Submitted:
29 September 2024
Posted:
30 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Simulation of BDR over Ni/Cr Catalyst
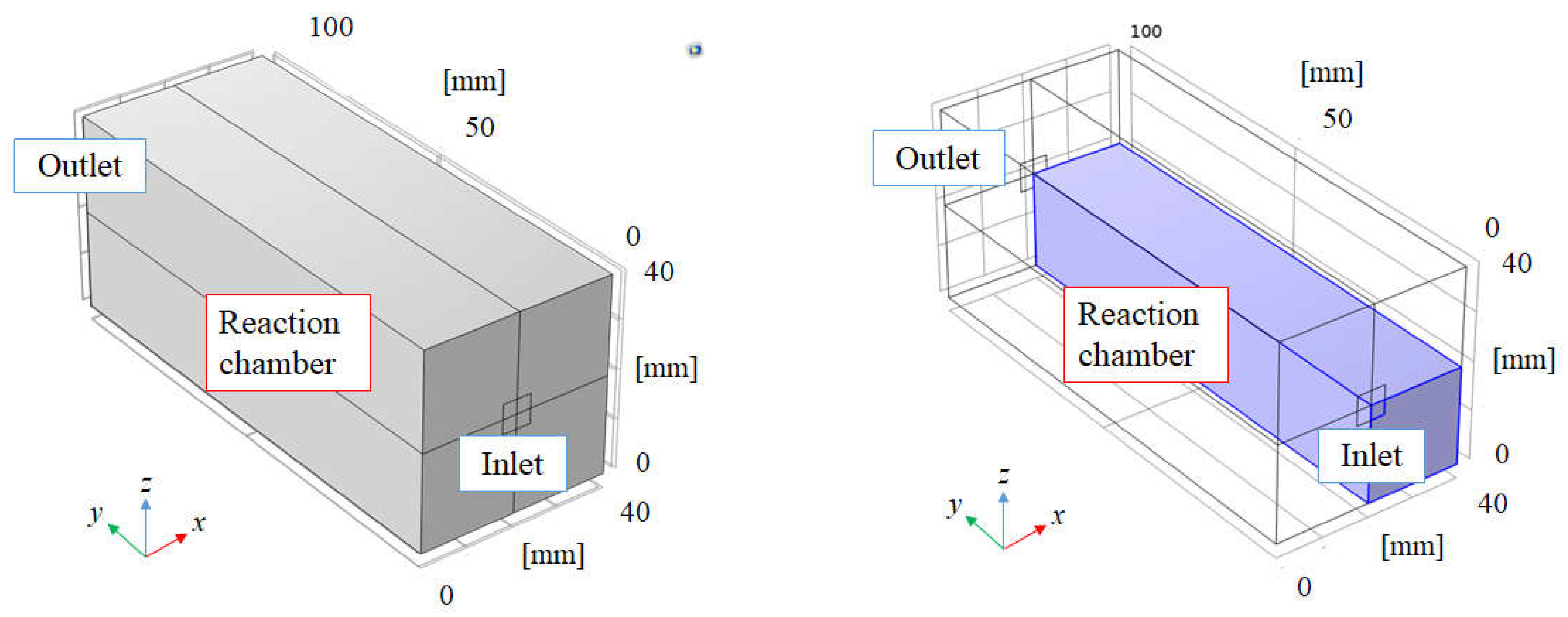
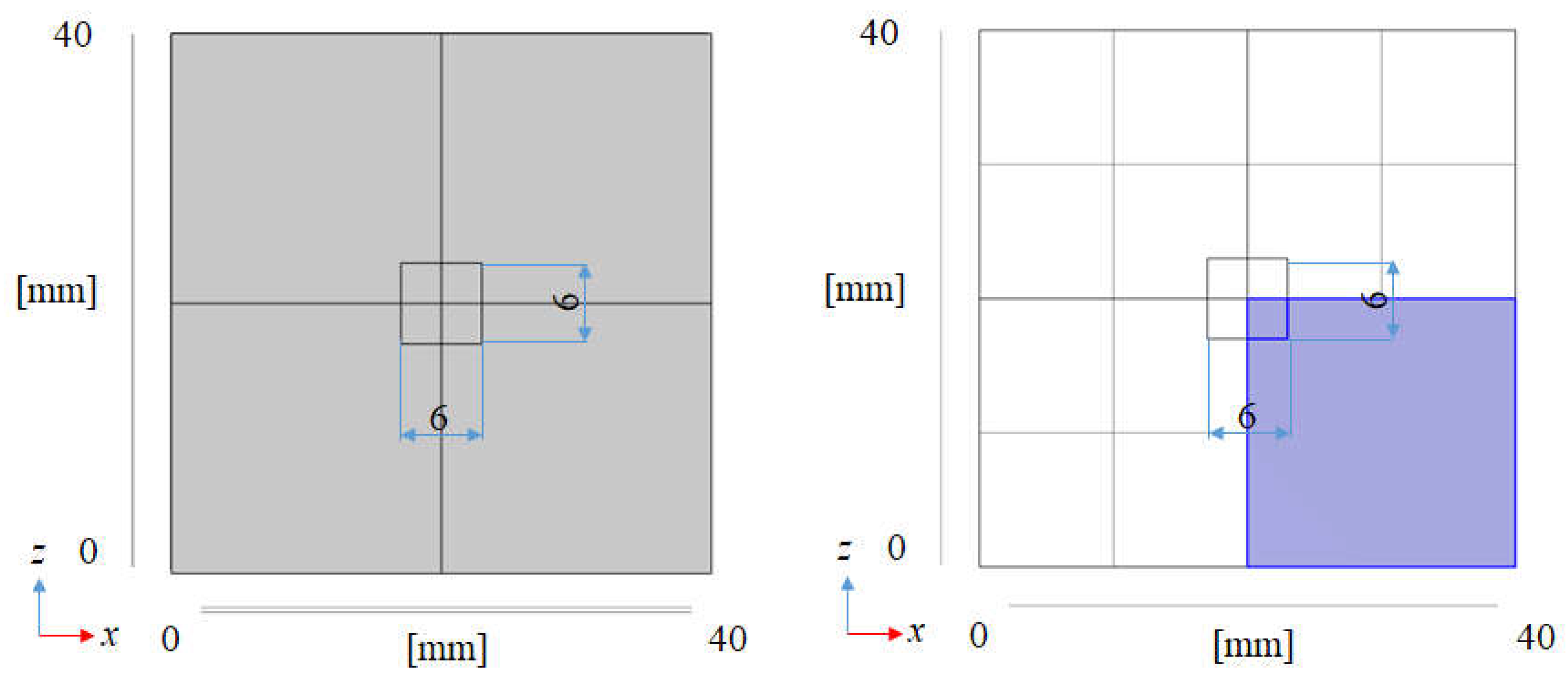
2.1. A Mathematical Formulation
2.3. Kinetic Modeling of BDR
2.4. Numerical Simulation Parameters and Conditions for BDR
- (i)
- Catalyst is a porous material. The porosity, permeability, constant pressure specific heat and thermal conductivity and isotropic.
- (ii)
- Wall temperature is isothermal.
- (iii)
- Gas is a Newton fluid and an ideal gas.
- (iv)
- Wall of reactor excluding inlet and outlet is no-slip.
- (v)
- The pressure of outlet is atmosphere (gauge pressure = 0 Pa).
- (vi)
- The temperature of inflow gas is same as the initial reaction temperature.
- (vii)
- The produced carbon is treated as a gas.
