Submitted:
01 October 2024
Posted:
01 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
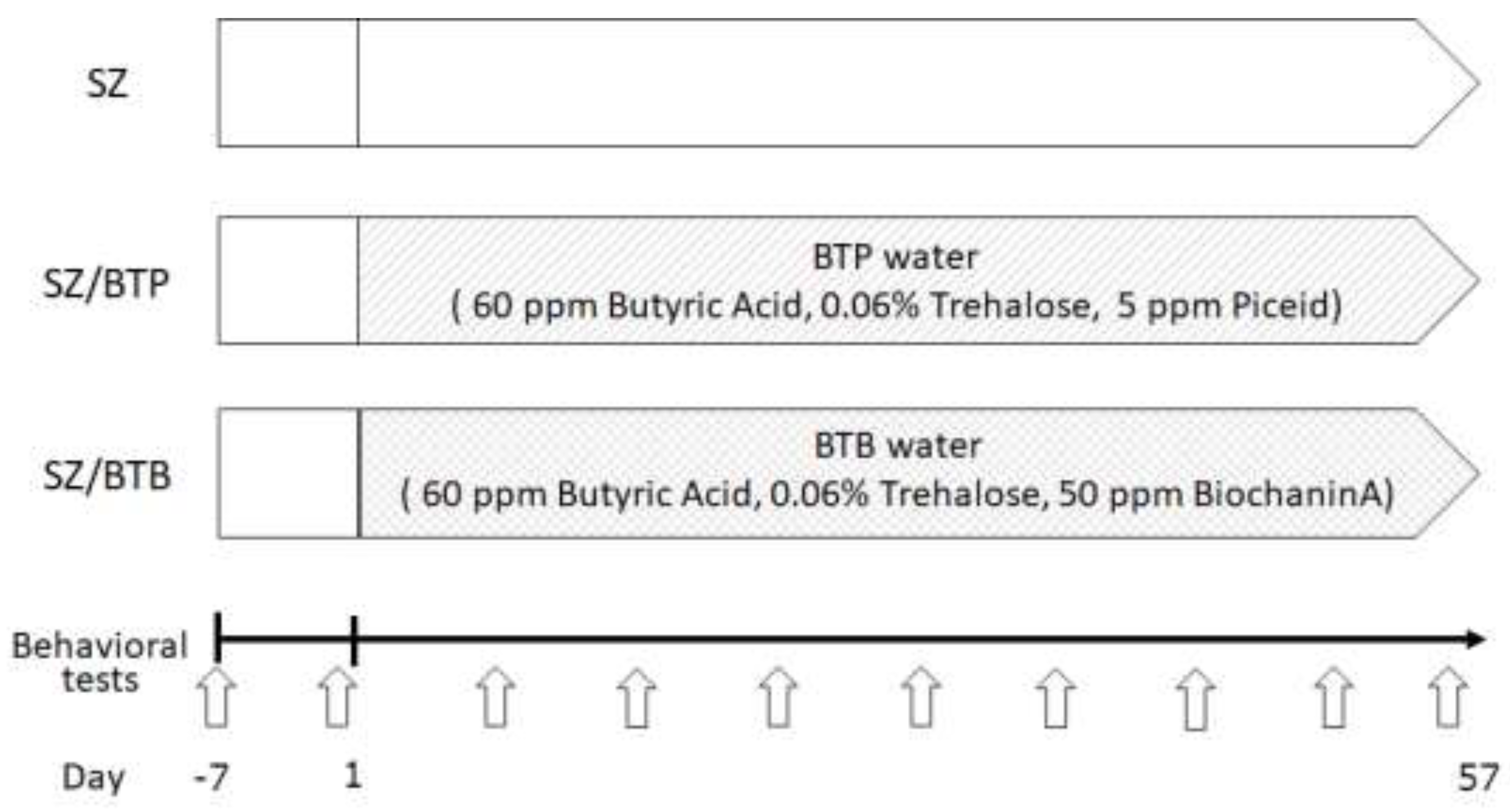
2.1. Mice
2.2. Materials
2.3. Behavioral Tests
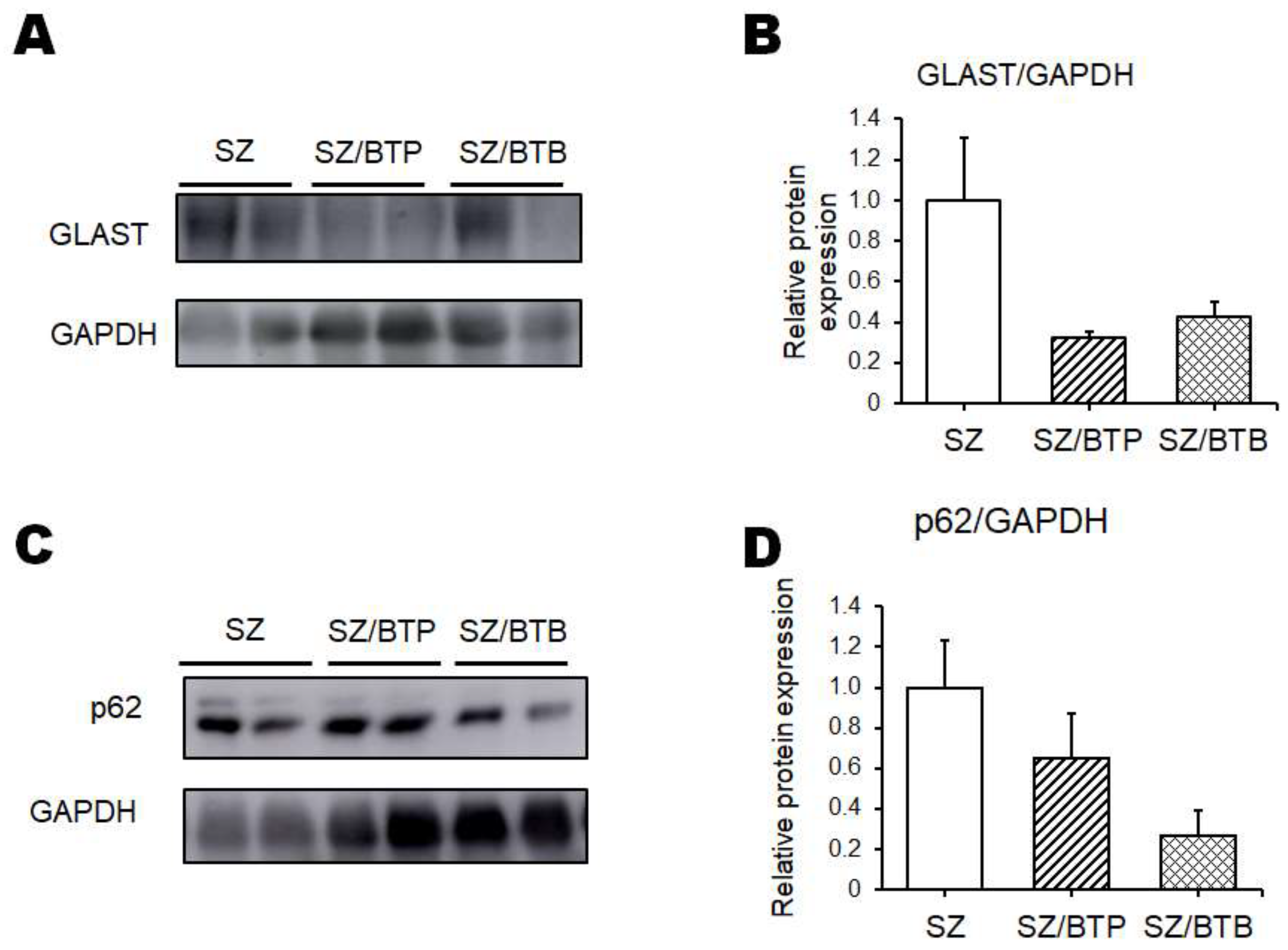
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Statistical Analyses
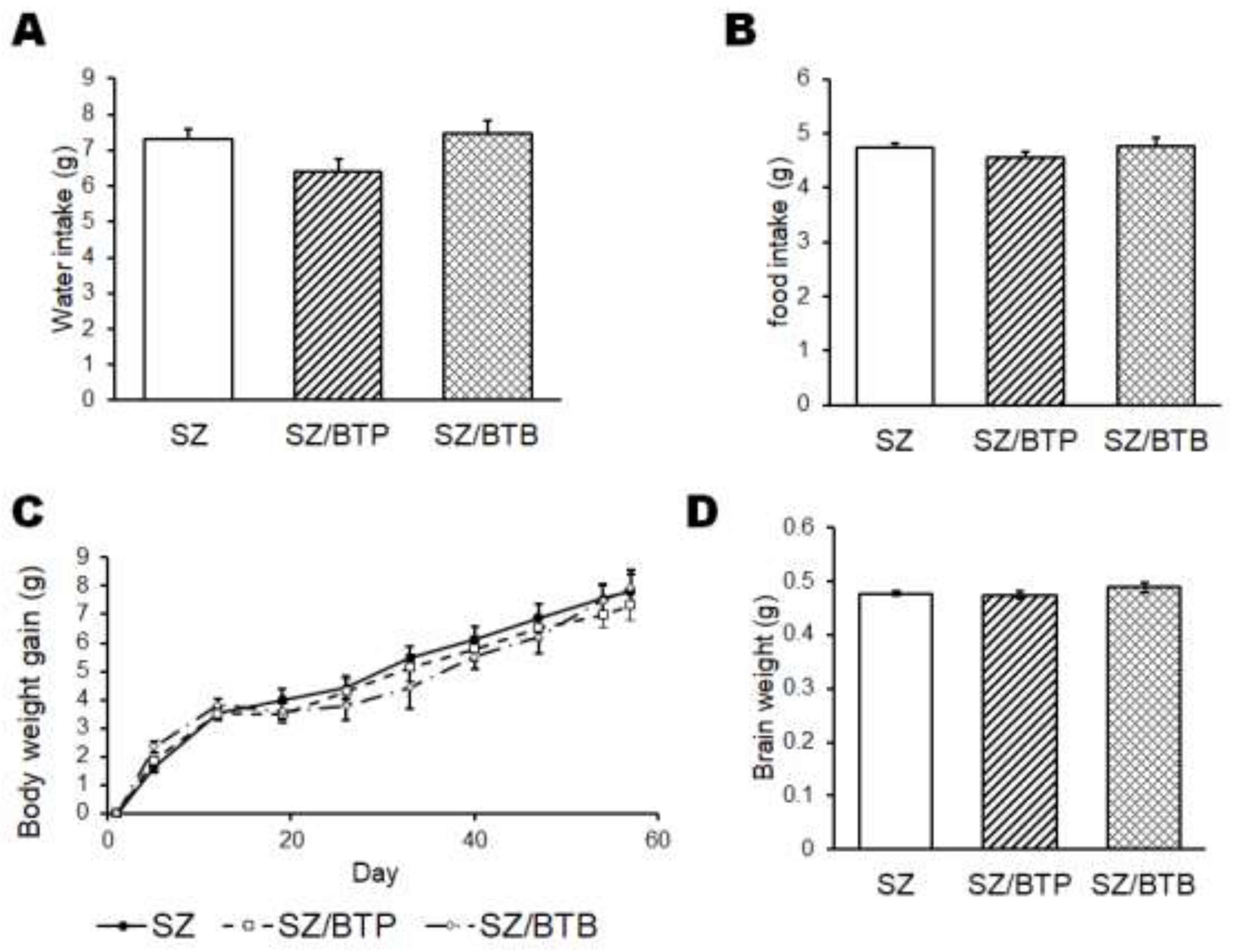
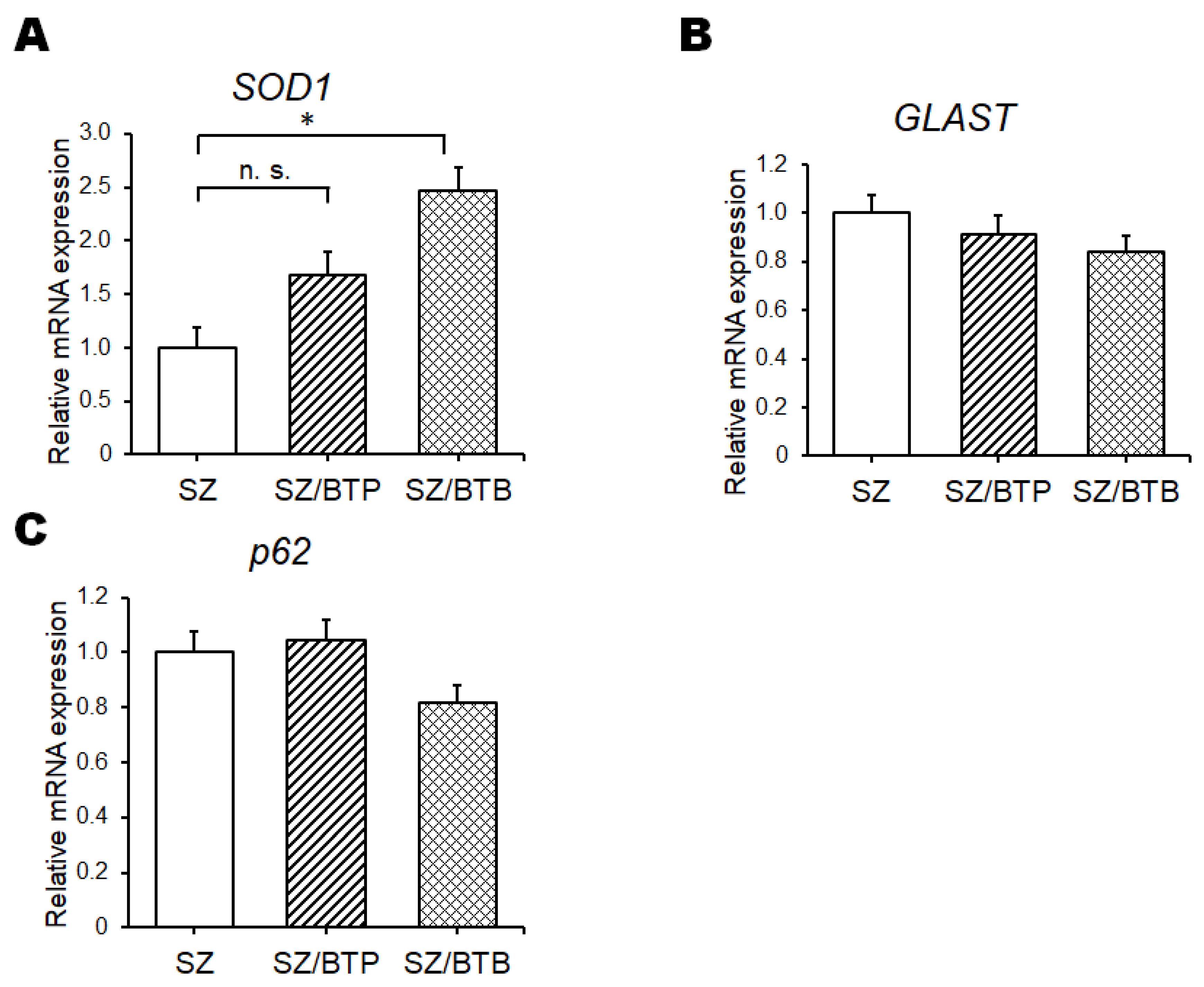
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Sample Availability
Competing interests statement:
Abbreviations
| CGN | carrageenan |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| DEHP | 2-ethylhexyl phthalate |
| DSS | sodium dextran sulfate |
| FMT | fecal microbiota transplantation |
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GLAST | glutamate aspartate transporter |
| KO | knockout |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| mRNA | messenger RNA |
| NAC | N-acetylcysteine |
| NMDA | N-methyl-d-aspartate |
| PBI | psychological behavior index |
| poly I:C | polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidilic acid |
| QOL | quality of life |
References
- Singh, M.; Agarwal, V.; Jindal, D.; Pancham, P.; Agarwal, S.; Mani, S.; Tiwari, RK.; Das, K.; Alghamdi, BS.; Abujamel, TS.; et al. Recent Updates on Corticosteroid-Induced Neuropsychiatric Disorders and Theranostic Advancements through Gene Editing Tools. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023, 13, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khokhar, JY.; Dwiel, LL.; Henricks, AM.; Doucette, WT.; Green, AI. The link between schizophrenia and substance use disorder: A unifying hypothesis. Schizophr Res. 2018, 194, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, MJ.; Sawa, A.; Mortensen, PB. Schizophrenia. Lancet. 2016, 388, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchioni, MM.; Murray, RM. Schizophrenia. BMJ. 2007, 335, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, KM.; Drake, R.; Goldstein, JM. Sex differences in schizophrenia. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2010, 22, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, TA. Fifty years chlorpromazine: a historical perspective. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2007, 3, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adler, CM.; Goldberg, TE.; Malhotra, AK.; Pickar, D.; Breier, A. Effects of ketamine on thought disorder, working memory, and semantic memory in healthy volunteers. Biol Psychiatry. 1998, 43, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weickert, CS.; Fung, SJ.; Catts, VS.; Schofield, PR.; Allen, KM.; Moore, LT.; Newell, KA.; Pellen, D.; Huang, XF.; Catts, SV.; et al. Molecular evidence of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor hypofunction in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2013, 18, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del, Arco, A. ; Segovia, G.; Mora, F. Blockade of NMDA receptors in the prefrontal cortex increases dopamine and acetylcholine release in the nucleus accumbens and motor activity. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008, 201, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, KL.; Grant, SE.; Funk, LH.; Schumann, CM.; Bauman, MD. Impact of Maternal Immune Activation on Nonhuman Primate Prefrontal Cortex Development: Insights for Schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2022, 92, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, CM.; Dincer, A.; Straubhaar, J.; Galler, JR.; Houston, IB.; Akbarian, S. Maternal immune activation alters behavior in adult offspring, with subtle changes in the cortical transcriptome and epigenome. Schizophr Res. 2012, 140, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Partida, JA.; Torres-Sanchez, S.; MacDowell, K.; Fernández-Ponce, MT.; Casas, L.; Mantell, C.; Soto-Montenegro, ML.; Romero-Miguel, D.; Lamanna-Rama, N.; Leza, JC.; et al. The effects of mango leaf extract during adolescence and adulthood in a rat model of schizophrenia. Front Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 886514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Miguel, D.; Casquero-Veiga, M.; MacDowell, KS.; Torres-Sanchez, S.; Garcia-Partida, JA.; Lamanna-Rama, N.; Romero-Miranda, A.; Berrocoso, E.; Leza, JC.; Desco, M.; et al. A Characterization of the Effects of Minocycline Treatment During Adolescence on Structural, Metabolic, and Oxidative Stress Parameters in a Maternal Immune Stimulation Model of Neurodevelopmental Brain Disorders. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 24, 734–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Bohár, Z.; Martos, D.; Telegdy, G.; Vécsei, L. Antidepressant-like effects of kynurenic acid in a modified forced swim test. Pharmacol Rep. 2020, 72, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadar, R.; Soto-Montenegro, ML.; Götz, T.; Wieske, F.; Sohr, R.; Desco, M.; Hamani, C.; Weiner, I.; Pascau, J.; Winter, C. Using a maternal immune stimulation model of schizophrenia to study behavioral and neurobiological alterations over the developmental course. Schizophr Res. 2015, 166, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howland, JG.; Cazakoff, BN.; Zhang, Y. Altered object-in-place recognition memory, prepulse inhibition, and locomotor activity in the offspring of rats exposed to a viral mimetic during pregnancy. Neuroscience. 2012, 201, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missig, G.; Mokler, EL.; Robbins, JO.; Alexander, AJ.; McDougle, CJ. ; Carlezon, WA, Jr. Perinatal Immune Activation Produces Persistent Sleep Alterations and Epileptiform Activity in Male Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018, 43, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröhn, C, Norgren, E. ; Eriksson, L. A systematic review of the neural correlates of multisensory integration in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res Cogn. 2021, 27, 100219. [Google Scholar]
- Otero, AM.; Antonson, AM. At the crux of maternal immune activation: Viruses, microglia, microbes, and IL-17A. Immunol Rev. 2022, 311, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, V.; Afsharian, P.; Shahhoseini, M.; Kalantar, SM.; Moini, A. A Review on Various Uses of N-Acetyl Cysteine. Cell J. 2017, 19, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Stekelenburg, JJ.; Maes, JP.; Van, Gool, AR. ; Sitskoorn, M.; Vroomen, J. Deficient multisensory integration in schizophrenia: an event-related potential study. Schizophr Res. 2013, 147, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomoda, T.; Sumitomo, A.; Shukla, R.; Hirota-Tsuyada, Y.; Miyachi, H.; Oh, H.; French, L.; Sibille, E. BDNF controls GABAAR trafficking and related cognitive processes via autophagic regulation of p. Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 47, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumitomo, A.; Yukitake, H.; Hirai, K.; Horike, K.; Ueta, K.; Chung, Y.; Warabi, E.; Yanagawa, T.; Kitaoka, S.; Furuyashiki, T.; et al. Ulk2 controls cortical excitatory-inhibitory balance via autophagic regulation of p62 and GABAA receptor trafficking in pyramidal neurons. Hum Mol Genet. 2018, 27, 3165–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumitomo, A.; Horike, K.; Hirai, K.; Butcher, N.; Boot, E.; Sakurai, T.; Nucifora, FC, Jr.; Bassett, AS.; Sawa, A.; Tomoda, T. A mouse model of 22q11.2 deletions: Molecular and behavioral signatures of Parkinson's disease and schizophrenia. Sci Adv 2018, 4, eaar6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, WEI. ; Xiang-Liang, T.; Yu, Z.; Bin, L.; Lian-Ju, S.; Chun-Lan, L.; Tao, LIN.; Da-Wei, HE.; Sheng-de, WU.; Guang-Hui, WEI. DEHP exposure destroys blood-testis barrier (BTB) integrity of immature testes through excessive ROS-mediated autophagy. Genes Dis. 2018, 5, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójtowicz, AK.; Sitarz-Głownia, AM.; Wnuk, A.; Kajta, M.; Szychowski, KA. Involvement of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (Pparγ) and matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 (Mmp-2 and -9) in the mechanism of action of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) in cultured mouse brain astrocytes and neurons. Toxicol In Vitro. 2023, 92, 105639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajarillo, E.; Rizor, A.; Lee, J.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. The role of astrocytic glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in neurological disorders: Potential targets for neurotherapeutics. Neuropharmacology. 