Submitted:
29 September 2024
Posted:
30 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Estimating Values and Their Variances from Psychometric Functions of Some Basic Sensory Discrimination Methods
2.2. Statistical Testing for Test Sample vs. Control Sample Based on Individual Estimator and Its Variance
2.2.1. Difference Test for Test Sample vs. Control Sample Based on Individual and Their Variance
2.2.2. Equivalence/Similarity Test for Test Sample vs. Control Sample Based on Individual and Its Variance
2.3. Statistical Testing for Multiple Test Samples Based on Multiple Values and Their Variances
2.3.1. Difference Test for Multiple Test Samples Based on Multiple Values and Their Variances
2.3.2. Multiple Comparisons for Multiple Test Samples Based on Vector and Co-Variance Matrix
2.3.3. TOST Equivalence/Similarity Test for Two Test Samples Based on Two Values and Their Variances
3. Results
3.1. Estimated Values and Their Variances from Psychometric Functions of 10 Basic Sensory Discrimination Methods
3.1. Statistical Testing for Test Sample vs. Control Sample Based on Individual Estimator and Its Variance
3.2.1. Difference Test Based on Individual and Their Variance
3.2.2. Equivalence/Similarity Test Based on Individual and Its Variance
3.3. Statistical Testing for Multiple Test Samples Based on Multiple Values and Their Variances
3.3.1. Difference test for multiple test samples based on multiple values and their variances
3.3.2. Multiple Comparisons for Multiple Test Samples Based on Vector and Co-Variance Matrix
3.3.3. TOST Equivalence/Similarity Test Based on Two Values and Their Variances
4. Discussion
4.1. Application of Sensory Discrimination Methods
4.2. Significance of d’ Differences
4.3. Advantages of Thurstonian Discriminal Distance ( or d′)
4.4. Application of Thurstonian Scaling for Food Quality and Safety
4.5. Government Organizations
4.6. Future Trends
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Credit authorship contribution statement
Data availability
Declaration of Competing Interest
References
- Meilgaard, M.; Civille, G.; Carr, B. Sensory Evaluation Techniques; Boca Raton, Florida: Taylor & Francis, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food: Principles and Practices, 2ed.; Springer: New York, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, H.; Bleibaum, R.; Thomas, H.A. Sensory Evaluation Practices; Academic press: New York, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, L. Discrimination Testing in Sensory Science: A Practical Handbook; Woodhead Publishing: Duxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, L.; Hort, J.; Kamp, S.E.; Hollowood, T. Discrimination Testing in Sensory Evaluation; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Vol. 14.03; ASTM International: West Conshocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- ASTM-E2262. Standard Practice for Estimating Thurstonian Discriminal Distances, E2262-03 (Re-approved 2020); ASTM International: West Conshocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Thurstone, L.L. A law of comparative judgement. Psychological Review 1927, 34, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ura, S. Pair, triangle, and duo-trio test. Rep. Stat. Appl. Res., JUSE 1960, 7, 107–119. [Google Scholar]
- David, H.A.; Trivedi, M.C. Pair, triangle, and duo-trio tests. Virginia Poly. Inst., Tech. Rep. 54, 1962.
- Bradley, R.A. Some relationship among sensory difference tests. Biometrics 1963, 19, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frijters, J.E.R. Variations of the triangular method and the relationship of its unidimensional probabilistic models to 3-altenative forced choice signal detection theory models. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology 1979, 32, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frijters, J.E.R. (1988). Sensory difference testing and the measurement of sensory discriminability. In Sensory Analysis of Foods, 2nd ed.; Piggott, J.R., Ed.; Elsevier Applied Science Publishers: London, UK, 1988; pp. 117–140. [Google Scholar]
- Ennis, D.M.; Mullen, K.; Frijters, J.E.R. Variants of the method of triads: Unidimensional Thurstonian models. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology 1988, 41, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, D.M. The power of discrimination methods. Journal of Sensory Studies 1993, 8, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, D.M. Thurstonian Models: Categorical Decision Making in the Presence of Noise. The Institute for Perception: Richmond, VA, USA. 2016, ISBN:9780990644606, 099064460X.
