Submitted:
27 September 2024
Posted:
30 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compounds Tested
2.2. Babesia Bovis In Vitro CULTURE
2.3. In Vitro Growth Inhibitory Assays
2.4. Post-Treatment Survival
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
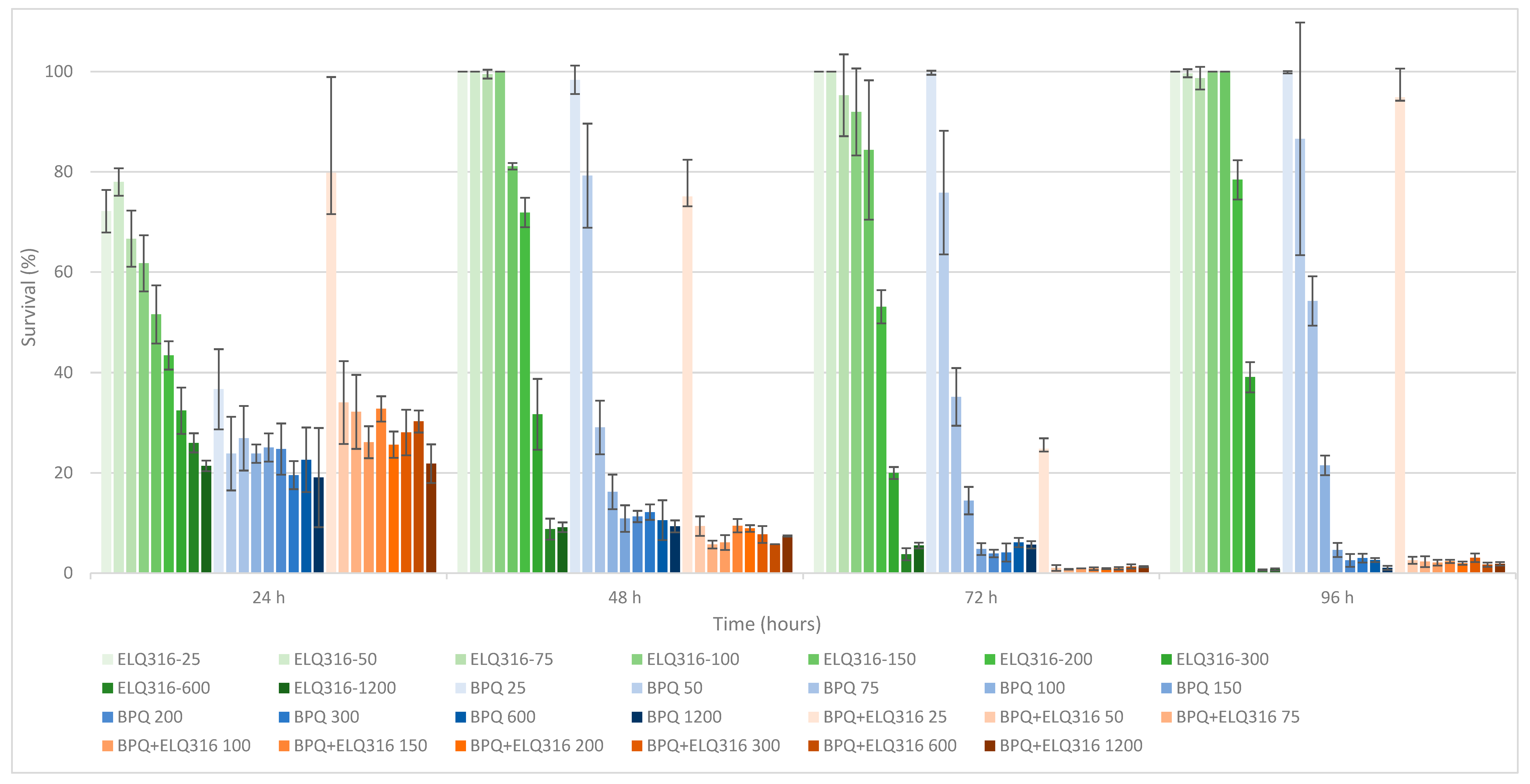
3.1. Comparative In Vitro Survival Effects of BPQ, ID, ELQ-316, BPQ+ ELQ-316 and ID+ ELQ-316 Combinations on B. bovis
