1. Introduction
Fluoride is one of the most common causes of natural groundwater contamination worldwide. This is dangerous to the health of the population of different countries, for example Sweden [
1], India [
2], Kenya [
3], China [
4]. Geogenic sources are a common mechanism that determines high concentrations of F
- ions in groundwater. Geogenic sources mean the following phenomena: long residence times facilitating the processes of interaction of water with rock; evaporation; change in hydrogeochemical type during water movement (from Ca-HCO
3 type to Na-HCO
3 type); weathering or dissolution of fluorine-containing minerals; geological setting, in other words, the presence of crystalline basement rocks in wells or salt-rich geological formations; sorption and ion exchange processes. The chemical composition of groundwater is characterized by high concentrations of HCO
3- and Na
+. And alkaline pH plays the most important role in the supply of fluoride to groundwater [
1,
3]. Fluoride concentrations vary depending on the type of rock through which the water flows, but typically do not exceed 10 mg/L; the highest natural level known in the literature is 2800 mg/l [
5]. Drinking water with elevated fluoride concentrations greater than 1.5 mg/L, according to WHO recommendations, can lead to health problems, such as dental or skeletal fluorosis or even hypocalcemia due to CaF
2 precipitation in the human body [
3].
Previously, we have studied how the chemical composition of the rocks of the Lovozero Massif influences changes in the chemical composition of natural waters. Natural waters are formed within the Lovozero massif and its nearest northern frame. The rock composition of the catchment area and anthropogenic influence were also important factors in the study. The research methods were modern precision analysis methods (inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP MS), etc.) and physicochemical modeling, namely the Selector software package (SP). Chemical analyzes of water (sampling was carried out in the fall of 2020) and the results of modeling the “water-rock-atmosphere” interaction showed that the concentrations of calcium, sodium, magnesium, bicarbonates, fluorine, chromium, cobalt, vanadium, lanthanum, cerium, zirconium, barium and pH values are comparable. The results of the study made us think about the need to take special control of water coming from flooded mines. An increase in the degree of interaction of water with the rock promotes the transition of fluorine, sulfur and chlorine into solution. This can increase the rate of dissolution of minerals in the rocks of the massif and the transition of rare elements into solution. Rare elements in living organisms regulate biological processes, and their impact on human health is not yet fully understood [
6].
The goal of the study was to assess how fluorine affects changes in the chemical composition of natural and waste waters in the Lovozero region. The research tools were modern precision analysis methods (ICP-MS, etc.) and physicochemical modeling using the Selector SP.
2. Objects and Methods
2.1. Objects of Research
The study of the mineralogy of the Lovozero and Khibiny massifs brought the following conclusions [
7]:
- the mineralogical relationship of ultra-agpaitic derivatives of the two massifs is clearly manifested, despite the sharp difference in mineragenic specialization: phosphate for Khibiny and rare metal for Lovozero;
- the rocks of the massifs are oversaturated with alkaline, “volatile” and rare elements. The rocks differ from other types of nepheline-syenite derivatives in the abundance of minerals. The latter are soluble in water (sodium salts of carbonic, silicic, phosphoric and hydrofluoric acids) and easily change under atmospheric conditions. The rocks are also characterized by an extraordinary variety of minerals extremely enriched in sodium and other strong bases (alkali metals);
- the second characteristic group consists of low-resistant ultra-alkaline titano-, niob- and zirconosilicates;
- wide distribution of williomite (NaF) and ussingite rocks, an increased role of Sr, REE, Zr, Nb is characteristic of the Lovozero Massif, mineralization is widespread;
- the Khibiny massif is characterized by a wide development of minerals of the soda group and other carbonates, the role of minerals K, Ba, Ti is increased, mineralization is realized along the central arc in a limited area.
