Submitted:
27 September 2024
Posted:
29 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
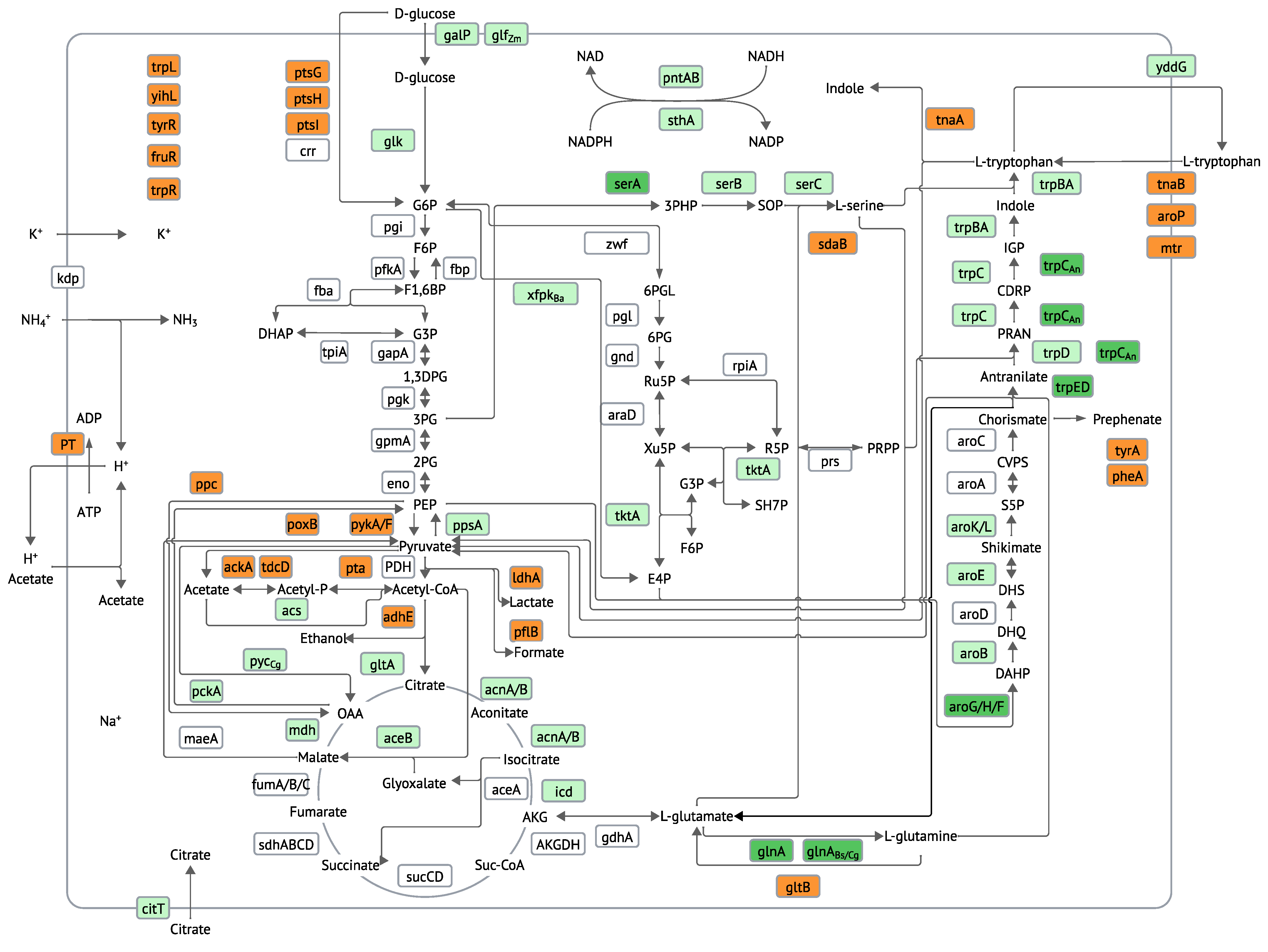
2. Genetic Modifications
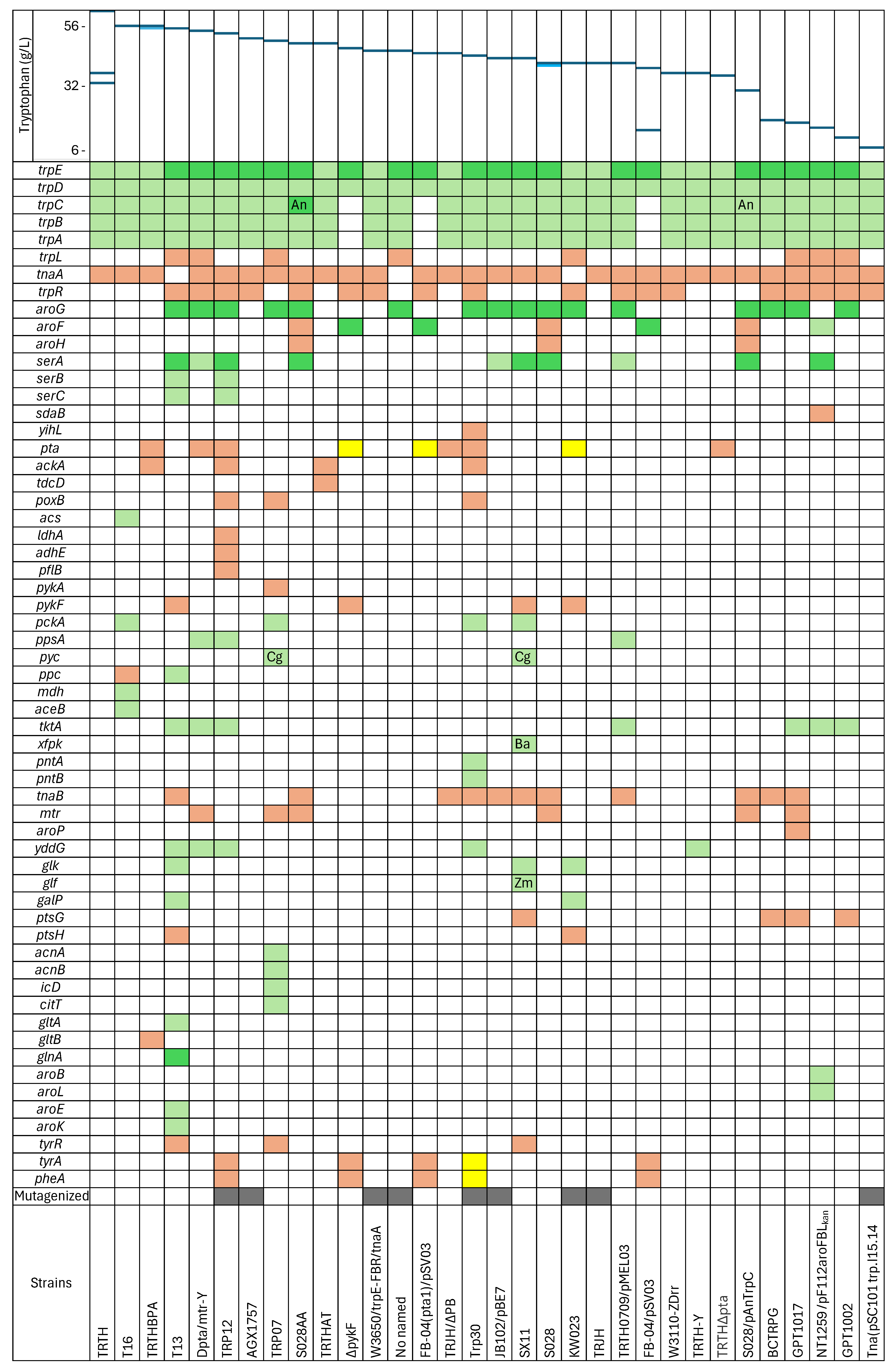
2.1. Strains Derived from Mutagenesis
2.2. Modification and Overexpression of the Tryptophan Operon
2.3. Eliminating the Degradation Pathway of Tryptophan
2.4. Modifications to the Central Metabolic Pathways
2.5. Modification of the Pathways Involved in Acetate Accumulation
2.6. Modification to the Common aromatic Amino Acid Pathway
2.7. Supply of Tryptophan Precursors
2.7.1. Glutamine
2.7.2. Serine
2.8. Modification of the Tryptophan Transport Systems
2.9. Silencing of Transcriptional Regulators
2.10. Modulating Pathways Competing for Precursors
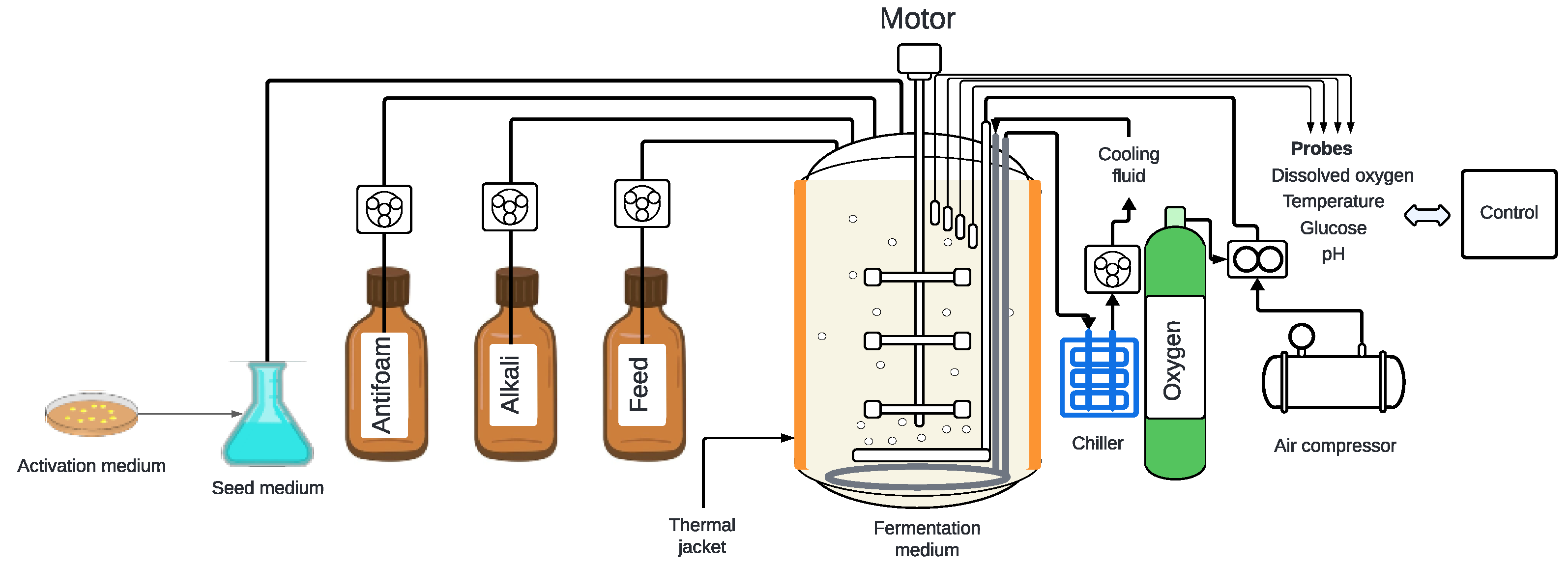
3. Fermentation Parameters
3.1. Factors Affecting Biomass Accumulation
