP, 10 mM Na-phosphocreatine and 0.6 mM EGTA at 7.25. After giga-seal formation, whole-cell configuration was made from the soma of pyramidal neurons, using an Axopatch1D amplifier (Molecular Devices Inc., San Jose, CA, USA) in the current clamp mode. The liquid junction potential was not corrected. The recordings were low-pass filtered (5 kHz), digitalized with a Digidata 1440 AD board and analyzed offline using the pCLAMP 10 software (Molecular Devices).
Resting membrane potential (RMP) was evaluated before the current injection. To study the relationship between firing frequency and current injection, a square step-current, ranging from -100 to +550 pA of 300 ms duration in 50 pA increments was injected. The number of spikes was counted and the current threshold or rheobase was determined as the minimum current intensity to evoke at least a single spike. The threshold potential of the first AP at 300 pA was derived from a point where dV/dt exceeded 10 mV/ms [
43]. The intrinsic properties of the membrane: membrane capacitance (C
m) and time constant (tau) were measured by the membrane test in the voltage-clamp mode with a holding potential of − 60 mV. Membrane resistance (R
m) was also calculated as the slope of the steady-state values of the voltage responses to a series of current steps from −100 to +100 pA with 50 pA increments per step fitted with linear regression [
43]. Riluzole (A2423; TCI, Tokyo, Japan) was firstly dissolved in DMSO followed by serial dilution in 0.9% NaCl to achieve desired concentrations and the preparation was added to the perfusate at increasing concentrations (2, 4, 10, and 20 µM) with an interval of 5 min. For experiments with riluzole, each slice was used for recording one cell as the effect of riluzole could not be completely washed off (data not shown).
4.7. Congo Red Staining
The rats were deeply anesthetized with an overdose of intraperitoneal ketamine (750 mg/kg)/ xylazine (60 mg/kg) injection and transcardially perfused with 0.9% NaCl followed by 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA). The brains were removed, post-fixed in 4% PFA for 24 hr and transferred to 10%, 20% and 30% sucrose in 4% PFA at 4°C. The fixed brains were cut on a microtome (Retritome REM-710; Yamato, Saitama, Japan) in 40 µm coronal sections. The slices were embedded in 0.8% gelatin, mounted on the glass slides and air-dried for 1 week. Congo Red staining was performed according to the manufacturer’s instruction (Congo Red staining kit, 101641; Milipore, Sigma-Aldrich, USA) with slight modification. Briefly, the sections were washed with distilled water for 1 min and incubated in Congo Red solution for 5 min followed by rinsing with tap water for 5 min. Next, they were treated with KOH solution for 30 s and washed with tap water. Then, they were serially dipped in 96% and 100% ethanol, each in two times, cleared in xylene for two times and coverslipped with mounting medium (Enthellan®, 107961; Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). The sections were processed at the same time using the same solutions to reduce variability in staining. The staining intensity of the pyramidal cells in the ROI (region of interest) was quantified by ImageJ software (National Institute of Health,
http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij) and expressed as integrated density (mean grey value x area).
4.8. Lecanemab for Immunostaining
The detail procedure for immunohistochemistry was described in our previous publication [
21]. Briefly, post-fixed brains were frozen by using OCT at -80°C and coronal sections were sliced at 30 µm using a cryostat (Leica CM1860; Leica Biosystems, Nussloch, Germany). The free-floating sections were first washed with PBS (pH 7.4) 2 times for 5 min and incubated with blocking solution (1.5% normal goat serum (NGS) with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS) at room temperature for 1 hr. They were washed with PBS 2 times for 5 min and further incubated overnight with the primary antibody, lecanemab (1:1000; A3112, Selleck Biotechnology, Ltd), diluted in PBS containing 1.5% NGS at 4°C under slight agitation. Then, the antigen-antibody complex in the slices was detected by using goat anti-human IgG, conjugated to Alexa Fluor
TM Plus 488 (1:500; A56869, Invitrogen, USA) diluted in PBS at room temperature for 1 hr in the dark. Next, after 3 times washing with PBS, they were slide-mounted and coverslipped with fluorescent mounting medium (Dako, S3023; Agilent, USA). The images were visualized under a fluorescence microscope (OLYMPUS BX51N-33-FLB2; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) and acquired by a digital microscope camera (OLYMPUS DP72; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). For semi-quantitative analysis with ImageJ software, 2-3 sections with ROI below the injection site per brain (number of rats = 3-4) were included. The CA1 region containing stratum oriens, stratum pyramidale and stratum radium was consistently captured at 20x magnification with the same exposure time and acquisition parameters such as frame dimension 4140 x 3096 pixels. The area of ROI was calculated in mm
2 and the cell density of immunopositive cells was expressed as cells/mm
2. The cell shape was verified under direct visualization and cell numbers were counted manually. Cells with morphological characteristics highly suggestive of either astrocytes or microglial [
59,
60] were collectively referred to as non-pyramidal cells.