The high content of “volatile” elements (Cl, F, S, SO
3, CO
2, H
2O) is a feature of the chemical composition of the Lovozero massif. This contributed to a slower solidification of the magma and its better differentiation and the formation of minerals containing these compounds [
8]. Chlorine-free shairerite - kogarkoite was discovered in one of the pegmatites of Mount Alluive. SO
42- is present in its composition. The mineral dissolves easily in water. Chemical formula: Na
21(SO
4)
7ClF
6 [
9]. Mount Alluive is one of the highest and fewest “thousanders” of this massif, its height is 1050.9 meters. The Shomiyok River originates from the northern slope of the mountain (flows into Lake Sikir), and the River Raslaka originates from the northeastern slope of the mountain Raslaka (flows into the River Sergevan’, Lake Lovozero). A few kilometers north is the village Revda. In addition, at the source of the river Raslaka, on the northern slope of Mount Alluaiv, was once the site of the village of Alluaiv (1940). It was the base of the first builders and geologists of Lovozero mining and processing plant (until 1948, “Alluaivstroy”). Later, on an industrial site adjacent to Lake Ilma, a small settlement of Ilma was built by a geological exploration party (from 1940 to 1970).
Mining was carried out on the slopes of Mount Alluive in the past. Abandoned adits testify to this. A large number of minerals, including the mineral alluaivite (titanium silicate), are contained in the depths of the mountain. The mineral alluaivite was found here in 1990. A.P. Khomyakov [
7] studied pegmatites directly in mine workings on Mount Alluive. Pegmatites are as follows:
1) relatively thin (up to 5-10, less often 20 cm) bodies of potassium feldspathic composition with sodalite, nepheline, sometimes analcime, cancrinite, ussingite (Na2AlSi3O8OH), eudialyte, catapteilite, zircon, lamprophyte, lorenzinite, and in places abundant allocations of salt minerals - villiomit (NaF), kogarkoite (Na3FSO4), cryolite (Na3AlF6), thermonatrite (Na2CO3∙H2O), nahcolite (NaHCO3) or trona (NaH(CO3)2∙2H2O) and many other minerals;
2) more powerful (up to 0.5-0.8 m) ussingite bodies with potassium feldspar, nepheline, sodalite, cancrinite, aegirine and a set of other minerals, including kogarkoite, williomite, halite (NaCl), sodium, trona, thermonatrium and a number of others [
7].
As is known, soda solution dissolves silica silicates and aluminosilicates well [
