1. Introduction
Smoking is a major public health problem, responsible for the deaths of more than eight million people worldwide each year [
1]. Lung cancer caused by direct exposure to cigarette smoke is responsible for these deaths [
2,
3], but up to 1.2 million of them are caused by passive smoking [
1]. Smoking cessation is therefore a first-line intervention to reduce lung cancer and smoking-related mortality [
4]. The use of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) and vaping devices for nicotine consumption is growing rapidly, especially among young people, raising new public health concerns [
5,
6]. The number of e-cigarette users worldwide is estimated to be 82 million in 2021 [
7]. And according to the World Health Organization (WHO), e-cigarette use among adolescents exceeds that of adults [
8]. Vaping has been linked to mental health problems such as attention deficit disorder, personality changes, learning disabilities and sleep disorders [
9,
10], and young people are more vulnerable to the neurological effects of nicotine in e-cigarettes [
11]. Vaping may also increase the risk of developing conditions such as recurrent spontaneous pneumothorax, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and asthma [
12,
13,
14].
The evolution of digital technologies offers new perspectives for health promotion and preventive health interventions [
15]. Interventions aimed at preventing smoking and/or vaping are benefiting from this evolution due to new generations’ familiarity with technology [
16,
17]. Interactive conversational agents, also known as chatbots, are computer programs that use natural language processing to engage in conversations with humans to provide or gather information [
18,
19,
20]. Chatbots use algorithms to simulate a human conversation via text or voice messages. They are easy to use and require minimal computer knowledge and skills [
21,
22]. Chatbots can use simple, pre-determined conversational algorithms to simulate a conversation, or more complex systems based on neural networks and deep learning to understand speech, produce a vocal response, and simulate social interaction [
23]. Interactive chatbots enable automated interventions with customizable, accessible, and inexpensive software [
24]. A recent review examined the acceptability and effectiveness of conversational agents to help people quit smoking [
25], but did not consider vaping cessation. In addition, this review did not focus on interactive chatbots, which are likely to be more effective than traditional chatbots [
24]. The present review focuses on chatbots that can adapt and simulate interactive conversations, as opposed to conversational agents that offer users limited multiple-choice options, thus reducing the impression of real, meaningful interactions.
The aim of this mixed methods systematic review is to assess the effectiveness and characteristics of interactive conversational agents in promoting smoking and vaping cessation.
2. Materials and Methods
This mixed methods systematic review grew out of a broader scoping review of interactive conversational agents used for health promotion, prevention, and care [
26]. This review focuses on a sub-analysis of studies that included the use of an interactive conversational agent or chatbot to promote smoking cessation or vaping cessation. The protocol was prospectively registered in the Open Science Framework (OSF) [
27]. According to the registered protocol, a scoping review was initially planned before conducting this systematic review. The scoping part aimed to assess the scope of available studies on chatbots for vaping cessation, as this is an emerging field. However, due to the limited number of studies on chatbot interventions for vaping cessation, the scoping review phase was integrated into the final systematic review. Our review questions were: (1) what is the effectiveness of interactive conversational agents for smoking and vaping cessation compared with other alternatives? and (2) what is the benefit of integrating these technologies into smoking and vaping cessation interventions? A mixed methods systematic review was conducted according to the framework of Stern et al. [
28]. The PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews) criteria were used to report the results [
29].
We considered all types of evidence that met the PICOS criteria (population, intervention, comparison, outcomes, setting or context):
Participants or population: We included all studies with lay participants (e.g., patients, students, citizens). Studies targeting only healthcare providers were excluded.
Interventions or phenomena of interest: We included all interactive conversational agents, i.e., those that involve a two-way exchange (written, oral or visual dialogue), aimed at laypeople for smoking or vaping cessation.
Comparator: We did not apply any restrictions.
Outcomes: We considered all outcomes reported in the trials. We looked for outcomes related to cigarette and e-cigarette smokers. These outcomes included barriers, facilitators, acceptability, feasibility, adoption, compliance, motivation to quit, abstinence rates, quit rates, smoking/ vaping-related disease morbidity, quality of life, satisfaction, cost and cost-effectiveness.
Setting: We included trials conducted in all settings. All study types were included (qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods).
The search strategy of the broader scoping review was reused, and terms related to smoking and vaping cessation were added. The original and modified versions of the search strategy were developed in collaboration with a university librarian (FB) experienced in systematic reviews. We conducted an iterative review process with the research team, and all relevant comments were incorporated into the final version of the search strategy and approved by all team members. We developed a specific search strategy for each of the following databases: MEDLINE (Ovid), Embase, CINAHL, Web of Science, and Inspec (Engineering Village). The search strategy is presented in
Appendix A. The search was limited to studies from the last 20 years due to the recent nature of conversational agents, and no linguistic restrictions were applied to the search. We used terms such as chatbot, conversational agent, virtual embodied agent, and their spelling variants. In addition, as innovation implementations are often driven by the private sector, we conducted an Internet search of the following sources and databases: Google, Google Scholar, Institut national d’excellence en santé et en services sociaux, Canadian Evaluation Society, EuroScan, OpenGrey, Grey Literature Report, GreyNet, and Grey Matters.We conducted backward handsearching for other relevant references.
