1. Introduction
Prostate cancer (PCa) continues to rank as the second most prevalent cancer in men globally [
1,
2] comprising roughly 15% of all cancer diagnoses worldwide. Forecasts indicate that the annual number of new prostate cancer cases is expected to increase from 1.4 million in 2020 to 2.9 million by 2040, based on the analysis of global demographic shifts and the rising rates of life expectancy [
3]. Considering that PCa is characterized as heterogeneous disease [
4] and variety of risk factors are involved in prostate cancer progression such as environmental as well as genetic and molecular factors [
5]. There is a pressing need for the development of innovative and efficient diagnostic tools to enhance prostate cancer detection, with a focus on personalized medicine approaches. Ongoing research studies are focused on developing noninvasive methods for clinically significant PCa diagnosis, such as liquid biopsy assays. PSMA (Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen), PCA3 (Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen), and AR (Androgen Receptor) are involved in the development of PCa and are variously used in its diagnostics [
6,
7,
8] along with soluble PD-L1 and PD-1 (sPD-L1 and sPD-1) which demonstrated prognostic significance in our previous research [
9], are obtained by utilizing minimally invasive methods. sPD-L1 and sPD-1, which originate from their membrane-bound counterparts, − PD-L1 and PD-1, have gained significant attention in recent research due to their potential as prognostic and predictive markers in different cancer types [
10,
11,
12]. Meanwhile PSMA is a cell surface protein highly expressed in prostate cancer cells and PSMA based imaging, such as PET/CT, has shown high sensitivity and specificity in detecting prostate cancer lesions, particularly in cases of biochemical recurrence and metastatic disease [
13,
14]. The AR signaling pathway plays a central role in the growth of prostate cancer and AR expression has been detected in nearly all cases of primary and metastatic prostate cancer, irrespective of their stage or grade [
15,
16]. PCA3 is overexpressed in PCa [
17] and provides greater diagnostic specificity and sensitivity than the main PCa serum biomarker PSA (prostate specific antigen) [
18]. Combining these genes and circulating soluble molecules may enhance the accuracy of detection and characterization of PCa. By integrating information from these different markers, a more comprehensive molecular and immune profile of the patient's prostate cancer could be obtained, which can aid in diagnosis, risk stratification, treatment selection, and monitoring of disease progression.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of PCa Population
In a cohort of PCa patients evaluated for soluble PD-L1 and PD-1 levels in our previous research [
9], gene expression was additionally examined in 72 cases to further assess their diagnostic value in this study. 4 cases were removed due to outlier values in gene expression, thus the study included 68 PCa patients. The PCa cases were divided into clinically significant and not clinically significant PCa groups where clinical significance was defined as cases with International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) ≥ 3. These patients are deemed to have unfavorable PCa risk. The clinical charac-teristics of the PCa group are provided in
Table 1.
The inclusion and exclusion criteria are well described in the paper of Bosas, clearly outlining the participant selection process [
19].
2.2. Blood Sampling
The blood sampling of sPD-L1 and sPD-1 was thoroughly detailed in our previous paper [
9].
2.3. Urine Sampling
The urine sampling is described in detail in previous research [
20].
2.4. Analysis of Soluble PD-L1 and PD-1
