Submitted:
28 September 2024
Posted:
30 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Genetic Background of ALS
2.1. Overview
2.1. ALS with SOD1 Mutations
3. Treatment of ALS
| Drug | Year | Administration | Mechanism | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| riluzole | 1995 | Oral | Glutamate antagonist | Thickened riluzole was approved in 2018. Oral film was approved in 2019. |
| edaravone | 2017 | Intravenous, Oral | Free radical scavenger | Oral formation was approved in 2022. |
| PB/TURSO | 2022 | Oral | Inhibition of motor neuron apoptosis | Voluntarily removed from the market in 2024 base on the results from Phase 3 PHOENIX trial. |
| tofersen | 2023 | Intrathecal | ASO (2′-MOE gapmer) | For ALS patients with SOD1 mutation |
4. ASO in CNS Disorders
4.1. ASO Overview
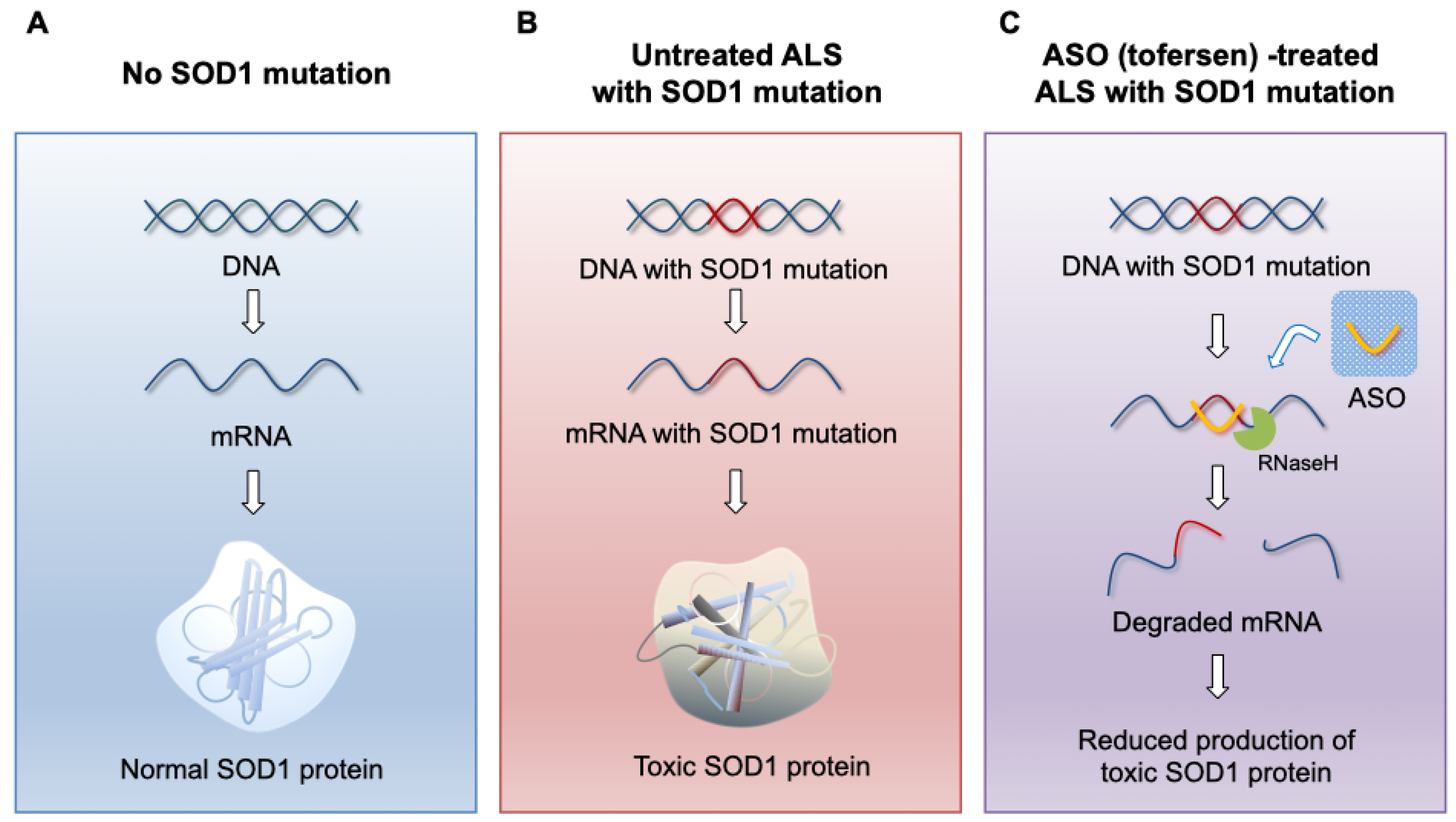
4.2. Challenges of ASO Therapy for CNS Disorders
5. ASO Therapy for SOD1 ALS
5.1. Background Leading to the Development of Tofersen
5.2. Preclinical Study of Tofersen
5.3. Clinical Study of Tofersen
5.3.1. Phase 1/2 VALOR
5.3.2. Phase 3 VALOR
5.3.3. Phase 3 Extension Study
5.4. Trends after Tofersen Approval
5.4.1. Phase 3 ATLAS
6. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, D. R.; Aslinia, F.; Yale, S. H.; Mazza, J. J., Jean-Martin Charcot: the father of neurology. Clin Med Res 2011, 9, (1), 46-9. [CrossRef]
- Akçimen, F.; Lopez, E. R.; Landers, J. E.; Nath, A.; Chiò, A.; Chia, R.; Traynor, B. J., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: translating genetic discoveries into therapies. Nat Rev Genet 2023, 24, (9), 642-658. [CrossRef]
- Rowland, L. P.; Shneider, N. A., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med 2001, 344, (22), 1688-700.