- Ennis, D.M.; Rousseau, B. A Thurstonian model for the degree of difference protocol. Food Quality and Preference 2015, 41, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Ennis, D.M.; O’Mahony, M. How to estimate and use the variance of d’ from difference tests. Journal of Sensory Studies 1997, 12, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J. The double discrimination methods. Food Quality and Preference 2001, 12, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J. Variance of d’ for the same-different method. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers 2002, 34, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J. Estimating population or group sensitivity and its precision from a set of individual d’. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology 2005, 58, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J. Similarity tests using forced-choice methods in terms of Thurstonian discriminal distance, d’. Journal of Sensory Studies 2011, 26, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J. Sensory Discrimination Tests and Measurements: Sensometrics in Sensory Evaluation. 2nd Edition; Wiley/Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015.
- Bi, J. An extension of Green’s area theorem. Journal of Mathematical Psychology 2018, 82, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J. A new form of the psychometric function for the unspecified tetrad. Food Quality and Preference 2020, 82, 103869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J. The methods of Tetrads, Hexads, and Octads: A type of more powerful sensory discrimination methods. Food Quality and Preference 2023, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; O’Mahony, M. Variance of d’ for the tetrad test and comparisons with other forced choice methods. Journal of Sensory Studies 2013, 28, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Kuesten, C. Estimating and testing parameters of the Thurstonian model for Torgerson’s method of triads. Journal of Sensory Studies 2015, 30, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Kuesten, C. A simplified form of the psychometric function for the m-Alternative Forced Choice (mAFC) method. Journal of Sensory Studies 2016, 31, 306–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Kuesten, C. The four-interval, two-alternative forced-choice (4I2AFC): A powerful sensory discrimination method to detect small, directional changes particularly suitable for visual or manual evaluations. Food Quality and Preference 2019, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Kuesten, C. Review and development of Thurstonian models for the triangle and duo-trio methods and paired versions of the methods. Journal of Sensory Studies 2020, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Kuesten, C. A more powerful non-attribute-specified sensory discrimination method: The paired unspecified tetrad with different order (AB and BA) pairs. Journal of Sensory Studies 2020, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Kuesten, C. The paired A-Not A with AB and BA pairs. Journal of Sensory Studies 2022, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Kuesten, C. Thurstonian models for three variants (specified, unspecified, and unspecified with forgiveness) of the Two-Out-of-Five method. Journal of Sensory Studies 2023, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Kuesten, C. (2024). Thurstonian models for the duo-trio and its variants. Journal of Sensory Studies 2024. [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Lee, H.S.; O’Mahony, M. d’ and variance of d’ for four-alternative forced choice (4-AFC). Journal of Sensory Studies 2010, 25, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Lee, H.S.; O’Mahony, M. Statistical analysis of ROC curves for the ratings of the A-Not A and the Same-Different methods. Journal of Sensory Studies 2013, 28, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Lee, H.S.; O’Mahony, M. Estimation of Thurstonian models for various forced-choice sensory discrimination methods as a form of the ‘M+N’ test. Journal of Sensory Studies 2014, 29, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Lee, H.S.; O’Mahony, M. A Thurstonian model and statistical inference for the 2-Alternative choice test with both test pairs and placebo pairs. Journal of Sensory Studies 2015, 30, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Lee, H.S.; O’Mahony, M. An analytical psychometric function for the dual reference duo-trio (DRDT) method. Food Quality and Preference 2022, 96, 104418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Lee, H.S.; O’Mahony, M. Thurstonian model for the four-interval oddity task. Food Quality and Preference 2023, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; O’Mahony, M.; Lee, H.S. Non-parametric estimation of d’ and its variance for the A-Not A with reminder. Journal of Sensory Studies 2013, 28, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; O’Mahony, M.; Lee, H.S. The performance of the dual reference duo-trio (DRDT) method using a balanced-reference mode. Food Quality and Preference 2016, 48, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Kuesten, C.; Lee, H.S.; O’Mahony, M. Paired versions of various sensory discrimination forced-choice methods and the same-different area theorem. Food Quality and Preference 2018, 63, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockhoff, B.P.; Christensen, R.H.B. Thurstonian models for sensory discrimination tests as generalized linear models. Food Quality and Preference 2010, 21, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, J.M. A Thurstonian analysis of the Two-Out-of-Five test. Journal of Sensory Studies 2013, 28, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, J.M.; Christenson, R.A. Thurstonian comparison of the Tetrad and Degree of Difference tests. Journal of Food Quality and Preference 2015, 40, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, J.M.; Rousseau, B.; Ennis, D.N. Sensory difference tests as measurement instruments: A review of recent advances. Journal of Sensory Studies 2014, 29, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, B.; O’Mahony, M. Sensory difference tests: Thurstonian and SSA predictions for vanilla flavored yogurts. Journal Sensory Studies 1997, 12, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, B.; Ennis, D.N. A Thurstonian model for the dual pair (4IAX) discrimination method. Perception & Psychophysics 2001, 63, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.M.; Swets, J.W. Signal detection theory and psychophysics. Wiley: New York, 1966.