A commercially available ELISA kits for PD-L1 and PD-1 were used to measure the soluble forms of both proteins in plasma, following the manufacturer's instructions (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Sci-entific, Vienna, Austria). sPD-L1 and sPD-1 control samples were included in each kit at known concentrations. The optical density was measured using plate reader BioTek Elx800 TM (BIO-Tek Instruments, Inc., Vermont, USA) at 450 nm. Two duplicates of each sample were measured. Blanks and standards were assayed as directed by manufacturer.
2.5. Analysis of mRNA Expression of PCA3, PSMA and AR Genes
Total RNA form washed urine sediment samples extracted using the TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific (TFS), Carsbad, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol. The RNA concentration and purity assessed using Nanodrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scien-tific, Wilmington, DE, USA). The RNA samples stored at -80°C until copy DNA (cDNA) synthesis step. Two-Step RT-qPCR was used to assay AR, PSMA, and PCA3 mRNA relative quantities in the urine sediment samples. The Maxima First Stand cDNA Synthesis Kit for RT-qPCR with dsDNase (TFS, Vilnius, Lithuania) and the Maxima SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix (2X), with separate ROX vial (TFS, Vilnius, Lithuania) was used for the two-step RT-qPCR following the manufactur-er’s protocols. The qPCR reactions performed on QuantStudio 5 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, TFS, Singapore). RT-qPCR data pre-processing performed on QuantStudio Design & Analysis software v1.4.3 (Applied biosystems, TFS). The quantification cycle (Ct) values reported using the automatic threshold baseline. Ct values <35 cycle was removed from subsequent analysis. For each sample, melt-curve analysis was performed to evaluate the amplicon size. The initial Ct values normalized to the HPRT1 gene expression using log22-ΔCt and then divided by the PSA gene expression, these normalized relative expression values were used in further statistical data analysis.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis and data visualization performed on Python 3.11.5 (Python Software Foundation) and Rx4.3.1 [
21,
22] software. Data normalcy determined using Shapiro-Wilk W test. Cases exceed ing three interquartile ranges deemed outliers and removed from all statistical analysis. Associations between two independent samples tested using Welch’s t test or Mann-Whitney U test as appropriate. Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis [
23] together with logistic regression was utilised to measure biomarker and feature combination accuracy to predict clinically significant PCa. Results considered significant when the p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Biomarker Association with Prostate Cancer Clinical Features
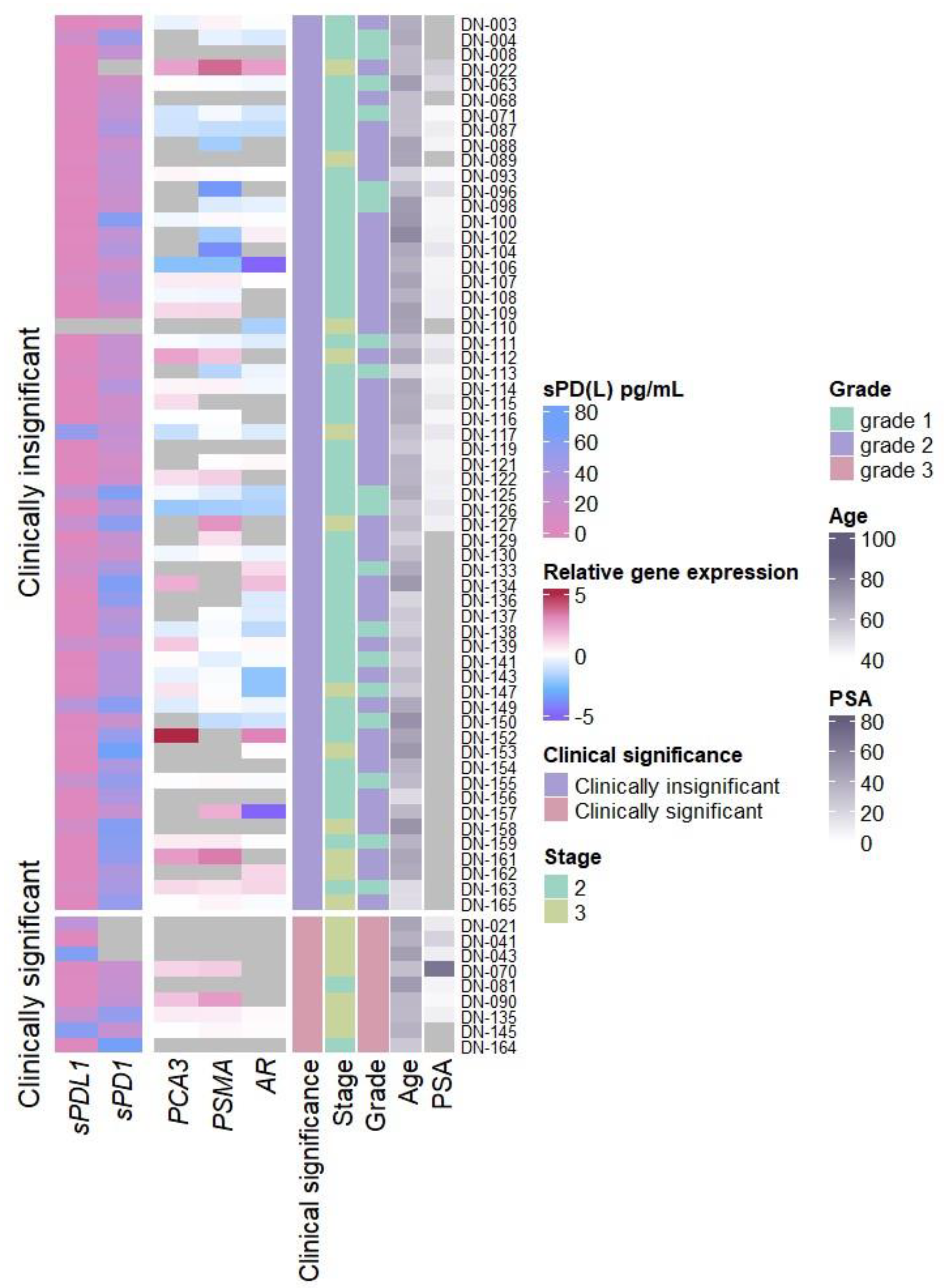
Analysis of relative
AR,
PCA3, and
PSMA mRNA expression in urine discovered significant increase in
PSMA expression in clinically significant PCa when compared with clinically insignificant PCa cases (p = 0.039) (
Figure 1 and
Figure S1A) as well as significant associations between pT3 and increase of
PCA3 and
PSMA relative expression (p = 0.031 and p < 0.001 respectively) (
Figure S2A) and
PSMA expression and tumor grade (grade 1
vs grade 3 p = 0.005, grade 1
vs grade 2 p = 0.011) (
Figure S3A).
Soluble PD-1 and PD-L1 revealed sPD-L1 association with clinically significant PCa (sPDL1 p = 0.033) (
Figure 1 and
Figure S1B), increased stage (sPDL1 p = 0.031) (
Figure S2B), and grade 3 PCa (grade 2 vs grade 3 sPDL1 = 0.026) (
Figure S3B), while sPD-1 showed no differences in any of the clinical features examined.
No significant association between relative AR, PCA3, and PSMA mRNA expression and either the plasma biomarkers (sPD-L1 or sPD-1) or other clinical features (age, serum PSA concentration or immune cell count) was discovered (data not shown).
