Submitted:
29 September 2024
Posted:
30 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Isolation and Phenotypic Identification of CD34+ Cells
Co-Culture System of MSCs with HSCs or with AML Cell Lines
Colony Forming Cell Assay
Transcriptional Expression Analysis
Protein Expression Analysis
Immunofluorescence Microscopy
Duo-Link In Situ Proximity Ligation Assay
Functional Assay of Adhesion and Communication
Osteogenic Differentiation Engagement
Alizarin Red Staining
Results
Reciprocal Direct Interaction between MSCs and CD34+ HSCs
Direct Cell-Cell Communication Is Decreased in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.
Discussion
Author Contribution
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, T.; Li, L. The Stem Cell Niches in Bone. J Clin Invest 2006, 116, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takizawa, H.; Schanz, U.; Manz, M.G. Ex Vivo Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells: Mission Accomplished? Swiss Med Wkly 2011, 141, w13316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Nilsson, S.K. Bone, Microenvironment and Hematopoiesis. Curr Opin Hematol 2012, 19, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinney, D.G.; Prockop, D.J. Concise Review: Mesenchymal Stem/Multipotent Stromal Cells: The State of Transdifferentiation and Modes of Tissue Repair--Current Views. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 2896–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.W.; Price, E.A.; Sahoo, D.; Beerman, I.; Maloney, W.J.; Rossi, D.J.; Schrier, S.L.; Weissman, I.L. Human Bone Marrow Hematopoietic Stem Cells Are Increased in Frequency and Myeloid-Biased with Age. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 20012–20017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, H.