2019, 161, 107559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.; McClellan, JM.; McCarthy, SE.; Addington, AM.; Pierce, SB.; Cooper, GM.; Nord, AS.; Kusenda, M.; Malhotra, D.; Bhandari, A.; et al. Rare structural variants disrupt multiple genes in neurodevelopmental pathways in schizophrenia. Science. 2008, 320, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, RM.; Tanaka, K.; Heilig, M.; Holmes, A. Loss of glial glutamate and aspartate transporter (excitatory amino acid transporter 1) causes locomotor hyperactivity and exaggerated responses to psychotomimetics: rescue by haloperidol and metabotropic glutamate 2/3 agonist. Biol Psychiatry. 2008, 64, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, RM.; Tanaka, K.; Saksida, LM.; Bussey, TJ.; Heilig, M.; Holmes, A. Assessment of glutamate transporter GLAST (EAAT1)-deficient mice for phenotypes relevant to the negative and executive/cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009, 34, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socała, K.; Żmudzka, E.; Lustyk, K.; Zagaja, M.; Brighenti, V.; Costa, AM.; Andres-Mach, M.; Pytka, K.; Martinelli, I.; Mandrioli, J.; et al. Therapeutic potential of stilbenes in neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders: A comprehensive review of preclinical and clinical evidence. Phytother Res. 2024, 38, 1400–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yu, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, HT.; Zhou, Y. Biochanin A alleviates cognitive impairment and hippocampal mitochondrial damage in ovariectomized APP/PS1 mice. Phytomedicine. 2022, 100, 154056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, M.; Suga, N.; Yoshikawa, S.; Matsuda, S. Caveolae with GLP-1 and NMDA Receptors as Crossfire Points for the Innovative Treatment of Cognitive Dysfunction Associated with Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules. 2024, 29, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakoty, V.; K, C, S. ; Dubey, SK.; Yang, CH.; Taliyan, R. Neuroprotective Effects of Trehalose and Sodium Butyrate on Preformed Fibrillar Form of alpha-Synuclein-Induced Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021, 12, 2643–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Yoshikawa, S.; Taniguchi, K.; Suga, N.; Matsuda, S. A Behavioral Test Score Could Be Linked to the Protein Expression Value of p62 and GLAST in the Brain of Mice with Neuropsychiatric Disorders-Related Behaviors. Preprints. 