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis and graphical expression were performed using GraphPad Prism 9 software (Graph Pad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA). Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. The normal distribution of data was checked by Shapiro-Wilk test. To analyze the object recognition and social recognition tasks, we used paired t-test to compare the time spent in touching the novel and familiar targets in test phase. For IA task and fear condition test, statistical comparisons were performed with two-way ANOVA in which the between-group factor was the oligomers, and the within-group factor was the training. Other behavioral tests and electrophysiological parameters were analyzed by one-way ANOVA in which the between-group factor was the oligomers followed by post hoc Sidak’s multiple comparison test. The relationship between the spike numbers and current was analyzed by using two-way repeated measures ANOVA in which the between-group factor was the oligomers, and the within-group factor was the current. For RLZ-treated cells, the data were analyzed by two-way repeated measures ANOVA in which the between-group factor was the drug, RLZ and the within-group factor was the current. F value (analysis of variance) was described, and statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
5. Conclusions
Microinjection of Aβ1-42 oligomers into the CA1 region induced selective learning and memory deficits with concomitant neuronal hyperexcitability and amyloid deposition in the target area. Given the contextual learning-induced hyperexcitability. of CA1 pyramidal neurons, the injection model is a useful technique for understanding the pathogenesis of AD and for testing drugs designed to protect against Aβ1-42 oligomers.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.M., H.K. and M.K.W.M.; methodology, D.M., H.K., J.I., Y.S., M.K.W.M. and R.K.; formal analysis, H.K. and M.K.W.M.; investigation, M.K.W.M., H.K., I.K., M.K., P.M.T.O. and D.M.; resources, R.K.; writing—original draft preparation, M.K.W.M.; writing—review and editing, D.M.; visualization, M.K.W.M. and D.M.; supervision, D.M.; funding acquisition, D.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research C (D.M. Grant No. 23K06348), Scientific Research B (D.M. Grants No. 16H05129 and 19H03402), and Scientific Research in Innovative Areas (D.M. Grant No. 26115518), from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan. This project was also supported by YU AI project of Center for Information and Data Science Education.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal housing and surgical procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Yamaguchi University Graduate School of Medicine (Approval No. 04-S02) and experiments were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Yamaguchi University. These guidelines comply with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the National Institute of Health (NIH Publication No. 85-23, revised 1996).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary informationsupplementary files.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank H. Tsurutani for various assistance in the experiment. We also thank S. Kato for her generous supply of lecanemab.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Hardy, J., & Selkoe, D. J. (2002). The Amyloid Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Progress and Problems on the Road to Therapeutics. Science, 297(5580), 353–356. [CrossRef]
- Vassar, R., Bennett, B. D., Babu-Khan, S., Kahn, S., Mendiaz, E. A., Denis, P., Teplow, D. B., Ross, S., Amarante, P., Loeloff, R., Luo, Y., Fisher, S., Fuller, J., Edenson, S., Lile, J., Jarosinski, M. A., Biere, A. L., Curran, E., Burgess, T., Citron, M. (1999). β-Secretase Cleavage of Alzheimer’s Amyloid Precursor Protein by the Transmembrane Aspartic Protease BACE. Science, 286(5440), 735–741. [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. (2009). γ-Secretase Catalyzes Sequential Cleavages of the AβPP Transmembrane Domain. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 16(2), 211–224. [CrossRef]
- Gravina, S. A., Ho, L., Eckman, C. B., Long, K. E., Otvos, L., Younkin, L. H., Suzuki, N., & Younkin, S. G. (1995). Amyloid β Protein (Aβ) in Alzheimeri’s Disease Brain. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 270(13), 7013–7016. [CrossRef]
- Bitan, G., Kirkitadze, M. D., Lomakin, A., Vollers, S. S., Benedek, G. B., & Teplow, D. B. (2003). Amyloid β-protein (Aβ) assembly: Aβ40 and Aβ42 oligomerize through distinct pathways. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100(1), 330–335. [CrossRef]
- Yang, M., & Teplow, D. B. (2008). Amyloid β-Protein Monomer Folding: Free-Energy Surfaces Reveal Alloform-Specific Differences. Journal of Molecular Biology, 384(2), 450–464. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M., Davis, J., Aucoin, D., Sato, T., Ahuja, S., Aimoto, S., Elliott, J. I., Van Nostrand, W. E., & Smith, S. O. (2010). Structural conversion of neurotoxic amyloid-β1–42 oligomers to fibrils. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 17(5), 561–567. [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, D., D’Hooge, R., Staufenbiel, M., Van Ginneken, C., Van Meir, F., & De Deyn, P. P. (2003). Age-dependent cognitive decline in the APP23 model precedes amyloid deposition. European Journal of Neuroscience, 17(2), 388–396. [CrossRef]
- Mucke, L., Masliah, E., Yu, G.-Q., Mallory, M., Rockenstein, E. M., Tatsuno, G., Hu, K., Kholodenko, D., Johnson-Wood, K., & McConlogue, L. (2000). High-Level Neuronal Expression of Aβ 1–42 in Wild-Type Human Amyloid Protein Precursor Transgenic Mice: Synaptotoxicity without Plaque Formation. The Journal of Neuroscience, 20(11), 4050–4058. [CrossRef]