-G.; Avecilla, S.T.; Hooper, A.T.; Rafii, S. The Bone Marrow Vascular Niche: Home of HSC Differentiation and Mobilization. Physiology (Bethesda) 2005, 20, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorshkind, K. Regulation of Hemopoiesis by Bone Marrow Stromal Cells and Their Products. Annu Rev Immunol 1990, 8, 111–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, K.; Campbell, T.B.; Passegué, E. Normal and Leukemic Stem Cell Niches: Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson, A.; Frenette, P.S. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Niche Maintenance during Homeostasis and Regeneration. Nat Med 2014, 20, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeltsch, K.S.; Radke, T.F.; Laufs, S.; Giordano, F.A.; Allgayer, H.; Wenz, F.; Zeller, W.J.; Kögler, G.; Fruehauf, S.; Maier, P. Unrestricted Somatic Stem Cells: Interaction with CD34+ Cells in Vitro and in Vivo, Expression of Homing Genes and Exclusion of Tumorigenic Potential. Cytotherapy 2011, 13, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, S.; Nagai, A.; Abdullah, S.; Matsuda, C.; Taketani, T.; Kumakura, S.; Shibata, H.; Ishikura, H.; Kim, S.U.; Masuda, J. Effective Ex Vivo Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells Using Osteoblast-Differentiated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Is CXCL12 Dependent. Eur J Haematol 2010, 84, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lévesque, J.-P.; Helwani, F.M.; Winkler, I.G. The Endosteal “osteoblastic” Niche and Its Role in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Homing and Mobilization. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1979–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, N.R.; Li, D.Y. Robo4-Dependent Slit Signaling Stabilizes the Vasculature during Pathologic Angiogenesis and Cytokine Storm. Curr Opin Hematol 2011, 18, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, D.; Fonseca, A.