1. Introduction
Spaceborne synthetic aperture radar (SAR) is an indispensable tool in Earth observation. SAR satellites produce images by actively transmitting and receiving microwave signals, therefore being able to work all day and in all weather. When high-resolution optical images are available, SAR images can still provide distinctive radiation information to help improve experimental results [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5], which is common in land classification research [
6,
7,
8].
As remote sensing technology develops, more and more Spaceborne satellites with excellent performance have been launched, providing a wealth of high-resolution data for research and applications. For example, the advanced TerraSAR-X and Tianhui-2 satellites offer stripmap products with a resolution of better than 5 meters. At this resolution level, most ground targets' outlines are recognizable, which enables SAR images to be applied in more domains, such as target change monitoring and urban feature extraction [
9]. Geolocation accuracy is crucial for utilizing the geometric information of high-resolution SAR images because the coregistration method cannot be used to match SAR images and other data [
10,
11,
12]. Images with high geolocation accuracy can even be used to correct the geometry of optical images [
13,
14] and complete surveying tasks [
15]. Besides, geolocation preprocessing is unnecessary for these images, which reduces the difficulty of experiments [
16,
17].
The factors affecting SAR geolocation accuracy are the solid Earth effects, the orbit error, the atmospheric error, and the ground elevation error. The influence of solid Earth effects is relatively minor, so we only discuss it in
Section 4. The orbital accuracy of advanced SAR satellites has exceeded that of early satellites by a large margin, benefitting from the improvements in SAR instruments and orbit observation accuracy, which ensures a high upper limit for SAR geolocation accuracy. The orbit error of TerraSAR-X is at the centimeter level [
18]. For Sentinel-1, Envisat, and COSMO-SkyMed, it is less than 1 meter [
18,
19]. Therefore, the focus of geolocation is the atmospheric error and the ground elevation error. The atmospheric error has been studied thoroughly in the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) domain. As SAR and GNSS both work on the microwave band and thus are subject to similar atmospheric effects, pertinent outcomes in GNSS can be applied directly to SAR geolocation [
18]. Interferometry SAR (InSAR) phase correction products such as Generic Atmospheric Correction Online Service for InSAR (GACOS) are also applicable [
20,
21,
22]. The ground elevation error has been studied in SAR satellite orbit correction research [
23,
24], affecting geolocation accuracy by introducing a range error.
Existing geolocation research focuses on the theoretical accuracy of SAR images and conducts experiments based on corner reflectors with ideal target coordinates and external parameters. However, application-oriented research has to depend on data with lower accuracy. To achieve high-accuracy SAR geolocation, we analyze properties and variation ranges of different errors and propose a set of geolocation procedures. The experimental results show that the geolocation accuracy can be better than 1 meter for TerraSAR-X, 2 meters and 4 meters for Tianhui-2 reference and secondary satellites, which meets most applications' requirements. The atmospheric error and the ground elevation error are the primary factors influencing the geolocation accuracy. Different tropospheric correction methods show similar accuracy in our research and are all effective. Due to its availability and usability, we claim that the GACOS mapping method has the best comprehensive performance. The digital elevation model (DEM) elevation error is universal and significantly affects the geolocation accuracy. The geolocation error is at most 5 meters for the TerraSAR-X image based on the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) and is at most 3 meters when on the WorldDEM. Therefore, the key to improving accuracy is to use higher-accuracy DEMs. Additionally, we propose and validate a geolocation model for the Tianhui-2 secondary satellite.
This article is organized as follows.
Section 2 analyzes the principles of the geolocation errors and introduces the geolocation procedures.
Section 3 presents the variation ranges of the errors and compares the effectiveness of different correction methods.
Section 4 discusses deficiencies in our experiment and other factors affecting the geolocation accuracy.
Section 5 contains the conclusions of this research.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Components of Geolocation Errors
The components of geolocation errors are different in azimuth and range. Typically, the azimuth geolocation accuracy is only affected by the satellite orbit error due to inaccuracy in satellite positions or mismatched instrumental time. Coregistrating SAR images with DEM-simulated amplitude images is a widely used orbit correction method without ground control points [
23]. However, it is not applicable for high-resolution images and meter-level-accuracy geolocation. We discuss this method in
Section 4. In this article, we assume that there is no significant geolocation error in azimuth.
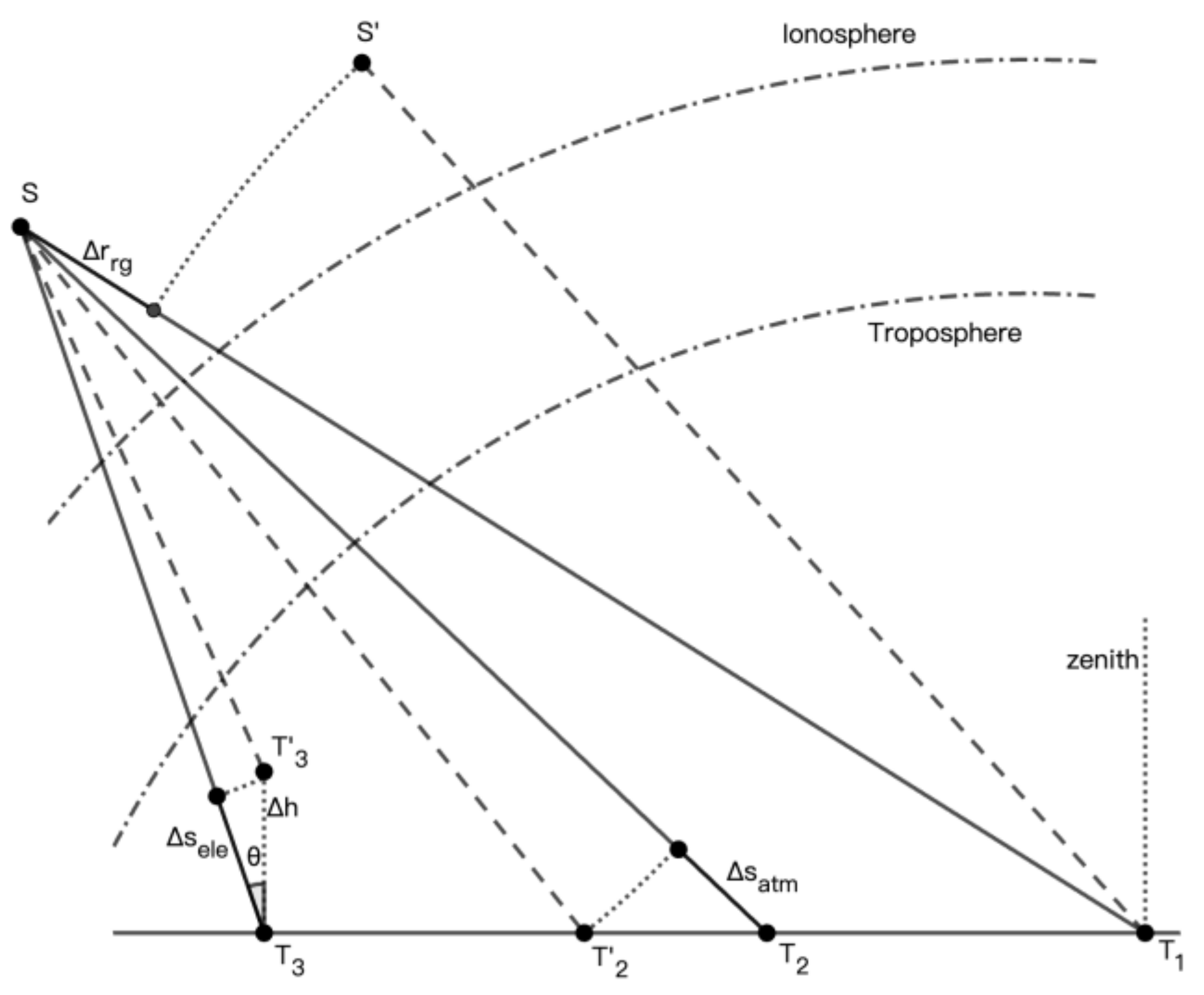
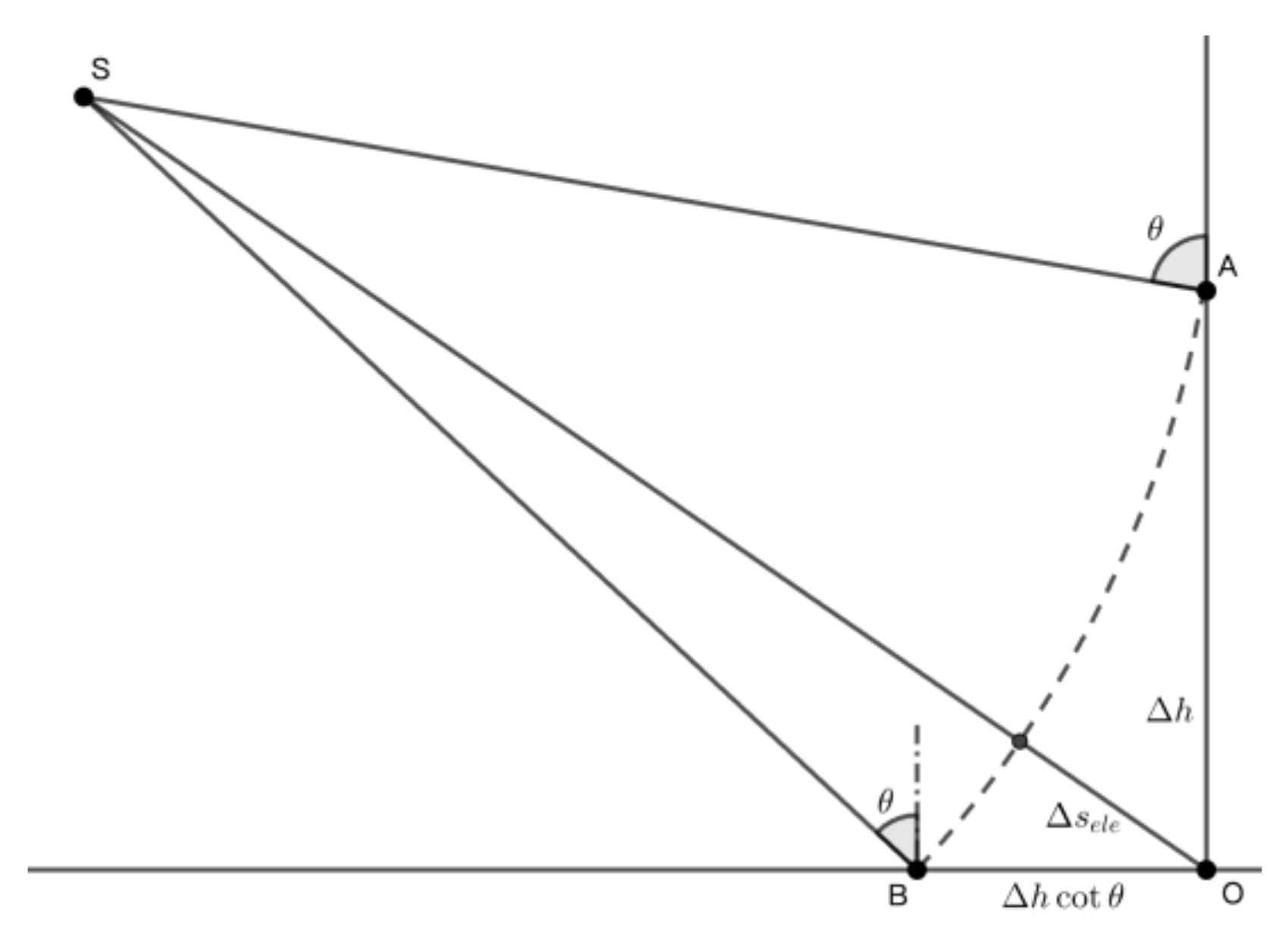
In addition to the orbit error, the range geolocation accuracy is also affected by the atmospheric error and the ground elevation error (
Figure 1). Influenced by the atmosphere, the signal's equivalent velocity
is smaller than the velocity of light in a vacuum
. The propagation time will be decreased by
when calculated using
, called the atmospheric delay [
18]. For convenience, the atmospheric delay can be approximated and expressed in a distance form
. The atmospheric delay comprises the ionospheric delay and the tropospheric delay. The ionospheric delay primarily depends on the ionospheric state and the signal's frequency. In extreme conditions, the ionospheric delay is at the decimeter level for X-band SAR, about 1 meter for C-band SAR, and may exceed 10 meters for L-band SAR [
18]. The tropospheric delay is mainly influenced by the tropospheric state and the length of the propagation path. Given that the signal's zenith angle
generally ranges from 20° to 70°, and the zenith tropospheric delay is typically 2 meters to 3 meters, the total tropospheric delay is about 2 meters to 4 meters.
The elevation error
causes a geolocation error
(
Figure 1). Since the accuracy of currently available DEMs is limited [
25], the elevation error tends to have the heaviest impact on the geolocation accuracy, potentially introducing an error of approximately 10 meters.