3.2. Prediction of Clinically Significant PCa Using Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers
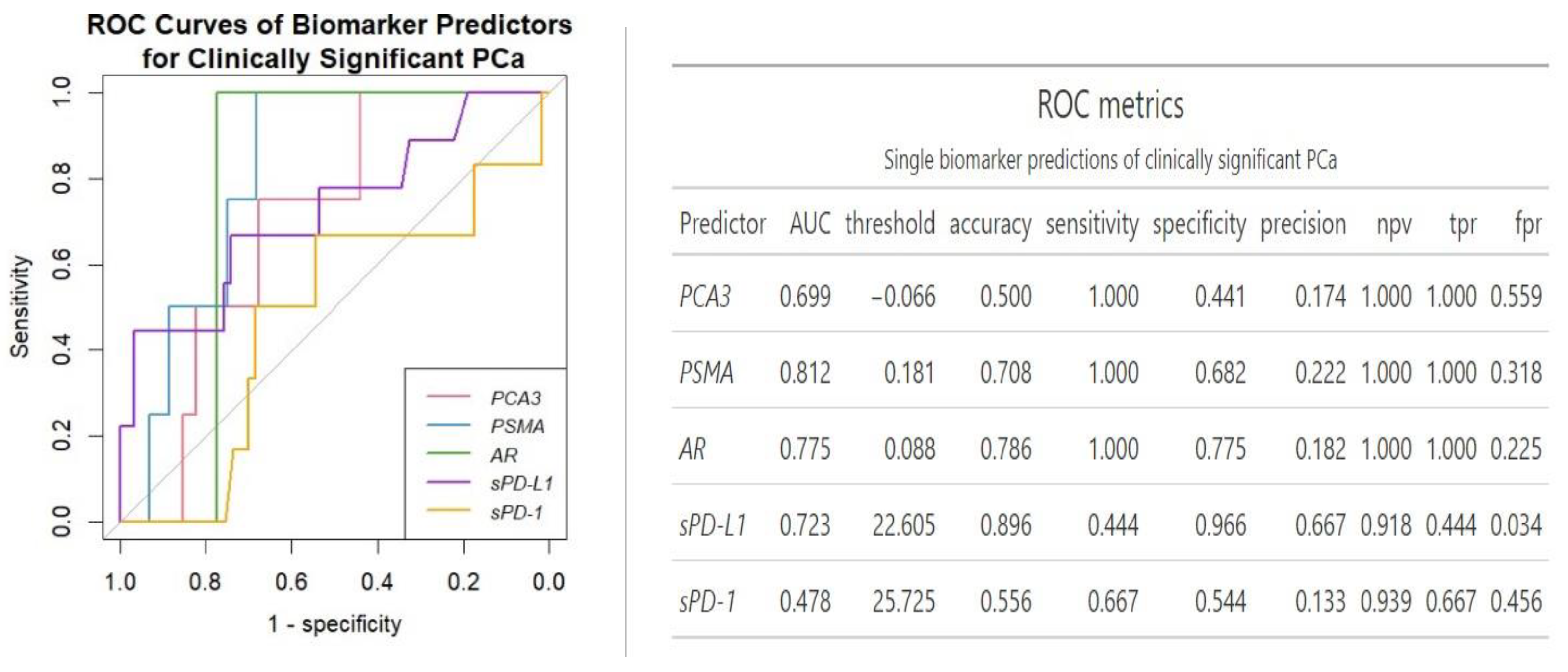
ROC analysis revealed
PSMA as the best single gene expression biomarker predictor of clinically significant PCa (AUC = 0.81) (
Figure 2). Overall, single urinary transcript biomarkers showed perfect sensitivity with
AR boasting highest sensitivity (0.78). On the other hand, sPD-L1 showed best single biomarker specificity (0.97), but lowest sensitivity (0.44).
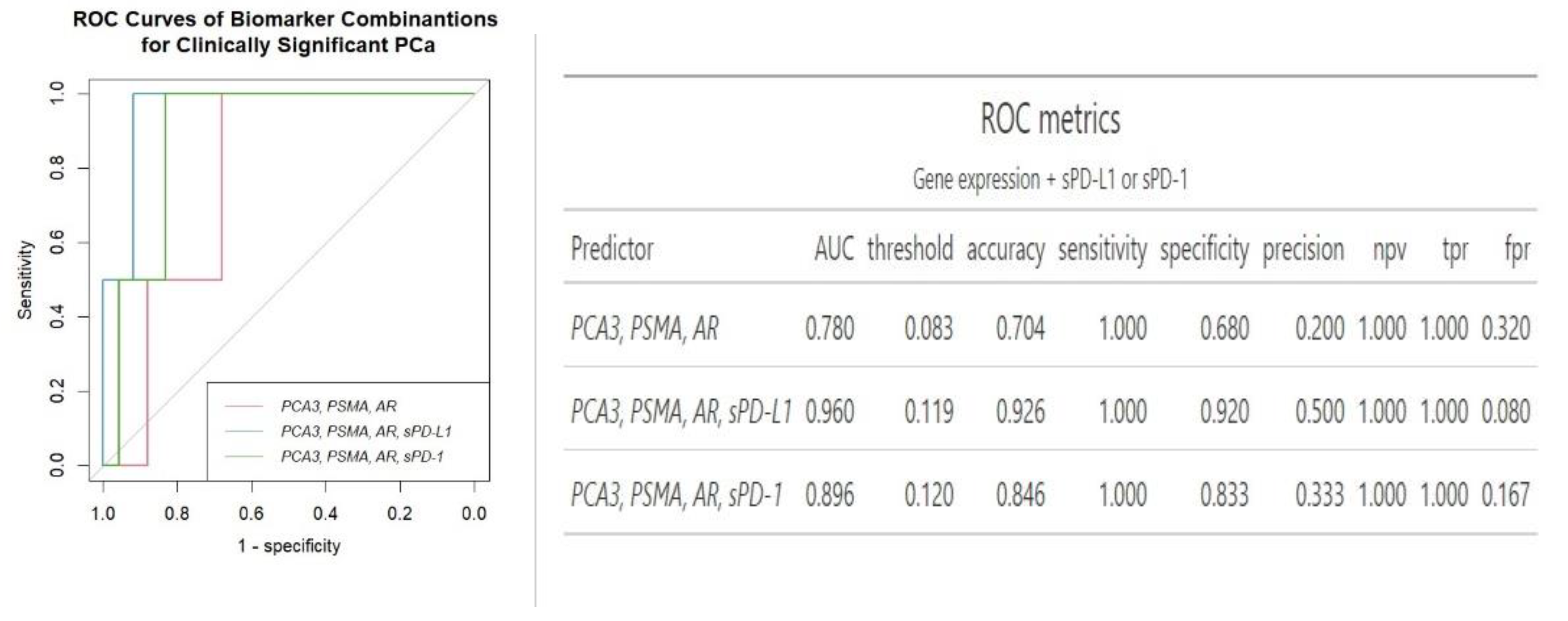
Regarding the combination of urine and plasma biomarkers together, an increase in the AUC values was noticed. While combining the three mRNA expression did not increase the prediction of clinically significant PCa (AUC 0.78
vs AUC 0.81 of
PSMA biomarker), a combination of gene expression and sPD-1 and sPD-L1 increases AUC and overall specificity and accuracy of clinically significant PCa prediction (AUC 0.96 for three gene signature + sPD-L1) (
Figure 3).