- Gandy, S., Simon, A. J., Steele, J. W., Lublin, A. L., Lah, J. J., Walker, L. C., Levey, A. I., Krafft, G. A., Levy, E., Checler, F., Glabe, C., Bilker, W. B., Abel, T., Schmeidler, J., & Ehrlich, M. E. (2010). Days to criterion as an indicator of toxicity associated with human Alzheimer amyloid-β oligomers. Annals of Neurology, 68(2), 220–230. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.-M., Emmerling, M. R., Vigo-Pelfrey, C., Kasunic, T. C., Kirkpatrick, J. B., Murdoch, G. H., Ball, M. J., & Roher, A. E. (1996). Water-soluble Aβ (N-40, N-42) Oligomers in Normal and Alzheimer Disease Brains. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271(8), 4077–4081. [CrossRef]
- Roher, A. E., Chaney, M. O., Kuo, Y.-M., Webster, S. D., Stine, W. B., Haverkamp, L. J., Woods, A. S., Cotter, R. J., Tuohy, J. M., Krafft, G. A., Bonnell, B. S., & Emmerling, M. R. (1996). Morphology and Toxicity of Aβ-(1-42) Dimer Derived from Neuritic and Vascular Amyloid Deposits of Alzheimer’s Disease. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271(34), 20631–20635. [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y., Chang, L., Viola, K. L., Lacor, P. N., Lambert, M. P., Finch, C. E., Krafft, G. A., & Klein, W. L. (2003). Alzheimer’s disease-affected brain: Presence of oligomeric Aβ ligands (ADDLs) suggests a molecular basis for reversible memory loss. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100(18), 10417–10422. [CrossRef]
- Forny-Germano, L., Lyra E Silva, N. M., Batista, A. F., Brito-Moreira, J., Gralle, M., Boehnke, S. E., Coe, B. C., Lablans, A., Marques, S. A., Martinez, A. M. B., Klein, W. L., Houzel, J.-C., Ferreira, S. T., Munoz, D. P., & De Felice, F. G. (2014). Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Pathology Induced by Amyloid-β Oligomers in Nonhuman Primates. The Journal of Neuroscience, 34(41), 13629–13643. [CrossRef]
- Haass, C., & Selkoe, D. J. (2007). Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: Lessons from the Alzheimer’s amyloid β-peptide. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 8(2), 101–112. [CrossRef]
- Rolls ET (2018). The storage and recall of memories in the hippocampo-cortical system. Cell Tissue Res, 373(3), 577-604. [CrossRef]
- Kesner RP, Lee I, Gilbert P (2004). A behavioral assessment of hippocampal function based on a subregional analysis. Rev Neurosci, 15(5), 333-51.
- Lee I & Kesner RP (2002). Differential contribution of NMDA receptors in hippocampal subregions to spatial working memory. Nat Neurosci, 5(2), 162-8. [CrossRef]
- Remondes, M., & Schuman, E. M. (2004). Role for a cortical input to hippocampal area CA1 in the consolidation of a long-term memory. Nature, 431(7009), 699–703. [CrossRef]
- Lee I & Kesner RP (2004). Differential contributions of dorsal hippocampal subregions to memory acquisition and retrieval in contextual fear-conditioning. Hippocampus, 14(3), 301-10. [CrossRef]
- Mitsushima, D., Ishihara, K., Sano, A., Kessels, H. W., & Takahashi, T. (2011). Contextual learning requires synaptic AMPA receptor delivery in the hippocampus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(30), 12503–12508. [CrossRef]
- Ásgeirsdóttir HN, Cohen SJ & Stackman RW Jr (2020). Object and place information processing by CA1 hippocampal neurons of C57BL/6J mice. J Neurophysiol, 123(3),1247-1264. [CrossRef]
- Heggland, I., Storkaas, I. S., Soligard, H. T., Kobro-Flatmoen, A., & Witter, M. P. (2015). Stereological estimation of neuron number and plaque load in the hippocampal region of a transgenic rat model of A lzheimer’s disease. European Journal of Neuroscience, 41(9), 1245–1262. [CrossRef]
- Wood ER, Dudchenko PA, Robitsek RJ & Eichenbaum H (2000). Hippocampal neurons encode information about different types of memory episodes occurring in the same location. Neuron, 27(3), 623-33. [CrossRef]
- Horsley, J. R., Jovcevski, B., Wegener, K. L., Yu, J., Pukala, T. L., & Abell, A. D. (2020). Rationally designed peptide-based inhibitor of Aβ42 fibril formation and toxicity: A potential therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemical Journal, 477(11), 2039–2054. [CrossRef]
- Wilcock, D. M., Gordon, M. N., & Morgan, D. (2006). Quantification of cerebral amyloid angiopathy and parenchymal amyloid plaques with Congo red histochemical stain. Nature Protocols, 1(3), 1591–1595. [CrossRef]
- Arndt, J. W., Qian, F., Smith, B. A., Quan, C., Kilambi, K. P., Bush, M. W., Walz, T., Pepinsky, R. B., Bussière, T., Hamann, S., Cameron, T. O., & Weinreb, P. H. (2018). Structural and kinetic basis for the selectivity of aducanumab for aggregated forms of amyloid-β. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 6412. [CrossRef]
- Söderberg, L., Johannesson, M., Nygren, P., Laudon, H., Eriksson, F., Osswald, G., Möller, C., & Lannfelt, L. (2023). Lecanemab, Aducanumab, and Gantenerumab-Binding Profiles to Different Forms of Amyloid-Beta Might Explain Efficacy and Side Effects in Clinical Trials for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics, 20(1), 195–206. [CrossRef]
- Marshall KE, Vadukul DM, Dahal L, Theisen A, Fowler MW, Al-Hilaly Y, Ford L, Kemenes G, Day IJ, Staras K & Serpell LC (2016). A Critical Role for the Self-Assembly of Amyloid-Β1-42 in Neurodegeneration. Sci Rep, 6, 30182. [CrossRef]
- Kravenska, Y., Nieznanska, H., Nieznanski, K., Lukyanetz, E., Szewczyk, A., & Koprowski, P. (2020). The monomers, oligomers, and fibrils of amyloid-β inhibit the activity of mitoBKCa channels by a membrane-mediated mechanism. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes, 1862(9), 183337. [CrossRef]
- Hirakura, Y., Lin, M. C., & Kagan, B. L. (1999). Alzheimer amyloid abeta1-42 channels: Effects of solvent, pH, and Congo Red. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 57(4), 458–466.