Table 1 lists the components of the range geolocation errors.
Based on the previous discussion, let
represent the tropospheric delay,
denote the ionospheric delay, and
signify the elevation-related error. We categorize the geolocation error caused by other factors, including the satellite orbit error, into residual terms
in range and
in azimuth. Let
and
denote the geolocation error in range and azimuth. We have
Next, we will introduce the tropospheric and ionospheric correction methods and the geolocation procedures.
2.2. Atmospheric correction
The most common atmospheric correction methods are the ray-tracing (RT) method and the zenith delay mapping (ZDM) method. The RT method models the actual signal propagation process, thus having superior accuracy. The ZDM method approximates the propagation process and has advantages in computational complexity. Many InSAR studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of the ZDM method in phase correction [
26]. This research aims to validate its efficacy in geolocation.
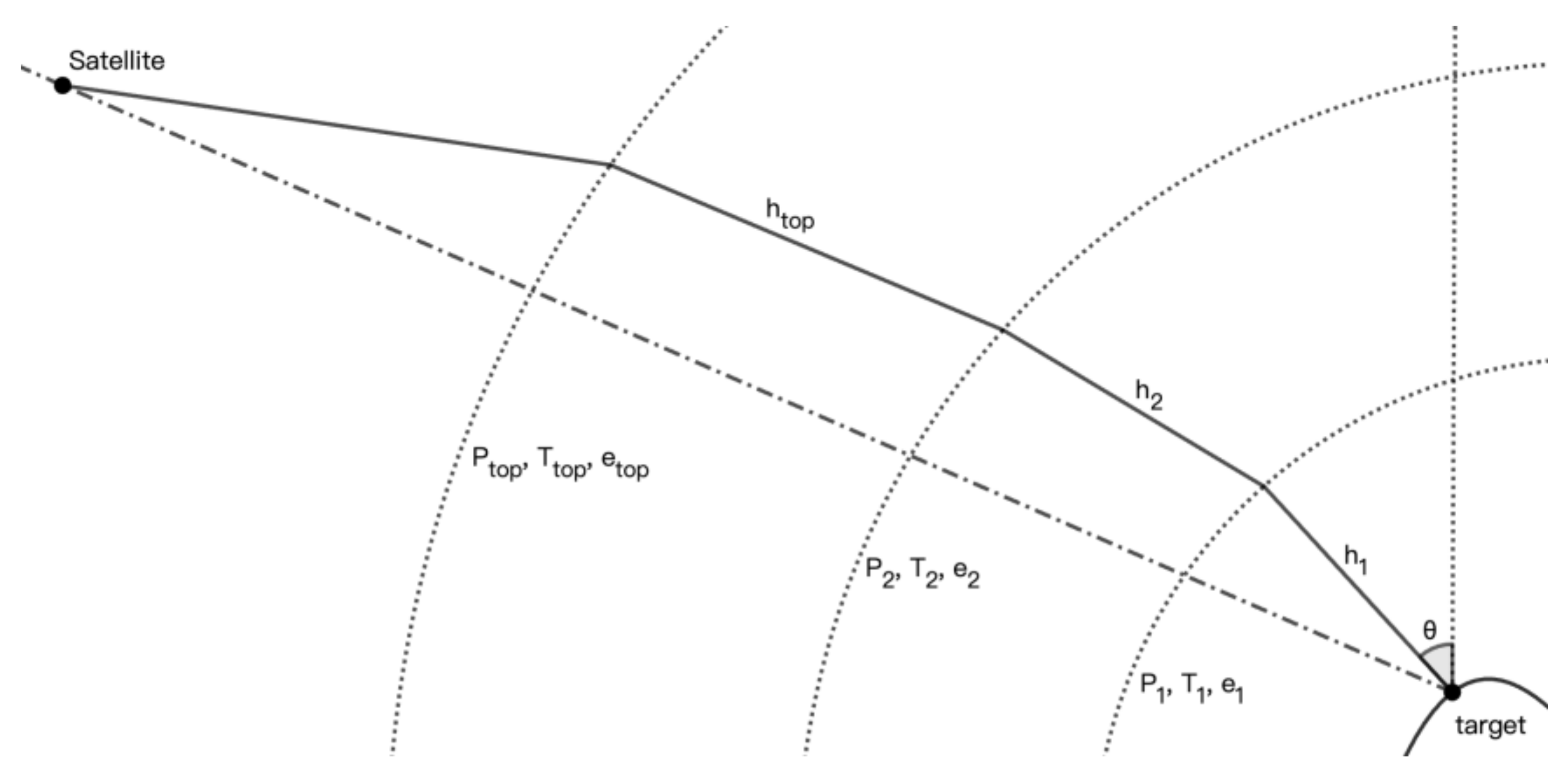
The RT method divides the propagation path into multiple segments, calculates the tropospheric delay corresponding to each segment, and sums them up (
Figure 2). Since the result is virtually unchanged when segments are more than 20 [
18], dividing the path into 20 segments is sufficient to meet the accuracy requirement for geolocation. The bending of the propagation path due to refraction has nearly no impact on results, so approximating the path as a straight line introduces only negligible errors [
27].
The implementation of the RT method requires the pressure
, the temperature
, the vapor partial pressure
, the path length
in each segment (Equations 3 & 4) [
28,
29].
is the zenith angle.
is the radio refractivity that equals
, where
is the refractivity.
We add an extra term to the conventional formula (Equation 4) to correct the delay above the tropopause. The vapor partial pressure is virtually zero; hence, the additional delay can be approximated as the hydrostatic delay, which can be estimated using the pressure at the tropopause.
The ZDM method estimates the tropospheric delay of the propagation path using the zenith delay. Given that the thickness of the troposphere is limited, generally not exceeding 30 km [
27], the tropospheric parameters along the propagation path do not differ significantly from those in the zenith at the same altitude, which is the theoretical foundation for the ZDM method. The mapping functions can be
or from related products, such as VMF1. The most significant advantage of the ZDM method is the simplification of the computation, allowing the zenith tropospheric delay to be potentially released as a standard product, such as the GACOS and station observation products.
2.3. Ionospheric Correction
The common practice for the ionospheric correction is to approximate the entire ionosphere as a thin layer located at the height of 450 km, referring to the intersection point of the signal with the thin layer as the piercing point. The ionospheric delay is calculated using the vertical total electron content (VTEC) at the piercing point (Equation 5) [
27].
The unit of the VTEC is the total electron content unit (TECU) that equals
,
(Hz) represents signal frequency, R is the radius of the Earth, H stands for the height of the ionosphere 450 km, and
denotes the zenith angle on the ground. As most SAR satellites orbit within the ionosphere, the result is larger than the actual ionospheric delay, so theoretically, an adjustment based on the satellite's orbital altitude is needed [
18]. However, Zhang et al. found that the adjustment contributes to only centimeter-level improvements for C-band Sentinel-1 and even worsens the accuracy for L-band ALOS-2 [
27]. Due to the insignificant improvement, we will not discuss the adjustment for the ionospheric delay further.
2.4. Geolocation Procedures
We use the Range-Doppler model to establish the connection between the geospatial coordinates and the SAR image coordinates. This paper does not discuss other models, such as the rational polynomial model based on photogrammetric principles with relatively lower accuracy [
30]. The transformation from the geographic coordinate into the SAR image coordinate is called indirect geolocation, while the reverse process is known as direct geolocation [
31,
32]. Given that our research serves for data registration and geographic information fusion, we focus solely on indirect geolocation.
Assuming that one of the geographic coordinates to be geolocated has been converted to the geocentric coordinate
, the range vector
can be obtained with the satellite's position
at the imaging time
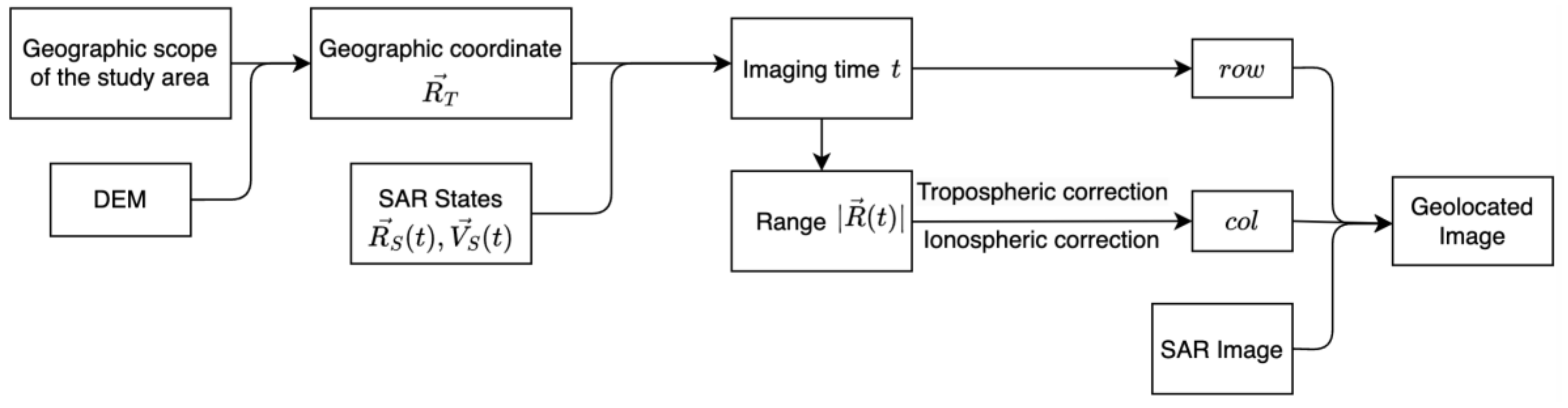
. The fundamental idea for the geolocation is to determine
and
, correct the tropospheric delay and ionospheric delay for
, calculate the image coordinate (row, col) and resample the image (
Figure 3).
The imaging time
is solved through the Doppler equation (Equation 6), where
represents the velocity of the satellite,
denotes the signal frequency, and
is the speed of light in a vacuum.
Most SAR images are produced in the zero Doppler geometry,
, so
is orthogonal to
. We solve for
using an iterative method (Equation 7).
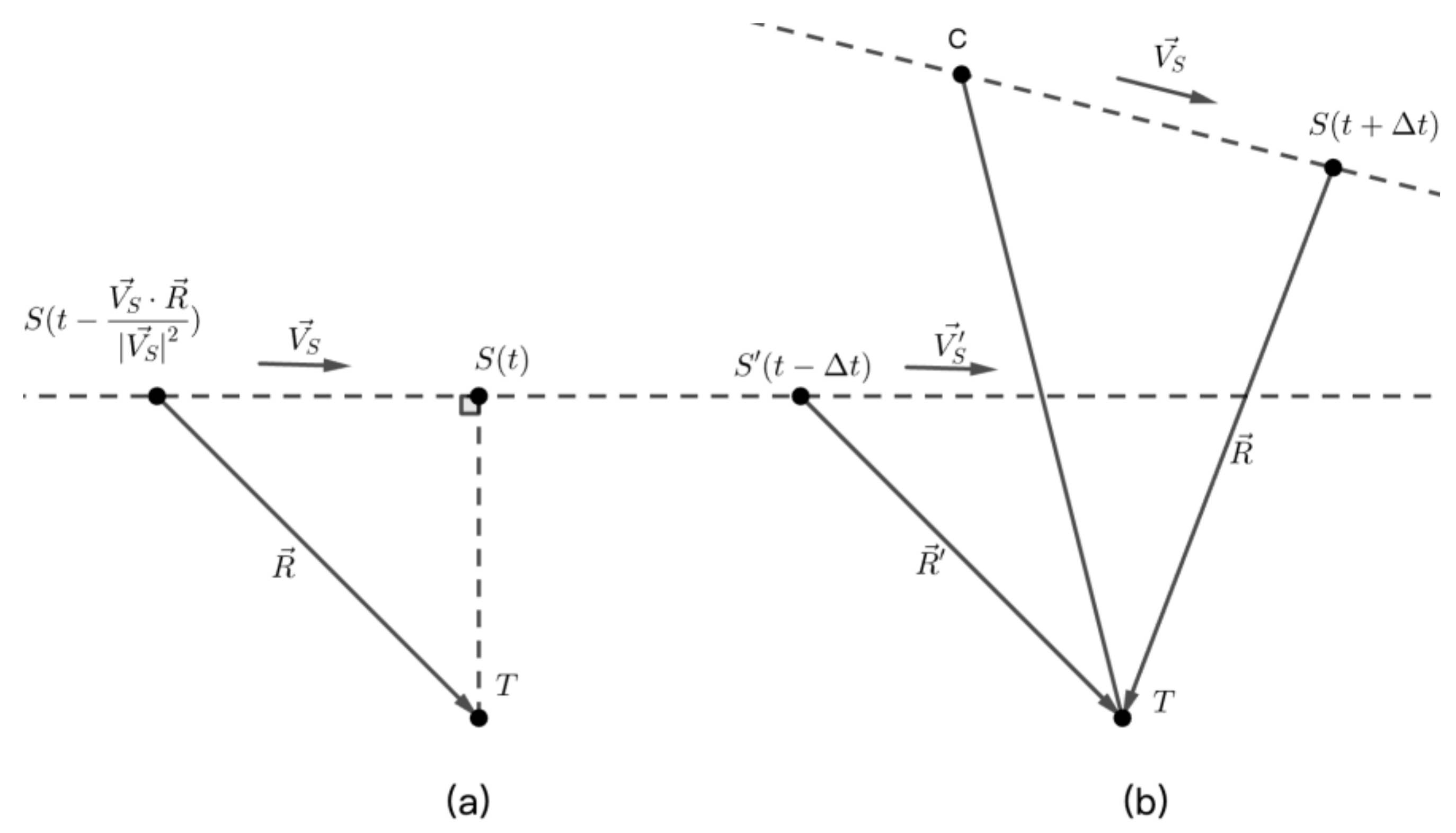
The principle is as follows (
Figure 4a).
is the projection of
in the direction of
. If
is orthogonal to
, the projection should be zero. We need to increase the imaging time
to meet the condition, with the increment value being
.