10,
11].
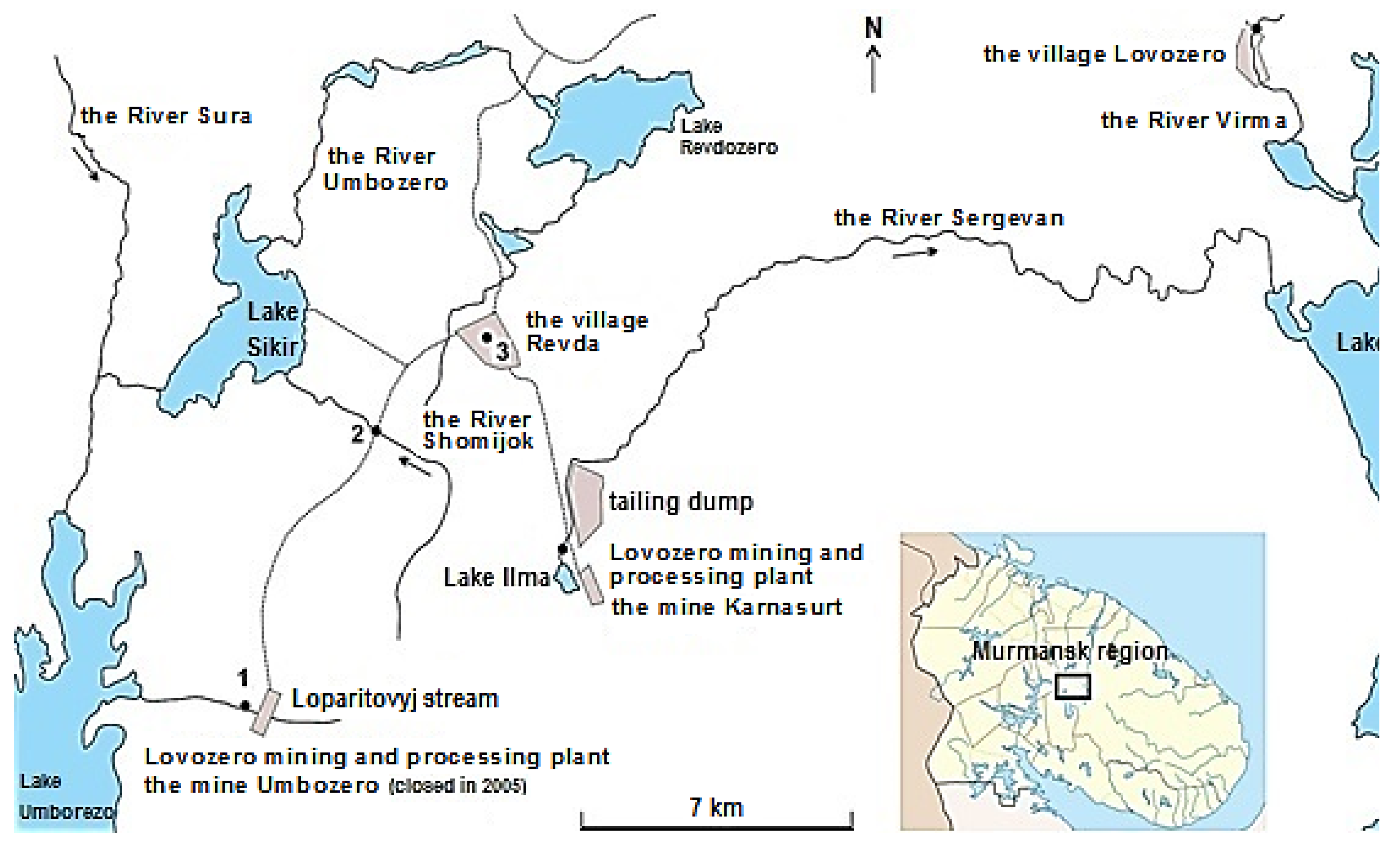
Water rushed through the mouth of the shaft of the Umbozero mine (
Figure 1) due to the fact that it stopped pumping out in 2009. Mine waters filled the lower horizons of the mine and came to the surface through transport passages. Water began to flow into Lake Umbozero. The most unique geological monuments known to all geologists in the world – the pegmatite body “Shkatulka” (
Figure 1), the pegmatite vein “Sirenevaya”, the unique body “Shomiokitovoe” [
12] – remained flooded deep inside Mount Alluive.
The relevance of the scientific task is justified by the following medical indicators: Kirovsk, Apatity and Lovozero district stand out among the cities and districts of the Murmansk region in diseases of the musculoskeletal system and urolithiasis. The peculiarity of these areas is that their population uses water that forms within large alkaline massifs: Khibiny and Lovozero. These massifs contain strontium, barium, trace and rare earth elements (REE), uranium, thorium and fluorine [
13]. 70 % of the small peoples of the North (of their total number in the Murmansk region) live in the Lovozero region. 4 drinking water supply pipelines are in operation in the area. They take water from surface water sources (2 communal and 2 departmental). Lovozero mining and processing plant (the River Sergevan’ and Lake Lovozero) and springs, drinking sources of the population, are located on the drainage areas of water bodies of the study area.
Samples of water from streams flowing from Mount Alluayv (the River Shomijok flows into Lake Sikir, which is a water intake for the village Revda; the Stream Loparitovyj flows into Lake Umbozero), as well as surface and groundwater (
Figure 2) were taken in 2021 during expeditionary works. The drainage area was limited from the south by a sublatitudinal watershed. It passed through several heights. All watercourses (the River Raslaka, the River Ilmayok, the River Kromka, the River Yagelny and streams of various ranks from this watershed) flow to the north and flow into the River Sergevan’. This river flows in a latitudinal direction and flows into Lake Lovozero (the exception is The River Shomijok which flows into Lake Sikir; The Stream Loparitovyj is also an exception. It flows into Lake Umbozero). The chemical composition of the waters of streams and springs (including the Spring “Parkovyj”, the village Revda) was studied.