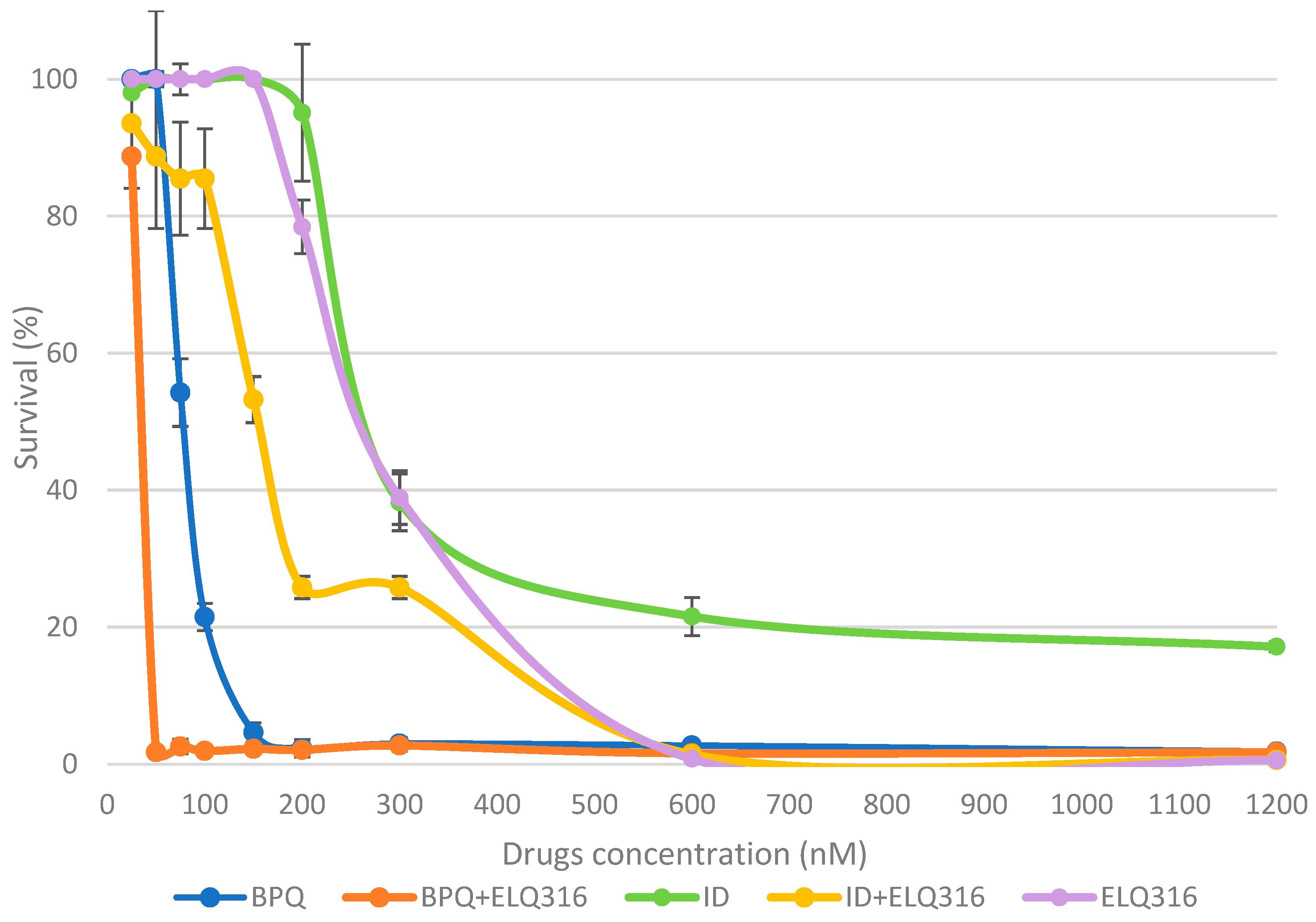
3.2. Drugs Potency
3.3. Time and Concentration of Drugs to Reach 0% Survival after Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Pipano, E.; Hadani, A. Control of Bovine Babesiosis. In Malaria and Babesiosis. Ristic, M. Ambroise-Thomas, P. Kreier, J.P.; 1984; pp. 263–303.