Since the satellite keeps moving between the signal transmitting and receiving moments, Equation 6 is only an approximation, but studies have shown that it is of sufficient accuracy [
33]. With
representing the azimuth start time of the image,
denoting the azimuth line time,
the nearest range of the image,
the range pixel spacing,
and
representing the tropospheric delay and ionospheric delay, the image coordinates
can be calculated (Equations 8 & 9). The signs of
and
are positive so that the range coordinate
is relatively more minor without atmospheric correction.
Due to the difference in the image standard, the azimuth coordinates of Tianhui-2 images are calculated using Equation 10 [
34].
For Tianhui-2 secondary images, the single satellite model (Equation 6) is not applicable. The range vector
and the velocity
of the reference satellite must be considered (Equations 11 – 13,
Figure 4b), where
. The azimuth coordinate
follows the same formula as reference images (Equation 10) [
34].
The final step is to sample the pixel (row, col) and put it to the original geographic coordinate.
The error
of the elevation will lead to a geolocation error
in range (
Figure 5). If the elevation with error is more significant than the actual elevation, the range coordinate
with error will be relatively minor. We discuss the range geolocation accuracy in the image coordinate system for the rest of this article, so here we use
to describe the range error. The distance
on the ground is
, which is more commonly seen in direct geolocation research.
2.5. Materials and Experiments
Our study area is located within the Changping District of Beijing, China, spanning latitudes from 40.15° N to 40.27° N and longitudes from 116.20° E to 116.35° E, covering an area of
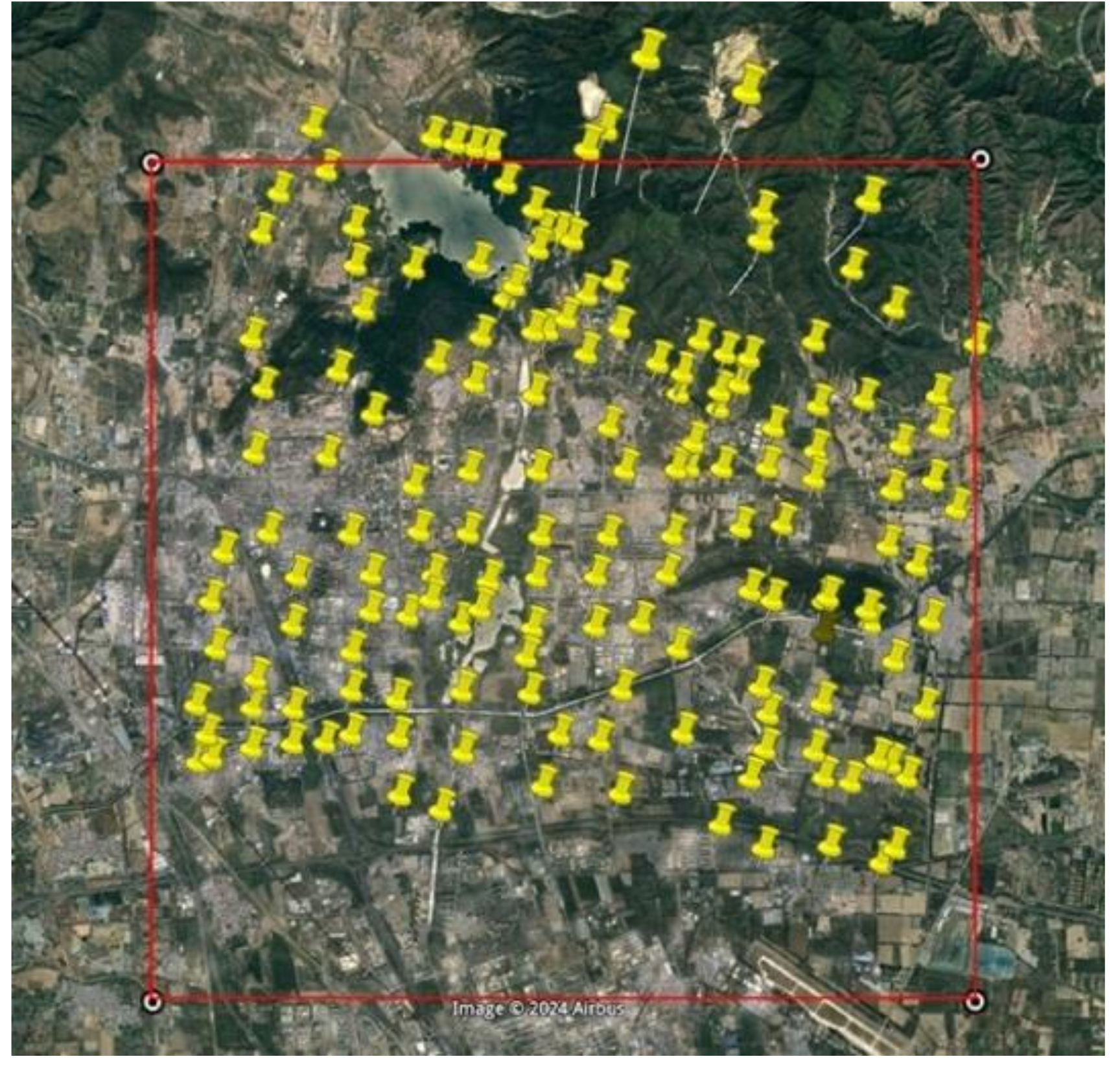
. The geomorphological types from northeast to southwest are the mountainous region, the piedmont alluvial fan, and the plain. The measurement points were obtained through GNSS differential measurement with centimeter-level 3D positioning accuracy. A total of 164 points are utilized (
Figure 6), among which 135 points are situated on flat locations within the plain or the piedmont alluvial fan area, while 29 measurement points are in mountainous regions.
This study uses 11 TerraSAR-X images and a pair of Tianhui-2 images. The TerraSAR-X satellite constellation comprises two identical satellites, TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X, respectively, launched in June 2007 and June 2010, operating in X-band at a frequency of 9.65 GHz. The TerraSAR-X images we use were acquired by the TanDEM-X satellite from July 3rd, 2018, to May 29th, 2019, and are Level 1B single look complex (SLC) slant-range HH-polarized images in stripmap mode. We number the images using dates. The ground resolution is azimuth range , the pixel size is azimuth range , and the swath is azimuth range .
The Tianhui-2 satellite constellation, similar to the TerraSAR-X, comprises two identical satellites that operate in X-band at a frequency of 9.60 GHz. The reference and secondary satellites acquired the selected images on October 28th, 2019, and are Level 1B SLC slant-range HH-polarized images. They share the same image parameters. The ground resolution is
in both azimuth and range, the pixel size is azimuth
range
, and the swath is azimuth
range
. The orbit accuracy of the Tianhui-2 satellites is lower than that of the TerraSAR-X, with potential errors reaching up to 2 meters [
35,
36].
We first verify the completeness of the geolocation error decomposition (Equations 1 & 2). In
Section 3.1, we geolocate the measurement points based on GNSS elevations, correct the tropospheric delay through the RT method, implement the ionospheric correction, and evaluate the results. When performing the tropospheric correction, we utilize the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) ERA5 data and the Weather Research & Forecasting Model (WRF) program. The ERA5 is a reanalysis dataset for the troposphere derived from global meteorological observations [
37], dividing the troposphere into 37 layers according to pressure, providing pressure, temperature, and vapor partial pressure for each layer, with a horizontal resolution of
and a temporal resolution of 1 hour. The WRF is a high-accuracy numerical weather model widely applied in InSAR research [
38]. We input the ERA5 data as the initial condition into the WRF to obtain atmospheric parameters at the imaging time with a resolution of
. For the ionospheric correction, we utilize the TEC products from the International GNSS Service (IGS). The TEC product, recorded in units of 0.1 TECU (
), comes with a spatial resolution of 2.5° × 5° and a temporal resolution of 2 hours [
39].
Section 3.2 checks the validity of the ERA5, analyzes the characteristics of the tropospheric delay, and compares the performance of the RT method and the ZDM method. Due to the lack of in situ data, we verify the ERA5 using the zenith path delay (ZPD) data from the BJFS station around the study area. The GACOS is an emerging ZPD data, quasi-real-time and globally acquirable with a high resolution of
. In this Section, it is proven to perform as well as the ERA5. In
Section 3.3, we will calculate the upper limit and variation ranges of the ionospheric delay throughout the whole year.
Section 3.4 analyzes the impact of the DEM elevation error on geolocation accuracy. The SRTM and the WorldDEM are used in this Section. The SRTM has a resolution of
, whose vertical datum reference is the EGM96 geoid model, and raw data were collected between February 11th and 22nd, 2000. The WorldDEM has a higher resolution of 12 meters [
40], whose vertical datum reference is the EGM2008 geoid model, and raw data were acquired in January 2011 and ceased around mid-2015.
