Submitted:
30 September 2024
Posted:
02 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
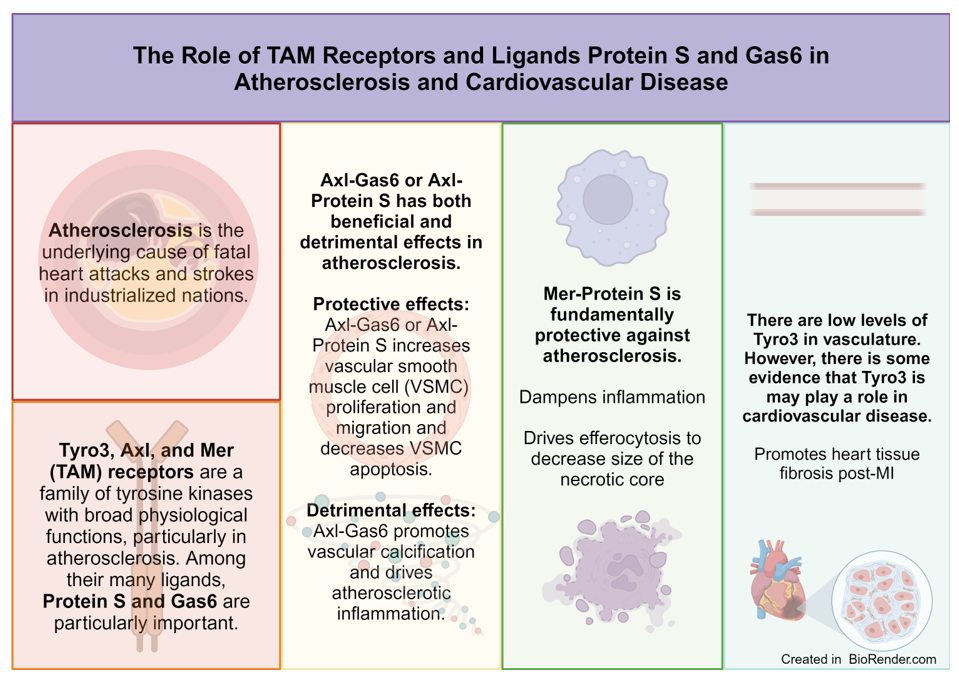
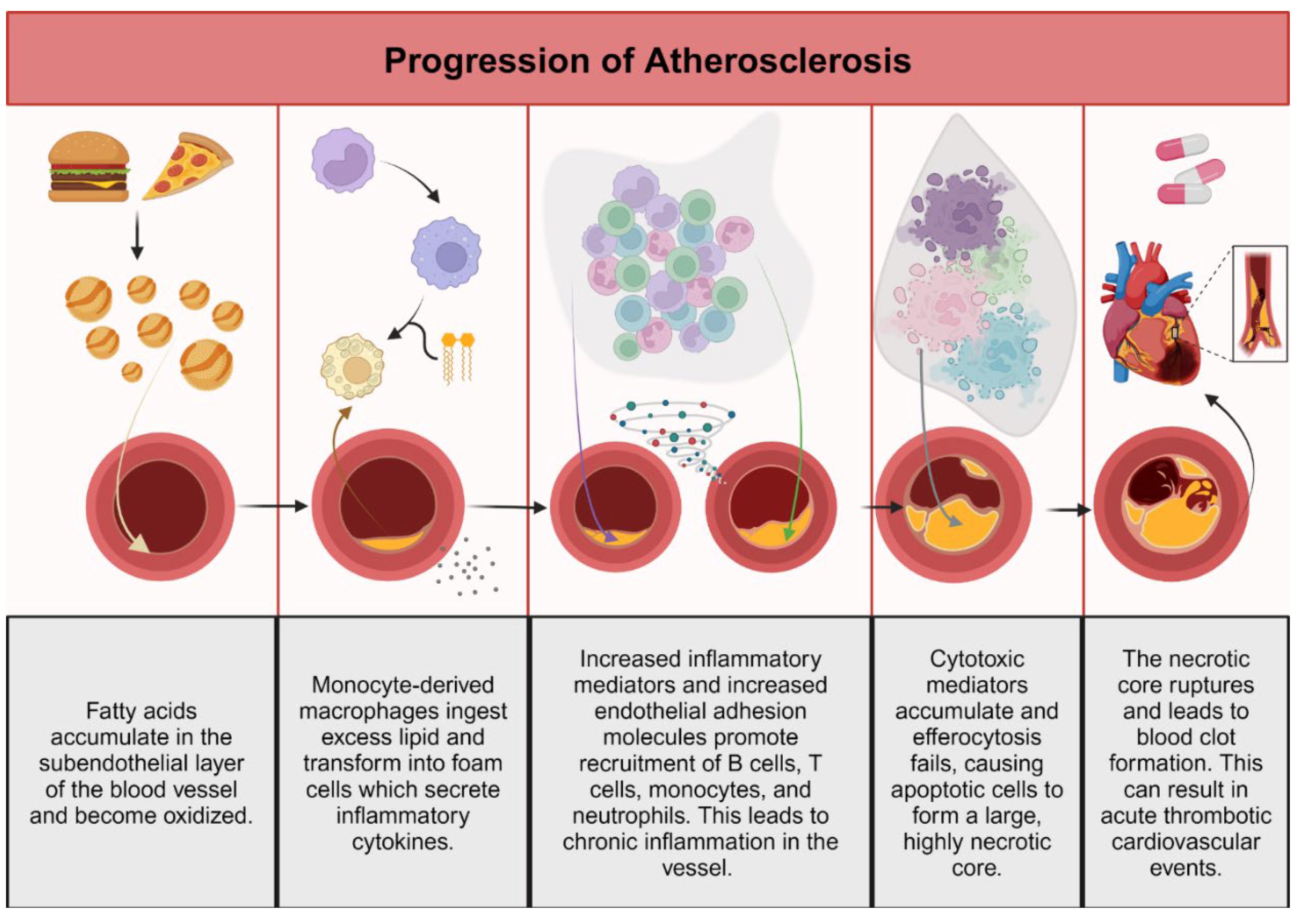
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Discussion
1. TAM Receptors
a. Structure
b. Function
c. Regulation
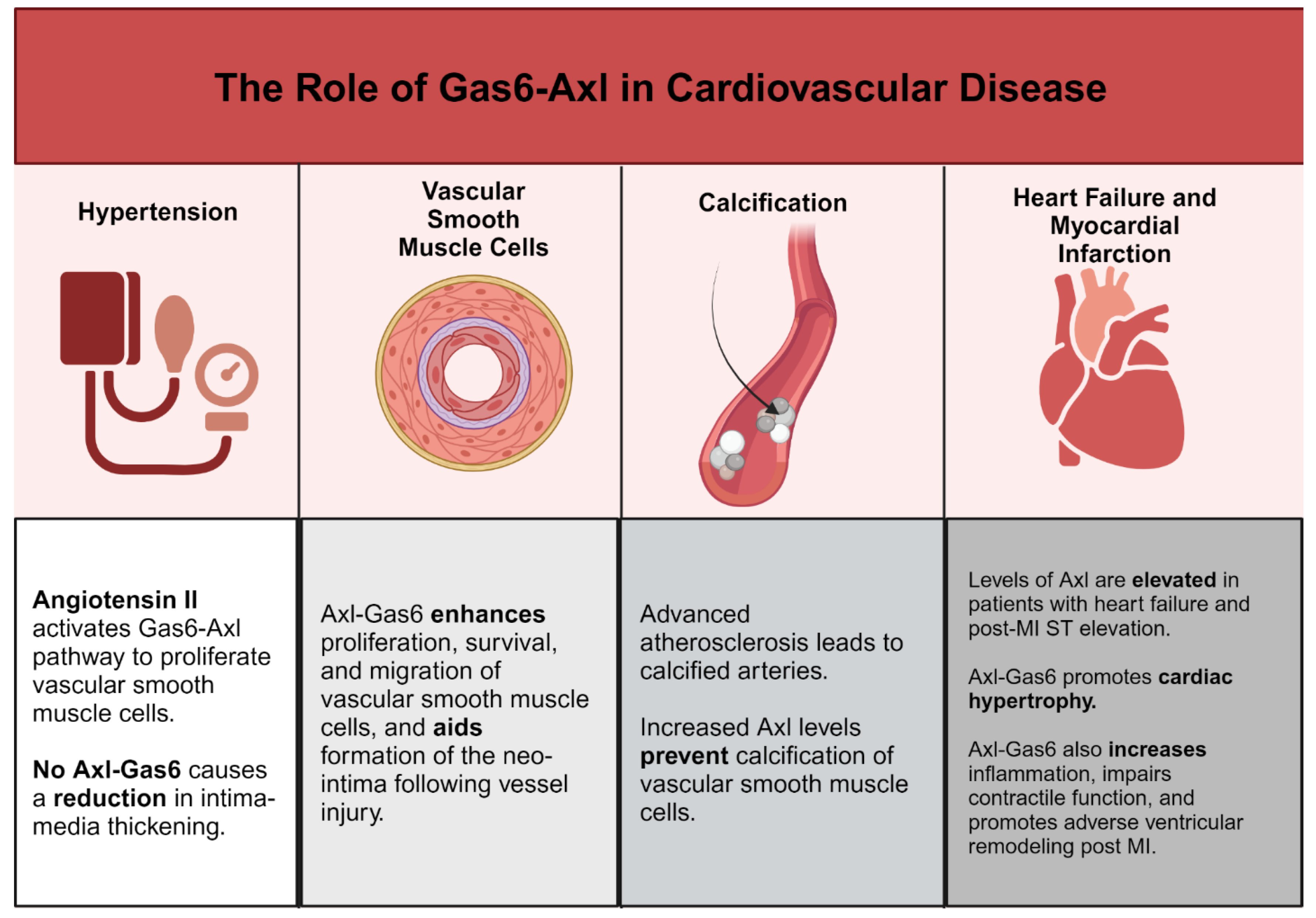
1. Gas6-Axl in Cardiovascular Disease
a. Gas6-Axl and Regulation of Cardiovascular Remodeling and Vascular Calcification
b. Gas6-Axl and Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease
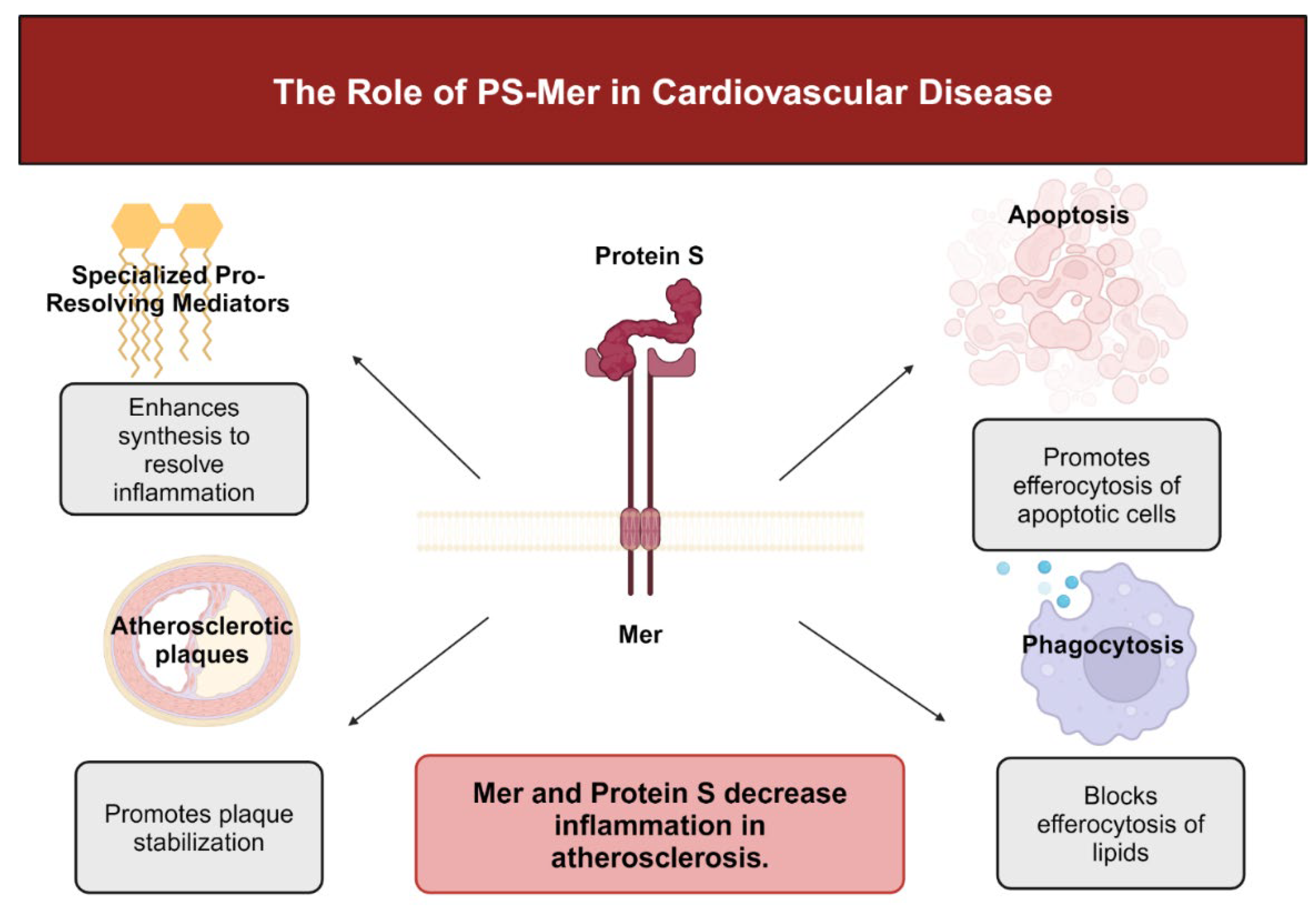
2. PS and Mer in Cardiovascular Disease
a. Mer-Mediated Resolution of Inflammation in Atherosclerosis
b. Mer-Mediated Efferocytosis in Myocardial Infarction
3. Tyro3 in Cardiovascular Disease
3. Conclusions
Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katan, M.; Luft, A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38(2), 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Watanabe, T. Atherosclerosis: Known and unknown. Pathol. Int. 2022, 72(3), 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature 2021, 592(7855), 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugsley, M.K.; Tabrizchi, R. The vascular system. An overview of structure and function. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44(2), 333–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pries, A.R.; Secomb, T.W. Control of blood vessel structure: Insights from theoretical models. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 288(3), H1010–H1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, W.C. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ. Res. 2007, 100(2), 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Shapiro, M.D. Apolipoproteins in vascular biology and atherosclerotic disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19(3), 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, E. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, (8 Suppl), C7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattoor, A.J.; Pothineni, N.V.K.; Palagiri, D.; Mehta, J.L. Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19(11), 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkley, H.; Counts, D.A.; VonCanon, E.; Lacy, M. T Cells in Atherosclerosis: Key Players in the Pathogenesis of Vascular Disease. Cells 2023, 12(17), 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, C.L.; Khan, S.; Zhang, X.; Yeh, Y.S.; Liu, Z.; Razani, B. Lipid-laden foam cells in the pathology of atherosclerosis: Shedding light on new therapeutic targets. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2023, 27(12), 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnatsch, A.; Ioannou, M.; Wang, Q.; Papayannopoulos, V. Inflammation. Neutrophil extracellular traps license macrophages for cytokine production in atherosclerosis. Science 2015, 349(6245), 316–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sage, A.P.; Mallat, Z. Multiple potential roles for B cells in atherosclerosis. Ann. Med. 2014, 46(5), 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badimon, L.; Vilahur, G. Thrombosis formation on atherosclerotic lesions and plaque rupture. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276(6), 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergallo, R.; Crea, F. Atherosclerotic Plaque Healing. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384(3), 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puylaert, P.; Zurek, M.; Rayner, K.J.; De Meyer, G.R.Y.; Martinet, W. Regulated Necrosis in Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2022, 42(11), 1283–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterpetti, A.V. Inflammatory Cytokines and Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression. Therapeutic Implications. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2020, 22(12), 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boren, J.; Chapman, M.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Packard, C.J.; Bentzon, J.F.; Binder, C.J.; Daemen, M.J.; Demer, L.L.; Hegele, R.A.; Nicholls, S.J.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Watts, G.F.; Bruckert, E.; Fazio, S.; Ference, B.A.; Graham, I.; Horton, J.D.; Landmesser, U.; Laufs, U.; Masana, L.; Pasterkamp, G.; Raal, F.J.; Ray, K.K.; Schunkert, H.; Taskinen, M.R.; van de Sluis, B.; Wiklund, O.; Tokgozoglu, L.; Catapano, A.L.; Ginsberg, H.N. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: Pathophysiological, genetic, and therapeutic insights: A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41(24), 2313–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, X.F.; Ng, C.Y.; Jaarin, K. Animal Models in Cardiovascular Research: Hypertension and Atherosclerosis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 528757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtubise, J.; McLellan, K.; Durr, K.; Onasanya, O.; Nwabuko, D.; Ndisang, J.F. The Different Facets of Dyslipidemia and Hypertension in Atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2016, 18(12), 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutusaus, A.; Mari, M.; Ortiz-Perez, J.T.; Nicolaes, G.A.F.; Morales, A.; Garcia de Frutos, P. Role of Vitamin K-Dependent Factors Protein S and GAS6 and TAM Receptors in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19-Associated Immunothrombosis. Cells 2020, 9(10), 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.S.; Kasikara, C. TAM receptors and their ligand-mediated activation: Role in atherosclerosis. Tam. Receptors in Health and Disease 2020, 357, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- McShane, L.; Tabas, I.; Lemke, G.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Maffia, P. TAM receptors in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115(8), 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, G. How macrophages deal with death. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19(9), 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, H.M.; Camenisch, T.D.; Lemke, G.; Earp, H.S.; Matsushima, G.K. Macrophages and dendritic cells use different Axl/Mertk/Tyro3 receptors in clearance of apoptotic cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 178(9), 5635–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Ji, Q. Tumor-Associated Macrophages Regulate PD-1/PD-L1 Immunosuppression. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 874589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryckere, D.; Huelse, J.M.; Earp, H.S.; Graham, D.K. TAM family kinases as therapeutic targets at the interface of cancer and immunity. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology 2023, 20(11), 755–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, L.; Négrier, C.; Boukerche, H. Protein S: A multifunctional anticoagulant vitamin K-dependent protein at the crossroads of coagulation, inflammation, angiogenesis, and cancer. Critical Reviews in Oncology Hematology 2013, 88(3), 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsey, A.; Pilli, V.S.; Fried, H.; Majumder, R. Protein S: A Multifunctional Anticoagulant. Biomed. Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 2(5). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Meer, J.H.; van der Poll, T.; van’t Veer, C. TAM receptors, Gas6, and protein S: Roles in inflammation and hemostasis. Blood 2014, 123(16), 2460–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, A.; Sasikumar, P.; Folgado, P.B.; Jones, D.; Xu, Y.X.; Ahnström, J.; Salles-Crawley, I.I.; Crawley, J.T.B. TFPIα anticoagulant function is highly dependent on protein S in vivo. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10(5). [Google Scholar]
- Myers, K.V.; Amend, S.R.; Pienta, K.J. Targeting Tyro3, Axl and MerTK (TAM receptors): Implications for macrophages in the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18(1), 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Khoshbakht, T.; Taheri, M.; Mokhtari, M. A review on the role of GAS6 and GAS6-AS1 in the carcinogenesis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 226, 153596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Lin, M.; Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, J.; Hong, G.; Zhao, G.; Lu, Z. Gas6 Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Tight Junction Injury and Vascular Endothelial Hyperpermeability via the Axl/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dihingia, A.; Kalita, J.; Manna, P. Implication of a novel Gla-containing protein, Gas6 in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance, impaired glucose homeostasis, and inflammation: A review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 128, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Pu, D.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, N.; Peng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Li, L. Gas6/AXL pathway: Immunological landscape and therapeutic potential. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1121130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.W.; Xie, Y.P.; Lin, Q.Y.; Yang, X.L.; An, X.B.; Xia, Y.L.; Du, J.; Wang, F.; Li, H.H. Immunoproteasome subunit β5i regulates diet-induced atherosclerosis through altering MERTK-mediated efferocytosis in knockout mice. J. Pathol. 2020, 250(3), 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; von Hundelshausen, P. CANTOS Trial Validates the Inflammatory Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis: Setting the Stage for a New Chapter in Therapeutic Targeting. Circ. Res. 2017, 121(10), 1119–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstyn-Cohen, T.; Fresia, R. TAM receptors in phagocytosis: Beyond the mere internalization of particles. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 319(1), 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, K. Post-translational modifications of the ligands: Requirement for TAM receptor activation. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 357, 35–55. [Google Scholar]
