1. Introduction
Infusion pumps are medical devices used to deliver fluids, such as nutrients and medications, into a patient’s body in controlled amounts. The evolution of infusion pumps from basic mechanical devices in the 1970s and 1980s to the advanced, multifunctional devices of today is well-documented. Modern infusion pumps incorporate various features and alarms designed to alert users about issues such as nearing completion of infusions or the need for attention due to detected anomalies [
1].
Infusion pumps for medications are essential devices used in intensive care units, emergency rooms, and neonatal units. They are employed when there is a need to administer precise or large amounts of medication to patients and to deliver an accurate volume of drugs per hour. In particular, when administering red blood cells and platelets to pediatric patients (newborns), a small volume of blood is required, and due to their small body size, there is a risk of circulatory volume overload. Therefore, it is crucial that the correct amount is transfused at a consistent rate [
2,
3]. In addition to pediatric patients, blood components such as red blood cells, plasma, and platelets are applied according to the therapeutic needs of the patient. Additionally, in cases of massive hemorrhage due to trauma, whole blood may be used [
4].
Generally, infusion pumps for medications inject a predetermined volume into the patient based on a program that rotates a motor. When using an infusion pump for blood transfusions, a constant pressure is applied, which may cause physical damage to red blood cells as they pass through the needle, increasing the risk of hemolysis. Therefore, when transfusing red blood cells or other blood products using an infusion pump, it is crucial to verify that the device is suitable for its intended purpose, especially since visible hemolysis can occur with red blood cell products. In the case of syringe-based infusion pumps, frequent syringe replacements pose a risk of infection, necessitating careful attention and leading to increased workload. Additionally, issues associated with the operation of traditional infusion pumps, such as infusion accuracy, backflow, and startup delays, can become problematic during low-volume transfusions. Conventional infusion pumps control flow through the peristaltic motion of tubing, which can result in flow variations of ±5% to 20% per hour, depending on the tubing material and elasticity. When issues like tubing recoil arise, the system may need to be reset or the tubing replaced. Furthermore, the drive mechanism that compresses the tubing may also lead to hemolysis.
Syringe pumps used for precise infusion have compatibility issues due to varying syringe specifications among manufacturers, and they require frequent resetting when large volumes are injected. The process of transferring blood into a syringe for precise infusion increases vulnerability to contamination and infection [
2,
5]. A method to improve this situation is to integrate the syringe injection method with the infusion method, and the Anyfusion H-100 device has been developed to achieve this. Anyfusion H-100 operates on the principle of two pistons attached to two disks within a donut-shaped cylinder, which rotate via two motors to aspirate and dispense liquids (medications), gases, and flowable solids (food, blood) regardless of gravity or position [
6].
In this study, we aimed to verify whether the drug delivery system, Anyfusion H-100, can accurately administer medications used for infants and neonates, and whether it can quickly and precisely deliver large amounts of fluids in emergency situations. Using research-grade blood, we tested if the blood could be infused at an accurate volume and rate, and examined hemolysis levels before and after blood transfusion to confirm its viability for transfusion. Through this, we aimed to demonstrate that this new type of infusion pump has no functional differences compared to conventional infusion pumps and to prove its suitability as a medical device.
2. Materials and Methods
The experiment was conducted with six different infusion rates: 10cc per hour for 3 hours, 15cc per hour for 2 hours, 30cc per hour for 1 hour, 60cc per hour for 1 hour, 120cc per hour for 1 hour, and 180cc per hour for 1 hour. Each experiment was repeated six times. Additionally, 20 tests were performed using a 1:1 dilution method with normal saline to simulate emergency blood transfusions. All experiments were carried out with an experimental group (Anyfusion H-100) and a control group (Terufusion TE-LM700).