As stated above, the Lovozero and Khibiny massifs represent a nepheline-syenite formation. And a comparison of their average compositions indicates a high concentration in the Lovozero Massif of such elements as zirconium (0.88 %), uranium (0.0015 %), lanthanum (0.0155 %), cerium (0.0318 %) and other rare earth elements [
8,
14].
2.2. Methods of Analysis
Analysis of water samples included the determination of pH, Eh, alkalinity, NH
4+ and anion composition (Cl
-, SO
42-, NO
3-, F
-, HCO
3-) by titrimetry and potentiometry methods (liquid analyzer Expert-001, Russia; ionomer I-160 MI, Russia). Elemental analysis was carried out by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ELAN 9000 DRC-e, Perkin Elmer, USA). To calibrate the device, multielement solutions IV-STOK-21, -26, -28, -29 (Inorganic Ventures, USA) were used. The accuracy of the analysis was controlled using standard samples CRM-TMDW-A, CWW-TM-A (High-purity Standards, USA) and STOK-16, STOK-10 (Inorganic Ventures, USA). Thermodynamic modeling was performed using the Selektor software package (version 3.01). The Selektor software package was developed at A.P. Vinogradov Institute of Geochemistry of the Siberian Branch of the RAS (Irkutsk, Russia). The software package implements the Gibbs energy minimization method based on the convex programming approach [
15,
16]. The Selektor has built-in thermodynamic databases [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23].
We have developed a physicochemical model (PCM) of the “water–rock” interaction. It is adapted to the conditions of the Murmansk region and helps to assess the environmental situation when the factor of natural or anthropogenic influence is relevant. PCM includes 42 independent components (Al, B, Br, Ar, He, Ne, C, Ca, Cl, F, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, N, Na, P, S, Si, Sr, Cu, Zn , Ni, Pb, V, Ba, U, Ag, Au, Co, Cr, Hg, As, Cd, Mo, Se, La, Ce, Zr, H, O, ē), 1062 dependent components, including aqueous solution (435), in the gas phase (76), liquid hydrocarbons (111), solid phases, organic and mineral substances (440). The set of solid phases of the multisystem is formed taking into account the mineral composition of the rocks of the Baltic Shield.
The set of solid phases of the multisystem is formed taking into account the mineral composition of the rocks of the Baltic Shield. According to ideas [
16], weathering is determined, on the one hand, by the physical and chemical state of water (temperature, pH, Eh, composition of dissolved gases), on the other hand, by the composition of rocks. In this case, the irreversible evolution of the multisystem (a computer analogue of a real system), its characteristics (pH, Eh), and the composition of the newly formed phases will be entirely controlled by independent thermodynamic factors of the state: temperature, total pressure and the magnitude of the vector of molar quantities of independent components (chemical composition of the system). The latter are a function of the independent coordinate of the entire nonequilibrium process, namely the parameter ξ. The number of moles of the solid phase v participating in the interaction, or the degree of interaction, i.e., the amount of rock that reacted simulates the rate of chemical processes. The number of moles varied from 1 to -0.25. Dependencies are presented on a logarithmic scale in the tables: ν = 10
-ξ or -lg ν = ξ.
The systems “water – rock – atmosphere” and “water – atmosphere”, where water is precipitation, rock is 100 g of rock from the Lovozero massif of average composition, are considered in the model for calculating equilibrium. Composition of 1 kg of atmosphere, mol: Ar 0.3209, C 0.01036, N 53.9478, Ne 0.000616, O 14.48472. The boundary conditions of the model were the composition of the rock, the amount of water (1000 kg), 100 kg of atmosphere. The temperature of 5°C was chosen as the average, this is the temperature of May and the autumn months (September, October). The snow cover disappears at this time, in the spring, and in the fall, in October, a new one forms. The temperature when performing chemical analyzes is +20°C.