3. Results
3.1. Geolocation Accuracy
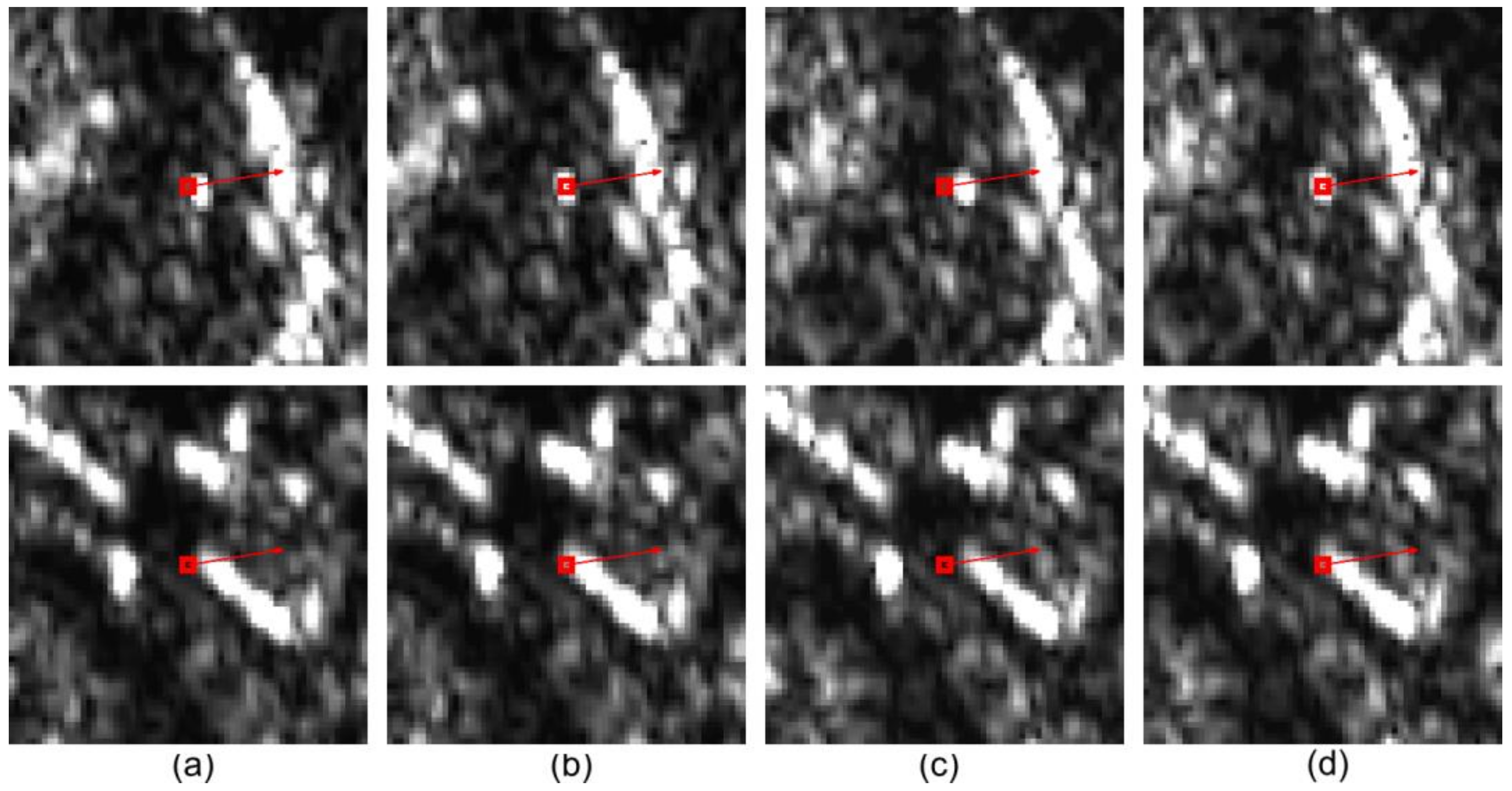
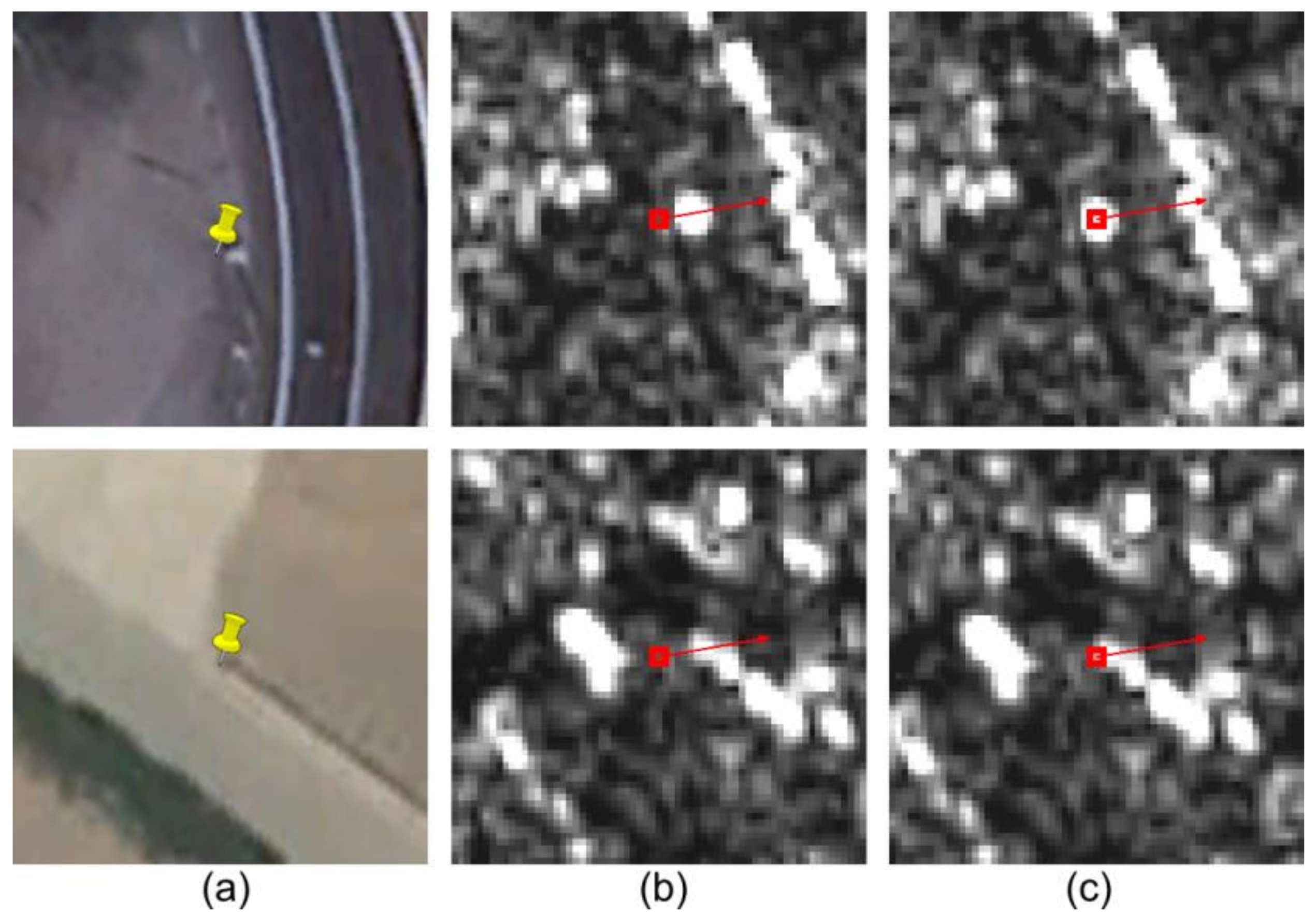
We first visually select measurement points on the TerraSAR-X image 20190117 and then coregister this image to other TerraSAR-X images to control the quality of point selection. For each measurement point (
Figure 7a), we select a
area surrounding it, subdivide it into
grids, and transfer the image onto this area based on the GNSS elevation. Given that the elevation-related geolocation error
is at the centimeter level, the range geolocation error
is approximately equivalent to the atmospheric delay
. The geolocation results without atmospheric correction have smaller range coordinates (
Figure 7b), consistent with the model (Equation 9). We have checked the geolocation results with the atmospheric correction for all 164 measurement points and find that every point is accurately geolocated to the expected coordinate (
Figure 7c), indicating the geolocation residuals
and
are less than
meter. The results substantiate the completeness of the geolocation error decomposition (Equations 1 &2) and the effectiveness of the atmospheric correction. Through the geolocation procedures proposed in
Section 2.4, TerraSAR-X images can achieve an accuracy better than
meter.
We coregister TerraSAR-X images using the Interferometric synthetic aperture radar Scientific Computing Environment (ISCE) software. ISCE samples the secondary image into the coordinate system of the reference image before coregistration to mitigate terrain effects, which is equal to geolocation without atmospheric correction (
Figure 7b) but in the radar center coordinate system. ISCE uses a constant offset in each direction to describe the coregistration result (
Figure 8). In azimuth, the offsets are all less than 0.1 pixels, indicating virtually no geolocation error. In range, the offsets are less than 0.2 pixels except for image 20180805. We inspected the tropospheric delay and found it about 0.3 pixels larger in 20180703 and 20180805 than in 20190117. Therefore, we infer that the main cause of the offset is the difference in the tropospheric delay. The offset affected by other factors, including the difference in the ionospheric delay, is usually less than 0.2 pixels.
In contrast, the geolocation results of the Tianhui-2 images exhibit noticeable residuals. The geolocation error of the reference image is approximately
meters in azimuth and
meters in range (
Figure 9a). For the secondary image, the azimuth geolocation error is
meters, too, while the range error is estimated to be
meters (
Figure 9c). Because the geolocation error aligns with those of other studies [
34], we infer that the primary source of the geolocation residual is the orbit error of the Tianhui-2 satellites. The secondary image's lower geolocation accuracy may be attributed to deficiencies in time synchronization between the two satellites. We shift the reference image by -1 meters in azimuth and -1.5 meters in range to correct the results and perform a similar correction for the secondary image (
Figure 9b & 9d). We find that both images can geolocate all the measured points accurately, indicating that the residual is irrelevant to imaging time, range, and Doppler frequency. The results also substantiate the effectiveness of the geolocation model for the secondary satellite in
Section 2.4.
3.2. Characteristics of the Tropospheric Delay
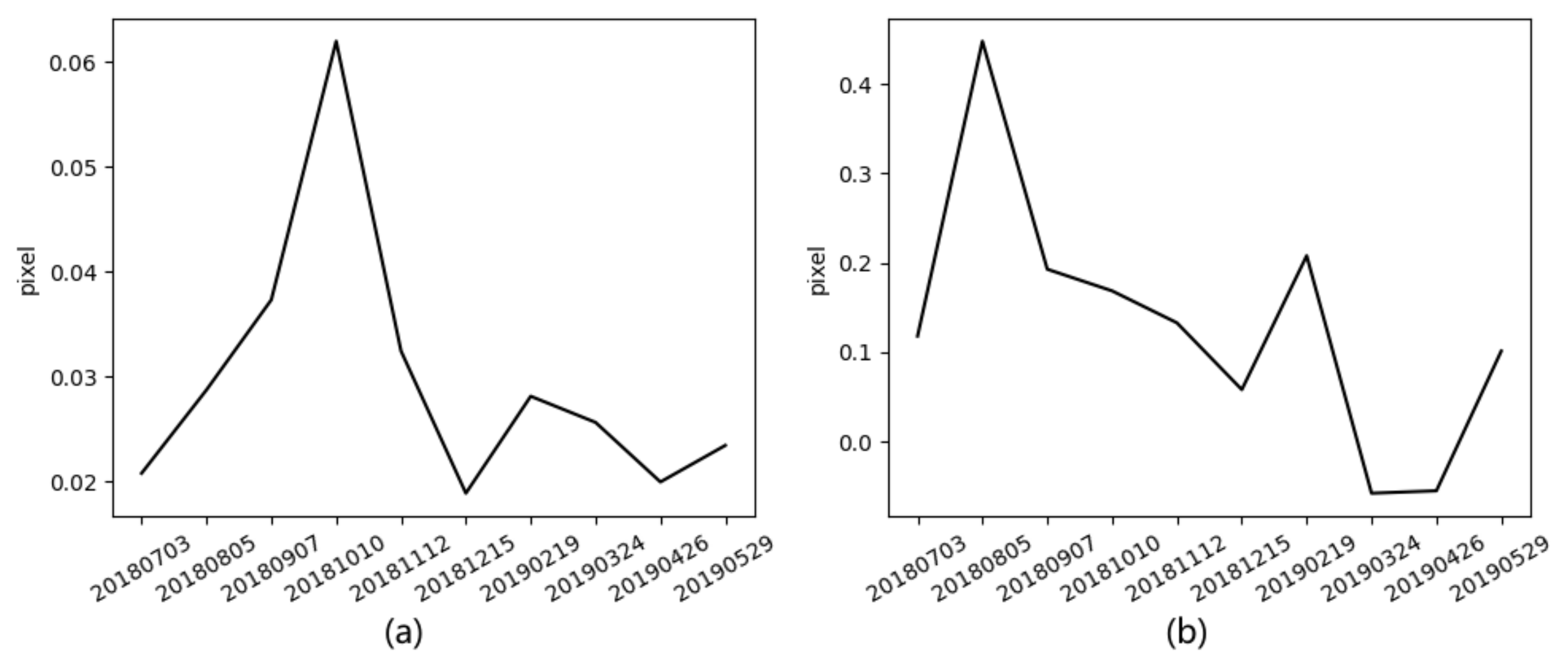
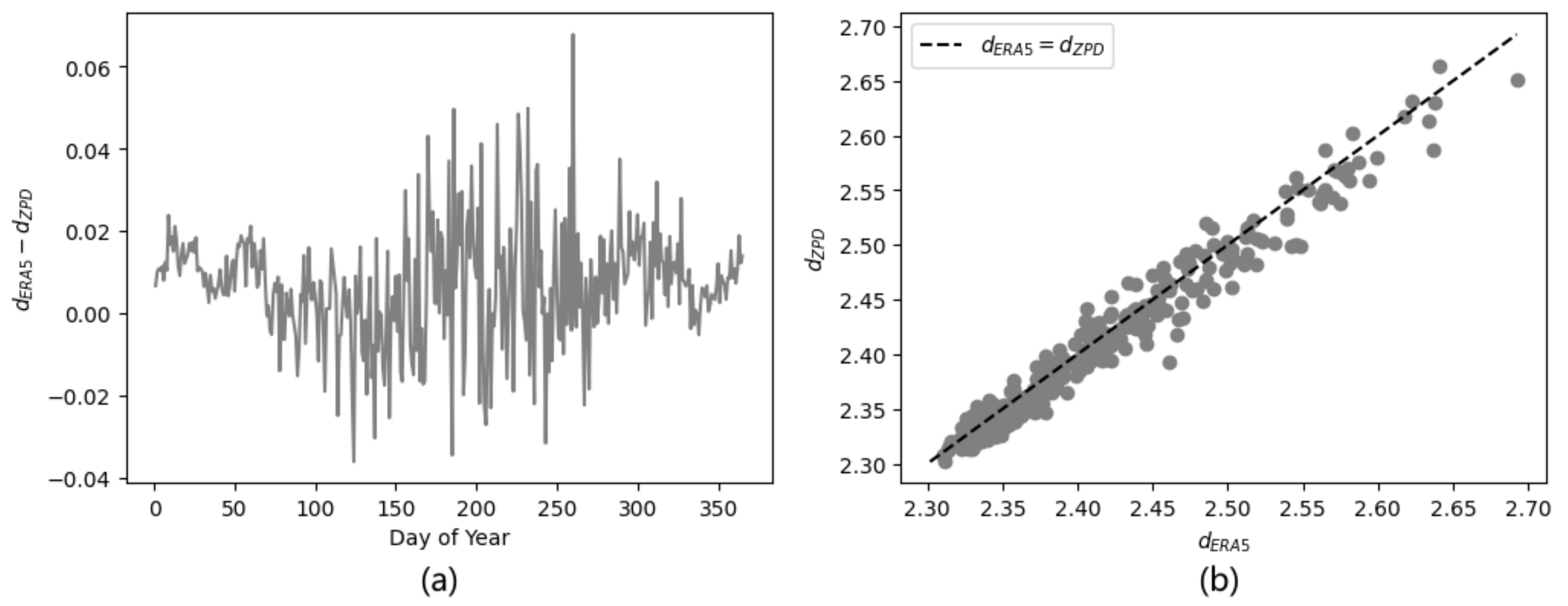
We calculate the zenith delay using the ERA5 and compare the result with the ZPD in the BJFS station (
Figure 10). The difference is larger in summer than in winter, perhaps due to the higher vapor pressure. The maximum difference is about 0.06 meters, corresponding to less than 0.1 pixels, so we believe that the accuracy of the ERA5 is enough for geolocation. The difference is not correlated with the delay value (
Figure 10b).
