Submitted:
27 September 2024
Posted:
30 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of Hevea bHLH Genes
2.2. Sequence Conservation and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Gene Structures, Conserved Motifs, Promoter and Chromosomal Location Analysis
2.4. Gene Duplication Patterns Analysis
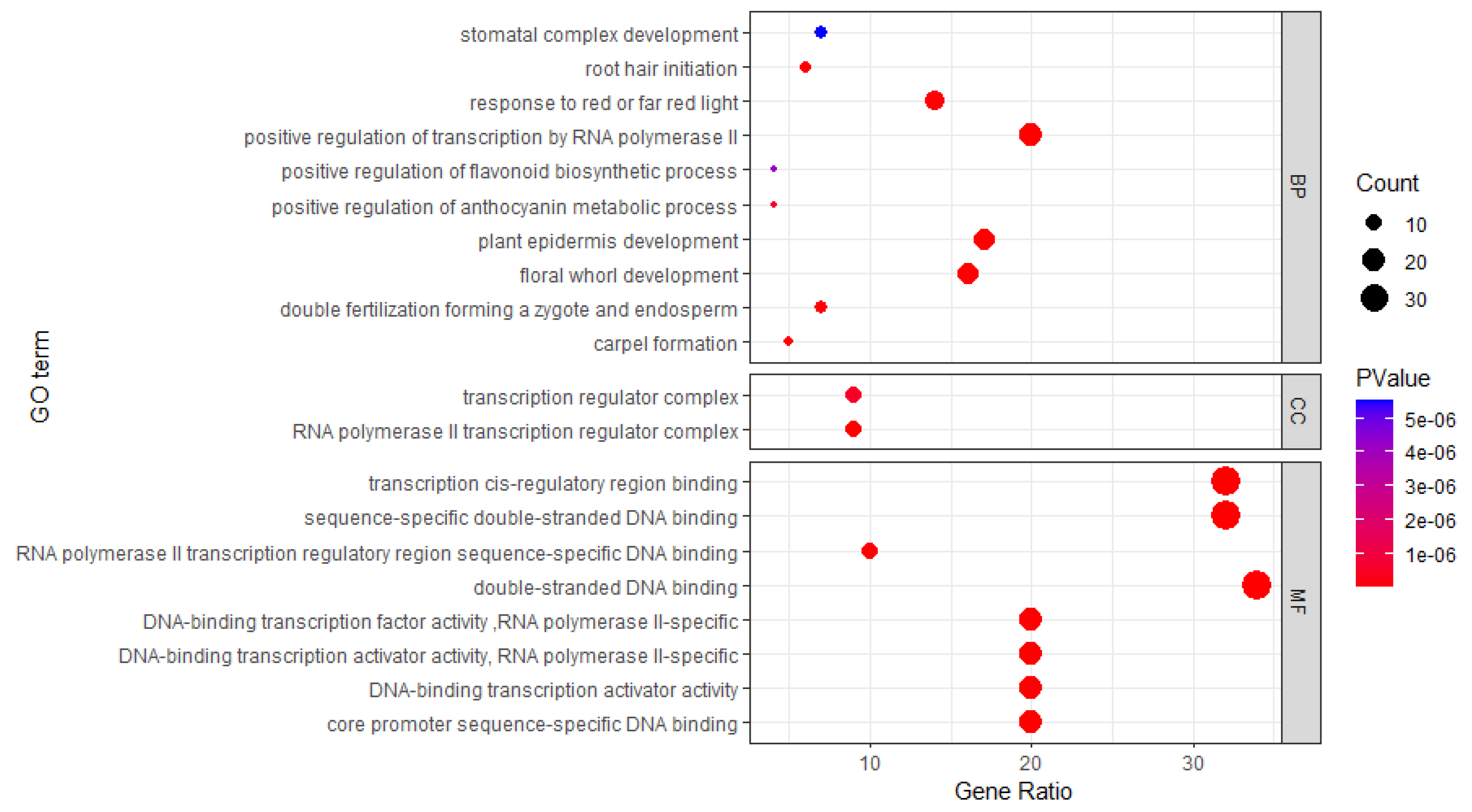
2.5. Gene Ontology Enrichment Analysis
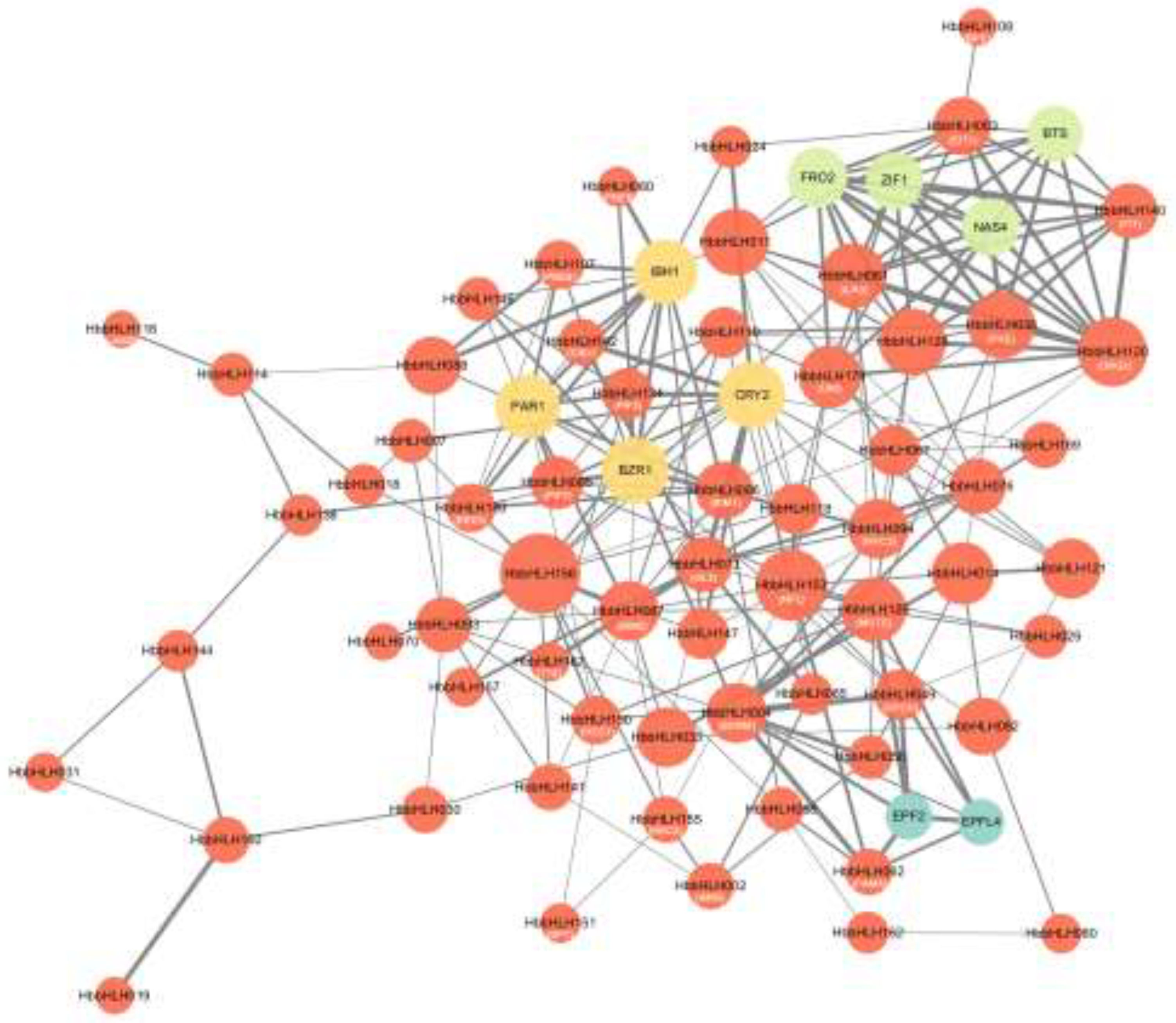
2.6. Interaction Network of Hevea Homologues in Arabidopsis
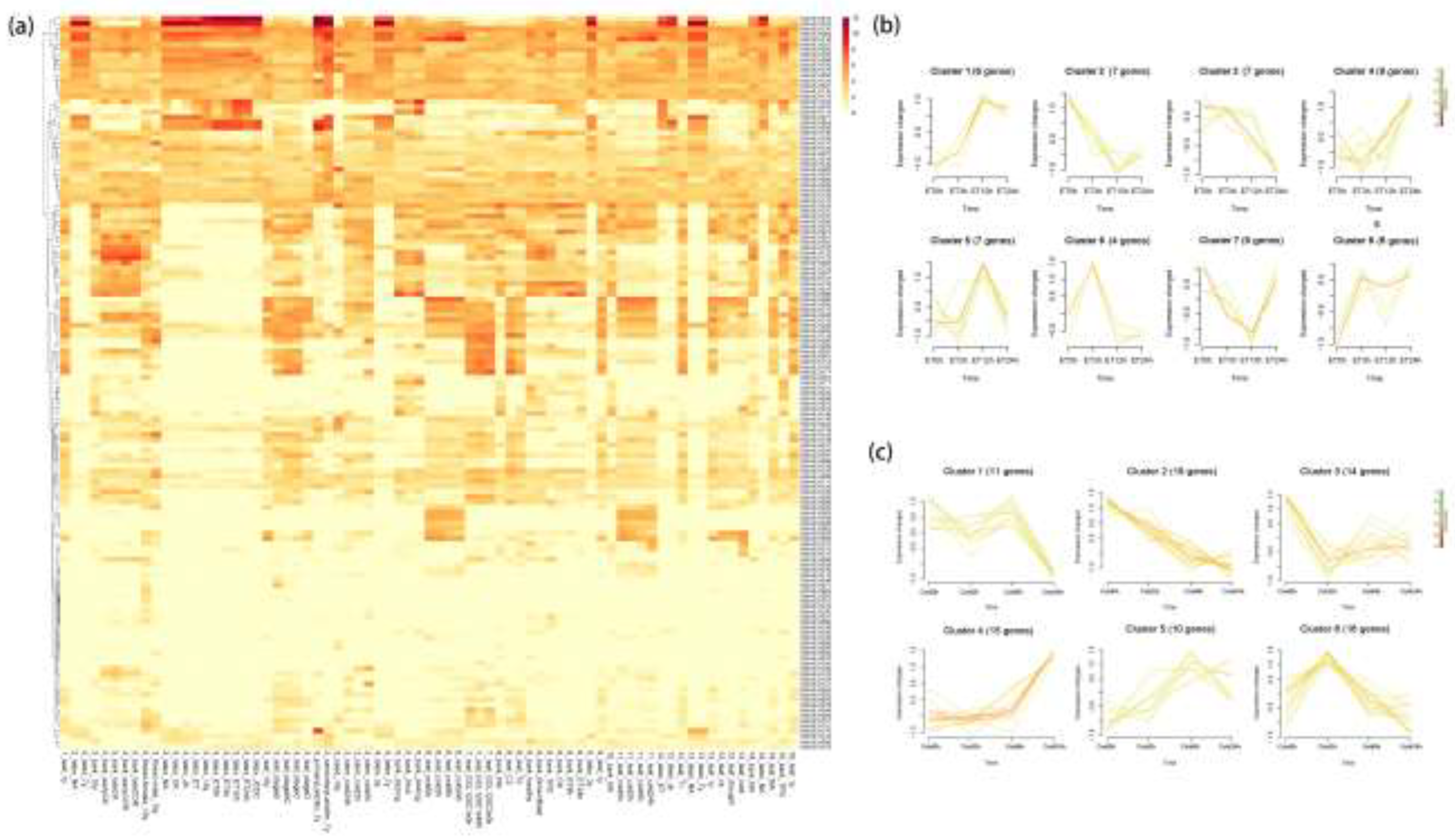
2.7. Expression Patterns Analysis
3. Results
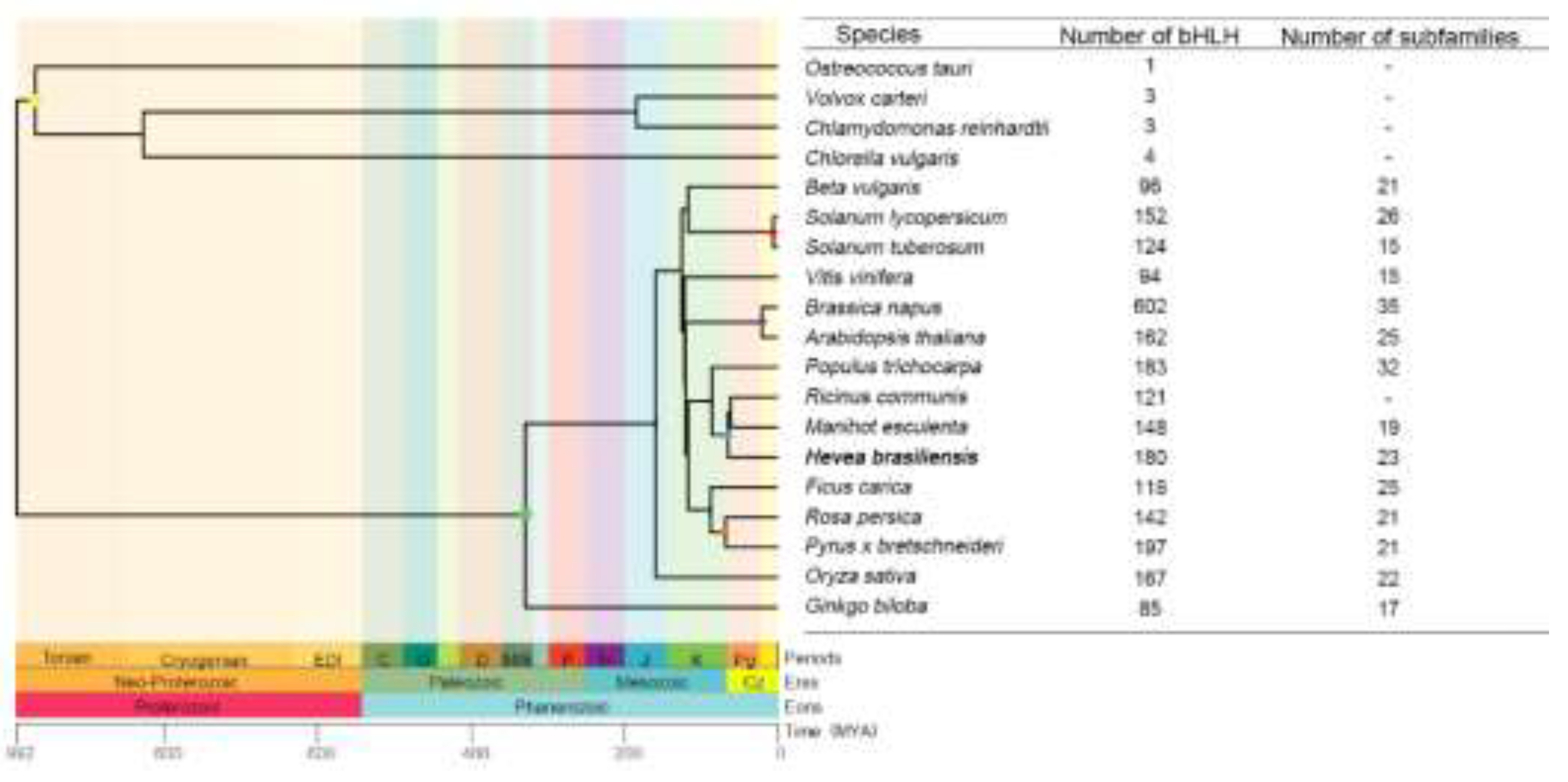
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification of Hevea bHLH