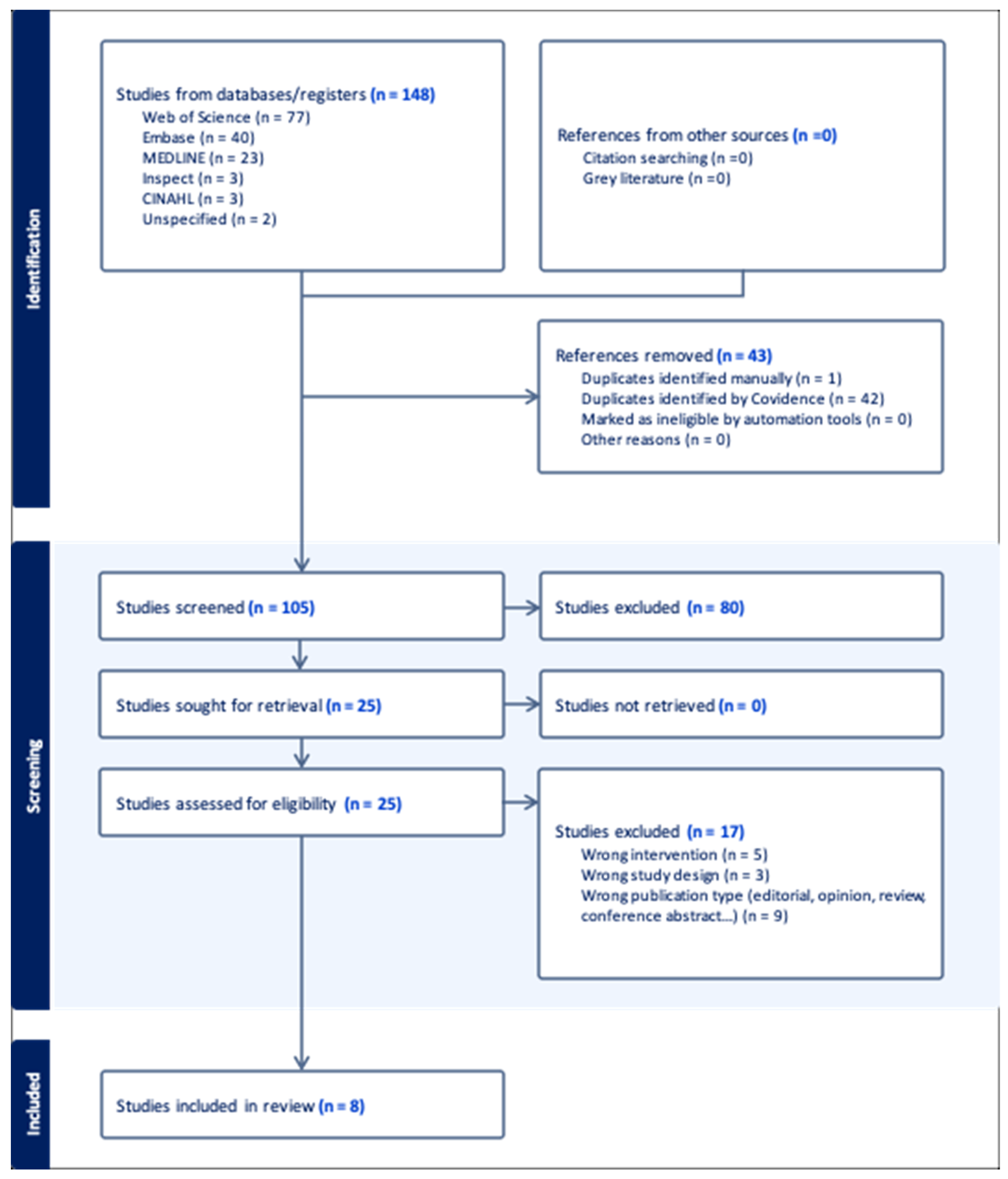
A search of the various databases included in the search strategy identified 148 publications. We exported all citations resulting from the application of the updated search strategy to Covidence, where duplicates were removed by its automated function. Pairs of reviewers (AL, AY, JP, SD, FN, FY) performed an independent blinded assessment of inclusion criteria based on titles and abstracts. The reviewers searched for and obtained all full text of the selected references and imported the files into Covidence [
30]. The same reviewers performed an independent blinded assessment of the full texts. Reasons for exclusion were recorded in Covidence and reported in the flowchart. We used the PRISMA diagram to describe the search strategy, selection process and reasons for exclusion [
31]. The PRISMA diagram is shown in
Figure 1.
We developed an extraction grid and tested it on an article during a team meeting. Team members completed the extraction, and the data quality was validated by an experienced researcher (MPG). We extracted descriptive data (title, year of publication, authors, country), study type (published or gray literature, study design), intervention data (technology name, technology language, delivery channel, and features such as audio, text, voice, avatar), setting data (target population, delivery site), sample data (comparators, number of participants, sample sizes), outcomes (processes, patients, providers, or systems), and type of outcome (qualitative and quantitative).
We presented the data synthesis with a narrative summary of the differences and similarities between interventions, highlighting strengths and weaknesses, key findings, key resources used, and trade-offs. We also compared the direction of effects on primary and secondary outcomes in the included studies. We used a convergent approach to consider both qualitative and quantitative evidence.
We assessed the quality of the included studies using the Mixed Methods Assessment Tool (MMAT) [
32,
33]. Pairs of reviewers performed a blinded methodological assessment. In case of disagreement, a third experienced reviewer (MPG) was consulted to reach a consensus.
3. Results
3.1. Overview
We identified 105 studies for review after excluding duplicates (see
Figure 1). After the abstract review, 25 full-text articles were assessed for inclusion. After full-text review and conflict resolution, eight studies met our inclusion criteria [
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41]. The eight included studies were conducted in European (Netherlands, Spain, Switzerland, UK) and North American (Canada, USA) countries between 2018 and 2023. All used either a chatbot alone or another technology with a chatbot (e.g., an app) to promote smoking cessation. We found one study on the use of chatbots that promoted both smoking and vaping cessation [
37]. This study targeted Swiss adolescents aged 16 to 19 years attending a vocational school. The remaining seven included studies [
34,
35,
36,
38,
39,
40,
41] targeted all cigarette smokers aged 18 years and older for recruitment. The number of participants recruited ranged from 153 to 688 for the clinical trials [
37,
38,
39,
40] to over 50,000 for the community study [
41]. One study [
34] was a prospective cohort study targeting a specific population; therefore, recruitment was much lower (six participants). Another study [
36] was a pre-post test study with recruitment of 349 participants. The last study [
35] was qualitative and involved semi-structured interviews with a smaller population (14 participants). All chatbots in the included studies had chat (text) functionality, two of them also had audio [
34,
40] and/or voice functionality [
40,
41], only one [
34] included an avatar and another [
37] included a quiz. Furthermore, in three studies [
34,
35,
36], the chatbot used in the intervention had no comparator. One study [
37] compared the chatbot condition with the condition without a chatbot. One study [
38] compared a motivational interviewing (MI) chatbot with a neutral chatbot, whereas another study [
39] compared a motivational interviewing chatbot with a confrontational advice chatbot. On the other hand, one study [
40] compared a chatbot with usual clinical practice for smoking cessation, and the last study [
41] compared an app with an integrated chatbot with the same app without the integrated chatbot. The characteristics of the studies are shown in
Table 1.