The tropospheric delay in the study area is calculated using the RT method, which ranges from
meters to
meters, demonstrating a strong correlation with the ground elevation (
Figure 11a,b). The delay in the plain varies on a smaller scale from
meters to
meters, while in the mountainous region, it is typically 2.6 meters to
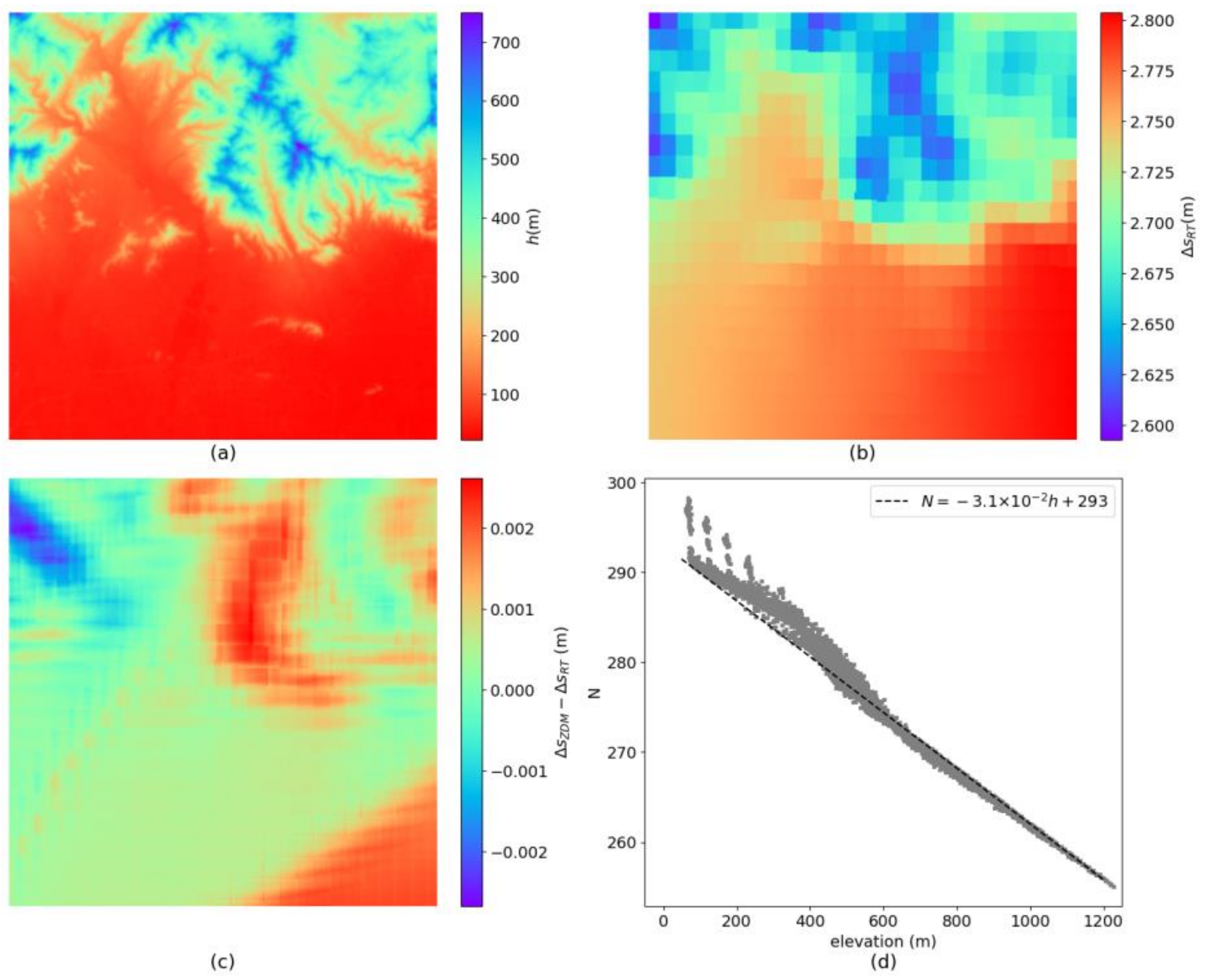
meters. The reason is that the signal must traverse a longer distance before it reaches lower altitude areas, and there is more tropospheric perturbation in mountainous regions.
We calculate the zenith tropospheric delay in the study area using the same tropospheric parameters as the RT method and then map it toward the line of sight (LOS) direction. The difference between it and the RT result is less than 0.3 cm (
Figure 11c). We examine the relationship between the radio refractivity
and the elevation under 1200 meters (
Figure 11d). Assuming N is 300, only 10 meters are needed to form a 0.3-centimeter delay (Equation 4). Considering that the accuracy of the elevation inside the ERA5 is usually less than 10 meters, the difference between the two methods is of little reference value. This distribution of N sustains the deduction (
Figure 11d). At the same elevation, the average fluctuation of N is at most 5 when the elevation is less than 600 and becomes less than 1 after that, which corresponds to only a 0.3-centimeter difference. Compared to the method, the accuracy of path length is more important. Therefore, we believe that the two methods perform equally well. The results suggest that the ZDM method generally meets the accuracy requirement for geolocation.
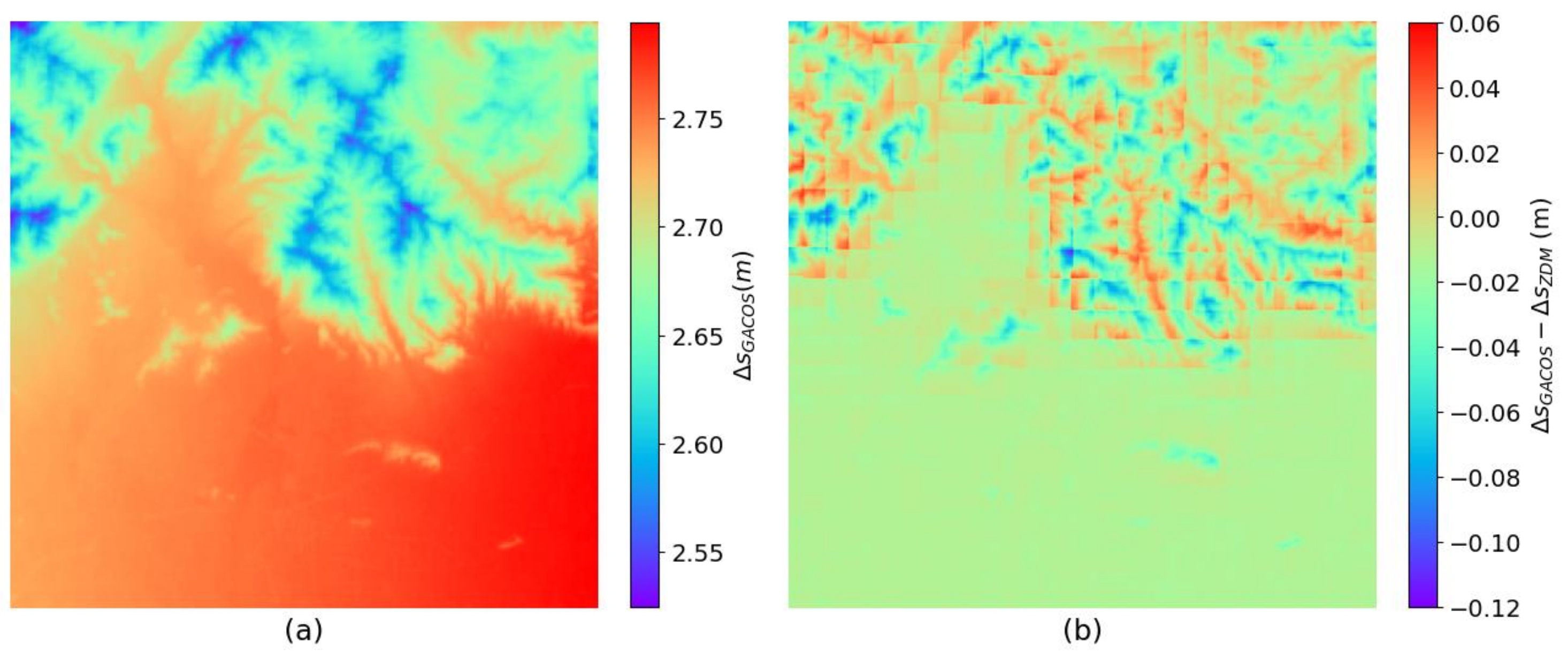
We compared the difference between the result of the GACOS-based ZDM method and the ERA5-based ZDM method (
Figure 12). The GACOS-based result exhibits the same characteristics as the ERA5-based result; that is, the tropospheric delay is about 5 cm larger in the east plain than in the west plain (
Figure 12a). The difference exhibits a noticeable texture associated with the terrain (
Figure 12b). It tends to be positive in valleys while negative in ridges, which is related to the WRF-processed ERA5's lower resolution of
than the 90-meter resolution of GACOS. The discrepancy is about -1 cm in the plain, whereas it barely reaches extremes of around -12 cm in mountainous regions. The difference between the two data sources is much larger than it is between the two methods. However, due to its advantages in resolution, although we have verified the high precision of ERA5, we still believe that the results from GACOS are at least as good as those from ERA5. Compared to the total geolocation error in range, we think that all three methods demonstrate enough tropospheric accuracy.
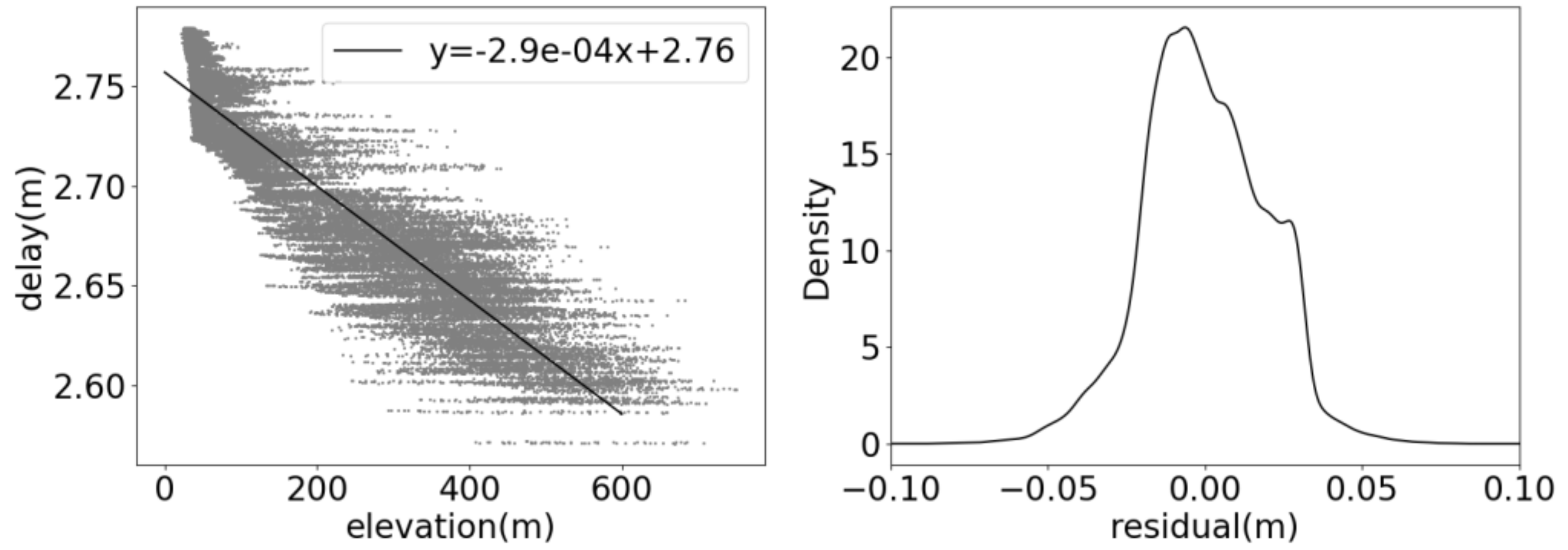
The relationship between the elevation and the tropospheric delay is linear, although the degree is notably weaker in the mountainous region than in the plain (
Figure 13a). A linear regression analysis shows that for every increase of 100 m in elevation within the study area, the tropospheric delay decreases approximately by 2.9 cm. In most cases, the residual of the fitting is less than 5 cm (
Figure 13b). Given that the resolution of the raw ERA5 data is only 0.25° × 0.25°, comparable in scale to the extent of the study area, we will get only a single value if the tropospheric correction is directly implemented based on the ERA5 data, which leads to a residual
in the tropospheric correction (
Figure 13a). Therefore, the accuracy of the tropospheric correction utilizing the raw ERA5 data is inferior to that achieved using the GACOS.