- Burstyn-Cohen, T.; Maimon, A. TAM receptors, Phosphatidylserine, inflammation, and Cancer. Cell Commun. Signal 2019, 17(1), 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Chen, Q.; Yan, K.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, Y.; Han, D. Breakdown of immune homeostasis in the testis of mice lacking Tyro3, Axl and Mer receptor tyrosine kinases. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2013, 91(6), 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yefimova, M.G.; Ravel, C.; Rolland, A.D.; Bourmeyster, N.; Jegou, B. MERTK-Mediated LC3-Associated Phagocytosis (LAP) of Apoptotic Substrates in Blood-Separated Tissues: Retina, Testis, Ovarian Follicles. Cells 2021, 10(6), 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, T.; Chen, Q.; Han, D. The roles of TAM receptor tyrosine kinases in the mammalian testis and immunoprivileged sites. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2016; 21, 2, 316–327. [Google Scholar]
- Rochette, L.; Dogon, G.; Rigal, E.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Interplay between efferocytosis and atherosclerosis. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 116(10), 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranta, A.; Kumar, S. Recent advancements in role of TAM receptors on efferocytosis, viral infection, autoimmunity, and tissue repair. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 357, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagata, S. Apoptosis and Clearance of Apoptotic Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 489–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malawista, A.; Wang, X.; Trentalange, M.; Allore, H.G.; Montgomery, R.R. Coordinated expression of tyro3, axl, and mer receptors in macrophage ontogeny. Macrophage (Houst) 2016, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Peeters, M.J.W.; Rahbech, A.; Thor Straten, P. TAM-ing T cells in the tumor microenvironment: Implications for TAM receptor targeting. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69(2), 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothlin, C.V.; Ghosh, S.; Zuniga, E.I.; Oldstone, M.B.; Lemke, G. TAM receptors are pleiotropic inhibitors of the innate immune response. Cell 2007, 131(6), 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, M.J.W.; Dulkeviciute, D.; Draghi, A.; Ritter, C.; Rahbech, A.; Skadborg, S.K.; Seremet, T.; Simoes, A.M.C.; Martinenaite, E.; Halldórsdóttir, H.R.; Andersen, M.H.; Olofsson, G.H.; Svane, I.M.; Rasmussen, L.J.; Met, Ö.; Becker, J.C.; Donia, M.; Desler, C.; Straten, P.T. MERTK Acts as a Costimulatory Receptor on Human CD8 T Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7(9), 1472–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera Silva, E.A.; Chan, P.Y.; Joannas, L.; Errasti, A.E.; Gagliani, N.; Bosurgi, L.; Jabbour, M.; Perry, A.; Smith-Chakmakova, F.; Mucida, D.; Cheroutre, H.; Burstyn-Cohen, T.; Leighton, J.A.; Lemke, G.; Ghosh, S.; Rothlin, C.V. T cell-derived protein S engages TAM receptor signaling in dendritic cells to control the magnitude of the immune response. Immunity 2013, 39(1), 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.R.; Rankin, E.B.; Giaccia, A.J. Therapeutic targeting of the functionally elusive TAM receptor family. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23(3), 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadiyar, V.; Patel, G.; Davra, V. Immunological role of TAM receptors in the cancer microenvironment. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 357, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Cheng, G.; Yao, R.; Pei, W.; Liang, R.; Liang, R.; Ye, H.; Jiang, S.; Niu, H.; Sun, X.; Su, Y. Tyro3 receptor tyrosine kinase contributes to pathogenic phenotypes of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis and disturbs immune cell balance in experimental arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 255, 109753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endisha, H.; Datta, P.; Sharma, A.; Nakamura, S.; Rossomacha, E.; Younan, C.; Ali, S.A.; Tavallaee, G.; Lively, S.; Potla, P.; Shestopaloff, K.; Rockel, J.S.; Krawetz, R.; Mahomed, N.N.; Jurisica, I.; Gandhi, R.; Kapoor, M. MicroRNA-34a-5p Promotes Joint Destruction During Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73(3), 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, A.; Qian, W. MicroRNA-7 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via TYRO3 and phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein B kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway suppression. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42(5), 2503–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Cheng, X.; Li, F.; Guan, Z.; Xu, J.; Wu, D.; Gao, Y.; Zhan, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, H.; Rao, Z.; Cheng, F. Defective efferocytosis by aged macrophages promotes STING signaling mediated inflammatory liver injury. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9(1), 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahey, K.C.; Varsanyi, C.; Wang, Z.; Aquib, A.; Gadiyar, V.; Rodrigues, A.A.; Pulica, R.; Desind, S.; Davra, V.; Calianese, D.C.; Liu, D.; Cho, J.H.; Kotenko, S.V.; De Lorenzo, M.S.; Birge, R.B. Regulation of Mertk Surface Expression via ADAM17 and gamma-Secretase Proteolytic Processing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(8), 4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Zheng, F.; Wu, N.; Zhu, G.Q.; Li, X.Z. Extracellular vesicles in vascular remodeling. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43(9), 2191–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Khalil, R.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases, Vascular Remodeling, and Vascular Disease. Adv. Pharmacol. 2018, 81, 241–330. [Google Scholar]
- Melaragno, M.G.; Wuthrich, D.A.; Poppa, V.; Gill, D.; Lindner, V.; Berk, B.C.; Corson, M.A. Increased expression of Axl tyrosine kinase after vascular injury and regulation by G protein-coupled receptor agonists in rats. Circ. Res. 1998, 83(7), 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Van Beusecum, J.P.; Xiao, L.; Patrick, D.M.; Ao, M.F.; Zhao, S.L.; Lopez, M.G.; Billings, F.T.; Cavinato, C.; Caulk, A.W.; Humphrey, J.D.; Harrison, D.G. Role of Axl in target organ inflammation and damage due to hypertensive aortic remodeling. Am. J. Physiol. -Heart Circ. Physiol. 2022, 323(5), H917–H933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Rauf, A.; Khan, H.; Abu-Izneid, T. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAAS): The ubiquitous system for homeostasis and pathologies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Xu, D.C.; Zhu, G.F.; Zhu, M.Y.; Tang, K.; Li, W.M.; Xu, Y.W. Growth Arrest-Specific 6 Exacerbates Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy. Hypertension 2016, 67(1), 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolock, E.M.; Korshunov, V.A. Pharmacological inhibition of Axl affects smooth muscle cell functions under oxidative stress. Vascul Pharmacol. 2010, 53(3-4), 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.S.; Cho, C.Y.; Hong, C.C.; Yan, M.D.; Hsieh, M.C.; Lay, J.D.; Lai, G.M.; Cheng, A.L.; Chuang, S.E. Oxidative stress enhances Axl-mediated cell migration through an Akt1/Rac1-dependent mechanism. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2013, 65, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Hung, Y.J.; Shieh, Y.S.; Chien, C.Y.; Hsu, Y.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Chiang, C.F.; Huang, C.L.; Hsieh, C.H. Cilostazol inhibits uremic toxin-induced vascular smooth muscle cell dysfunction: Role of Axl signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2017, 312(3), F398–F406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Park, M.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, W.K.; Lim, S.C.; Kang, K.W. Circulating small extracellular vesicles promote proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via AXL and MerTK activation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44(5), 984–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Ando, T.; Izumi, H.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Shintani, T.; Gutkind, J.S.; Yanamoto, S.; Miyauchi, M.; Kajiya, M. AXL activates YAP through the EGFR-LATS1/2 axis and confers resistance to EGFR-targeted drugs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2023, 42(39), 2869–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saab, S.; Chang, O.S.; Nagaoka, K.; Hung, M.C.; Yamaguchi, H. The potential role of YAP in Axl-mediated resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9(12), 2719–2729. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Niu, Y.; Pei, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Wu, M.; Zheng, J.; Yang, P.; Hao, H.; Pang, Y.; Bao, L.; Dai, Y.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, R. Gas6-Axl signal promotes indoor VOCs exposure-induced pulmonary fibrosis via pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells-fibroblasts cross-talk. J Hazard Mater 2024, 474, 134786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gutierrez, L.; Ferrara, N. Biology and therapeutic targeting of vascular endothelial growth factor A. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24(11), 816–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.B.; Peng, Y.Q.; Zhou, X.M.; Yang, B.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, L.M.; Song, F.L.; Li, J.M.; Zhou, K.; Meng, J.C.; Yuan, L.Q.; Xie, H. Taurine restores Axl/Gas6 expression in vascular smooth muscle cell calcification model. Amino Acids 2010, 39(2), 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happonen, K.E.; Tran, S.; Morgelin, M.; Prince, R.; Calzavarini, S.; Angelillo-Scherrer, A.; Dahlback, B. The Gas6-Axl Protein Interaction Mediates Endothelial Uptake of Platelet Microparticles. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291(20), 10586–10601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alciato, F.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Sola, D.; Castello, L.; Avanzi, G.C. TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1 expression is inhibited by GAS6 in monocytes/macrophages. J Leukocyte Biol 2010, 87(5), 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdzalik-Bielecka, D.; Poswiata, A.; Kozik, K.; Jastrzebski, K.; Schink, K.O.; Brewinska-Olchowik, M.; Piwocka, K.; Stenmark, H.; Miaczynska, M. The GAS6-AXL signaling pathway triggers actin remodeling that drives membrane ruffling, macropinocytosis, and cancer-cell invasion. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118(28). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei-Yuan, Z.; Yu-Wei, L.; Xiang-Nan, Z.; Song, T.; Rong, Z.; Xiao-Xiao, H.; Sheng-Shuai, S.; Kun, W.; Cheng-Yun, L. Overexpression of Axl reverses endothelial cells dysfunction in high glucose and hypoxia. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120(7), 11831–11841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, J.A. Vascular calcification: Mechanisms of vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 25(4), 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, I.K.; Jeon, J.H. Vascular Calcification-New Insights into Its Mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21(8), 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collett, G.; Wood, A.; Alexander, M.Y.; Varnum, B.C.; Boot-Handford, R.P.; Ohanian, V.; Ohanian, J.; Fridell, Y.W.; Canfield, A.E. Receptor tyrosine kinase Axl modulates the osteogenic differentiation of pericytes. Circ. Res. 2003, 92(10), 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Zheng, H.; Tao, H.; Yu, W.; Jiang, X.; Li, A.; Jin, H.; Lv, A.; Li, H. Vitamin K2 inhibits rat vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by restoring the Gas6/Axl/Akt anti-apoptotic pathway. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2017, 433(1-2), 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badi, I.; Mancinelli, L.; Polizzotto, A.; Ferri, D.; Zeni, F.; Burba, I.; Milano, G.; Brambilla, F.; Saccu, C.; Bianchi, M.E.; Pompilio, G.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Raucci, A. miR-34a Promotes Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Calcification by Downregulating SIRT1 (Sirtuin 1) and Axl (AXL Receptor Tyrosine Kinase). Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38(9), 2079–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, B.K.; Kozaki, K.; Iijima, K.; Eto, M.; Nakano, T.; Akishita, M.; Ouchi, Y. Gas6/Axl-PI3K/Akt pathway plays a central role in the effect of statins on inorganic phosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 556(1-3), 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerloff, J.; Korshunov, V.A. Immune modulation of vascular resident cells by Axl orchestrates carotid intima-media thickening. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180(5), 2134–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Shieh, Y.S.; Tsai, C.S.; Hung, Y.J.; Tsai, Y.T.; Lin, C.Y. Expression of growth arrest-specific protein 6 and Axl molecules in the left internal mammary artery of patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 67(6), 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Yang, Q.F.; Zuo, P.Y.; Xiao, C.L.; Chen, X.L.; Liu, C.Y. Elevated serum levels of soluble Axl in acute coronary syndrome. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 349(2), 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunbul, M.; Cagman, Z.; Gerin, F.; Ozgen, Z.; Durmus, E.; Seckin, D.; Ahmad, S.; Uras, F.; Agirbasli, M. Growth arrest-specific 6 and cardiometabolic risk factors in patients with psoriasis. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2015, 33(2), 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Z.; Chi, H. Lipid metabolism in dendritic cell biology. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 317(1), 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batchu, S.N.; Xia, J.; Ko, K.A.; Doyley, M.M.; Abe, J.; Morrell, C.N.; Korshunov, V.A. Axl modulates immune activation of smooth muscle cells in vein graft remodeling. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309(6), H1048–H1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beusecum, J.P.; Barbaro, N.R.; Smart, C.D.; Patrick, D.M.; Loperena, R.; Zhao, S.; de la Visitacion, N.; Ao, M.F.; Xiao, L.; Shibao, C.A.; Harrison, D.G. Growth Arrest Specific-6 and Axl Coordinate Inflammation and Hypertension. Circulation Research 2021, 129(11), 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchu, S.N.; Dugbartey, G.J.; Wadosky, K.M.; Mickelsen, D.M.; Ko, K.A.; Wood, R.W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Fowell, D.J.; Korshunov, V.A. Innate Immune Cells Are Regulated by Axl in Hypertensive Kidney. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188(8), 1794–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.N.; Wang, J.L.; Ge, L.N.; Shan, J.H.; Zhang, C.B.; Liu, J.P. Growth arrest-specific protein 6 (Gas6) as a noninvasive biomarker for early detection of diabetic nephropathy. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2017, 39(4), 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, M.; Recarte-Pelz, P.; Roig, E.; Castel, M.A.; Cardona, M.; Farrero, M.; Ortiz, J.T.; Campos, B.; Pulgarín, M.J.; Ramírez, J.; Pérez-Villa, F.; de Frutos, P.G. AXL receptor tyrosine kinase is increased in patients with heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 173(3), 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristobal, H.; Enjuanes, C.; Batlle, M.; Tajes, M.; Campos, B.; Francesch, J.; Moliner, P.; Farrero, M.; Andrea, R.; Ortiz-Perez, J.T.; Morales, A.; Sabate, M.; Comin-Colet, J.; Garcia de Frutos, P. Prognostic Value of Soluble AXL in Serum from Heart Failure Patients with Preserved and Reduced Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13(3), 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldentey, G.; Garcia De Frutos, P.; Cristobal, H.; Garabito, M.; Berruezo, A.; Bosch, X.; San Antonio, R.; Flores-Umanzor, E.; Perea, R.J.; De Caralt, T.M.; Rodriguez, J.; Ortiz-Perez, J.T. Serum levels of Growth Arrest-Specific 6 protein and soluble AXL in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2019, 8(8), 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBerge, M.; Glinton, K.; Subramanian, M.; Wilsbacher, L.D.; Rothlin, C.V.; Tabas, I.; Thorp, E.B. Macrophage AXL receptor tyrosine kinase inflames the heart after reperfused myocardial infarction. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131(6). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vago, J.P.; Valdrighi, N.; Blaney-Davidson, E.N.; Hornikx, D.; Neefjes, M.; Barba-Sarasua, M.E.; Thielen, N.G.M.; van den Bosch, M.H.J.; van der Kraan, P.M.; Koenders, M.I.; Amaral, F.A.; van de Loo, F.A.J. Gas6/Axl Axis Activation Dampens the Inflammatory Response in Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes and Synovial Explants. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2023, 16(5), 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Back, M.; Yurdagul, A., Jr.; Tabas, I.; Oorni, K.; Kovanen, P.T. Inflammation and its resolution in atherosclerosis: Mediators and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16(7), 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454(7203), 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymut, N.; Heinz, J.; Sadhu, S.; Hosseini, Z.; Riley, C.O.; Marinello, M.; Maloney, J.; MacNamara, K.C.; Spite, M.; Fredman, G. Resolvin D1 promotes efferocytosis in aging by limiting senescent cell-induced MerTK cleavage. FASEB J. 2020, 34(1), 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasikara, C.; Doran, A.C.; Cai, B.; Tabas, I. The role of non-resolving inflammation in atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Invest. 2018, 128(7), 2713–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla-Madrigal, R.; Gil-Iturbe, E.; Lopez de Calle, M.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J.; Lostao, M.P. DHA and its derived lipid mediators MaR1, RvD1 and RvD2 block TNF-alpha inhibition of intestinal sugar and glutamine uptake in Caco-2 cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 76, 108264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Libreros, S.; Nshimiyimana, R. E-series resolvin metabolome, biosynthesis and critical role of stereochemistry of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) in inflammation-resolution: Preparing SPMs for long COVID-19, human clinical trials, and targeted precision nutrition. Semin. Immunol. 2022, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredman, G.; Serhan, C.N. Specialized pro-resolving mediators in vascular inflammation and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2024. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkar, S.S.; Leeper, N.J. Efferocytosis in atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2024. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlyarov, S.; Kotlyarova, A. Molecular Pharmacology of Inflammation Resolution in Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23(9). [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach, B.D.; Marinello, M.; Heinz, J.; Rymut, N.; Sansbury, B.E.; Riley, C.O.; Sadhu, S.; Hosseini, Z.; Kojima, Y.; Tang, D.D.; Leeper, N.J.; Spite, M.; Barroso, M.; Rayner, K.J.; Fredman, G. Resolvin D1 promotes the targeting and clearance of necroptotic cells. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27(2), 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhadoun, A.; Manikpurage, H.D.; Deschildre, C.; Zalghout, S.; Dubourdeau, M.; Urbach, V.; Ho-Tin-Noe, B.; Deschamps, L.; Michel, J.B.; Longrois, D.; Norel, X. DHA, RvD1, RvD5, and MaR1 reduce human coronary arteries contractions induced by PGE(2). Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 2023, 165, 106700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, J.R.; Lemnitzer, P.; Jansen, Y.; Csaba, G.; Winter, C.; Neideck, C.; Silvestre-Roig, C.; Dittmar, G.; Doring, Y.; Drechsler, M.; Weber, C.; Zimmer, R.; Cenac, N.; Soehnlein, O. Resolving Lipid Mediators Maresin 1 and Resolvin D2 Prevent Atheroprogression in Mice. Circ. Res. 2016, 119(9), 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajbakhsh, A.; Rezaee, M.; Kovanen, P.T.; Sahebkar, A. Efferocytosis in atherosclerotic lesions: Malfunctioning regulatory pathways and control mechanisms. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 188, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Thorp, E.B.; Doran, A.C.; Sansbury, B.E.; Daemen, M.J.; Dorweiler, B.; Spite, M.; Fredman, G.; Tabas, I. MerTK receptor cleavage promotes plaque necrosis and defective resolution in atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Invest. 2017, 127(2), 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zheng, J.; Xu, S.; Fang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Shao, A.; Shi, L.; Lu, J.; Mei, S.; Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J. Mer regulates microglial/macrophage M1/M2 polarization and alleviates neuroinflammation following traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18(1), 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.; Bansal, S.S.; Ismahil, M.A.; Hamid, T.; Rokosh, G.; Mack, M.; Prabhu, S.D. CCR2(+) Monocyte-Derived Infiltrating Macrophages Are Required for Adverse Cardiac Remodeling During Pressure Overload. JACC Basic. Transl. Sci. 2018, 3(2), 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, M.R.; Jaffrey, S.R. Gas6-Axl Signaling Induces SRF/MRTF-A Gene Transcription via MICAL2. Genes-Basel 2023, 14(12), 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justynski, O.; Bridges, K.; Krause, W.; Forni, M.F.; Phan, Q.M.; Sandoval-Schaefer, T.; Carter, K.; King, D.E.; Hsia, H.C.; Gazes, M.; Vyce, S.D.; Driskell, R.R.; Miller-Jensen, K.; Horsley, V. Apoptosis recognition receptors regulate skin tissue repair in mice. Elife 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Bu, T.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Zhou, T.; Hu, W.; Yang, G.; Yuan, L.; Duan, Y.; Xing, C. Targeted delivery of MerTK protein via cell membrane engineered nanoparticle enhances efferocytosis and attenuates atherosclerosis in diabetic ApoE(-/-) Mice. J. Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22(1), 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Kasikara, C.; Doran, A.C.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Birge, R.B.; Tabas, I. MerTK signaling in macrophages promotes the synthesis of inflammation resolution mediators by suppressing CaMKII activity. Sci. Signal 2018, 11(549). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penberthy, K.K.; Ravichandran, K.S. Apoptotic cell recognition receptors and scavenger receptors. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 269(1), 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Levy, B.D. Resolvins in inflammation: Emergence of the pro-resolving superfamily of mediators. J. Clin. Invest. 2018, 128(7), 2657–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Seo, J.Y.; Yoon, Y.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, J.L. Mer signaling increases the abundance of the transcription factor LXR to promote the resolution of acute sterile inflammation. Sci. Signal 2015, 8(365), ra21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhabyeyev, P.; McLean, B.; Bassiouni, W.; Valencia, R.; Paul, M.; Darwesh, A.M.; Seubert, J.M.; Hazra, S.; Oudit, G.Y. Loss of PI3Kalpha Mediates Protection From Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Linked to Preserved Mitochondrial Function. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12(12), e022352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- !!! INVALID CITATION !!! [124–126].