2.5. Evaluaion Factors and Reaction Pathways in BDR
3. Results and Discussion
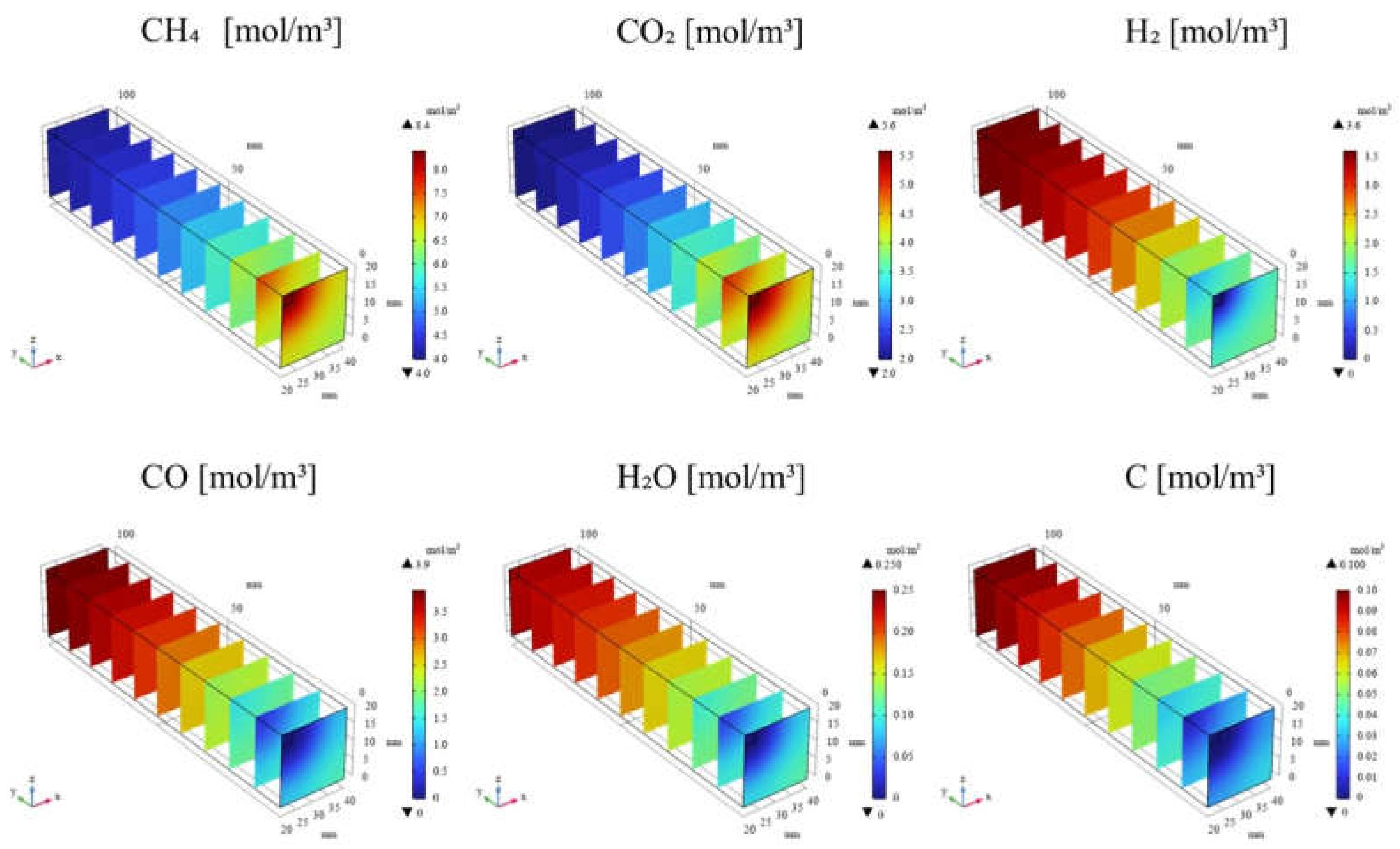
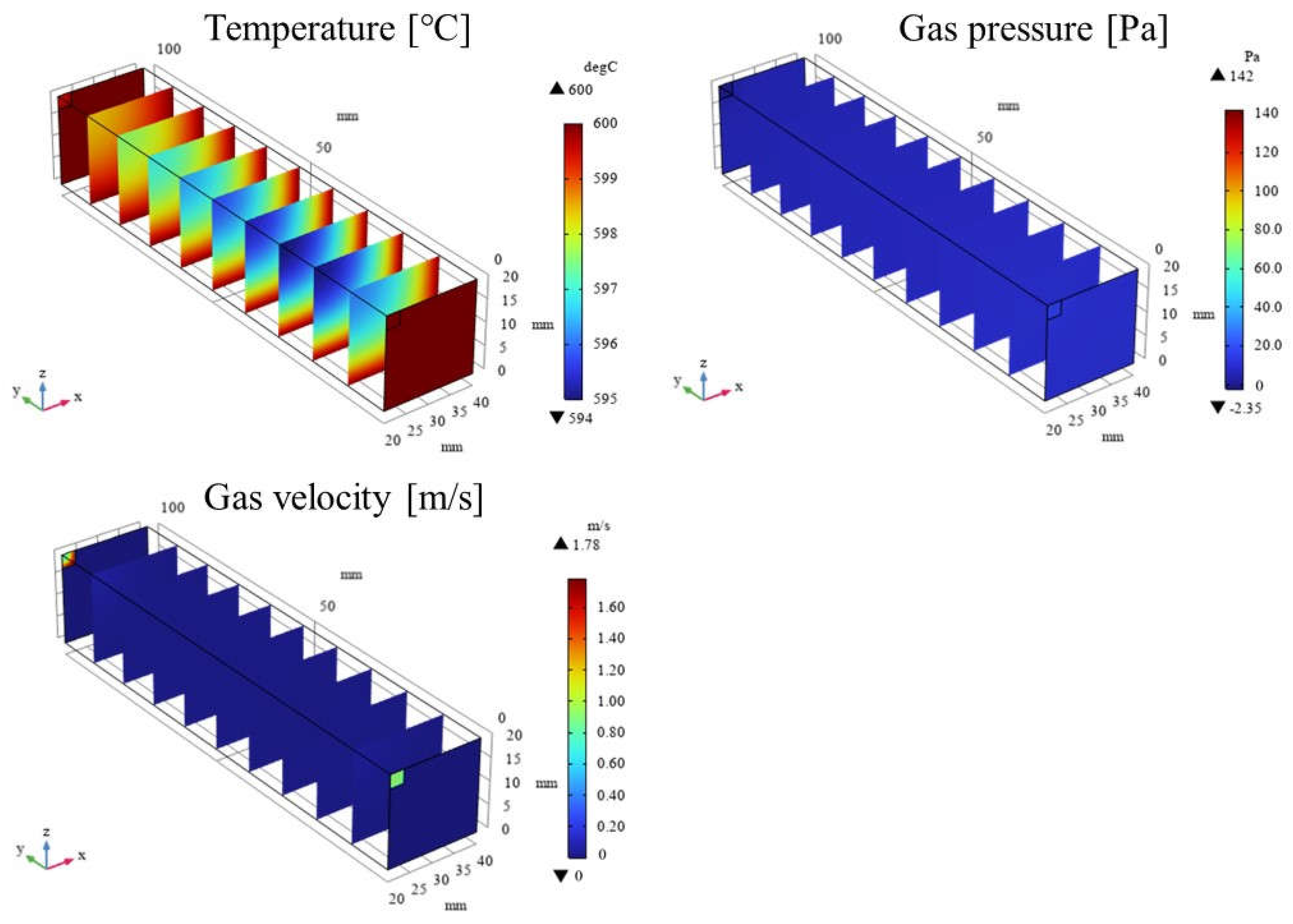
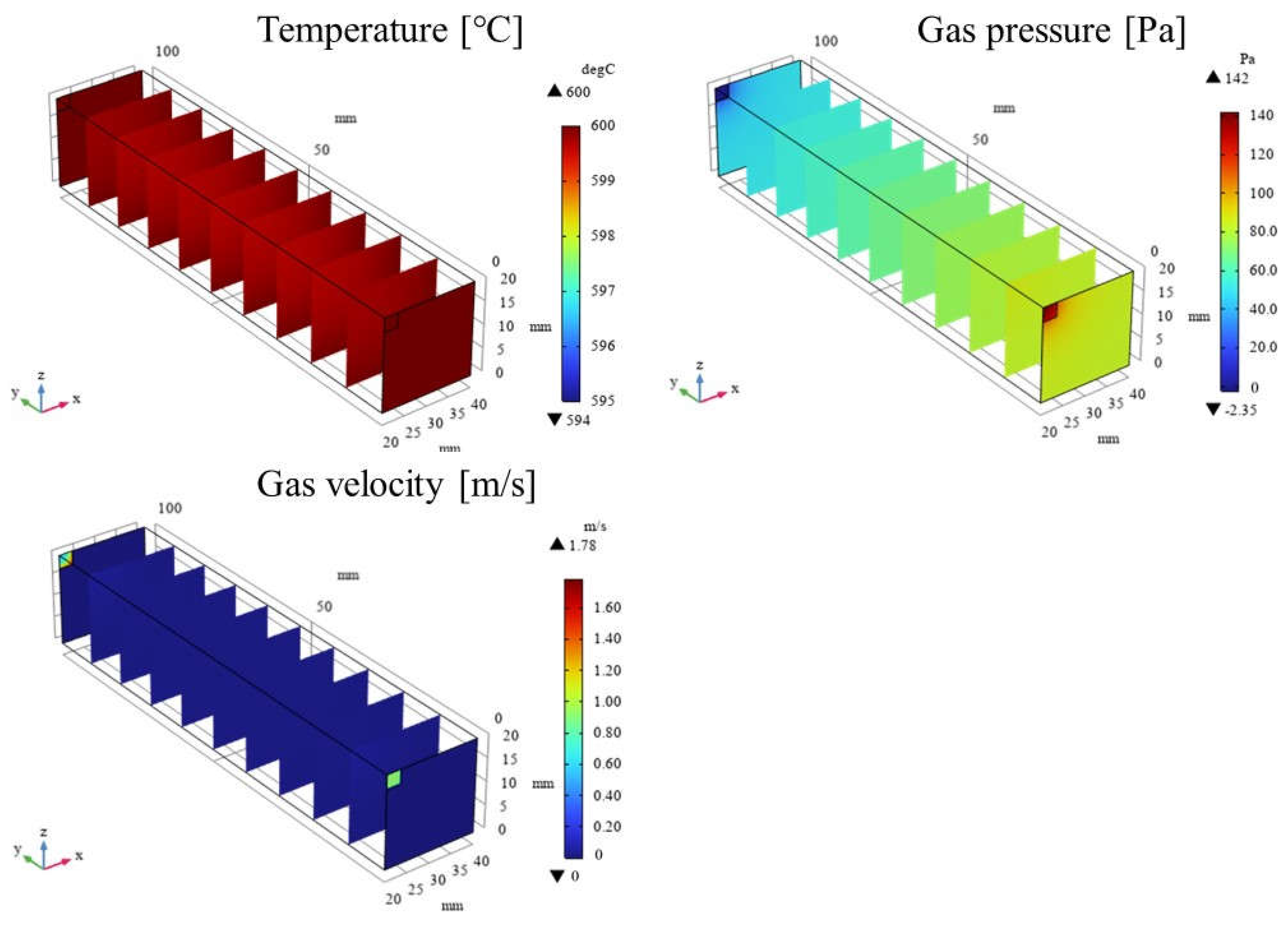
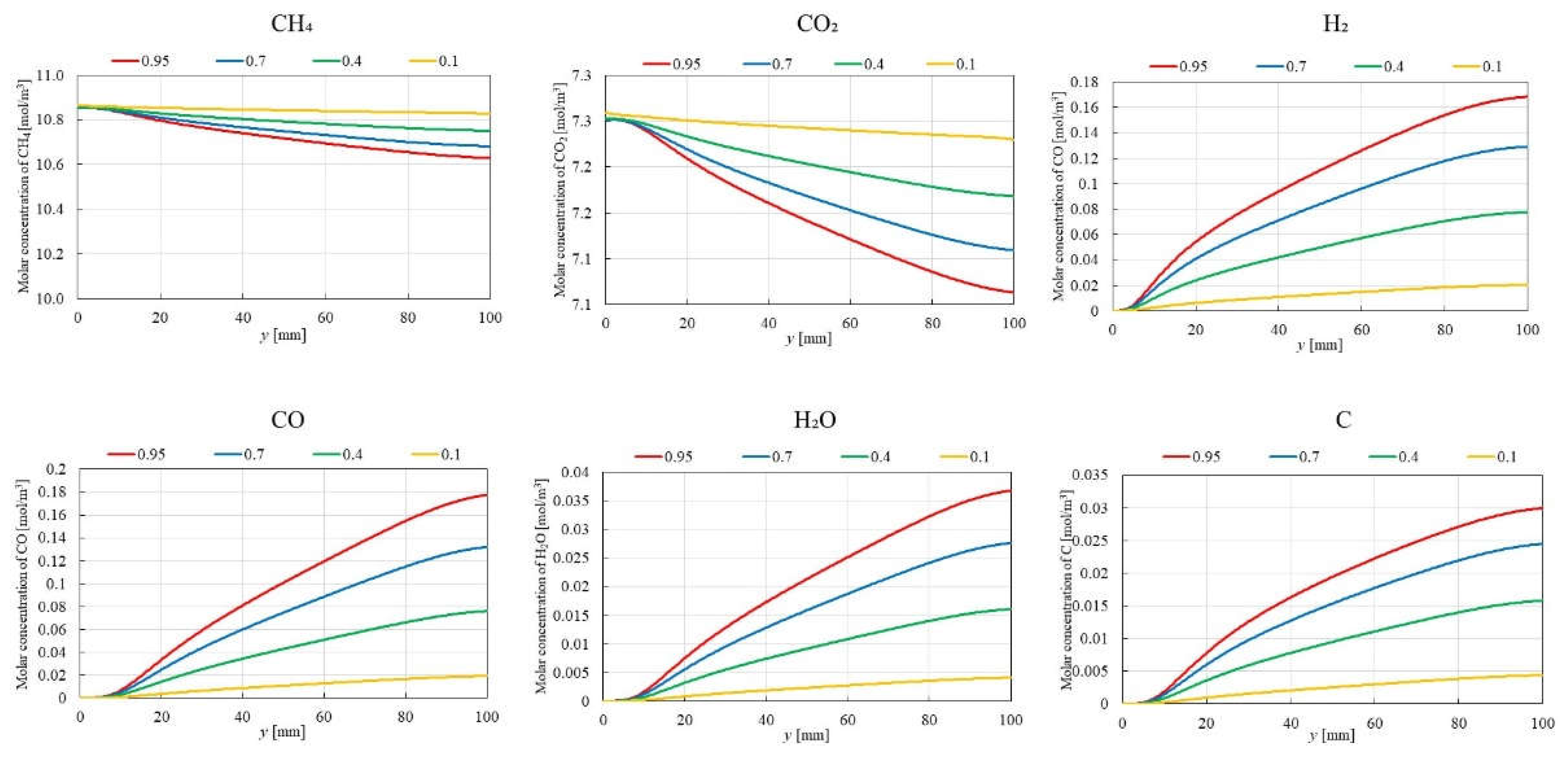
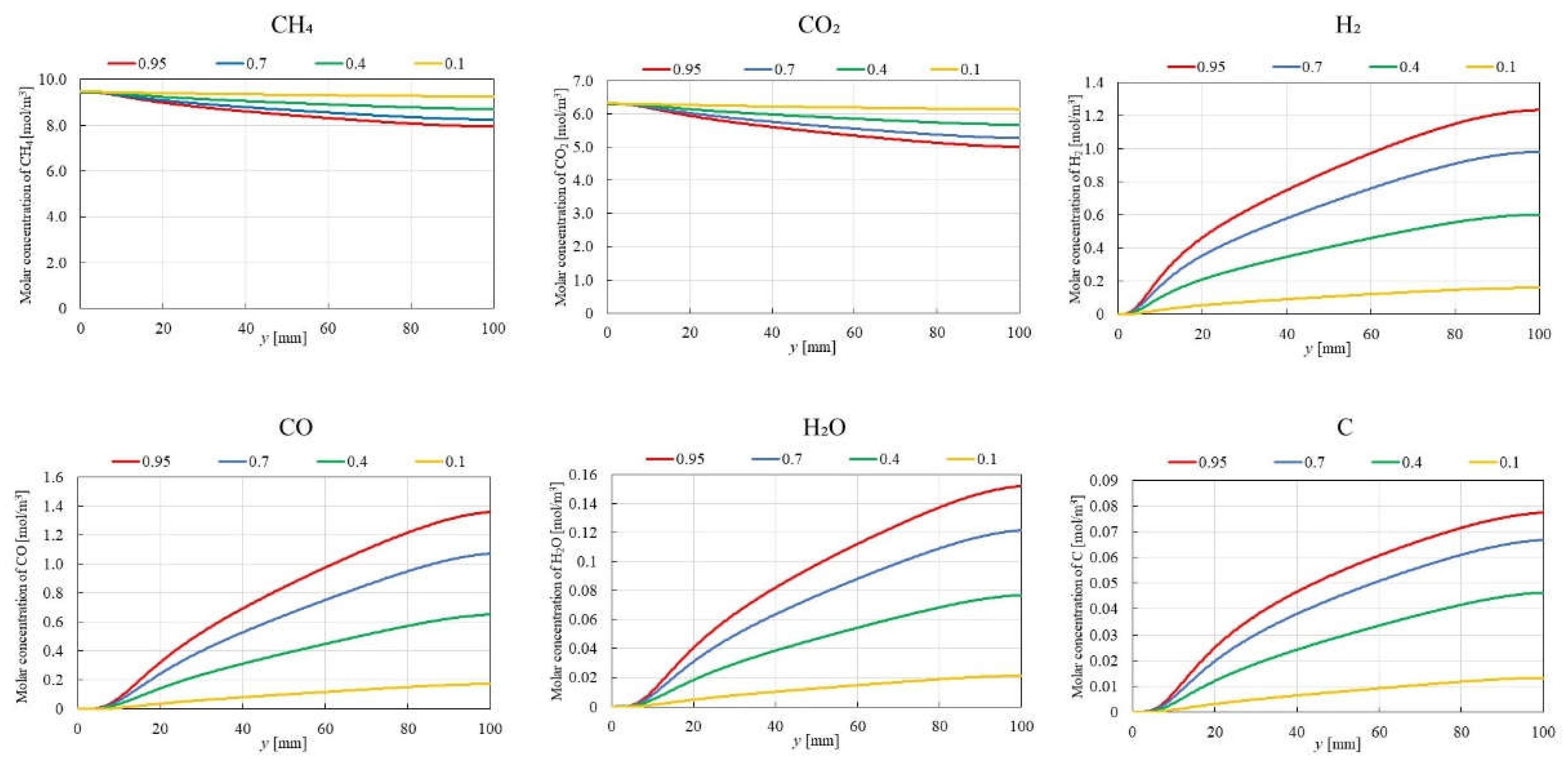
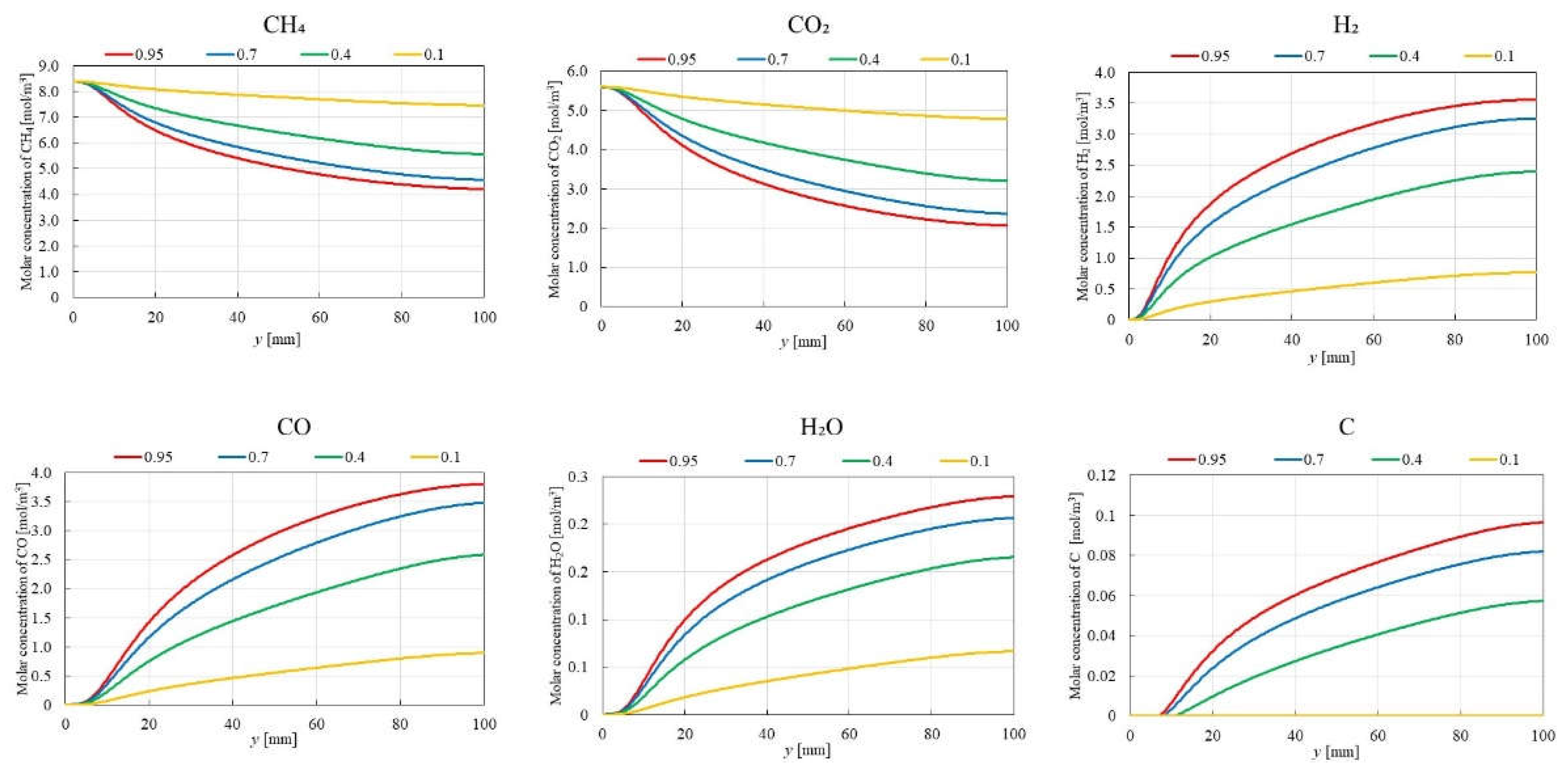
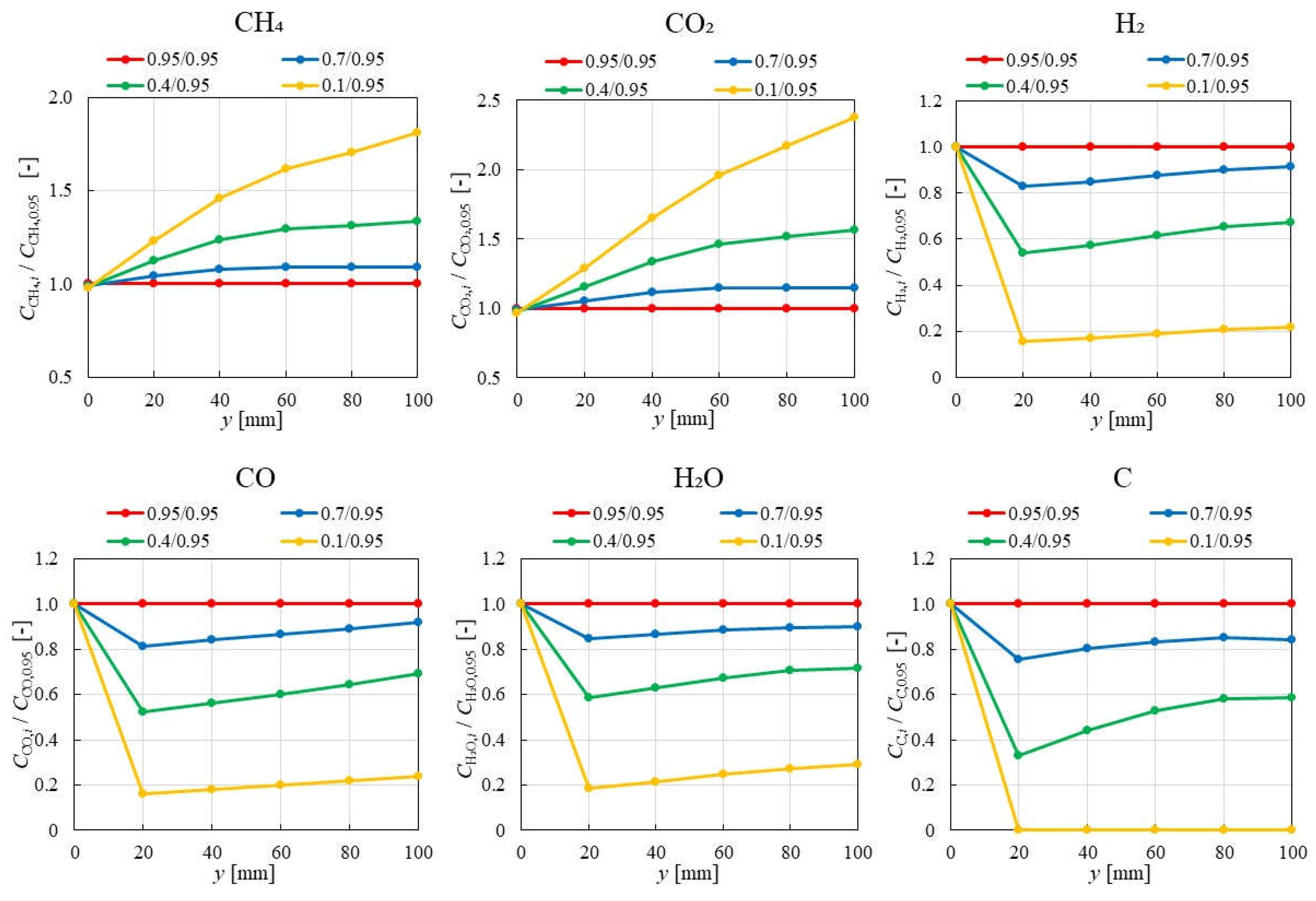
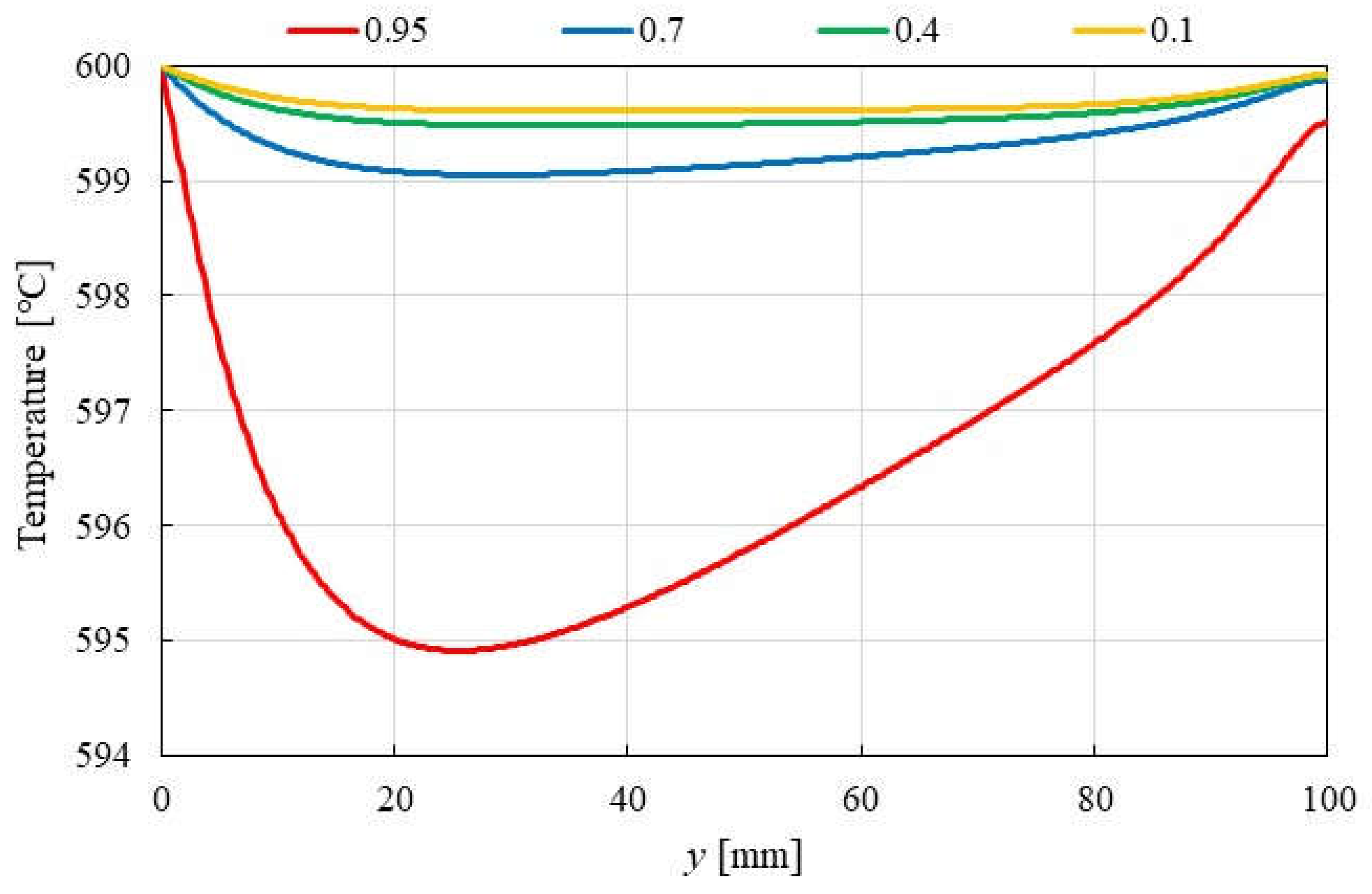
3.1. Impact of Catalyst Porosity on Reaction, Heat, and Mass Transfer Phenomena in BDR