- Koh, M. T., Haberman, R. P., Foti, S., McCown, T. J., & Gallagher, M. (2010). Treatment Strategies Targeting Excess Hippocampal Activity Benefit Aged Rats with Cognitive Impairment. Neuropsychopharmacology, 35(4), 1016–1025. [CrossRef]
- Yassa, M. A., Stark, S. M., Bakker, A., Albert, M. S., Gallagher, M., & Stark, C. E. L. (2010). High-resolution structural and functional MRI of hippocampal CA3 and dentate gyrus in patients with amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. NeuroImage, 51(3), 1242–1252. [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.-Q., Yao, W., Yan, J.-Z., Jin, C., Yin, J.-J., Yuan, J., Yu, S., & Cheng, Z. (2018). Amyloid β causes excitation/inhibition imbalance through dopamine receptor 1-dependent disruption of fast-spiking GABAergic input in anterior cingulate cortex. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 302. [CrossRef]
- George, A. A., Vieira, J. M., Xavier-Jackson, C., Gee, M. T., Cirrito, J. R., Bimonte-Nelson, H. A., Picciotto, M. R., Lukas, R. J., & Whiteaker, P. (2021). Implications of Oligomeric Amyloid-Beta (oAβ42) Signaling through α7β2-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors (nAChRs) on Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neuronal Intrinsic Excitability and Cognitive Decline. The Journal of Neuroscience, 41(3), 555–575. [CrossRef]
- Taverna S, Tkatch T & Metz AE, Martina M (2005). Differential expression of TASK channels between horizontal interneurons and pyramidal cells of rat hippocampus. J Neurosci, 25(40), 9162-70. [CrossRef]
- Hu H, Vervaeke K & Storm JF. Two forms of electrical resonance at theta frequencies, generated by M-current, h-current and persistent Na+ current in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells (2002). J Physiol, 545(3), 783-805. [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, R., Yamamoto, H., Hayakawa, T., Katsurabayashi, S., Niwano, M., & Hirano-Iwata, A. (2018). Dependence and Homeostasis of Membrane Impedance on Cell Morphology in Cultured Hippocampal Neurons. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 9905. [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, A.-A., Benilova, I., Krylychkina, O., Braeken, D., De Strooper, B., Van Haesendonck, C., Dotti, C. G., & Bartic, C. (2016). Amyloid beta oligomers induce neuronal elasticity changes in age-dependent manner: A force spectroscopy study on living hippocampal neurons. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 25841. [CrossRef]
- Demuro, A., Mina, E., Kayed, R., Milton, S. C., Parker, I., & Glabe, C. G. (2005). Calcium Dysregulation and Membrane Disruption as a Ubiquitous Neurotoxic Mechanism of Soluble Amyloid Oligomers. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280(17), 17294–17300. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Perez, E. J., Muñoz, B., Bascuñan, D. A., Peters, C., Riffo-Lepe, N. O., Espinoza, M. P., Morgan, P. J., Filippi, C., Bourboulou, R., Sengupta, U., Kayed, R., Epsztein, J., & Aguayo, L. G. (2021). Synaptic dysregulation and hyperexcitability induced by intracellular amyloid beta oligomers. Aging Cell, 20(9), e13455. [CrossRef]
- Nimmrich, V., Grimm, C., Draguhn, A., Barghorn, S., Lehmann, A., Schoemaker, H., Hillen, H., Gross, G., Ebert, U., & Bruehl, C. (2008). Amyloid β Oligomers (Aβ1–42 Globulomer) Suppress Spontaneous Synaptic Activity by Inhibition of P/Q-Type Calcium Currents. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28(4), 788–797. [CrossRef]
- Tamagnini, F., Scullion, S., Brown, J. T., & Randall, A. D. (2015). Intrinsic excitability changes induced by acute treatment of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons with exogenous amyloid β peptide. Hippocampus, 25(7), 786–797. [CrossRef]
- Ferrara NC, Jarome TJ, Cullen PK, Orsi SA, Kwapis JL, Trask S, Pullins SE & Helmstetter FJ (2019). GluR2 endocytosis-dependent protein degradation in the amygdala mediates memory updating. Sci Rep, 9(1), 5180. [CrossRef]
- Piromalli Girado D, Miranda M, Giachero M, Weisstaub N & Bekinschtein P (2023). Endocytosis is required for consolidation of pattern-separated memories in the perirhinal cortex. Front Syst Neurosci, 17, 1043664. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto K, Ueta Y, Wang L, Yamamoto R, Inoue N, Inokuchi K, Aiba A, Yonekura H & Kato N (2011). Suppression of a neocortical potassium channel activity by intracellular amyloid-β and its rescue with Homer1a. J Neurosci, 31(31), 11100-9. [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, R., Franco, C., Piccialli, I., Boscia, F., Casamassa, A., De Rosa, V., Cepparulo, P., Cataldi, M., Annunziato, L., & Pannaccione, A. (2019). Amyloid β-Induced Upregulation of Nav1.6 Underlies Neuronal Hyperactivity in Tg2576 Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 13592. [CrossRef]
- Jin S, Kedia N, Illes-Toth E, Haralampiev I, Prisner S, Herrmann A, Wanker EE & Bieschke J (2016). Amyloid-β(1-42) Aggregation Initiates Its Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem, 291(37), 19590-606. [CrossRef]
- Chatelier, A., Zhao, J., Bois, P., & Chahine, M. (2010). Biophysical characterisation of the persistent sodium current of the Nav1.6 neuronal sodium channel: A single-channel analysis. Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology, 460(1), 77–86. [CrossRef]
- Vervaeke, K., Hu, H., Graham, L. J., & Storm, J. F. (2006). Contrasting Effects of the Persistent Na+ Current on Neuronal Excitability and Spike Timing. Neuron, 49(2), 257–270. [CrossRef]
- Ren, S., Chen, P., Jiang, H., Mi, Z., Xu, F., Hu, B., Zhang, J., & Zhu, Z. (2014). Persistent sodium currents contribute to Aβ1-42-induced hyperexcitation of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Neuroscience Letters, 580, 62–67. [CrossRef]