- Bock, R.; Jackson, L.; De Vos, A.; Jorgensen, W. Babesiosis of Cattle. Parasitology 2004, 129, S247–S269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, S.S.; Sengupta, P.P.; Paramanandham, K.; Suresh, K.P.; Chamuah, J.K.; Rudramurthy, G.R.; Roy, P. Bovine Babesiosis: An Insight into the Global Perspective on the Disease Distribution by Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Vet Parasitol 2020, 283, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asrar, R.; Farhan, H.R.; Sultan, D.; Ahmad, M.; Hassan, S.; Kalim, F.; Shakoor, A.; Muhammad Taimoor Ihsan, H.; Shahab, A.; Ali, W.; et al. Review Article Bovine Babesiosis; Review on Its Global Prevalence and Anticipatory Control for One Health. Continental Vet J 2022, 2, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.D.; Evans, D.E.; Martins, J.R.; Ceresér, V.H.; Correa, B.L.; Cardozo, C.P.H.; Solari, M.A.; Nari, A. Babesiosis (Babesis Bovis) Stability in Unstable Environments. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2000, 916, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zintl, A.; Mcgrath, G.; O’grady, L.; Fanning, J.; Downing, K.; Roche, D.; Casey, M.; Gray, J.S. Changing Incidence of Bovine Babesiosis in Ireland. Ir Vet J 2014, 67, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorovic, R.A.; Viscaino, O.G.; Gonzalez, E.F.; Adams, L.G. Chemoprophylaxis (Imidocarb) against Babesia Bigemina and Babesia Argentina Infections. Am J Vet Res 1973, 34, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Vial, H.J.; Gorenflot, A. Chemotherapy against Babesiosis. Vet Parasitol 2006, 138, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazan, C.; Tipacamu, G.A.; Rodriguez, S.; Mosqueda, J.; Perez De Leon, A. Immunological Control of Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases That Impact Cattle Health and Production. Frontiers in Bioscience 2018, 23, 1535–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.A.; Rojas, C.; Figueroa, J.V. An Overview of Current Knowledge on in Vitro Babesia Cultivation for Production of Live Attenuated Vaccines for Bovine Babesiosis in Mexico. Front Vet Sci 2020, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, M.; Gadahi, J.A.; Bhutto, B.; Tunio, S.; Vistro, W.A.; Tunio, H.; Bhutto, S.; Ram, T. Babesiosis: Current Status and Future Perspectives in Pakistan and Chemotherapy Used in Livestock and Pet Animals. Heliyon 2023, e17172, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosqueda, J.; Olvera-Ramírez, A.; Aguilar-Tipacamú, G.; Cantó, G.J. Current Advances in Detection and Treatment of Babesiosis; 2012; Vol. 19;
- Kuttler, K.L.; Aliu, Y.O. Chemotherapy of Babesiosis. In Malaria and Babesiosis. Ristic, M., Kreier, J.P., Eds. Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; 1984; pp. 151–172.