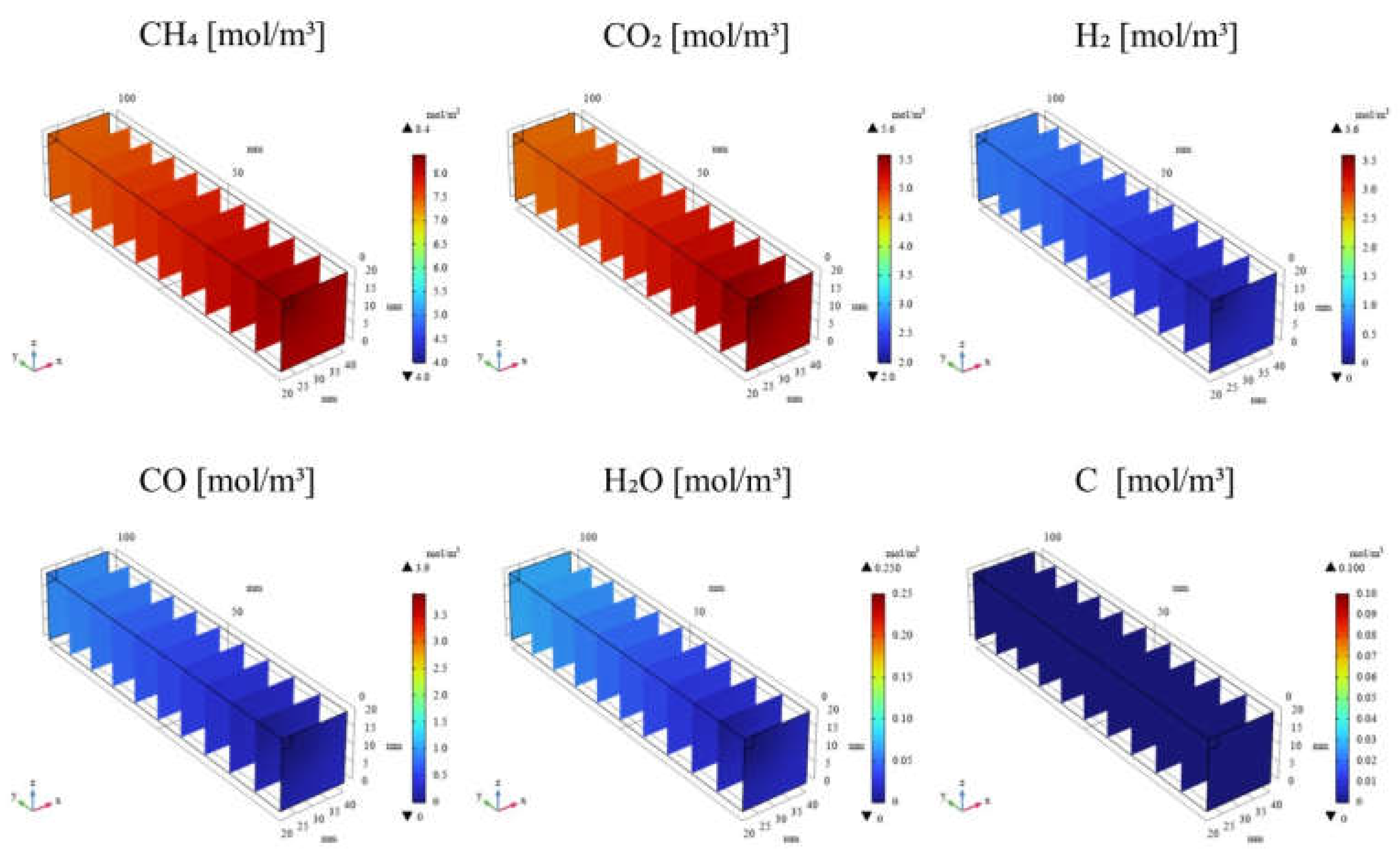
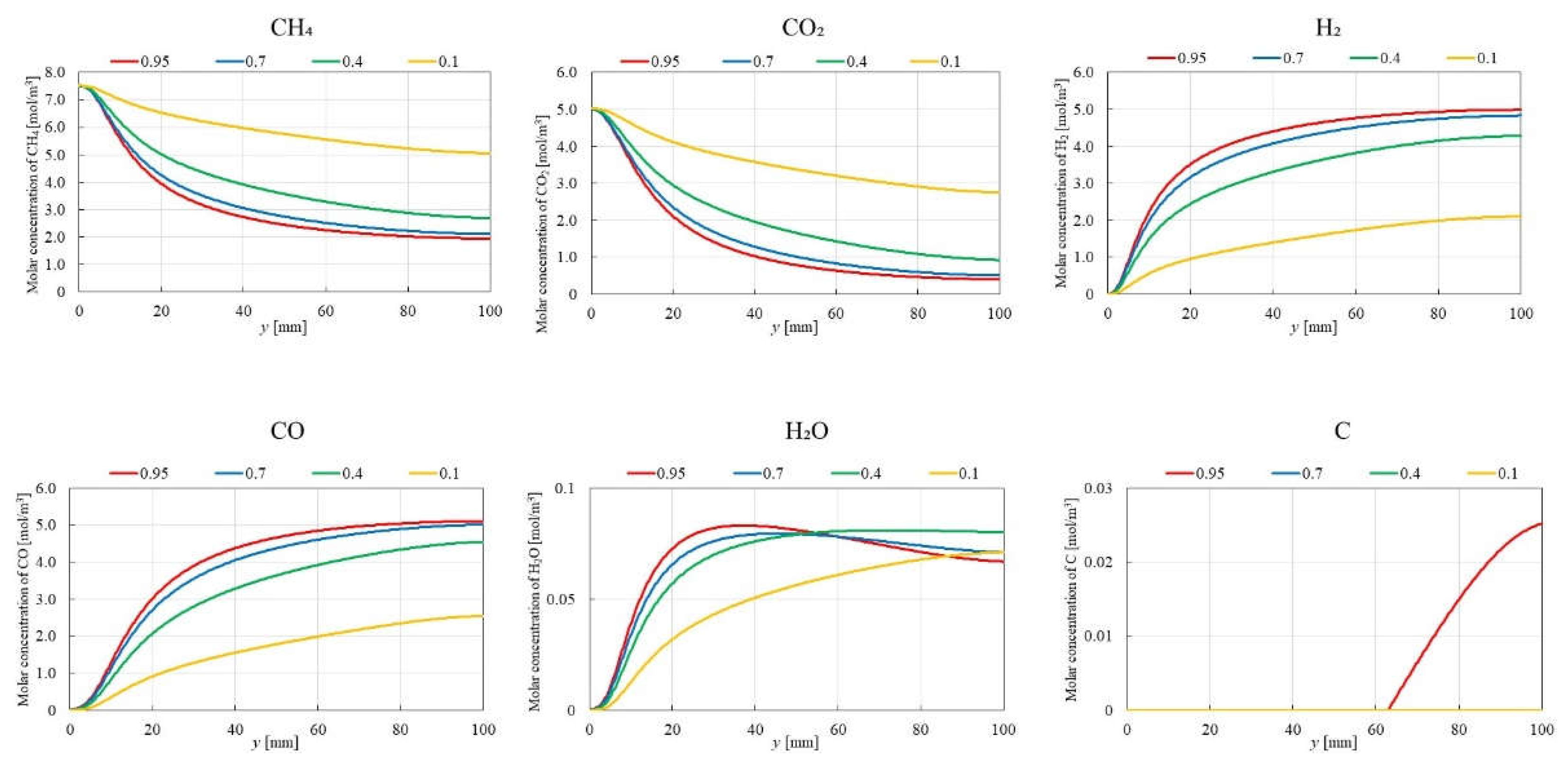
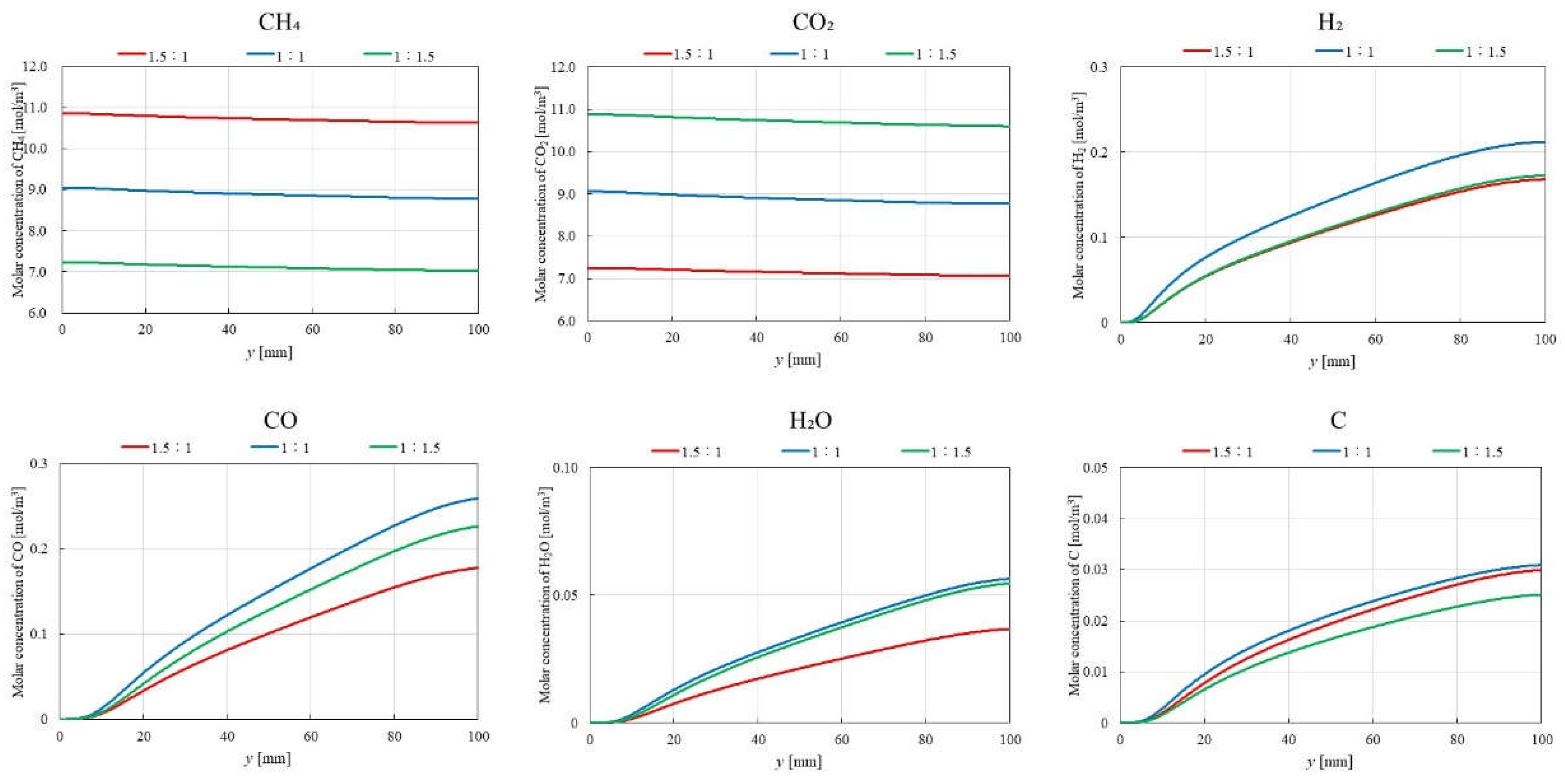
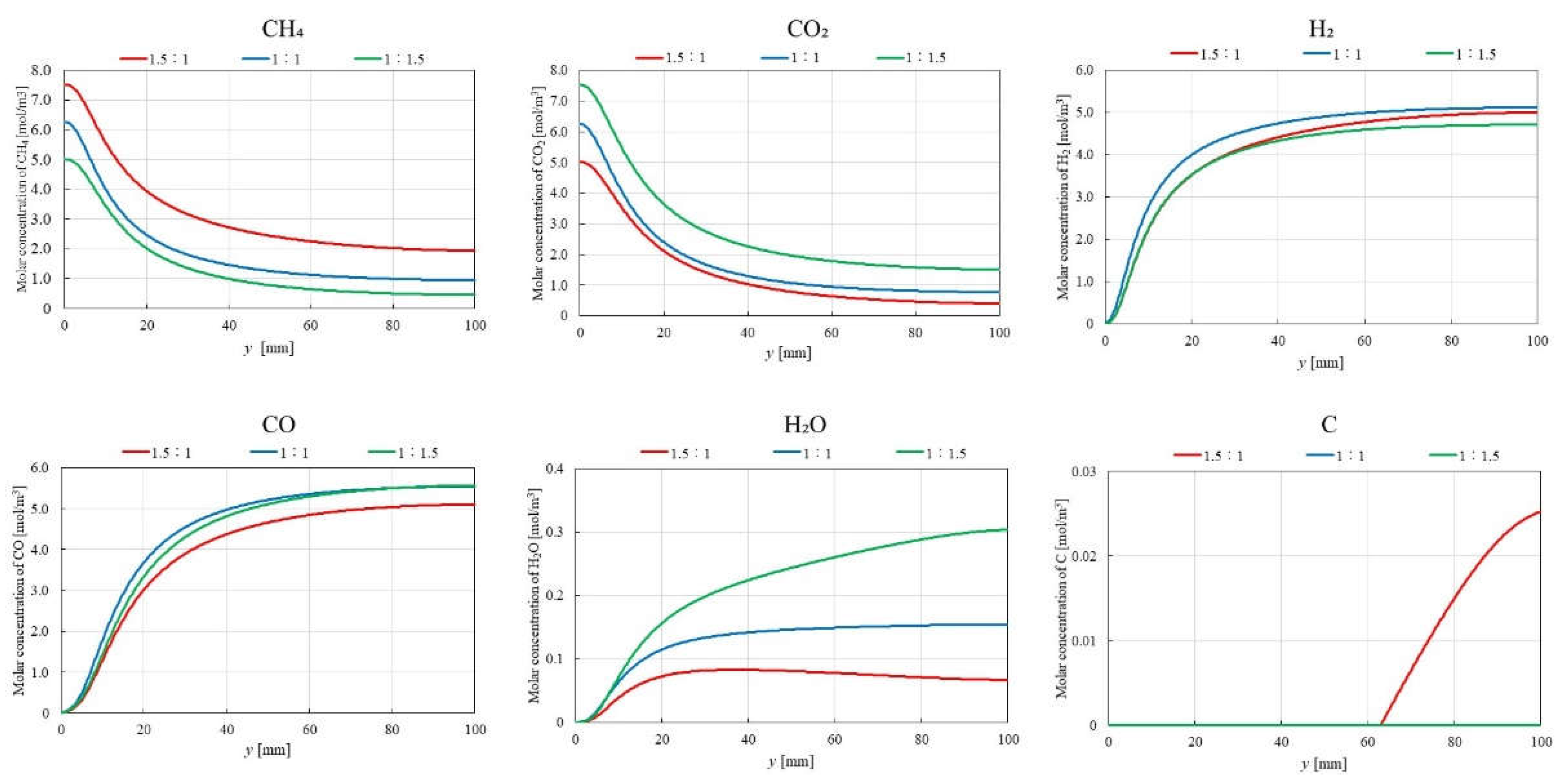
3.2. Influence of Molar Ratio of CH4:CO2 on BDR over Ni/Cr Catalyst
3.3. Comparison of Numerical Simulation and Experimental Results for BDR
4. Conclusion
- The results indicate that increasing εp leads to a decrease in the molar concentrations