3.2. Outcomes Measured
The reported effects of interventions on patient outcomes are shown in
Table 2. One study [
36] evaluated the impact of several versions of a motivational interviewing (MI)-focused chatbot using generative thinking on smokers’ progress toward a decision to quit. The study assessed participants’ willingness to quit smoking through three attributes: confidence, importance, and willingness. Only the fourth version (v5.2), which in addition to the improved reflection generator included extended interaction on some of the questions, showed a positive result for the three variables assessing willingness to quit smoking. The same study also showed that the chatbot with deep reflection and extended conversations had a positive effect on perceived empathy, compared to the chatbot without generative reflection. Haug et al. [
37] evaluated the reduction of addictive behaviors, specifically smoking and/or vaping. The use of the chatbot did not show a positive effect on reducing smoking and/or vaping. Of these eight studies, only one [
39] assessed smoking cessation intentions by comparing the use of a MI-based chatbot with a confrontational counseling-based chatbot. Neither chatbot communication style showed a significant effect on the intention to quit smoking. However, exposure to the chatbot, regardless of communication style, had a positive effect on smokers’ intention to quit. Two studies [
40,
41] showed a positive effect of the intervention on abstinence. In addition, one of the eight included studies [
38] assessed motivation to quit smoking. Differences in scores were not statistically significant between groups but increases in motivation to quit were significant in both control and intervention groups. Three studies [
38,
40,
41] measured engagement, with Olano-Espinosa et al. [
40] and Perski et al. [
41] showing a positive effect and He et al. [
38] showing no difference in engagement in the intervention group compared to the control group. One study [
38] measured the effect of an MI-based chatbot on therapeutic alliance and perceived empathy compared to a neutral chatbot but found no significant difference. The same study [
38] reported higher perceived communication competence of the chatbot in the intervention group compared to the control group. Quality of life was only measured in one study [
40], where both intervention and comparison had a positive effect on quality of life, with the intervention having a smaller effect than the comparison.
Abdullah et al. [
34] did not report patient outcomes but presented descriptive data from six participants on the feasibility and acceptability of smoking cessation promotion. This study showed that the conversational agent was acceptable to participants and helped them set a quit date. Five participants reduced the average number of cigarettes smoked, and three tried to quit after the intervention. In addition, five participants adopted stricter smoke-free rules in their homes during the intervention period [
34]. The final study [
35] did not report quantitative results. This study showed that many users attributed human-like characteristics, thoughts, and behaviors to the chatbot.
We originally planned to conduct meta-analyses in the review protocol, but outcome data were insufficient.
3.3. Methodological Quality Assessment
Of the five methodological quality criteria for RCTs included in the MMAT [
31], only the criterion related to blinding of participants was not met in all five RCTs [
37,
38,
39,
40,
41]. Overall, these studies received a score of 4/5, indicating high methodological quality. Of the three remaining studies, the pre-post test study [
36] used a non-randomized quantitative design. Because confounding was not considered in the design and analysis, this study received an MMAT score of 4/5, indicating high methodological quality. The prospective cohort study [
34] used a quantitative descriptive design and achieved an MMAT score of 4/5 due to the risk of selection bias in the sampling method and incentives given to participants. Therefore, the sample may not have been representative of the target population. For the semi-structured interview study [
35] with a qualitative design, the five methodological quality criteria for qualitative studies included in the MMAT were considered. The study received a score of 5/5, indicating very high methodological quality.
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Findings
This review aimed to describe current interactive conversational agents used in smoking and vaping cessation interventions, and to evaluate their features and effectiveness. Seven of the eight included studies targeted smoking among adult smokers using interactive conversational agents that were comparable in terms of features. The eighth study targeted both smoking and vaping among teenagers [
37]. These studies did not address smoking and vaping in the same way in terms of parameters, comparators, and study designs. As a result, the primary and secondary outcomes reported in these studies were heterogeneous. This review considered all outcomes that could be sensitive to an interactive chatbot intervention according to predefined criteria. Reported outcomes included continued abstinence, motivation to quit, engagement, therapeutic alliance, perceived empathy, quality of life, willingness to quit, reduction in smoking and vaping, intention to quit, and anthropomorphism. Two studies [
40,
41] showed a positive effect of the intervention on sustained abstinence. Perski et al. [
36] measured self-reported abstinence at one month, while Olano-Espinosa et al. [
40] measured continuous abstinence at six months using biochemically validated quit rates. Continuous abstinence has also been measured in previous systematic reviews of digital interventions for smoking cessation [
42,
43,
44]. For example, Do et al. [
42] reported that interactive, tailored, web-based programs showed increased cessation effects for interventions with 6-month follow-up and moderate increases in smoking cessation for interventions with less than 6-month follow-up. The results of our review tend to confirm these findings, but due to the limited number of included studies and the different measurement methods used, no definitive conclusions can be drawn regarding the effect of chatbots on abstinence. Motivation to quit smoking was documented in a study comparing an MI-based chatbot with a neutral chatbot [
38]. Participants in both conditions reported increased motivation to quit smoking after interacting with the chatbot. However, a previous systematic review of combined pharmacotherapy and behavioral interventions for smoking cessation [
43] reported that motivation to quit was not considered an effect modifier for quit rates, meaning that quit rates were not significantly higher in more motivated populations. Therefore, motivation to quit should be interpreted with caution in future smoking and vaping cessation studies.