- Chiò, A.; Logroscino, G.; Traynor, B. J.; Collins, J.; Simeone, J. C.; Goldstein, L. A.; White, L. A., Global epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review of the published literature. Neuroepidemiology 2013, 41, (2), 118-30. [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, T.; Liu, L.; Yao, X.; Chen, L.; Fan, D.; Zhan, S.; Wang, S., Global variation in prevalence and incidence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol 2020, 267, (4), 944-953.
- Rosen, D. R., Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 1993, 364, (6435), 362.
- Blair, H. A., Tofersen: First Approval. Drugs 2023, 83, (11), 1039-1043. [CrossRef]
- Goutman, S. A.; Hardiman, O.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Chió, A.; Savelieff, M. G.; Kiernan, M. C.; Feldman, E. L., Emerging insights into the complex genetics and pathophysiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 2022, 21, (5), 465-479. [CrossRef]
- Chia, R.; Chiò, A.; Traynor, B. J., Novel genes associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: diagnostic and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol 2018, 17, (1), 94-102. [CrossRef]
- Renton, A. E.; Chiò, A.; Traynor, B. J., State of play in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis genetics. Nat Neurosci 2014, 17, (1), 17-23. [CrossRef]
- Keller, M. F.; Ferrucci, L.; Singleton, A. B.; Tienari, P. J.; Laaksovirta, H.; Restagno, G.; Chiò, A.; Traynor, B. J.; Nalls, M. A., Genome-wide analysis of the heritability of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. JAMA Neurol 2014, 71, (9), 1123-34. [CrossRef]
- Al-Chalabi, A.; Fang, F.; Hanby, M. F.; Leigh, P. N.; Shaw, C. E.; Ye, W.; Rijsdijk, F., An estimate of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis heritability using twin data. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2010, 81, (12), 1324-6. [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Kamel, F.; Lichtenstein, P.; Bellocco, R.; Sparén, P.; Sandler, D. P.; Ye, W., Familial aggregation of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2009, 66, (1), 94-9. [CrossRef]
- Grassano, M.; Calvo, A.; Moglia, C.; Sbaiz, L.; Brunetti, M.; Barberis, M.; Casale, F.; Manera, U.; Vasta, R.; Canosa, A.; D'Alfonso, S.; Corrado, L.; Mazzini, L.; Dalgard, C.; Karra, R.; Chia, R.; Traynor, B.; Chiò, A., Systematic evaluation of genetic mutations in ALS: a population-based study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2022, 93, (11), 1190-3. [CrossRef]
- Vasta, R.; Chia, R.; Traynor, B. J.; Chiò, A., Unraveling the complex interplay between genes, environment, and climate in ALS. EBioMedicine 2022, 75, 103795. [CrossRef]
- van Rheenen, W.; van der Spek, R. A. A.; Bakker, M. K.; van Vugt, J.; Hop, P. J.; Zwamborn, R. A. J.; de Klein, N.; Westra, H. J.; Bakker, O. B.; Deelen, P.; Shireby, G.; Hannon, E.; Moisse, M.; Baird, D.; Restuadi, R.; Dolzhenko, E.; Dekker, A. M.; Gawor, K.; Westeneng, H. J.; Tazelaar, G. H. P.; van Eijk, K. R.; Kooyman, M.; Byrne, R. P.; Doherty, M.; Heverin, M.; Al Khleifat, A.; Iacoangeli, A.; Shatunov, A.; Ticozzi, N.; Cooper-Knock, J.; Smith, B. N.; Gromicho, M.; Chandran, S.; Pal, S.; Morrison, K. E.; Shaw, P. J.; Hardy, J.; Orrell, R. W.; Sendtner, M.; Meyer, T.; Başak, N.; van