- Macmillan, N.A.; Creelman, C.D. Detection theory: A user’s guide, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.: New York, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hautus, M.J.; Macmillan, N.A.; Creelman, C.D. Detection theory: A user’s guide, 3rd ed.; New York: Taylor & Francis:New York, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, R.H.B.; Brockhoff, B.P.; Kuznetsova, A.; Birot, S.; Stachlewska, K.A.; Rafacz, D. Package ‘sensR’. Available from: http://www.r-project.org. 2023.
- R Core Team R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2023. https://www.R-project.org/.
- Gilbert, P.; Varadhan, R. Accurate Numerical Derivatives, R Package “numDeriv.” Retrieved Dec.1, 2020, from http://www.r-project.org. 2019.
- Ennis, J.; Ennis, D.; Yip, D.; O’Mahony, M. Thurstonian models for variants of the method of tetrads. Brit. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 1998, 51, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marascuilo, L.A. Large sample multiple comparisons. Psychological Bulletin 1966, 65, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marascuilo, L.A. Extension of the significance test for one-parameter signal detection hypotheses. Psychometrika 1970, 35, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insightful. S-PLUS 6. Guide to Statistics Vol.1. for Windows; Insightful Corporation: Seattle, Washington, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hothorn, T.; Bretz, F.; Westfall, P.; Heiberger, R.M.; Schuetzenmeister, A.; Scheibe, S. R package “multcomp”: Simultaneous Inference in General Parametric Models. http://www.r-project.org. 2023.
- Westlake, W.J. Response to T.B.L. Kirkwood: Bioequivalence testing – a need to rethink. Biometrics 1981, 37, 589–594. [Google Scholar]
- Schuirmann, D.J. On hypothesis testing to determine if the mean of a normal distribution is contained in a known interval. Biometrics 1981, 37, 617. [Google Scholar]
- Schuirmann, D.J. A comparison of the two one-sided tests procedure and the power approach for assessing the equivalent of average bioavailability. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 1987, 15, 657–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, R.L. Multiparameter hypothesis testing and acceptance sampling. Technometrics 1982, 24, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, G.; Berger, R.L. Statistical Reference; Wadsworth and Brooks/Cole, Pacific: Grove, CA, 1990.
- Berger, R.L.; Hsu, J.C. Bioequivalence trials, intersection union tests and equivalence confidence set. Statistical Science 1996, 11, 283–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvapulle, M.J.; Sen, P.K. Constrained statistical inference: Inequality, order, and shape restrictions. Wiley: New York, 2004.
- Lakens, D.; Caldwell, A. R package “TOSTER”: Two One-Sided Tests (TOST) Equivalence Testing. http://www.r-project.org, 2023.