- Sipos, E., Kurunczi, A., Kasza, Á., Horváth, J., Felszeghy, K., Laroche, S., Toldi, J., Párducz, Á., Penke, B., & Penke, Z. (2007). β-Amyloid pathology in the entorhinal cortex of rats induces memory deficits: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience, 147(1), 28–36. [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-W., Zong, H.-F., Ma, K.-G., Zhai, W.-Y., Yang, W.-N., Hu, X.-D., Xu, J.-H., Chen, X.-L., Ji, S.-F., & Qian, Y.-H. (2008). Activation of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alleviates Aβ1-42-induced neurotoxicity via downregulation of p38 and JNK MAPK signaling pathways. Neurochemistry International, 120, 238–250. [CrossRef]
- Koppensteiner, P., Trinchese, F., Fà, M., Puzzo, D., Gulisano, W., Yan, S., Poussin, A., Liu, S., Orozco, I., Dale, E., Teich, A. F., Palmeri, A., Ninan, I., Boehm, S., & Arancio, O. (2016). Time-dependent reversal of synaptic plasticity induced by physiological concentrations of oligomeric Aβ42: An early index of Alzheimer’s disease. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 32553. [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R., Marcussen, A. B., Wörtwein, G., Knudsen, G. M., & Aznar, S. (2008). Aβ (1–42) injection causes memory impairment, lowered cortical and serum BDNF levels, and decreased hippocampal 5-HT2A levels. Experimental Neurology, 210(1), 164–171. [CrossRef]
- Brouillette, J., Caillierez, R., Zommer, N., Alves-Pires, C., Benilova, I., Blum, D., De Strooper, B., & Buee, L. (2012). Neurotoxicity and Memory Deficits Induced by Soluble Low-Molecular-Weight Amyloid- 1-42 Oligomers Are Revealed In Vivo by Using a Novel Animal Model. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(23), 7852–7861. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y., Ji, W., Zhu, Z., Wu, Y., Zhang, Z., & Qu, S. (2018). Rhynchophylline suppresses soluble Aβ1-42-induced impairment of spatial cognition function via inhibiting excessive activation of extrasynaptic NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. Neuropharmacology, 135, 100–112. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M., Liu, J., Ruan, Z., Tian, S., Ma, Y., Zhu, J., & Li, G. (2013). Intrahippocampal injection of Aβ 1-42 inhibits neurogenesis and down-regulates IFN-γ and NF-κB expression in hippocampus of adult mouse brain. Amyloid, 20(1), 13–20. [CrossRef]
- Cerbai, F., Lana, D., Nosi, D., Petkova-Kirova, P., Zecchi, S., Brothers, H. M., Wenk, G. L., & Giovannini, M. G. (2012). The Neuron-Astrocyte-Microglia Triad in Normal Brain Ageing and in a Model of Neuroinflammation in the Rat Hippocampus. PLoS ONE, 7(9), e45250. [CrossRef]
- Lana, D., Ugolini, F., Nosi, D., Wenk, G. L., & Giovannini, M. G. (2017). Alterations in the Interplay between Neurons, Astrocytes and Microglia in the Rat Dentate Gyrus in Experimental Models of Neurodegeneration. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 9, 296. [CrossRef]
- O’Hare, E., Weldon, D. T., Mantyh, P. W., Ghilardi, J. R., Finke, M. P., Kuskowski, M. A., Maggio, J. E., Shephard, R. A., & Cleary, J. (1999). Delayed behavioral effects following intrahippocampal injection of aggregated Aβ (1–42). Brain Research, 815(1), 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Sakimoto, Y., Shintani, A., Yoshiura, D., Goshima, M., Kida, H., & Mitsushima, D. (2022). A critical period for learning and plastic changes at hippocampal CA1 synapses. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 7199. [CrossRef]
- Beninger, R. J., Jhamandas, K., Boegman, R. J., & El-Defrawy, S. R. (1986). Effects of scopolamine and unilateral lesions of the basal forebrain on T-maze spatial discrimination and alternation in rats. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 24(5), 1353–1360. [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K., Hiramatsu, M., Noda, Y., Mamiya, T., Murai, M., Kameyama, T., Komori, Y., Nikai, T., Sugihara, H., & Nabeshima, T. (1996). Role of nitric oxide and cyclic GMP in the dizocilpine-induced impairment of spontaneous alternation behavior in mice. Neuroscience, 74(2), 365–374. [CrossRef]
- Arrant, A. E., Schramm-Sapyta, N. L., & Kuhn, C. M. (2013). Use of the light/dark test for anxiety in adult and adolescent male rats. Behavioural Brain Research, 256, 119–127. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y., Kim, H., & Han, P.-L. (2018). Striatal Inhibition of MeCP2 or TSC1 Produces Sociability Deficits and Repetitive Behaviors. Experimental Neurobiology, 27(6), 539–549. [CrossRef]
- Takase, K., Sakimoto, Y., Kimura, F., & Mitsushima, D. (2014). Developmental trajectory of contextual learning and 24-h acetylcholine release in the hippocampus. Scientific Reports, 4(1), 3738. [CrossRef]
- Kulesskaya, N., & Voikar, V. (2014). Assessment of mouse anxiety-like behavior in the light–dark box and open-field arena: Role of equipment and procedure. Physiology & Behavior, 133, 30–38. [CrossRef]
- Lehner M, Wisłowska-Stanek A, Maciejak P, Szyndler J, Sobolewska A, Krzaścik P & Płaźnik A. (2010). The relationship between pain sensitivity and conditioned fear response in rats. Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis, 70(1), 56–66. [CrossRef]
- Kida, H., Sakimoto, Y., & Mitsushima, D. (2017). Slice Patch Clamp Technique for Analyzing Learning-Induced Plasticity. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 129, 55876. [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G. & Watson, C, The Rat Bain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed. Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA; 2006.