Regarding engagement, Olano-Espinosa et al. [
40] and Perski et al. [
41] reported that the intervention chatbot led to better engagement in treatment compared to usual clinical practice and a regular smoking cessation app, respectively. The prospective cohort study by Abdullah et al. [
34] also seems to suggest that participants were more engaged with their treatment when using the chatbot. On the other hand, He et al. [
38] reported that participants who interacted with either the MI-based intervention chatbot or the neutral control chatbot perceived them as equally engaging and empathetic, and developed similar levels of the therapeutic alliance with them. In their study, He et al. [
38] suggested that these results may be due to the interactions not being frequent or long enough for MI to have an impact. This hypothesis was also supported by a systematic review of the use of MI for smoking cessation by Lindson-Hawley et al. [
44]. However, in the study by Brown et al. [
36], the perceived empathy of the chatbot that integrated enhanced generative reflections and more extended interaction on specific topics was significantly higher than that of the chatbot that did not generate reflections. This difference appears to be related to the use of generative reflections as opposed to the scripted reflections and responses in He et al.‘s study [
38]
In addition, while Brown et al. [
36]) demonstrated that a chatbot that integrated generative reflections and extended interaction was associated with statistically significant quit intentions compared to a chatbot without generative reflections, they also emphasized that of the three attributes measuring quit intentions, only the self-efficacy related confidence attribute was the best predictor of successful quitting. This finding is supported by other studies showing that confidence is a significant predictor of smoking behavior, as the more confident an individual is, the more likely he or she is to attempt and succeed in quitting smoking [
45,
46]. Furthermore, He et al. [
48] reported that the perceived communication competence of the conversational agent was positively associated with both the intervention and comparison chatbots. These findings suggest that chatbots, regardless of their conceptual framework, may provide sufficient support to be more effective smoking cessation tools than other common practices. The only study that measured reductions in smoking and/or vaping was conducted by Haug et al. [
37]. This study found that adolescent use of a chatbot did not contribute to reductions in smoking or vaping. Regarding vaping, this finding contradicts that of Graham et al. [
47,
48]. These authors demonstrated in their studies that a tailored and interactive text messaging intervention was effective in promoting vaping cessation in both adolescents and young adults [
47,
48]. This difference in results may be related to the composite nature of the primary outcome measure in the study by Haug et al. [
37], which may not account for confounding factors. As for Leeuwis and He [
39], their study showed that interaction with a chatbot, regardless of whether it incorporated a motivational interviewing communication style or a confrontational counseling style, did not positively contribute to smoking cessation intention. However, it is noteworthy that in some digital interventions, particularly online smoking cessation interventions, the intention to quit was significantly higher among smokers who successfully quit and those who relapsed compared to persistent smokers [
49]. This finding is consistent with the secondary outcome of the study by Leeuwis and He [
39], which showed that exposure to the chatbot, regardless of communication style, had a positive effect on smokers’ intention to quit.
Quality of life (QoL) was only measured in the study by Olano-Espinosa et al. [
40]. Although there was no statistically significant difference between the groups in terms of smoking cessation rates, QoL was further improved among participants assigned to the chatbot compared to usual clinical practice. However, according to this study [
40], this result does not necessarily mean that the chatbot itself had a better effect on QoL, as it could be related to the higher abstinence rates observed in the intervention group. Alphonse et al. [
35] indicated in their study results that the chatbot thought and behaved like a human. However, these results contradict the study by Bendotti et al. [
50]. In their study, they reported that participants expressed that they felt like they were talking to a robot, and that they initially felt like they were talking to a human, but that errors in the chatbot’s responses diminished this effect, causing frustration that discouraged them from continuing to use it [
50]. Their findings may be related to functionality issues that are not present in the chatbot in Alphonse et al.‘s study [
35].
4.2. Main Contributions
The current scope of interactive conversational agents available for smoking cessation was previously reported in a scoping review [
51], although an update was needed given the rapid development of chatbot technologies in recent years. A systematic review of chatbots for smoking cessation was also published during our review [
25], but this review did not include vaping. Like He et al. in their review [
25], we found some support for the use of chatbots for smoking cessation. Our review found that compared to other smoking cessation methods, chatbots can lead to increased willingness to quit smoking and vaping, better engagement in treatment, and eventually higher sustained abstinence rates and improved quality of life. Our review also found that chatbots may be perceived as empathetic and may establish an appropriate therapeutic alliance due to their communication skills, which may explain the higher engagement observed. Other systematic reviews of digital health interventions for smoking cessation have reported that participants were generally satisfied with the use of internet-based interventions [
42,
44]. However, given the small number of included studies and the heterogeneity of outcome measures, it is important to update this review as new studies become available.
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
Neither the previous scoping review [
51] nor the systematic review [
25] included studies on electronic cigarette vaping, which, like smoking, is a growing public health threat [
5,
6]. We considered it relevant to include both smoking and vaping behaviors in our review, given their similarities in terms of potential health effects and intervention design. Therefore, our review included an examination of the effectiveness of chatbots in reducing vaping, which is a strength that makes our study original. However, it also highlights a lack of knowledge about the effectiveness and feasibility of this technology in the context of vaping, and whether the effects differ from those of smoking cessation. One of the strengths of this review is that it only considered interventions that used interactive conversational agents that can adapt to the individual, rather than static conversational agents that use a predefined set of questions and answers.
This systematic review has certain limitations. First, the small number of studies found and the variability in their designs and outcome measures limit the ability to make a quantitative synthesis of the reported effects. Unlike the review by He et al. [
25], our review considered interactive chatbots, which is why the number of studies included in our review (n=8) is lower than theirs (n=13). The fact that there is only one study targeting vaping cessation is another limitation of our review. However, given the similarities and nature of interventions targeting smoking and vaping cessation, it is likely that most of the findings could apply to both smoking and vaping. As e-cigarette vaping is now considered an important public health issue, it is likely that more chatbot interventions for vaping cessation will be implemented, and their results should be incorporated into an update of this review.