der Kooi, A. J.; Ratti, A.; Fogh, I.; Gellera, C.; Lauria, G.; Corti, S.; Cereda, C.; Sproviero, D.; D'Alfonso, S.; Sorarù, G.; Siciliano, G.; Filosto, M.; Padovani, A.; Chiò, A.; Calvo, A.; Moglia, C.; Brunetti, M.; Canosa, A.; Grassano, M.; Beghi, E.; Pupillo, E.; Logroscino, G.; Nefussy, B.; Osmanovic, A.; Nordin, A.; Lerner, Y.; Zabari, M.; Gotkine, M.; Baloh, R. H.; Bell, S.; Vourc'h, P.; Corcia, P.; Couratier, P.; Millecamps, S.; Meininger, V.; Salachas, F.; Mora Pardina, J. S.; Assialioui, A.; Rojas-García, R.; Dion, P. A.; Ross, J. P.; Ludolph, A. C.; Weishaupt, J. H.; Brenner, D.; Freischmidt, A.; Bensimon, G.; Brice, A.; Durr, A.; Payan, C. A. M.; Saker-Delye, S.; Wood, N. W.; Topp, S.; Rademakers, R.; Tittmann, L.; Lieb, W.; Franke, A.; Ripke, S.; Braun, A.; Kraft, J.; Whiteman, D. C.; Olsen, C. M.; Uitterlinden, A. G.; Hofman, A.; Rietschel, M.; Cichon, S.; Nöthen, M. M.; Amouyel, P.; Traynor, B. J.; Singleton, A. B.; Mitne Neto, M.; Cauchi, R. J.; Ophoff, R. A.; Wiedau-Pazos, M.; Lomen-Hoerth, C.; van Deerlin, V. M.; Grosskreutz, J.; Roediger, A.; Gaur, N.; Jörk, A.; Barthel, T.; Theele, E.; Ilse, B.; Stubendorff, B.; Witte, O. W.; Steinbach, R.; Hübner, C. A.; Graff, C.; Brylev, L.; Fominykh, V.; Demeshonok, V.; Ataulina, A.; Rogelj, B.; Koritnik, B.; Zidar, J.; Ravnik-Glavač, M.; Glavač, D.; Stević, Z.; Drory, V.; Povedano, M.; Blair, I. P.; Kiernan, M. C.; Benyamin, B.; Henderson, R. D.; Furlong, S.; Mathers, S.; McCombe, P. A.; Needham, M.; Ngo, S. T.; Nicholson, G. A.; Pamphlett, R.; Rowe, D. B.; Steyn, F. J.; Williams, K. L.; Mather, K. A.; Sachdev, P. S.; Henders, A. K.; Wallace, L.; de Carvalho, M.; Pinto, S.; Petri, S.; Weber, M.; Rouleau, G. A.; Silani, V.; Curtis, C. J.; Breen, G.; Glass, J. D.; Brown, R. H., Jr.; Landers, J. E.; Shaw, C. E.; Andersen, P. M.; Groen, E. J. N.; van Es, M. A.; Pasterkamp, R. J.; Fan, D.; Garton, F. C.; McRae, A. F.; Davey Smith, G.; Gaunt, T. R.; Eberle, M. A.; Mill, J.; McLaughlin, R. L.; Hardiman, O.; Kenna, K. P.; Wray, N. R.; Tsai, E.; Runz, H.; Franke, L.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Van Damme, P.; van den Berg, L. H.; Veldink, J. H., Common and rare variant association analyses in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis identify 15 risk loci with distinct genetic architectures and neuron-specific biology. Nat Genet 2021, 53, (12), 1636-1648.
- Bandres-Ciga, S.; Noyce, A. J.; Hemani, G.; Nicolas, A.; Calvo, A.; Mora, G.; Tienari, P. J.; Stone, D. J.; Nalls, M. A.; Singleton, A. B.; Chiò, A.; Traynor, B. J., Shared polygenic risk and causal inferences in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2019, 85, (4), 470-481. [CrossRef]
- Pingault, J. B.; O'Reilly, P. F.; Schoeler, T.; Ploubidis, G. B.; Rijsdijk, F.; Dudbridge, F., Using genetic data to strengthen causal inference in observational research. Nat Rev Genet 2018, 19, (9), 566-580. [CrossRef]
- Bunton-Stasyshyn, R. K.; Saccon, R. A.; Fratta, P.; Fisher, E. M., SOD1 Function and Its Implications for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Pathology: New and Renascent Themes. Neuroscientist 2015, 21, (5), 519-29.