2.1. Equpment and the Packed RBC
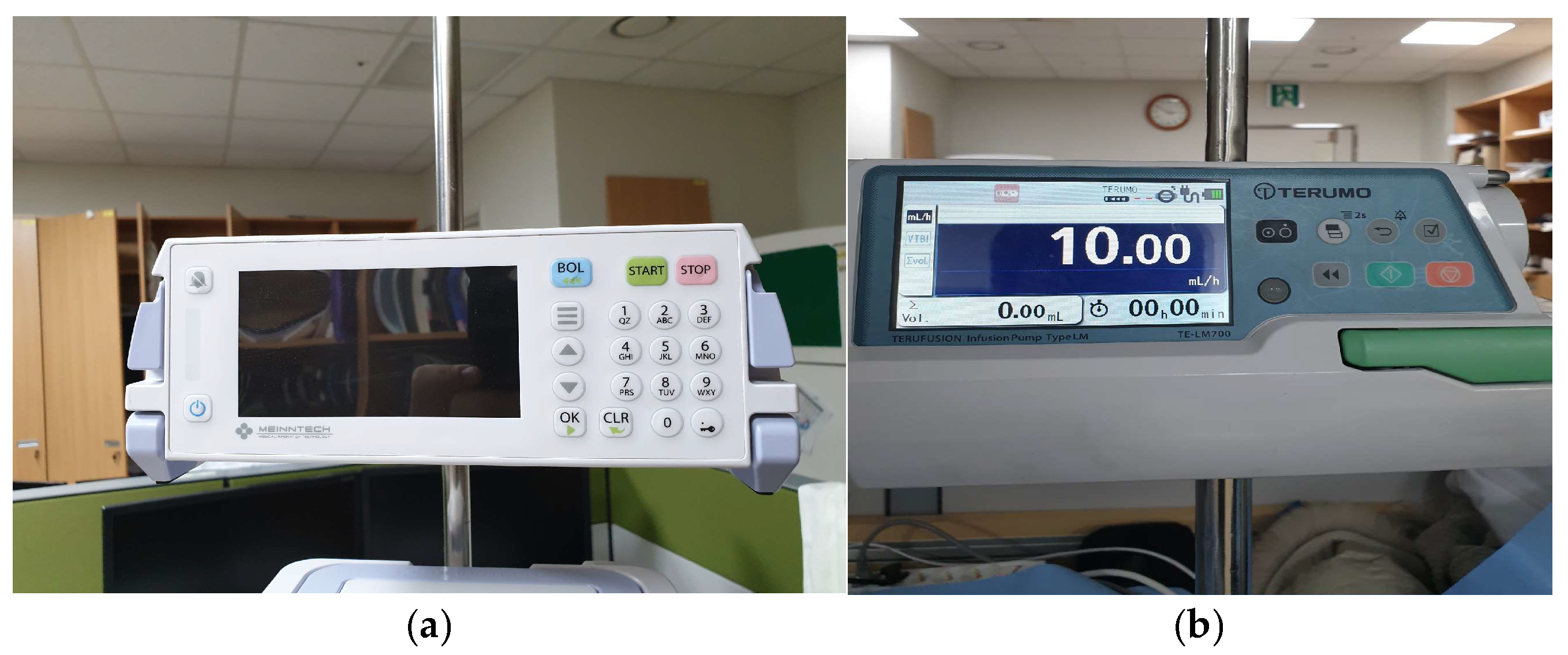
The Anyfusion H-100 (Meinntech Corporation, Anyang, Republic of Korea), which combined a syringe and an infusion pump into a single pump unit, was used as the investigational device. Also, the pump-type Terufusion TE-LM700 (Terumo Medical Corporation, Tokyo, Japan), which was equipped with a transfusion set with a diameter of 4.0 mm, was used as the comparator (
Figure 1). This study was also carried out with approval from the Research Ethics Committee of Yonsei University Wonju Severance Christian Hospital (IRB approval number: CR320345).
Blood safety center-certified research-grade blood from the KOREAN Redcross (blood that was collected for transfusion but discarded due to slight increases in factors such as AST) was supplied to the transfusion cartridge. For the clinical trial, the blood was stored in a temperature-controlled storage device designed for blood. Blood tests, including CBC and electrolyte tests, were conducted. SST tubes were stored at room temperature for 30 minutes before being centrifuged at 2,500-3,000 RPM for 10 minutes and then refrigerated. EDTA tubes were mixed immediately and refrigerated, with tests requested within one day of sample collection. In cases of sample ineligibility, additional test results were verified through point-of-care testing on the stored samples. (
Figure 2).