Figure 1.
Effect of Aβ1-42 oligomers on inhibitory avoidance (IA) task. (A) Schematic illustration of the IA task paradigm. Rats were subjected to the IA task 1 week after bilateral injections of Aβ1-42 oligomers into dorsal CA1. On the training day, a brief electrical foot shock (1.6 mA, 2 s) was applied when the rats entered the dark compartment of IA box. After 30 minutes, they were placed in the light side and latency to enter the dark side was measured. (B) A shorter latency was observed in both Aβ1-42 and Aβ42-1 oligomer-injected rats. The number of rats was shown at the bottom of each bar. Data were plotted as individual points and expressed as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01 vs. saline. ap < 0.05 and aap < 0.01 vs. training.
Figure 1.
Effect of Aβ1-42 oligomers on inhibitory avoidance (IA) task. (A) Schematic illustration of the IA task paradigm. Rats were subjected to the IA task 1 week after bilateral injections of Aβ1-42 oligomers into dorsal CA1. On the training day, a brief electrical foot shock (1.6 mA, 2 s) was applied when the rats entered the dark compartment of IA box. After 30 minutes, they were placed in the light side and latency to enter the dark side was measured. (B) A shorter latency was observed in both Aβ1-42 and Aβ42-1 oligomer-injected rats. The number of rats was shown at the bottom of each bar. Data were plotted as individual points and expressed as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01 vs. saline. ap < 0.05 and aap < 0.01 vs. training.
Figure 2.
Effect of Aβ1-42 oligomers on the intrinsic properties of CA1 pyramidal neurons. (A) Schematic illustration of the slice patch experiment. To assess the intrinsic properties of CA1 pyramidal neurons 1 hr after IA learning, a current clamp experiment was performed 1 week after unilateral injection of Aβ1-42 oligomers. (B) Example traces of action potentials induced by current injections (left panel) and input-output relationship in the saline, Aβ1-42 and Aβ42-1 oligomer-injected rats with the IA task (right panel). (C) Membrane capacitance, Cm. (D) Membrane resistance, Rm. (E) Membrane time constant, tau. (F) Resting membrane potential, RMP. (G) Threshold potential. (H) Threshold current or rheobase of the saline, Aβ1-42 and Aβ42-1 oligomer-injected rats with the IA task. The number of cells was shown at the bottom of each bar. Data were plotted as individual points and expressed as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01 vs. saline +IA. aap < 0.01 vs Aβ1-42 +IA.
Figure 2.
Effect of Aβ1-42 oligomers on the intrinsic properties of CA1 pyramidal neurons. (A) Schematic illustration of the slice patch experiment. To assess the intrinsic properties of CA1 pyramidal neurons 1 hr after IA learning, a current clamp experiment was performed 1 week after unilateral injection of Aβ1-42 oligomers. (B) Example traces of action potentials induced by current injections (left panel) and input-output relationship in the saline, Aβ1-42 and Aβ42-1 oligomer-injected rats with the IA task (right panel). (C) Membrane capacitance, Cm. (D) Membrane resistance, Rm. (E) Membrane time constant, tau. (F) Resting membrane potential, RMP. (G) Threshold potential. (H) Threshold current or rheobase of the saline, Aβ1-42 and Aβ42-1 oligomer-injected rats with the IA task. The number of cells was shown at the bottom of each bar. Data were plotted as individual points and expressed as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01 vs. saline +IA. aap < 0.01 vs Aβ1-42 +IA.
Figure 3.
Effect of riluzole on the Aβ1-42 oligomer-induced hyperexcitability of CA1 pyramidal neurons. (A, C) Example traces of action potentials induced by current injections before and after riluzole in the Aβ1-42 oligomer and saline-injected rats with IA. (B, D) Input-output relationships in the Aβ1-42 oligomer and saline-injected rats before and after bath application of different concentrations of riluzole. The number of cells was shown in the graph. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01 vs pre.