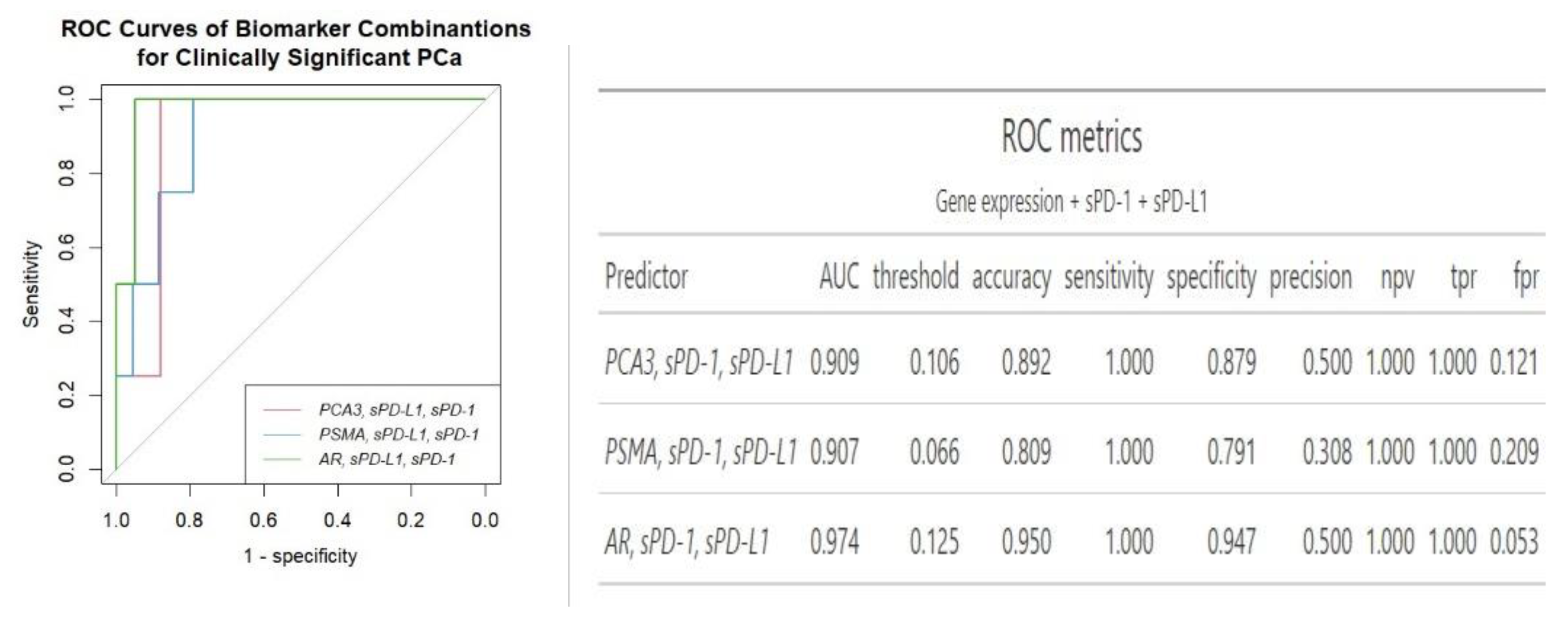
Of note, the addition of plasma sPD-L1 and sPD-1 to
PCA3 or
AR gene expression biomarkers combination increased the prediction specificity, when compared to other biomarker combinations (
Figure 4). The combination of
AR and 2 plasma biomarkers showed overall the best separation of clinically significant PCa cases from the clinically insignificant PCa (AUC = 0.97) out of all biomarkers and biomarker combinations examined.
