Submitted:
29 September 2024
Posted:
30 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
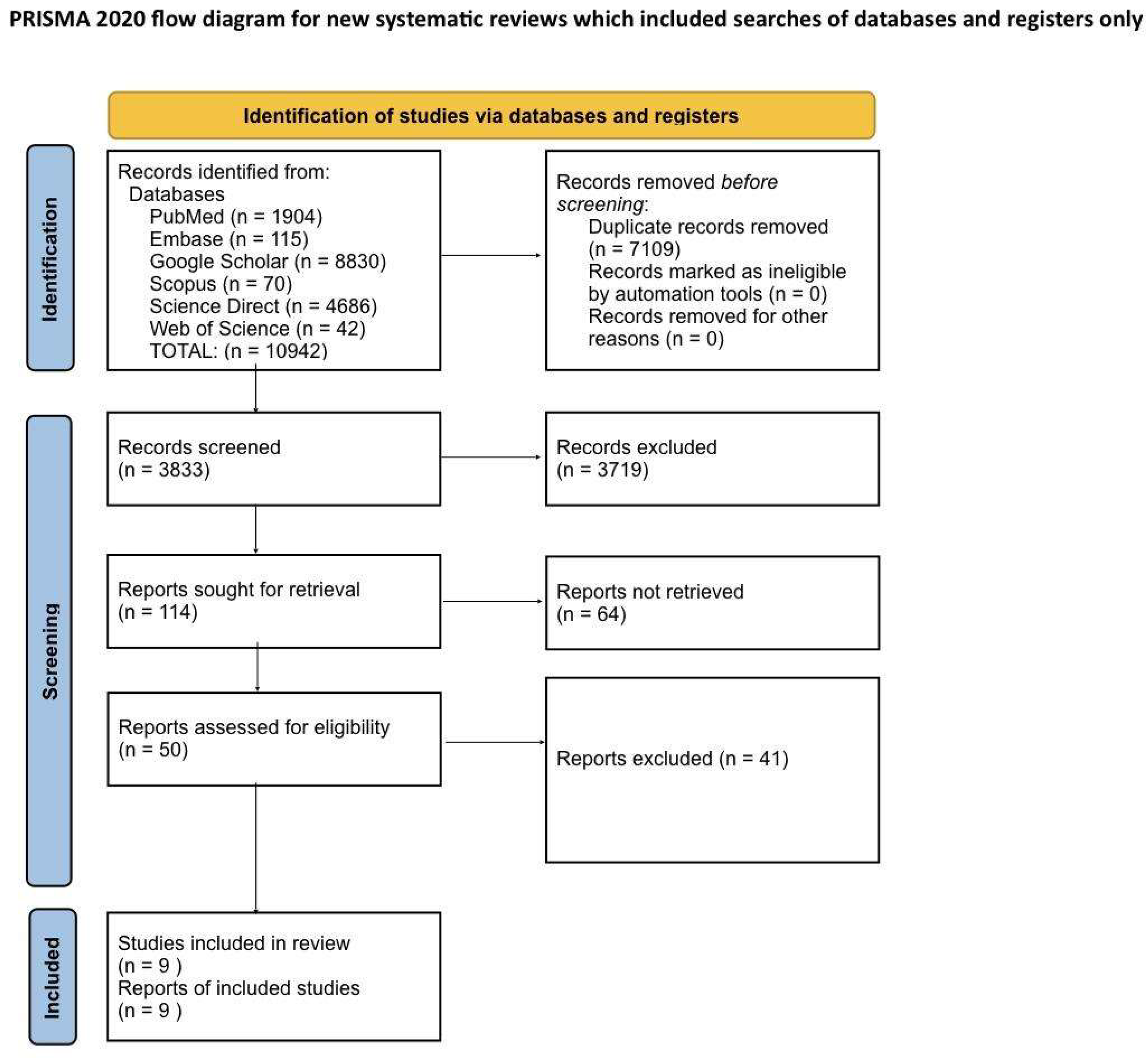
Systematic Literature Search and Study Selection
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- Population: adult patients diagnosed with Narcolepsy.