Due to the continuity of the tropospheric parameters and the strong correlation between the tropospheric delay and the elevation, the accuracy of different tropospheric methods is close. Considering that the GACOS has the highest resolution, which ensures it performs well even under complex terrain conditions and is easy to access and use, we propose that the GACOS-based ZDM method is relatively the most optimal.
3.3. Characteristics of the Ionospheric Delay
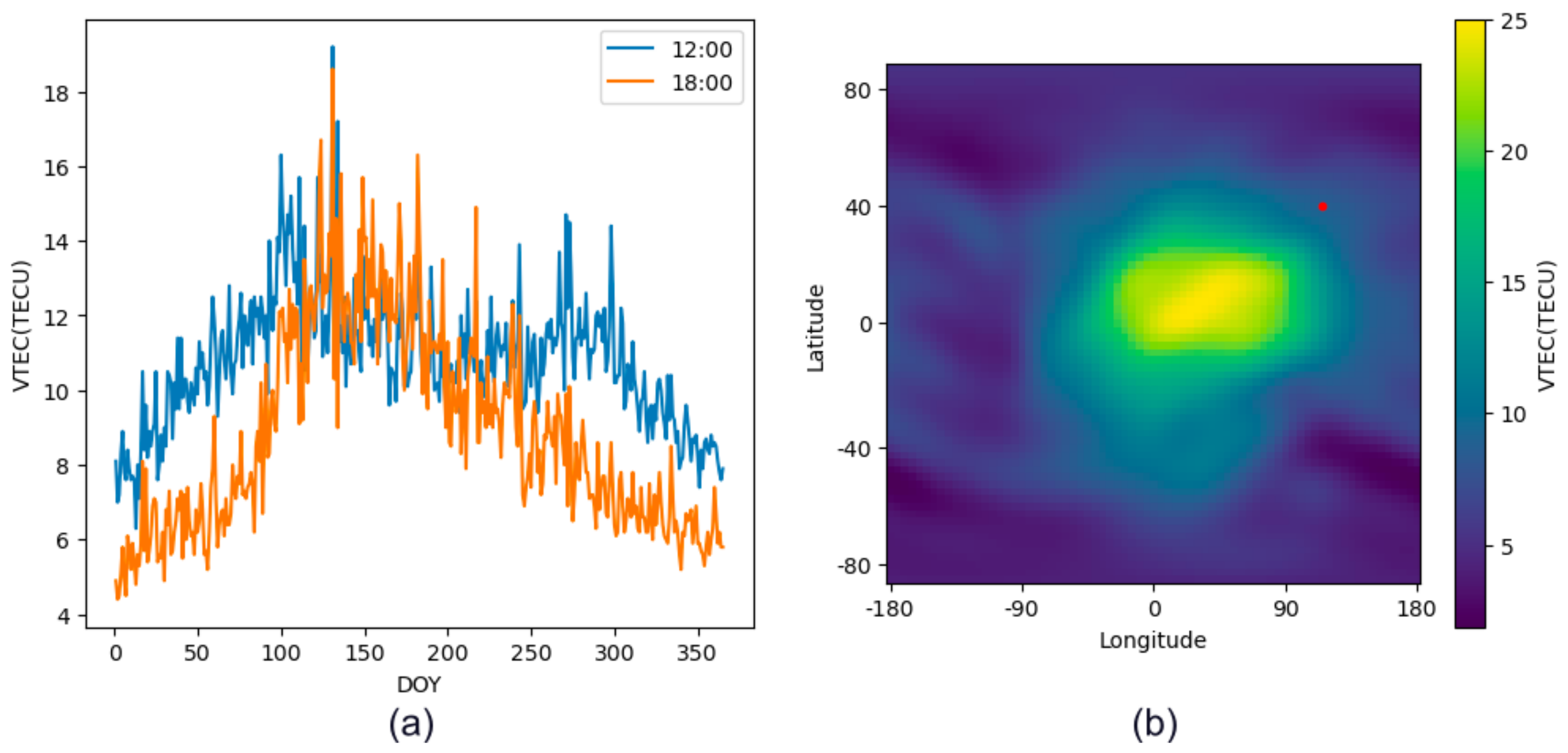
Since the impact of the ionospheric delay on X-band satellites, including the TerraSAR-X and the Tianhui-2, is insignificant, we focus primarily on the numerical characteristics of the ionospheric delay. Given that SAR satellites are typically in dawn-dusk or noon/midnight orbits, we collect the VTEC of the study area at local time 12 PM and 6 PM in 2019 (
Figure 14a), finding that the variation ranges from the two moments are approximately the same, with a maximum value around 20 TECU. Due to the direct sunlight in the tropics, the average VTEC there is more significant than that in the study area (
Figure 14b), reaching up to 25 TECU.
We take the SAR satellites TerraSAR-X, Sentinel-1, and ALOS-2 across three signal bands as examples and calculate the ionospheric delay when the VTEC is 25 TECU and the zenith angle θ is 45° (Equation 5,
Table 2). Generally, the ionospheric delay for X-band satellites is comparable in magnitude to the residual of the tropospheric correction, thus having a minimal impact on geolocation accuracy, rendering the non-necessity of the ionospheric correction. The variation of the ionospheric delay is even smaller (Discussed in
Section 3.1). For the C-band, the ionospheric delay is usually less than 1 meter. The accuracy of the ionospheric correction is acceptable even if residual remains. However, in the case of the L-band, the ionospheric delay poses the most significant influence among all factors on geolocation, potentially causing an error as high as 10 meters. Employing higher-resolution data such as the Jet Propulsion Laboratory high resolution Global Ionospheric Maps (JHR) enhances the positioning precision significantly [
27].
3.4. Characteristics of the Elevation-related Error
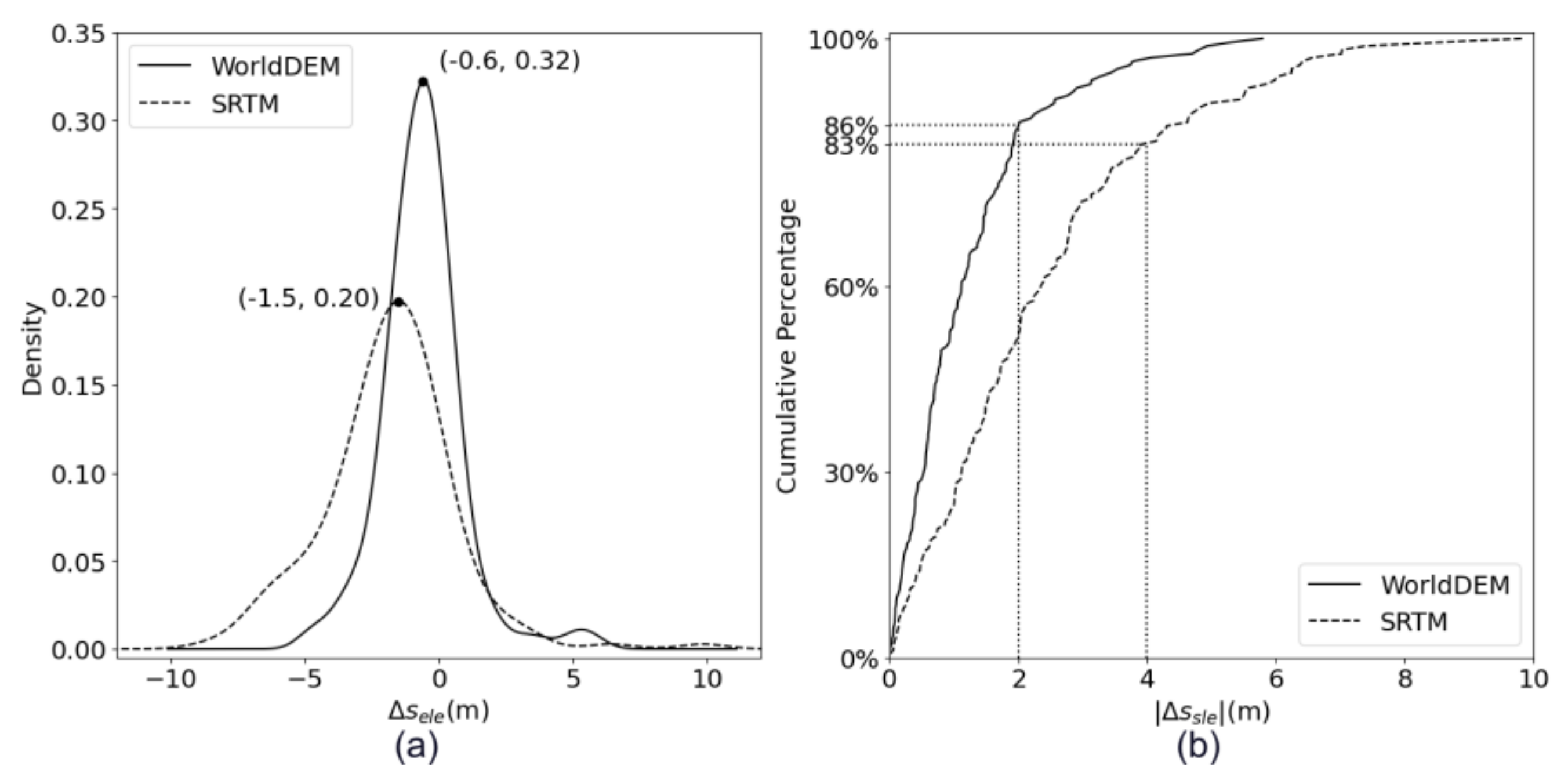
We calculate the elevation-related error by subtracting the GNSS-based result from the DEM-based result. When geolocation is implemented on the WorldDEM and the SRTM, the elevation-related error
corresponding to the peak probability density is negative in both cases (
Figure 15a), indicating a tendency for the DEM elevation to be larger than the GNSS elevation on measurement points. Specifically, the peak-density error is -1.5 meters for the SRTM, and the absolute error is less than 4.0 meters for 83% of the measured points. For the WorldDEM, the peak-density error is -0.6 meters, and the absolute error is less than 2.0 meters for 86% of the points (
Figure 15b). Considering that the atmospheric correction residual is typically less than 1 meter and often around 0.1 meters, we conclude that the range geolocation error
can generally be controlled within 5 meters when using the SRTM and within 3 meters when using the WorldDEM. There is no relatively effective method for correcting the elevation-related error, so the influence of this error is considered the most severe among all contributing factors.
We analyze the distribution of
and find that it exhibits a significant correlation with the slope of the measurement points (
Figure 16). As the slope increases, the distribution of
becomes less focused, and the average gradually drifts away from the origin point. For the points with the same slope intervals,
is smaller overall for the WorldDEM than the SRTM. By comparing the optical images at the time the SAR images were acquired and when the DEMs were obtained, we discover the terrain around the points with the largest
has undergone significant changes, indicating that the utilization of the DEM close to the time the image is obtained can help prevent extreme conditions.