3.2. Modulation of Growth Rate
3.3. Ensuring Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Concentration
3.3.1. Avoiding Acetate Accumulation
3.3.2. Redistribution of Flows between Metabolic Pathways
3.3.3. Oxidative Stress
3.4. Effect of pH
3.5. Culture Feeding Strategies
3.5.1. Exponential Feeding
3.5.2. Glucose-Stat Feeding Strategy
3.5.3. DO Feedback Control
3.5.4. DO-Stat Control
3.5.5. DO Stage Control Strategy
3.6. Composition of the Culture Medium
3.6.1. Effect of calcium on fermentation
3.6.2. Addition of Betaine Monohydrate
3.6.3. Citrate supplementation
3.6.4. Effect of Organic Nitrogen on Tryptophan Production
3.6.5. Inorganic Nitrogen Supply
3.6.6. Increased Phosphate in the Medium
3.6.7. The addition of Surfactants
3.6.8. Accumulation of Sodium and Potassium Cations
3.6.9. Addition of Tryptophan Precursors in Media
3.6.10. Effect of Methionine on Tryptophan Production
3.6.11. Effect of Carbon Sources
4. Models for Tryptophan Production
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohamed, H.; El Nady, G.; Ali, A.; Abdel-Razik, A.; Ibrahim, S. Production of L-Tryptophan by Mutants of Corynebacterium Glutamicum. Arab Universities Journal of Agricultural Sciences 2018, 26, 1187–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, D.M.; Dawes, M.A.; Mathias, C.W.; Acheson, A.; Hill-Kapturczak, N.; Dougherty, D.M. L-Tryptophan: Basic Metabolic Functions, Behavioral Research and Therapeutic Indications. International Journal of Tryptophan Research 2009, 2, IJTR–S2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Xu, Q.; Liang, J.; Xie, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, N. Control Strategy of Specific Growth Rate in L-Tryptophan Production by Escherichia Coli. In; 2014; pp. 241–249.