- Abel, O.; Powell, J. F.; Andersen, P. M.; Al-Chalabi, A., ALSoD: A user-friendly online bioinformatics tool for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis genetics. Hum Mutat 2012, 33, (9), 1345-51. [CrossRef]
- McCann, E. P.; Henden, L.; Fifita, J. A.; Zhang, K. Y.; Grima, N.; Bauer, D. C.; Chan Moi Fat, S.; Twine, N. A.; Pamphlett, R.; Kiernan, M. C.; Rowe, D. B.; Williams, K. L.; Blair, I. P., Evidence for polygenic and oligogenic basis of Australian sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Med Genet 2020. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Nishiyama, A.; Warita, H.; Aoki, M., Genetics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: seeking therapeutic targets in the era of gene therapy. J Hum Genet 2023, 68, (3), 131-152. [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, A.; Niihori, T.; Warita, H.; Izumi, R.; Akiyama, T.; Kato, M.; Suzuki, N.; Aoki, Y.; Aoki, M., Comprehensive targeted next-generation sequencing in Japanese familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol Aging 2017, 53, 194.e1-194.e8. [CrossRef]
- Bernard, E.; Pegat, A.; Svahn, J.; Bouhour, F.; Leblanc, P.; Millecamps, S.; Thobois, S.; Guissart, C.; Lumbroso, S.; Mouzat, K., Clinical and Molecular Landscape of ALS Patients with SOD1 Mutations: Novel Pathogenic Variants and Novel Phenotypes. A Single ALS Center Study. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, (18).
- Miller, T. M.; Cudkowicz, M. E.; Genge, A.; Shaw, P. J.; Sobue, G.; Bucelli, R. C.; Chiò, A.; Van Damme, P.; Ludolph, A. C.; Glass, J. D.; Andrews, J. A.; Babu, S.; Benatar, M.; McDermott, C. J.; Cochrane, T.; Chary, S.; Chew, S.; Zhu, H.; Wu, F.; Nestorov, I.; Graham, D.; Sun, P.; McNeill, M.; Fanning, L.; Ferguson, T. A.; Fradette, S., Trial of Antisense Oligonucleotide Tofersen for SOD1 ALS. N Engl J Med 2022, 387, (12), 1099-1110. [CrossRef]
- Radunovíc, A.; Leigh, P. N., Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene mutations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: correlation between genotype and clinical features. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1996, 61, (6), 565-72.
- Berdyński, M.; Miszta, P.; Safranow, K.; Andersen, P. M.; Morita, M.; Filipek, S.; Żekanowski, C.; Kuźma-Kozakiewicz, M., SOD1 mutations associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis analysis of variant severity. Sci Rep 2022, 12, (1), 103. [CrossRef]
- Cudkowicz, M. E.; McKenna-Yasek, D.; Sapp, P. E.; Chin, W.; Geller, B.; Hayden, D. L.; Schoenfeld, D. A.; Hosler, B. A.; Horvitz, H. R.; Brown, R. H., Epidemiology of mutations in superoxide dismutase in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 1997, 41, (2), 210-21.
- Saeed, M.; Yang, Y.; Deng, H. X.; Hung, W. Y.; Siddique, N.; Dellefave, L.; Gellera, C.; Andersen, P. M.; Siddique, T., Age and founder effect of SOD1 A4V mutation causing ALS. Neurology 2009, 72, (19), 1634-9. [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z. Y.; Liu, M. S.; Li, X. G.; Cui, L. Y., H46R SOD1 mutation is consistently associated with a relatively benign form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with slow progression. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 2016, 17, (7-8), 610-613. [CrossRef]
- Sau, D.; De Biasi, S.; Vitellaro-Zuccarello, L.; Riso, P.; Guarnieri, S.; Porrini, M.; Simeoni, S.; Crippa, V.; Onesto, E.; Palazzolo, I.; Rusmini, P.; Bolzoni, E.; Bendotti, C.; Poletti, A., Mutation of SOD1 in ALS: a gain of a loss of function. Hum Mol Genet 2007, 16, (13), 1604-18. [CrossRef]
- Ekhtiari Bidhendi, E.; Bergh, J.; Zetterström, P.; Forsberg, K.; Pakkenberg, B.; Andersen, P. M.; Marklund, S. L.; Brännström, T., Mutant superoxide dismutase aggregates from human spinal cord transmit amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 2018, 136, (6), 939-953. [CrossRef]
- Gurney, M. E.; Pu, H.; Chiu, A. Y.; Dal Canto, M. C.; Polchow, C. Y.; Alexander, D. D.; Caliendo, J.; Hentati, A.; Kwon, Y. W.; Deng, H. X.; et al., Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science 1994, 264, (5166), 1772-5. [CrossRef]