2.2. Study Protocols
- i.
Quantification and Error Rate According to Infusion Rate and Time
- ii.
Degree of Hemolysis According to Infusion Rate
2.3. Statistical Analysis
In this study, the choice between parametric and non-parametric statistical methods is determined by conducting normality tests on each variable based on the test results. For additional data analysis, the Windows-based statistical software SPSS Ver. 25.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, USA) is used. The test results (such as volume, rate, and comparison with the control group) are presented as descriptive statistics, followed by further analysis. In the event of missing data, the listwise deletion method is applied.
Errors occurring during blood transfusion were verified for differences between the two medical devices using chi-square tests, and the hemolysis rate was verified for statistical significance using independent sample t-tests. In addition, the performance equality of the two medical devices was verified using Bland-Altman plots.
3. Results
3.1. Overall Comparison by Infusion Rate of Each Device
Six trials were conducted for each experiment, along with 20 trials using saline-mixed dilutions. During the experiments, one device error occurred with the Anyfusion H-100, leading to one additional trial, resulting in a total of 57 trials. The comprehensive comparison table of average error rates for each infusion rate is shown in (Clinical Trial Comprehensive Comparison
Table 1). The average volume was not included, as the volume varied by infusion rate. The average error rate was 3.86% for Anyfusion H-100 and 3.98% for Terumo TE-LM700, with both groups showing an error rate of less than 4%. After the clinical trials, the average blood temperature was 25.1°C for the Anyfusion H-100 and 24.6°C for the Terumo TE-LM700 control group, showing a difference of 0.5°C (
Table 1).
3.2. Comparison of Error According to Infusion Rate
The comparison of issues according to infusion rate, excluding the dilution test, is shown in
Table 2. In low-speed transfusions at 10 ㏄/hr and 15 ㏄/hr, visually observable clot formation occurred in both groups with 4 cases each, accounting for 10.8%. However, at infusion rates of 30 ㏄/hr or higher, no visually observable clot formation was detected in either group. In the Anyfusion H-100, air was detected in 8 cases (21.6%), sample ineligibility in 4 cases (10.8%), and 1 error (2.7%). In the Terumo control group, air was detected in 6 cases (16.2%), sample ineligibility in 8.1%, and no errors occurred. Sample ineligibility occurred due to microclot formation or when the research blood had been collected for an excessively long period. It should be noted that the data may vary when transfusing blood to actual patients as opposed to research samples.
3.3. Transfusion Volume Error Rate and Laboratory Temperature for Eace Experiment
A total of 57 clinical trials were conducted (37 non-dilution trials and 20 dilution trials). The final transfusion error rate for the Anyfusion H-100 was 3.77%, while the Terumo TE-LM700 had a final error rate of 4.00%, indicating slightly higher accuracy for the Anyfusion H-100 compared to the Terumo TE-LM700. When comparing the error rates of the 37 non-dilution trials to the total trials, the following results were observed:
- i.
Anyfusion H-100: Non-dilution: 3.86%, Dilution: 3.60%, Overall: 3.77%
- ii.
Terufusion TE-LM700: Non-dilution: 3.98%, Dilution: 4.05%, Overall: 4.00%
After the final transfusions, the temperatures were 25.0°C for Anyfusion H-100 and 24.6°C for Terumo TE-LM700, showing a temperature difference of approximately 0.4°C (
Table 3).
3.4. Overall Experiment Error Rate
In
Table 4, Out of a total of 56 trials, Air trapping was reported in 9 cases (15.8%) for Anyfusion H-100 and in 7 cases (12.3%) for Terumo TE-LM700. Clots occurred in 4 cases (7.0%) each. In the chi-square test, the X
2 value was 0.294 and the p value was 0.863, failing to confirm statistical significance.