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations of Orbit Correction Based on DEM-Simulated Image Coregistration
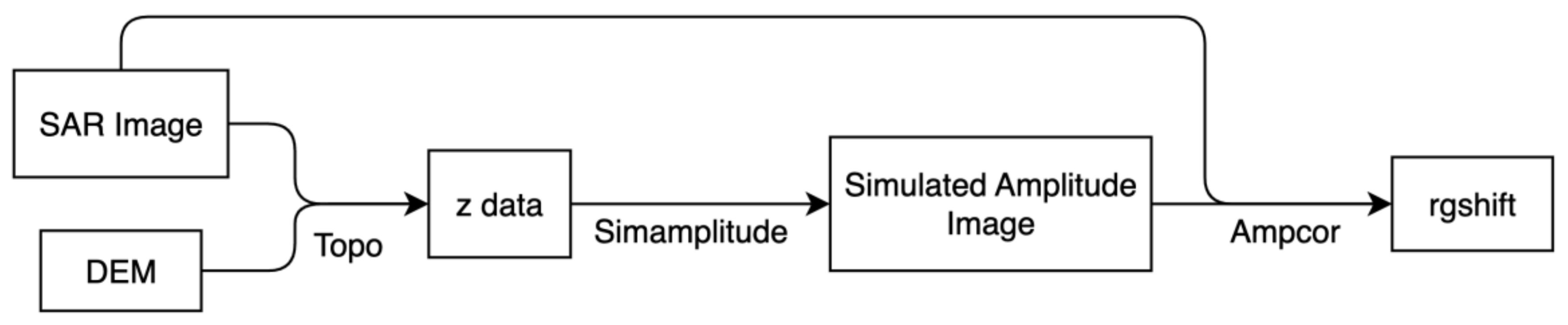
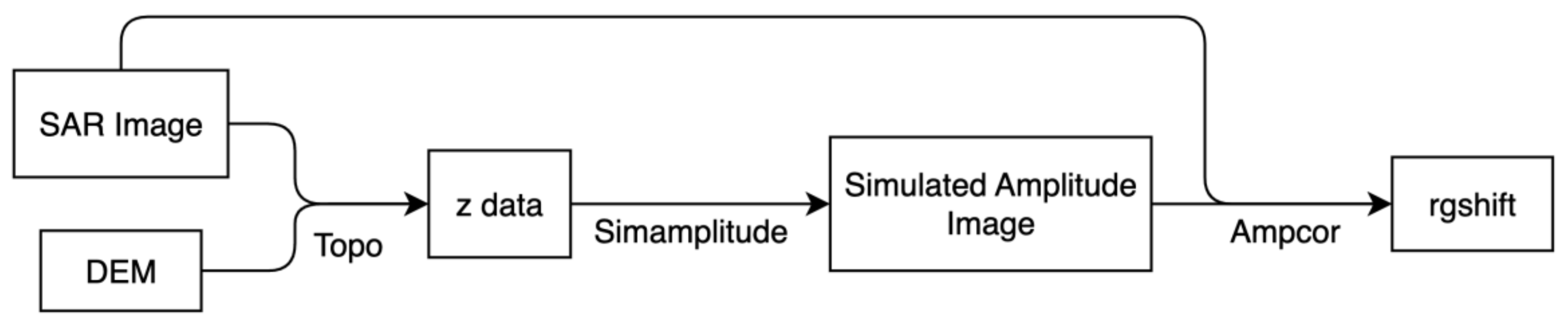
The SRTM used to be a reference for estimating the geolocation error of SAR images due to its high horizontal accuracy, and a common method was to register SAR images and the DEM-simulated amplitude image. We test the effectiveness of this method using ISCE (
Figure 17).
We project the SRTM onto the SAR image coordinate system using the Topo module and refer to the result as z data, which the Simamplitude module can further utilize to generate a simulated amplitude image with the same horizontal accuracy as the SRTM. Finally, the Ampcor module calculates the range shift between the two images.
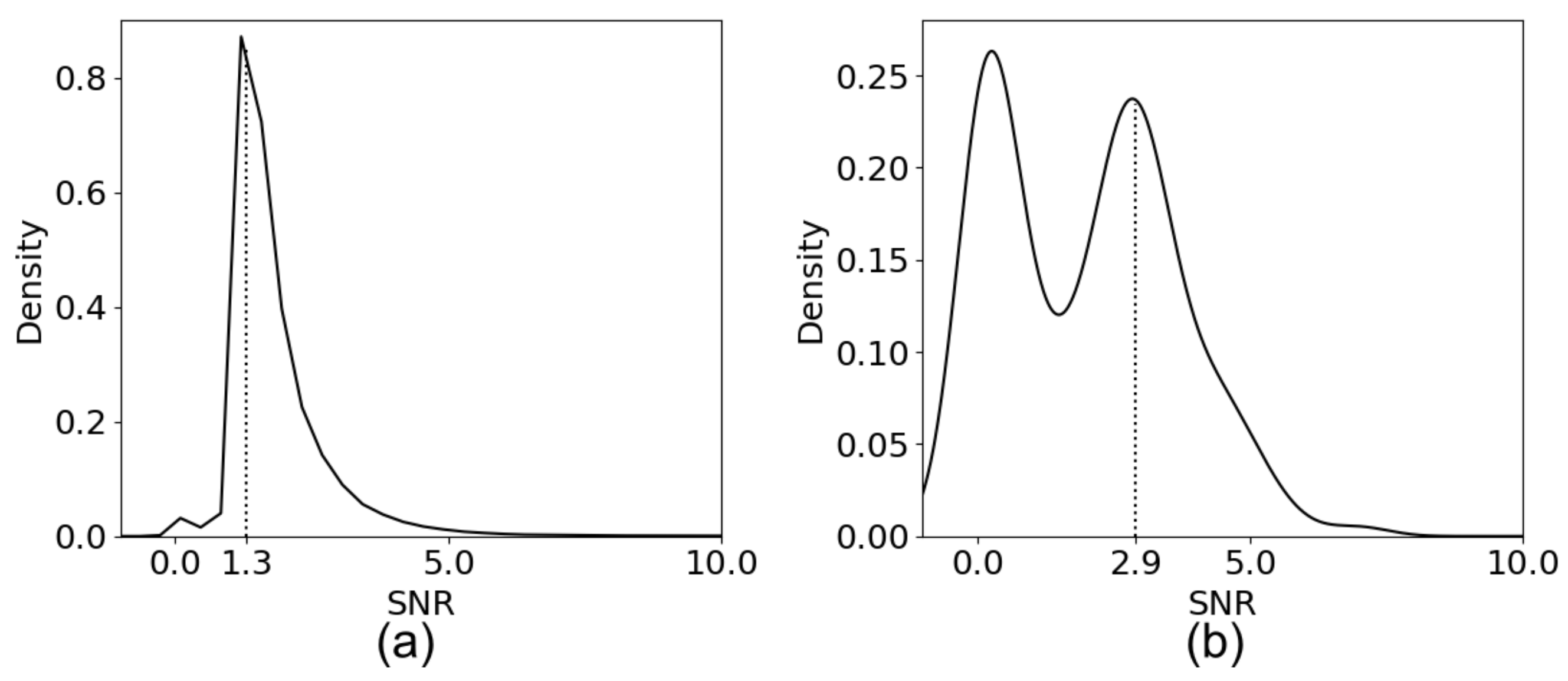
Due to substantial differences between the SAR image and the simulated image, the Ampcor result generally has a much lower signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) than the result of two real SAR images. The SNR corresponding to the peak of the probability density is 1.3 for the TerraSAR-X image (
Figure 18a) and 2.9 for the Tianhui-2 reference image (
Figure 18b), and most of them are weaker than 5.0, which is a common threshold for SAR image coregistration. Therefore, we do not think this method is applicable to high-resolution SAR geolocation.
4.2. Other Geolocation Error Sources
Solid Earth effects and approximations in image production may also introduce geolocation errors in addition to the satellite orbit error, the atmospheric error, and the elevation-related error. Among the solid Earth effects, the solid Earth tides (SET) has the most significant impact on geolocation accuracy, which is induced by the tidal force from the Moon and Sun [
41], potentially causing elevation changes of up to half a meter in equatorial regions and up to 40 cm in the mid-latitude areas. Apart from the SET, the ocean tidal loading and the atmospheric tidal loading can also introduce a centimeter-level error [
42,
43]. Commonly, studies employ programs written by Milbert to eliminate these effects [
44]. Due to the relatively minor influence of the solid Earth effects and the fact that they are hardly considered when processing other data, we have not discussed them.
Approximations applied in SAR image production can lead to geolocation errors. For Sentinel-1 images, the bistatic effect, the Doppler shift in range, and the Doppler FM-rate mismatch are three typical error sources [
18,
45]. The bistatic effect arises due to the "stop-and-go" model assuming that the sensor receives all signals corresponding to the same LOS direction simultaneously. In contrast, they are not simultaneously in reality, introducing an error of about 2 meters to 3 meters in azimuth. The Doppler shift results from neglecting the variation of the Doppler frequency matching the same LOS, leading to a range error as large as 0.4 meters. The Doppler FM-rate mismatch affects the azimuth geolocation accuracy, and the error is typically less than 1.5 meters. We have not discussed these factors because these approximations are not applied to TerraSAR-X images [
18].
5. Conclusions
SAR satellites can acquire data all day and in all weather to periodically provide images for research areas. The radiometric features of SAR images make them highly complementary to optical images and other data. With the improvements in the resolution of SAR images, the progressively finer geometric features make SAR applicable in more and more domains. High-accuracy geolocation is crucial for high-resolution SAR images to ensure the correct match of features. This study analyzes the properties of SAR geolocation errors and examines correction methods, proposing an effective procedure for SAR geolocation. We employ a TerraSAR-X image and a pair of Tianhui-2 images to validate the geolocation procedure, with results demonstrating:
The theoretical SAR geolocation accuracy meets the requirement for common SAR applications. The TerraSAR-X images in this research achieve geolocation accuracy better than 1 meter based on GNSS elevations. Affected by the orbital error and other factors, the geolocation accuracy of the Tianhui-2 reference and secondary images are approximately 2 meters and 4 meters, respectively. Considering that most advanced SAR satellites have orbit data that is more accurate than 1 meter, the result of TerraSAR-X is of more reference value.
The accuracy of elevation data primarily constrains the SAR geolocation accuracy, and using high-accuracy elevation data is critical to enhancing geolocation accuracy. When geolocating the TerraSAR-X image using the SRTM, the accuracy is better than 5 meters for most measurement points. Upon switching to the higher-accuracy WorldDEM, the geolocation error for most measurement points fell below 3 meters.
The GACOS-mapping method is the most optimal tropospheric correction method because the ZDM method provides accuracy comparable to that of the RT method. At the same time, the GACOS has advantages in resolution and ease of use.
The Tianhui-2 secondary satellite receives signals transmitted by the reference satellite. The geolocation results of the secondary image validate the effectiveness of the secondary-image geolocation model proposed in this research. Maybe due to the inaccuracy of time synchronization, the geolocation accuracy of the secondary image is inferior to that of the reference image.
The difficulties in obtaining high-accuracy DEMs are the principal bottleneck in high-accuracy SAR geolocation. In the future, it might be possible to eliminate the dependence on DEMs through 3D geolocation methods and enhance the applicability of SAR geolocation.
Author Contributions
Facheng Li wrote the paper and conducted the experiments. Qiming Zeng guided the experiments, checked the paper, and provided suggestions.
Acknowledgments
The GNSS measurement points used in this study were collected by the team led by Qiming Zeng at the Institute of Remote Sensing and GIS, Peking University. The measurement team also included Jian Jiao, Wei Li, Zhiliang Zhang, Jiang Long, Shangzong Lu, and Haijiao Han. This survey was implemented from October 23rd to October 25th, 2020. The instrument used was a Hi-TARGET iRTK2 GNSS receiver, receiving the differential data through the FindCM service provided by Qianxun Positioning Network Co., Ltd. This research is supported by High-performance Computing Platform of Peking University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang Liangpei; Shen Huanfeng Progress and Future of Remote Sensing Data Fusion. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 20, 1050–1061.
- Dalla Mura, M.; Prasad, S.; Pacifici, F.; Gamba, P.; Chanussot, J.; Benediktsson, J.A. Challenges and Opportunities of Multimodality and Data Fusion in Remote Sensing. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 1585–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X.X. Data Fusion and Remote Sensing: An Ever-Growing Relationship. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2016, 4, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, J.K.; Shah, M. Multi-Sensor Fusion: A Perspective. In Proceedings of the Proceedings., IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation; IEEE Comput. Soc. Press: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1990; pp. 1324–1330.
- Zhang, J. Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data Fusion: Status and Trends. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2010, 1, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idol, T.; Haack, B.; Mahabir, R. Comparison and Integration of Spaceborne Optical and Radar Data for Mapping in Sudan. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 1551–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdikan, S.; Bilgin, G.; Sanli, F.B.; Uslu, E.; Ustuner, M. Enhancing Land Use Classification with Fusing Dual-Polarized TerraSAR-X and Multispectral RapidEye Data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 096054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamba, P. Image and Data Fusion in Remote Sensing of Urban Areas: Status Issues and Research Trends. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2014, 5, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.C.; Rege, P.P. Pixel Level Fusion Techniques for SAR and Optical Images: A Review. Inf. Fusion 2020, 59, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Eo, Y.D.; Lee, M.H.; Park, W.Y. Fusion of SAR and Multispectral Images Using Random Forest Regression for Change Detection. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, D.; Lemoine, G.; Bruzzone, L. Earthquake Damage Assessment of Buildings Using VHR Optical and SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2403–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawn, S.; Saxena, V.; Sharma, B. Remote Sensing Image Registration Techniques: A Survey. In Image and Signal Processing; Elmoataz, A., Lezoray, O., Nouboud, F., Mammass, D., Meunier, J., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2010; Vol. 6134, pp. 103–112. ISBN 978-3-642-13680-1.