2023, 2023071075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z, Tao, X. ; Wang, D.; Pu, J.; Liu, Y.; Gui, S.; Zhong, X.; Yang, D.; Zhou, H.; Tao, W.; et al. Alterations of the gut microbiota in patients with schizophrenia. Front Psychiatry. 2024, 15, 1366311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, A.; Ikeda, Y.; Yoshikawa, S.; Taniguchi, K.; Sawamura, H.; Morikawa, S.; Nakashima, M.; Asai, T.; Matsuda, S. The Tryptophan and Kynurenine Pathway Involved in the Development of Immune-Related Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, S.; Taniguchi, K.; Sawamura, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Tsuji, A.; Matsuda, S. A New Concept of Associations between Gut Microbiota, Immunity and Central Nervous System for the Innovative Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Metabolites. 2022, 12, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, T.; Yoshikawa, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Taniguchi, K.; Sawamura, H.; Tsuji, A.; Matsuda, S. Encouraging Tactics with Genetically Modified Probiotics to Improve Immunity for the Prevention of Immune-Related Diseases including Cardio-Metabolic Disorders. Biomolecules. 2022, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, S.; Taniguchi, K.; Sawamura, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Tsuji, A.; Matsuda, S. Encouraging probiotics for the prevention and treatment of immune-related adverse events in novel immunotherapies against malignant glioma. Explor. Target. Antitumor Ther. 2022, 3, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Tian, X.; Hei, G.; Kang, D.; Gao, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhao, J.; et al. Metformin improves cognitive impairment in patients with schizophrenia: associated with enhanced functional connectivity of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Transl Psychiatry. 