-V.; Alakel, N.; Fierro, F.A.; Muller, K.; Bornhauser, M.; Ehninger, G.; Corbeil, D.; Ordemann, R. Hematopoietic Stem Cells in Co-Culture with Mesenchymal Stromal Cells--Modeling the Niche Compartments in Vitro. Haematologica 2010, 95, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willecke, K.; Eiberger, J.; Degen, J.; Eckardt, D.; Romualdi, A.; Güldenagel, M.; Deutsch, U.; Söhl, G. Structural and Functional Diversity of Connexin Genes in the Mouse and Human Genome. Biol Chem 2002, 383, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürig, J.; Rosenthal, C.; Halfmeyer, K.; Wiemann, M.; Novotny, J.; Bingmann, D.; Dührsen, U.; Schirrmacher, K. Intercellular Communication between Bone Marrow Stromal Cells and CD34+ Haematopoietic Progenitor Cells Is Mediated by Connexin 43-Type Gap Junctions. Br J Haematol 2000, 111, 416–425. [Google Scholar]
- Kouzi, F.; Zibara, K.; Bourgeais, J.; Picou, F.; Gallay, N.; Brossaud, J.; Dakik, H.; Roux, B.; Hamard, S.; Le Nail, L.-R.; Hleihel, R.; Foucault, A.; Ravalet, N.; Rouleux-Bonnin, F.; Gouilleux, F.; Mazurier, F.; Bene, M.C.; Akl, H.; Gyan, E.; Domenech, J.; El-Sabban, M.; Herault, O. Disruption of Gap Junctions Attenuates Acute Myeloid Leukemia Chemoresistance Induced by Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Oncogene 2020, 39, 1198–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maître, J.-L.; Heisenberg, C.-P. Three Functions of Cadherins in Cell Adhesion. Curr Biol 2013, 23, R626–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimperti, S.; Andreadis, S.T. CDH2 and CDH11 Act as Regulators of Stem Cell Fate Decisions. Stem Cell Res 2015, 14, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dbouk, H.A.; Mroue, R.M.; El-Sabban, M.E.; Talhouk, R.S. Connexins: A Myriad of Functions Extending beyond Assembly of Gap Junction Channels. Cell Commun Signal 2009, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiel, M.J.; Acar, M.; Radice, G.L.; Morrison, S.J. Hematopoietic Stem Cells Do Not Depend on N-Cadherin to Regulate Their Maintenance. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 4, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, K.; Arai, F.; Yoshihara, H.; Iwasaki, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Gomei, Y.; Suda, T. Knockdown of N-Cadherin Suppresses the Long-Term Engraftment of Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Blood 2010, 116, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stölzel, F.; Mohr, B.; Kramer, M.; Oelschlägel, U.; Bochtler, T.; Berdel, W.E.; Kaufmann, M.; Baldus, C.D.; Schäfer-Eckart, K.; Stuhlmann, R.; Einsele, H.; Krause, S.W.; Serve, H.; Hänel, M.; Herbst, R.; Neubauer, A.; Sohlbach, K.; Mayer, J.; Middeke, J.M.; Platzbecker, U.; Schaich, M.; Krämer, A.; Röllig, C.; Schetelig, J.; Bornhäuser, M.; Ehninger, G. Karyotype Complexity and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood Cancer J 2016, 6, e386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Bloomfield, C.D. Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med 2015, 373, 1136–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendall, L.J.; Daniel, A.; Kortlepel, K.; Gottlieb, D.J. Bone Marrow Adherent Layers Inhibit Apoptosis of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Exp Hematol 1994, 22, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Konopleva, M.; Konoplev, S.; Hu, W.; Zaritskey, A.Y.; Afanasiev, B.V.; Andreeff, M. Stromal Cells Prevent Apoptosis of AML Cells by Up-Regulation of Anti-Apoptotic Proteins. Leukemia 2002, 16, 1713–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhong, H. Roles of the Bone Marrow Niche in Hematopoiesis, Leukemogenesis, and Chemotherapy Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Hematology 2018, 23, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.C.; Tykocinski, M.L. Bone Marrow Stromal Cell Blockade of Human Leukemic Cell Differentiation. Blood 1994, 83, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.J.; Scadden, D.T. The Bone Marrow Niche for Haematopoietic Stem Cells. Nature 2014, 505, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, S.K.; Johnston, H.M.; Whitty, G.A.; Williams, B.; Webb, R.J.; Denhardt, D.T.; Bertoncello, I.; Bendall, L.J.; Simmons, P.J.; Haylock, D.N. Osteopontin, a Key