Overall, while
PSMA exhibited the strongest clinical significance as a standalone biomarker,
AR demonstrated comparatively modest results of an AUC. However, according to ROC analysis, mRNA of
AR from urine in addition of two plasma biomarkers, sPD-L1 and sPD-1, achieved the best separation between clinically significant and clinically insignificant PCa cases, with an AUC of 0.97, accuracy of 0.95, sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 95%. Notably, the inclusion of two soluble biomarkers significantly enhanced diagnostic accuracy from 0.79 to 0.95, specifically, the AUC for
AR rose from 0.78 to 0.97, and for
PCA3, it increased from 0.70 to 0.91. Additionally, it enhanced specificity, increasing it from 77.5% to 95.0% for
AR and doubled it from 44.1% to 88.0% for
PCA3, compared to the use of a single genetic biomarker. sPD-L1 and sPD-1 had the least impact on enhancing the predictive value of
PSMA, increasing its AUC of 0.81 to 0.91 and specificity from 68.0 to 79.0 (
Figure 2 and
Figure 4). The panel comprising three mRNA transcripts along with sPD-L1 offers a similar enhancement in diagnostic properties compared to combining
AR with two plasma biomarkers with an AUC of 0.96 and 0.97, accuracy of 0.93 and 0.95, specificity of 0.92 and 0.95, respectively (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). The combination of sPD-L1 and sPD-1 yields an AUC of 0.72, with an accuracy of 0.52, sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 0.47 (data not shown).
4. Discussion
4.1. Significance of sPD-L1 and sPD-1 along with mRNA of PSMA, PCA3 and AR Genes in PCa
In the context of the intensive investigations for convenient biomarkers, a novel multifactorial approach that combines urine and blood biomarkers encompassing various aspects of the disease not only enhances detection but also offers a comprehensive assessment of prostate cancer. This approach highlights the potential of non-invasive liquid biopsies in improving the diagnosis and management of PCa. Building on our previous research which identified plasma sPD-L1/sPD-1 as a potential biomarker of PCa [
9], we investigated gene expression in the urine samples of the same patients. As it is shown in
Figure 1 and
Figure S1B–S3B, sPD-L1 can differentiate between clinically significant and non-significant prostate cancer (p = 0,033) and is associated with higher tumor stages (p = 0.031) and ISUP grading (p = 0.026) in PCa. Similarly, elevated sPD-L1 levels are consistently linked to larger tumors, advanced stages, and metastasis across different cancers [
24,
26].
In our study significant associations were identified between
PSMA expression and clinically significant prostate cancer (p = 0.039) (
Figure 1 and
Figure S1A), as well as among the three genes examined,
PSMA emerged as the most reliable single biomarker for predicting clinically significant PCa with an AUC of 0.81 (
Figure 2). Similarly, Rigau reported
PSMA (AUC 0.74) outperformed
PSGR (AUC 0.66) and
PCA3 (AUC 0.61) in predicting PCa within the PSA "gray zone" of 4–10 ng/ml [
27]. Furthermore, we found that the expression levels of both
PSMA and
PCA3 were associated with the pT3 stage (p < 0.05) (
Figure 1 and
Figure S2A), while PSMA also was linked to ISUP grading (
Figure 1 and
Figure S3A) indicating their potential as biomarkers for disease severity and progression. Despite
AR not demonstrating any association with cancer advancement, in single-biomarker assessment it‘s AUC was slightly lower compared to
PSMA, however it exhibited higher diagnostic accuracy than all the three urine biomarkers combined (0.70
vs 0.79) (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). Comparative analysis to other studies also suggests the involvement of
PSMA,
PCA3, and
AR genes into prognosis and prediction of PCa. Blood PSMA-based biomarkers have been linked to malignancy risk [
28] and predicted worse survival rates in metastatic PCa [
29]. Higher PSMA expression correlated with advanced tumor stages and grades in biopsies and prostatectomy specimens [
30]. Urine exosomal PSMA showed high diagnostic accuracy for significant PCa, correlating strongly with Gleason scores [
31]. Similarly,
PCA3 scores have been associated with tumor aggressiveness [
32], higher Gleason scores [
18,
33] and advanced clinical stages [
33]. Moreover, various non-coding RNAs have been shown to influence prostate cancer progression by modulating
AR signaling, highlighting their potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets [
34].
Although mentioned studies have shown that monitoring an RNA transcript from PSMA, PCA3, and AR genes can be beneficial for prostate cancer diagnosis, however relying on disease specific markers may not fully reflect the disease's complexity and heterogenous nature.
4.2. Combinations of Plasma sPD-L1/sPD-1 with mRNA of PSMA, PCA3 and AR Genes in PCa
To improve PCa diagnosis the combination of several different markers has been shown promising. While in our study the combination of all three mRNA expressions did not enhance the prediction of clinically significant prostate cancer (AUC 0.78) compared to the
PSMA and
AR biomarkers alone (AUC 0.81 and 0.78 respectively) (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). The addition of sPD-L1 to a triple gene expression panel has significantly enhanced the model’s performance, resulting in diagnostic accuracy of 0.93 and in an AUC of 0.96, and rise of specificity from 68% to 92%, as illustrated in
Figure 3. The composition of three genes along with sPD-1 also increased diagnostic accuracy from 0.70 to 0.85 for predicting clinically significant PCa and reflected in an AUC (0.90
vs 0.78) (
Figure 3). Such multiaspected approach of combining mRNA of
PCA3/
PSMA/
AR gene expression with sPD-L1/sPD-1 offers a comprehensive coverage, including tumor biology, immune response, and heterogeneity of prostate cancer. sPD-L1 has emerged as a promising biomarker for various cancers, including gastric [
24] and lung cancers [
35]. These findings highlight sPD-L1's broader applicability across cancers, making it valuable for diagnostics and treatment monitoring, due to its direct involvement in immune suppression [
36], correlation with tumor burden, aggressiveness [
37] and consistent association with clinical outcomes [
11,
38,
39]. In contrast, sPD-1 primarily reflects immune activation, however high pretherapeutic sPD-1 levels suggest worse prognosis [
12,
40]. Previous studies have described correlations rather than combinations involving sPD-L1 and sPD-1. sPD-L1 is linked to neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in advanced cancers [
39]. Higher levels linked to low hemoglobin and albumin and elevated C-reactive protein in gastric cancer [
41]. In pancreatic cancer, combining sPD-L1/PD-L2/B7-H5/CA19-9 improves diagnostic sensitivity, though sPD-1 did not add significance [
42]. In PD-1 blockade therapy, sPD-1 and sPD-L1 levels together indicate treatment outcomes [
43,
44].