2023, 13, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxenkrug, G.; Forester, B. Anthranilic Acid, a GPR109A Agonist, and Schizophrenia. Int J Tryptophan Res. 2024, 17, 11786469241239125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjan, A.; Kaushik, I.; Srivastava, SK. Pimozide Suppresses the Growth of Brain Tumors by Targeting STAT3-Mediated Autophagy. Cells.; 2020, 9, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N.; Yoshimori, T.; Ohsumi, Y. The role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011, 27, 107–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumitomo, A.; Tomoda, T. Autophagy in neuronal physiology and disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2021, 60, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rk3 is a novel PI3K/AKT-targeting therapeutics agent that regulates autophagy and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pharm Anal. 2023, 13, 463–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, WS.; Lee, SM.; Hwang, D.; Park, HJ.; Kim, JW. Association between Unc-51-like autophagy activating kinase 2 gene polymorphisms and schizophrenia in the Korean population. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022, 101, e28745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stertz, L.; Di, Re, J. ; Pei, G.; Fries, GR.; Mendez, E.; Li, S.; Smith-Callahan, L.; Raventos, H.; Tipo, J.; Cherukuru, R.; et al. Convergent genomic and pharmacological evidence of PI3K/GSK3 signaling alterations in neurons from schizophrenia patients. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021, 46, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emamian, ES.; Hall, D.; Birnbaum, MJ.; Karayiorgou, M.; Gogos, JA. Convergent evidence for impaired AKT1-GSK3beta signaling in schizophrenia. Nat Genet. 2004, 36, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamian, ES. AKT/GSK3 signaling pathway and schizophrenia. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karege, F.; Perroud, N.; Burkhardt, S.; Schwald, M.; Ballmann, E.; La, Harpe, R. ; Malafosse, A. Alteration in kinase activity but not in protein levels of protein kinase B and glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in ventral prefrontal cortex of depressed suicide victims. Biol Psychiatry. 