- Bruijn, L. I.; Cleveland, D. W., Mechanisms of selective motor neuron death in ALS: insights from transgenic mouse models of motor neuron disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 1996, 22, (5), 373-87. [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Okada, Y.; Nakamichi, M.; Nakamura, M.; Toyama, Y.; Sobue, G.; Nagai, M.; Aoki, M.; Itoyama, Y.; Okano, H., Disease progression of human SOD1 (G93A) transgenic ALS model rats. J Neurosci Res 2006, 83, (1), 119-33. [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Homma, K.; Ichijo, H., SOD1 in neurotoxicity and its controversial roles in SOD1 mutation-negative ALS. Adv Biol Regul 2016, 60, 95-104. [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, H.; Almer, G.; Yamashita, S.; Guégan, C.; Nagai, M.; Xu, Z.; Sosunov, A. A.; McKhann, G. M., 2nd; Przedborski, S., Spinal cord endoplasmic reticulum stress associated with a microsomal accumulation of mutant superoxide dismutase-1 in an ALS model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, (15), 6025-30. [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, H.; Polymenidou, M.; Cleveland, D. W., Non-cell autonomous toxicity in neurodegenerative disorders: ALS and beyond. J Cell Biol 2009, 187, (6), 761-72. [CrossRef]
- Masrori, P.; Van Damme, P., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a clinical review. Eur J Neurol 2020, 27, (10), 1918-1929. [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L. R.; Li, Y.; Asress, S. A.; Jones, D. P.; Glass, J. D., Absence of SOD1 leads to oxidative stress in peripheral nerve and causes a progressive distal motor axonopathy. Exp Neurol 2012, 233, (1), 163-71. [CrossRef]
- Reaume, A. G.; Elliott, J. L.; Hoffman, E. K.; Kowall, N. W.; Ferrante, R. J.; Siwek, D. F.; Wilcox, H. M.; Flood, D. G.; Beal, M. F.; Brown, R. H., Jr.; Scott, R. W.; Snider, W. D., Motor neurons in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase-deficient mice develop normally but exhibit enhanced cell death after axonal injury. Nat Genet 1996, 13, (1), 43-7. [CrossRef]
- Doble, A., The pharmacology and mechanism of action of riluzole. Neurology 1996, 47, (6 Suppl 4), S233-41. [CrossRef]
- Bensimon, G.; Lacomblez, L.; Meininger, V., A controlled trial of riluzole in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. ALS/Riluzole Study Group. N Engl J Med 1994, 330, (9), 585-91. [CrossRef]
- Lacomblez, L.; Bensimon, G.; Leigh, P. N.; Guillet, P.; Meininger, V., Dose-ranging study of riluzole in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis/Riluzole Study Group II. Lancet 1996, 347, (9013), 1425-31. [CrossRef]
- Hinchcliffe, M.; Smith, A., Riluzole: real-world evidence supports significant extension of median survival times in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis 2017, 7, 61-70. [CrossRef]
- Exploratory double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study of edaravone (MCI-186) in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Japan ALS severity classification: Grade 3, requiring assistance for eating, excretion or ambulation). Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 2017, 18, (sup1), 40-48.
- Takahashi, F.; Takei, K.; Tsuda, K.; Palumbo, J., Post-hoc analysis of MCI186-17, the extension study to MCI186-16, the confirmatory double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study of edaravone in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 2017, 18, (sup1), 32-39. [CrossRef]
- Safety and efficacy of edaravone in well defined patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 2017, 16, (7), 505-512.