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, L.S.; Deng, F.X.; Shu, S.; Wang, L.J.; Wu, Y.; Guo, N.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, Z.Y. Angiotensin II deteriorates advanced atherosclerosis by promoting MerTK cleavage and impairing efferocytosis through the ATR/ROS/p38 MAPK/ADAM17 pathway. Am. J. Physiol-Cell Ph 2019, 317(4), C776–C787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Elliott, K.J.; Scalia, R.; Eguchi, S. Contribution of ADAM17 and related ADAMs in cardiovascular diseases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78(9), 4161–4187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Li, W.; Pang, Z.; Weng, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Yang, H.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, G.; Tan, Y.; Fu, Y.; Han, C.; Cai, S.; Qian, J.; Huang, Z.; Song, Y.; Ge, J. Genetically Engineered Macrophages Co-Loaded with CD47 Inhibitors Synergistically Reconstruct Efferocytosis and Improve Cardiac Remodeling Post Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13(16), e2303267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Thorp, E.B.; Doran, A.C.; Subramanian, M.; Sansbury, B.E.; Lin, C.S.; Spite, M.; Fredman, G.; Tabas, I. MerTK cleavage limits proresolving mediator biosynthesis and exacerbates tissue inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2016, 113(23), 6526–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufit, A.; Lee-Sherick, A.B.; DeRyckere, D.; Rupji, M.; Dwivedi, B.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Pierce, A.M.; Kowalski, J.; Wang, X.; Frye, S.V.; Earp, H.S.; Keating, A.K.; Graham, D.K. MERTK Inhibition Induces Polyploidy and Promotes Cell Death and Cellular Senescence in Glioblastoma Multiforme. PLoS One 2016, 11(10), e0165107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.H.; Kuan, A.P.; Wang, C.; Abraham, V.; Waldman, M.A.; Vogelgesang, A.; Wittenburg, G.; Choudhury, A.; Tsao, P.Y.; Miwa, T.; Eisenberg, R.A.; Cohen, P.L. Disrupted Mer receptor tyrosine kinase expression leads to enhanced MZ B-cell responses. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 35(4), 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinger, J.G.; Omari, K.M.; Marsden, K.; Raine, C.S.; Shafit-Zagardo, B. Up-regulation of soluble Axl and Mer receptor tyrosine kinases negatively correlates with Gas6 in established multiple sclerosis lesions. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175(1), 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Banerjee, O.; Shi, H.; Xue, B.; Ding, Z. Disturbed flow impairs MerTK-mediated efferocytosis in aortic endothelial cells during atherosclerosis. Theranostics 2024, 14(6), 2427–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Wang, X.W.; Li, M.; Lin, P.H.; Yao, Q.Z.; Chen, C.Y. Human protein S inhibits the uptake of AcLDL and expression of SR-A through Mer receptor tyrosine kinase in human macrophages. Blood 2009, 113(1), 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatana, C.; Saini, N.K.; Chakrabarti, S.; Saini, V.; Sharma, A.; Saini, R.V.; Saini, A.K. Mechanistic Insights into the Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Atherosclerosis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.C.; Xu, J.W.; Huang, W.C.; Chang, H.C.; Tung, Y.T. Plasma Proteomic Changes of Atherosclerosis after Exercise in ApoE Knockout Mice. Biology (Basel) 2022, 11(2), 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBerge, M.; Yeap, X.Y.; Dehn, S.; Zhang, S.; Grigoryeva, L.; Misener, S.; Procissi, D.; Zhou, X.; Lee, D.C.; Muller, W.A.; Luo, X.; Rothlin, C.; Tabas, I.; Thorp, E.B. MerTK Cleavage on Resident Cardiac Macrophages Compromises Repair After Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Circ. Res. 2017, 121(8), 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arandjelovic, S.; Ravichandran, K.S. A MERry response after myocardial infarction. Circ. Res. 2013, 113(8), 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas-Avila, J.A.; Sanchez-Diaz, M.; Hidalgo, A. Isolation of exophers from cardiomyocyte-reporter mouse strains by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. STAR Protoc. 2021, 2(1), 100286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas-Avila, J.A.; Lechuga-Vieco, A.V.; Esteban-Martinez, L.; Sanchez-Diaz, M.; Diaz-Garcia, E.; Santiago, D.J.; Rubio-Ponce, A.; Li, J.L.; Balachander, A.; Quintana, J.A.; Martinez-de-Mena, R.; Castejon-Vega, B.; Pun-Garcia, A.; Traves, P.G.; Bonzon-Kulichenko, E.; Garcia-Marques, F.; Cusso, L.; N, A.G.; Gonzalez-Guerra, A.; Roche-Molina, M.; Martin-Salamanca, S.; Crainiciuc, G.; Guzman, G.; Larrazabal, J.; Herrero-Galan, E.; Alegre-Cebollada, J.; Lemke, G.; Rothlin, C.V.; Jimenez-Borreguero, L.J.; Reyes, G.; Castrillo, A.; Desco, M.; Munoz-Canoves, P.; Ibanez, B.; Torres, M.; Ng, L.G.; Priori, S.G.; Bueno, H.; Vazquez, J.; Cordero, M.D.; Bernal, J.A.; Enriquez, J.A.; Hidalgo, A. A Network of Macrophages Supports Mitochondrial Homeostasis in the Heart. Cell 2020, 183(1), 94–109 e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yeap, X.Y.; Grigoryeva, L.; Dehn, S.; DeBerge, M.; Tye, M.; Rostlund, E.; Schrijvers, D.; Zhang, Z.J.; Sumagin, R.; Tourtellotte, W.G.; Lee, D.; Lomasney, J.; Morrow, J.; Thorp, E.B. Cardiomyocytes induce macrophage receptor shedding to suppress phagocytosis. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2015, 87, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horckmans, M.; Ring, L.; Duchene, J.; Santovito, D.; Schloss, M.J.; Drechsler, M.; Weber, C.; Soehnlein, O.; Steffens, S. Neutrophils orchestrate post-myocardial infarction healing by polarizing macrophages towards a reparative phenotype. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38(3), 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, F.; Xiong, W.; Song, S.; Yin, Y.; Hu, J.; Yang, K.; Yang, L.; Xu, B.; Ge, J. Mononuclear phagocyte system blockade using extracellular vesicles modified with CD47 on membrane surface for myocardial infarction reperfusion injury treatment. Biomaterials 2021, 275, 121000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Volkmer, J.P.; McKenna, K.; Civelek, M.; Lusis, A.J.; Miller, C.L.; Direnzo, D.; Nanda, V.; Ye, J.; Connolly, A.J.; Schadt, E.E.; Quertermous, T.; Betancur, P.; Maegdefessel, L.; Matic, L.P.; Hedin, U.; Weissman, I.L.; Leeper, N.J. CD47-blocking antibodies restore phagocytosis and prevent atherosclerosis. Nature 2016, 536(7614), 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, S.K.; Vasileiadi, E.; Wang, X.D.; DeRyckere, D.; Graham, D.K. The Emerging Role of TYRO3 as a Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10(12), 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, B.; Abasolo, N.; Muñoz, X.; García, N.; Benavente, Y.; Rubio, F.; de Frutos, P.G.; Krupinski, J.; Sala, N. Association study between polymorphims in GAS6-TAM genes and carotid atherosclerosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 104(3), 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.Y.; Silva, E.A.C.; De Kouchkovsky, D.; Joannas, L.D.; Hao, L.M.; Hu, D.L.; Huntsman, S.; Eng, C.; Licona-Limón, P.; Weinstein, J.S.; Herbert, D.R.; Craft, J.E.; Flavell, R.A.; Repetto, S.; Correale, J.; Burchard, E.G.; Torgerson, D.G.; Ghosh, S.; Rothlin, C.V. The TAM family receptor tyrosine kinase TYRO3 is a negative regulator of type 2 immunity. Science 2016, 352(6281), 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grebe, A.; Hoss, F.; Latz, E. NLRP3 Inflammasome and the IL-1 Pathway in Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2018, 122(12), 1722–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Matsushima, G.K. Tyro3, Axl, Mertk receptor-mediated efferocytosis and immune regulation in the tumor environment. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 361, 165–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