5. Conclusions
This systematic mixed methods review provides an overview of interactive conversational agents for smoking and vaping cessation. This knowledge could be useful for the development of interactive conversational agents better suited to the context of smoking and vaping cessation. While the number of cigarette smokers remains stable worldwide, the growing popularity of vaping among young people may have serious public health implications. Alternative intervention tools for younger generations, such as chatbots, may provide public health professionals with an additional means of reaching them. It is important to continue research on this topic and provide up-to-date evidence to inform policymakers and researchers about the effectiveness and success predictors of interactive conversational agents in smoking and e-cigarette vaping cessation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L., M.S. and M-P.G.; methodology, A.L., A.Y. and F.B.; formal analysis, A.L., SMARD., A.Y., J.P., FN, and FY.; writing—original draft preparation, A.L., SMARD., A.Y., J.P., A.D., MPG; writing—review and editing, All authors; supervision, MPG; project administration, A.L.; funding acquisition, M-P.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was funded by a Research Development Grant from the Faculty of Nursing Sciences, Université Laval.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A. Database Search Strategy
Medline (OVID)
Date of the search: 21-07-2022
Database limit: limit results to publications date between 2021-07-23 to 2022-07-21
| # |
Search strategy |
Results |
| 1 |
(“chat bot?” or chatterbot? or chatbot? or medbot? or “chatter bot?” or smart bot? or smartbot?).ti,ab,kw |
526 |
| 2 |
(Conversational adj2 (host or coach or avatar or advisor or assistant or interface or avatar or agent? or system or computer or humanoid or character or bot? or AI)).ti,ab |
355 |
| 3 |
((virtual or intelligent or chat or computer or AI or “artificial intelligence” or relational or embodied) adj2 agent?).ti,ab |
938 |
| 4 |
1 or 2 or 3 |
1582 |
| 5 |
exp Smoking/ OR Tobacco Use Disorder/ OR exp “Tobacco Use Disorder”/ OR Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems/ OR Smoking Cessation/ OR “Tobacco Use Cessation”/ |
181214 |
| 6 |
(Smoking OR Smoker? OR Tobacco OR Nicotine OR Cigarette? OR Vape* OR Vaping? OR Ecigarette? OR ECig OR “E-Cig”).ti,ab,kw,kf |
384819 |
| 7 |
5 OR 6 |
419866 |
| 8 |
4 AND 7 |
18 |
| 9 |
limit 8 to ed=20210723-20220721 |
3 |
Embase (Embase.com)
Date of the search: 21-07-2022
Database limit: limit results to publications date between 2021-07-23 to 2022-07-21
| # |
Search strategy |
Results |
| 1 |
(“chat bot$” OR chatterbot$ OR chatbot$ OR medbot$ OR “chatter bot$” OR “smart bot$” OR smartbot$):ti,ab,kw |
507 |
| 2 |
(Conversational NEAR/2 (host OR coach OR avatar OR advisor OR assistant OR interface OR avatar OR agent$ OR system OR computer OR humanoid OR character OR bot$ OR AI)):ti,ab |
324 |
| 3 |
((virtual OR intelligent OR chat OR computer OR AI OR “artificial intelligence” OR relational OR embodied) NEAR/2 agent$):ti,ab |
964 |
| 4 |
#1 OR #2 OR #3 |
1,612 |
| 5 |
‘smoking’/exp OR ‘tobacco dependence’/de OR ‘tobacco use’/exp OR ‘smoking cessation’/de OR ‘electronic cigarette’/de |
499,263 |
| 6 |
(Smoking OR Smoker$ OR Tobacco OR Nicotine OR Cigarette$ OR Vape* OR Vaping$ OR Ecigarette$ OR ECig OR “E-Cig”):ti,ab,kw |
549,408 |
| 7 |
#5 OR #6 |
670,935 |
| 8 |
#4 AND #7 |
24 |
| 9 |
#8 AND [23-07-2021]/sd |
9 |
CINAHL
Date of the search: 21-07-2022
Database limit: limit results to publications date between 2021-07-23 to 2022-07-21
| # |
Search strategy |
Results |
| 1 |
TI (“chat bot?” OR chatterbot? OR chatbot? OR medbot? OR “chatter bot?” OR smart bot? OR smartbot?) OR AB (“chat bot?” OR chatterbot? OR chatbot? OR medbot? OR “chatter bot?” OR smart bot? OR smartbot?) |
281 |
| 2 |
TI (Conversational N2 (host OR coach OR avatar OR advisor OR assistant OR interface OR avatar OR agent? OR system OR computer OR humanoid OR character OR bot? OR AI)) OR AB (Conversational N2 (host OR coach OR avatar OR advisor OR assistant OR interface OR avatar OR agent? OR system OR computer OR humanoid OR character OR bot? OR AI)) |
188 |
| 3 |
TI ((virtual OR intelligent OR chat OR computer OR AI OR “artificial intelligence” OR relational OR embodied) N2 agent?) OR AB ((virtual OR intelligent OR chat OR computer OR AI OR “artificial intelligence” OR relational OR embodied) N2 agent?) |
300 |
| 4 |
S1 OR S2 OR S3 |
658 |
| 5 |
MH “Smoking+” OR MH “Electronic Cigarettes” |
78,928 |
| 6 |
TI (Smoking OR Smoker# OR Tobacco OR Nicotine OR Cigarette# OR Vape* OR Vaping# OR Ecigarette# OR ECig OR “E-Cig”) OR AB (Smoking OR Smoker# OR Tobacco OR Nicotine OR Cigarette# OR Vape* OR Vaping# OR Ecigarette# OR ECig OR “E-Cig”) |
122,238 |
| 7 |
S5 OR S6 |
142,303 |
| 8 |
S4 AND S7 |
7 |
| 9 |
S8 AND DT 20210723-20220721 |
1 |