Component of the Hematopoietic Stem Cell Niche and Regulator of Primitive Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells. Blood 2005, 106, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatmadar, S.; Sharma, S.; Cabana, R.; Powell, S.; Ruiz, P.; Krishan, A. Electronic Volume of CD34 Positive Cells from Peripheral Blood Apheresis Samples. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2008, 74, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vescio, R.A.; Hong, C.H.; Cao, J.; Kim, A.; Schiller, G.J.; Lichtenstein, A.K.; Berenson, R.J.; Berenson, J.R. The Hematopoietic Stem Cell Antigen, CD34, Is Not Expressed on the Malignant Cells in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 1994, 84, 3283–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P. MSC and HSPC Coculture: Mimicking Ex Vivo Bone Marrow Niche. Methods Mol Biol 2023, 2567, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wu, Y. Paracrine Molecules of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Hematopoietic Stem Cell Niche. Bone Marrow Res 2011, 2011, 353878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, S.P.; Balduino, A.; Bôdi, E.C.A.; El-Cheikh, M.C.; Campos de Carvalho, A.C.; Borojevic, R. Connexin Expression and Gap-Junction-Mediated Cell Interactions in an in Vitro Model of Haemopoietic Stroma. Cell Tissue Res 2004, 316, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancelas, J.A.; Koevoet, W.L.; de Koning, A.E.; Mayen, A.E.; Rombouts, E.J.; Ploemacher, R.E. Connexin-43 Gap Junctions Are Involved in Multiconnexin-Expressing Stromal Support of Hemopoietic Progenitors and Stem Cells. Blood 2000, 96, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecino-Rodriguez, E.; Dorshkind, K. Regulation of Hematopoiesis by Gap Junction-Mediated Intercellular Communication. J Leukoc Biol 2001, 70, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi Ishikawa, E.; Gonzalez-Nieto, D.; Ghiaur, G.; Dunn, S.K.; Ficker, A.M.; Murali, B.; Madhu, M.; Gutstein, D.E.; Fishman, G.I.; Barrio, L.C.; Cancelas, J.A. Connexin-43 