3. Results and Discussion
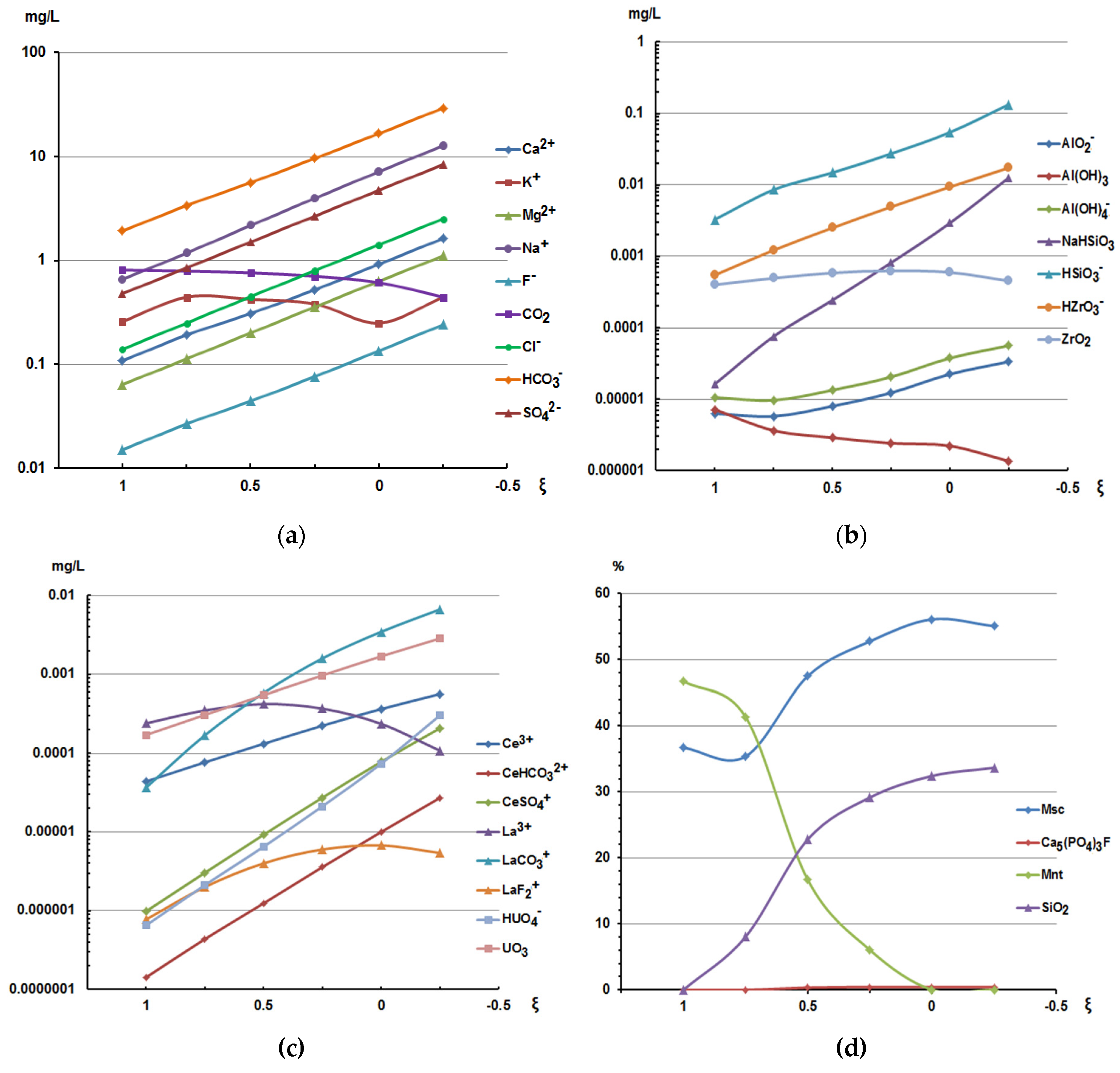
The results of a comprehensive study, the chemical compositions of the River Shomijok and the Stream Loparitovyj coming from different slopes of Mount Alluive, their computer analogues, and calculations of the “water-rock” interaction are presented in
Figure 3a–d and Table 1.3.1.
The results of modeling the interaction “water – rock – atmosphere” showed:
- an increase in the degree of interaction (ξ) “water-rock” increases the concentrations of NaHSiO
3, HSiO
3- and SiO
2 from 2.71 to 3.91 mg/l, the concentrations of these compounds are comparable to the concentrations of these compounds in the waters of the River Shomijok (
Table 1).