- Reinartz, P.; Muller, R.; Suri, S.; Schwind, P. Improving Geometric Accuracy of Optical VHR Satellite Data Using Terrasar-X Data. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Aerospace Conference; IEEE: Big Sky, MT, March 2010; pp. 1–10.
- Reinartz, P.; Müller, R.; Schwind, P.; Suri, S.; Bamler, R. Orthorectification of VHR Optical Satellite Data Exploiting the Geometric Accuracy of TerraSAR-X Data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisinger, C.; Willberg, M.; Balss, U.; Klügel, T.; Mähler, S.; Pail, R.; Eineder, M. Differential Geodetic Stereo SAR with TerraSAR-X by Exploiting Small Multi-Directional Radar Reflectors. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, D.; Biegger, S.; Nüesch, D. AUTOMATED TIEPOINT RETRIEVAL THROUGH HETEROMORPHIC IMAGE SIMULATION FOR SPACEBORNE SAR SENSORS.
- Barnhart, W.D.; Lohman, R.B. Characterizing and Estimating Noise in InSAR and InSAR Time Series with MODIS. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2013, 14, 4121–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisinger, C.; Schubert, A.; Breit, H.; Garthwaite, M.; Balss, U.; Willberg, M.; Small, D.; Eineder, M.; Miranda, N. In-Depth Verification of Sentinel-1 and TerraSAR-X Geolocation Accuracy Using the Australian Corner Reflector Array. Ieee Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 1154–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheenathayalan, P.; Small, D.; Hanssen, R.F. 3-D Positioning and Target Association for Medium-Resolution SAR Sensors. Ieee Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6841–6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna, N.T.; Crippa, P. Generic Atmospheric Correction Model for Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 9202–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna, N.T. Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Atmospheric Correction Using a GPS-Based Iterative Tropospheric Decomposition Model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Penna, N.T.; Li, Z. Generation of Real-Time Mode High-Resolution Water Vapor Fields from GPS Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2017, 122, 2008–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen Jiwei; Zeng Qiming; Jiao Jian; Ye Fawang; Zhu Lijiang Spaceborne SAR Image Geometric Rectification Method without Ground Control Points Using Orbit Parameters Modulation. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2016, 45, 1434–1440.
- Palubinskas, G.; Reinartz, P.; Bamler, R. Image Acquisition Geometry Analysis for the Fusion of Optical and Radar Remote Sensing Data. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2010, 1, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Zeng, Q.; Jiao, J. Quality Assessment of TanDEM-X DEMs, SRTM and ASTER GDEM on Selected Chinese Sites. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.D.; Bekaert, D.P.S.; Lohman, R.B. Tropospheric Corrections for InSAR: Statistical Assessments and Applications to the Central United States and Mexico. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fattahi, H.; Pi, X.; Rosen, P.; Simons, M.; Agram, P.; Aoki, Y. Range Geolocation Accuracy of C-/L-Band SAR and Its Implications for Operational Stack Coregistration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doin, M.; Lasserre, C.; Peltzer, G.; Cavalié, O.; Doubre, C. Corrections of Stratified Tropospheric Delays in SAR Interferometry: Validation with Global Atmospheric Models. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Hu, J.; Hu, C.; Long, T.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y. Modeling and Quantitative Analysis of Tropospheric Impact on Inclined Geosynchronous SAR Imaging. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yu, A.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Q. Comparison and Analysis of Geometric Correction Models of Spaceborne SAR. Sensors 2016, 16, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YANG Jie; PAN Bin; LI Deren; ZHONG Yongzheng Location of Spaceborne SAR Imagery Without Reference Points. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2006, 31, 144–147.
- Yan Li; Li Zhen Research on the Production and Accuracy Analysis of Terra SAR-X DOM. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2010, 1–3.
- Chen Gang; Qian Fangming; Liu Zhiming; Lou Liangsheng Algorithm to Changing Bistatic Imaging Geometric Model for TH-2 Satellite. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 2417–2424.
- Qian, F. Research on Key Technologies of Interferometric Calibration for Microwave Interferometric Surveying and Mapping Satellites. PhD Thesis, Information Engineering University, 2020.
- Li Shizhong; Ye Yu; Fan Weikang; Cong Lin; Gao Jingkun; Shao Long A Brief Analysis of the Positioning Accuracy for the TH-2 Satellite System. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 2481–2492.
- Lou Liangsheng; Liu Zhiming; Zhang Hao; Qian Fangming; Zhang Xiaowei Key Technologies of TH-2 Satellite System. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 2403–2416.
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nico, G.; Tome, R.; Catalao, J.; Miranda, P.M.A. On the Use of the WRF Model to Mitigate Tropospheric Phase Delay Effects in SAR Interferograms. Ieee Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4970–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.M.; Sanz, J.; Orus, R.; Garcia-Rigo, A.; Feltens, J.; Komjathy, A.; Schaer, S.C.; Krankowski, A. The IGS VTEC Maps: A Reliable Source of Ionospheric Information since 1998. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegler, G.; Hennig, S.D.; Weber, M. WORLDDEM – A NOVEL GLOBAL FOUNDATION LAYER. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-3-W2, 183–187. [CrossRef]
- Schubert, A.; Jehle, M.; Small, D.; Meier, E. Mitigation of Atmospheric Perturbations and Solid Earth Movements in a TerraSAR-X Time-Series.
- Balss, U.; Gisinger, C.; Cong, X.Y.; Brcic, R.; Steigenberger, P.; Eineder, M.; Pail, R.; Hugentobler, U. High Resolution Geodetic Earth Observation with TerraSAR-X: Correction Schemes and Validation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium - IGARSS; IEEE: Melbourne, Australia, July 2013; pp. 4499–4502.
- Dheenathayalan, P.; Small, D.; Schubert, A.; Hanssen, R.F. High-Precision Positioning of Radar Scatterers. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 403–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milbert, D. Solid Earth Tide, FORTRAN Computer Program 2018.
- Gisinger, C.; Balss, U.; Pail, R.; Zhu, X.X.; Montazeri, S.; Gernhardt, S.; Eineder, M. Precise Three-Dimensional Stereo Localization of Corner Reflectors and Persistent Scatterers With TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1782–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Three kinds of SAR geolocation errors in range. (1) : related to the satellite orbit error. is the correct position, while is the incorrect one. . (2) : associated with the atmospheric error. The signal's velocity in the atmosphere is smaller than in a vacuum . . (3) : related to the elevation error . .
Figure 1.
Three kinds of SAR geolocation errors in range. (1) : related to the satellite orbit error. is the correct position, while is the incorrect one. . (2) : associated with the atmospheric error. The signal's velocity in the atmosphere is smaller than in a vacuum . . (3) : related to the elevation error . .
Figure 2.
The signal propagation model that the RT method is based on. The propagation path in the troposphere is divided into multiple segments.
Figure 2.
The signal propagation model that the RT method is based on. The propagation path in the troposphere is divided into multiple segments.
Figure 3.
The geolocation procedures.
Figure 3.
The geolocation procedures.
Figure 4.
The geometry for solving the imaging time t (a) the single satellite model. (b) the Tianhui-2 secondary satellite model.
Figure 4.
The geometry for solving the imaging time t (a) the single satellite model. (b) the Tianhui-2 secondary satellite model.
Figure 5.
The relationship between the elevation-related geolocation error in range and on the ground. The range error is , while on the ground is .
Figure 5.
The relationship between the elevation-related geolocation error in range and on the ground. The range error is , while on the ground is .
Figure 6.
A Google-Earth optical image displaying the measurement points.
Figure 6.
A Google-Earth optical image displaying the measurement points.
Figure 7.
The geolocation results for two representative measurement points. (a) Measurement points depicted on the Google Earth image. (b) Results of the TerraSAR-X image without the atmospheric correction. The red box indicates the measurement point, and the arrow denotes the range direction. (c) Results of the TerraSAR-X image with the atmospheric correction.
Figure 7.
The geolocation results for two representative measurement points. (a) Measurement points depicted on the Google Earth image. (b) Results of the TerraSAR-X image without the atmospheric correction. The red box indicates the measurement point, and the arrow denotes the range direction. (c) Results of the TerraSAR-X image with the atmospheric correction.
Figure 8.
Offsets between image 20190117 and other images in (a) azimuth (b) range.
Figure 8.
Offsets between image 20190117 and other images in (a) azimuth (b) range.
Figure 9.
The geolocation results of the Tianhui-2 images corresponding to
Figure 7a with the atmospheric correction (a) Reference image. (b) Reference image with the overall shift. (c) Secondary image. (d) Secondary image with the overall shift.
Figure 9.
The geolocation results of the Tianhui-2 images corresponding to
Figure 7a with the atmospheric correction (a) Reference image. (b) Reference image with the overall shift. (c) Secondary image. (d) Secondary image with the overall shift.
Figure 10.
Comparison between the zenith delay calculated using the ERA5 and the ZPD data. (a) the difference changing with day of year. (b) statistical result of the original data.
Figure 10.
Comparison between the zenith delay calculated using the ERA5 and the ZPD data. (a) the difference changing with day of year. (b) statistical result of the original data.
Figure 11.
(a) The DEM of the study area. (b) The tropospheric delay in 20190117 derived using the RT method. (c) The difference between the ZDM result and the RT result. (d) The relationship between the radio refractivity and the elevation in the study area. when the elevation is larger than 500 meters.
Figure 11.
(a) The DEM of the study area. (b) The tropospheric delay in 20190117 derived using the RT method. (c) The difference between the ZDM result and the RT result. (d) The relationship between the radio refractivity and the elevation in the study area. when the elevation is larger than 500 meters.
Figure 12.
(a) The tropospheric delay calculated using the GACOS-based ZDM method. (b) The GACOS-based ZDM result subtracts the ERA5-based ZDM result.
Figure 12.
(a) The tropospheric delay calculated using the GACOS-based ZDM method. (b) The GACOS-based ZDM result subtracts the ERA5-based ZDM result.
Figure 13.
(a) The relationship between the elevation and the tropospheric delay. (b) The KDE curve of the tropospheric delay residual estimated using the regression equation.
Figure 13.
(a) The relationship between the elevation and the tropospheric delay. (b) The KDE curve of the tropospheric delay residual estimated using the regression equation.
Figure 14.
(a) The variation of the VTEC at local time 12 PM and 6 PM in the study area during 2019. (b) The average VTEC at the local time 6 PM in the study area in 2019. The red dot indicates the location of the study area.
Figure 14.
(a) The variation of the VTEC at local time 12 PM and 6 PM in the study area during 2019. (b) The average VTEC at the local time 6 PM in the study area in 2019. The red dot indicates the location of the study area.
Figure 15.
(a) The KDE curve of the geolocation error based on the WorldDEM and the SRTM. (b) Cumulative percentage curve of the geolocation error when based on the two DEMs.
Figure 15.
(a) The KDE curve of the geolocation error based on the WorldDEM and the SRTM. (b) Cumulative percentage curve of the geolocation error when based on the two DEMs.
Figure 16.
(a) KDE curve of the geolocation error based on the WorldDEM. Measurement points are divided into four groups based on the slope, using the threshold values at 0, 25%, 50%, and 75%. (b) KDE curve of based on the SRTM.
Figure 16.
(a) KDE curve of the geolocation error based on the WorldDEM. Measurement points are divided into four groups based on the slope, using the threshold values at 0, 25%, 50%, and 75%. (b) KDE curve of based on the SRTM.
Figure 17.
Registration procedures using ISCE. The DEM is projected to the radar center coordinate system as the z data and is used to generate a simulated amplitude image. The orbit can be corrected using the rgshift calculated by registering the SAR image and the simulated image.
Figure 17.
Registration procedures using ISCE. The DEM is projected to the radar center coordinate system as the z data and is used to generate a simulated amplitude image. The orbit can be corrected using the rgshift calculated by registering the SAR image and the simulated image.
Figure 18.
The registration SNR. (a) The TerraSAR-X image. (b) The Tianhui-2 reference image.
Figure 18.
The registration SNR. (a) The TerraSAR-X image. (b) The Tianhui-2 reference image.
Table 1.
SAR Geolocation errors in range.
Table 1.
SAR Geolocation errors in range.
| Geolocation Errors |
Typical Value |
Factors |
| Tropospheric delay |
2 m~4 m |
Atmospheric state, zenith angle |
| Ionospheric delay |
0.1 m~10 m |
Electronic density, signal frequency |
| Elevation-related error |
0.01 m~10 m |
Elevation accuracy |
Table 2.
Parameters associated with the ionospheric delay of the three bands.
Table 2.
Parameters associated with the ionospheric delay of the three bands.
| Satellite |
Band |
Frequency |
Ionospheric delay corresponding to 25 TECU |
VTEC leads to 1 m of the delay |
| TerraSAR-X |
X |
9.65 GHz |
0.19 m |
134.6 TECU |
| Sentinel-1 |
C |
5.41 GHz |
0.59 m |
42.3 TECU |
| ALOS-2 |
L |
1.26 GHz |
10.89 m |
2.3 TECU |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).