Prevents Hematopoietic Stem Cell Senescence through Transfer of Reactive Oxygen Species to Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109, 9071–9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perucca, S.; Di Palma, A.; Piccaluga, P.P.; Gemelli, C.; Zoratti, E.; Bassi, G.; Giacopuzzi, E.; Lojacono, A.; Borsani, G.; Tagliafico, E.; Scupoli, M.T.; Bernardi, S.; Zanaglio, C.; Cattina, F.; Cancelli, V.; Malagola, M.; Krampera, M.; Marini, M.; Almici, C.; Ferrari, S.; Russo, D. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs) Induce Ex Vivo Proliferation and Erythroid Commitment of Cord Blood Haematopoietic Stem Cells (CB-CD34+ Cells). PLoS One 2017, 12, e0172430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beederman, M.; Lamplot, J.D.; Nan, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Yin, L.; Li, R.; Shui, W.; Zhang, H.; Kim, S.H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Kong, Y.; Denduluri, S.; Rogers, M.R.; Pratt, A.; Haydon, R.C.; Luu, H.H.; Angeles, J.; Shi, L.L.; He, T.-C. BMP Signaling in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation and Bone Formation. J Biomed Sci Eng 2013, 6, 32–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.W. Review of Signaling Pathways Governing MSC Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation. Scientifica (Cairo) 2013, 2013, 684736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradi, G.; Baldazzi, C.; Očadlíková, D.; Marconi, G.; Parisi, S.; Testoni, N.; Finelli, C.; Cavo, M.; Curti, A.; Ciciarello, M. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Myelodysplastic and Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients Display in Vitro Reduced Proliferative Potential and Similar Capacity to Support Leukemia Cell Survival. Stem Cell Res Ther 2018, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Ross, C.; Srivastava, S. Ally to Adversary: Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Transformation