- the presence of chromium, cobalt, vanadium, lanthanum, cerium, zirconium and barium in the waters. Their presence was confirmed during expeditionary works in 2020-2021. Their forms of migration are presented in
Table 1 and
Figure 3; - the presence of fluorine, sulfur, and chlorine in the system affects the forms of migration of aluminum, calcium, magnesium, lanthanum, cerium, increasing the mobility of these elements;
- the composition of the newly formed phases of goethite, muscovite (Msc), montmorillonite (Mnt) and amorphous silica corresponds to new formations as a result of weathering of rocks of the Baltic Shield [
6,
24];
- higher pH values and concentrations of Na, Al, Mg, K, Fe, Ba, U, La, Ce, Si, F and bicarbonate were determined in the waters of the Stream Loparitovyj. This entails an increase in the concentrations of HSiO3– and NaHSiO3 (aqueous), CaHSiO3, MgHSiO3, carbonates and bicarbonates of Ca, Mg, La, Ce and fluorides of Na, Ca, Mg, Mn, La and Ce.
Analysis of the modeling results (
Table 1) shows that the silicon concentration increases in solutions containing fluorine and bicarbonate. This increases the concentrations of HSiO
3– and NaHSiO
3 (aqueous), CaHSiO
3, MgHSiO
3, carbonates and bicarbonates of Ca, Mg, La, Ce, fluorides of Na, Ca, Mg, Mn, La and Ce. This proves that F
- and HCO
3- can promote the breaking of silicon bonds in silicates and the release of silicon in solution. Therefore, fluorine and bicarbonate may play a key role in increasing the porosity of host rocks and breccias and in mineral replacement reactions. Taken together, this will enhance the reaction between water and rock.
Analysis of the form of migration of uranium, lanthanum and cerium in the waters of the River Shomijok and the Stream Loparitovyj shows the predominance of the following forms of migration: CeO2H (7,15E-04), CeOH2+ (5,26E-05), CeF2+ (3,30E-05), the Stream Loparitovyj; Ce3+, CeF2+, CeSO4+ (1,33E-05), the River Shomijok; and LaCO3+ (4,30E-04 и 9,40E-05), respectively.
La and Ce were chosen to represent the REE group for the following reasons: 1) the chemical and thermodynamic properties of all REE are similar, they usually have similar geochemical behavior; 2) compared to cerium, lanthanum has the only thermodynamically stable oxidation state, La(III), and cerium can form Ce(III) and Ce(IV). In our case, both of these elements are in the +3 oxidation state, uranium is in the +6 oxidation state - HUO4-, UO3 (the Stream Loparitovyj) and UO3 (the River Shomijok).
The results of a comprehensive study showed a fundamental difference in the chemical composition of natural waters and waters polluted by the waters of the flooded Umbozero mine.
The long stay of water in a flooded mine increases the degree of “water-rock” interaction; the concentrations of F, Cl, SO42-, HCO3- in the solution increase. This affects the mobility of lanthanum, cerium and other elements due to the formation of complex compounds. The relatively high content of fluorine, phosphorus, HCO3- (weak and moderate acids) in the solution promotes the dissolution of metals and silicates, the Si-O bonds are broken, and Si, Al, P are released into the solution.
The obtained information is necessary to evaluate the health risk of the population of the study region.
Table 2 shows the forms of migration of lanthanides and uranium in the waters of the Spring “Parkovyj” which is popular among residents of the village Revda.
Analysis of the results (
Table 2) shows that the concentration of fluorine in the waters of the Spring “Parkovyj” is lower by more than 2 orders of magnitude and the concentrations of uranium, cerium and lanthanum are an order of magnitude lower than in the waters of The Stream Loparitovyj, and the dominant forms of migration are Ce
3+, LaCO
3+ and UO
2.