Web of Science
Date of the search: 21-07-2022
Database limit: limit results to publications date between 2021-07-23 to 2022-07-21
| # |
Search strategy |
Results |
| 1 |
TS=(“chat bot$” OR chatterbot$ OR chatbot$ OR medbot$ OR “chatter bot$” OR smart bot$ OR smartbot$) |
40,548 |
| 2 |
TS=(Conversational NEAR/2 (host OR coach OR avatar OR advisor OR assistant OR interface OR avatar OR agent$ OR system OR computer OR humanoid OR character OR bot$ OR AI)) |
3,878 |
| 3 |
TS=((virtual OR intelligent OR chat OR computer OR AI OR “artificial intelligence” OR relational OR embodied) NEAR/2 agent$) |
16,274 |
| 4 |
#1 OR #2 OR #3 |
58,623 |
| 5 |
TS=(Smoking OR Smoker$ OR Tobacco OR Nicotine OR Cigarette$ OR Vape* OR Vaping$ OR Ecigarette$ OR ECig OR “E-Cig”) |
526,665 |
| 6 |
#4 AND #5 |
130 |
| 7 |
Database publications date limit from 2021-07-23 to 2022-07-21 |
22 |
Inspec (Engineering Village)
Date of the search: 21-07-2022
Database limit: limit results to publications date between 2021-07-23 to 2022-07-21
| # |
Search strategy |
Results |
| 1 |
chatbots WN CV |
555 |
| 2 |
“chat bot*” WN TI OR chatterbot* WN TI OR chatbot* WN TI OR medbot* WN TI OR “chatter bot*” WN TI OR smart bot* WN TI OR smartbot* WN TI OR “chat bot*” WN AU OR chatterbot* WN AU OR chatbot* WN AU OR medbot* WN AU OR “chatter bot*” WN AU OR smart bot* WN AU OR smartbot* WN AU |
1,306 |
| 3 |
(Conversational NEAR/2 host) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 coach) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 avatar) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 advisor) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 assistant) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 interface) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 avatar) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 agent*) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 system) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 computer) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 humanoid) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 character) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 bot*) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 AI) WN TI OR (Conversational NEAR/2 host) WN AU OR (Conversational NEAR/2 coach) WN AU OR (Conversational NEAR/2 avatar) WN AU OR (Conversational NEAR/2 advisor) WN AU OR (Conversational NEAR/2 assistant) WN AU OR (Conversational NEAR/2 interface) WN AU OR (Conversational NEAR/2 avatar) WN AU OR (Conversational NEAR/2 agent*) WN AU OR (Conversational NEAR/2 system) WN AU OR (Conversational NEAR/2 computer) WN AU OR (Conversational NEAR/2 humanoid) WN AU OR (Conversational NEAR/2 character) WN AU OR (Conversational NEAR/2 bot*) WN AU OR (Conversational NEAR/2 AI) WN AU |
1,065 |
| 4 |
(virtual NEAR/2 agent) WN TI OR (intelligent NEAR/2 agent) WN TI OR (chat NEAR/2 agent) WN TI OR (computer NEAR/2 agent) WN TI OR (AI NEAR/2 agent) WN TI OR (“artificial intelligence” NEAR/2 agent) WN TI OR (relational NEAR/2 agent) WN TI OR (embodied NEAR/2 agent) WN TI OR (virtual NEAR/2 agent) WN AU OR (intelligent NEAR/2 agent) WN AU OR (chat NEAR/2 agent) WN AU OR (computer NEAR/2 agent) WN AU OR (AI NEAR/2 agent) WN AU OR (“artificial intelligence” NEAR/2 agent) WN AU OR (relational NEAR/2 agent) WN AU OR (embodied NEAR/2 agent) WN AU |
2,075 |
| 5 |
#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 |
4,505 |
| 6 |
Tobacco WN CV OR Nicotine WN CV |
4,392 |
| 7 |
Smoking WN TI OR Smoker* WN TI OR Tobacco WN TI OR Nicotine WN TI OR Cigarette* WN TI OR Vape* WN TI OR Vaping* WN TI OR Ecigarette* WN TI OR ECig WN TI OR “E-Cig” WN TI OR Smoking WN AB OR Smoker* WN AB OR Tobacco WN AB OR Nicotine WN AB OR Cigarette* WN AB OR Vape* WN AB OR Vaping* WN AB OR Ecigarette* WN AB OR ECig WN AB OR “E-Cig” WN AB |
11,204 |
| 8 |
#6 OR #7 |
11,433 |
| 9 |
#5 AND #8 |
3 |
| 10 |
Database publications years limit from 2021 to 2022 |
0 |
References
- Global Burden of Disease (database). Washington, DC: Institute of Health Metrics; 2019. IHME, accessed 17 July 2024.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health. How Tobacco Smoke Causes Disease: The Biology and Behavioral Basis for Smoking-Attributable Disease: A Report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2010. https://scholar-google-com.acces.bibl.ulaval.ca/scholar_lookup?title=How+Tobacco+Smoke+Causes+Disease:+The+Biology+and+Behavioral+Basis+for+Smoking-Attributable+Disease:+A+Report+of+the+Surgeon+General&publication_year=2010&.
- United States Public Health Service, Office of the Surgeon General, Office on Smoking and Health. The Health Consequences of Smoking: A Report of the Surgeon General. Rockville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service; 2004. https://scholar-google-com.acces.bibl.ulaval.ca/scholar_lookup?title=The+Health+Consequences+of+Smoking:+A+Report+of+the+Surgeon+General&publication_year=2004&.