of CH4 and CO2, while simultaneously enhancing the molar concentrations of H2, CO, H2O and C. This enhancement is attributed to the improved mass diffusion within the porous catalyst structure, while facilitates the progress of the reforming reactions.
- A positive correlation is observed between the reaction temperature and the molar concentrations of H2 and CO. The enhancement of H2 and CO production is attributed to the promotion of DR, SR, RWGS and MR at elevated reaction temperatures.
- The results indicate that the influence of εp on the distribution of molar concentration of all gases increases with rising εp. Notably, the impact of εp on the product species (H2, CO, H2O and C) is more pronounced near the inlet (y = 20 m), whereas the effect of εp on reactant species (CH4 and CO2) is more significant near the outlet (y > 60 m).
- A more pronounced temperature drop near the inlet (y = 20 m) is observed with increasing εp. This phenomenon is attributed to the dominance of the endothermic reactions in this region, which absorb heat from the surroundings, leading to a localized temperature decrease.
- The highest molar concentration of H2 and CO2 are consistently obtained for CH4:CO2 = 1:1, regardless of the reaction temperature. This finding aligns with the theoretical stoichiometry of DR, where equal molar amounts of CH4 and CO2 are converted to H2 and CO2. Therefore, the optimal CH4:CO2 for maximizing product yields in BDR is 1:1.
- The highest molar concentration of H2O is observed at 700 ℃ for CH4:CO2 = 1:1.5, whereas the highest molar concentration of H2O at 400 ℃ occurred with CH4:CO2 = 1:1 and 1:1.5. Additionally, the molar concentration of C is found to be lower at 700 ℃ compared to 400 ℃, suggesting a reduced contribution of BD at higher reaction temperatures.