Many studies have been devoted to the study of possible adverse effects of long-term intake of fluoride in drinking water. These studies clearly show that fluoride primarily affects skeletal tissues (bones and teeth). Low concentrations provide protection against dental caries in both children and adults. However, the authors’ data on the safe concentration of fluoride differ. According to the World Health Organization, the minimum required concentration of fluoride in drinking water is approximately 0.5 mg/l [
5]. Other data suggest that the protective effect of fluoride increases at concentrations of up to approximately 2 mg/l fluoride in drinking water. However, fluoride can also have an adverse effect on tooth enamel and can lead to mild dental fluorosis when the concentration in drinking water is from 0.9 to 1.2 mg/l, the prevalence of the disease is 12-33 % depending on the volume of drinking water consumption and exposure to fluoride from other sources. Drinking water is fluoridated in a number of countries, for example in the United States, but recently medical institutions have begun to identify other pathologies associated with long-term intake of fluoridated water. No less important is the change in the forms of REE and U migration (
Table 2). Their solubility increases with increasing fluorine concentration, and the likelihood of them entering the body of residents living in the surrounding area also increases.
5. Conclusions
Thermodynamic modeling of the weathering processes of the Lovozero Massif within the framework of the “water-rock-atmosphere” system at a temperature of 5°C showed the influence of elements contained in the rocks of the studied massif on the formation of the chemical composition of natural waters. An increase in the degree of “water-rock” interaction increases the concentrations of F, Cl, SО42-, HCO3- in the solution. This affects the mobility of La, Ce and other elements due to the formation of complexes with them. The relatively high content of fluorine, phosphorus, HCO3- in the solution promotes the dissolution of silicates, the Si-O bonds are broken, and the transition of Si, Al, P into the solution occurs. Monitoring of water coming from a flooded mine, where there is an increase in the degree of interaction of water with rock, showed higher pH values and concentrations of Na, Na, HCO3-, F-, P, Al, Si, V, U, La, Ce than in natural waters.
A special feature of the development of the Khibiny and Lovozero tundras is the industrial development of the mining industry. Industrial development meant a high technogenic load on Lake Umbozero, and Lake Umbozero is a fishery reservoir of the highest category. The water environment in the lake is changing not for the better. These changes can provoke the emergence and development of acute environmental situations. Their expression may be a deterioration in the habitat conditions of valuable fish species, especially loved by the local population as food. And this will lead to high rates of environmentally-related diseases among residents of this area.
The information obtained is necessary to evaluate the health risk of the population of the study region. The research results can be used in the fields of geochemistry, hydrology, ecology, and medicine.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M. and S.D.; methodology, S.M. and S.D.; software, S.M.; validation, S.D., S.M. and V.M.; formal analysis, S.D.; investigation, S.D. and V.P.; resources, S.S.; data curation, S.M., S.D. and E.K.; writing—original draft preparation, S.M.; writing—review and editing, S.D.; visualization, S.D.; supervision, V.M.; project administration, V.M.; funding acquisition, V.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Please add: The study was carried out with the financial support of the Russian Science Foundation 24-17-00114 “Evaluation of the chemical state of natural and drinking waters of the Murmansk region, forms of migration, impact on the elemental status of residents”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results
References
- Berger, T.; Mathurin, F.A.; Drake, H.; Astrom, M. Fluoride abundance and controls in fresh groundwater in Quaternary deposits and bedrock fractures in an area with fluorine-rich granitoid rocks. Sci Total Environ. 2016, 569, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanse, A.; Chabukdhara, M.; Gohain Baruah, S.; Boruah, H.; Gupta, S.K. Fluoride contamination in groundwater and associated health risks in Karbi Anglong District, Assam. Northeast India. Environ Monit. Assess. 2019, 12, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusiniak, P.; Sekuła, K.; Sracek, O.; Stopa, P. Fluoride ions in groundwater of the Turkana County, Kenya, East Africa. Acta Geo Chim. 2021, 6, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, X.; Qian, C.; Zhu, G. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment of high fluoride levels in the Yanchi endorheic region northwest. China. Appl Geochem. 2018, 98, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, Environmental Health Criteria. WHO. Geneva. 2017; http://www.who.int.