- Silva, M.G.; Villarino, N.F.; Knowles, D.P.; Suarez, C.E. Assessment of Draxxin® (Tulathromycin) as an Inhibitor of in Vitro Growth of Babesia Bovis, Babesia Bigemina and Theileria Equi. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist 2018, 8, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, K.; Knowles, D.; Dinkel, K.; Mshelia, P.W.; Onzere, C.; Silva, M.; Fry, L. Imidocarb Dipropionate Lacks Efficacy against Theileria Haneyi and Fails to Consistently Clear Theileria Equi in Horses Co-Infected with T. Haneyi. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.G.; Bastos, R.G.; Stone Doggett, J.; Riscoe, M.K.; Pou, S.; Winter, R.; Dodean, R.A.; Nilsen, A.; Suarez, C.E. Endochin-like Quinolone-300 and ELQ-316 Inhibit Babesia Bovis, B. Bigemina, B. Caballi and Theileria Equi. Parasit Vectors 2020, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, J.; Aguado-Martinez, A.; Manser, V.; Balmer, V.; Winzer, P.; Ritler, D.; Hostettler, I.; Solís, D.A.; Ortega-Mora, L.; Hemphill, A. Buparvaquone Is Active against Neospora Caninum in Vitro and in Experimentally Infected Mice. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist 2015, 5, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, M.A.; El-Sayed, S.A.E.-S.; Igarashi, I. Diminazene Aceturate and Imidocarb Dipropionate-Based Combination Therapy for Babesiosis – A New Paradigm. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2023, 14, 102145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardillo, N.M.; Lacy, P.A.; Villarino, N.F.; Doggett, J.S.; Riscoe, M.K.; Bastos, R.G.; Laughery, J.M.; Ueti, M.W.; Suarez, C.E. Comparative Efficacy of Buparvaquone and Imidocarb in Inhibiting the in Vitro Growth of Babesia Bovis. Front Pharmacol 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloli, C.; Crescenzo, G.; Lai, O.; Carofiglio, V.; Marang, O.; Ormas, P. Pharmacokinetics of Imidocarb Dipropionate in Horses after Intramuscular Administration. Equine Vet J 2002, 34, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mdachi, R.E.; Murilla, G.A.; Omukuba, J.N.; Cagnolati, V. Disposition of Diminazene Aceturate (Berenil®) in Trypanosome-Infected Pregnant and Lactating Cows. Vet Parasitol 1995, 58, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-J.; Yamasaki, M.; Nakamura, K.; Sasaki, N.; Murakami, M.; Kumara, B.; Rajapakshage, W.; Ohta, H.; Maede, Y.; Takiguchi, M. Development and Characterization of a Strain of Babesia Gibsoni Resistant to Diminazene Aceturate In Vitro. J. Vet. Med. Sci 2010, 72, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuntasuvan, D.; Jarabrum, W.; Viseshakul, N.; Mohkaew, K.; Borisutsuwan, S.; Theeraphan, A.; Kongkanjana, N. Chemotherapy of Surra in Horses and Mules with Diminazene Aceturate. Vet Parasitol 2003, 110, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez de León, A.A.; Strickman, D.A.; Knowles, D.P.; Fish, D.; Thacker, E.; de la Fuente, J.; Krause, P.J.; Wikel, S.K.; Miller, R.S.; Wagner, G.G.; et al. One Health Approach to Identify Research Needs in Bovine and Human Babesioses: Workshop Report. Parasit Vectors 2010, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez de Leon, A.A.; Teel, P.D.; Auclair, A.N.; Messenger, M.T.; Guerrero, F.D.; Schuster, G.; Miller, R.J. Integrated Strategy for Sustainable Cattle Fever Tick Eradication in USA Is Required to Mitigate the Impact of Global Change. Front Physiol 2012, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CVM- FDA FOI Summary for Original Approval of IMIZOL - NADA 141-071; 1997.
- Todorovic, R.A.; Viscaino, O.G.; Gonzalez, E.F.; Adams, L.G. Chemoprophylaxis (Imidocarb) against Babesia Bigemina and Babesia Argentina Infections. Am J Vet Res 1973, 34, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.; Corrier, D.; Williams, J. A Study of the Toxicity of Imidocarb Dipropionate in Cattle. Res Vet Sci. 1980, 28, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Yu, N.; Liu, C.; Han, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Kang, J.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Residue Depletion of Imidocarb in Bovine Tissues by UPLC-MS/MS. Animals 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coldham, N.G.; Moore, A.S.; Sivapathasundaram, S.; Sauer, M.J. Lmidocarb Depletion from Cattle Liver and Mechanism of Retention in Isolated Bovine Hepatocytes*t; 1994; Vol. 119;
- Fray, M.; Pudney, M. Site of Action of the Antimalarial Hydroxynaphthoquinone,2- [Trans-4-(40chlorophenyl)Cyclohexyl]-3-Hydroxy-1,4,-Naphthoquinone (566c80). Biochem. Pharmacol. 1992, 40, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, A.T.; Randall, A.W.; Fry, M.; Ginger, C.D.; Hill, B.; Latter, V.S.; McHardy, N.; Williams, R.B. Novel Anti-Malarial Hydroxynpahthoquinones with Potent Broad Spectrum Anti-Protozoal Activity. Parasitology 1985, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifiyazdi, H.; Namazi, F.; Oryan, A.; Shahriari, R.; Razavi, M. Point Mutations in the Theileria Annulata Cytochrome b Gene Is Associated with Buparvaquone Treatment Failure. Vet Parasitol 2012, 187, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhadhbi, M.; Chaouch, M.; Ajroud, K.; Darghouth, M.A.; BenAbderrazak, S. Sequence Polymorphism of Cytochrome b Gene in Theileria Annulata Tunisian Isolates and Its Association with Buparvaquone Treatment Failure. PLoS One 2015, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, P. Assessment of the Efficacy of Buparvaquone for the Treatment of “benign” Bovine Theileriosis. Tick Fever Centre Department of Employment, Economic Development and Innovation. 2011, 1–12.