To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first successfully combining sPD-1 with a non sPD-L1 biomarker across multiple cancers, demonstrating that incorporating sPD-1 with mRNA transcripts improves diagnostic accuracy for clinically significant prostate cancer (
Figure 3). Remarkably how non-specific PCa biomarkers like sPD-L1 and sPD-1, can enhance the diagnostic accuracy of PCa-specific biomarkers (
Figure 2,
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). This improvement highlights sPD-L1 and sPD-1 role in tumor development and suggests that combined biomarkers could refine diagnostic panels by capturing the complexity of disease progression for better prognostic assessment.
Interpreting our best biomarkers combination (
AR, sPD-L1, sPD-1), – mRNA of urinary
AR provides insights into the androgen receptor pathway, which is implicated in PCa development and progression [
45,
46]. Meanwhile, plasma sPD-L1 and PD-1 levels potentially reflect the tumor's immune microenvironment [
12,
40]. The combination of
AR, PSMA, PCA3 transcripts plus sPD-L1 shows comparable diagnostic properties and is likely more comprehensive for PCa assessment, as it incorporates multiple prostate cancer-specific markers and offers detailed insights into the cancer's characteristics. However, AR paired with sPD-L1 and sPD-1 require fewer biomarkers and offer slightly improved accuracy overall (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). Furthermore, androgen receptor signaling has been found to affect the expression of PD-L1 in prostate cancer, with AR activation linked to higher PD-L1 levels [
47,
48]. Additionally, scores for AR activity were significantly positively correlated with PD-1 methylation, resulting in an association with significantly reduced BCR (biochemical recurrence) - free survival after radical prostatectomy [
49], suggesting an AR influence on the PD-L1/PD-1 axis. Further studies are warranted to explore potential associations between AR, sPD-L1 and sPD-1, particularly considering the economic advantages and convenience of implementing such a diagnostic panel.
Integrating blood and urine biomarkers together significantly improves PCa detection and are supported by commercially available tests. SelectMDx Urine Test, including
DLX1,
HOXC6,
KLK3(PSA) and other parameters achieved an AUC of 0.85 with 93% sensitivity and 47% specificity [
50]. While the Michigan Prostate Score (MiPS), consisting of urine mRNA of
T2-ERG and
PCA3, and serum PSA also outperformed regular PSA test [
51]. Additionally, scientific studies confirm the effectiveness of combining biomarkers obtained from different body fluids. Urinary exosomal
PCA3 and
PSMA with serum PSA and PI-RADS achieved higher AUC than PSA alone [
52], as well as urinary
PCA3 enhanced diagnostic performance of PSA in high-risk populations [
53].
5. Conclusions
Urine and plasma are easily accessible biofluids, allowing for less invasive and repeatable sampling, longitudinal monitoring and potentially reducing unnecessary biopsies [
54]. Our results demonstrate that the inclusion of sPD-L1 and sPD-1 in a diagnostic panel, together with
PSMA, PCA3, and
AR mRNA transcripts, has the potential significantly to improve the accuracy and specificity of PCa diagnostics. Future efforts should focus on refining multi-biomarker panels for greater diagnostic accuracy and developing multifactorial approaches for more personalized prostate cancer management.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org, Figure S1: Relative expression values of
AR,
PCA3, and
PSMA mRNAs as well as sPD-L1 and sPD-1 in clinicly significant and insignificant PCa cases. Figure S2: Relative expression values of
AR,
PCA3, and
PSMA mRNAs as well as sPD-L1 and sPD-1 in association with tumor stage. Figure S3: Relative expression values of
AR,
PCA3, and
PSMA mRNAs as well as sPD-L1 and sPD-1 in association with ISUP grading.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: MZ,IV,RS,VP; Methodology: MZ,IV,ZS,ND,AM; Validation: MZ,IV,RS,VP; Formal analysis: IV,ZS, MZ; Investigation: MZ,IV,ZS,PB,ND,AM; Data curation: MZ,IV,ZS,PB,ND,AM; Writing – original draft preparation: MZ,IV; Writing – review and editing RS,VP; Visualization MZ,IV,RS,VP; Supervision:RS,VP; Project administration:VP; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The present study was supported by National Cancer Institute, Lithuania, scientific fund and in part supported by Research Council of Lithuania as a grant for MZ PhD studies.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Regional Review Board (Vilnius, Lithuania, 158200-17-928-442). All research methods were carried out in accordance with the relevant Lithuanian national guidelines and regulations.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to protection of participants privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
PCa - prostate cancer; PSMA - prostate-specific membrane antigen; PCA3 - prostate-specific membrane antigen; AR - androgen receptor; sPD-L1 soluble PD- L1, sPD-1 – soluble PD-1; PSA - prostate specific antigen; ISUP - International Society of Urological Pathology; ELISA - Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay; ROC – Receiver Operating Characteristic; AUC – Area Under Curve.