- Sandimirov, S.S.; Pozhilenko, V.I.; Mazukhina, S.I.; Drogobuzhskaya, S.V.; Shirokaya, A.A.; Tereshchenko, P.S. Chemical Composition of Natural Waters of the Lovozero Massif, Russia. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment. 2022, 8, 4307–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomyakov, A.P. Mineralogy of ultraagpaitic alkaline rocks. Science: Moscow, Russia, 1990; pp.
- Vlasov, K.A.; Kuzmenko, M.V.; Eskova, E.M. Lovozersky alkaline massif (rocks, pegmatites, mineralogy, geochemistry and genesis). Publishing House of the USSR Academy of Sciences: Moscow. 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimovsky, V.I.; Volkov, V.P.; Kogarko, L.N.; Polyakov, A.I.; Saprykina, T.V.; Balashov, Yu.A. Geochemistry of the Lovozero alkaline massif. Science: Moscow. Russia, 1966; p.
- Kostyleva-Labuntsova, E.E.; Borutsky, B.E.; Sokolova, M.N.; et al. Mineralogy of the Khibiny massif (minerals). Science: Moscow. Russia, 1978.
- Vernadsky, V.I. History of natural waters. Science: Moscow, Russia, 2003, p.
- Pekov, I.V. Lovozersky massif: the history of research, pegmatites, minerals. Creative association Earth: Moscow. Russia, 2001, p.
- Nikanov, А.N.; Gudkov, А.B.; Popova, О.N.; Smolina, V.S.; Chaschin, V.P. Blood Mineral Composition in Residents of the Arctic Region with Low Water Mineralization Rates in Centralized Tap Water Supply Systems. Ekologiya cheloveka (Human Ecology) 2021, 3, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupletsky, B.M. Petrography of the Kola Peninsula. Publishing House of the USSR Academy of Sciences: Leningrad, Russia, 1968, p.
- Karpov, I.K.; Chudnenko, K.V.; Kulik, D.A.; Bychinskii, V.A. The convex programming minimization of five thermodynamic potentials other than Gibbs energy in geochemical modeling. Amer J Sci. 2002, 302, 4–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudnenko, K.V. Thermodynamic modeling in geochemistry: theory, algorithms, software, applications. Akadem. publishing house “Geo”: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2010, p.
- Reid, R.C.; Prausnitz, J.M.; Sherwood, T.K. The properties of gases and liquids. McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, USA, 1977, p.
- Shock, E.L. , Helgeson, H.C. Calculation of the thermodynamic and transport properties of aqueous species at high pressures and temperatures: correlation algorithms for ionic species and equation of state predictions to 5 kb and 1000C. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 1988, 52, 2009–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokokawa, H. Tables of thermodynamic properties of inorganic compounds. J Nat Chem Lab Indust. 1988, 83, 27–121. [Google Scholar]
- Shock, E.L. , Helgeson, H.C., Sverjensky, D.A. Calculation of the thermodynamic and transport properties of aqueous species at high pressures and temperatures: Standard partial molal properties of inorganic neutral species. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 1989, 53, 2157–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.W.; Oelkers, E.H.; Helgeson, H.C. SUPCRT92: Software package for calculating the standard molal thermodynamic properties of mineral, gases, aqueous species, and reactions from 1 to 5000 bars and 0 to 1000C. Comput Geosci. 1992, 18, 899–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robie, R.A.; Hemingway, B.S. Thermodynamic properties of minerals and related substances at 298.15 K and 1 Bar (105 Pascals) pressure and at higher temperatures. United States Geological Survey: Washington, USA, 1995.
- Shock, E.L.; Sassani, D.C.; Willis, M.; Sverjensky, D.A. Inorganic species in geologic fluids: correlation among standard molal thermodynamic properties of aqueous ions and hydroxide complexes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 1997, 61, 907–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazukhina, S.I.; Maksimova, V.V.; Chudnenko, K.V.; Masloboev, V.A.; Sandimirov, S.S.; Drogobuzhskaya, S.V.; Tereshchenko, P.S.; Senzhenko, V.I.; Gudkov, A.V. Water quality of the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation: physico-chemical modeling of water formation, forms of migration of elements, influence on the human body. Publishing house of the FIS of the KSC RAS: Apatity, Russia, 2020.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).