- Müller, J.; Aguado-Martínez, A.; Manser, V.; Wong, H.N.; Haynes, R.K.; Hemphill, A. Repurposing of Antiparasitic Drugs: The Hydroxy-Naphthoquinone Buparvaquone Inhibits Vertical Transmission in the Pregnant Neosporosis Mouse Model. Vet Res 2016, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraguri, G.R.; Ngumi, P.N.; Wesonga, D.; Ndungu, S.G.; Wanjohi, J.M.; Bang, K.; Fox, A.; Dunne, J.; McHardy, N. Clinical Efficacy and Plasma Concentrations of Two Formulations of Buparvaquone in Cattle Infected with East Coast Fever (Theileria Parva Infection). Res Vet Sci 2006, 81, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, P. Animal Health Assessment of the Efficacy of Buparvaquone for the Treatment of “benign” Bovine Theileriosis; 2011. ISBN 9781741916591.
- Bailey, G. Buparvaquone Tissue Residue Study; 2013. ISBN 9781925045475.
- Wilkie, G.M.; Kirvar, E.; Thomas, E.M.; Sparagano, O.; Brown, C.G.D. Stage-Specific Activity in Vitro on the Theileria Infection Process of Serum from Calves Treated Prophylactically with Buparvaquone. Vet Parasitol 1998, 80, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goud, S.K.; Vijayakumar, K.; Davis, J.; Tresamol, P.V.; Ravishankar, C.; Devada, K. Efficacy of Different Treatment Regimens against Oriental Theileriosis in Naturally Infected Cattle. Indian J. Vet. Med 2021, 40, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur, P.; Lecoublet, S.; Kapel, N.; Favennec, L.; Ballet, J.J. In Vitro Evaluation of Drug Susceptibilities of Babesia Divergens Isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1998, 42, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasheminasab, S.S.; Moradi, P.; Wright, I. A Four Year Epidemiological and Chemotherapy Survey of Babesiosis and Theileriosis, and Tick Vectors in Sheep, Cattle and Goats in Dehgolan, Iran. Ann Parasitol 2018, 64, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.D.; Bhikane, A.U.; Jadhav, R.K.; Chavhan, S.G.; Mohan, A. Therapeutic Management of Babesiosis Alone and Its Mixed Infection with Theileriosis in Cattle. Indian J. Vet. Med. Vol. 2019, 39, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- McConnell, E.V.; Bruzual, I.; Pou, S.; Winter, R.; Dodean, R.A.; Smilkstein, M.J.; Krollenbrock, A.; Nilsen, A.; Zakharov, L.N.; Riscoe, M.K.; et al. Targeted Structure–Activity Analysis of Endochin-like Quinolones Reveals Potent Qi and Qo Site Inhibitors of Toxoplasma Gondii and Plasmodium Falciparum Cytochrome Bc 1 and Identifies ELQ-400 as a Remarkably Effective Compound against Acute Experimental Toxoplasmosis. ACS Infect Dis 2018, 4, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, N.; Meunier, B.; Biagini, G.A. The Cytochrome Bc1 Complex as an Antipathogenic Target. FEBS Lett 2020, 594, 2935–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawres, L.A.; Garg, A.; Kumar, V.; Bruzual, I.; Forquer, I.P.; Renard, I.; Virji, A.Z.; Boulard, P.; Rodriguez, E.X.; Allen, A.J.; et al. Radical Cure of Experimental Babesiosis in Immunodeficient Mice Using a Combination of an Endochin-like Quinolone and Atovaquone. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2016, 213, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, A.; Miley, G.P.; Forquer, I.P.; Mather, M.W.; Katneni, K.; Li, Y.; Pou, S.; Pershing, A.M.; Stickles, A.M.; Ryan, E.; et al. Discovery, Synthesis, and Optimization of Antimalarial 4(1 H)-Quinolone-3-Diarylethers. J Med Chem 2014, 57, 3818–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.G.; Ristic, M. Babesia Bovis: Continuous Cultivation in a Microaerophilous Stationary Phase Culture. Science (1979) 1980, 207, 1218–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlhorn, H. Babesiacidal Drugs. In Encyclopedia of Parasitology; Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2016; pp. 1–11.