References
- Bergengren, O.; Pekala, K.R.; Matsoukas, K.; Fainberg, J.; Mungovan, S.F.; Bratt, O.; et al. 2022 Update on Prostate Cancer Epidemiology and Risk Factors—A Systematic Review. European Urology 2023, 84, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; et al. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. International Journal of Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, M.C.; Zwart, W.; Roudier, M.P.; True, L.D.; Nelson, W.G.; Epstein, J.I.; et al. Genomic and phenotypic heterogeneity in prostate cancer. Nature Reviews Urology 2021, 18, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemailem, K.S.; Almatroudi, A.; Alrumaihi, F.; Makki Almansour, N.; Aldakheel, F.M.; Rather, R.A.; et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in prostate cancer: its implications in diagnostics and therapeutics. American Journal of Translational Research 2021, 13, 3868–3889. [Google Scholar]
- Hofman, M.S.; Lawrentschuk, N.; Francis, R.J.; Tang, C.; Vela, I.; Thomas, P.; et al. Prostate-specific membrane antigen PET-CT in patients with high-risk prostate cancer before curative-intent surgery or radiotherapy (proPSMA): a prospective, randomised, multicentre study. The Lancet 2020, 395, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Nonomura, N. Role of Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer: A Review. The World Journal of Men’s Health 2019, 37, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Nonomura, N. Urinary biomarkers of prostate cancer. International Journal of Urology 2018, 25, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvirble, M.; Survila, Z.; Bosas, P.; Dobrovolskiene, N.; Mlynska, A.; Zaleskis; et al. Prognostic significance of soluble PD-L1 in prostate cancer. Frontiers in Immunology 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, C.; Thuru, X.; Quesnel, B. Soluble Programmed Death Ligand-1 (sPD-L1): A Pool of Circulating Proteins Implicated in Health and Diseases. Cancers 2021, 13, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Jiang, J.; Wu, C. Prognostic significance of circulating soluble programmed death ligand-1 in patients with solid tumors: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Zhao, Z.; Arooj, S.; Fu, Y.; Liao, G. Soluble PD-1: Predictive, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Value for Cancer Immunotherapy. Frontiers in Immunology 2020, 11, 587460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Woo, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Suh, C.H. Impact of 68 Ga-PSMA PET on the Management of Patients with Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. European Urology 2018, 74, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravaccini, S.; Puccetti, M.; Bocchini, M.; Ravaioli, S.; Celli, M.; Scarpi, E.; et al. PSMA expression: a potential ally for the pathologist in prostate cancer diagnosis. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurilio, G.; Cimadamore, A.; Mazzucchelli, R.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Verri, E.; Scarpelli, M.; et al. Androgen Receptor Signaling Pathway in Prostate Cancer: From Genetics to Clinical Applications. Cells 2020, 9, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Koo, K.C. Current Status and Future Perspectives of Androgen Receptor Inhibition Therapy for Prostate Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos AE, G.; Matos A da, R.; Ferreira, L.B.; Gimba, E.R.P. The long non-coding RNA PCA3 : an update of its functions and clinical applications as a biomarker in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 6589–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunhua, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, H.; Lu, Y.; Wu, J.; Gao, Z.; et al. Clinical Significance of Peripheral Blood PCA3 Gene Expression in Early Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. Translational Oncology 2018, 11, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosas, P. , Zaleskis, G., Dabkevičiene, D., Dobrovolskiene, N., Mlynska, A., Tikuišis, R.; et al. Immunophenotype Rearrangement in Response to Tumor Excision May Be Related to the Risk of Biochemical Recurrence in Prostate Cancer Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2021, 10, 3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januskevicius, T.; Sabaliauskaite, R.; Dabkeviciene, D.; Vaicekauskaite, I.; Kulikiene, I.; Sestokaite, A.; et al. Urinary DNA as a Tool for Germline and Somatic Mutation Detection in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Patients. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T. M. A Package for Survival Analysis in R. 2024. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival.
- R Core team. _R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2023. https://www.R-project.org/.
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; et al. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chivu-Economescu, M.; Herlea, V.; Dima, S.; Sorop, A.; Pechianu, C.; Procop, A.; et al. Soluble PD-L1 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in resectable gastric cancer patients. Gastric Cancer : Official Journal of the International Gastric Cancer Association and the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association 2023, 26, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikerfors, A.; Davidsson, S.; Frey, J.; Jerlström, T.; Carlsson, J. Soluble PD-L1 in Serum and Urine in Urinary Bladder Cancer Patients. Cancers 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z. , Bu, Z., Liu, X., Zhang, L., Li, Z., Wu, A.,et al. Level of circulating PD-L1 expression in patients with advanced gastric cancer and its clinical implications. Chinese Journal of Cancer Research = Chung-Kuo Yen Cheng Yen Chiu 2014, 26, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigau, M. , Ortega, I., Mir, M. C., Ballesteros, C., Garcia, M., Llauradó, M.; et al. A three-gene panel on urine increases PSA specificity in the detection of prostate cancer. The Prostate 2021, 71, 1736–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.M.; Abdel Hamid, F.F.; Abdelgawad, I.; Ismail, A.; Malash, I.; Ibrahim, D.M. Diagnostic Efficacy of PSMA and PSCA mRNAs Combined to PSA in Prostate Cancer Patients. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention: APJCP 2023, 2, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Halabi, S.; Yang, Q.; Roy, A.; Tubbs, A.; Gore, Y.; et al. PSMA-positive Circulating Tumor Cell Detection and Outcomes with Abiraterone or Enzalutamide Treatment in Men with Metastatic Castrate-resistant Prostate Cancer. Clinical Cancer Research : An Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2023, 29, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hupe, M.C.; Philippi, C.; Roth, D.; Kümpers, C.; Ribbat-Idel, J.; Becker, F.; et al. Expression of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) on Biopsies Is an Independent Risk Stratifier of Prostate Cancer Patients at Time of Initial Diagnosis. Frontiers in Oncology 2018, 8, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-B.; Chen, S.