- Intervention: treatment with Modafinil.
- Comparison: placebo or no intervention.
- Outcome: excessive daytime sleepiness symptoms were measured by the Maintenance of Wakefulness Test (MWT) and Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS).
Search Strategy
Quality Appraisal

Data Extraction and Outcome Measures
Meta-Analysis
Results
| Author, year | Country | Study Design | Number of patients | Intervention | Follow up duration | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moldofsky et. al, 2000 [35] | Canada | Randomised Double Blind Crossover study |
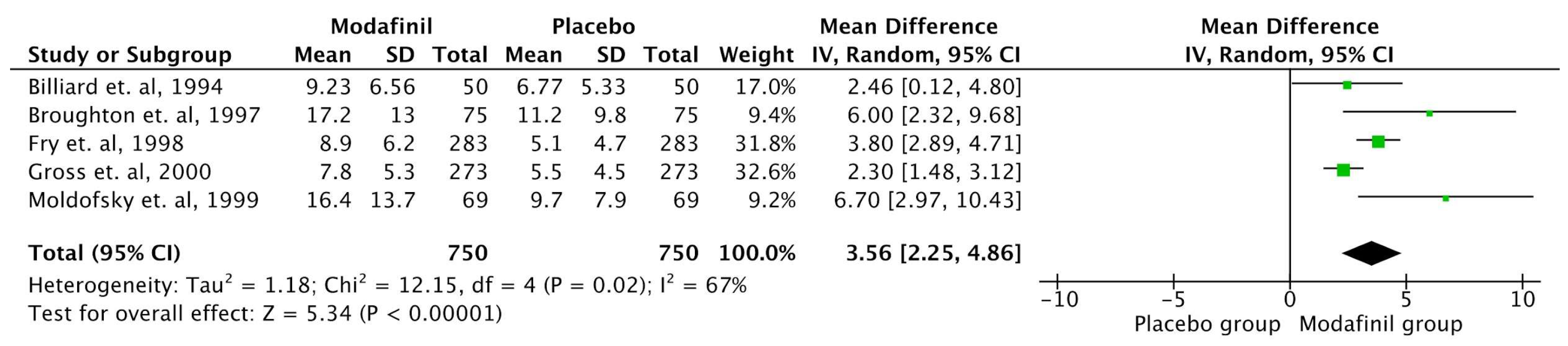
63 | Modafinil 500 mg daily dose during open label and were continued with either Modafinil or Placebo during double blind period. | 24 weeks | This study demonstrated that modafinil is effective and well-tolerated in the long-term treatment of EDS in narcoleptic patients. Over a 16-week open-label period, followed by a 2-week randomized, double-blind phase, patients on modafinil (mean dose 330 mg) showed a significant reduction in EDS. The MWT revealed a 70% longer sleep latency in the modafinil group compared to placebo. Similarly, the ESS scores were lower in the modafinil group, and episodes of severe somnolence and sleep were reduced. Importantly, no significant effects on nocturnal sleep, blood pressure, heart rate, ECG, or mood were observed, confirming the continued efficacy and safety of modafinil over the treatment period. |
| Billiard et. al, 1994 [28] | France | Randomized controlled, double blinded | 50 | Administration of Modafinil 300 mg | 12 weeks | The results showed no significant change in nighttime sleep duration, wake time, or number of awakenings. However, daytime sleepiness episodes significantly decreased, and total daytime sleep time reduced. No changes were noted in cataplexy or feelings upon awakening. Modafinil improved excessive daytime sleepiness as measured by the MWT. Side effects were lower with Modafinil compared to placebo. |
| Boivin et. al, 1993 [29] | France | Randomized Double blind crossover study | 10 | 4 weeks of either Modafinil 200 mg morning + 100 mg noon or Placebo | 12 weeks | The clinical evaluation by the sleep-disorder physician indicated that modafinil produced nonsignificant alerting effects. There was no change in the daily number of cataplectic attacks after modafinil treatment compared to placebo. However, modafinil significantly reduced the number of gaps and the percentage of errors on the Four-Choice Reaction Time Test (FCRTT) compared to placebo. Although a reduction in mean reaction time was observed during modafinil treatment, this change did not reach statistical significance. Modafinil did not produce any changes in nocturnal sleep parameters. Eight out of 10 narcoleptic patients had a pathological Periodic Limb Movement (PLM) index (>5). A nonsignificant reduction in both the number and index of PLMs was observed with modafinil compared to placebo. |