- Lu, N.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Fu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, H. Gene Modification of Escherichia Coli and Incorporation of Process Control to Decrease Acetate Accumulation and Increase ʟ-Tryptophan Production. Ann Microbiol 2017, 67, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, B.-B.; Xu, J.-Z.; Zhang, W.-G. Engineering of Shikimate Pathway and Terminal Branch for Efficient Production of L-Tryptophan in Escherichia Coli. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, D.; Jiang, S.; Fan, X.; Ma, Q.; Wu, H.; Xie, X. Flux Redistribution of Central Carbon Metabolism for Efficient Production of L-tryptophan in Escherichia Coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 2021, 118, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanofsky, C.; Horn, V.; Gollnick, P. Physiological Studies of Tryptophan Transport and Tryptophanase Operon Induction in Escherichia Coli. J Bacteriol 1991, 173, 6009–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deal, I.; Macauley, M.; Davies, R. Boolean Models of the Transport, Synthesis, and Metabolism of Tryptophan in Escherichia Coli. Bull Math Biol 2023, 85, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghiyan-Rizi, T.; Fooladi, J.; Sadrai, S. Preliminary Study on Cost-Effective L-Tryptophan Production from Indole and L-Serine by E. Coli Cells. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol 2016, 8, 188–192. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, D.; Bai, D.; Li, J.; Mao, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, P.; Lin, J.; Ma, H.; Zhang, D. Analyzing the Genetic Characteristics of a Tryptophan-Overproducing Escherichia Coli. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 2021, 44, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minliang, C.; Chengwei, M.; Lin, C.; Zeng, A.-P. Integrated Laboratory Evolution and Rational Engineering of GalP/Glk-Dependent Escherichia Coli for Higher Yield and Productivity of L-Tryptophan Biosynthesis. Metab Eng Commun 2021, 12, e00167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, W.; Lang, S.; Sahm, H.; Wagner, F. Production L-tryptophan by Escherichia Coli Cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 1983, 25, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gang, S.; Sharma, S.; Saraf, M.; Buck, M.; Schumacher, J. Analysis of Indole-3-Acetic Acid (IAA) Production in Klebsiella by LC-MS/MS and the Salkowski Method. Bio Protoc 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, K.; Yokozeki, K.; Eguchi, C.; Kagawa, T.; Noda, I.; Mitsugi, K. Enzymatic Production of L-Tryptophan from l- and Dl-5-Indolyl-Methylhydantoin by Newly Isolated Bacterium. Agric Biol Chem 1977, 41, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoppel, K.; Trachtmann, N.; Korzin, E.J.; Tzanavari, A.; Sprenger, G.A.; Weuster-Botz, D. Metabolic Control Analysis Enables Rational Improvement of E. Coli L-Tryptophan Producers but Methylglyoxal Formation Limits Glycerol-Based Production. Microb Cell Fact 2022, 21, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, Z.-L.; Zeng, A.-P.; Deckwer, W.-D. Model Analysis Concerning the Effects of Growth Rate and Intracellular Tryptophan Level on the Stability and Dynamics of Tryptophan Biosynthesis in Bacteria. J Biotechnol 1997, 58, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M. Towards Bacterial Strains Overproducing L-Tryptophan and Other Aromatics by Metabolic Engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2006, 69, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A. Enzymatic Production of L-Tryptophan by a Thermophilic Strain of Bacillus Licheniformis Isolated from a Local Hot Spring of Paniphala, Asansol Area of West Bengal. J Pure Appl Microbiol 2023, 17, 2307–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jin, Z.W.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. Effect of Yeast Extract on L-Tryptophan Production in Batch Culture of Escherichia Coli. Adv Mat Res 2013, 807–809, 2009–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.; Boesch, B.W.; Palsson, B.O. Biochemical Production Capabilities of Escherichia Coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 1993, 42, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribe, D.E.; Pittard, J. Hyperproduction of Tryptophan by Escherichia Coli: Genetic Manipulation of the Pathways Leading to Tryptophan Formation. Appl Environ Microbiol 1979, 38, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Li, R.; Liang, Q.; Qi, Q.; Li, Q.; Gu, P. Metabolic Engineering for Improving <scp>l</Scp> -Tryptophan Production in Escherichia Coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 2019, 46, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, J.W.; Mauch, K.; Reuss, M.; Gilles, E.D.; Kremling, A. Metabolic Design Based on a Coupled Gene Expression—Metabolic Network Model of Tryptophan Production in Escherichia Coli. Metab Eng 2004, 6, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Ding, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, C.; Hu, G.; Song, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, L. Enhancing Tryptophan Production by Balancing Precursors in Escherichia Coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 2022, 119, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.K. L-Tryptophan Production by Auxotrophic and Analogue Resistant Mutants of Aureobacterium Flavescens. International Journal of Tryptophan Research 2011, 4, IJTR–S5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodge, T.C.; Gerstner, J.M. Optimization of the Glucose Feed Rate Profile for the Production of Tryptophan from Recombinant E Coli. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology 2002, 77, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiba, S.; Tsunekawa, H.; Imanaka, T. New Approach to Tryptophan Production by Escherichia Coli: Genetic Manipulation of Composite Plasmids in Vitro. Appl Environ Microbiol 1982, 43, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malin, B.; Westhead, J. Production of L-tryptophan in Submerged Culture. Journal of Biochemical and Microbiological Technology and Engineering 1959, 1, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.; Vue, J.; Morgan, J. Combining Random Mutagenesis and Metabolic Engineering for Enhanced Tryptophan Production in Synechocystis Sp. Strain PCC 6803. Appl Environ Microbiol 2020, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, J.-Z.; Zhang, W.-G. Advances and Prospects in Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia Coli for L-Tryptophan Production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2022, 38, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Nakanishi, K.; Kino, K.; Katsumata, R. Fermentative Production of Tryptophan by a Stable Recombinant Strain of Coryne-Bacterium Glutamicum with a Modified Serine-Biosynthetic Pathway. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 1994, 58, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachý, J.; Ulbert, S. Production of L-tryptophan. Acta Biotechnol 1990, 10, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, S.; Wu, J. Phosphoenolpyruvate:Glucose Phosphotransferase System Modification Increases the Conversion Rate during <scp>l</Scp> -Tryptophan Production in Escherichia Coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 2017, 44, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, A. Improving Production of Aromatic Compounds in Escherichia Coli by Metabolic Engineering. Trends Biotechnol 1996, 14, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Ma, C.; Zeng, A.-P. Discovery of Feed-Forward Regulation in L-Tryptophan Biosynthesis and Its Use in Metabolic Engineering of E. Coli for Efficient Tryptophan Bioproduction. Metab Eng 2018, 47, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-López, D.A.; González de la Vara, L.E.; Santillán, M.; Martínez-Antonio, A. A Molecular Dynamic Model of Tryptophan Overproduction in Escherichia Coli. Fermentation 2022, 8, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillán, M.; Mackey, M.C. Dynamic Regulation of the Tryptophan Operon: A Modeling Study and Comparison with Experimental Data. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2001, 98, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Cheng, L.; Wang, J.; Shen, Z.; Chen, N. Impact of Deletion of the Genes Encoding Acetate Kinase on Production of L-Tryptophan by Escherichia Coli. Ann Microbiol 2016, 66, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-J.; Zou, C.; Zhu, Y.-X.; Dai, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, D.; Wu, J.; Chen, J. Development of L-Tryptophan Production Strains by Defined Genetic Modification in Escherichia Coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 2011, 38, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Duan, X.; Wu, J. L-Tryptophan Production in Escherichia Coli Improved by Weakening the Pta-AckA Pathway. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0158200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Fang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Lin, C.; Shen, Z.; Cheng, L. Application of Fermentation Process Control to Increase <scp>l</Scp> -tryptophan Production in <scp> Escherichia Coli </Scp>. Biotechnol Prog 2020, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-Y.; Wu, W.-J.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Zhou, B.; Niu, K.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Zheng, Y.-G. Calcium Carbonate Addition Improves L-Methionine Biosynthesis by Metabolically Engineered Escherichia Coli W3110-BL. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiong, H.; Xu, Q. L-Tryptophan Fermentation by High Cell Density Culture of Escherichia Coli. Food and Fermentation Industries 2019, 45, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mears, L.; Stocks, S.M.; Sin, G.; Gernaey, K. V. A Review of Control Strategies for Manipulating the Feed Rate in Fed-Batch Fermentation Processes. J Biotechnol 2017, 245, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panichkin, V.B.; Livshits, V.A.; Biryukova, I. V.; Mashko, S. V. Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia Coli for L-Tryptophan Production. Appl Biochem Microbiol 2016, 52, 783–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Bilal, M.; Luo, H.; Zhao, Y.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Metabolic Engineering and Fermentation Process Strategies for L-Tryptophan Production by Escherichia Coli. Processes 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Chen, N. New Strategy for Removing Acetic Acid as a By-Product during L-Tryptophan Production. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment 2019, 33, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Chen, N. Central Metabolic Pathway Modification to Improve L-Tryptophan Production in Escherichia Coli. Bioengineered 2019, 10, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Duan, X.; Wu, J. Modulating the Direction of Carbon Flow in Escherichia Coli to Improve l -Tryptophan Production by Inactivating the Global Regulator FruR. J Biotechnol 2016, 231, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tröndle, J.; Schoppel, K.; Bleidt, A.; Trachtmann, N.; Sprenger, G.A.; Weuster-Botz, D. Metabolic Control Analysis of L-Tryptophan Production with Escherichia Coli Based on Data from Short-Term Perturbation Experiments. J Biotechnol 2020, 307, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Pan, X.; Yang, T.; You, J.; Zhu, R.