Figure 3.
Effect of riluzole on the Aβ1-42 oligomer-induced hyperexcitability of CA1 pyramidal neurons. (A, C) Example traces of action potentials induced by current injections before and after riluzole in the Aβ1-42 oligomer and saline-injected rats with IA. (B, D) Input-output relationships in the Aβ1-42 oligomer and saline-injected rats before and after bath application of different concentrations of riluzole. The number of cells was shown in the graph. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01 vs pre.
Figure 4.
Effect of Aβ1-42 oligomers on the sensory/motor functions, pain sensitivity and emotional state. (A) Schematic illustration of the experimental design. Rats underwent the behavioral test battery 1 week after bilateral injections of Aβ1-42 oligomers into dorsal CA1 followed by Congo red and lecanemab staining. (B) The center time (upper panel) and travelled distance (lower panel) were not different in the open field test. (C) The time spent in the lit chamber and latency to enter as well as number of visits in the light/dark test were similar. (D) In the flinch-jump test, the current thresholds for finch, vocalization and jump were not changed. The number of rats was shown at the bottom of each bar. Data were plotted as individual points and expressed as mean ± SEM.
Figure 4.
Effect of Aβ1-42 oligomers on the sensory/motor functions, pain sensitivity and emotional state. (A) Schematic illustration of the experimental design. Rats underwent the behavioral test battery 1 week after bilateral injections of Aβ1-42 oligomers into dorsal CA1 followed by Congo red and lecanemab staining. (B) The center time (upper panel) and travelled distance (lower panel) were not different in the open field test. (C) The time spent in the lit chamber and latency to enter as well as number of visits in the light/dark test were similar. (D) In the flinch-jump test, the current thresholds for finch, vocalization and jump were not changed. The number of rats was shown at the bottom of each bar. Data were plotted as individual points and expressed as mean ± SEM.
Figure 5.
Effect of Aβ1-42 oligomers on other hippocampus-dependent tasks. (A) In the fear conditioning test, rats were allowed to explore the conditioning chamber and subjected to electrical foot shock (0.8 mA, 2 s) 3 times. After 24 hr, re-exposure to the conditioning chamber increased freezing time which was significantly reduced in the Aβ1-42 oligomer-injected rats. *p < 0.05 vs. saline. aap < 0.01 vs. training. (B) Exploration of the familiar and novel objects in object recognition task. Training did not increase the touch time of the novel object in the Aβ1-42 oligomer-injected group. The exploration time of the novel object was also reduced in the Aβ1-42 oligomer group compared to the saline group. *p < 0.05 vs. saline. aap < 0.01 vs. familiar object. (C) Similarly, the social interaction time of both social targets were not different in the Aβ1-42 oligomer-injected group after training. There was no significant difference in the touch time of the novel target in the Aβ1-42 oligomer-injected group compared to the saline group. aap < 0.01 vs. familiar social target. (D, E) The alternation ratio and number of arm entry in the Y-maze test were not different. The number of rats was shown at the bottom of each bar. Data were plotted as individual points and expressed as mean ± SEM.
Figure 5.
Effect of Aβ1-42 oligomers on other hippocampus-dependent tasks. (A) In the fear conditioning test, rats were allowed to explore the conditioning chamber and subjected to electrical foot shock (0.8 mA, 2 s) 3 times. After 24 hr, re-exposure to the conditioning chamber increased freezing time which was significantly reduced in the Aβ1-42 oligomer-injected rats. *p < 0.05 vs. saline. aap < 0.01 vs. training. (B) Exploration of the familiar and novel objects in object recognition task. Training did not increase the touch time of the novel object in the Aβ1-42 oligomer-injected group. The exploration time of the novel object was also reduced in the Aβ1-42 oligomer group compared to the saline group. *p < 0.05 vs. saline. aap < 0.01 vs. familiar object. (C) Similarly, the social interaction time of both social targets were not different in the Aβ1-42 oligomer-injected group after training. There was no significant difference in the touch time of the novel target in the Aβ1-42 oligomer-injected group compared to the saline group. aap < 0.01 vs. familiar social target. (D, E) The alternation ratio and number of arm entry in the Y-maze test were not different. The number of rats was shown at the bottom of each bar. Data were plotted as individual points and expressed as mean ± SEM.