- Doggett, J.S.; Nilsen, A.; Forquer, I.; Wegmann, K.W.; Jones-Brando, L.; Yolken, R.H.; Bordón, C.; Charman, S.A.; Katneni, K.; Schultz, T.; et al. Endochin-like Quinolones Are Highly Efficacious against Acute and Latent Experimental Toxoplasmosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109, 15936–15941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Painter, H.J.; Morrisey, J.M.; Mather, M.W.; Vaidya, A.B. Specific Role of Mitochondrial Electron Transport in Blood-Stage Plasmodium Falciparum. [CrossRef]
- Tomavo, S.; Boothroydt, J.C. Interconnection between Organellar Functions, Development and Drug Resistance in the Protozoan Parasite, Toxoplasma Gondii; 1995; Vol. 25;
- Nugraha, A.B.; Tuvshintulga, B.; Guswanto, A.; Tayebwa, D.S.; Rizk, M.A.; Gantuya, S.; El-Saber Batiha, G.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Sivakumar, T.; Yokoyama, N.; et al. Screening the Medicines for Malaria Venture Pathogen Box against Piroplasm Parasites. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist 2019, 10, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Yu, N.; Liu, C.; Han, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Kang, J.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Residue Depletion of Imidocarb in Bovine Tissues by UPLC-MS/MS. Animals 2023, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coldham, N.G.; Moore, A.S.; Sivapathasundaram, S.; Sauer, M.J. Lmidocarb Depletion from Cattle Liver and Mechanism of Retention in Isolated Bovine Hepatocytes. Analyst 1994, 119, 2549–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, A.T.; Randall, A.W.; Fry, M.; Ginger, C.D.; Hill, B.; Latter, V.S.; McHardy, N.; Williams, R.B. Novel Anti-Malarial Hydroxynpahthoquinones with Potent Broad Spectrum Anti-Protozoal Activity. Parasitology 1985, 90, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, J.E.; Renard, I.; Pal, A.C.; Singh, P.; Vydyam, P.; Thekkiniath, J.; Kumar, M.; Gihaz, S.; Pou, S.; Winter, R.W.; et al. Effective Therapy Targeting Cytochrome Bc1prevents Babesia Erythrocytic Development and Protects from Lethal Infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2021, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, A.; Lacrue, A.N.; White, K.L.; Forquer, I.P.; Cross, R.M.; Marfurt, J.; Mather, M.W.; Delves, M.J.; Shackleford, D.M.; Saenz, F.E.; et al. Quinolone-3-Diarylethers: A New Class of Drugs for a New Era of Malaria Eradication. [CrossRef]
- Miley, G.P.; Pou, S.; Winter, R.; Nilsen, A.; Li, Y.; Kelly, J.X.; Stickles, A.M.; Mather, M.W.; Forquer, I.P.; Pershing, A.M.; et al. ELQ-300 Prodrugs for Enhanced Delivery and Single-Dose Cure of Malaria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2015, 59, 5555–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, S.; Hillerton, J.E.; Pegram, D. Concentrations of Buparvaquone in Milk and Tissue of Dairy Cows. N Z Vet J 2016, 64, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallarida, R.J. Drug Synergism and Dose-Effect Data Analysis. Drug Synergism and Dose-Effect Data Analysis. [CrossRef]