- Paganoni, S.; Hendrix, S.; Dickson, S. P.; Knowlton, N.; Macklin, E. A.; Berry, J. D.; Elliott, M. A.; Maiser, S.; Karam, C.; Caress, J. B.; Owegi, M. A.; Quick, A.; Wymer, J.; Goutman, S. A.; Heitzman, D.; Heiman-Patterson, T. D.; Jackson, C. E.; Quinn, C.; Rothstein, J. D.; Kasarskis, E. J.; Katz, J.; Jenkins, L.; Ladha, S.; Miller, T. M.; Scelsa, S. N.; Vu, T. H.; Fournier, C. N.; Glass, J. D.; Johnson, K. M.; Swenson, A.; Goyal, N. A.; Pattee, G. L.; Andres, P. L.; Babu, S.; Chase, M.; Dagostino, D.; Hall, M.; Kittle, G.; Eydinov, M.; McGovern, M.; Ostrow, J.; Pothier, L.; Randall, R.; Shefner, J. M.; Sherman, A. V.; St Pierre, M. E.; Tustison, E.; Vigneswaran, P.; Walker, J.; Yu, H.; Chan, J.; Wittes, J.; Yu, Z. F.; Cohen, J.; Klee, J.; Leslie, K.; Tanzi, R. E.; Gilbert, W.; Yeramian, P. D.; Schoenfeld, D.; Cudkowicz, M. E., Long-term survival of participants in the CENTAUR trial of sodium phenylbutyrate-taurursodiol in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 2021, 63, (1), 31-39. [CrossRef]
- Ketabforoush, A.; Faghihi, F.; Azedi, F.; Ariaei, A.; Habibi, M. A.; Khalili, M.; Ashtiani, B. H.; Joghataei, M. T.; Arnold, W. D., Sodium Phenylbutyrate and Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid: A Story of Hope Turned to Disappointment in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Treatment. Clin Drug Investig 2024, 44, (7), 495-512. [CrossRef]
- Mead, R. J.; Shan, N.; Reiser, H. J.; Marshall, F.; Shaw, P. J., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a neurodegenerative disorder poised for successful therapeutic translation. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2023, 22, (3), 185-212. [CrossRef]
- Lauffer, M. C.; van Roon-Mom, W.; Aartsma-Rus, A., Possibilities and limitations of antisense oligonucleotide therapies for the treatment of monogenic disorders. Commun Med (Lond) 2024, 4, (1), 6. [CrossRef]
- Shadid, M.; Badawi, M.; Abulrob, A., Antisense oligonucleotides: absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2021, 17, (11), 1281-1292. [CrossRef]
- Leckie, J.; Yokota, T., Potential of Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Conjugated Antisense Oligonucleotides for the Treatment of SMA. Molecules 2024, 29, (11). [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T. C.; Langer, R.; Wood, M. J. A., Advances in oligonucleotide drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2020, 19, (10), 673-694. [CrossRef]
- Stein, H.; Hausen, P., Enzyme from calf thymus degrading the RNA moiety of DNA-RNA Hybrids: effect on DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Science 1969, 166, (3903), 393-5. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lima, W. F.; Zhang, H.; Fan, A.; Sun, H.; Crooke, S. T., Determination of the role of the human RNase H1 in the pharmacology of DNA-like antisense drugs. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, (17), 17181-9. [CrossRef]
- Rigo, F.; Hua, Y.; Chun, S. J.; Prakash, T. P.; Krainer, A. R.; Bennett, C. F., Synthetic oligonucleotides recruit ILF2/3 to RNA transcripts to modulate splicing. Nat Chem Biol 2012, 8, (6), 555-61. [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, M. L.; Zamecnik, P. C., Inhibition of Rous sarcoma viral RNA translation by a specific oligodeoxyribonucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1978, 75, (1), 285-8. [CrossRef]
- Haque, U. S.; Yokota, T., Recent Progress in Gene-Targeting Therapies for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Promises and Challenges. Genes (Basel) 2024, 15, (8). [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M. D.; Zhao, Z.; Montagne, A.; Nelson, A. R.; Zlokovic, B. V., Blood-Brain Barrier: From Physiology to Disease and Back. Physiol Rev 2019, 99, (1), 21-78. [CrossRef]
- Barchet, T. M.; Amiji, M. M., Challenges and opportunities in CNS delivery of therapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2009, 6, (3), 211-25. [CrossRef]
- Smith, R. A.; Miller, T. M.; Yamanaka, K.; Monia, B. P.; Condon, T. P.; Hung, G.; Lobsiger, C. S.; Ward, C. M.; McAlonis-Downes, M.; Wei, H.; Wancewicz, E. V.; Bennett, C. F.; Cleveland, D. W., Antisense oligonucleotide therapy for neurodegenerative disease. J Clin Invest 2006, 116, (8), 2290-6. [CrossRef]
- Kordasiewicz, H. B.; Stanek, L. M.; Wancewicz, E. V.; Mazur, C.; McAlonis, M. M.; Pytel, K. A.; Artates, J. W.; Weiss, A.; Cheng, S. H.; Shihabuddin, L. S.; Hung, G.; Bennett, C. F.; Cleveland, D. W., Sustained therapeutic reversal of Huntington's disease by transient repression of huntingtin synthesis. Neuron 2012, 74, (6), 1031-44.