- The results indicate that increasing εp leads to higher CH4 conversion, CO2 conversion, H2 yield and H2 selectivity. Conversely, CO selectivity decreases with increasing εp. Furthermore, both numerical simulations’ and experiments’ data demonstrate a positive correlation between the reaction temperature and H2 yield and H2 selectivity. This enhancement is attributed to the endothermic nature of the reactions producing H2, which are favored at higher reaction temperatures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalai, D.Y.; Stangeland, K.; Jin, R.; Tucho, W.M.; Yu, Z. Biogas dry reforming for syngas production on La promoted hydrotalcitederived Ni catalyst. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 2018, 43, 19438–19450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2. World Bioenergy Association. Available online: https:worldbioenergy.org/global-bienergy-statistics (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- The Japan Gas Association. Available online: https://www.gas.or.jp/gas-life/biogas/ (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Nishimura, A.; Takada, T.; Ohata, S.; Kolhe, M.L. Biogas dry reforming for hydrogen through membrane reactor utilizing negative pressure. fuels. 2021, 2, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Ito, S.; Kolhe, M.L. Performance analysis of hydrogen production for a solid oxide fuel cell system using a biogas dry reforming membrane reactor with Ni and Ni/Cr catalysts. fuels. 2023, 4, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, A.; Sato, R.; Hu, E. An energy production system powered by solar heat with biogas dry reforming reactor and solar heat with biogas dry reforming reactor and solid oxide fuel cell. Smart Grid and Renewable Energy. 2023, 14, 85–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Dhir, A. Hydrogen augmentation of biogas through dry reforming over bimetallic nickel-cobalt catalysts supported on titania. Fuel. 2020, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.; Farooqi, A.S.; Keong, L.K.; Hellgardt, K.; Abdullah, B. Contemporary trends in composite Ni-based catalysts for CO2 reforming of methane. Chemical Engineering Science. 2021, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sache, E.L.; Moreno, A.A.; Reina, T.R. Biogas conversion to syngas using advanced Ni-promoted pyrochlore catalysts: effect of the CH4/CO2 ratio. Frontiers in Chemistry. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosset, M.; Feris, L.A.; Perez-Lopez, O.W. Biogas dry reforming using Ni-Al-LDH catalysts reconstructed with Mg and Zn. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 2021, 46, 20359–20376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Modal, P. Optimization of CO2 reforming of methane process for the syngas production over Ni-Ce/TiO2-ZrO2 catalyst using the Taguchi method. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 2021, 46, 22799–22812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.A.; Ramirez-Reina, T.; Ivanoya, S.; Roger, A.C.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Bimetallic Ni-Ru and Ni-Re catalysts for dry reforming of methane: understanding the synergies of the selected promoters. Frontiers in Chemistry. [CrossRef]
- Ha, Q.L.M.; Atia, H.; Kreyenschulte, C.; Lund, H.; Bartling, S.; Lisak, G.; Wohlrab, S.; Armbruster, U. Effects of modifier (Gd, Sc, La) addition on the stability of low Ni content catalyst for dry reforming of model biogas. Fuel. 2022, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviani, M.; Rezaei, M.; Alavi, S.M.; Akbari, E. High coke resistance Ni-SiO2@SiO2 core-shell catalyst for biogas dry reforming: effects of Ni loading and calcination temperature. Fuel. 2022, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviani, M.; Rezaei, M.; Alavi, S.M.; Akbari, E. Biogas dry reforming over nickel-silica sandwiched core-shell catalysts with various shell thicknesses. Fuel. 2024, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, A.G.; Siakavelas, G.I.; Tsiotsias, A.I.; Charisiou, N.D.; Ehrhardt, B.; Wang, W.; Sebastian, V.; Hinder, S.J.; Baker, M.A.; Mascotto, S.; Goula, M.A. Biogas dry reforming over Ni/LnOx-type catalysts (Ln = La, Ce, Sm or Pr). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 2023, 48, 19953–19971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chava, R.; Varma, D.B.A; Roy, B.; Appari, S. Recent advances and perspectives of perovskite-derived Ni-based catalysts for CO2 reforming of biogas. Journal of CO2 Utilization. 2022, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Ito, S.; Kolhe, M.L. Performance analysis of hydrogen production for a solid oxide fuel cell system using a biogas dry reforming membrane reactor with Ni and Ni/Cr catalysts. fuels. 2023, 4, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, A.; Ichikawa, M.; Yamada, S.; Ichii, R. The characteristics of a Ni/Cu/Ru catalyst for a biogas dry reforming membrane reactor using a Pd/Cu membrane and a comparison of it with a Ni/Cr catalyst. hydrogen. 2024, 5, 414–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lim, H. The power of molten salt in methane dry reforming: conceptual design with a CFD study. Chemical Engineering and Processing- Process Intensification. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lim, H. The effect of changing the number of membranes in methane carbon dioxide reforming: a CFD study. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. 2020, 87, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, K.; Ghahremani, M.; Amiri, T.Y.; Basile, A. Performance evaluation of Pd-Ag membrane reactor in glyceol steam reforming process: development of the CFD model. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 2019, 44, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Lee, S.; Lim, H. Numerical modeling studies for a methane dry reforming in a membrane reactor. Journal of Nature Gas Science and Engineering. 2016, 34, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, A.; Mishima, D.; Ito, S.; Konbu, T.; Hu, E. Impact of separator thickness on relationship between temperature distribution and mass & current density distribution in single HT-PEMFC. Thermal Science and Engineering. 2023, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lim, H. The power of molten salt in methane dry reforming: conceptual design with a CFD study. Chemical Engineering and Processing. 2020, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, A.; Sedaghat, M.H.; Jamshidi, S.; Shariati, A.; Rahimpour, M.R. A comprehensive CFD simulation of an industrial-scale side-fired steam methane reformer to enhance hydrogen production. Chemical Engineering and Processing. 2023, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benguerbaa, Y.; Virginieb, M.; Dumas, C. Computational fluid dynamics study of the dry reforming of methane over Ni/Al2O3 catalyst in membrane reactor – coke deposition. Kinetic and Catalysis. 2017, 58, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Initial reaction temperature [℃] | 400, 500, 600 |
| Pressure in reactor [Pa] | 1.013×105 |
| Inlet flow rate of CH4 [NL/min] (CH4:CO2 = 1.5:1, 1:1, 1:1.5) |
1.088, 0.725, 0.725 |
| Inlet flow rate of CO2 [NL/min] (CH4:CO2 = 1.5:1, 1:1, 1:1.5) |
0.725, 0.725, 1.088 |
| Outlet pressure [Pa] | 1.013×105 |
| Density of catalyst [kg/m3] | 8901, 8752, 8709, 8664, 8619 (@20 ℃, 400 ℃, 500 ℃, 600 ℃, 700 ℃) |
| Porosity of catalyst (εp) [-] | 0.95, 0.7, 0.4, 0.1 |
| Permeability of catalyst [m2] | 1.9×10-8, 1.4×10-8, 8.0×10-9, 2.0×10-9 (εp = 0.95, 0.7, 0.4, 0.1) |
| Constant pressure specific heat of catalyst [J/(kg・K)] | 458, 558, 551, 541, 538 (@20 ℃, 400 ℃, 500 ℃, 600 ℃, 700 ℃) |
| Thermal conductivity of catalyst [W/(m・K)] | 91.2, 65.3, 66.5, 69.1, 72.2 (@20 ℃, 400 ℃, 500 ℃, 600 ℃, 700 ℃) |
| Apparent density of catalyst bed in reactor [kg/m3] | 418, 2504, 5008, 7511 (εp = 0.95, 0.7, 0.4, 0.1) |
| Apparent thermal conductivity of catalyst bed in reactor [W/(m・K)] | 3.5, 20.9, 41.7, 62.5 (εp = 0.95, 0.7, 0.4, 0.1) |
| εp [-] | CH4 conversion [%] | CO2 conversion [%] | H2 yield [%] | H2 selectivity [%] | CO selectivity [%] |
| 0.95 | 49.9 | 63.5 | 21.3 | 48.2 | 51.8 |
| 0.7 | 45.6 | 58.2 | 19.5 | 48.1 | 51.9 |
| 0.4 | 33.8 | 43.3 | 14.3 | 47.8 | 52.2 |
| 0.1 | 11.1 | 14.8 | 4.6 | 45.9 | 54.1 |
| Reaction temperature [℃] | CH4 conversion [%] | CO2 conversion [%] | H2 yield [%] | H2 selectivity [%] | CO selectivity [%] |
| 400 | 2.1 | 2.7 | 0.8 | 48.0 | 52.0 |
| 500 | 16.2 | 21.0 | 6.5 | 47.1 | 52.9 |
| 600 | 49.9 | 63.5 | 21.3 | 48.2 | 51.8 |
| 700 | 74.4 | 92.1 | 33.2 | 49.4 | 50.6 |
| Reaction temperature [℃] | CH4 conversion [%] | CO2 conversion [%] | H2 yield [%] | H2 selectivity [%] | CO selectivity [%] |
| 400 | 24.1 | -29.7 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 99.8 |
| 500 | 8.24 | -3.08 | 1.01 | 2.09 | 97.9 |
| 600 | 12.7 | 0.08 | 4.48 | 7.24 | 92.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