- Winter, R.; Kelly, J.X.; Smilkstein, M.J.; Hinrichs, D.; Koop, D.R.; Riscoe, M.K. Optimization of Endochin-like Quinolones for Antimalarial Activity. [CrossRef]
- Proma, F.H.; Shourav, M.K.; Choi, J. Post-Antibiotic Effect of Ampicillin and Levofloxacin to Escherichia Coli and Staphylococcus Aureus Based on Microscopic Imaging Analysis. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazuz, M.L.; Golenser, J.; Fish, L.; Haynes, R.K.; Wollkomirsky, R.; Leibovich, B.; Shkap, V. Artemisone Inhibits in Vitro and in Vivo Propagation of Babesia Bovis and B. Bigemina Parasites. Exp Parasitol 2013, 135, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Drug Treatment Concentration#break#(nM) | BPQ | BPQ+ ELQ-316 | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (%) | CI 95% | Mean (%) | CI 95% | ||
| 25 | 99.87 | (99.78 - 99.96) | 97.31 | (96.16 – 98.46) | p=0.72 |
| 50 | 86.6 | (77.56 – 95.64) | 2.9 | (2.8 - 3.00) | p<0.05 |
| 75 | 54.25 | (52.33 – 56.17) | 2.31 | (1.89 – 2.73) | p<0.01 |
| 100 | 21.5 | (20.74 – 22.26) | 2.1 | (1.87 – 2.33) | p<0.01 |
| 150 | 4.64 | (4.1 – 5.18) | 2.37 | (2.24 – 2.50) | p<0.05 |
| 200 | 2.55 | (2.05 – 3.05) | 1.99 | (1.86 - 2.12) | p=0.51 |
| 300 | 3.01 | (2.67 – 3.35) | 3.06 | (2.73 – 3.39) | p=0.94 |
| 600 | 2.62 | (2.51 – 2.73) | 1.72 | (1.60 – 1.84) | p<0.01 |
| 1200 | 1.08 | (0.88 – 1.28) | 1.88 | (1.75 - 2.01) | p=0.1 |
| Drug Treatment Concentration (nM) | ID | ELQ316 + ID | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (%) | CI 95% | Mean (%) | CI 95% | ||
| 25 | 98.04 | N/A | 95.16 | (93.5 – 96.82) | p=0.36 |
| 50 | 99.22 | (98.90 – 99.54) | 89.25 | (85.16 – 93.34) | p=0.24 |
| 75 | 99.22 | N/A | 87.63 | (84.41 – 90.85) | p=0.13 |
| 100 | 100 | N/A | 81.18 | (79.37 – 82.99) | p<0.05 |
| 150 | 100 | N/A | 52.15 | (50.84 – 53.46) | p<0.01 |
| 200 | 89.22 | (77.98 – 100) | 25.27 | (24.81 – 25.73) | p<0.05 |
| 300 | 38.24 | (36.26 – 40.22) | 25.81 | (25.18 – 26.44) | p<0.05 |
| 600 | 21.57 | (20.25 – 22.89) | 1.33 | (1.29 - 1.37) | p<0.05 |
| 1200 | 17.16 | (16.83 – 17.49) | 0.59 | (0.49 – 0.69) | p<0.01 |
| Drug | IC50 (nM) | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | 95% CI | |
| BPQ | 77.06 | (70.16 - 86.01) |
| BPQ + ELQ-316 | 31.21 | (15.06 - 68.48) |
| ID | 635.1 | (280.9 – 2119) |
| ELQ-316 | 654.9 | (362.3 – 1411) |
| ID + ELQ-316 | 197 | (129.0 - 311.2) |
| Single drugs and combination treatments | Time post-treatment without drug (h) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | 48 | 72 | 96 | 120 | |
| Control | N/A | ||||
| BPQ | 200 to 1200 | 150 to 1200 | |||
| BPQ + ELQ-316 | 200 to 1200 | 100 to 1200 | 50 to 1200 | ||
| ELQ-316 | 600 to 1200 | ||||
| ID+ELQ-316 | 600 to 1200 | 300 to 1200 | |||
| ID | 1200 | 300 to 1200 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