3.5. Comparison of the Mean Hemolysis Rates of Each Medical Device
Excluding the 20 diluted cases, among the 37 cases analyzed using the t-Test, the hemolysis rates by speed were 0.566 ± 0.095 for the Anyfusion H-100 and 0.518 ± 0.126 for the Terumo TE-LM700. The t-value was -0.745, and the p-value was 0.697, indicating no statistical significance, which suggests that there is no functional difference between the two infusion pumps (
Table 5).
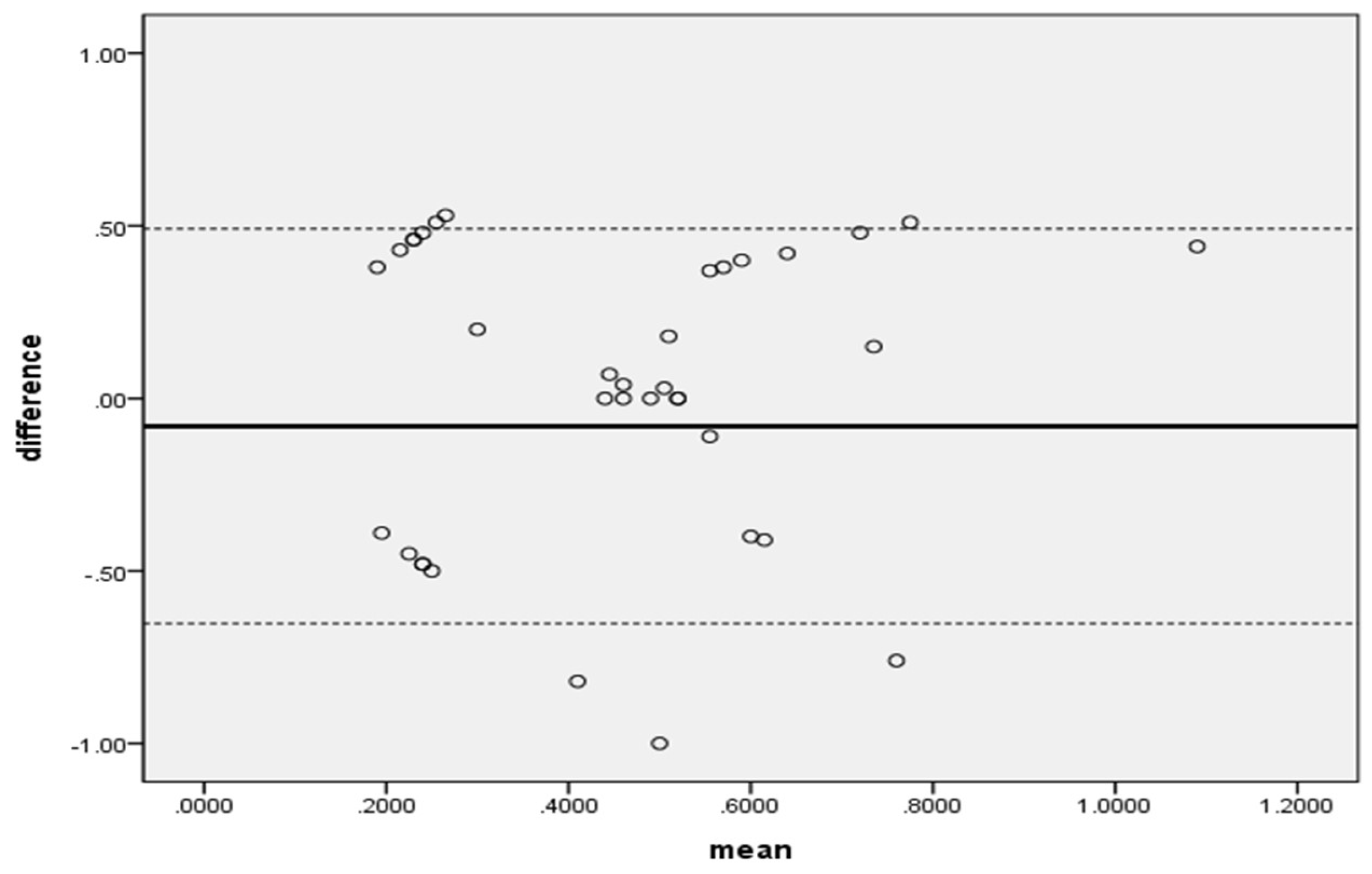
In addition, when the distribution of hemolysis rates of the two medical devices was confirmed using a Bland-Altman plot, most of the differences were within the range, so it can be said that the two medical devices exhibited the same performance during transfusion (
Figure 3).