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X.; Xu, M.; Rao, Z. Multidimensional Engineering of Escherichia Coli for Efficient Synthesis of L-Tryptophan. Bioresour Technol 2023, 386, 129475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.; Yang, F.; Li, F.; Liang, Q.; Qi, Q. Knocking out Analysis of Tryptophan Permeases in Escherichia Coli for Improving L-Tryptophan Production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2013, 97, 6677–6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Xie, X.; Xu, Q.; Chen, N. Modification of Tryptophan Transport System and Its Impact on Production of L-Tryptophan in Escherichia Coli. Bioresour Technol 2012, 114, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Valdovinos, M.A.; Salas-Navarrete, P.C.; Amores, G.R.; Hernández-Orihuela, A.L.; Martínez-Antonio, A. Qualitative Perturbation Analysis and Machine Learning: Elucidating Bacterial Optimization of Tryptophan Production. Algorithms 2024, 17, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Shi, J.; Xu, Q.; Xie, X.; Chen, N. Fermentation Characterization of an L-Tryptophan Producing Escherichia Coli Strain with Inactivated Phosphotransacetylase. Ann Microbiol 2013, 63, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Q. Using Enzymatic Hydrolyzate as New Nitrogen Source for L-Tryptophan Fermentation by E.Coli. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandiera, M.; Morpurgo, G.; Ricci, R. Tryptophan Production by Mutant Strains of Escherichia Coli K 12. Experientia 1967, 23, 724–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Chen, L.; Zeng, A.-P. CRISPR/Cas9-Facilitated Engineering with Growth-Coupled and Sensor-Guided in Vivo Screening of Enzyme Variants for a More Efficient Chorismate Pathway in E. Coli. Metab Eng Commun 2019, 9, e00094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zeng, A.-P. Rational Design and Metabolic Analysis of Escherichia Coli for Effective Production of L-Tryptophan at High Concentration. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2017, 101, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Bai, F.; Chen, N.; Bai, G. Removing the By-Products Acetic Acid and NH 4 + from the l -Tryptophan Broth by Vacuum Thin Film Evaporation during l -Tryptophan Production. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology 2018, 33, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.-K.; Wang, J.; Xu, Q.-Y.; Zhao, C.-G.; Shen, Z.-Q.; Xie, X.-X.; Chen, N. Strategy for PH Control and PH Feedback-Controlled Substrate Feeding for High-Level Production of l-Tryptophan by Escherichia Coli. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2013, 29, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Cheng, L.; Xu, Q.; Wang, J.; Shen, Z.; Chen, N. Improvement of the Production of L-Tryptophan in Escherichia Coli by Application of a Dissolved Oxygen Stage Control Strategy. Ann Microbiol 2016, 66, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ding, D.; Cong, L.; Zhang, D. Rational Design and Analysis of an Escherichia Coli Strain for High-Efficiency Tryptophan Production. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 2018, 45, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, K.; Tang, Y.; Yao, C.; del Rio-Chanona, E.A.; Ling, X.; Zhang, D. Overproduction of L-tryptophan via Simultaneous Feed of Glucose and Anthranilic Acid from Recombinant Escherichia Coli W3110: Kinetic Modeling and Process Scale-up. Biotechnol Bioeng 2018, 115, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Huang, J.; Zhu, X.; Huang, L.; Cai, J.; Xu, Z. Enhanced Production of L-Tryptophan with Glucose Feeding and Surfactant Addition and Related Metabolic Flux Redistribution in the Recombinant Escherichia Coli. Food Sci Biotechnol 2013, 22, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Cheng, L.; Xie, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Ning, C. Effect of Sodium Citrate on L-Tryptophan Fermentation by Escherichia Coli. In; 2015; pp. 335–342.
- Azuma, S.; Tsunekawa, H.; Okabe, M.; Okamoto, R.; Aiba, S. Hyper-Production of l-Trytophan via Fermentation with Crystallization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 1993, 39, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.-K.; Wang, J.; Xu, Q.-Y.; Xie, X.-X.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Zhao, C.-G.; Chen, N. Effect of Feeding Strategy on L-Tryptophan Production by Recombinant Escherichia Coli. Ann Microbiol 2012, 62, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.; Yang, F.; Kang, J.; Wang, Q.; Qi, Q. One-Step of Tryptophan Attenuator Inactivation and Promoter Swapping to Improve the Production of L-Tryptophan in Escherichia Coli. Microb Cell Fact 2012, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Bai, F.; Chen, N.; Bai, G. Gene Modification of the Acetate Biosynthesis Pathway in Escherichia Coli and Implementation of the Cell Recycling Technology to Increase L-Tryptophan Production. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0179240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Liu, Q.; Xie, X.; Xu, Q.; Chen, N. Improved Production of Tryptophan in Genetically Engineered Escherichia Coli with TktA and PpsA Overexpression. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012, 2012, 605219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Young, K.D. Indole Production by the Tryptophanase TnaA in Escherichia Coli Is Determined by the Amount of Exogenous Tryptophan. Microbiology (N Y) 2013, 159, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Kamp, A.; Klamt, S. Growth-Coupled Overproduction Is Feasible for Almost All Metabolites in Five Major Production Organisms. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 15956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ding, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Fang, H.; Chen, T.; Zhang, D. Engineering Escherichia Coli to Improve Tryptophan Production via Genetic Manipulation of Precursor and Cofactor Pathways. Synth Syst Biotechnol 2020, 5, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gecse, G.; Labunskaite, R.; Pedersen, M.; Kilstrup, M.; Johanson, T. Minimizing Acetate Formation from Overflow Metabolism in Escherichia Coli: Comparison of Genetic Engineering Strategies to Improve Robustness toward Sugar Gradients in Large-Scale Fermentation Processes. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.-E.; Jung, H.-C.; Rhee, J.-S.; Pan, J.-G. Homofermentative Production of D- or L-Lactate in Metabolically Engineered Escherichia Coli RR1. Appl Environ Microbiol 1999, 65, 1384–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, L. V.; Fisher, S.H. Functional Roles of the Conserved Glu304 Loop of Bacillus Subtilis Glutamine Synthetase. J Bacteriol 2010, 192, 5018–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, D.J.; Chen, C.S.; Mascarenhas, Desmond. Direct Observation of Tryptophan Biosynthesis in Escherichia Coli by Carbon-13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Anal Chem 1986, 58, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütze, A.; Benndorf, D.; Püttker, S.; Kohrs, F.; Bettenbrock, K. The Impact of AckA, Pta, and AckA-Pta Mutations on Growth, Gene Expression and Protein Acetylation in Escherichia Coli K-12. Front Microbiol 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phue, J.-N.; Shiloach, J. Impact of Dissolved Oxygen Concentration on Acetate Accumulation and Physiology of E. Coli BL21, Evaluating Transcription Levels of Key Genes at Different Dissolved Oxygen Conditions. Metab Eng 2005, 7, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Jung, J.; Jang, I.-A.; Madsen, E.L.; Park, W. Role of Glyoxylate Shunt in Oxidative Stress Response. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2016, 291, 11928–11938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Gong, A.-D. Engineering the Glyoxylate Cycle for Chemical Bioproduction. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, B.; Shen, T.; Zhou, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, X.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Zheng, H.; Shi, Y. A Systematic Investigation of Escherichia Coli Central Carbon Metabolism in Response to Superoxide Stress. BMC Syst Biol 2010, 4, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millard, P.; Enjalbert, B.; Uttenweiler-Joseph, S.; Portais, J.-C.; Létisse, F. Control and Regulation of Acetate Overflow in Escherichia Coli. Elife 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cai, N.; Han, C.; Mao, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, N.; Xie, X. Betaine Supplementation Improved L-Threonine Fermentation of Escherichia Coli THRD by Upregulating Zwf (Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase) Expression. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology 2019, 39, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayley, S.; Lewis, B.A.; Record, M.T. Origins of the Osmoprotective Properties of Betaine and Proline in Escherichia Coli K-12. J Bacteriol 1992, 174, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, M.J.; Flatau, G.N.; Le Rudulier, D.; Clément, R.L.; Combarro Combarro, M.P. Intracellular Accumulation of Potassium and Glutamate Specifically Enhances Survival of Escherichia Coli in Seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol 1991, 57, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaggan, D.; Naprstek, J.; Buurman, E.T.; Epstein, W. Interdependence of K+ and Glutamate Accumulation during Osmotic Adaptation of Escherichia Coli. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1994, 269, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazuya-Murayama, K.; Aramaki, H.; Mishima, M.; Saito, K.; Ishida, S.; Yamada, K. Effect of L-Serine on the Biosynthesis of Aromatic Amino Acids in Escherichia Coli. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 2006, 52, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.-N.T.; Eom, G.T.; Hong, S.H. Improving L-Serine Production in Escherichia Coli via Synthetic Protein Scaffold of SerB, SerC, and EamA. Biochem Eng J 2019, 148, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S. Theoretical Study of Tryptophan Operon: Application in Microbial Technology. Biotechnol Bioeng 1988, 31, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, C.P.; Imanaka, T.; Aiba, S. Instability of Plasmid-harboring Strain of E. Coli in Continuous Culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 1982, 24, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Shimizu, K. Metabolic Regulation of Escherichia Coli and Its GdhA, GlnL, GltB, D Mutants under Different Carbon and Nitrogen Limitations in the Continuous Culture. Microb Cell Fact 2010, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kang, Y.; Yu, C.; Dai, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Yao, J.; Li, P.; Zheng, G.; Chen, X. Exponential Feeding Strategy of High-Density Cultivation of a Salt-Tolerant Aroma-Producing Yeast Zygosaccharomyces Rouxii in Stirred Fermenter. Biochem Eng J 2016, 111, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Doucette, C.D.; Fowler, W.U.; Feng, X.; Piazza, M.; Rabitz, H.A.; Wingreen, N.S.; Rabinowitz, J.D. Metabolomics-driven