- Tammemägi, M. C., Berg, C. D., Riley, T. L., Cunningham, C. R., & Taylor, K. L. (2014). Impact of lung cancer screening results on smoking cessation. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 106(6), dju084. [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, H., Rajabi, A., Ghelichi- Ghojogh, M. et al. (2022). The prevalence of electronic cigarettes vaping globally: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Public Health 2022. 80, 240 . [CrossRef]
- Fadus, M. C., Smith, T. T., & Squeglia, L. M. (2019). The rise of e-cigarettes, pod mod devices, and JUUL among youth: Factors influencing use, health implications, and downstream effects. Drug and alcohol dependence, 201, 85–93. [CrossRef]
- Jerzyński, T., Stimson. G. V. (2023). Estimation of the global number of vapers: 82 million worldwide in 2021. Drugs Habits Soc Policy;24(2):91-103. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. World Health Organization. 2024. Tobacco and nicotine industry tactics addict youth for life. Disponible sur: https://www.who.int/news/item/23-05-2024-tobacco-and-nicotine-industry-tactics-addict-youth-for-life.
- Stephan, Y., Sutin, A. R., Luchetti, M., Caille, P., & Terracciano, A. (2019). Cigarette smoking and personality change across adulthood: Findings from five longitudinal samples. Journal of Research in Personality, 81, 187-194. [CrossRef]
- US Department of Health and Human Services. (2016). E-cigarette use among youth and young adults: A report of the Surgeon General.
- Goriounova, N. A., & Mansvelder, H. D. (2012). Short-and long-term consequences of nicotine exposure during adoles-cence for prefrontal cortex neuronal network function. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine, 2(12), a012120.
- Bonilla, A., Blair, A. J., Alamro, S. M., Ward, R. A., Feldman, M. B., Dutko, R. A., ... & Vyas, J. M. (2019). Recurrent spontaneous pneumothoraces and vaping in an 18-year-old man: a case report and review of the literature. Journal of Medical Case Reports, 13(1), 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2022). What Does Vaping Do to Your Lungs? Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/what-does-vapingdo-to-your-lungs.
- Canadian Cancer Society. (2020). Risk factors for lung cancer. Retrieved 2022, from https://cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-types/lung/risks#:~:text=About%2072%25%20of%20lung%20cancer,and%20have%20other%20risk%20factors.
- Alami H, Fortin JP, Gagnon MP, Lamothe L, Ghandour EK, Ag Ahmed MA, Roy D. Cadre stratégique pour soutenir l’évaluation des projets complexes et innovants en santé numérique. Sante Publique. 2020;32(2):221-228. French. PMID: 35724215. [CrossRef]
- Berg, C. J., Romm, K. F., Patterson, B., Wysota, C., & Abroms, L. C. (2021). Appeal of novel cessation intervention ap-proaches among young-adult users of traditional and alternative tobacco products. Tobacco use insights, 14, 1179173X211041123. [CrossRef]
- Graham, A. L., Amato, M. S., Cha, S., Jacobs, M. A., Bottcher, M. M., & Papandonatos, G. D. (2021). Effectiveness of a Vaping Cessation Text Message Program Among Young Adult e-Cigarette Users: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA in-ternal medicine. [CrossRef]
- Denecke K, Tschanz M, Dorner TL, May R. (2019). Intelligent conversational agents in healthcare: hype or hope? Stud Health Technol Inform;259:77-84. (Medline: 30923277). [CrossRef]
- Montenegro JLZ, da Costa CA, da Rosa Righi R. Survey of conversational agents in health. Expert Syst Appl 2019 Sep;129:56-67. [CrossRef]
- Tudor Car L, Dhinagaran DA, Kyaw BM, Kowatsch T, Joty S, Theng Y, et al. Conversational agents in health care: scoping review and conceptual analysis. J Med Internet Res 2020 Aug 07;22(8):e17158 (FREE Full text) (Medline: 32763886). [CrossRef]
- Gabarron E, Larbi D, Denecke K, Årsand E. What do we know about the use of chatbots for public health? Stud Health Technol Inform 2020 Jun 16;270:796-800. (Medline: 32570492). [CrossRef]
- Parmar P, Ryu J, Pandya S, Sedoc J, Agarwal S. Health-focused conversational agents in person-centered care: a review of apps. NPJ Digit Med 2022 Feb 17;5(1):21 (FREE Full text) (Medline: 35177772). [CrossRef]
- Oh KJ, Lee D, Ko B, Choi HJ. A chatbot for psychiatric counseling in mental healthcare service based on emotional dialogue analysis and sentence generation. 2017 Presented at: 8th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management (MDM); May 29 - Jun 1; Daejeon, Korea p. 371-375 URL: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7962482. [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic M, Baez M, Casati F. Chatbots as conversational healthcare services. IEEE Internet Comput 2021 May;25(3):44-51 (FREE Full text). [CrossRef]
- He, L., Balaji, D., Wiers, R. W., Antheunis, M. L., & Krahmer, E. (2022). Effectiveness and acceptability of conversational agents for smoking cessation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nicotine & tobacco research : official journal of the Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco, ntac281. Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
- Sasseville, M., Barony Sanchez, R. H., Yameogo, A. R., Bergeron-Drolet, L. A., Bergeron, F., & Gagnon, M. P. (2022). Interactive Conversational Agents for Health Promotion, Prevention, and Care: Protocol for a Mixed Methods Systematic Scoping Review. JMIR research protocols, 11(10), e40265. [CrossRef]
- Lachance, A., Yameogo, A. R., Plaisimond, J., Da, S., Bergeron, F., Sasseville, M., & Gagnon, M. (2023, February 10). Interactive conversational agents for cigarette smoking and vaping cessation: A protocol for a mixed-methods systematic scoping review. [CrossRef]
- Stern C, Lizarondo L, Carrier J, Godfrey C, Rieger K, Salmond S, et al. (2021). Methodological guidance for the conduct of mixed methods systematic reviews. JBI Evid Implement, 19(2), 120-129. [CrossRef]
- Selçuk AA. A guide for systematic reviews: PRISMA. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2019 Mar 10;57(1):57-58 (FREE Full text) (Medline: 31049257)2021;19(2):120-9. [CrossRef]
- Covidence. Veritas Health Innovation. URL: https://www.covidence.org/ (accessed 2022-10-03).
- Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021 Mar 29;372:n71 (FREE Full text) (Medline: 33782057). [CrossRef]
- Pluye P, Robert E, Cargo M, Bartlett G, O’Cathain A, Griffiths F, et al. Proposal: A Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool for systematic mixed studies reviews 2011. Available at http://mixedmethodsappraisaltoolpublic.pbworks.com. Accessed No-vember 15, 2013.
- Hong, Q. N., Pluye, P., Fàbregues, S., Bartlett, G., Boardman, F., Cargo, M., Dagenais, P., Gagnon, M. P., Griffiths, F., Nicolau, B., O’Cathain, A., Rousseau, M. C., & Vedel, I. (2019). Improving the content validity of the mixed methods ap-praisal tool: a modified e-Delphi study. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 111, 49–59.e1. [CrossRef]
- Abdullah AS, Gaehde S, Bickmore T. A Tablet Based Embodied Conversational Agent to Promote Smoking Cessation among Veterans: A Feasibility Study. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 31 déc 2018;8(3-4):225-30. [CrossRef]
- Alphonse A, Stewart K, Brown J, Perski O. Exploring Users’ Experiences With a Quick-Response Chatbot Within a Popular Smoking Cessation Smartphone App: Semistructured Interview Study. JMIR Form Res. 7 juill 2022;6(7):e36869. [CrossRef]
- Brown A, Kumar AT, Melamed O, Ahmed I, Wang YH, Deza A, et al. A Motivational Interviewing Chatbot With Generative Reflections for Increasing Readiness to Quit Smoking: Iterative Development Study. JMIR Ment Health. 17 oct 2023;10(1):e49132. [CrossRef]
- Haug S, Boumparis N, Wenger A, Schaub MP, Paz Castro R. Efficacy of a Mobile App-Based Coaching Program for Addiction Prevention among Apprentices: A Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. janv 2022;19(23):15730. [CrossRef]
- He L, Basar E, Wiers RW, Antheunis ML, Krahmer E. Can chatbots help to motivate smoking cessation? A study on the effectiveness of motivational interviewing on engagement and therapeutic alliance. BMC Public Health. déc 2022;22(1):1-14. [CrossRef]
- Leeuwis L, He L. Hi, I’m Cecil(y) the Smoking Cessation Chatbot: The Effectiveness of Motivational Interviewing and Confrontational Counseling Chatbots and the Moderating Role of the Need for Autonomy and Self-efficacy. In: Følstad A, Araujo T, Papadopoulos S, Law ELC, Luger E, Goodwin M, et al., éditeurs. Chatbot Research and Design. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2023. p. 3-17. [CrossRef]
- Olano-Espinosa E, Avila-Tomas JF, Minue-Lorenzo C, Matilla-Pardo B, Serrano MES, Martinez-Suberviola FJ, et al. Effectiveness of a Conversational Chatbot (Dejal@bot) for the Adult Population to Quit Smoking: Pragmatic, Multicenter, Controlled, Randomized Clinical Trial in Primary Care. JMIR MHealth UHealth. 27 juin 2022;10(6):e34273. [CrossRef]
- Perski O, Crane D, Beard E, Brown J. Does the addition of a supportive chatbot promote user engagement with a smoking cessation app? An experimental study. Digit Health. janv 2019;5:2055207619880676. [CrossRef]
- Do, H. P., Tran, B. X., Le Pham, Q., Nguyen, L. H., Tran, T. T., Latkin, C. A., Dunne, M. P., & Baker, P. R. (2018). Which eHealth interventions are most effective for smoking cessation? A systematic review. Patient preference and adherence, 12, 2065–2084. [CrossRef]
- Stead, L. F., Koilpillai, P., Fanshawe, T. R., & Lancaster, T. (2016). Combined pharmacotherapy and behavioural inter-ventions for smoking cessation. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, 3(3), CD008286. [CrossRef]
- Lindson-Hawley N, Thompson TP, Begh R. Motivational interviewing for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015(3). [CrossRef]
- Gwaltney CJ, Metrik J, Kahler CW, Shiffman S. Self-Efficacy and Smoking Cessation: A Meta-Analysis. Psychol Addict Behav J Soc Psychol Addict Behav [Internet]. mars 2009 [cité 19 sept 2024];23(1). Disponible sur: https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.acces.bibl.ulaval.ca/pmc/articles/PMC3829471/. [CrossRef]
- Von Ah D, Ebert S, Ngamvitroj A, Park N, Kang DH. Factors Related to Cigarette Smoking Initiation and Use among College Students. Tob Induc Dis. 15 déc 2005;3(1):27. [CrossRef]
- Graham AL, Amato MS, Cha S, Jacobs MA, Bottcher MM, Papandonatos GD. Effectiveness of a Vaping Cessation Text Message Program Among Young Adult e-Cigarette Users: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med. 1 juill 2021;181(7):923. [CrossRef]
- Graham AL, Cha S, Jacobs MA, Amato MS, Funsten AL, Edwards G, et al. A Vaping Cessation Text Message Program for Adolescent E-Cigarette Users: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 3 sept 2024;332(9):713-21. [CrossRef]
- Smit ES, Hoving C, Schelleman-Offermans K, West R, de Vries H. Predictors of successful and unsuccessful quit attempts among smokers motivated to quit. Addict Behav. sept 2014;39(9):1318-24. [CrossRef]
- Bendotti H, Lawler S, Ireland D, Gartner C, Marshall HM. Co-Designing a Smoking Cessation Chatbot: Focus Group Study of End Users and Smoking Cessation Professionals. JMIR Hum Factors. 19 août 2024;11(1):e56505. [CrossRef]
- Leung, T., Arnold, V., Reinfelde, M., Perski, O., Cummins, K., Whittaker, R., Dobson, R., & Garner, K. (2022). Chatbots for smoking cessation: scoping review. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 24(9). [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).