-H.; Zhao, L.; Jin, X.; Chen, X.; Ji, J.; et al. Urine-derived exosomal PSMA is a promising diagnostic biomarker for the detection of prostate cancer on initial biopsy. Clinical & Translational Oncology: Official Publication of the Federation of Spanish Oncology Societies and of the National Cancer Institute of Mexico 2023, 25, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merola, R.; Tomao, L.; Antenucci, A.; Sperduti, I.; Sentinelli, S.; Masi, S.; et al. PCA3 in prostate cancer and tumor aggressiveness detection on 407 high-risk patients: a National Cancer Institute experience. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Leng, J.; Shao, H.; Wang, W. High PCA3 scores in urine correlate with poor-prognosis factors in prostate cancer patients. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2015, 8, 16606–16612. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, K.Y.; Liu, Q.; Cao, Q. Androgen Receptor-Related Non-coding RNAs in Prostate Cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021, 9, 660853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Dai, L. Soluble PD-L1 as a predictive biomarker in lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Future Oncology (London, England) 2022, 18, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassounah, N. B. , Malladi, V. S., Huang, Y., Freeman, S. S., Beauchamp, E. M., Koyama.; et al. Identification and characterization of an alternative cancer-derived PD-L1 splice variant. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy : CII, 2019, 68, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, K.M.; Ross-Macdonald, P.; Yuan, L.; Song, L.; Veras, E.; Wind-Rotolo, M.; et al. Soluble PD-L1 as an early marker of progressive disease on nivolumab. Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirocchi, F.; Strigari, L.; Di Filippo, A.; Napoletano, C.; Pace, A.; Rahimi, H.; et al. Soluble PD-L1 as a Prognostic Factor for Immunotherapy Treatment in Solid Tumors: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Keam, B.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, D.-W. Soluble PD-L1 is a predictive and prognostic biomarker in advanced cancer patients who receive immune checkpoint blockade treatment. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 19712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Lang, J. Soluble PD-1 and PD-L1: predictive and prognostic significance in cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 97671–97682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Kano, M.; Shiraishi, T.; Suito, H.; Murakami, K.; et al. Soluble PD-L1 reflects cachexia status in patients with gastric cancer and is an independent prognostic marker for relapse-free survival after radical surgery. Molecular and Clinical Oncology 2023, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Xia, X.; Cheng, C.; Niu, L.; Wu, J.; Qian, Y. Serum Soluble PD-L1, PD-L2, and B7-H5 as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Human Pancreatic Cancer. Clinical Laboratory 2021, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaki, T. , Chamoto, K., Suzuki, S., Kanemura, H., Mitani, S., Tanaka.; et al. The combination of soluble forms of PD-1 and PD-L1 as a predictive marker of PD-1 blockade in patients with advanced cancers: a multicenter retrospective study. Frontiers in Immunology, 2023, 14, 1325462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugurel, S.; Schadendorf, D.; Horny, K.; Sucker, A.; Schramm, S.; Utikal, J.; et al. Elevated baseline serum PD-1 or PD-L1 predicts poor outcome of PD-1 inhibition therapy in metastatic melanoma. Annals of Oncology : Official Journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology 2020, 31, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messner, E.A.; Steele, T.M.; Tsamouri, M.M.; Hejazi, N.; Gao, A.C.; Mudryj, M.; et al. The Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer: Effect of Structure, Ligands and Spliced Variants on Therapy. Biomedicines 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, A.; Raj, R.; Allison, D.B.; Myint, Z.W. Androgen Receptor Signaling in Prostate Cancer and Therapeutic Strategies. Cancers 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevensleben, H.; Dietrich, D.; Golletz, C.; Steiner, S.; Jung, M.; Thiesler, T.; et al. The Immune Checkpoint Regulator PD-L1 Is Highly Expressed in Aggressive Primary Prostate Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; He, M.; Chen, J.; Gao, Y.; et al. The Clinicopathologic and Prognostic Significance of Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression in Patients With Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goltz, D.; Gevensleben, H.; Dietrich, J.; Ellinger, J.; Landsberg, J.; Kristiansen, G.; et al. Promoter methylation of the immune checkpoint receptor PD-1 (PDCD1) is an independent prognostic biomarker for biochemical recurrence-free survival in prostate cancer patients following radical prostatectomy. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1221555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haese, A.; Trooskens, G.; Steyaert, S.; Hessels, D.; Brawer, M.; Vlaeminck-Guillem, V.; et al. Multicenter Optimization and Validation of a 2-Gene mRNA Urine Test for Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer before Initial Prostate Biopsy. J Urol. 2019, 202, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, W.; Shi, G.; Zhao, G.; Cen, Z.; Xu, F.; et al. Accuracy of novel urinary biomarker tests in the diagnosis of prostate cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Frontiers in Oncology 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Zeng, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Lei, P.; Wang, Z.; et al. Effective Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer Based on mRNAs From Urinary Exosomes. Frontiers in Medicine, 2022, 9, 736110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Lee, C.H.; Ning, J.; Handy, B.C.; Wagar, E.A.; Meng, Q.H. Combination of Prostate Cancer Antigen 3 and Prostate-Specific Antigen Improves Diagnostic Accuracy in Men at Risk of Prostate Cancer. Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine 2018, 142, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirahata, T.; Ul Quraish, R.; Quraish, A.U.; Ul Quraish, S.; Naz, M.; Razzaq, M.A. Liquid Biopsy: A Distinctive Approach to the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cancer. Cancer Informatics 2021, 21, 11769351221076062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).