Quantitative Analysis of Ammonia Assimilation in E. Coli. Mol Syst Biol 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buurman, EdT. ; Joost Teixeira de Mattos, M.; Neijssel, OenseM. Futile Cycling of Ammonium Ions via the High Affinity Potassium Uptake System (Kdp) of Escherichia Coli. Arch Microbiol 1991, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.K.; Liu, W. Dynamic Analysis of Genetic Control and Regulation of Amino Acid Synthesis: The Tryptophan Operon in Escherichia Coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 1990, 35, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santillán, M.; Zeron, E.S. Dynamic Influence of Feedback Enzyme Inhibition and Transcription Attenuation on the Tryptophan Operon Response to Nutritional Shifts. J Theor Biol 2004, 231, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhartiya, S.; Rawool, S.; Venkatesh, K. V. Dynamic Model of Escherichia Coli Tryptophan Operon Shows an Optimal Structural Design. Eur J Biochem 2003, 270, 2644–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, Z.; Chang, Z.; Zeng, A. Nonlinear Dynamics of Regulation of Bacterial Trp Operon: Model Analysis of Integrated Effects of Repression, Feedback Inhibition, and Attenuation. Biotechnol Prog 2002, 18, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Gómez, D.I.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Gallardo-Navarro, Ó.A.; Santana-Solano, J.; Santillán, M. Bistable Behaviour and Medium-Dependent Post-Translational Regulation of the Tryptophanase Operon Regulatory Pathway in Echerichia Coli. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Mu, X.; Li, Z.; Teng, H.; Xiu, Z. Robustness and Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis for Trp Operon and Optimization of Tryptophan Production: An Integrated Model Considering Gene Regulation, Genes Interaction and Product Excretion. In Proceedings of the 2010 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering; IEEE, June 2010; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Petersen, S.D.; Radivojevic, T.; Ramirez, A.; Pérez-Manríquez, A.; Abeliuk, E.; Sánchez, B.J.; Costello, Z.; Chen, Y.; Fero, M.J.; et al. Combining Mechanistic and Machine Learning Models for Predictive Engineering and Optimization of Tryptophan Metabolism. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Pathways | Genes* | Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low DO | Acetate, glyoxylate shunt, TCA cycle | pta, ackA, poxB, tdcD, gltA, icd | Acetyl-CoA, pyruvate, lactate and acetate accumulation. | [4,38,41,55,62,79,80] |
| High DO | Acetate degradation, glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, PTS, PPP, glutamate and tryptophan | fba, rpoS, acs, pckA, ppsA, ppc, maeA, pfk, zwf, pgl, tktA, araD, aroG, aroK, trpEDCBA, gdhA, pntAB | Acetate consumption, production of PEP, E4P, NADPH, tryptophan and glutamate, reduction of glucose consumption and oxidative stress. | [4,38,41,62,74,81,82,83] |
| Low pH | Glycolysis, acetate and TCA cycle | pfk, sucB, sucC | Low growth rate, stable plasmids, low acetate production and tryptophan crystallization. | [4,25,32,41,61] |
| High pH | Acetate, shikimate and tryptophan | pta, aroK, tnaA, tnaB | Accumulation of acetate, NH4+ and K+, and tryptophan production. | [12,41,61] |
| Low growth rate | Glycolysis, acetate | Plasmid stability, low acetate production, increase tryptophan production. | [3,16,53,61] | |
| High growth rate | Glycolysis, acetate | Biomass and acetate accumulation. | [3,61,64,68,75] | |
| Low feed rate | Glycolysis, acetate and tryptophan | Low production of acetate, biomass and tryptophan. | [4,26,38,41,55,62,63,64,68] | |
| High feed rate | Acetate and glutamate | gdhA | Acetate and glutamate accumulation. | [4,26,47,61,68,75,80,84] |
| Calcium | TCA cycle | gltA, icd, sucC | Increase ATP and biomass production | [40,42] |
| Betaine | PPP, stress response and K+ uptake | zwf | Activation of PPP, osmotic stress relief, reduce glutamate accumulation, reduce K+ uptake. | [85,86] |
| Citrate | Ca2+ uptake, glycolysis, PPP and TCA cycle | pykAF, zwf, gltA | Reduce production of acetate and glutamate while increase accumulation of PEP, NADH, NADPH and ATP. | [48,66] |
| High organic nitrogen | Incrase acetate and biomass production. | [56,66] | ||
| Inorganic nitrogen | Glutamate, tryptophan, glutamine | glnA | Increase energy waste, change pH, affect ionic strength, provide of NH4+ for tryptophan production and reduce plasmid stability. | [3] |
| Phosphate | Glycolysis | Increase growth rate, increase acetate accumulation. | [12,43,65] | |
| Surfactants | PPP, tryptophan transport, glutamate | zwf, yddG, trpBA | Enhance crystallization and secretion of tryptophan, reduce inhibition and is a sink for indole. | [9,12,65] |
| Cation’s accumulation | Change pH and ionic strength, difficult the purification of tryptophan and increase glutamate accumulation. | [41,61,86,87,88] | ||
| Precursors | Tryptophan, isoleucine, threonine | trpC, serA, thrA | Improve tryptophan production, feedback inhibition of precursor pathway. | [9,41,64] |
| Phenylalanine | Relieves serine inhibition, block common pathways of aromatic amino acids. | [5,89] | ||
| Leucine | Relieves serine inhibition. | [89] | ||
| Isoleucine | Isoleucine | Relieves serine inhibition. | [89] | |
| Methionine | Methionine | Increase production of proteins and reduce accumulation of acetate. | [6,19,51,66,68] | |
| High volume of inoculum | Increase rate growth and reduce lag-phase. | [43,59] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