- Passini, M. A.; Bu, J.; Richards, A. M.; Kinnecom, C.; Sardi, S. P.; Stanek, L. M.; Hua, Y.; Rigo, F.; Matson, J.; Hung, G.; Kaye, E. M.; Shihabuddin, L. S.; Krainer, A. R.; Bennett, C. F.; Cheng, S. H., Antisense oligonucleotides delivered to the mouse CNS ameliorate symptoms of severe spinal muscular atrophy. Sci Transl Med 2011, 3, (72), 72ra18. [CrossRef]
- Chiriboga, C. A.; Swoboda, K. J.; Darras, B. T.; Iannaccone, S. T.; Montes, J.; De Vivo, D. C.; Norris, D. A.; Bennett, C. F.; Bishop, K. M., Results from a phase 1 study of nusinersen (ISIS-SMN(Rx)) in children with spinal muscular atrophy. Neurology 2016, 86, (10), 890-7. [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.; To, T. M.; Seetasith, A.; Patel, A. M.; Iannaccone, S. T., Adherence and Persistence to Nusinersen for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: A US Claims-Based Analysis. Adv Ther 2023, 40, (3), 903-919. [CrossRef]
- Cantara, S.; Simoncelli, G.; Ricci, C., Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) in Motor Neuron Diseases: A Road to Cure in Light and Shade. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, (9). [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shinobu, L. A.; Ward, C. M.; Young, D.; Cleveland, D. W., Elevation of the Hsp70 chaperone does not effect toxicity in mouse models of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem 2005, 93, (4), 875-82. [CrossRef]
- Miller, T. M.; Pestronk, A.; David, W.; Rothstein, J.; Simpson, E.; Appel, S. H.; Andres, P. L.; Mahoney, K.; Allred, P.; Alexander, K.; Ostrow, L. W.; Schoenfeld, D.; Macklin, E. A.; Norris, D. A.; Manousakis, G.; Crisp, M.; Smith, R.; Bennett, C. F.; Bishop, K. M.; Cudkowicz, M. E., An antisense oligonucleotide against SOD1 delivered intrathecally for patients with SOD1 familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a phase 1, randomised, first-in-man study. Lancet Neurol 2013, 12, (5), 435-42. [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, C.; Wood, M. J. A., Antisense oligonucleotides: the next frontier for treatment of neurological disorders. Nat Rev Neurol 2018, 14, (1), 9-21. [CrossRef]
- McCampbell, A.; Cole, T.; Wegener, A. J.; Tomassy, G. S.; Setnicka, A.; Farley, B. J.; Schoch, K. M.; Hoye, M. L.; Shabsovich, M.; Sun, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, M.; Comfort, N.; Wang, B.; Amacker, J.; Thankamony, S.; Salzman, D. W.; Cudkowicz, M.; Graham, D. L.; Bennett, C. F.; Kordasiewicz, H. B.; Swayze, E. E.; Miller, T. M., Antisense oligonucleotides extend survival and reverse decrement in muscle response in ALS models. J Clin Invest 2018, 128, (8), 3558-3567. [CrossRef]
- Lu, C. H.; Petzold, A.; Kalmar, B.; Dick, J.; Malaspina, A.; Greensmith, L., Plasma neurofilament heavy chain levels correlate to markers of late stage disease progression and treatment response in SOD1(G93A) mice that model ALS. PLoS One 2012, 7, (7), e40998. [CrossRef]
- McCombe, P. A.; Pfluger, C.; Singh, P.; Lim, C. Y.; Airey, C.; Henderson, R. D., Serial measurements of phosphorylated neurofilament-heavy in the serum of subjects with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 2015, 353, (1-2), 122-9. [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.; Cudkowicz, M.; Shaw, P. J.; Andersen, P. M.; Atassi, N.; Bucelli, R. C.; Genge, A.; Glass, J.; Ladha, S.; Ludolph, A. L.; Maragakis, N. J.; McDermott, C. J.; Pestronk, A.; Ravits, J.; Salachas, F.; Trudell, R.; Van Damme, P.; Zinman, L.; Bennett, C. F.; Lane, R.; Sandrock, A.; Runz, H.; Graham, D.; Houshyar, H.; McCampbell, A.; Nestorov, I.; Chang, I.; McNeill, M.; Fanning, L.; Fradette, S.; Ferguson, T. A., Phase 1-2 Trial of Antisense Oligonucleotide Tofersen for SOD1 ALS. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, (2), 109-119. [CrossRef]
- Cedarbaum, J. M.; Stambler, N.; Malta, E.; Fuller, C.; Hilt, D.; Thurmond, B.; Nakanishi, A., The ALSFRS-R: a revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. BDNF ALS Study Group (Phase III). J Neurol Sci 1999, 169, (1-2), 13-21. [CrossRef]
- Thouvenot, E.; Demattei, C.; Lehmann, S.; Maceski-Maleska, A.; Hirtz, C.; Juntas-Morales, R.; Pageot, N.; Esselin, F.; Alphandéry, S.; Vincent, T.; Camu, W., Serum neurofilament light chain at time of diagnosis is an independent prognostic factor of survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 2020, 27, (2), 251-257. [CrossRef]