4. Discussion
The electromechanical infusion device can deliver liquid preparations at a constant rate and accurately measure the amount infused, making it commonly used for pediatric patients or those with chronic kidney disease. In clinical settings, various commercially available infusion devices are utilized, and factors such as osmotic pressure of drugs or blood products, infusion volume, medication administration procedures, consistency, accuracy, and infusion rate should all be considered to enhance effective patient management and reduce wasted medication [
7,
8,
9].
The error rate for the infusion rate of a typical intravenous pump is reported to be less than ±5%. In addition, the error rate for the infusion rate of an elastic infusion pump is reported to be less than ±15% [
10]. The Meintech device, using a cylinder-type medication infusion method with a blood transfusion cartridge, demonstrated a slightly better error rate in time-speed-volume comparisons at 3.77% compared to the control group, Terufusion TE-LM700, which had an error rate of 4.00%. When compared to the error rates presented by manufacturers for drug or fluid infusion (Terumo: ±5%, Baxter: ±7%), Terumo maintained an error rate within 5% for all samples except for two blood specimens, while Baxter had no blood specimens within the error rate. Compared to the error rate standards for infusion pumps, Terumo’s average error rate for infusion speed was below 5%, indicating that it could reliably deliver the set volume to patients. Although this evaluation focused on medications, there was no significant difference in accuracy when compared to existing literature [
10]. However, due to the difference in viscosity between blood and intravenous fluids, it is challenging to apply the same standards to both. Additionally, this study used blood diluted with fresh frozen plasma, but the viscosity of concentrated red blood cells used for transfusions is higher, which may lead to a greater actual error.
The hemolysis rate showed little difference, at 0.52% compared to 0.57%, suggesting that this device could serve as a viable alternative to the widely used Terufusion TE-LM700 in South Korea. However, the incidence of air trapping was slightly higher, at 15.8% compared to 12.2% for the Terufusion TE-LM700. If this issue is addressed, the device could be utilized as a more advanced medical device.
The degree of damage to red blood cells during infusion is influenced by various factors, including the storage duration of blood products after collection, the diameter of the needle used, and the pressure applied to maintain a constant infusion rate. However, the most significant factors are the characteristics and operating methods of the infusion device itself [
11,
12,
13].
It has been reported that peristaltic pumps are associated with hemolysis. Among 13 existing studies, hemolysis was observed in 10 studies using peristaltic infusion devices. In contrast, volumetric infusion devices that use a cassette mechanism showed no association with hemolysis in 4 out of 6 studies [
14]. In a study conducted in South Korea comparing the degree of hemolysis during pediatric transfusions based on infusion devices, no increase in plasma hemoglobin was observed when whole blood was administered. However, an increase in plasma hemoglobin was noted when concentrated red blood cells were infused, although this change was not statistically significant [
15].
Based on the results of this study and a review of previous research, it is determined that the Anyfusion H-100 can sufficiently fulfill its role as an infusion pump capable of performing blood transfusions.
5. Conclusions
This study aims to verify whether a device that integrates the syringe infusion method with the infusion method can deliver accurate volumes and rates with the same performance as other infusion pump devices and whether there is no statistically significant difference in hemolysis rates, thereby demonstrating the potential applicability of this new type of infusion pump.