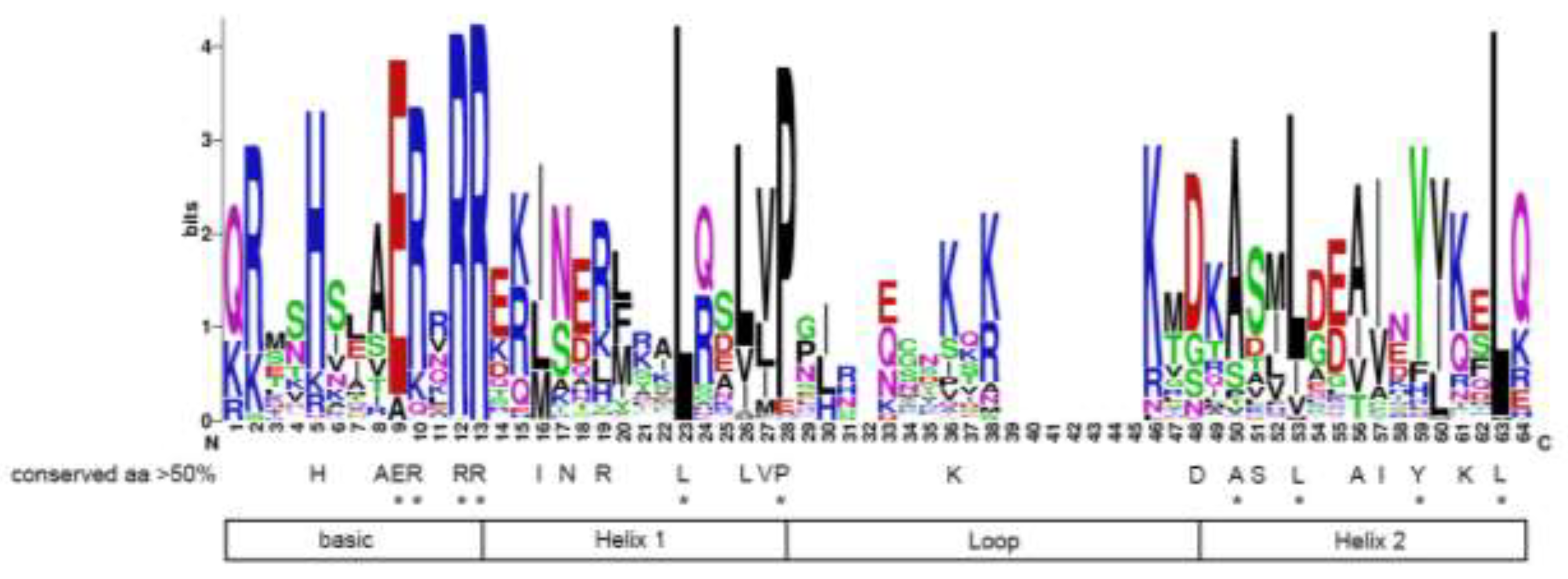
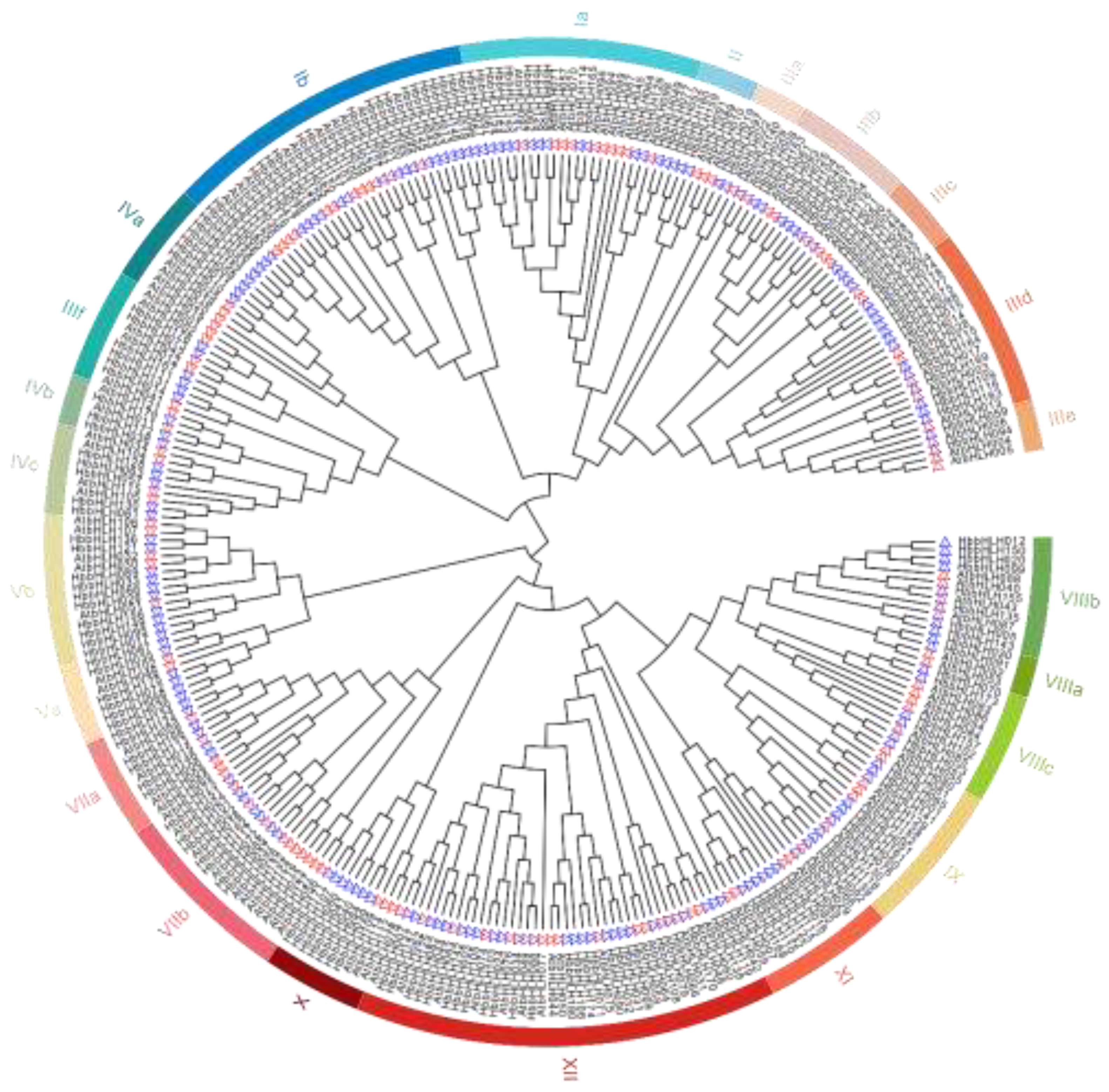
3.2. Conserved Domain and Phylogenetic Analysis of Hevea bHLH
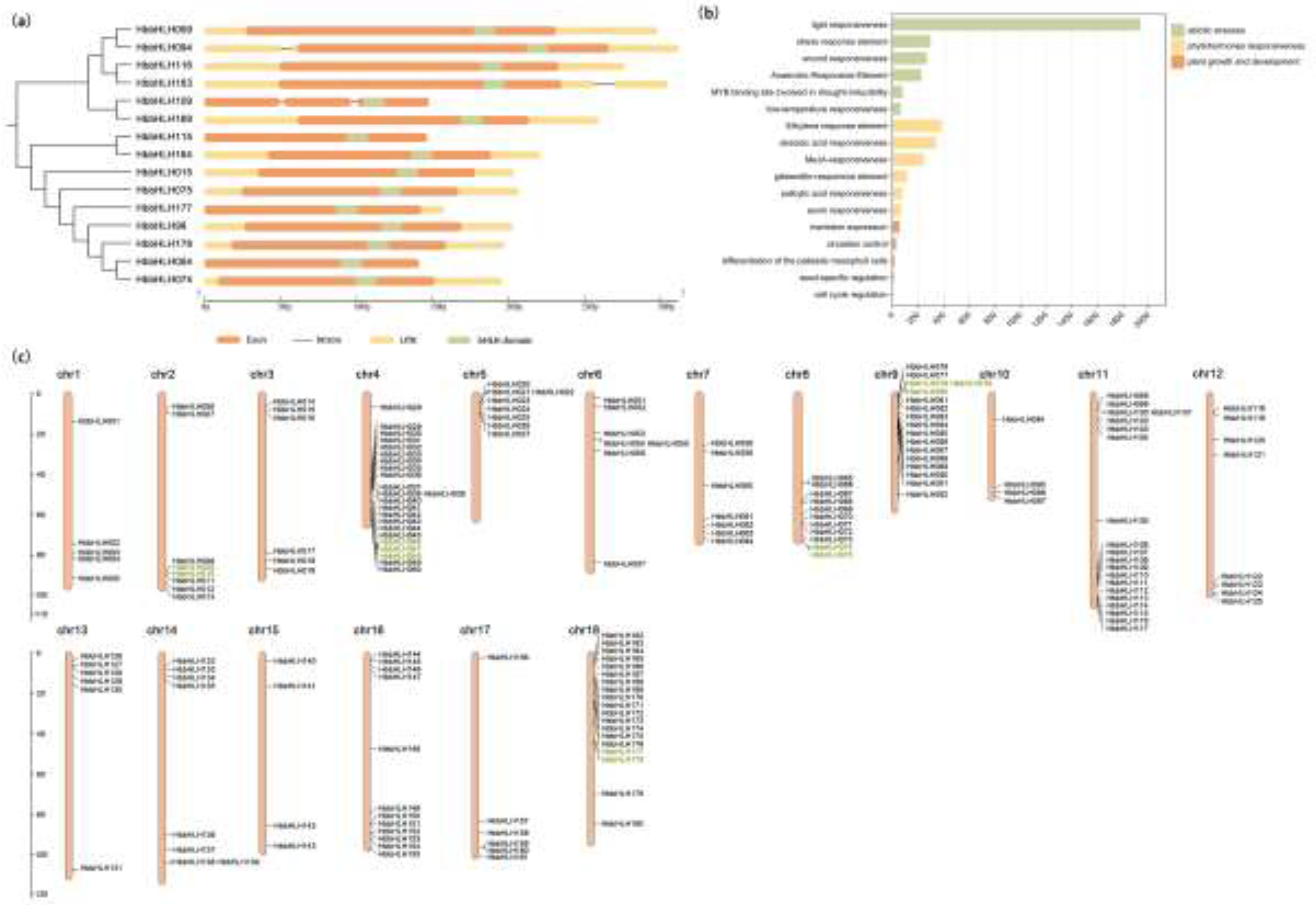
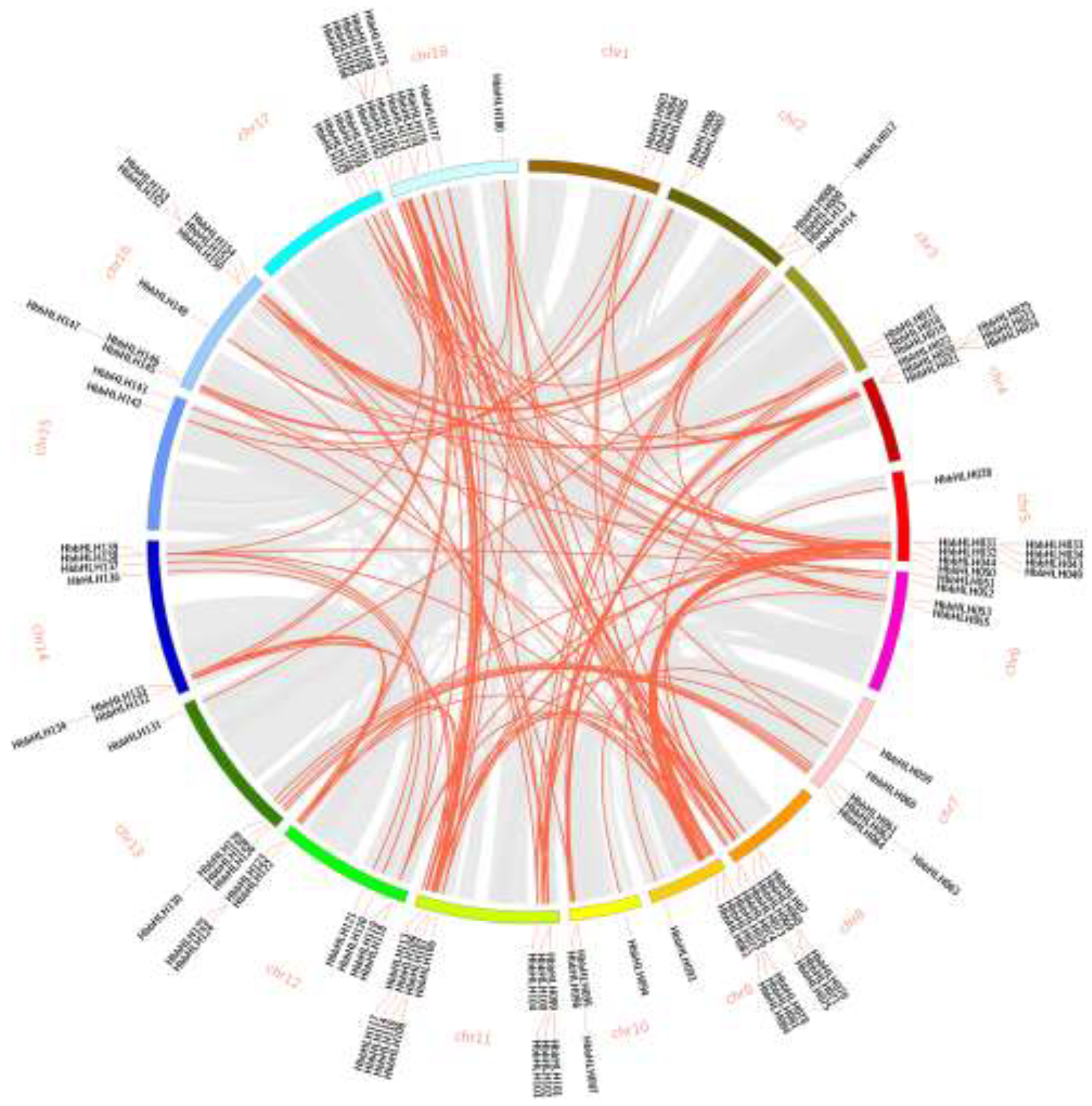
3.3. Gene Structural, Regulatory Elements, Chromosomal Location, and Synteny Analysis of Hevea bHLH
3.4. Gene Ontology and Interaction Network Analysis of Hevea bHLH
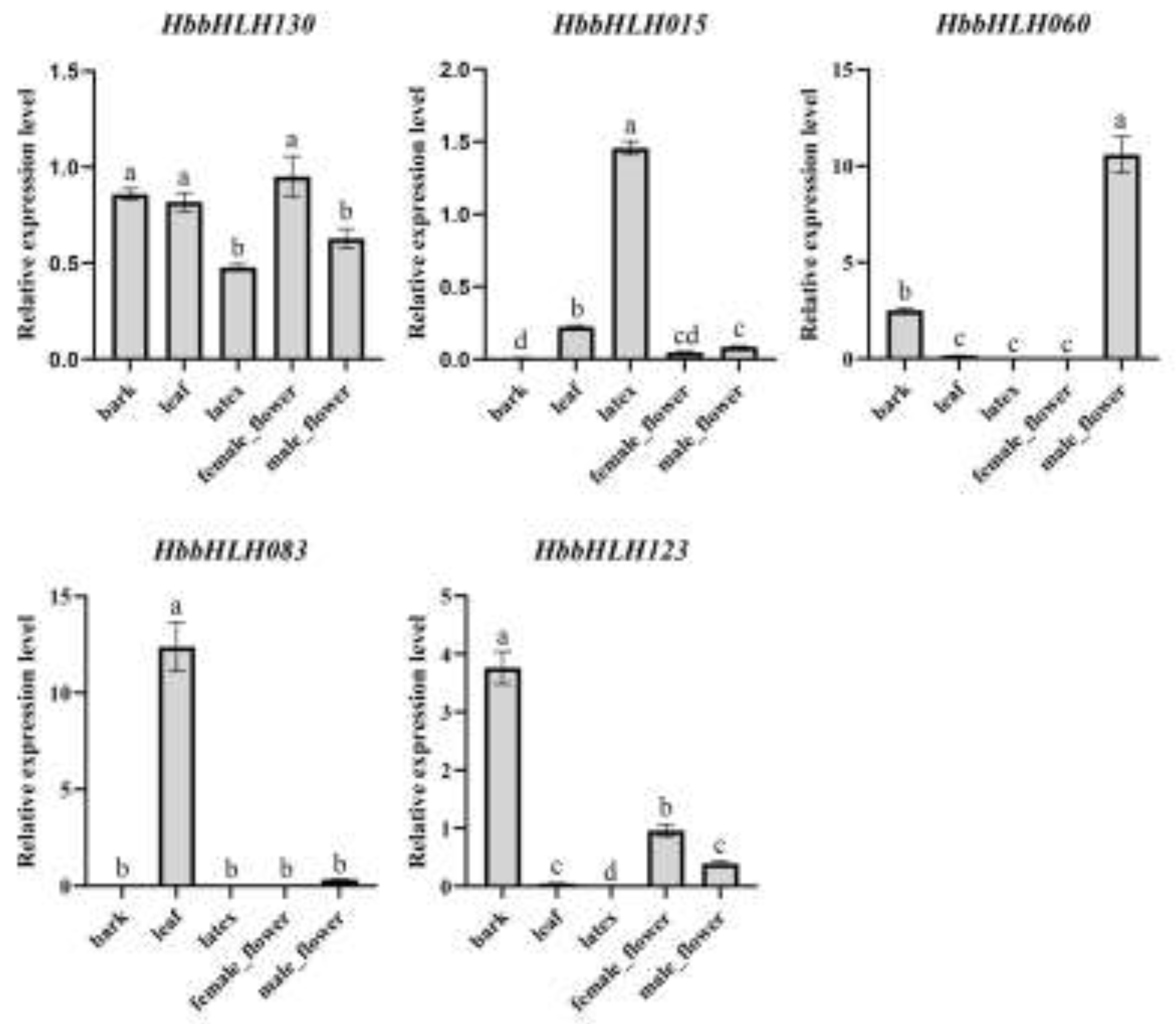
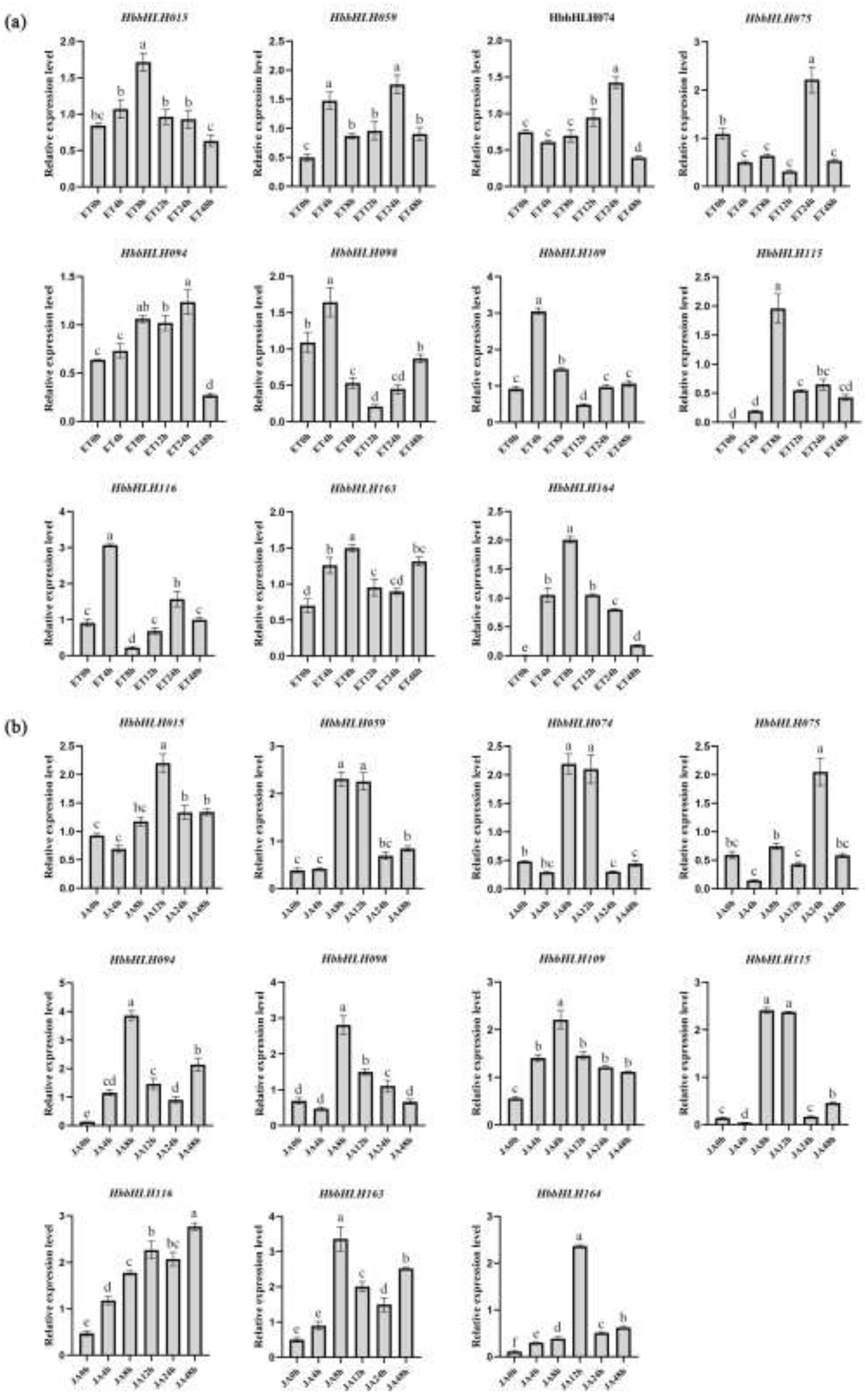
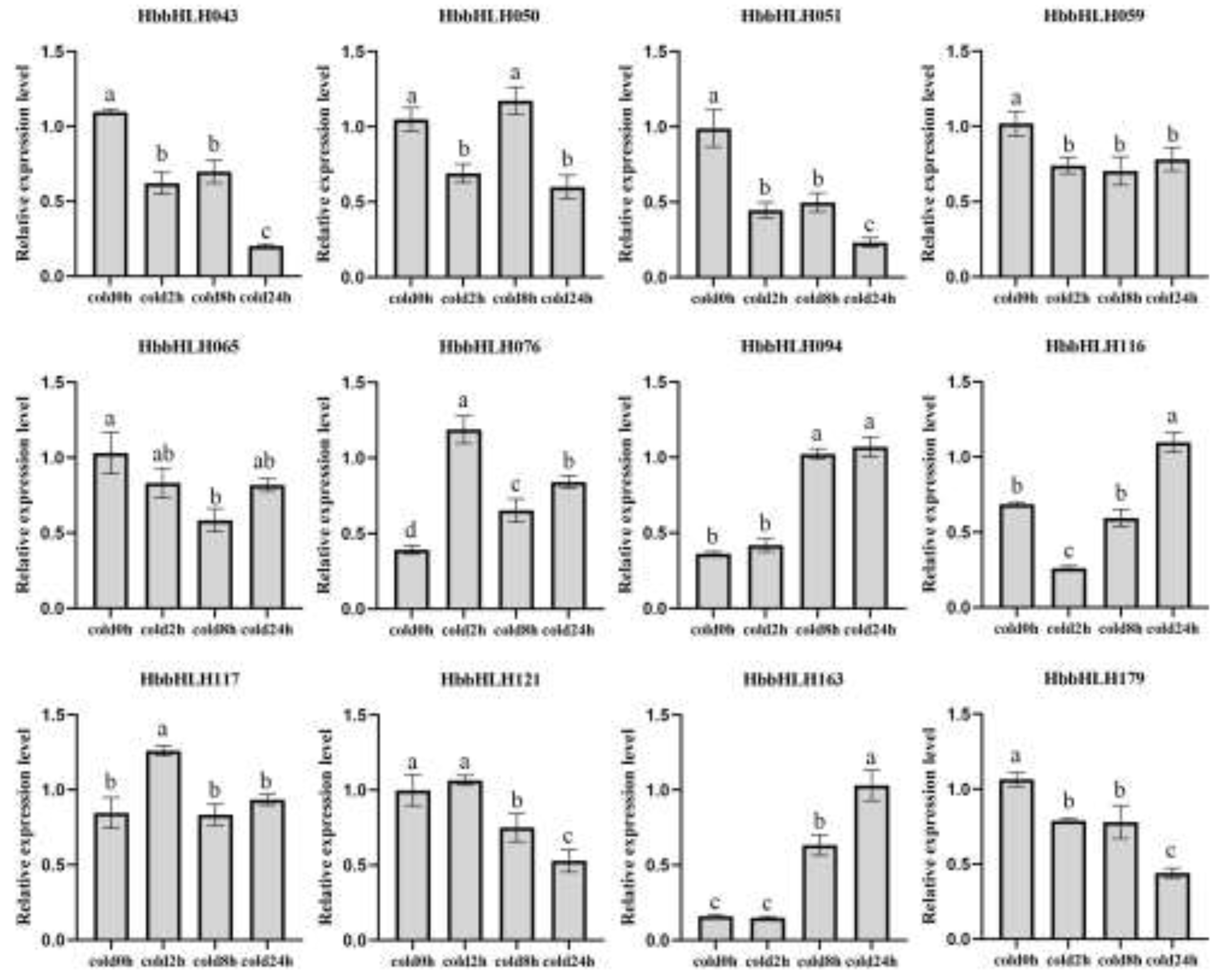
3.5. Expression Patterns of Hevea bHLH in Diverse Environmental and Physiological Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Evolutionary Analysis of the bHLH Family