- Wiesenfarth, M.; Dorst, J.; Brenner, D.; Elmas, Z.; Parlak, Ö.; Uzelac, Z.; Kandler, K.; Mayer, K.; Weiland, U.; Herrmann, C.; Schuster, J.; Freischmidt, A.; Müller, K.; Siebert, R.; Bachhuber, F.; Simak, T.; Günther, K.; Fröhlich, E.; Knehr, A.; Regensburger, M.; German, A.; Petri, S.; Grosskreutz, J.; Klopstock, T.; Reilich, P.; Schöberl, F.; Hagenacker, T.; Weyen, U.; Günther, R.; Vidovic, M.; Jentsch, M.; Haarmeier, T.; Weydt, P.; Valkadinov, I.; Hesebeck-Brinckmann, J.; Conrad, J.; Weishaupt, J. H.; Schumann, P.; Körtvélyessy, P.; Meyer, T.; Ruf, W. P.; Witzel, S.; Senel, M.; Tumani, H.; Ludolph, A. C., Effects of tofersen treatment in patients with SOD1-ALS in a "real-world" setting - a 12-month multicenter cohort study from the German early access program. EClinicalMedicine 2024, 69, 102495. [CrossRef]
- Kimura, F.; Fujimura, C.; Ishida, S.; Nakajima, H.; Furutama, D.; Uehara, H.; Shinoda, K.; Sugino, M.; Hanafusa, T., Progression rate of ALSFRS-R at time of diagnosis predicts survival time in ALS. Neurology 2006, 66, (2), 265-7. [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.; Schumann, P.; Weydt, P.; Petri, S.; Weishaupt, J. H.; Weyen, U.; Koch, J. C.; Günther, R.; Regensburger, M.; Boentert, M.; Wiesenfarth, M.; Koc, Y.; Kolzarek, F.; Kettemann, D.; Norden, J.; Bernsen, S.; Elmas, Z.; Conrad, J.; Valkadinov, I.; Vidovic, M.; Dorst, J.; Ludolph, A. C.; Hesebeck-Brinckmann, J.; Spittel, S.; Münch, C.; Maier, A.; Körtvélyessy, P., Clinical and patient-reported outcomes and neurofilament response during tofersen treatment in SOD1-related ALS-A multicenter observational study over 18 months. Muscle Nerve 2024, 70, (3), 333-345. [CrossRef]
- Benatar, M.; Wuu, J.; Andersen, P. M.; Bucelli, R. C.; Andrews, J. A.; Otto, M.; Farahany, N. A.; Harrington, E. A.; Chen, W.; Mitchell, A. A.; Ferguson, T.; Chew, S.; Gedney, L.; Oakley, S.; Heo, J.; Chary, S.; Fanning, L.; Graham, D.; Sun, P.; Liu, Y.; Wong, J.; Fradette, S., Design of a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial of Tofersen Initiated in Clinically Presymptomatic SOD1 Variant Carriers: the ATLAS Study. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, (4), 1248-1258. [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.; Schumann, P.; Weydt, P.; Petri, S.; Koc, Y.; Spittel, S.; Bernsen, S.; Günther, R.; Weishaupt, J. H.; Dreger, M.; Kolzarek, F.; Kettemann, D.; Norden, J.; Boentert, M.; Vidovic, M.; Meisel, C.; Münch, C.; Maier, A.; Körtvélyessy, P., Neurofilament light-chain response during therapy with antisense oligonucleotide tofersen in SOD1-related ALS: Treatment experience in clinical practice. Muscle Nerve 2023, 67, (6), 515-521. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Santos, M.; de Carvalho, M., Profiling tofersen as a treatment of superoxide dismutase 1 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Expert Rev Neurother 2024, 24, (6), 549-553. [CrossRef]
- Aartsma-Rus, A.; Dooms, M.; Le Cam, Y., Orphan Medicine Incentives: How to Address the Unmet Needs of Rare Disease Patients by Optimizing the European Orphan Medicinal Product Landscape Guiding Principles and Policy Proposals by the European Expert Group for Orphan Drug Incentives (OD Expert Group). Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 744532. [CrossRef]
| Drug | Phase Study type Study objective |
Number of patients Administration, dose |
Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASO 333611 | Phase 1 (NCT01041222) Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled Safety and tolerability study of ASO 333611 in SOD1 ALS |
33 patients 12hr intrathecal infusion of 0.15, 0.5, 1.5 and 3 mg |
No drug-related safety issues. No reduction in SOD1 protein levels in CSF. |
| BIIB067 tofersen |
Phase 1/2 VALOR (NCT02623699) Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics study of tofersen in SOD1 ALS |
50 patients Intrathecal injection of 20, 40, 60, 100 mg |
Tofersen was generally well tolerated and safe. The highest concentration of tofersen decreased CSF SOD1 concentrations the most. |
| BIIB067 tofersen |
Phase 3 VALOR (NCT02623699) Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled Efficacy study of tofersen in SOD1 ALS |
108 patients Intrathecal injection of 100 mg |
Tofersen did not improve the ALSFRS-R total score from baseline to week 28 in faster progression group. Tofersen resulted in a greater reduction in CSF SOD1 and pNFL concentrations. |
| BIIB067 tofersen |
Phase 3 (NCT03070119) Open-label extension Long-term Evaluation of tofersen in SOD1 ALS |
138 patients Intrathecal injection of 100 mg |
Ongoing |
| BIIB067 tofersen |
Phase 3 ATLAS (NCT04856982) Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled and subsequent open-label extension Long-term, efficacy study of tofersen in presymptomatic carriers of SOD1 |
150 patients (estimated) Intrathecal injection of 100 mg |
Ongoing |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