in Leukaemia. Cancer Cell Int 2019, 19, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Fan, X.; Houghton, J. Tumor Microenvironment: The Role of the Tumor Stroma in Cancer. J Cell Biochem 2007, 101, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trédan, O.; Galmarini, C.M.; Patel, K.; Tannock, I.F. Drug Resistance and the Solid Tumor Microenvironment. J Natl Cancer Inst 2007, 99, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraguassú-Braga, F.H.; Borojevic, R.; Bouzas, L.F.; Barcinski, M.A.; Bonomo, A. Bone Marrow Stroma Inhibits Proliferation and Apoptosis in Leukemic Cells through Gap Junction-Mediated Cell Communication. Cell Death Differ 2003, 10, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, P.; Ju, S.; Chen, P.; Li, J.; Fu, J. Impact of Connexin 43 Coupling on Survival and Migration of Multiple Myeloma Cells. Arch Med Sci 2017, 13, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
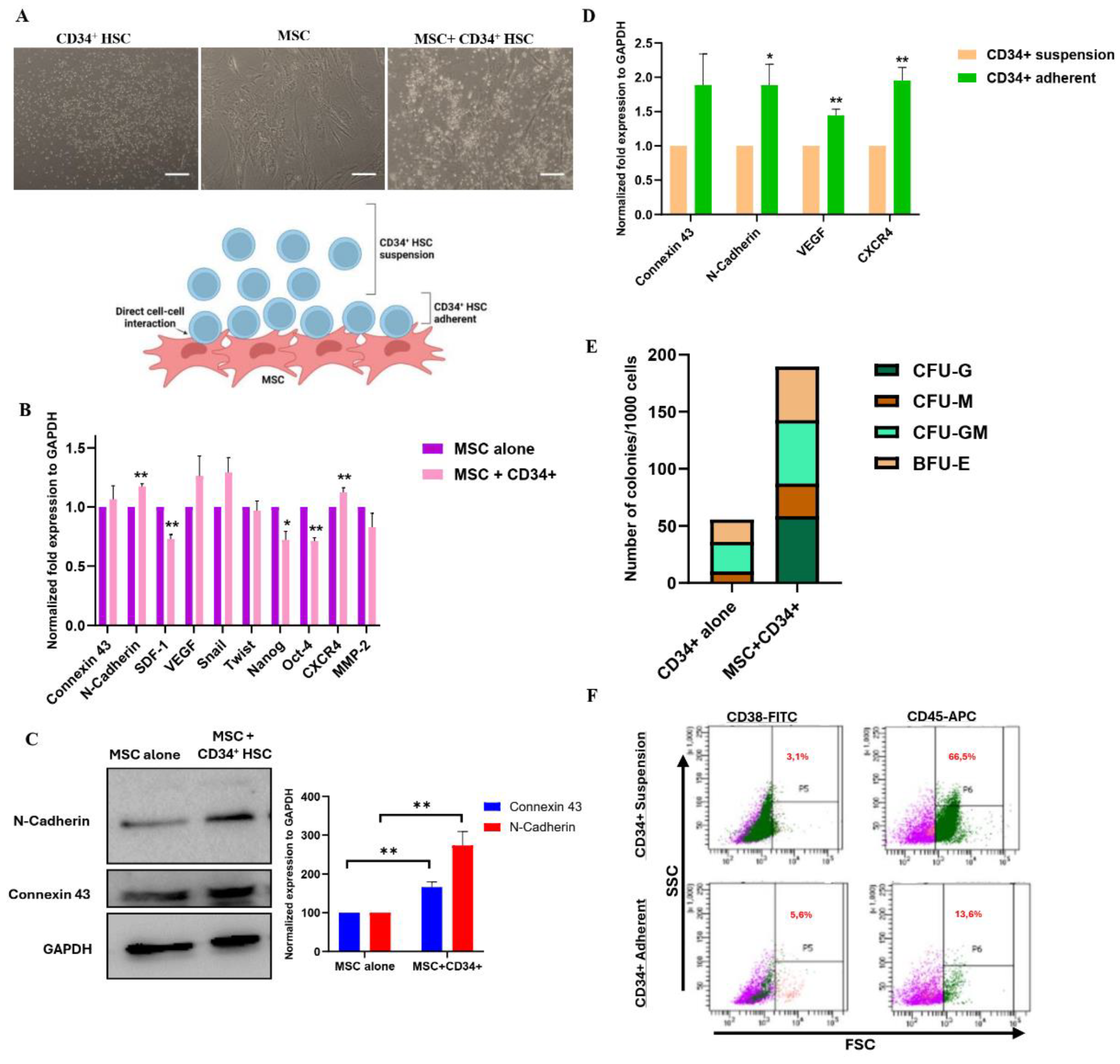
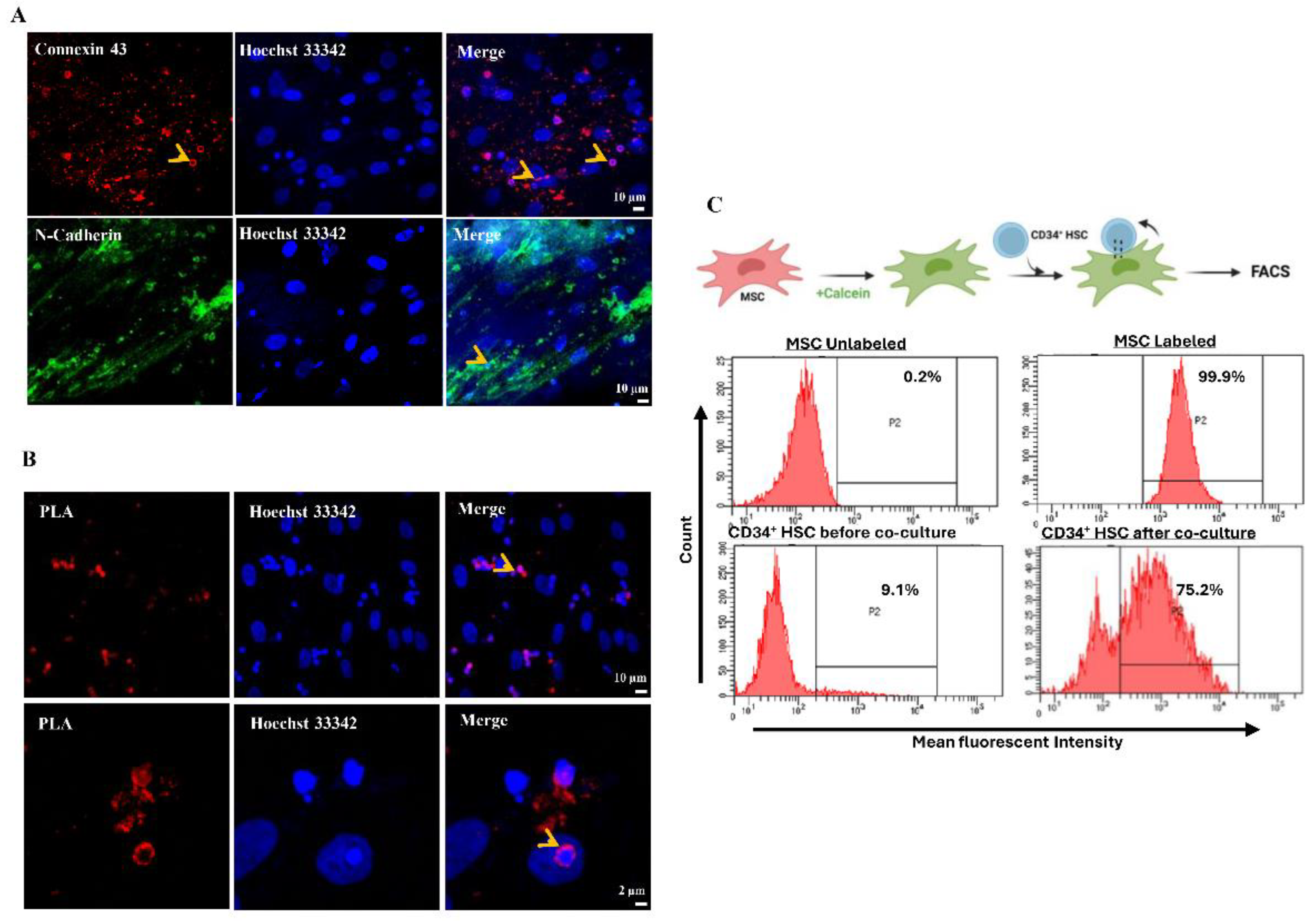
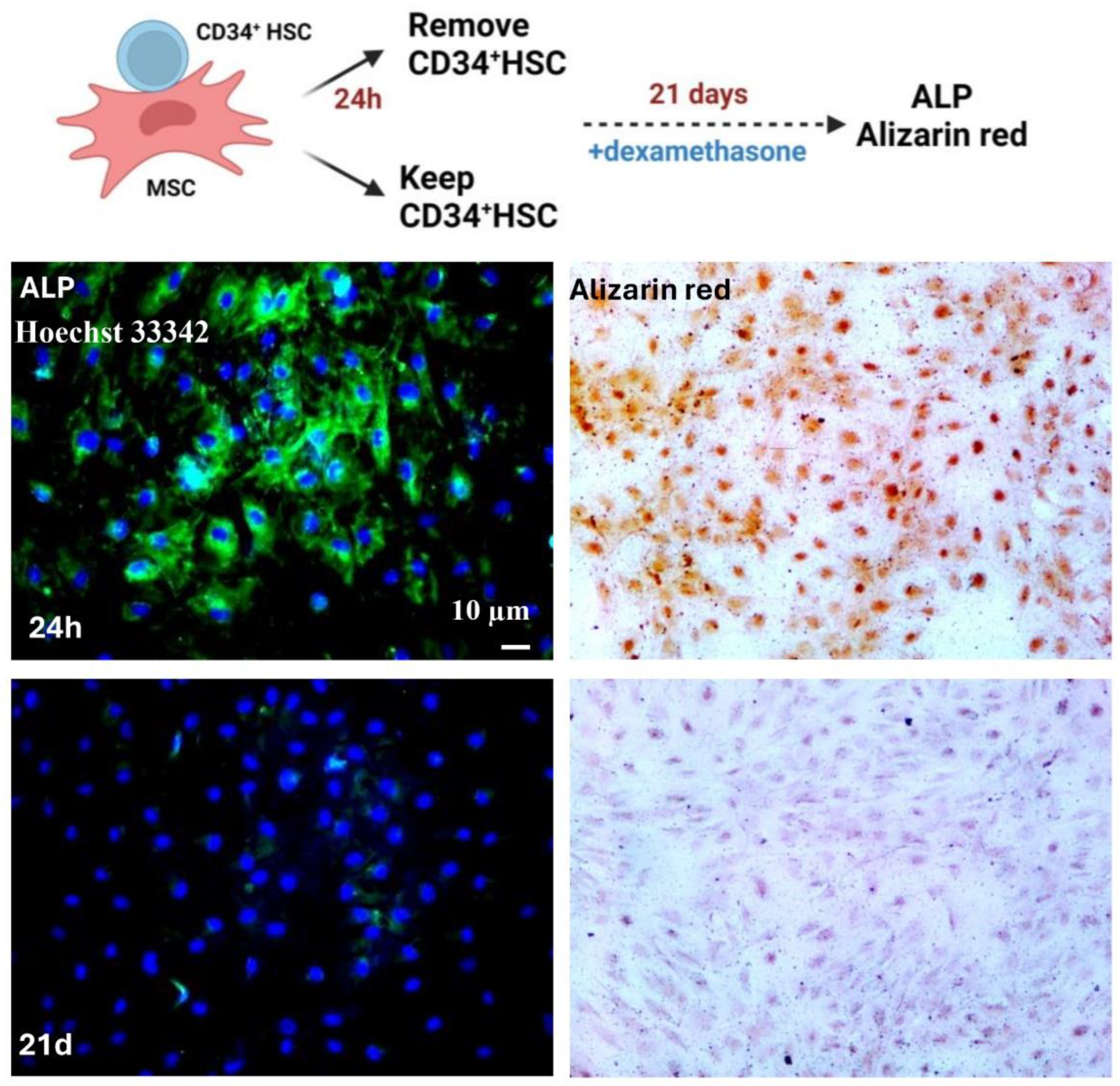
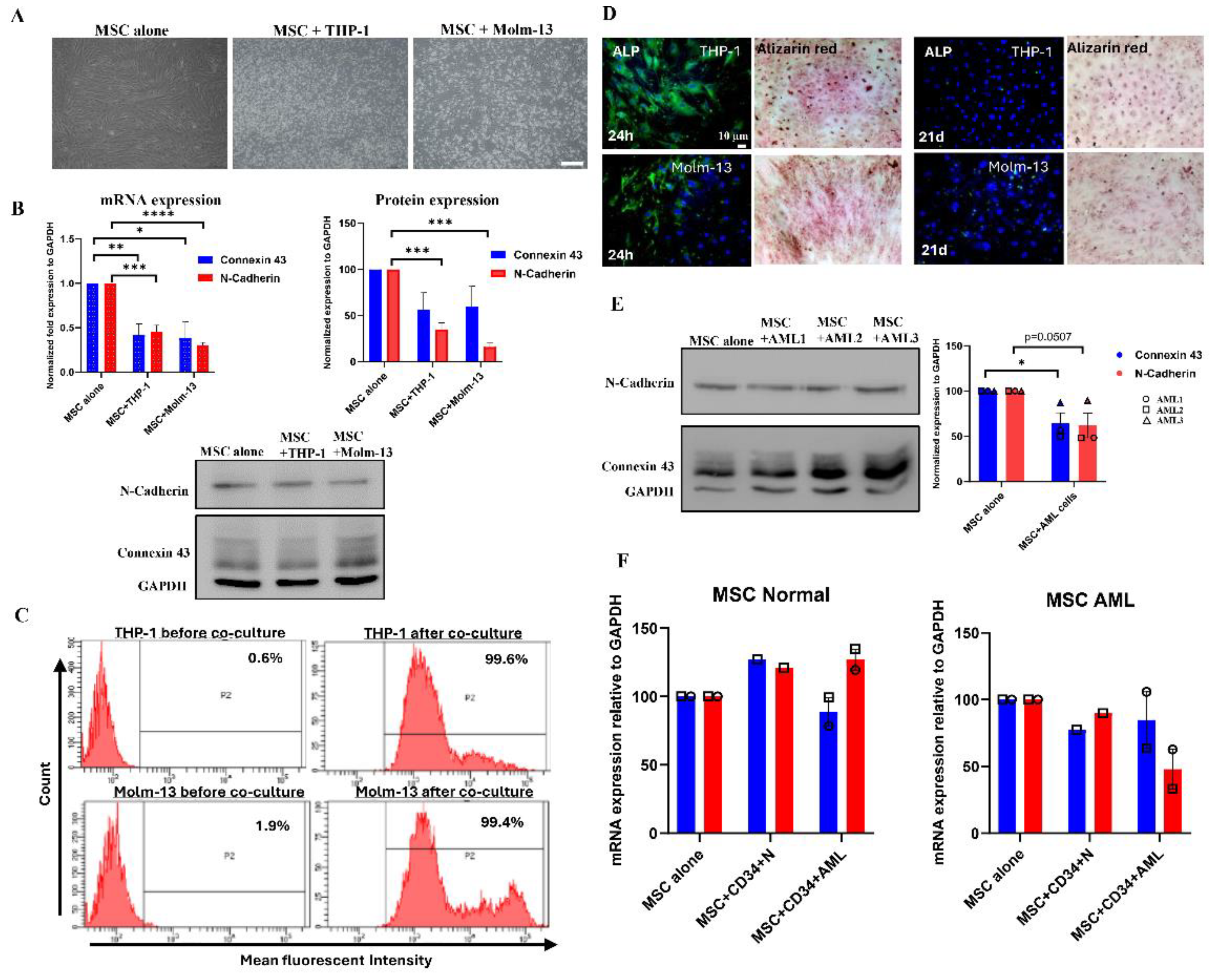
| Genes | Sequence |
|---|---|
| Connexin 43 | F: GGA AGA TGG GCT CAT GAA AA R: GCA AAG GCC TGT AAC ACC AT |
| N-cadherin | F: GGT GGA GGA GAA GAA GAC CAG R: GGC ATC AGG CTC CAC AGT |
| MMP2 | F: TTG ACG GTA AGG ACG GAC TC R: ACT TGC AGT ACT CCC CAT CG |
| SDF-1 | F: GCC CGT CAG CCT GAG CTA CA R: TTC TTC AGC CGG CGT ACA ATC T |
| VEGF | F: AGG CCC ACA GGG ATT TTC TT R: ATC AAA CCT CAC CAA GGC CA |
| Snail | F: CTT CCA GCA GCC CTA CGA C R: CGG TGG GGT TGA GGA TCT |
| Twist | F: AGC TAC GCC TTC TCG GTC T R: CCT TCT CTG GAA ACA ATG ACA TC |
| Nanog | F: CAG AAG GCC TCA GCA CCT AC R: ATT GTT CCA GGT CTG GTT GC |
| Oct-4 | F: CAG TGC CCG AAA CCC ACA C R: GGA GGAC CCA GCA GCC TCA AA |
| CXCR4 | F: CCT CCT GCT GAC TAT TCC CGA R: GGA ACA CAA CCA CCC ACA AGT |
| GAPDH | F: TGG TGC TCA GTG TAG CCC AG R: GGA CCT TGA CCT GCC GTC TAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