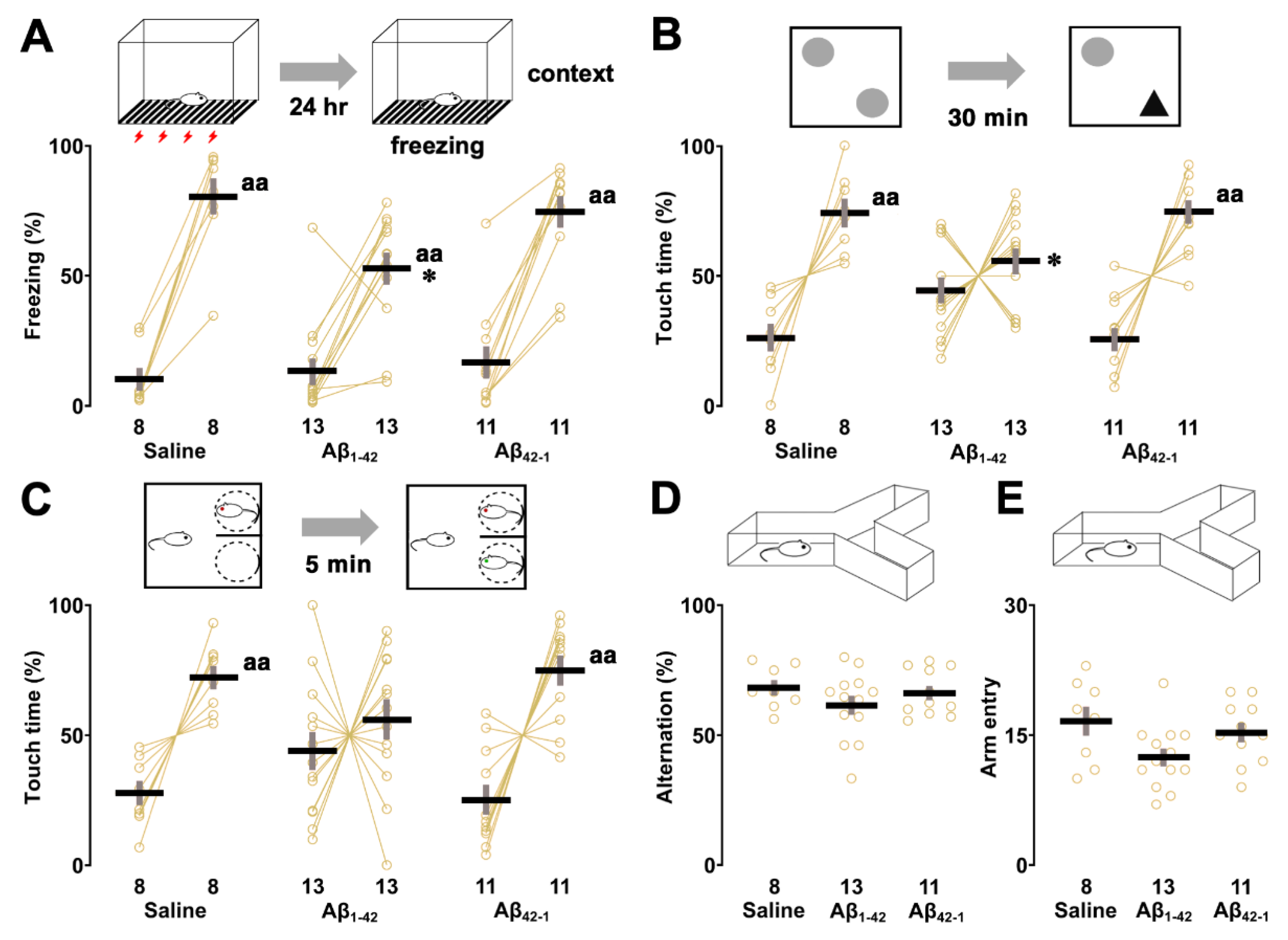
Figure 6.
Quantification of amyloid deposition after 1 week of oligomer injection. (A) Diagram of coronal brain section and representative micrographs of Congo red staining in the CA1 region. (B) Cumulative distribution of staining density of individual CA1 pyramidal cells. The number of cells was shown in parentheses. AU, arbitrary unit. (C) Diagram of coronal brain section and representative fluorescence images of lecanemab immunoreactivity. (D) Semi-quantitative analysis of lecanemab-positive CA1 pyramidal cell counts per mm2. (E) Diagram of coronal brain section and representative fluorescence images of lecanemab-positive non-pyramidal cells at the Aβ1-42 oligomer-injected site. The magnifications are x100 (left) and x200 (right) with the arrow indicating the injection track and arrowheads showing non-pyramidal cells. CA1, cornu ammonis 1; CC, corpus callosum; Ctx, cortex. (F) Semi-quantitative analysis of lecanemab-positive non-pyramidal cell counts per mm2 in the stratum pyramidale (s.p.), stratum oriens (s.o.) and stratum radiatum (s.r.) of the CA1 region. Scale bars: 100 μm. The number of slices was shown at the bottom of each bar. Data were plotted as individual points and expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs. saline. ap < 0.05 and aap < 0.01 vs. Aβ1-42.
Figure 6.
Quantification of amyloid deposition after 1 week of oligomer injection. (A) Diagram of coronal brain section and representative micrographs of Congo red staining in the CA1 region. (B) Cumulative distribution of staining density of individual CA1 pyramidal cells. The number of cells was shown in parentheses. AU, arbitrary unit. (C) Diagram of coronal brain section and representative fluorescence images of lecanemab immunoreactivity. (D) Semi-quantitative analysis of lecanemab-positive CA1 pyramidal cell counts per mm2. (E) Diagram of coronal brain section and representative fluorescence images of lecanemab-positive non-pyramidal cells at the Aβ1-42 oligomer-injected site. The magnifications are x100 (left) and x200 (right) with the arrow indicating the injection track and arrowheads showing non-pyramidal cells. CA1, cornu ammonis 1; CC, corpus callosum; Ctx, cortex. (F) Semi-quantitative analysis of lecanemab-positive non-pyramidal cell counts per mm2 in the stratum pyramidale (s.p.), stratum oriens (s.o.) and stratum radiatum (s.r.) of the CA1 region. Scale bars: 100 μm. The number of slices was shown at the bottom of each bar. Data were plotted as individual points and expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs. saline. ap < 0.05 and aap < 0.01 vs. Aβ1-42.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).