| Schwartz et. al, 2003 [31] | USA | Randomised Double Blind Crossover study | 32 | Modafinil 400 mg once daily / 400 mg split in split doses / 200 mg once daily. | 3 weeks | The study showed that split-dose regimens (400 mg and 600 mg) were significantly more effective in maintaining wakefulness in the late afternoon/evening compared to the 200 mg once-daily regimen. After 3 weeks, 60% of patients on the 400 mg split-dose regimen and 58% on the 600 mg split-dose regimen could stay awake for at least 20 minutes in the evening, compared to just 9% of patients on the 200 mg once-daily regimen. All regimens were well tolerated, with mild or moderate adverse events reported in 18% of participants. |
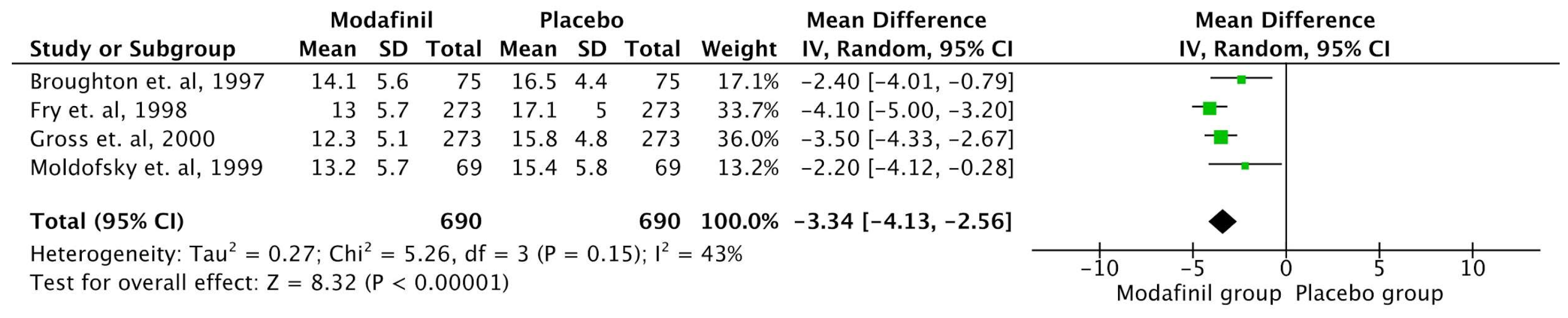
| Broughton et. al, 1997 [30] | Canada | Randomised Double Blind Crossover study | 75 | Placebo vs Modafinil 200 mg vs Modafinil 400 mg divided dose. | 6 weeks | The study found that modafinil effectively reduces EDS in patients with narcolepsy. Compared to placebo, the 200 mg and 400 mg doses increased sleep latency by 40% and 54%, respectively, on the MWT. Both doses significantly reduced the likelihood of falling asleep during daily activities, as measured by the ESS, with a reduction of 24% for 200 mg and 26% for 400 mg in involuntary sleep episodes and severe somnolence. Patients preferred modafinil over placebo, with 84% choosing modafinil as their best treatment, and side effects were more frequent with the 400 mg dose. The 200 mg dose was equally effective with fewer side effects, making it a well-tolerated option. |
| Fry et. al, 1997 [34] | USA | Randomized controlled, double blinded | 285 | Modafinil (400 mg) 100 mg×4 tablets daily or a placebo were given to participants during the double-blind phase. | 9 weeks | The study showed that Modafinil significantly improved subjective and objective measures of sleepiness, including the ESS and the Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT). The mean sleep latency increased by up to 4 minutes in modafinil groups compared to placebo, and Clinical Global Impression scores also improved significantly in modafinil groups. Adverse effects were dose-dependent but mostly mild to moderate, with headache being the most common. The study demonstrated that modafinil is an effective and well-tolerated treatment for EDS in narcolepsy, with sustained efficacy over long-term use. |