When comparing the Anyfusion H-100 and the Terufusion TE-LM700 using research blood samples, no statistically significant differences were observed in transfusion volume, errors, or hemolysis amounts, indicating equivalent performance. The Bland-Altman plot also showed that the distribution of hemolysis rates mostly fell within the acceptable range, confirming no functional differences between the devices.
Therefore, the Anyfusion H-100, as an infusion pump capable of performing blood transfusions, is expected to be highly useful as a medical device that integrates the syringe infusion method and the infusion method, effectively addressing each method’s functional issues.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Y.; methodology, S.-J.K. and I.-H.P.; formal analysis, S.-J.K. and H.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-Y.L.; writing—review and editing, H.-Y.L. and H.-J.J.; project administration, H.-Y.L. and K.-H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (No. HR21C0885).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was also carried out with approval from the Research Ethics Committee of Yonsei University Wonju Severance Christian Hospital (IRB approval number: CR320345).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the KOREAN Red Cross for providing research-grade blood products used for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Syroid, N.; Liu, D.; Albert, R.; Agutter, J.; Egan, T.D.; Pace, N.L.; Johnson, K.B.; Dowdle, M.R.; Pulsipher, D.; Westenskow, D.R. Graphical user interface simplifies infusion pump programming and enhances the ability to detect pump-related faults. Anesth Analg, 2021, 115, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidelines for blood transfusion. 2nd ed. Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2016.
- Klem, S.A.; Farrington, J.M.; Leff, R.D. Influence of infusion pump operation and flow rate on hemodynamic stability during epinephrine infusion. Crit Care Med, 1993, 21, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gent, J.M.; Clements, T.W.; Cotton, B.A. Resuscitation and care in the trauma bay. Surg Clin, 2024, 104, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, K.; Levine, W.C. Infusion Pumps. In Anesthesia equipment, WB Saunders, 2021;. pp. 351-367.
- Min, J.J.; Kim, D.K.; Hong, K.Y.; Choi, J.W.; Choi, K.Y. Comparison of operator workloads associated with the single-unit Anyfusion® pump and the changeover from a syringe pump to an infusion pump. J Korean Med Sci, 2019, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurdy, D.E.; Arnold, M.T. Development and implementation of a pediatric/neonatal iv syringe pump delivery system. Neonatal Netw, 1995, 14, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Golpaygani, T.A.; Movahedi, M.M.; Reza, M.; Hassani, K. A study on performance and safety test of infusion pump devices. Biomed Res India, 2017, 28, 5179–5181. [Google Scholar]
- Ilfeld, B.M.; Morey, T.E.; Enneking, F.K. The delivery rate accuracy of portable infusion pumps used for continuous regional analgesia. Anesth Analg, 2002, 95, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohseni, M.; Ebneshahidi, A. The flow rate accuracy of elastomeric infusion pumps after repeated filling. Anesthesiology and pain medicine. 2014, 4, E14989. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calkins, J.M.; Vaughan, R.W.; Cork, R.C.; Barberii, J.; Eskelson, C. Effects of dilution, pressure, and apparatus on hemolysis and flow rate in transfusion of packed erythrocytes. Anesth Analg, 1982, 61, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, A.J.; Corless, J. Blood transfusions: effect of speed of infusion and of needle gauge on hemolysis. J Pediatr, 1981, 99, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusahara, D.M.; Pedreira, M.; Avelar, A.M.; Peterlini, M.A. Performance of a linear peristaltic infusion pump during red blood cells administration and the influence of infusion rates. Intensive Care Med Exp 2015, 3 (Suppl 1), A548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.M.M.M.; Peterlini, M.A.S.; Pedreira, M.D.L.G. Infusion pumps and red blood cell damage in transfusion therapy: an integrative revision of the academic literature. Rev Latino-Am Enfermagem, 2016, 24, e2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, J.S.; Lim, E.; Park, H.; Hwang, S.H.; Oh, H.B.; Ko, D.H. Performance Evaluation of Infusion Systems for Red Blood Cell Transfusion. J Lab Med Qual Assur, 2019, 41, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).