2007, 61, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippai, M.; Lőw, P. The role of the selective adaptor p62 and ubiquitin-like proteins in autophagy. Biomed Res Int. 2014, 2014, 832704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lech, MA.; Leśkiewicz, M.; Kamińska, K.; Rogóż, Z.; Lorenc-Koci, E. Glutathione Deficiency during Early Postnatal Development Causes Schizophrenia-Like Symptoms and a Reduction in BDNF Levels in the Cortex and Hippocampus of Adult Sprague-Dawley Rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Chen, L.; Zeng, Y.; Xiao, G.; Tian, W.; Wu, Q.; Tang, J.; He, S.; Tanzhu, G.; Zhou, R. The scheme, and regulative mechanism of pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and necroptosis in radiation injury. Int J Biol Sci. 2024, 20, 1871–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevelkin, AV.; Terrillion, CE.; Hasegawa, Y.; Mychko, OA.; Jouroukhin, Y.; Sawa, A.; Kamiya, A.; Pletnikov, MV. Astrocyte DISC1 contributes to cognitive function in a brain region-dependent manner. Hum Mol Genet. 2020, 29, 2936–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, RM.; Adermark, L.; Molander, A.; Perreau-Lenz, S.; Singley, E.; Solomon, M.; Holmes, A.; Tanaka, K.; Lovinger, DM.; Spanagel, R.; et al. Reduced alcohol intake and reward associated with impaired endocannabinoid signaling in mice with a deletion of the glutamate transporter GLAST. Neuropharmacology. 2012, 63, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, M.; Hida, H.; Mori, K.; Yoshimi, A.; Kitagaki, S.; Yamada, K.; Hiraoka, Y.; Aida, T.; Tanaka, K.; Ozaki, N.; et al. Functional roles of the glial glutamate transporter (GLAST) in emotional and cognitive abnormalities of mice after repeated phencyclidine administration. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, DA.; González-Burgos, G. Neuroplasticity of neocortical circuits in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008, 33, 141–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