| Gross et. al, 2000 [36] | USA | Randomized controlled, double blinded | 271 | Modafinil 200 mg once daily / modafinil 400 mg once daily / placebo | 9 weeks | The study showed that both dosages of modafinil significantly improved objective measures of EDS, as indicated by the MSLT and MWT. Specifically, the modafinil 400 mg group showed a mean MSLT sleep latency increase to 5.1 minutes compared to 3.5 minutes in the placebo group, and the MWT sleep latency was significantly extended at every follow-up visit. Subjective sleepiness also improved as reflected by the ESS. The treatment was well tolerated, with headache being the most common adverse effect, but its incidence was not significantly higher than that in the placebo group. The study concluded that modafinil is an effective and safe treatment option for managing EDS in narcolepsy, with no evidence of dependence or withdrawal symptoms over the treatment duration. |
| Schwartz et. al, 2005 [32] | USA | Randomized controlled, double blinded | 56 | Varying doses of modafinil (200 mg, 400 mg, 600 mg) in either once-daily or split-dose regimens. | 3 weeks | The study showed that split-dose regimens (400 mg and 600 mg) were significantly more effective in maintaining wakefulness in the late afternoon/evening compared to the 200 mg once-daily regimen. After 3 weeks, 60% of patients on the 400 mg split-dose regimen and 58% on the 600 mg split-dose regimen could stay awake for at least 20 minutes in the evening, compared to just 9% of patients on the 200 mg once-daily regimen. All regimens were well tolerated, with mild or moderate adverse events reported in 18% of participants. |
| Dauvilliers et. al, 2017 [33] | USA | Randomized controlled, double blinded | 155 | Sodium Oxybate 9 g nightly / Modafinil 200-600 mg once daily / their combination | 8 weeks | The post hoc analysis of polysomnography data from 155 patients revealed that SXB, alone or with modafinil, significantly reduced shifts from deep sleep stages (N2/3/REM) to light sleep or wakefulness. Sleep quality, measured using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, also improved significantly with SXB and SXB+modafinil, but not with modafinil alone. These results suggest that SXB has a specific effect on consolidating sleep and improving sleep quality, while modafinil alone had minimal impact on Distrupted nightime sleep (DNS). |
MWT
ESS
Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
Conclusion
Ethical Approval
Competing interests
Supplementary Materials
References
- Dauvilliers Y, Billiard M, Montplaisir J. Clinical aspects and pathophysiology of narcolepsy. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003 Nov;114(11):2000-17. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpy MJ, Hiller G. The medical and economic burden of narcolepsy: Implications for managed care. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2017;10(5):233-41. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5620503/.