4.2. Functional Prediction of Hevea bHLH Genes
4.3. Potential Role of IIId and IIIe Subfamilies in Latex Biosynthesis in Hevea
4.4. Regulatory Mechanism of bHLH Response to Cold Stress
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, H.; Song, X.; Hu, Y.; Wu, T.; Yang, Q.; An, Z.; et al. Chromosome-level wild Hevea brasiliensis genome provides new tools for genomic-assisted breeding and valuable loci to elevate rubber yield. Plant Biotechnology Journal. 2023, 21, 1058–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo-Ortiz, G.; Huq, E.; Quail, P.H. The Arabidopsis Basic/Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor Family. The Plant Cell. 2003, 15, 1749–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchley, W.R.; Fitch, W.M. A natural classification of the basic helix–loop–helix class of transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997, 94, 5172–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vervoort, M.; Ledent, V. The Evolution of the Neural Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Proteins. ScientificWorldJournal. 2002, 1, 396–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Mo, Q.; Zhang, D.; Li, W.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of the bHLH Gene Family in Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum: Identification, Classification, Evolution, and Diversity of Expression Patterns under Cultivation. Plants (Basel). 2023, 12, 3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, M.A. The Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor Family in Plants: A Genome-Wide Study of Protein Structure and Functional Diversity. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 2003, 20, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.C.; Martin, C.; Toledo-Ortiz, G.; Quail, P.H.; Huq, E.; Heim, M.A.; et al. Update on the Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor Gene Family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell. 2003, 15, 2497–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carretero-Paulet, L.; Galstyan, A.; Roig-Villanova, I.; Martínez-García, J.F.; Bilbao-Castro, J.R.; Robertson, D.L. Genome-Wide Classification and Evolutionary Analysis of the bHLH Family of Transcription Factors in Arabidopsis, Poplar, Rice, Moss, and Algae. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1398–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Duan, X.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of Basic/Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor Family in Rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology. 2006, 141, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, T.; Yang, Y.; Chen, T.; Yang, M.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of bHLH transcription factor and involvement in the infection by yellow leaf curl virus in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). BMC Genomics. 2015, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, T.; Han, J.; Ren, Z. Genome-wide identification and characterization of cucumber bHLH family genes and the functional characterization of CsbHLH041 in NaCl and ABA tolerance in Arabidopsis and cucumber. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, P.; Kong, N.; Lu, R.; Pei, Y.; Huang, C.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the Potato bHLH Transcription Factor Family. 2018.
- Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Ding, L.; Soppe, W.J.J.; Xiang, Y. REVERSAL OF RDO5 1, a Homolog of Rice Seed Dormancy4, Interacts with bHLH57 and Controls ABA Biosynthesis and Seed Dormancy in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2020, 32, 1933–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, E.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kamiya, Y.; Bae, G.; Chung, W.-I.; Choi, G. Light activates the degradation of PIL5 protein to promote seed germination through gibberellin in Arabidopsis. Plant, J. 2006, 47, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Song, Y.H.; Josephson-Day, A.R.; Miller, R.J.; Breton, G.; Olmstead, R.G.; et al. FLOWERING BHLH transcriptional activators control expression of the photoperiodic flowering regulator CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012, 109, 3582–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Xin, R.; Kim, D.-H.; Sung, S.; Lange, T.; Huq, E. NO FLOWERING IN SHORT DAY (NFL) is a bHLH transcription factor that promotes flowering specifically under short-day conditions in Arabidopsis. Development. 2016, 143, 682–690. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.V.; Lucyshyn, D.; Jaeger, K.E.; Alós, E.; Alvey, E.; Harberd, N.P.; et al. Transcription factor PIF4 controls the thermosensory activation of flowering. Nature. 2012, 484, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, N.; Li, J.; Zhao, W.; Du, J.; et al. FIT interacts with AtbHLH38 and AtbHLH39 in regulating iron uptake gene expression for iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H.; Du, J.; Huang, Z.; et al. Requirement and functional redundancy of Ib subgroup bHLH proteins for iron deficiency responses and uptake in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant. 2013, 6, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, C.; Du, J.; Liu, H.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Co-overexpression FIT with AtbHLH38 or AtbHLH39 in Arabidopsis-enhanced cadmium tolerance via increased cadmium sequestration in roots and improved iron homeostasis of shoots. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Kasuga, M.; Sakuma, Y.; Abe, H.; Miura, S.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; et al. Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought- and low-temperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1998, 10, 1391–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Tepperman, J.M.; Quail, P.H. PIF3, a phytochrome-interacting factor necessary for normal photoinduced signal transduction, is a novel basic helix-loop-helix protein. Cell. 1998, 95, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leivar, P.; Monte, E. PIFs: systems integrators in plant development. Plant Cell. 2014, 26, 56–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairchild, C.D.; Schumaker, M.A.; Quail, P.H. HFR1 encodes an atypical bHLH protein that acts in phytochrome A signal transduction. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2377–2391. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Ai, Q.; Liang, G.; Yu, D. Two bHLH Transcription Factors, bHLH34 and bHLH104, Regulate Iron Homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 2478–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweizer, F.; Fernández-Calvo, P.; Zander, M.; Diez-Diaz, M.; Fonseca, S.; Glauser, G.; et al. Arabidopsis basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4 regulate glucosinolate biosynthesis, insect performance, and feeding behavior. Plant Cell. 2013, 25, 3117–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.-Y. Molecular characterization of a bHLH transcription factor involved in Arabidopsis abscisic acid-mediated response. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006, 1759, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Guo, H.; Dai, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, K.; Wang, X.; et al. An ABA down-regulated bHLH transcription repressor gene, bHLH129 regulates root elongation and ABA response when overexpressed in Arabidopsis. Sci Rep. 2015, 5, 17587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Urao, T.; Ito, T.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYB2 (MYB) function as transcriptional activators in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell. 2003, 15, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Kurihara, Y.; Makita, Y.; Okubo-Kurihara, E.; Kageyama, A.; Osada, E.; et al. Regulatory Potential of bHLH-Type Transcription Factors on the Road to Rubber Biosynthesis in Hevea brasiliensis. Plants. 2020, 9, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-J.; Wang, X.; Yan, S.; Huang, X.; Yuan, H.-M. The ICE-like transcription factor HbICE2 is involved in jasmonate-regulated cold tolerance in the rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). Plant Cell Rep. 2019, 38, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Li, H.-L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.-H.; Peng, S.-Q. A myelocytomatosis transcription factor from Hevea brasiliensis positively regulates the expression of the small rubber particle protein gene. Industrial Crops and Products. 2019, 133, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer ELL, et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Research. 2021, 49, D412–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, S.C.; Luciani, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Park, Y.; Lopez, R.; Finn, R.D. HMMER web server: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Research. 2018, 46, W200–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Bryant, S.H. CD-Search: protein domain annotations on the fly. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W327–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Khedkar, S.; Bork, P. SMART: recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Research. 2021, 49, D458–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol Plant. 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Park, K.-J.; Obayashi, T.; Fujita, N.; Harada, H.; Adams-Collier, C.J.; et al. WoLF PSORT: protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2. 0. Bioinformatics. 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.-M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A Sequence Logo Generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6. 0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, B.; Gao, S.; Lercher, M.J.; Hu, S.; Chen, W.-H. Evolview v3: a webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W270–W275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; et al. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombauts, S.; Dehais, P.; Van Montagu, M.; Rouze, P. PlantCARE, a plant cis-acting regulatory element database. Nucleic Acids Research. 1999, 27, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorrips, R.E. MapChart: Software for the Graphical Presentation of Linkage Maps and QTLs. Journal of Heredity. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; et al. MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; et al. Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation. 2021, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, F.; Luo, Y.; Bie, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y. OrthoVenn3: an integrated platform for exploring and visualizing orthologous data across genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H. HeveaDB: A Hub for Rubber Tree Genetic and Genomic Resources. In: Matsui M, Chow K-S, editors. The Rubber Tree Genome. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2020. p. 137–52.
- Kumar, L.; Futschik, M.E. Mfuzz: a software package for soft clustering of microarray data. Bioinformation. 2007, 2, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, N.; Dolan, L. Origin and Diversification of Basic-Helix-Loop-Helix Proteins in Plants. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 2010, 27, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferré-D’Amaré, A.R.; Prendergast, G.C.; Ziff, E.B.; Burley, S.K. Recognition by Max of its cognate DNA through a dimeric b/HLH/Z domain. Nature. 1993, 363, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchley, W.R.; Terhalle, W.; Dress, A. Positional Dependence, Cliques, and Predictive Motifs in the bHLH Protein Domain. J Mol Evol. 1999, 48, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Lyu, H.-M.; Zhu, K.; Van de Peer, Y.; (Max) Cheng, Z.-M. The emergence and evolution of intron-poor and intronless genes in intron-rich plant gene families. The Plant Journal. 2021, 105, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, M.J.; Atchley, W.R. Phylogenetic Analysis of Plant Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Proteins. J Mol Evol. 2003, 56, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaoka, M.M.; Pillitteri, L.J.; Fujii, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Bogenschutz, N.L.; Takabayashi, J.; et al. SCREAM/ICE1 and SCREAM2 specify three cell-state transitional steps leading to arabidopsis stomatal differentiation. Plant Cell. 2008, 20, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Robe, K.; Gaymard, F.; Izquierdo, E.; Dubos, C. The Transcriptional Control of Iron Homeostasis in Plants: A Tale of bHLH Transcription Factors? Front Plant Sci. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, B. Laticifer Differentiation in Hevea brasiliensis: Induction by Exogenous Jasmonic Acid and Linolenic Acid. Annals of Botany. 2000, 85, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z. Ethylene stimulation of latex production in Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Signaling & Behavior. 2009, 4, 1072–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Chen, Q.; Dai, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X. Genome-wide identification of PbrbHLH family genes, and expression analysis in response to drought and cold stresses in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Li, Y.; Yin, H.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Jiang, S.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Expression Analysis under Abiotic Stresses of the UBP Gene Family in Rice (Oryza sativa L. ). Agronomy. 2023, 13, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi-Ito, K.; Bergmann, D.C. Arabidopsis FAMA Controls the Final Proliferation/Differentiation Switch during Stomatal Development. Plant Cell. 2006, 18, 2493–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, K.M.; Rychel, A.L.; Torii, K.U. Out of the Mouths of Plants: The Molecular Basis of the Evolution and Diversity of Stomatal Development. The Plant Cell. 2010, 22, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, J.; Hao, H.; Xiao, H.; Cao, Y.; Lin, X.; Huang, X. Identification of JAZ-interacting MYC transcription factors involved in latex drainage in Hevea brasiliensis. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, N.; Qu, C.; Jiang, S.; et al. Methyl jasmonate enhances apple’ cold tolerance through the JAZ–MYC2 pathway. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult. 2019, 136, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