- Swets, J.A. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science 1988, 240, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, M. Understanding discrimination tests: A user-friendly treatment of response bias, rating and ranking R-Index tests and their relationship to signal detection. Journal of Sensory Studies 1992, 7, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, D.M.; Rousseau, B.; Ennis, J.M. Tools and Applications of Sensory and Consumer Science. The Institute for Perception, www.IFPress.com, Richmond, VA 2017.
- Lee, H.-S.; Van Hout, D. Quantification of Sensory and Food Quality: The R-Index Analysis. Journal of Food Science 2009, 74, R57–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; O’Mahony, M. Sensory difference testing: Thurstonian models. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2004, 13, 841–847. [Google Scholar]
- Lawless, H.T. Chapter 4 Thurstonian Models for Discrimination and Preference. In Quantitative Sensory Analysis Psychophysics, Models and Intelligent Design; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Wiley Blackwell, Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 71–123.
- O’Mahony, M. Understanding Discrimination Tests: A User-Friendly Treatment of Response Bias, Rating and Ranking R-Index Tests and Their Relationship to Signal Detection. Journal of Sensory Studies 1992, 7, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J. Statistical models for the Degree of Difference method. Journal of Food Quality and Preference 2002, 13, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Gong, C.; Zeng, J. Publication review of Food Quality and Safety during 2017–2022. Food Quality and Safety 2023, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S. Sensory Properties of Foods and Their Measurement Methods. In Techniques to Measure Food Safety and Quality. Khan, M.S., Shafiur Rahman, M. Eds.; Springer, Cham. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Castro, M.; Feller, J.