- Black J, Reaven NL, Funk SE, McGaughey K, Ohayon M, Guilleminault C, et al. The Burden of Narcolepsy Disease (BOND) study: Health-care utilization and cost findings. Sleep Med. 2014;15(5):522-9. [CrossRef]
- Ohayon MM, Black J, Lai C, Eller M, Guinta D, Bhattacharyya A. Increased mortality in narcolepsy. Sleep. 2014;37(3):439-44. [CrossRef]
- Longstreth WT Jr, Koepsell TD, Ton TG, Hendrickson AF, van Belle G. The epidemiology of narcolepsy. Sleep. 2007 Jan;30(1):13-26. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruoff C, Rye D. The ICSD-3 and DSM-5 guidelines for diagnosing narcolepsy: Clinical relevance and practicality. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016;32(10):1611-22. [CrossRef]
- . [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehrs T, Zorick F, Wittig R, Paxton C, Sicklesteel J, Roth T. Alerting effects of naps in patients with narcolepsy. Sleep. 1986;9(1 Pt 2):194-9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers AE, Aldrich MS, Lin X. A comparison of three different sleep schedules for reducing daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy. Sleep. 2001 Jun 15;24(4):385-91. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garma L, Marchand F. Non-pharmacological approaches to the treatment of narcolepsy. Sleep. 1994 Dec;17(8 Suppl):S97-102. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers AE. Problems and coping strategies identified by narcoleptic patients. J Neurosurg Nurs. 1984 Dec;16(6):326-34. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maski K, Trotti LM, Kotagal S, Robert Auger R, Swick TJ, Rowley JA, Hashmi SD, Watson NF. Treatment of central disorders of hypersomnolence: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine systematic review, meta-analysis, and GRADE assessment. J Clin Sleep Med. 2021 Sep 1;17(9):1895-1945. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- DOYLE JB, DANIELS LE. SYMPTOMATIC TREATMENT FOR NARCOLEPSY. JAMA. 1931;96(17):1370–1372. [CrossRef]
- PRINZMETAL M, BLOOMBERG W. THE USE OF BENZEDRINE FOR THE TREATMENT OF NARCOLEPSY. JAMA. 1935;105(25):2051–2054. [CrossRef]
- Maski K, Trotti LM, Kotagal S, Robert Auger R, Rowley JA, Hashmi SD, Watson NF. Treatment of central disorders of hypersomnolence: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine clinical practice guideline. J Clin Sleep Med. 2021 Sep 1;17(9):1881-1893. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bastuji H, Jouvet M. Successful treatment of idiopathic hypersomnia and narcolepsy with modafinil. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1988;12(5):695-700. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignot E, Nishino S, Guilleminault C, Dement WC. Modafinil binds to the dopamine uptake carrier site with low affinity. Sleep. 1994 Aug;17(5):436-7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisor JP, Nishino S, Sora I, Uhl GH, Mignot E, Edgar DM. Dopaminergic role in stimulant-induced wakefulness. J Neurosci. 2001 Mar 1;21(5):1787-94. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Logan J, Alexoff D, Zhu W, Telang F, Wang GJ, Jayne M, Hooker JM, Wong C, Hubbard B, Carter P, Warner D, King P, Shea C, Xu Y, Muench L, Apelskog-Torres K. Effects of modafinil on dopamine and dopamine transporters in the male human brain: clinical implications. JAMA. 2009 Mar 18;301(11):1148-54. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mitler MM, Aldrich MS, Koob GF, Zarcone VP. Narcolepsy and its treatment with stimulants. ASDA standards of practice. Sleep. 1994 Jun;17(4):352-71. [PubMed]
- Darwish M, Kirby M, Hellriegel ET, Robertson P Jr. Armodafinil and modafinil have substantially different pharmacokinetic profiles despite having the same terminal half-lives: analysis of data from three randomized, single-dose, pharmacokinetic studies. Clin Drug Investig. 2009;29(9):613-23. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca G, Bandarabadi M, Konofal E, Lecendreux M, Ferrié L, Figadère B, Tafti M. Lauflumide (NLS-4) Is a New Potent Wake-Promoting Compound. Front Neurosci. 2018 Aug 15;12:519. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Spreitzer I, Keife J, Strasser T, Kalaba P, Lubec J, Neuhaus W, Lubec G, Langer T, Wackerlig J, Loryan I. Pharmacokinetics of Novel Dopamine Transporter Inhibitor CE-123 and Modafinil with a Focus on Central Nervous System Distribution. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 29;24(23):16956. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- 24. Erman M, Emsellem H, Black J, Mori F, Mayer G. Correlation between the Epworth Sleepiness Scale and the Maintenance of Wakefulness Test in patients with narcolepsy participating in two clinical trials of sodium oxybate. Sleep medicine. 2017 Oct 1;38:92-5.
- Johns MW. A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep. 1991 Dec;14(6):540-5.
- 26. Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. 2nd ed. Chichester (UK): John Wiley & Sons; 2019.
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JP, Altman DG, Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. 2019 Sep 23:241–84.