-F. Review on Sensor Array-Based Analytical Technologies for Quality Control of Food and Beverages. Sensors 2023, 23, 4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Yang, X.; Ying, X.; Shi, C.; Jia, Z.; Jia, B. Applications of Gas Sensing in Food Quality Detection: A Review. Foods 2023, 12, 3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.S.; Dias, L.G.; Telxeria, A. Emerging Methods for the Evaluation of Sensory Quality of Food: Technology at Service. Current Food Science and Technology Reports 2024, 2, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirangelo, T.M. Sensory Descriptive Evaluation of Food Products: A Review. Journal of Food Science and Nutrition Research 2019, 2, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Special Edition: Recent Advances in the Food Safety and Quality Management Techniques; Perumal, A.B.; Li, X.; He, Y. Eds.; Foods 2023 (ISSN 2304-8158).
- Huang, Y.; Luo, C.; Xia, F.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, F. ; Multi-analyte sensing strategies towards wearable and intelligent devices. Chemical Science 2022, 13, 12309–12325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberty, J.T.; Sun, S.; Kucha, C.; Adedeji, A.A.; Agidi, G.; Ngadi, M.O. Augmented reality for food quality assessment: Bridging the physical and digital worlds. Journal of Food Engineering 2024, 367, 111893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Zheng, S.; Wang, D.; Tan, X.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Li, T. Recent advances in shelf life prediction models for monitoring food quality. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety – Wiley Online Library 2023 22, 2, 1257-1284. [CrossRef]
- Special Edition: Predictive Modelling of Food Quality and Safety; Valdramidis, V.; Cummins, E.; Celayeta, J.M.F. Eds.; Food Control 2013 29:2, pp. 289–470. [CrossRef]
| .No. | Methods | R-code |
| 1 | 2-AFC | TwoAFC(x,n) |
| 2 | 3-AFC | ThreeAFC(x,n) |
| 3 | Triangle | TRI(x,n) |
| 4 | Duo-trio | DUTR(x,n) |
| 5 | Specified Tetrad | STETR(x,n) |
| 6 | Unspecified Tetrad | UTETR(x,n) |
| 7 | A-Not A | ANAdv(a,an,n,nn) |
| 8 | Same-different | SDdv(sn,n1,dn,n2) |
| 9 | Ratings of A-Not A | ANARAT(rfal,rhit) |
| 10 | Ratings of Same-different | SDRAT(rsam,rdif) |
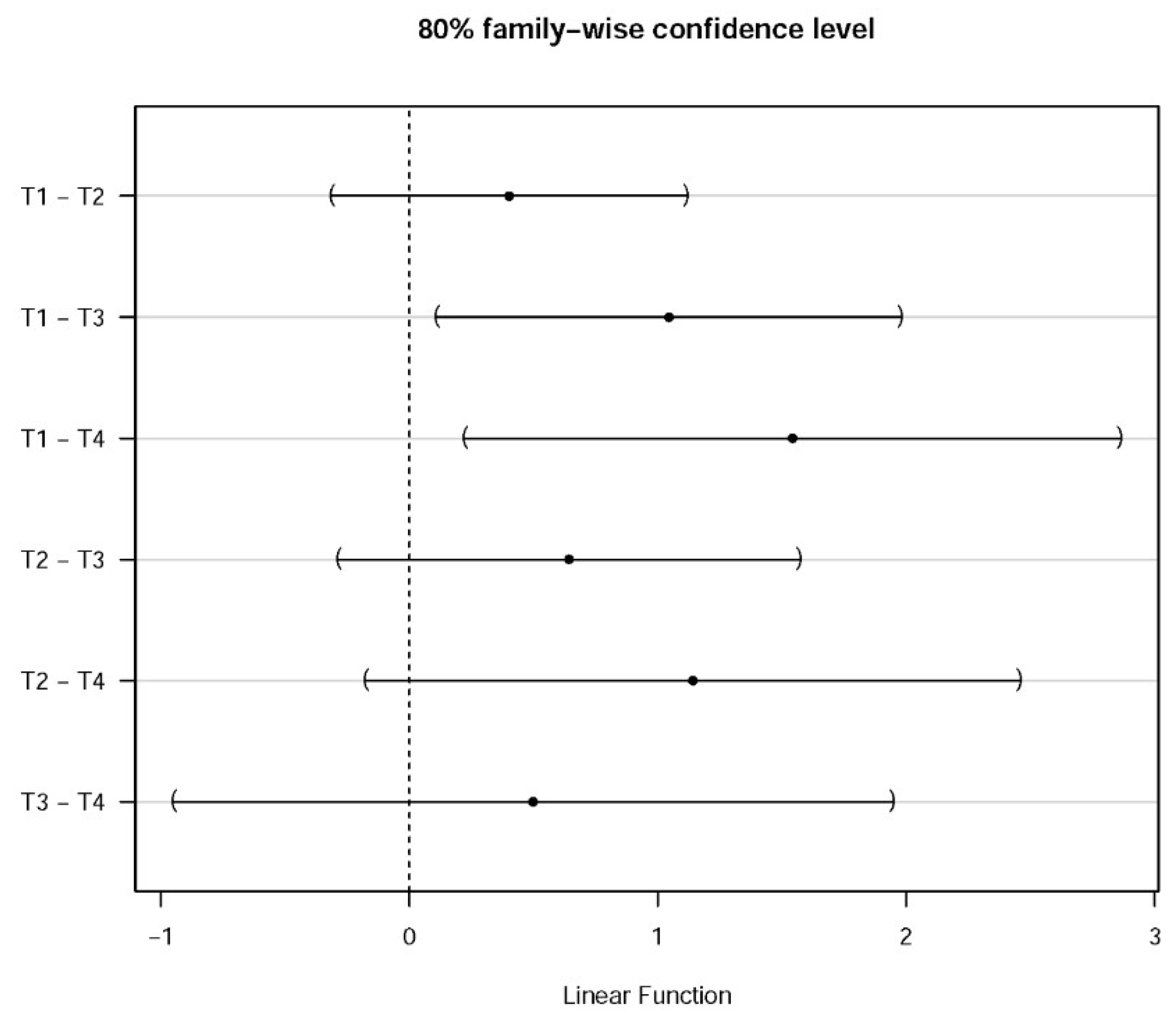
| .No. | Variance of | |
| 1 | 2.4868 | 0.0687 |
| 2 | 2.0849 | 0.0662 |
| 3 | 1.4422 | 0.1628 |
| 4 | 0.9442 | 0.3927 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