- Billiard M, Besset A, Montplaisir J, Laffont F, Goldenberg F, Weill JS, Lubin S. Modafinil: a double-blind multicentric study. Sleep. 1994 Dec 1;17(suppl_8):S107-12.
- Boivin DB, Montplaisir J, Petit D, Lambert C, Lubin S. Effects of modafinil on symptomatology of human narcolepsy. Clinical neuropharmacology. 1993 Feb 1;16(1):46-53.
- Moldofsky H, Morehouse RL. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial of rnodafinil in the treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy. Neurology. 1997;49:444451.
- Schwartz JR, Feldman NT, Bogan RK, Nelson MT, Hughes RJ. Dosing regimen effects of modafinil for improving daytime wakefulness in patients with narcolepsy. Clinical neuropharmacology. 2003 Sep 1;26(5):252-7.
- Schwartz JR, Feldman NT, Bogan RK. Dose effects of modafinil in sustaining wakefulness in narcolepsy patients with residual evening sleepiness. The Journal of neuropsychiatry and clinical neurosciences. 2005 Aug;17(3):405-12.
- Dauvilliers Y, Roth T, Guinta D, Alvarez-Horine S, Dynin E, Black J. Effect of sodium oxybate, modafinil, and their combination on disrupted nighttime sleep in narcolepsy. Sleep medicine. 2017 Dec 1;40:53-7.
- Fry, US Modafinil in Narcolepsy Multicenter Study Group. Randomized trial of modafinil for the treatment of pathological somnolence in narcolepsy. Annals of Neurology. 1998 Jan;43(1):88-97.
- Moldofsky H, Broughton RJ, Hill JD. A randomized trial of the long-term, continued efficacy and safety of modafinil in narcolepsy. Sleep medicine. 2000 Apr 1;1(2):109-16.
- US Modafinil in Narcolepsy Multicenter Study Group. Randomized trial of modafinil as a treatment for the excessive daytime somnolence of narcolepsy. Neurology. 2000 Mar 14;54(5):1166-75.
- Bassetti CL, Adamantidis A, Burdakov D, Han F, Gay S, Kallweit U, et al. Narcolepsy—clinical spectrum, aetiopathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Oct;18(10):999-1012.
- Thorpy MJ, Dauvilliers Y. Narcolepsy in the modern era: Advances in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017 Mar 23;3:16100.
- Minzenberg MJ, Carter CS. Modafinil: A review of neurochemical actions and effects on cognition. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008 Jun;33(7):1477-502.
- Thorpy MJ, Westbrook PR, Ferber R, et al. The clinical use of modafinil in treatment of narcolepsy: Implications for the clinician. Sleep Med Rev. 2001 Dec;5(6):483-509.
- Ballon JS, Feifel D. A systematic review of modafinil: Potential clinical uses and mechanisms of action. CNS Drug Rev. 2006;12(3-4):207-38.
- Morgenthaler TI, Kapur VK, Brown T, et al. Practice parameters for the treatment of narcolepsy and other hypersomnias of central origin. Sleep. 2007 Dec;30(12):1705-11.
- Schwartz JR, Feldman NT, Bogan RK, et al. Armodafinil for excessive sleepiness associated with shift work disorder or obstructive sleep apnea: A 12-month, open-label extension study. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2013 Oct;2(4):281-90.
- Veatch OJ, Goldman SE, Adkins KW, Malow BA. Efficacy of modafinil in the treatment of narcolepsy: A meta-analysis. J Clin Sleep Med. 2005 Dec;1(4):331-6.
- Morgenthaler TI, Kapur VK, Brown T, et al. Practice parameters for the treatment of narcolepsy and other hypersomnias of central origin. Sleep. 2007 Dec;30(12):1705-11.
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Human Studies | Animal Studies |
| From 1990 to 2024 | Only pathophysiology /methodological studies with no outcome data |
| English text | Non-English text |
| Gender: All | Age: <18 years of age |
| Age: >18 years of age | Papers that needed to be purchased |
| Free papers | Studies involving clinical data other than Narcolepsy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





